Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |

Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
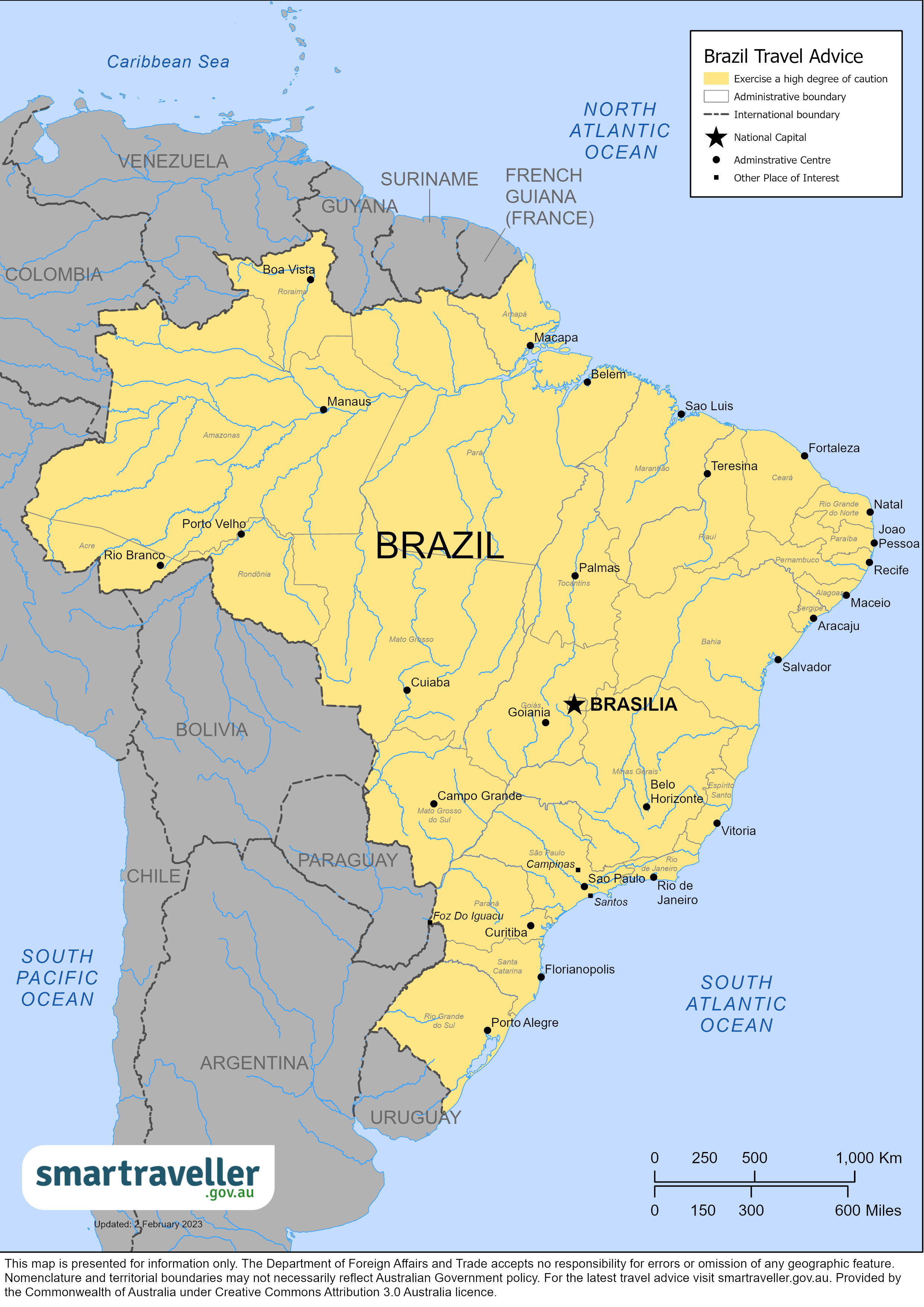
Brazil Travel Advisory
Travel advisory october 19, 2023, brazil - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with updates to Country Summary.
Exercise increased caution in Brazil due to crime . Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Do not travel to:
- Any areas within 150 km/100 miles of Brazil’s land borders with Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and Paraguay due to crime . (Note: This does not apply to the Foz do Iguacu National Park or Pantanal National Park.)
- Informal housing developments (commonly referred to in Brazil as favelas, vilas, comunidades, and/or conglomerados) at any time of day due to crime (see additional information below).
- Brasilia’s administrative regions (commonly known as “satellite cities”) of Ceilandia, Santa Maria, Sao Sebastiao, and Paranoa during non-daylight hours due to crime (see additional information below).
Country Summary: Violent crime, such as murder, armed robbery, and carjacking, is common in urban areas, day and night. Gang activity and organized crime is widespread. Assaults, including with sedatives and drugs placed in drinks, are common. U.S. government personnel are discouraged from using municipal buses in all parts of Brazil due to an elevated risk of robbery and assault at any time of day, and especially at night.
If you decide to travel to Brazil:
- Be aware of your surroundings.
- Do not physically resist any robbery attempt.
- Do not accept food or drinks from strangers.
- Use caution when walking or driving at night.
- Avoid going to bars or nightclubs alone.
- Avoid walking on beaches after dark.
- Do not display signs of wealth, such as wearing expensive watches or jewelry.
- Be extra vigilant when visiting banks or ATMs.
- Use caution at, or going to, major transportation centers or on public transportation, especially at night. Passengers face an elevated risk of robbery or assault using public, municipal bus transportation throughout Brazil.
- Use increased caution when hiking in isolated areas.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Brazil.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
International Borders – Level 4: Do Not Travel
U.S. government personnel are not permitted to travel to areas within 150 km/100 miles of the international land borders with Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and Paraguay without advance approval from security officials due to crime. Travel to the Foz do Iguacu National Park and Pantanal National Park is permitted.
Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
Informal Housing Developments (commonly known as “Favelas”) – Level 4: Do Not Travel
Do not travel to informal housing developments (commonly referred to in Brazil as favelas, vilas, comunidades, and/or conglomerados), even on a guided tour. Neither the tour companies nor the police can guarantee your safety when entering these communities. Even in these communities that the police or local governments deem safe, the situation can change quickly and without notice. While some informal housing developments have clear boundaries or gates, or even names such as “favela”, “vila”, “comunidade”, or “conglomerado”, other such developments may be less obvious, and may be identified by crowded quarters, poorer conditions, and/or irregular construction. In addition, exercise caution in areas surrounding these communities, as occasionally, inter-gang fighting and confrontations with police move beyond the confines of these communities. Except under limited circumstances and with advance approval, U.S. government personnel are not permitted to enter any informal housing developments in Brazil. Read the Safety and Security Section on the country information page and consult the maps on the Embassy’s website for further information regarding favelas.
Visit our website for Travel High-Risk Areas .
Brasilia’s Administrative Regions (commonly known as “Satellite Cities”) – Level 4: Do Not Travel
Without advance approval from security officials, U.S. government personnel are not permitted to travel to Brasilia’s Administrative Regions of Ceilandia, Santa Maria, Sao Sebastiao, and Paranoa between the hours of 6:00 p.m. and 6:00 a.m. (non-daylight hours) due to crime.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
- English (EN)
- Español (ES)
- Português (BR)
Is Brazil Safe? Crime Rates & Safety Report

- Brazil : Safety by City
- Belo Horizonte
- Florianopolis
- Porto Alegre
- Rio de Janeiro
Brazil, the largest country in South America and the fifth-largest in the world, is probably the most famous one in the entire continent.
A dream for football lovers, since it’s the cradle of football tradition and a paradise for fans of festivals, music and partying, this country hosts around 6 million tourists each year.
The vibrant urban life is more than obvious in São Paulo, and the spirit of this joyous country can be felt at the famous Carnaval in Rio de Janeiro, as well as those in Salvador, Recife, and Olinda.
You can experience the cultural energy of Pernambuco and Bahia, and, of course, immerse yourself in the wilderness of the Amazon rainforest and the world-famous Iguaçu Falls,
There is so much to see and do in Brazil, just concerning nature, that you probably won’t have time to do it all during one trip.
There’s the Amazon River Basin that holds more than half of the world’s remaining rainforest, and as much as 60% of it lies in the North of Brazil – it is truly a natural sight worth seeing, a mesmerizing proof that nature itself is a wonder.
Brazil’s waterfalls of all shapes and sizes are a different story, with Iguaçu Falls stealing breaths in eastern Parana.
These are among the most spectacular waterfalls in the world.
- Warnings & Dangers in Brazil
OVERALL RISK: MEDIUM
Brazil is somewhat safe but you should take precaution on the streets of major cities, and after dark. Be wary of pickpockets and bag snatching and keep your valuables safely by your side. Never carry all your money in one place or leave your valuables in plain sight in a car or at a beach when swimming.
TRANSPORT & TAXIS RISK: MEDIUM
Public transport is generally safe in Brazil, though it has its dangers. Be careful on buses and bus stops since that's where pickpockets and petty thieves operate.
PICKPOCKETS RISK: HIGH
Pickpockets are a common occurrence on the streets of Brazil and tourists are recommended to remain vigilant at all times when on the street. Make sure you don't flash your valuable possessions on the street, or better yet, leave them in your accommodation. When in Rio, be extremely aware of your surroundings.
NATURAL DISASTERS RISK: MEDIUM
There are some natural threats in Brazil, such as dangerous insects and diseases they carry, and riptides. This is why it is important never to go swimming alone.
MUGGING RISK: MEDIUM
Mugging is not altogether uncommon on the streets of Brazil. In such a situation, hand over all your possessions immediately and do not resist. Avoid poorly lit and deserted areas.
TERRORISM RISK: LOW
Although there haven't been any terrorist attacks in Brazil's recent history, they shouldn't be ruled out so remain vigilant at all times.
SCAMS RISK: HIGH
Scams are very common in Brazil, so double check your change, never pay anything upfront and negotiate everything in advance. Be very careful around ATMs and be wary of people trying to distract you. Also, be careful around children as they're probably trying to distract you too - they are skillful pickpockets.
WOMEN TRAVELERS RISK: MEDIUM
Traveling to Brazil is generally safe for solo women, but bear in mind that you should always hike in company, never alone. Be especially careful in the North East and the remote area of Amazon. Stay away from poorly lit and deserted streets and areas and from people that are visibly intoxicated or under the influence.
- So... How Safe Is Brazil Really?
Brazil is one of the most criminalized countries in the world, and therefore, it is not the safest choice.
But if you keep your wits with you and follow rules of precaution, you will minimize the chances of something going wrong.
The golden rule in Brazil is never to wear bling in public, or anything gilded, diamond-encrusted or oversized.
You are advised to always keep a small amount of cash with you (preferably cleverly hidden, concealed in a money belt under your clothes, in secret sewn-in pockets, or in your shoes) and to avoid carrying bank cards.
If you go out shopping, it is smart to return your purchases to your accommodation before you head out to dinner or to a bar.
The statistics when it comes to violent crime in Brazil do not offer a sunny prognosis: though the cities of Rio, São Paulo, Recife, and Salvador are ridden with crime throughout the year, it skyrockets when tourists arrive in hordes during Carnival and festive holiday periods.
Never assume that you’re safe if you remain on-the-beaten-path.
Tourists are walking targets, be it day or night, in tourist-frequented areas including Copacabana Beach, Corcovado Mountain, Tijuca Forest, and Leblon.
Pickpockets have a bunch of creative diversions to distract you long enough for them to steal your wallet.
Never carry all your money in the same place and keep your belongings close to you at all times.
- How Does Brazil Compare?
- Useful Information
Brazil has a reciprocity standard when it comes to issuing visas and the rule goes like this: whatever restriction or visa prices apply to Brazilians when traveling abroad, also apply to foreigners from these countries. If you are not sure about your visa status, visit www.doyouneedvisa.com which will let you know whether or not you need visa based on your nationality and the country you want to visit.
Brazilian real is the official currency in Brazil. ATMs are available throughout the country, and are the easiest way of getting cash in big cities. They are also available in many smaller towns, but they sometimes don't work for non-Brazilian cards.
Located within the tropics, Brazil is wonderful to visit all-year round as its temperatures rarely go below 20°C with the exception of mountainous areas and southern regions. The climate varies in Brazil, from hot and dry in the inner areas to humid and sticky in the tropical Amazon jungle rainforests.
São Paulo/Guarulhos–Governador André Franco Montoro International Airport, also known as GRU Airport, or simply GRU, is the primary and busiest international airport serving São Paulo. It is located in the Greater São Paulo area.
Travel Insurance
Just like anywhere else, we recommend getting travel insurance when traveling to Brazil, since it covers not only the costs of medical problems, but also theft and loss of valuables.
Brazil Weather Averages (Temperatures)
- Average High/Low Temperature
Brazil - Safety by City
Explore brazil.
- 10 Cheapest Places to Live in Brazil
- 10 Best Beaches in Brazil
- 10 Most Dangerous Cities in Brazil
- 10 Best Zoos & Aquariums in Brazil
- 13 Most Beautiful Castles in Brazil
- 15 Best Flea Markets in Brazil
- 16 Pros and Cons of Living in Brazil
- 10 Safest Cities in Brazil
- Top 7 Brazilian Cocktails You Should Try
- Where to Next?

42 Reviews on Brazil
Big fall from grace.
I just want to say that the only reason terrorism is low on this rating is because it is out of their reach. Brazil is one of those places that are beautiful to visit for historical reasons but it just is not safe. It gets worse each year too. There is crime in all the streets and if you travel alone, you will end up having to look over your shoulder the entire time. Hardly enjoyable.
I tend to disagree with you. Brazil isn´t safe in some places like all countries. Go to favelas for exemple isn´t a good idea in any place of the world but when you go to christ of redeemer for exemple is all safe. São Paulo is way saffer than Rio but in my opinion Rio is the best city to visiti in the whole Latin America.
Very dirty cities, racist people, violent and extreme poverty overall
Rafal from Brazil “tend” to disagree about an honest opinion about his country… who would have thought?
Rafael from Brazil lives in Brazil. I can assure you he knows better than you about the country! 😉
As you point out Rafael is a local and therefore less likely to be targeted than a tourist.😉
Rafael, thank you I’m traveling to Brazil for the first time in April. I will stay at cocoabana beach for a few days then travel around the country. any recommendations on traveling to other cities
I’m Brazilian and I say that tourism in Brazil is very dangerous! You can’t be too careful, you can’t relax security at any time.
Use common sense and stay safe
Moved to Brazil about a year ago, have travelled along coast and in interior. Mostly feel safe here, but I always take the precautions normal for any big city – avoid display, don’t wear flashy jewellery or walk along the street carrying your new phone visibly, don’t go to dodgy areas at the wrong time of day. The landscape is beautiful, there are amazing and well maintained national parks with waterfalls, panoramas and terrific hiking. Brazilians are mostly friendly and courteous.
How did you move there and where did you move I’m looking to move there?
I won't be going there!
My family moved from Brazil to Canada when I was a baby. I hardly remember the place. I wanted to visit and my family wouldn’t stand for it. They said they left for a reason and it is way worse now than when they left. Needless to say, I will take their word for it and go elsewhere.
So you’ve never been to Brazil and yet you have an opinion, you know what opinions are like?
Is bad too much
It was safe before now is medium safe is not good at all
Regret going
Your family is completeley right, going is a waste of time and extemely dangerous.
Be smart when traveling
Why are you taking your time here to comment poorly about the country on every post? What happened to you there? I’m curious. Brazil is huge, a continental country. There are good things and bad. If you are from a first world country where anyone can freely walk at the streets at night with no fears whatsoever, don’t go there. But if you know how a big city works, that are places and behaviors you should avoid, no problem. Minimize your risks by not using blings and enjoy the beautiful country it is
It was safe before now is medium safe the is not good at all
Safe if you go to the right places
I have been to Brazil 4 times, and I partially agree with this article. It is mostly safe, but there is a relative risk of danger, mostly from thieves. However, if you go to the right places, it is very safe, and there is little to no danger- also, criminals tend to not target tourists. I would recommend going to Brazil with someone from the country, so that they can advise you with the right places to go. Lastly I would add that you should be careful driving in Brazil, as lorry drivers in particular sometimes don’t drive completely safely-especially on motorways. Go, and have fun, if you’re careful you will come to no harm.
If you want to be a World Traveler pay attention to your surrounding
Just an observation of your threads. I have spent the last 2 years on 4 trips averaging 60 days for each trip in Brazil. I live in Florida. I grew up in Miami, Florida in the ’80s-’90s. Back then crime back then was horrendous. Oh, and New York is way up there I would say like more Rio today. My friends would as me if is it dangerous. I would reply well at the farm 30 km south of Vitoria No, not at all. In Vela Vehla I felt safer than anywhere I have ever visited. In Vitoria in the city yes pay attention to your surrounding as I do anywhere I go. Some Americans walk around anywhere with no clue what “situational awareness ” is! What does that mean? Scan your surroundings. If you think you’re a baller with your Rolex and big gold chain you will probably get robbed or maybe kidnapped for $10,000. Also where you are, and what time, don’t walk alone like anywhere else in the world. There are crimes but no active shooters, It’s so nice we are building a home in Brazil.
Awful place
It’s really funny that the ones who “tend” to disagree are, of course, brazilians.
It’s extremely difficult to find people who had not been robbed or assaulted, unless you go to small and quite ugly cities with nothing to do or see (they’ll tell you there are things to do but there are not! beware! you didn’t cross the ocean for that). Also, a lot of white brazilians are very very racist (and most of them wouldn’t be considered white in north america).
Finally, unless you go for the beach and gals (careful, most of people are overweight in big cities) you will find all major cities very dirty, full of graffities (even in higher floors of buildings), blocks and blocks of abandoned buildings, tents with homeless in every park… it’s really disgusting.
Oh wow, you are incredibly disrespectful. Good thing you didn’t like it here, please don’t come back.
Food had salmonella on it
Unsafe and they are destroying the only one nice thing they have: landscape
JUST DON’T GO. YOUR LIFE IS AT RISK IN EVERY WAY
Too many pickpocketers at best
Not magic at all it’s VERY DIRTY at least all main tourist destinations, and full of graffiti and homeless. Plus people are kinda rude if you are foreigner and not blonde.
Hell on earth as a group of women backpackers. Do not recommend, plus police is the most corrupted in South America by far according to our experiences.
Disappointing, a new Turkey
Yes, most major cities are very violent, whether targeting tourists or not. And countryside not worth visiting, though…
But, what a resentment, uh? I would even think you spent a lot of time among Brazilians or be one yourself. BR is such a racist country, yet many southern Europeans are not considered white either in a Nordic-centred POV.
Too much jungle
Very nice apes
It’s ok! Not that bad as they say. I strongly recommend trying a delicious dish of traditional Brazilian coussine called “Monkey Soup” or Sopa Do Macaco in local language. Google it.
Very beautiful country with an amazing culture, it is pretty dangerous though. Haven´t felt safe in any moment. Without the danger Brazil would be paradise and I would still recommend going.
Don't be spoiled!
I am pretty sure the people complaining this much about the country being dirty and dangerous have all just visited big cities like Rio and São Paulo. People saying the countryside isn’t worth visiting, are you kidding me?? The absolutely beautiful and amazing mountains, the untouched forest we have in so many places, the friendly people and nice food, the amazing ecosystem in general are all unworthy of your holy presence? And we’re talking about a country with absolutely divine beaches in cities like Arraial do Cabo, Buzios, Ilha Grande… and these places aren’t dangerous, at least not nearly as dangerous as people in the comments are making it out to be. I’ve lived in this country for over 20 years and have never been robbed, neither have my parents. I’ve lived in big and small cities. You just have to have some common sense and it will not happen. If you’re unsatisfied please request that the first world countries some of you come from stop interfering with our politics so maybe we can grow economically.
YOU’RE GOING TO BRAZIL
Come to Brazil you will love it!
I live in the USA and I believe that many cities in the USA are more dangerous than any city in South America! The cities gangs and thieves , the White Supremacists, the KKK the Qnon and the racism are high. Brazil population in general are very welcoming and they know how to party and enjoy life! The food is great and the music and arts and sports superb! Millions of people visit Brazil and many more move to live there. I being visiting Brazil since 2005 and had never had been exposed to any crime or violence!
First of all racism is at an all-time low in the US. In Brazil it’s higher, and most Brazilian cities are in the top 50 all of them being In a worse position then American states, gun battles just don’t randomly happen in America like in Brazil, the most dangerous city in Brazil is the 8th most dangerous in the world while the most dangerous city in America is the 40tg so don’t make me laugh, do not compare Brazil to America. Brazil is in a worse place politically, economically, and dangerous.
Obviously paranoid—and I speak as an African American—gangs yes; kkk, qnon???!!! Been watching too much conspira-fantasy cable-Tel-Lie-Vision!!! Not saying R.ism isn’t real but the hair on fire race hustling in media is almost just as odious especially when innocent people are labeled, branded, castigated and punished (cancelled for no reason at all).
Racism is actually lower in USA than most countries, look it up.
I’m from Canada and that’s even more racist than USA.
Brasil, o paradiso na Terra!!!!
I’m an American citizen and have traveled around the world; I lived in São Paulo, Brasil with my family for the happiest years of our lives and I will not hesitate to relocate permanently to São Paulo, Brasil; we speak several languages fluently English (naturally), Portuguese, Spanish and a smattering of others; we thoroughly enjoyed the people, the year-round weather, International cuisine, and ALL things related to Brasil.
Eu nao sou brasileiro mais o meu coracao ficou sendo mais brasileiro do que muitos dos Cariocas e Paulistas e outros mais.
Para nous, Brasil eis o País mais semelhante ao paradiso. Si eu pudese, voltaria pea la’ ONTEM!!!
Could be better, but sadly is not anymore.
Thank you for your opinion Jose! I’m a Brazilian that moved to Canada with my wife and kids 4 years ago. I love Canada so much that makes me not even think about living in Brazil again. I had problems with security a couple of times in my life living there, and I’m talking about 37 years. Yes, Brazil is a BEAUTIFUL country! Yes, Brazil has an amazing culture and people. But some aspects make (sadly I’m talking about the crab culture and our bad politics) the country deteriorate more and more every year. Still, I have Brazil in my heart, all my family still there. But I can live there anymore, for me does not worth it. I used to say that Brazilians that still are living there today, and being VERY generalist, are like frogs in a saucepan. They don’t feel the heat anymore and when they figure out is too late, they die. If you want to visit the country go, but be careful, and everything will be fine. But I will not suggest living there anymore.
Don’t Go Brazil or you going to have a lot of lag in the lounge, trust me I know some brazil players that are very laggy
It can be an amazing place but it has it’s dark side
Like someone already said Brazil is safe if you go to the right places. The favelas should be a no-go zone as the poverty there will drive people to do all sorts of stupid things. Thieves are present in all crowded areas so watch your pockets. I agree that Sao Paolo is safer than Rio although Rio is a beautiful city. It’s best to go to Brazil in groups of at least 4 people and just avoid the bad areas. Doing so will result in a great vacation as Brazil has so much to offer.
If you rent a car or drive your own, be careful as some drivers here have nothing in common with the rules of driving. Keep your eyes open and try to avoid overcrowded roads if/when possible.
As a woman, I would never go here alone. Last time I was there we were 7 people and I didn’t feel unsafe. Even when I saw a small group of pickpockets I wasn’t afraid as we had 5 guys with us. But it’s clear that the poverty in this country does “encourage” some people (even kids) to try and steal money or things. It’s always best to keep a close look on your belongings and not waver money, credit cards or your phone around as someone may steal it.
As for where to go, there are so many amazing destinations. The Tijuca National Park for example, is beautiful and here you will find the Cristo Redentor statue. Seeing this in pictures or even on video is nothing, just wait until you are here! It’s so big and if you look down from there, the view is absolutely breathtaking! And the park is so fantastic, with countless birds, springs and waterfalls.
The Iguacu Falls is also something you don’t see everywhere. Some of the falls are 100+ meters high and they mark the meeting point for Brazil, Paraguay and Argentina. The best view is from the Brazilian side but you can also go a bit into the Argentinian side for some different views.
There are many other interesting places that one should visit if they have the time. Pernambuco Beaches, the beautiful art museums of Sao Paolo, Belo Horizonte, Ipanema, Copacabana.
Too much poverty
DO NOT TAKE YOUR NEW IPHONE TO THE BEACH IN RIO IT WILL BE SNATCHED. Bring a cheap back up phone or no phone at all at the beach or when walking in the streets.
Lovely, don't let the fear get to you
There’s absolutely so much to do in Brazil, and the “imminent danger” is absurdly overstated. Don’t let the bad fame get to you. Watch vlogs from small Youtube channels that went there. You can stay in that country for 90 days till your Visa expires and you will still have so much to do.
It is very unlikely anything happens to you, and still, if it does it probably will be just a pickpocket snatching your wallet on a city. Tourists are not targeted at all, most crime apparently happens in poor neglected neighborhoods.
I’ve never been to Brazil, but am interested in Candomble. I’ve read much about it, and have met practitioners here in St. Louis, Missouri. U.S.A. Can anyone commenting here offer insights on this fascinating faith, or better yet, relate some personal experience?
Love the people and culture. Be respectful and you should be fine!
I have been to Brazil 3 times, I fly into Salvador, Bahia. All my experiences in Brazil have been excellent. I tell you why. It is because I respect their country and their culture. On top of this I go with the flow, which means I am able to meet people easily. I have made excellent and close friendships in Bahia state. I have been rewarded with seeing the real Brazil and that is why I goto Brazil, to be a part of Brazil, to try and fit in. Yes my nickname to my friends in Brazil is “Gringo Louco” and that is fine, it does not bother me in the slightest. I am laid back and just go with the flow. I think this is where a lot of people go wrong in Brazil, is they go out their, you can tell a Brit when you see one or an American. Brits are red from sun burn and they just stand out and that makes them a target. Americans tend to be blinged up and loud mouthed. All of this attracts the wrong type of people, no matter where these types visit in the World.
Me, well I am lucky to be Portugues, Maori bloodline, I am olive color skin, I speak some Portugues and given the right circumstances, when around my friends in Brazil, I feel integrated and no one is looking at me, no threats it seems, because I dont look like a tourist, because I have friends and go to places regular tourists will never be able to go. I have a friend that lives in a favela in Aracaju. I have stayed there, it did not bother me in the slightest. I felt welcomed and again, I was with friends who know what is right and what is wrong. Out of respect that evening I was in Aracaju, I stayed at my friends place, even though another friend had booked into a hotel and was surprised I was staying at my friends place in a so called Favela. Although it is not like a Rio or Sao Paulo favela, in all honesty. But again, I was not complacent, I am respectful of other countries rules and again, with a friend or two, you just look like one of the locals.
I love Brazil, I am in particular fond of Bahia state. It is laid back, the beaches are amazing, the people in Salvador are exceedingly friendly from my experience and because I have made friends I end up going to their houses for lunch and dinners, going to hidden beachside restaurants that the regular tourist would never know about unless you have Bahian friends, etc, etc.
Maybe I am lucky when I travel, because I like to meet new people, I am laid back and I respect the culture. This is why I do not have trouble I think. Not being frightened, but keeping your wits about you, means you are more likely to blend in.
Personally, I goto places like Bahia to get away from British people who I find to be obnoxious and arrogant. In Bahia, this place is not for them, it is too risky for them probably, because they do not respect the culture, or very few do, so they stand out. Being red you stand out, even in the South of Brazil, Brits just stand out.
So no I love Brazil, its people, I feel welcome and even though I am olive color skin, I have never experienced any racism in Brazil. I know white and black people, it does not matter to me. That mentality helps you to get along.
Share Your Experience Cancel reply
Your Review
Title of your review
Article Contents
- Overall Risk
- Transport & Taxis Risk
- Pickpockets Risk
- Natural Disasters Risk
- Mugging Risk
- Terrorism Risk
- Women Travelers Risk
- Weather Averages (Temperatures)
- User Reviews
- Share Your Experience
Popular Destinations

Safety Index
Recent reviews & comments.
- Kristof Kelp on 10 Most Dangerous Cities in Arizona
- Martin Lee on Stateline
- Sonny Andrews on Stateline
- Jayven Cruz on Stateline
- Jose Rivera on Old Saybrook
Popular US States
- Pennsylvania
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Brazil travel advice
Latest updates: Risk levels - added information on regional risk levels for border areas
Last updated: May 24, 2024 09:04 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, brazil - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Brazil due to high crime rates and regular incidents of gang-related and other violence in urban areas.
Border areas - Avoid non-essential travel
- within 20 km of the border with Argentina, excluding Iguazú National Park
- within 20 km of the border with Bolivia, excluding Pantanal National Park
- within 20 km of the border with Colombia
- within 20 km of the border with French Guiana
- within 20 km of the border with Guyana
- within 20 km of the border with Paraguay
- within 20 km of the border with Peru
- within 20 km of the border with Suriname
- within 50 km of the border with Venezuela
Back to top
Crime rates are high throughout the country, particularly in:
- Porto Alegre
- Rio de Janeiro
- São Paulo
Tourists are most commonly affected by theft, but incidents of violent crime have occurred.
Violent crime
Violent crime occurs, namely:
- home invasion
- armed robbery
- sexual assault
Violent crime, often involving weapons, is common.
The following areas have high incidences of violent crime:
- Rio de Janeiro
- Christ the Redeemer statue
- Copacabana Beach
- Corcovado Trail
- Ipanema Beach
- Lapa neighbourhood
- Santa Teresa neighbourhood
- around São Paulo Cathedral
- Avenida Paulista
- Central market
- historical downtown area
- Princess Isabel Square
- Station of light
- Ceilândia
- Paranoá
- Santa Maria
- São Sebastião
If you decide to travel to these areas:
- exercise a high degree of caution at all times
- avoid travelling alone, especially at night
- avoid parks or central areas of major cities
- avoid poorly lit and isolated streets
- avoid walking on isolated and unsupervised beaches, especially at night
- if you’re threatened by robbers, don’t resist.
Robberies, often armed with weapons such as guns and knives, occur regularly. Victims are generally selected on the basis of perceived wealth, including using cell phones and laptops.
Robberies occur in and around:
- ATMS and currency exchange bureaus
- hiking trails
- outdoor markets
- parking lots
- public transport
- restaurants
- road closures
- traffic jams
- unregistered taxis
Drive-by snatching by armed thieves on motorcycles occurs regularly, particularly in São Paulo and Porto Alegre.
- Keep car windows and doors locked at all times
- If you feel threatened while driving at any time, do not stop
Victims have been seriously injured or killed when resisting perpetrators, who may be armed or under the influence of drugs.
Spiked food and drinks
Spiked food and drink incidents are increasing in Brazil, particularly in Rio de Janeiro .
Incidents of spiked food and drinks to force victims to use their debit or credit card to withdraw money from ATMs has been reported, including on beaches in Rio de Janeiro and crowded restaurants in São Paulo.
The use of drugs to facilitate sexual assault and robbery against foreigners has also been reported. Assaults frequently occur in unofficial taxis.
Incidents occur:
- in bars and restaurants
- in nightclubs
- at public beaches
While you’re in Brazil:
- never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers
- be wary of accepting these items from new acquaintances
- ask for drinks coming from sealed bottles or cans instead of in plastic cups
- in restaurants, avoid sitting close to the entrance
Petty crime
Street crime, including pickpocketing, purse snatching and theft from cars, is common in Brazil’s large cities. Tourists are a favourite target.
Petty theft on buses and the metro is common. It is a significant concern in Recife.
Incidents of opportunistic crime increase significantly at large-scale sporting events, international conferences and during holidays such as the Carnival and New Year’s celebrations.
Flash mob robberies ( arrastões ) have occurred sporadically on Rio’s city beaches and in other crowded tourist areas. This type of crime involves a group of thieves (often young children and youth originating from nearby favelas) that swarm an area and snatch valuable items such as cash, jewellery and cell phones.
A common ruse used by criminals is the Good Samaritan scam, where a criminal offers to help a tourist who looks lost. If you are lost, go into a nearby business or hotel to ask for help.
- Ensure that your personal belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- Remain vigilant when visiting tourist destinations such as:
- hotel grounds
- bars and nightclubs
- airports and bus stations
- Avoid showing signs of affluence such as expensive jewellery, watches, clothing and bags
- Carry only small amounts of cash
- Keep cameras and portable electronic devices concealed
- Be aware of ploys to distract your attention
- Remain cautious with new acquaintances who ask for information or offer hospitality or assistance
- Book tours with reliable agencies
Express kidnappings
The number of kidnappings in the Rio de Janeiro Metropolitan area has significantly increased since 2022.
Criminals may kidnap a victim for a few hours and force them to withdraw funds at an ATM for their release. Thieves may put drugs into food and drinks, temporarily incapacitating victims, who become quickly disoriented and are vulnerable to kidnapping.
- Use only a reputable taxi company or a trusted ride-sharing app
- Avoid showing signs of affluence, such using cell phones, headphones and wearing jewelry
- Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers
- Be wary of accepting these items from new acquaintances
Borders with Colombia and Venezuela
There is a concerning level of serious criminal activity by organized criminal groups along the border areas with countries bordering Brazil, particularly Colombia and Venezuela. Incidents of attacks on tourists and kidnapping have occurred. Be extremely cautious when crossing into bordering countries.
Vulnerable neighborhoods
Vulnerable neighborhoods (commonly referred to as “favelas”), are characterized by informal housing developments, crowded quarters, poorer conditions, and/or irregular construction.
Gang-related violence and organized crime is prevalent in these areas and police assistance is very limited.
Avoid renting accommodations in vulnerable neighborhoods, and travelling to these areas, even on a guided tour.
Police operations
Armed clashes and shootouts between police forces and alleged criminals regularly occur in vulnerable neighbourhoods. Police operations have led to retaliation by criminal gangs. Vulnerable neighbourhoods are located across major cities, as a result, there is an ongoing risk of violence spilling over to neighbouring areas, including affluent neighbourhoods and tourist destinations. There have been incidents of injuries and deaths as a result of stray bullets near, and in, vulnerable neighbourhoods.
Credit card and ATM fraud is a major problem. Be cautious when using debit or credit cards:
- pay careful attention when your cards are being handled by others
- use ATMs located in well-lit public areas or inside a bank or business
- avoid using card readers with an irregular or unusual feature
- cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements
Cybercrime is also a growing problem. Perpetrators monitor social media sites and eavesdrop on your conversations when you are in the country.
- Do not discuss travel plans or any other personal information within earshot of strangers
- Be cautious when posting information on social media
- Be particularly vigilant in internet cafes
Overseas fraud
Pirate attacks and armed robbery against ships occur in coastal waters. Mariners should take appropriate precautions.
Live piracy report - International Maritime Bureau’s Piracy Reporting Centre
Demonstrations
Demonstrations take place regularly. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
Protests can cause delays on main roads, including to airports, such as to the Guarulhos International Airport i n São Paulo . Demonstrations tend to increase in frequency and intensity during major events that attract foreign visitors.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Women’s safety
Women travelling alone may be subject to some forms of harassment and verbal abuse.
- Avoid travelling alone at night
- Avoid carrying purses
Advice for women travellers
Coastal waters can be dangerous.
- Swim or surf in areas where lifeguards are located
- Avoid swimming where there are strong currents
- Be wary of sharks, especially in Brazil’s north east near Recife
- Follow the instructions and warnings of local authorities.
Robberies are frequent and occur in tourist destinations, including on hiking trails. Be especially cautious on the Corcovado trail in Rio, where several robberies have happened.
If you intend on trekking:
- never do so alone
- always hire an experienced guide from a reputable company
- buy travel insurance
- ensure that your physical condition is good enough to meet the challenges of your activity
- ensure that you’re properly equipped and well informed about weather and other conditions that may pose a hazard
- inform a family member or friend of your itinerary, including when you expect to be back
- obtain detailed information on trekking routes before setting out
- ensure the trail doesn’t pass through a favela
- do not venture off marked trail
Adventure tourism
Amazon border regions and the Pantanal wetlands are largely uninhabited and dangerous areas.
Travel in these regions only with trained guides.
Public transportation
The subway systems in Rio and in São Paulo are generally safe during the day. Be extremely cautious using public transportation at night
There have been reports of theft and violence on city buses in Rio de Janeiro and near vulnerable neighbourhoods across the country, especially during rush hour.
Inter-city buses are generally reliable. Ensure that you use a reputable company before you book your travel.
Bus accidents occur regularly.
Major bus services charge fixed, pre-paid rates.
Do not use public vans.
Local law requires the use of the taxi meter to determine the legal fare. Adding surcharges to a fare is illegal.
Should taxi rates change and their taxi meters have not been adjusted, drivers may indicate these changes by showing an authorized paper with the new fares.
Many tourists hire “radio taxis”, also known as “commun taxis.” These taxis operate at a fixed price irrespective of the time of the day and the time it takes to arrive at your destination.
- Only use official taxis
- Upon arrival to Brazil, purchase your fare from licensed taxi offices in the airport arrival hall or near the taxi queues
- During your stay, use licensed taxis from taxi stands
Road safety
Brazil has one of the highest road accident rates in the world.
Road conditions are generally acceptable in large cities but badly maintained in the rest of the country. Poor signage and construction also pose a hazard.
Drivers do not respect traffic laws. Drivers are extremely aggressive and reckless and often drive at excessive speeds.
At night, it is common for drivers to treat red lights as stop signs to protect against hold-ups at intersections. Pedestrians and motorists proceeding through green lights during these hours should be particularly cautious.
- Be careful when stopping on the side of any highway because of traffic
- Be careful of motorbikes when changing lanes
- When driving in the city, pay particular attention to your surroundings while waiting at traffic lights
- If you feel threatened at any time, do not stop
- If you are in a traffic accident, call the police immediately
- Never confront the driver of another vehicle
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Visitor visas
Effective April 10, 2025, Canadian passport holders will be required to obtain a visa to enter Brazil.
For more information, contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Brazil.
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Brazilian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Brazil.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: not required for stays of up to 90 days Business visa: not required for stays of up to 90 days without remuneration Student visa: not required for stays of up to 90 days
Length of stay
A tourist stay can be granted for up to 90 days. The permitted length of stay for tourists is determined by the immigration officer upon entry.
If you intend to stay more than 90 days, you must obtain an extension from the Federal Police for a maximum stay of 180 days per period of 12 months.
To request a visa extension, you will have to:
- request such an extension prior to the expiration of the authorized stay
- provide your detailed (long-form) birth certificate
In order for your Canadian long form birth certificate to be accepted in Brazil, it must be presented to the Brazilian Embassy or one of its consulates prior to departure from Canada. Neither the Embassy of Canada nor its consulates in Brazil can authenticate a Canadian birth certificate outside of Canada.
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Zika virus: Advice for travellers - 31 August, 2023
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
- Dengue: Advice for travellers - 6 May, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is a risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is not required to enter this country.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is recommended depending on your itinerary.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites.
About Yellow Fever Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by an animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. Rabies treatment is often available in this destination.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
There is a risk of schistosomiasis in this destination. Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by tiny worms (blood flukes) which can be found in freshwater (lakes, rivers, ponds, and wetlands). The worms can break the skin, and their eggs can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, flu-like symptoms, or urinary problems. Schistosomiasis mostly affects underdeveloped and r ural communities, particularly agricultural and fishing communities.
Most travellers are at low risk. Travellers should avoid contact with untreated freshwater such as lakes, rivers, and ponds (e.g., swimming, bathing, wading, ingesting). There is no vaccine or medication available to prevent infection.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
Cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis causes skin sores and ulcers. It is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a female sandfly.
Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from sandfly bites, which typically occur after sunset in rural and forested areas and in some urban centres. There is no vaccine or medication to protect against leishmaniasis.
Visceral leishmaniasis (or kala azar) affects the bone marrow and internal organs. It is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a female sandfly. It can also be transmitted by blood transfusion or sharing contaminated needles. If left untreated it can cause death. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from sandfly bites, which typically occur after sunset in rural and forested areas and in some urban centres. There is no vaccine or medication to protect against leishmaniasis.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Zika virus is a risk in this country.
Zika virus is primarily spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can also be sexually transmitted. Zika virus can cause serious birth defects.
During your trip:
- Prevent mosquito bites at all times.
- Use condoms correctly or avoid sexual contact, particularly if you are pregnant.
If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, you should discuss the potential risks of travelling to this destination with your health care provider. You may choose to avoid or postpone travel.
For more information, see Zika virus: Pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease) is a risk in this country. It is caused by a parasite spread by infected triatomine bugs. The infection can be inactive for decades, but humans can eventually develop complications causing disability and even death.
Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from triatomine bugs, which are active at night, by using mosquito nets if staying in poorly-constructed housing. There is no vaccine available for Chagas disease.
Oropouche fever is a disease caused by the Oropouche virus, which is spread to humans through the bite of an infected midge or mosquito. Symptoms of Oropouche fever are similar to dengue, and usually include fever, headache, joint and muscle pain, chills, and sometimes nausea and vomiting. In some cases, aseptic meningitis (inflammation of the membranes that surround the brain) may occur.
Most travellers are at low risk. Individuals travelling in the Amazon rainforest, or travelling to work in agriculture or forestry are at higher risk.
Protect yourself from midge and mosquito bites. There is no vaccine or medication that protects against Oropouche fever.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Medical services and facilities
Good health care is only available in major cities. Quality of care varies greatly throughout the country.
Private hospitals and clinics located in cities are often better staffed and equipped than public or rural facilities.
Some medical facilities in the state of Rio de Janeiro have closed or are providing limited services, due to lack of funding for their operations. Private hospitals remain operational.
Certain medications may not be available.
Physicians and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment.
Medical evacuation can be very expensive and you may need it in case of serious illness or injury.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe.
Avoid areas of known drug trafficking. Travellers should not, under any circumstances, carry any items for strangers, especially baggage and parcels.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Child sex tourism
Brazil is actively seeking to prevent child sex tourism. A number of tourists have been convicted of offences relating to the corruption of minors.
The legal age of consent in Brazil is 18. Prison sentences are severe.
Child Sex Tourism: It’s a Crime
Identification
You must carry photo identification, such as a passport or driver’s license. Keep a photocopy of your passport in a safe place, in case it’s lost or confiscated.
Not carrying identification can lead to problems and delays if stopped by police or in case of a medical emergency.
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is legally recognized in Brazil.
If you are a Canadian citizen, but also a citizen of Brazil, our ability to offer you consular services may be limited while you're there. You may also be subject to different entry/exit requirements .
Travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. The convention applies between Canada and Brazil.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Brazil, and if the applicable conditions are met, you may apply for the return of your child to the Brazilian court.
If you are in this situation:
- act as quickly as you can
- contact the Central Authority for your province or territory of residence for information on starting an application under The Hague Convention
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Brazil to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- List of Canadian Central Authorities for the Hague Convention
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- The Hague Convention - Hague Conference on Private International Law
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
The legal blood alcohol limit is 0.00% in Brazil. If the police suspect you of drinking and driving, they could confiscate your driver’s licence on the spot. If convicted, you can expect heavy fines and possible jail sentences.
You can drive in Brazil for up to 180 days with a valid Canadian driver’s licence. Obtain an official Portuguese translation of your Canadian driver’s licence to help when dealing with local authorities.
You should carry an international driving permit.
International Driving Permit
The currency is the real (BRL).
Canadian bank cards may not work in ATMs. They should have a pin with a maximum of 4 digits to work in Brazil.
Canadian dollars are not generally accepted, except by some exchange bureaus, most likely at airports. Do not exchange money on the street.
Carry small bills, as change is often unavailable for small transactions.
Flooding in southern Brazil
On May 1, 2024, heavy rains caused severe flooding in southern Brazil, particularly in the following states:
- Rio Grande do Sul
- Santa Catarina
Rio Grande do Sul is the worst affected, especially Porto Alegre, resulting in several casualties. The governor of Rio Grande do Sul has declared a state of calamity. There are reports of significant damage to buildings and infrastructure. Evacuation efforts are underway. More rain is expected in the region in the days to come.
The following essential services could face further disruptions:
- emergency services
- fuel supply
- medical care
- power distribution
- telecommunications networks
- transportation
- water and food supply
If you're in an affected area:
- shelter in a safe place and stay indoors
- exercise caution
- monitor local news and weather reports
- follow the instructions of local authorities, including evacuation orders
If you are in Brazil, sign up for the Civil Defense SMS service to be notified of weather alerts in your region.
Useful links:
- Weather alerts – National Institute of Meteorology (in Portuguese)
- Warnings and alerts – Government of Brazil (in Portuguese)
El Niño
The complex weather phenomenon called El Niño happens at irregular intervals of 2 to 7 years and can last 9 months to 2 years. El Niño generally generates droughts and heavy rainfalls, which could cause flooding, landslides, and mudslides, and could severely disrupt travel. Extreme droughts and heavy rains could limit access to food, drinking water, hygiene products, and medication. Severe weather could occur, such as:
- Below-average rainfall and droughts in the north and northeast
- Excessive rains in the south and southeast of the country
- Above-average temperatures in all regions
Keep informed of regional weather forecasts before and during your travels, and plan accordingly. Ensure you have adequate insurance to cover the consequences of such events, including the disruption of travel plans.
Learn about El Niño
Rainy seasons
The rainy seasons extend from:
- January to July in the north
- October to April in the south and southeast
- April to July in the northeast
Flash floods can occur outside of the rainy season.
They can hamper overland travel, especially in rural areas. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged. Travel conditions on mountain roads and on highways leading to beaches can be dangerous. Seasonal flooding can also reduce the provision of essential services. Power outages are frequent during the rainy season.
Avoid the affected areas, keep informed of regional weather forecasts and follow the instructions of local authorities.
- Weather warnings – National Institute of Meteorology (in Portuguese)
- Weather forecast – Climatempo (in Portuguese)
- More about hurricanes, typhoons, cyclones and monsoons
Landslides
Landslides are becoming more common in Brazil and are the result of heavy rainfall. During heavy rainfall, landslides are more likely to occur.
Dry season
Brasilia and the interior of the country experiences extreme dry periods between June and September. Humidity levels can drop below 10% and heat levels rise significantly.
Stay informed of regional weather forecasts and plan accordingly.
A severe drought is affecting the south east of Brazil.
The water supply in São Paulo, including to the city of São Paulo, has been significantly affected. Some areas of São Paulo are experiencing water shortages, and the water quality has diminished.
Use only bottled water for drinking and cooking.
Bush and forest fires are common between May to September, particularly in Brasilia.
The air quality in areas near active fires may deteriorate due to heavy smoke. In case of a major fire:
- stay away from the affected area, particularly if you suffer from respiratory ailments
- follow the instructions of local emergency services personnel
- monitor local media for up-to-date information on the situation
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police (military): 190
- medical assistance: 192
- firefighters: 193
Tourist police
- Rio de Janeiro: (21) 2332 2924 or 2334 6802
- São Paulo: (11) 3120 4447 or 3151 4167
- Salvador: (71) 3116-6817
- Recife: (81) 3322-4867
Consular assistance
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Brazil, in Brasilia, or the Consulate General of Canada in São Paulo or Rio de Janeiro and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
You may call the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa toll-free at 0 800 891-6614.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise a high degree of caution in Brazil due to the threat of violent crime.
Brazil (PDF 1.24 MB)
Americas (PDF 3.25 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 192 or go to a hospital.
Call 190 or go to the local police station.
Advice levels
Exercise a high degree of caution in Brazil.
- The wet season is from November to July, however heavy rainfall can occur all year, depending on the region. Landslides and flooding can occur, and severe storms often delay flights. Be prepared to change your travel plans.
- Large scale protests can occur at any time in Brazil. Monitor the media. Follow the instructions of local authorities and review our guidance on staying safe when there are demonstrations .
- Violent crime, including mugging, armed robbery and carjacking is common. These occur more often in large cities and during festivals, such as Carnaval. Don't go out alone at night. Avoid isolated areas, including beaches. Crime rates are particularly high in shanty towns or 'favelas'. Don't enter favelas, even with a tour group.
- Use only prepaid or official taxis. If using rideshare apps such as Uber, ensure you enter the vehicle with the same plate number and name shown in the app. If you're driving yourself, keep doors locked and windows closed. Ensure your route avoids favelas.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Brazil experiences recurrent measles outbreaks. It is important to get vaccinated.
- Common insect-borne diseases include dengue, malaria, yellow fever, Zika virus, chikungunya, filariasis and leishmaniasis. The 2024 seasonal increase in dengue fever is much higher than usual. Protect yourself from insect bites. Get vaccinated against yellow fever where possible.
- HIV/AIDS is a serious risk. Take precautions if you're taking part in high-risk activities.
- Food-related, waterborne and other infectious diseases include cholera, typhoid and hepatitis. Drink boiled or bottled water. Avoid raw or undercooked food.
Full travel advice: Health
- Don't use or carry illegal drugs. Penalties for drug offences are severe and include long prison sentences.
- You must carry proof of identity with you. Always carry photo ID, such as a driver's licence and a photocopy of your passport.
- Dual nationals must enter Brazil on their Brazilian passport. If you're male and aged over 18, you may need to do military service. Contact a Brazilian embassy or consulate for advice.
- Same-sex relationships are legal but aren't always accepted in rural communities. Avoid public displays of affection.
- Don't drink and drive. Penalties are severe for driving with a blood-alcohol level reading over 0%.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- Australian passport holders do not need a visa to enter Brazil for short stays. For more information, contact an embassy or consulate of Brazil .
- Entry and exit conditions may change without warning. Follow the advice of border and health authorities and comply with local regulations. Contact the nearest Brazilian embassy or consulate for the latest details.
- Brazilian children (including dual nationals) must have written consent from any non-accompanying parent to depart Brazil.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
- For full consular assistance, contact the Australian Embassy in Brasilia or the Australian Consulate-General in São Paulo .
- The Australian Consulate in Rio de Janeiro does not provide notarial (document legalisation) services and only provides limited services, for example interviews for an Australian Passport.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Violent crime.
Violent crime, often involving weapons, is common, especially in large cities. Most crime is opportunistic. Common examples which involve tourists include the theft of valuables at the beach or from bags and valuables snatched while sightseeing. Tourists have also been robbed at knife or gunpoint. Local authorities advise against taking valuables and passports to the beach. Carry a photocopy of your passport or another form of identity.
Muggings and other violent crimes are common in and around:
- tourist spots, hotels, nightclubs and bars
- historical centres
- public transport
- public beaches
- outdoor markets
- unregistered taxis
- ATMs and currency exchange facilities
Other common crimes include:
- home invasion
- food and drink spiking
- sexual assault
- kidnapping and scams
In Rio de Janeiro, crime hotspots include:
- Copacabana Beach
- Ipanema Beach
- the Santa Teresa area
- the Lapa neighbourhood
- the Christ the Redeemer statue
- the Corcovado Trail
In São Paulo, crime hotspots are in the downtown area and around the historical centre of the city and include:
- around the São Paulo Cathedral
- Station of light (Estação da Luz)
- Princess Isabel Square
- Central market
In Brasilia, crime hotspots include the central bus station and two adjacent shopping centres.
Crime levels in shanty towns, or 'favelas', and many satellite cities are especially high.
Crimes relating to drug trafficking and illicit goods are common along Brazil's western and northern border areas, posing a risk of violent crime to travellers. Affected areas include:
- the states of Amazonas, Acre, Rondônia, Mato Grosso, Roraima, Pará and Amapa
- river travel in the Amazon, particularly Itaquai, Japura and Rio Negro rivers and tributaries.
- the tri-border area of Argentina, Brazil (Foz do Iguaçu city) and Paraguay
Your safety is your main priority. Don't chase after a perpetrator or resist. Criminals may be armed and, if challenged, they may respond with violence. They will often have accomplices nearby. If you're robbed, report it to the local police.
To protect yourself from violent crime:
- avoid crime hotspots, especially late at night
- stay alert in public places, especially where there are lots of people, including other tourists
- leave valuables and passport in a hotel safe
- keep mobile devices and other valuables out of sight
- keep your belongings and baggage close to you when you're outside
- lock the doors and windows of your accommodation, including balcony doors
- avoid going out alone, especially at night
- avoid isolated areas on the beach
- don't leave your luggage, food or drinks unattended
- never accept drinks, food, gum or cigarettes from people you've just met
- don't enter favelas, even with a tour group
If you're a victim of violent crime, including rape, seek immediate medical help. The risk of HIV/AIDS is high.
Female survivors of domestic violence or sexual assault can access a dedicated hotline that provides access to local support services, including police, by calling 180 or via the WhatsApp phone messaging application on +55 61 99610 0180.
Partying safely
Crime levels increase before and during festivals such as Carnaval, with tourists frequently being targeted.
Make sure you follow these tips:
- watch out for drink spiking and know your alcohol limits
- don’t use drugs – penalties for drug offences in Brazil are high
- don’t drink and drive – penalties are severe for driving with a blood-alcohol reading over 0%
- keep your valuables out of sight, as petty crime, such as bag or phone snatching, is common
- be mindful of where you’re going, get recommendations from your hotel and plan your transport options in advance
More information:
Scammers take advantage of people looking for romantic partners, often via dating websites, apps or social media, by pretending to be prospective companions. Be wary of any online invitation you receive to travel to an unfamiliar location, especially if the location is changed at late notice and if someone is offering romance. The scammer may kidnap you and force you to transfer or withdraw money and then extort your loved ones for more money to secure your release.
Take caution when purchasing food and beverages from vendors, especially at the beach when paying by card. Confirm the price before and check the figure on the card machine is correct and hasn't been inflated. Don’t give your card to the vendor when making payments.
- Theft and robbery
- Scams that affect travellers
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you’re connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions, or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Kidnapping occurs across the world with political, ideological and criminal motives. Foreigners, including Australians, have been kidnapped overseas while travelling. Kidnaps can happen anywhere, anytime, including in destinations that are typically at lower risk. The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
Kidnappings occur in Brazil, and in some cases, individuals of perceived wealth are targeted. There have been instances of kidnapping-for-ransom, express, tiger, and virtual kidnappings. There were more express and tiger kidnaps in Brazil than in any other country worldwide during the first half of 2023.
Civil unrest and political tension
Large-scale protests are common. Public protests and events that draw large crowds can turn violent and authorities have used tear gas and other riot-control measures.
Demonstrations and protests often interrupt traffic and public transport.
During periods of unrest:
- avoid protests and rallies
- monitor the news for possible unrest and avoid those areas
- if a protest occurs, leave if it's safe to do so
- prepare for long waits and be ready to adjust your travel plans
- follow instructions from the local authorities
You should follow the instructions of local authorities and review our guidance on staying safe when there are demonstrations .
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
Major events are attractive targets for terrorists.
To protect yourself from terrorism:
- be alert to possible threats
- report suspicious activity or items to police
- monitor the news for emerging threats
- take official warnings seriously
- follow the advice from local authorities
If there's an attack, leave the affected area straight away if you can.
Avoid the affected area after an attack in case there are secondary attacks.
Swimming safety
Many beaches, including in Rio de Janeiro and Fortaleza, have strong, dangerous rips.
Shark attacks are possible, especially at many north-eastern beaches. Obey warning signs.
Climate and natural disasters
Brazil experiences severe droughts and flooding.
If there's a natural disaster :
- secure your passport in a safe, waterproof location
- keep in contact with your friends and family
- monitor the media and local sources
- follow the advice of local authorities
Register with the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System to receive alerts on major disasters.
Heavy rainfall is causing significant flooding in the State of Rio Grande do Sul. There's damage to infrastructure and essential services, including transport, may be disrupted. A state of emergency has been declared in some cities. If you're in an affected area, follow the advice of local authorities and monitor the media for updates.
The wet season is from January to July in the north, November to March in the south and south-east and April to July in the north-east. Landslides, flooding and flash flooding can happen, especially in poorer urban areas.
It's common for flooding and severe storms to damage transport infrastructure, including roads and bridges and can delay domestic and international flights. Monitor local media for weather advice and follow any instructions given by local authorities.
Staying safe in the heat
If you're travelling during extreme hot weather, plan your days to avoid being outside during the hottest part of the day. If you go out in the heat, rest often and stay in the shade as much as possible.
- Drink plenty of water. Even if you're not thirsty. Avoid alcohol
- Wear sunscreen, a hat and sunglasses
- Wear loose, lightweight, light-coloured clothing
Avoid strenuous outdoor activities such as hiking or biking in extreme hot weather, particularly if you're not usually active or used to high temperatures.
- Extreme hot weather
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare, or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Medications
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in Brazil. Take enough legal medicine for your trip.
Carry a copy of your prescription or a dated letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Health risks
Insect-borne diseases.
Insect-borne diseases are a serious risk in Brazil. Yellow fever , dengue , malaria and the zika virus are common. Other insect-borne diseases include:
- chikungunya
- leishmaniasis
You're most at risk during the wet season, in poorer urban areas or in regional areas where there are stagnant bodies of water, including the Pantanal or Amazon.
Take the following steps to avoid insect bites:
- cover exposed skin with light-coloured long-sleeved shirts and long pants
- use insect repellents. If you use both sunscreen and insect repellent, apply the sunscreen first and then the repellent
- treat your clothing and gear with insecticides
- sleep in screened or air-conditioned rooms. Use bed nets if you can't keep mosquitoes from coming inside the room
- consider taking anti-malarial medication
- Infectious diseases
- Immunisation (Department of Health and Aged Care)
HIV/AIDS is a significant risk. Take precautions if you're taking part in activities that put you at risk of infection, such as avoiding contact with contaminated objects and sharing personal items. Practice safe sex.
Other health risks
There are recurrent measles outbreaks in Brazil. To protect yourself, stay up to date with your vaccinations, wash your hands regularly and avoid close contact with people who are sick and wild or domestic animals.
Food-related, waterborne and other infectious diseases are common, including:
- bilharzia (schistosomiasis)
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid raw and undercooked food, such as salads
- avoid contact with dogs and other mammals
- avoid swimming in fresh water
If you're bitten or scratched by an animal, get medical help immediately.
Make sure your vaccinations are up to date.
- Measles immunisation service
Medical care
Medical facilities.
You can access free health care at public hospitals and clinics in Brazil. The standard of emergency care is generally high but can vary, with access being more limited and of a lower standard outside of major urban areas.
When accessing public health care, you will likely experience overcrowding, longer wait times and more rudimentary facilities than you are accustomed to in Australia. It is very unlikely your treating doctor will speak English.
Private health care at hospitals and clinics in larger cities is often similar or superior to Australia. Doctors will often speak at least some English. Private medical care is very expensive, even more expensive if you need a medical evacuation. You may be charged upfront or be required to produce proof of insurance prior to receiving treatment.
Public mental health care facilities are basic and overcrowded with a focus on more severe chronic and acute care, using a pharmaceutical-based treatment approach.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Brazil has severe penalties for possession of or trafficking illegal drugs. These include long sentences in local jails.
- Carrying or using drugs
You must always carry proof of identity. Carry a photocopy of your passport with some original identification, such as your driver's licence or another government-issued identity document.
Don't drink and drive, penalties are severe for driving with a blood-alcohol level reading over 0%.
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law
Dual citizenship
Dual nationals must enter and exit Brazil using their Brazilian passport.
If you're a dual national male over 18, you'll have to do military service if you stay in Brazil for 12 months.
Contact a Brazilian embassy or consulate for advice.
- Dual nationals
Local customs
Same-sex relationships are legal but aren't always accepted. Avoid public displays of affection.
- Advice for LGBTI travellers
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Currently, you don't need a visa to enter Brazil for:
- artistic or sports activities
You can stay in Brazil for 90 days over a 12-month period. This will be counted from the date of your first entry to Brazil. You can also extend your stay for another 90 days. If you require visa advice or assistance, you should contact the Brazilian Federal Police or a visa agency.
In other cases, apply for your visa through an embassy or consulate of Brazil .
If you plan to live in Brazil, you'll need to get a visa before arrival. The Brazilian Government strongly enforces immigration and entry laws.
If you need a visa and arrive without one, authorities will send you back on the next available flight.
Entry and exit conditions may change at short notice. Contact an embassy or consulate of Brazil for details about visas, currency and customs.
- Brazilian Ministry of Foreign Affairs
Travel via Chile
If you’re travelling via Chile, ensure you meet all current entry or transit requirements.
- Travel advice for Chile
Other formalities
Entry and exit stamps.
When you arrive, authorities will stamp your passport. This may be inspected by immigration authorities when you leave.
If you plan to leave Brazil and return during your trip, get an exit stamp in your passport from Brazilian immigration when you leave.
Yellow fever vaccination
You may need a valid yellow fever vaccination certificate to enter Brazil. Some airlines may want to see a copy when you depart to Australia or other countries.
Find out about returning to Australia after exposure to yellow fever .
- Countries with a risk of yellow fever
Travel with children
Dual-national children must enter and exit Brazil using their Brazilian passports.
Brazilian and dual-national children travelling in the company of only one parent must provide proof of consent to travel from the non-accompanying parent. If you can't produce proof of parental consent, local authorities will stop your children from departing Brazil. Unaccompanied children, or children travelling in the company of a non-parent, will require the consent of both parents.
Parental consent will usually be in the form of an observation note inserted into the child's Brazilian passport when it is issued by the Brazilian authorities. Alternatively, a Brazilian Embassy, Consulate or Juvenile Court can witness and notarise written parental consent or proof of residence outside Brazil.
If one or both parents are deceased, you'll require a death certificate notarised by a Brazilian Embassy, Consulate or Juvenile Court.
Parents of dual-national children should contact a Brazilian embassy or consulate for advice.
- Advice for people travelling with children
Authorities won't let you enter Brazil unless your passport is valid for at least 6 months from the date of your entry. This may apply even if you're just transiting.
Some immigration authorities and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Tourists can receive conflicting advice from different sources. You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can’t guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTI travellers
The local currency is the Brazilian Real (BRL).
Declare amounts over USD 10,000 (or foreign currency equivalent) when you arrive and depart. This includes all forms of currency, not just cash. US dollars are the easiest to exchange. Credit cards are widely accepted.
Ask your bank in Australia if your ATM card will work and if it has an affiliate bank in Brazil, as some local machines may be unreliable.
Credit card fraud and ATM tampering are widespread. Check your bank statements for unauthorised charges. To combat fraud and theft, many ATMs may limit the amount you can withdraw per day.
Local travel
Remote areas.
You're at risk of becoming lost or injured while trekking in remote parts of Brazil. This includes the Amazon border regions and the Pantanal wetlands.
Use an experienced guide.
Driving permit
You can drive in Brazil for up to 180 days after your arrival, as long as you carry a valid Australian driver’s licence. It is also recommended that you carry a translation of your licence. After this period, you will need to obtain a local driver’s licence.
Road travel
You're more likely to die in a motor vehicle accident in Brazil than in Australia.
Hazards on the road include:
- aggressive driving
- poorly maintained roads
- large numbers of trucks and other slow vehicles on main routes
Traffic lights are often not obeyed, especially at night in larger cities. Don't assume cars will stop.
Carjacking and other vehicle-related crimes can occur. To stay safe while driving and guard against carjacking:
- keep vehicle doors locked, windows up, and valuables out of sight, even when moving
- make sure your GPS route isn't via a favela — if in doubt, ask your hotel or tour guide
- be alert to threats, including when stopped in traffic
- when stopped in traffic, including at traffic lights, be alert to threats and maintain extra distance from other cars.
- always approach your car with the keys ready
- don't stay in a parked vehicle
If you plan to drive:
- check you have enough insurance
- learn local traffic laws and practices
- don't drink and drive – penalties are severe for driving with a blood-alcohol reading over 0%
- guard against carjacking and other vehicle-related crimes
If you're in an accident:
- call 193 for the fire department if there are injuries
- call 190 for the police if there are no injuries
- Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Check if your insurance policy covers you when using a motorbike, quad bike or similar vehicle.
Always wear a helmet.
Registered taxis, rideshares such as Uber and the metro are generally safe. To reduce your risk:
- only use licensed taxis or rideshare booked through apps
- find out what transport services are available at the airport before you travel; most airports have licenced taxi desks inside the baggage reclaim areas and allow payment before travel
- follow signage or advice of authorities to official taxi services only
- always ask if the driver will use the meter, or agree on the fare before you get in a taxi
- ensure you enter the vehicle with the same plate number and name as shown in the app, and don't get into a taxi or rideshare if other passengers are already inside.
- avoid using motorcycle taxis
Public transport
Brazil has a well-developed network of inter-city buses, as well as metro systems in some of the major cities such as Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo.
Travel can be risky due to poor vehicle maintenance, local driving habits and petty crime.
Be alert when using public transport, especially during busy times and at night.
Criminals often work in gangs robbing people gathered in the same place. Public transport hubs can be hotspots.
People have reported hijacking and robbery of tour buses in recent years.
- Transport and getting around safely
Boat travel
International cruise liners visit Brazil.
Commercial riverboats are common in some parts. Keep your belongings close.
Tourist operators often use basic vessels for river outings in jungle areas.
You should always wear a life jacket. Boat accidents can occur.
Piracy happens, particularly in the north-east. Armed groups, including pirates and drug traffickers, travel rivers in the Amazonas state, where there is a low presence of police and local authorities. Cruise ships and lodges have been attacked.
The International Maritime Bureau (IMB) issues piracy reports on its website.
- Going on a cruise
- Travelling by boat
Domestic and international flight delays are common. Airport strikes also occur.
Ask your travel agent if your itinerary allows for delays.
Be prepared for the possibility of extended waits at airports.
If you need to make or change airline bookings while in Brazil, ensure your payment method will be accepted.
Most major airlines, such as LATAM, Gol and Azul, accept international credit cards, although some may only accept them on their international websites.
Travel and tour agents may also have restrictions. You may need to pay cash at the airline office or ask your Australian travel provider.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Brazil's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.

Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Operators may not speak English.
Tourist Police who speak English are available in Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo and at some major airports.
Rio de Janeiro Special Police Unit for Tourism Support Av. Afrânio de Melo Franco, 159 Leblon, Rio de Janeiro – RJ Phone: +55 21 2334 6802 or +55 21 2332 2924
São Paulo Special Police Unit for Tourism Support Rua da Cantareira, 390 Centro, São Paulo - SP Phone: +55 11 3257 4475
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy in Brasilia , the Australian Consulate-General in São Paulo or the Consulate in Rio de Janeiro . The Consulate in Rio de Janeiro does not provide notarial (document legalisation) services and only provides limited services, for example, interviews for an Australian Passport.
Australian Embassy, Brasilia
SES QD 801, Conjunto K, Lote 07 Brasilia - DF, Brazil ZIP/CEP: 70200-010 Phone: +55 61 3226 3111 Email: [email protected] , or [email protected] Website: brazil.embassy.gov.au Facebook: Embaixada da Austrália no Brasil X: @EmbAusBrasil Instagram: australianobrasil
Check the Embassy website for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
Australian Consulate-General, São Paulo
Edificio Trianon Corporate – Cerqueira Cesar Alamenda Santos 700 9th Floor, Unit 92 São Paulo - SP, Brazil ZIP/CEP: 01418-100 Phone: +55 11 2112 6200 Email: [email protected]
Australian Honorary Consulate, Rio de Janeiro
Av. Bartolomeu Mitre, 770 Leblon, Rio de Janeiro - RJ, Brazil ZIP/CEP: 22431-003 Phone: +55 21 3824 4624 Email: [email protected]
The Australian Consulate in Rio de Janeiro does not provide notarial (document legalisation) services and only provides limited services, for example interviews for an Australian Passport.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Brazil?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.

Is Brazil Safe to Visit?

Offering pristine nature and access to the Amazon rainforest, historic cities and colonial architecture, and lots of affordable food and activities, Brazil has some something for every traveler.
But is it safe?
Brazil has a reputation for being a rough-and-tumble destination, one where travelers need to be extra cautious and on their guard at all times.
Due to one of the highest rates of income inequality in the world , the country also has some of the highest crime and homicide rates . Luckily, these rates have been declining in recent years, with Brazil’s homicide rate at its lowest in over a decade .
Still, petty theft and street crime are common in Brazil, so travelers here need to be vigilant. But that doesn’t mean you should avoid the country. You just need to be a smart traveler. Millions of people visit every year and don’t have a problem. As long as you follow the suggested safety tips below, you’ll minimize the likelihood anything bad will happen to you.
Here is everything you need to know to stay safe in Brazil and make the most out of your next trip.
Table of Contents
13 Safety Tips for Brazil
Is street food in brazil safe, can you drink the water in brazil, is brazil safe for solo travelers, is brazil safe for solo female travelers, why is rio de janeiro dangerous, is it safe to travel to rio de janeiro, what’s the safest area to stay in rio de janeiro, is carnival in brazil dangerous, is it safe to drive in brazil, are taxis in brazil safe, what part of brazil is safest.
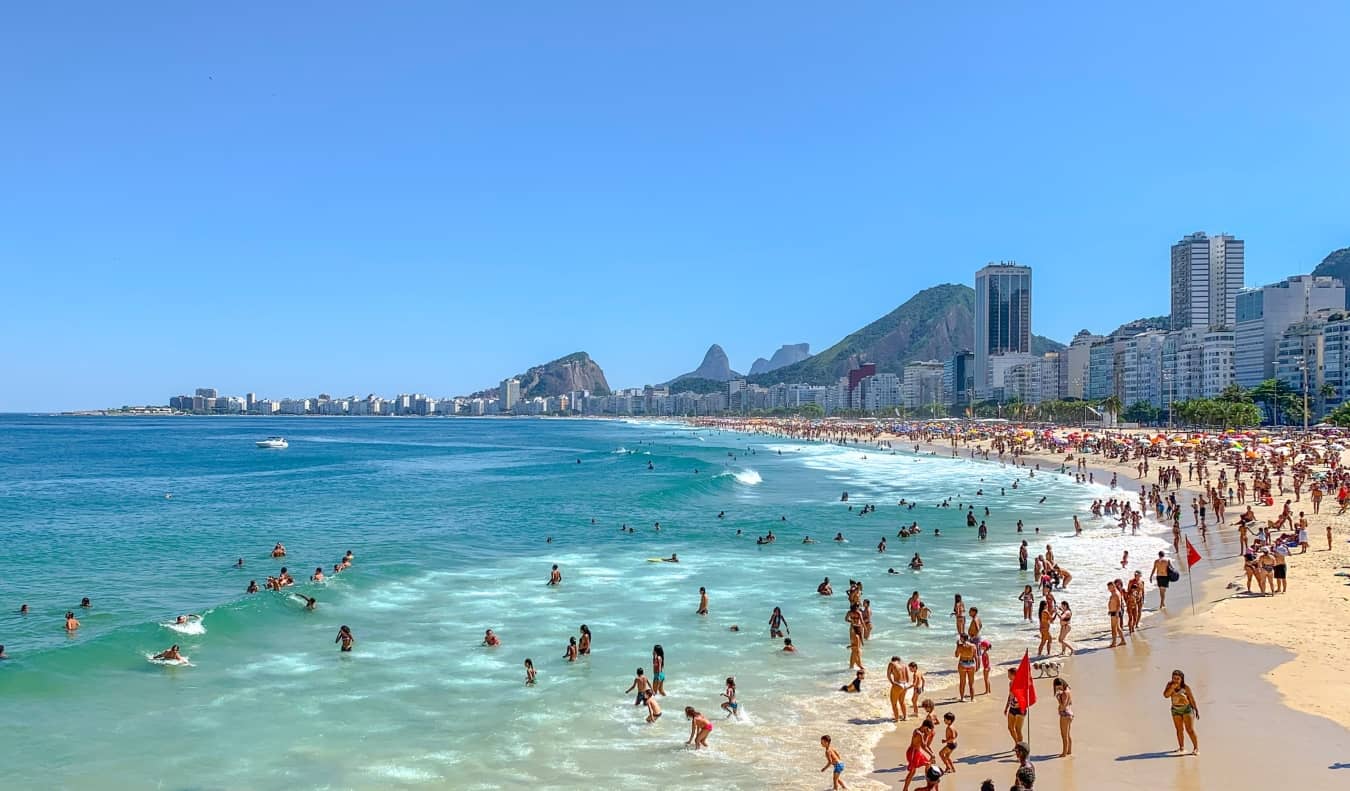

1. Walk with purpose – When out exploring, always walk with purpose. Look like you’re heading somewhere in specific, even if you’re not. Pickpockets and muggers look for travelers who are unsure of themselves. Don’t look like a target and definitely don’t walk with your cell phone in your hand. Keep it safely stowed away in a front (never back) pocket or a zippered pocket in your bag.
2. Carry a spare wallet with only a small amount of cash – Bring a spare wallet and only carry the minimum cash needed for the day in it. Keep the rest locked up back in your accommodation. That way, if you get robbed or pickpocketed they won’t get your real wallet (where you’ll keep the rest of your cash and cards).
3. Separate your cards – If you have more than one credit or debit card, keep them separate. Bring one with you for the day (if you think you’ll need it) and leave the other one locked up in your room. That way, should something happen, you always have at least one card remaining.
4. Don’t bring valuables to the beach – When you go to the beach, don’t take anything unnecessary. Towel, bathing suit, and a small amount of cash. That’s it! Anything else you bring is likely to disappear!
5. Dress to fit in – When out and about, dress to fit in. Leave any valuables or jewelry at home. Don’t walk around flashing your camera or phone (this is the biggest thing that Brazilians will warn you about again and again). If you need to use them, be discreet. Stand with your back to a wall so that no one can approach you from behind.
6. Download the Prey app to your phone and laptop – If either device gets stolen, you’ll be able to track it and remotely turn on your camera to photograph the thief (you can also wipe the data and message the thief too). The Prey app costs just $1.30/month.
7. Avoid outdoor ATMs – If you need to withdraw cash, only use ATMs inside buildings. Always be aware of your surroundings before you take out your wallet.
8. Double-check your accommodation – No matter where you are staying, be sure to check the doors and windows before leaving for the day and before settling in at night. Don’t leave anything valuable lying around your room; lock everything up in your hostel locker or hotel room safe.
9. Don’t accept free food/drinks – Never accept drinks or food from strangers. Drugging victims before they are robbed is common, so decline free food or drinks from strangers. And if you’re out drinking, always keep your eyes on your drink. Drinks can be spiked at any moment, so only hand it to someone you trust if you need to.
10. Watch out for distractions – Thieves will often try to distract you before they rob you. They often work in teams, with one person distracting you by asking questions (like for directions) and the other pickpocketing you. Be mindful of this and other common travel scam . Always stay vigilant when other people approach you and stay on your guard in crowds.
11. Don’t walk around at night alone – If you have to, avoid city beaches, parks, and empty streets. Generally, even local Brazilians don’t walk around much at night. Take an Uber or taxi (they’re super affordable) back to your accommodation if you’ve been out late.
12. Take precautions when driving – If traveling by car, always keep your doors locked. By on guard at stop signs or red lights, especially at night. Many Brazilians won’t even stop for them to avoid the risk of carjacking.
13. Buy travel insurance – I never leave home without it and you shouldn’t either. With travel insurance, you’re protected against unexpected costs that might arise should something bad happen on the road. It’s always better to be safe than sorry!
I recommend SafetyWing for travelers under 70, while Insure My Trip is the best choice for travelers over 70.
You can check out this widget to get a quote for SafetyWing:
For more information on travel insurance, check out these posts:
- What Does Travel Insurance ACTUALLY Cover?
- The Best Travel Insurance Companies
- How to Buy the Best Travel Insurance
Yep! You’ll find all sorts of amazing street food stands in cities like Rio de Janeiro as well as near the beaches and you’d be missing out if you didn’t try them! Just make sure to stick to places where there are a lot of locals gathered. That’s how you know the food is not only safe but delicious too.
I’d suggest avoiding street food with shrimp or seafood as it spoils quickly. For the most part, you’ll encounter places that sell various kinds of meat. As long as it is fully cooked and hasn’t been in the sun all day, dive in and give it a try!
The water in Brazil is generally not safe to drink. Most Brazilians caution against it and instead use filters or drinking bottled water, especially in more remote areas or regions with questionable water quality. The tap water has something of an odd taste, due to the purification process, so while it’s fine for brushing your teeth, you don’t really want to drink it when you’re thirsty.
If you’re staying in a hostel or a hotel, you may have access to a filter, though not always. It’s a good idea to bring your own as well, so you’re prepared for any situation. Lifestraw is my go-to choice for a water bottle with a built in filter. If you do buy bottled water, make sure it is properly sealed before opening and drinking it.
Brazil is safe for solo travelers, though I would only suggest solo travelers visit here if they have some experience traveling solo already. It’s not the best place for newbie travelers to test the waters.
If you are concerned as a solo traveler, try to meet-up with other travelers at hostels. Traveling together, you can keep each other company and deter any potential petty theft or robberies.
Brazil faces real issues of poverty and crime so solo female travelers will need to be on guard. This is not a destination for new travelers and I would only suggest solo female travelers visit here if they are experienced solo travelers. Even then, you’ll want to make sure you take every precaution that you can.
Check with your hostel or hotel staff to find out if you should avoid any specific areas. Also, learn as much as the local language as you can so you don’t stand out.
Rio de Janeiro gets a bad reputation due to massive favelas (shantytowns), where high rates of crime occur. Historically, these areas have been run entirely by gangs and drug dealers, though in recent years, certain favelas have started to be managed by Pacifying Police Units. Still, these areas are generally not safe for outsiders, and you shouldn’t be exploring there on your own.
Outside of the favelas though, Rio is a big city like any other, and you can enjoy traveling there as long as you exercise normal precautions.
Rio can absolutely be a safe destination for travelers, as long as you stick to the safer areas (avoid favelas) and keep your wits about you. Just like in any major city, it’s important to take precautions. Stay in well-populated and well-lit areas, avoid displaying valuable items, and be cautious at night. Stay informed about local safety concerns and follow the advice of locals and authorities.
The safest areas to stay in Rio de Janeiro are Ipanema and Copacabana. These areas are right along the city’s iconic stretch of beach and popular among tourists. You’ll find a range of accommodation options (most travelers stay here and most of the best hostels in Rio are here), restaurants, and attractions in the area. It’s perfectly safe to walk around during the day (exercising normal precautions), though like anywhere in Rio, you might want to take a taxi or Uber at night.
Going to Carnival in Brazil is a once-in-a-lifetime, bucket list experience for many travelers. But because of the big crowds and rowdy atmosphere, it’s essential to exercise caution. Pickpocketing and petty theft are rampant during this time. Thieves know that people are partying, drinking, and generally not paying much attention to their surroundings. Always stay extra vigilant and only go out with what you absolutely need. Be wary of drinking too much and if you can, always stick with a buddy. Adhere to the above tips extra closely during Carnival.
I’ll be honest, I don’t recommend renting a car here. It’s unnecessary, the traffic is terrible, the roads are poorly maintained, drivers are aggressive, and parking is expensive. While major highways are generally safe, driving in urban areas, especially during rush hour or at night, requires extra caution. Break-ins and carjackings are common.
Taxis, Ubers, long-distance buses, and domestic flights are generally so cheap in Brazil that, personally, I’d avoid renting a car unless you really need to.
Taxis in Brazil are safe and plentiful. They use meters as well, though it’s always a good idea to ask your hotel or hostel staff for an approximate fare before you head out. There are always a few bad apples that will try to rip you off, so just be sure to pay attention to the meter and make sure it isn’t rising abnormally fast.
Also, it’s always best to call your taxi in advance; you can use the 99 app (formerly 99Taxis) to hail a cab. Never flag a taxi on the street (this is especially true at night). Ubers are also plentiful and affordable across the country.
Florianópolis , Brasilia (the country’s capital), Curitiba, and Belo Horizonte are among the safest cities in Brazil, with some of the lowest crime rates in the country.
Vacation destinations like Fernanda do Noronha are also quite safe.
However, even big cities like Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro , which have higher crime rates, are well-traveled, and as long as you follow the tips above and stay vigilant, you can stay safe while enjoying these incredible cities.
Brazil is an amazing, vibrant country. But it’s not without its risks. Travelers here will need to be on guard and keep their wits about them. Petty theft is common and can be rampant during big events like Carnival, where the many distractions and crowds make pickpocketing easy. But if you follow the tips above you should be able to have an incredible visit while still staying safe.
Trust your gut, use common sense, and make sure you have comprehensive travel insurance . Do that, and you’ll be able to stay safe in Brazil and have a memorable visit to this energetic country.
Book Your Trip to Brazil: Logistical Tips and Tricks
Book Your Flight Use Skyscanner to find a cheap flight. They are my favorite search engine because they search websites and airlines around the globe so you always know no stone is left unturned!
Book Your Accommodation You can book your hostel with Hostelworld as they have the biggest inventory and best deals. If you want to stay somewhere other than a hostel, use Booking.com as they consistently return the cheapest rates for guesthouses and cheap hotels. My favorite places to stay are:
- Discovery Hostel (Rio)
- Geckos Hostel (Florianopolis)
Don’t Forget Travel Insurance Travel insurance will protect you against illness, injury, theft, and cancellations. It’s comprehensive protection in case anything goes wrong. I never go on a trip without it as I’ve had to use it many times in the past. My favorite companies that offer the best service and value are:
- Safety Wing (best for everyone)
- Insure My Trip (for those over 70)
- Medjet (for additional evacuation coverage)
Looking for the Best Companies to Save Money With? Check out my resource page for the best companies to use when you travel. I list all the ones I use to save money when I’m on the road. They will save you money when you travel too.
Want More Information on Brazil? Be sure to visit our robust destination guide to Brazil for even more planning tips!
Hi, I’m Nomadic Matt, the New York Times best-selling author of How to Travel the World on $50 a Day and Ten Years a Nomad, as well as the founder of this website! And I’m here to help you save money on your next trip.
Got a comment on this article? Join the conversation on Facebook , Instagram , or Twitter and share your thoughts!
Disclosure: Please note that some of the links above may be affiliate links, and at no additional cost to you, I earn a commission if you make a purchase. I recommend only products and companies I use and the income goes to keeping the site community supported and ad free.
Related Posts

GET YOUR FREE TRAVEL STARTER KIT
Enter your email and get planning cheatsheets including a step by step checklist, packing list, tips cheat sheet, and more so you can plan like a pro!

Get Daily Travel Tips & Deals!
By proceeding, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .

Is Rio de Janeiro Safe to Visit? Warnings and Dangers Travelers Should Know
The Editors
We are the editors of SmarterTravel! Together we have appeared in countless travel publications including ABC News, Huffington Post, Travel + Leisure, USA Today, and more. We dedicate our days to creating and producing expert travel content, including packing tips, general travel advice, destination inspiration, and helpful videos. Follow us across social media on YouTube , Pinterest , Facebook , Instagram , and Twitter or drop us a line to say hi at [email protected]!
Travel Smarter! Sign up for our free newsletter.
Rio de Janeiro, Brazil’s second largest city, is considered the nation’s cultural and economic center, with an abundance of museums and galleries, incomparable shopping, iconic beaches such as Copacabana , and, of course, the epically festive Carnaval. Rio is also home to a travelers’ bucket-list mainstay: the massive, art deco-style Christ the Redeemer statue atop Mount Corcovado.
But is Rio de Janeiro safe to visit? Unfortunately, the Rio crime rate is fairly high. Violent crime is a “frequent occurrence,” according to the Overseas Security Advisory Council (OSAC), while street crimes such as pickpocketing and purse snatching are “a constant concern,” happening all over Rio at all times of year. The 2016 Olympics actually exacerbated the Rio de Janeiro crime rate, though the city did see a reduction in shootings in 2019 .
Rio crime, then, is to be taken quite seriously. “Criminals [in Rio] most often target their victims due to perceived wealth and lack of awareness,” according to OSAC, so it’s wise not to flaunt what you’ve got and always to appear alert and engaged with your surroundings.
If you are considering a trip and find yourself wondering, “Is Rio safe to visit?” read on for important advice on Rio de Janeiro safety.
Tips for Rio de Janeiro Safety
- Is it safe to travel to Rio de Janeiro? That depends on where you go. Areas to avoid in Rio de Janeiro include Rocinha, Vila Mimosa, most of the city’s north zone, its favelas, and their neighboring areas including Del Castilho, Cascadura, Bangu, and Pavuna. Keep in mind, too, that even the safest neighborhoods in Rio de Janeiro can turn dangerous after dark.
- Taking a cab in Rio? Make sure that it’s official and licensed by checking to see that it’s yellow with a blue stripe and red license plates; otherwise, you risk getting into an illegal or pirate taxi.
- Keep away from Rio de Janeiro’s dangerous favelas; tourists who have wandered into these slums of Rio have ended up shot. Know where you’re going at all times, check maps, and don’t go down any unpaved or cobbled streets.
Areas to Avoid in Rio de Janeiro
A key element of being able to stay safe in this iconic Brazilian city is knowing which areas to avoid in Rio de Janeiro, as well as which are the safest neighborhoods in Rio de Janeiro. If you’re looking to sidestep Rio crime, stay away from Rocinha , Rio’s largest favela, where recent drug-related violence has been so severe that the military has needed to get involved.
It’s also wise to steer clear of Vila Mimosa, which is notorious for prostitution , as well as the city’s north zone , its favelas, and their neighboring areas including Del Castilho, Cascadura, Bangu, and Pavuna.
There are also certain areas in Rio that are safe to wander around in during the day—but where things change after dark. These include Centro, where nighttime muggings are common; Santa Teresa, where driving can be dangerous and it’s easy to end up in a violent favela; and Botafogo Beach and Flamengo Park, which are adjacent to each other and have a large population of people living in poverty, so thefts and violence spike at night.
12 Life-Saving Travel Hacks for Your Next Trip
How to Get Around Safely in Rio de Janeiro
How safe is Rio de Janeiro for tourists to navigate? Again, that depends on how you handle yourself and how you opt to get around.
There are lots of taxis in Rio, and using them can be relatively safe, though you’ll want to make sure that any cab you get into is licensed and metered—and that you call a taxi in advance or use a taxi app rather than hailing one off the street. To save yourself the risk of entering one of Rio’s many illegal or pirate taxis , only use yellow cabs with a blue stripe and state-issued red livery license plates, and never agree to pay your fare in advance of your ride, unless it’s at the airport’s licensed taxi desk.
Taking taxis is always preferable to taking Rio’s mini-buses, which host lots of crime and are unregulated. The metro, on the other hand, is considered a safe way for travelers to get around Rio de Janeiro, although tourists should always be alert for petty criminals, as they’re common on all forms of public transit in Rio; keep in mind that they often work in groups. Women should consider using the system’s women-only cars during crowded periods.
Wherever you are in Rio de Janeiro, always keep your bearings, plot all your routes in advance, and know exactly you are—especially in relation to your hotel. If you’re using GPS, make sure that the route doesn’t veer you into a dangerous favela. Don’t dress like a tourist, either—only wear beachwear at the beach, and leave all valuables at your hotel (or at home), bringing along only what you absolutely need.
Most places in Rio accept credit cards, but if you find the need to carry cash, stay away from shady-looking ATMs, using only those that are in reputable locations, like a bank or your hotel. One common form of crime in Rio de Janeiro are “ express kidnappings ,” during which a victim is forced to withdraw money from an ATM machine that they were just seen using, or taken around to different ATMs to withdraw money for the kidnappers; usually the victims are let go after the cash is stolen. This is yet another reason to avoid ATMs if at all possible.
If you’re in Rio to party, that’s great—the nightlife here is some of the world’s best—but proceed with caution and don’t lose sight of the fact that Rio crime is a real concern, especially after dark. Stay in the popular areas, don’t wander off by yourself, watch how many caipirinhas you’ve consumed, and never leave your drink unattended.
Keep in mind, too, that Rio de Janeiro does experience occasional natural disasters, including floods, mudslides, and major storms. If you find yourself in the midst of one of these events, head to higher ground and heed officials’ instructions. It’s also worth noting that the Zika virus is still a concern throughout Brazil , so take every precaution to protect yourself against mosquito bites while in Rio.
Do Travelers Still Need to Worry About the Zika Virus in 2020?
Favelas in Rio de Janeiro
Favelas are Rio’s neglected slums on the outskirts of the city. Violence within them is ever present and growing, thanks in large part to organized crime that centers around drug trafficking in Brazil. Travelers who have accidentally wandered into Rio’s favelas have gotten shot and injured .
Tourists in Rio, then, are advised not to go down unpaved, cobbled, or narrow streets, as these may lead into a favela. Check a map of the city that shows where Rio’s favelas are located (there’s a good one here ), but if you’re unsure, ask at your hotel or inquire with local authorities.
Rio de Janeiro’s government began a “ favela pacification program ” to bring favelas under police control, but results were mixed . Unfortunately, they are still dangerous places with an increasing amount of violent crime, so travelers should steer clear. Though favela tours have become more popular as a safe way to learn about life in these areas, the U.K. government says they are best avoided.
More from SmarterTravel:
- 9 Incredible Brazilian Beaches for Every Type of Traveler
- What You Need to Know About Tipping in Brazil
- 10 Travel Safety Tips You Can Learn from the CIA
—original reporting by Avital Andrews
We hand-pick everything we recommend and select items through testing and reviews. Some products are sent to us free of charge with no incentive to offer a favorable review. We offer our unbiased opinions and do not accept compensation to review products. All items are in stock and prices are accurate at the time of publication. If you buy something through our links, we may earn a commission.
Top Fares From

Don't see a fare you like? View all flight deals from your city.
Today's top travel deals.
Brought to you by ShermansTravel
Croatia, Slovenia & Montenegro: 9-Night, Small-Group...
Indus Travels

5-Star, All-Inclusive Exploration Small-Ship Cruises w/Up...
Swan Hellenic

Ohio: Daily Car Rentals from Cincinnati

Trending on SmarterTravel

21 Jul 21 Dos and Don’ts to Travel Safe in Brazil

When I mention that I traveled to Brazil (majority of the time alone) one of the first questions I always get is, “Is Brazil safe to travel to?” Or more specifically, did I feel safe as a solo female traveler in Brazil. Both are fair questions, and my answer is…it’s complicated.
In short, yes, Brazil is safe enough to travel to – but read my more in-depth response here . My personal experience is that I had no negative incidents involving safety or theft while in Brazil and I loved the country so much I stayed for 3 months and would go back in a heartbeat. However , I simultaneously know many tourists who were victims of theft in Rio de Janeiro especially.
You could call me lucky that nothing happened to me, which is fair because sometimes things just happen. But I was also extremely cautious and extremely aware. Specifically, I followed the tips mentioned in this blog post and I think that made a huge difference.
So if you’re traveling to Brazil, here are 21 dos and don’ts to stay safe:
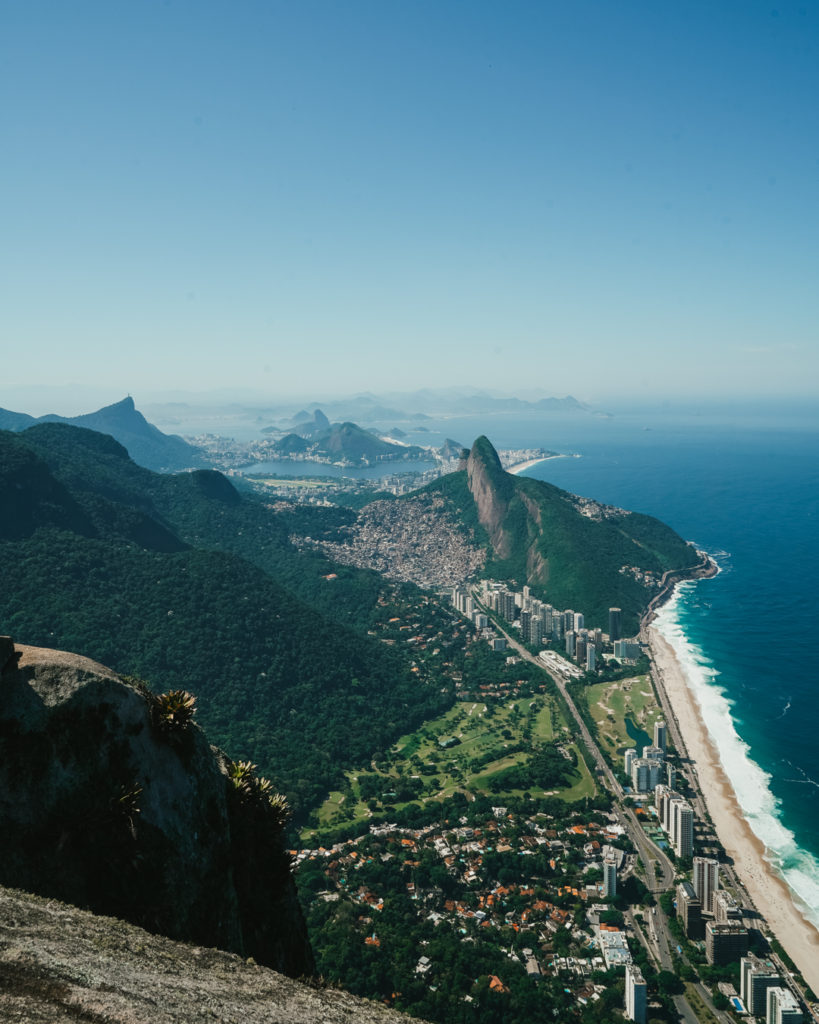

*This post includes affiliate links and I may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. By using my links you’re merely supporting what I love to do: write this blog! I only recommend products/companies that I use myself.
1. pull your phone out on the street
Walking around with your phone out is really the worst possible thing you could do – especially in Rio. No matter how hard you grip that phone, there’s a decent chance someone will swipe it even in broad daylight. If you must look at your phone (for example directions or ordering an Uber), I recommend stepping into a shop. If that’s not possible, step away from walking traffic and look around before pulling it out quickly. If you’d like to take a photo, consider if it’s a smart move and be conscious of people walking by.
This is by far the most important tip on this list. I think we’re so accustomed to pulling out our phones constantly to scroll through social media or just walking with our phone in hand. But in Brazil I strongly discourage you from doing this.
2. Don't walk alone at night
Walking alone at night makes you an easy target, especially in places like Copacabana in Rio, so try to avoid it at all costs.
During the day, it’s obviously okay to walk alone, but it’s good practice to be mindful of your surroundings and the area you’re in. I wouldn’t recommend walking near a favela alone and suggest staying in more populated areas.
3. don't Put valuables in your pockets
If you’re in the habit of putting valuables in your pockets – break it! This is an easy way to be pick-pocketed. Instead I highly recommend having a cross- body sling. A standard sling like this one works, but for safety I most recommend the PacSafe sling which is an excellent investment if you travel often or live in a city.
4. don't wear showy items like gold jewelry
Flashy items make you a target in Brazil. Personally I love gold jewelry, but even though all of mine is fake, wearing it would make me a target. Studs and small hoop earrings should be fine, but necklaces and bracelets I would refrain from wearing – as recommended to me by local Brazilians.
5. don't leave your valuables unattended to
Never leave your valuables unattended to in Brazil. This includes at coffee shops where you may have your laptop or iPad out while going to the bathroom. It’s not to say that the people around you are bad or won’t watch your things when you ask, because they will. But usually when we ask someone, “Hey can you watch my stuff?” we don’t actually believe someone is going to come and swipe our stuff while you’re gone and the person watching your things will actually need to run after them… However, in some places of Brazil this can totally happen. Especially if you’re sitting near a window near the street. I knew of a girl who lost her iPad this way..so just don’t do it.
6. don't use the metro at night
The metro in Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro are great. I took the metro in Rio many times and it was cheap, safe, and clean. However, I wouldn’t recommend it in two scenarios: at night and with a laptop or camera. Otherwise I actually recommend it during the day especially if you’re on a tight budget.
Now that you know what not to do to stay safe in Brazil while traveling, let’s jump into what you should do.

Also read: The Ultimate List of things to do in Rio de Janeiro
7. pack a theft-safe cross body bag.
A lot of pick-pocketing happens when someone’s wallet or phone is in their pocket or open bag. Do yourself a favor, and get yourself a sling, cross body bag so that your valuables are always zipped away and close to your chest.
My favorite cross-body slings are from Pac-Safe . They’re RFID blocking, have theft-proof zippers, and cut-proof straps. They check all my boxes for a safe cross-body travel sling including having inside zipper compartments and a clip in the front vs. in the back.
But if you’re looking for a cheaper option, I suggest this highly-rated one on Amazon .

8. Be cautious of your valuables while sunbathing on the beach in Rio
The beaches in Rio are stunning, but while sunbathing be wary of your belongings. I recommend keeping everything in your bag (i.e don’t leave your phone or kindle out on the towel) and have your bag secured somewhere. Personally, when I would close my eyes I put the strap around my arm so my bag could not be grabbed in passing.
If you go to the beach alone (which I did often) also don’t leave your valuables unattended when you swim. I use a waterproof fanny pack or you can ask someone to watch your things if you feel comfortable doing so.

9. leave one bank card in your suitcase
When you go out, it’s best not to bring all your bank cards in case, god forbid, your wallet is stolen. I always leave my debit and credit cards locked at my place and take only one travel credit card. The Chase Sapphire Preferred is my go-to.
Read more about why I recommend the Chase Sapphire Preferred card here.
Note: this tip is good practice always when you travel, not just in Brazil.
10. Use Uber if possible
Uber is a really convenient way to get around, and for safety reasons I love it because you have more control as the passenger: you have a set price, the information of the driver, and you can share your trip for added security. Uber is available in the major cities of Brazil, so if it makes you feel safer, use it.
11. Leave your passport in a safe place, and bring copies to the country
Whenever you go somewhere (unless it’s required or needed) it’s best to not walk around with your passport in your day bag, just in case you lose it. But in the worst case scenario that you do, it’s also good to travel with printed copies in your suitcase if you needed to go to your embassy for a lost passport.
12. Bring minimal stuff when you go out to party
Now that I’ve mentioned to leave your passport and any unnecessary cards locked at your place, make sure you DEFINITELY do this when you go out to party in Brazil. This is when many people are pickpocketed because they’re drunk or high and less mindful. I know some people who even use burner or their old phones when partying in “high-risk” destinations like Rio or Salvador during Carnaval. Not a terrible idea if you have an extra or old phone.
13. Try not to stand out as a tourist too much
Being a tourist is not a bad thing and to be honest, even if you try not to stand out, you probably still will. And that’s okay! It’s more about not standing out too much and making yourself a massive target for pick pocketing. So don’t wear flashy items, be protective of your phone and camera, and maybe switch your “I Love Rio” shirt for a Flamengo jersey (Flamengo is a local and very popular team in Rio de Janeiro).
14. Practice extra caution in heavily touristic areas
Touristic areas of every destination always have a downside…they seem to attract the most sketchy characters. This is the same for Brazil. For example, in Rio you should practice extra caution in Copacabana, Lapa and other touristic places.
15. Be mindful of your things at an outdoor restaurant
When seated at an outdoor restaurant (which will happen often because Brazil loves al fresco dining), again be mindful of your things. Don’t plop your phone on the table and swing your purse over the back of your chair which faces the street. This behavior may be a habit to you, but like all the other tips in this list – think about your valuables and make sure they’re secured and can’t be swiped.
16. Avoid deserted areas
In general, it’s best to stay away from deserted areas. When you’re alone there’s no one to help so it’s always best to stay where others are too.
17. Double check the area of your accommodation before booking
Before booking your stay, it’s always good practice to do a little research on the area and read reviews from other travelers with location safety in mind.
18. Party safely
Partying in Brazil is not only a must, but a difficult thing to avoid. And as someone who was there for two Carnavals, I full heartedly support this! Just make sure you party safely by:
- Going out with people you trust
- Leaving any unnecessary valuables locked at your stay
- Keeping everything in a zipped sling
- Being mindful of how much you drink
- Having a plan how to get home
- Don’t do random drugs off the street
- Don’t ever leave your drink unattended and then drink it
- Don’t accept a drink you didn’t see poured
You’re an adult, you know the drill.
19. Use lockers and padlocks for your belongings
If you’re staying in a hostel this is always a must for your valuables. I recommend using this padlock which works for both lockers and your luggage and is TSA approved.
If you’re staying in an Airbnb or hotel, for some peace of mind you should also lock your things in the safe if available.
None of this is specific to Brazil, it’s just standard practice. Theft from your accommodation isn’t common for tourists in Brazil, although there are wild stories around Carnaval time when the country is full of tourists, so best to be cautious.

20. Be careful when you withdraw money
Like many destinations, in Brazil you should always be careful when withdrawing cash. I recommend only doing so during daylight hours, going with a friend if you can, and trying to find an ATM located indoors. As a standard practice (since seeing those ATM scamming videos) I also always tug on the card reader first and only go to an ATM when I see someone else go before me. That way if it’s going to eat a card, it won’t be mine!
After withdrawing money, make sure you have plans to return to your place immediately so you’re not walking around with loads of cash on you.
21. Make sure you're covered with Travel insurance
Travel insurance is a must for every trip, but especially for a destination like Brazil where you may be engaging in adventurous activities, have a lot of reservations, and you’re at risk for theft as mentioned in this post.
So do yourself a favor and make sure you’re covered! No one wants to think about unfortunate scenarios like robbery, delays, cancellations, injury or sickness happening while traveling, but they do and almost every traveler can attest to a time when travel insurance really saved them.
Check out World Nomads travel insurance here which is made for backpackers.
*Disclosure: World Nomads provides travel insurance for travelers in over 100 countries. As an affiliate, I receive a fee when you get a quote from World Nomads using this link. I do not represent World Nomads. This is information only and not a recommendation to buy travel insurance.

I’ve mentioned a lot in this blog post, but all of it will prove useful to staying safe in Brazil. Overall, I hope I didn’t scare any readers; I think Brazil is a wildly amazing place and one of my all-time favorite travel destinations. Just stay aware, stay safe and you’ll have a smooth and wonderful trip.
Also read: The Ultimate List of Things to Do in Rio
More resources for your trip to brazil:.
Planning your own trip? Here’s everything I used to book and coordinate my itinerary through Brazil.
If you’re a budget traveler or looking for an easy way to meet others, Hostelworld is the best place to search.
Booking.com has so many options in Brazil from affordable to more luxurious stays.
Flights to Brazil and within Brazil can be pricey if not booked ahead of time. To get the best prices I recommend using Skyscanner . The cheapest airport to fly into will most likely be São Paulo, but if visiting Rio de Janeiro it’s worth it to fly directly there.
No matter the destination, I always check Rome2Rio to see options on how to travel. However I found using Brazilian bus companies to book could be a pain because you need a CPF often. The most useful sites to me were BusBud & FlixBus .
Travel insurance is a must for every trip, and I highly recommend it for Brazil. My go to is always WorldNomads which is made for backpackers. You can search for coverage here .
Tours & Experiences
There’s a lot of free thing to do in Rio but joining a tour does have its advantages, and if you’re a solo traveler looking to meet people then tours are a great option. In Rio you can find awesome experiences on GetYourGuide , Viator , & Airbnb Experiences (hit or miss but mostly good).
Liked this post? Pin it!

Related posts

Carnival Rio de Janeiro 2024: Your Guide to the World’s Largest Party
Carnaval in Rio de Janeiro is one of the world’s biggest parties! Brazilians in costumes dance in th...

21 Dos and Don’ts to Travel Safe in Brazil
When I mention that I traveled to Brazil (majority of the time alone) one of the first questions I a...

The Ultimate List of Things to Do in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro is one of the most amazing cities to visit in the world. It’s one of the few......
Bea Adventurous
I’ve heard a rio can be bad with theft so these tips are really helpful so thank you! I definitely think it shouldn’t deter anyone from visiting but to take these precautions for sure! Thanks Caroline!
Caroline Rose
You’re welcome!! So glad you found these helpful. Have the best time in Brazil!
Mary Candler
Thanks for your information about Brazil. I am hoping to go to Rio to volunteer as a English teacher for 3 weeks then head to Minas Gerais to see a friend. Any specific comments for a 70 Yr old who doesn’t take too many risks and has done a fair amount of solo travelling. I’ll be staying in medium hotels when not in the volunteer programme.
Hi Mary! I don’t have any specific safety recommendations other than what I’ve listed here. As for things to do, there are some really great tours I think you’d enjoy like to Christ the Redeemer and Sugar loaf mountain. Also check out the botanical garden, it’s beautiful! I have a full list of things to do in this blog post!
David Young
So how do you take photos? I love taking photos with my phone when I’m traveling. It sounds like that would be risky at most outdoor locations in Brazil. Also how was intercity travel? Did you take buses or fly? I know not to take the bus at nighttime, but I wonder if there are other precautions advised. Thank you.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe me to Caroline Rose Travel
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Section 10 - Tanzania & Zanzibar
- Section 10 - Cusco & Machu Picchu
CDC Yellow Book 2024
Author(s): Alexandre Macedo de Oliveira
Destination Overview
Infectious disease risks, environmental hazards & risks, safety & security, availability & quality of medical care.
At nearly 3.3 million square miles in size, Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world and the largest country in South America, occupying nearly half the land area of the continent. With >210 million people, Brazil is home to the world’s largest Portuguese-speaking population. The world’s eighth largest economy, Brazil is classified as an upper-middle-income country. Nearly 85% of Brazilians live in urban areas.
Brazil is the most popular tourist destination in South America, and the second most popular in all Latin America. In 2018, >6 million international visitors traveled to Brazil; the country hosted the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) World Cup in 2014 and the Summer Olympic and Paralympic Games in 2016. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil’s second-largest city (population >7 million) and most frequently visited tourist destination, is famous for its beaches, landmarks, and annual Carnival festivities. São Paulo, one of the world’s largest cities with >21 million people in the greater metropolitan area, is the economic center of Brazil and the most visited destination for business travel. Brazilian people prize many of their major cities, including Florianópolis, Fortaleza, Manaus, Recife, and Salvador, for their coastlines and regional culture.
The country also boasts multiple UNESCO World Heritage sites, including Iguaçu National Park in Paraná, home to the largest waterfalls in the Americas; the historic towns of Olinda (Pernambuco), Ouro Preto (Minas Gerais), Salvador (Bahia), and São Luis (Maranhão); the modern capital of Brasília; and natural areas of the Amazon Forest and the Pantanal Conservation Area, which extends from one state (Mato Grosso do Sul) into another (Mato Grosso) and into portions of two countries (Bolivia and Paraguay). The Atlantic forests and the archipelago of Fernando de Noronha in the Atlantic Ocean are World Heritage sites (see Map 10-06 ).
The Amazon Forest, large portions of which extend into the countries that neighbor Brazil, attracts travelers in search of exotic adventures. The region presents unique risks, and careful planning and attention to travelers’ health needs before, during, and after the trip is critical. Because mosquito-borne diseases (chikungunya, dengue, malaria, yellow fever, and Zika) are endemic throughout the Amazon, advise travelers to complete all relevant vaccinations and provide them with detailed instruction on the proper use of chemoprophylaxis and mosquito avoidance. The hot and humid climate throughout the forest increases the risks for dehydration and heat stroke; travelers should practice extreme caution and, whenever possible, resist the temptation to consume potentially unsafe food and beverages.
Map 10-06 Brazil
View Larger
Travelers to Brazil should be up to date on routine vaccines, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), influenza, measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), and diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis. Hepatitis A vaccination also is recommended. Consider hepatitis B vaccination for most travelers, but especially for anyone who could be exposed to blood or other body fluids (e.g., through medical services, sexual contact, tattooing).
Enteric Infections & Diseases
Travelers’ diarrhea.
Travelers should take food and water precautions throughout Brazil, including in the big cities (see Sec. 2, Ch. 8, Food & Water Precautions ). Travelers’ diarrhea (TD) is the most common travel-related ailment, and visitors consuming raw fruits and vegetables, unpasteurized dairy products, and food from street vendors increase their risk for foodborne infections. Oral rehydration salts are available from public health clinics and in almost all pharmacies in Brazil. For further information about travelers’ diarrhea, see Sec. 2, Ch. 6, Travelers’ Diarrhea .
Typhoid Fever
Consider vaccinating “adventurous eaters” against typhoid, along with travelers who stay with friends or relatives or who visit smaller cities, villages, or rural areas (see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 24, Typhoid & Paratyphoid Fever ).
Respiratory Infections & Diseases
Coronavirus disease 2019.
All travelers going to Brazil should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines .
Endemic Fungi
A variety of fungi (e.g., Paracoccidioides in the south and southeast) are endemic to Brazil. Inhaling the spores of fungi typically present in the soil (e.g., Coccidioides , Cryptococcus neoformans , Histoplasma , P aracoccidioides ) can cause respiratory illness and occasionally more severe disease (e.g., meningitis, bone infections). For more details, see Sec. 5, Part 4, Ch. 1, Coccidioidomycosis / Valley Fever , and Sec. 5, Part 4, Ch. 2, Histoplasmosis . Travelers should beware of bat guano in caves and use caution before disturbing soil, particularly if contaminated by bat or bird feces.
Peak influenza circulation occurs during April–September in most of Brazil but can occur throughout the year in tropical areas. The influenza vaccine recommended for use in the Northern Hemisphere each year confers protection against the virus strains circulating in the Southern Hemisphere that same year. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends seasonal influenza vaccination ≥2 weeks before travel, and pneumococcal vaccination for people ≥65 years of age, and for younger adults and children with chronic medical conditions.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is prevalent in Brazil, but short-term travelers are not considered to be at high risk for infection unless visiting specific crowded environments. Before they leave the United States, consider TB testing for travelers who anticipate prolonged exposure to people known to have, or at high risk for having, TB (e.g., people in clinics, hospitals, prisons, homeless shelters). For more detailed information, see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 22, Tuberculosis , and Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 23, . . . perspectives: Testing Travelers for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection.
Sexually Transmitted Infections & HIV
The HIV infection rate in Brazil is 0.5% among adults aged 15–49 years, comparable to other countries in South America. Discuss options for preexposure prophylaxis with travelers at greater risk for acquiring HIV infection (see www.cdc.gov/hiv/prep, and Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 11, Human Immunodeficiency Virus / HIV ). In Brazil, people who use drugs, men who have sex with men, and female sex workers are more likely than the general population to be infected with HIV.
In Brazil, condoms are available free of charge in public health clinics, tourist service centers, and other distribution points in many cities. Male condoms are also available throughout Brazil in pharmacies, convenience stores, and supermarkets; female condoms are available in some locations.
Soil- & Waterborne Infections
Leptospirosis.
In urban areas of Brazil, outbreaks of leptospirosis have occurred after heavy flooding (see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 10, Leptospirosis ). Travelers who have contact with standing water or mud after heavy rainfall are at increased risk. Advise travelers to avoid entering bodies of freshwater potentially contaminated with animals’ body fluids.
Schistosomiasis
Schistosoma spp. are parasites found in freshwater lakes and rivers in many states of Brazil, especially in the northeast. Advise travelers to avoid bathing, swimming, or wading in fresh, unchlorinated water, where they could contract schistosomiasis (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 20, Schistosomiasis ). Bathing or swimming in saltwater is not a source of infection.
Vectorborne Diseases
Vectorborne diseases (bacterial, viral, parasitic) are present in many areas of Brazil; these infections are among the leading causes of febrile illness in travelers returning from South America.
Chikungunya & Dengue
Risk for chikungunya and dengue infection is increased in many large Brazilian cities due to large populations of Aedes mosquitoes, which transmit these viruses (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 2, Chikungunya , and Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 4, Dengue ). During 2000–2015, cases of dengue surged throughout Brazil, with epidemics reported in large cities, including Rio de Janeiro and Salvador. Preliminary data show that in 2019, Brazil recorded ≈132,000 cases of chikungunya and ≈1.5 million probable cases of dengue. Travelers to Brazil should take measures to protect themselves from mosquito bites (see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods ).
Leishmaniasis
Cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis occur in Brazil and are most common in the Amazon and northeast regions (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 14, Cutaneous Leishmaniasis , and Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 15, Visceral Leishmaniasis ). The risk for transmission is greatest from dusk to dawn because the sand fly vector typically feeds (bites) at night and during twilight hours. Ecotourists and adventure travelers might be at increased risk, but even short-term travelers in endemic areas have developed leishmaniasis. Travelers should take measures to avoid insect bites (see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods ).
Lymphatic Filariasis
Brazil is actively participating in the global program to eliminate lymphatic filariasis (LF); LF is considered endemic to only 4 cities in Brazil, all located in the Recife Metropolitan Region (northeastern coast) of the country. As of 2020, all regions had achieved the targets set by the World Health Organization (WHO) to stop annual treatment, suggesting low likelihood of ongoing disease transmission and minimal risk to travelers. Brazil is still working to achieve all targets demonstrating elimination of LF as a public health problem (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 9, Lymphatic Filariasis , and the WHO website .
Almost all malaria in Brazil occurs in the Amazon Basin, although less competent malaria vector species are present in other parts of the country. Plasmodium vivax is the main malaria species; only ≈10%–20% of malaria cases are caused by P. falciparum . CDC recommends chemoprophylaxis for travelers going to malaria-endemic areas of Brazil (see Sec. 2, Ch. 5, Yellow Fever Vaccine & Malaria Prevention Information, by Country ; Map 2-04 ; and the CDC Malaria webpage. No malaria transmission occurs in the cities of Brasília (the capital), Rio de Janeiro, or São Paolo, or at Iguaçu Falls.
Map 2-04 Malaria prevention in Brazil
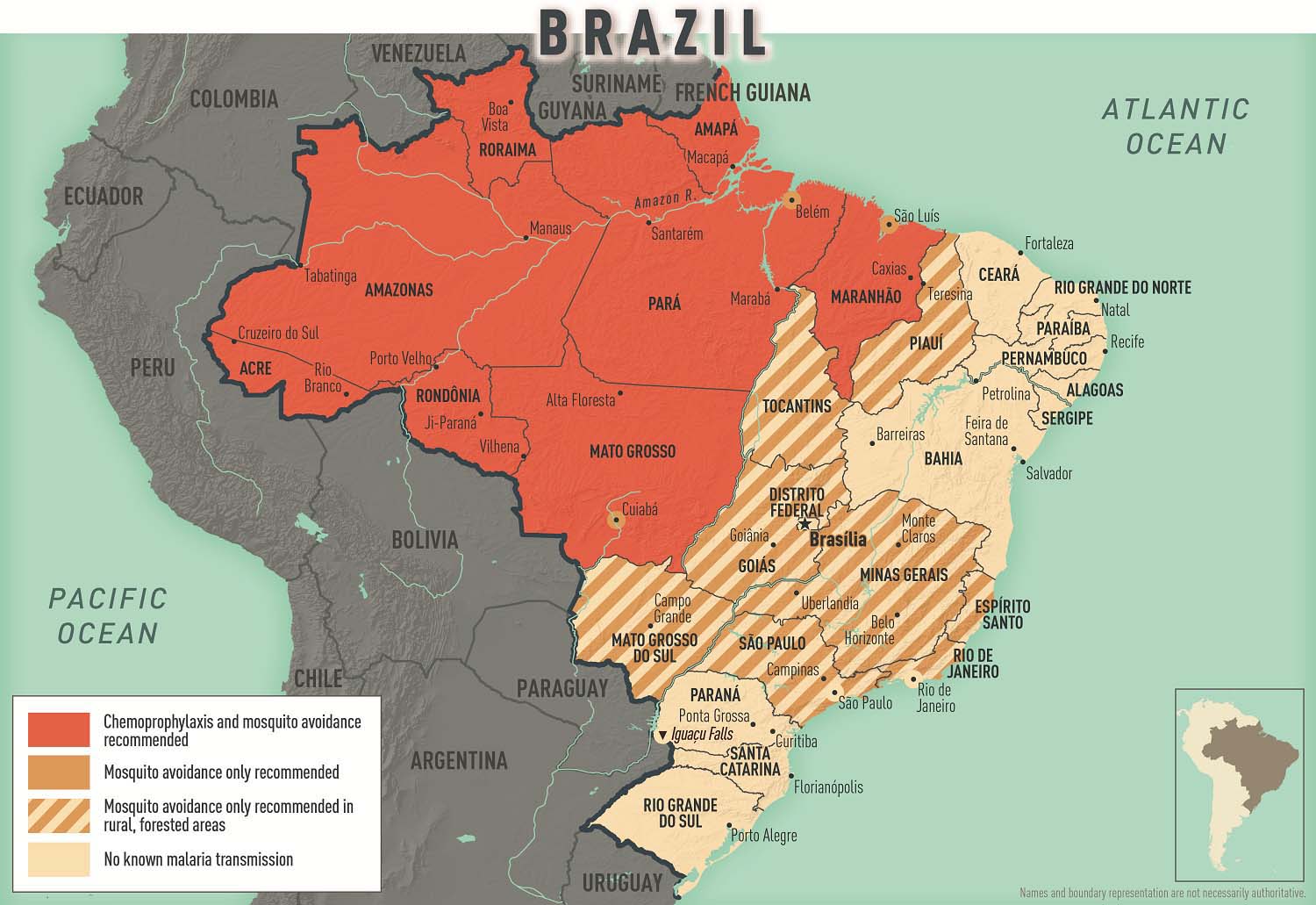
Rickettsial Diseases
Tickborne rickettsial diseases in Brazil include febre maculosa and Brazilian spotted fever, which are caused by etiologic agents from the same genus (Rickettsia) that causes Rocky Mountain spotted fever in the United States (see Sec. 5, Part 1, Ch. 18, Rickettsial Diseases ). Travelers should take precautions (e.g., wearing appropriate clothing, applying insect repellants on clothes and skin) to avoid tick bites both indoors and outdoors (see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods ).
Trypanosomiasis
Except in the north of the country where cases continue to rise, most states in Brazil have eliminated Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) through improved housing conditions and insecticide spraying for the vector. Although the risk is extremely low, travelers and ecotourists staying in poor-quality housing, especially in the Amazon region, might be at greater risk for this disease.
Outbreaks have been associated with consuming food or beverages containing açaí, an Amazonian fruit eaten throughout Brazil, and sugar cane juice ( caldo de cana ). Oral transmission occurs when people consume food or beverages contaminated with triatomines—the bloodsucking insects that transmit the etiologic agent of Chagas disease ( Trypanosoma cruzi )—or their feces (see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 25, American Trypanosomiasis / Chagas Disease ).
Yellow Fever
Mosquitoes that transmit yellow fever virus can be found throughout the Amazon Basin and in forested regions along all major river basins in Brazil, including Iguaçu Falls and as far south as Rio Grande do Sul. During 2016–2017, outbreaks of sylvatic yellow fever extended to the southeastern coast of Brazil, including the cities of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo, areas with historically low risk for transmission. Several unvaccinated travelers visiting these areas became ill with the disease, and some died.
Evidence of an expanded range of yellow fever transmission in Brazil led WHO and CDC to broaden their vaccination coverage recommendations for the country in 2017. Although Brazil does not require proof of vaccination against yellow fever for entry into the country, CDC recommends yellow fever vaccination for all travelers aged ≥9 months going to areas with risk for transmission. Updated information on areas of risk can be found on the CDC Travelers’ Health website; see Sec. 2, Ch. 5, Yellow Fever Vaccine & Malaria Prevention Information, by Country .
People planning travel to other countries in South America (e.g., Colombia) could be required to show proof of yellow fever vaccination at airline counters before exiting Brazil.
Map 2-03 Yellow fever vaccine recommendations for Brazil & neighboring countries
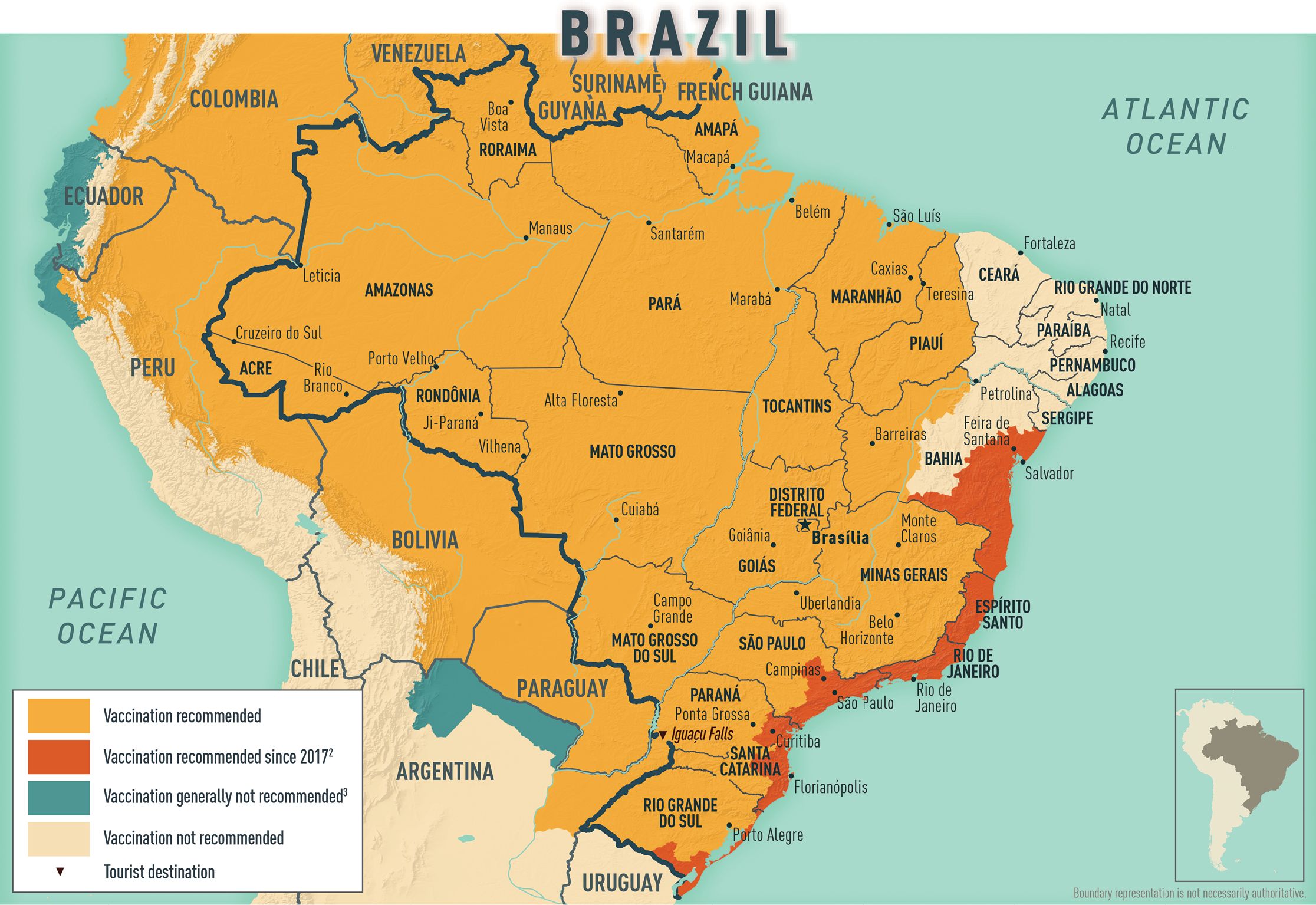
Zika virus is an arbovirus (genus Flavivirus ) transmitted mainly by mosquitoes, typically, although not exclusively, Aedes aegypti . Zika virus also can be sexually transmitted and transmitted during pregnancy to a fetus. First reported in Brazil in 2015, Zika was likely introduced to the country 2 years prior. A large Zika outbreak occurred in 2016, and >215,000 probable cases were reported. By 2019, the number of cases had dropped to 10,000.
Most Zika infections are asymptomatic and, when present, symptoms are mild. Commonly reported signs and symptoms include arthralgia, conjunctivitis, fever, and maculopapular rash; Guillain-Barré syndrome and encephalopathy have also been reported (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 27, Zika ).
Vertical transmission leads to congenital Zika virus infection; sequelae can include microcephaly with central nervous system anomalies, other serious neurologic consequences, and fetal loss. Because of the risk for birth defects in infants born to people infected with Zika during pregnancy, CDC encourages a pretravel discussion of risks with anyone who is pregnant or trying to become pregnant. Zika travel information is available at the CDC Travelers’ Health website.
Animal Bites
Overall, the risk for rabies infection in Brazil is very low. Preexposure rabies vaccination is recommended for travelers with extended itineraries, particularly children, and people planning trips to rural areas (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 18, Rabies ). For shorter stays, preexposure rabies vaccination is recommended for adventure travelers, those who might be occupationally exposed to animals, and people staying in locations >24 hours away from access to rabies immune globulin (e.g., the Amazon Forest).
Poisonous snakes are a hazard in many places in Brazil, although deaths from snake bites are rare (see Sec. 4, Ch. 7, Zoonotic Exposures: Bites, Stings, Scratches & Other Hazards ). Counsel travelers to seek immediate medical attention any time a bite wound breaks the skin, or if a snake sprays venom into their eyes. In some areas of the country, specific antivenoms are available, and being able to identify the snake species (or taking a picture) might prove critical to delivery of optimal medical care. The national toll-free number for intoxication and poisoning assistance is 0800-722-6001 (in Portuguese only).
Climate & Sun Exposure
Ensure travelers to Brazil are familiar with climatic conditions at their destinations before they go. Except in the south, where temperatures peak at 85°F (30°C), temperatures >104°F (40°C) are common in cities along the coast and in the Amazon region during October–March (see Sec. 4, Ch. 2, Extremes of Temperature ).
Travel in Brazil is generally safe, although crime remains a problem in urban areas and has spread to rural areas. The incidence of crime against tourists is greater in areas surrounding beaches, hotels, nightclubs, and other tourist destinations (see Sec. 4, Ch. 11, Safety & Security Overseas ). Drug-related violence has resulted in clashes with police in tourist areas. Several Brazilian cities have established specialized police units that patrol areas frequented by tourists and provide assistance to crime victims.
Political Unrest
Political demonstrations might disrupt public and private transportation. Encourage travelers to register with the US Department of State’s Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive advisories and alerts for areas they plan to visit.
Prostitution
Although commercial sex work is legal in Brazil, operating a brothel and financial exploitation of sex workers are both against the law.
Traffic-Related Injuries
As in many foreign countries, motor vehicle accidents in Brazil are a leading cause of injury and death among US travelers (see Sec. 8, Ch. 5, Road & Traffic Safety ). Road conditions in Brazil differ significantly from those in the United States, and driving at night can be dangerous. The national toll-free number for emergency roadside assistance (193) is in Portuguese only. Driving after drinking alcohol, even small quantities, is illegal, and travelers can expect police checkpoints during evenings and nights in many urban areas. Seatbelt use is mandatory, and motorcyclists are required by law to wear helmets.
Children aged ≤10 years must be seated in the back seat. Brazilian federal law requires infants ≤1 year of age to use rear-facing car seats, children 1–4 years of age to use forward-facing car seats, and children 4–7.5 years of age to use booster seats. Anyone traveling with small children should bring their own car or booster seats, in the event these are limited or unavailable.
Quality health care is available in most sizable Brazilian cities. Brazilian public health services are free, even for visitors. Foreign visitors can seek treatment in the emergency care network of Brazil’s public health system, known as the Unified Health System, or by its Portuguese acronym, SUS, or through private facilities. A non-comprehensive list of private medical services can be found on the US Embassy in Brazil website. The toll-free emergency number for ambulance services throughout Brazil is 192. The Brazilian Ministry of Health provides information in Portuguese for international visitors , including a list of reference hospitals for mass gathering events in Brazil.
Medical Tourism
Brazil has a growing number of private clinics that cater to international clientele and offer medical procedures using advanced technologies. Travel to Brazil for cosmetic surgery, assisted reproductive technology, or other elective medical procedures has increased in recent years, becoming a major part of the medical industry. Although the quality of care overall can vary widely, Brazil has many cosmetic surgery facilities on par with those found in the United States. Travelers seeking cosmetic surgery or other elective procedures should do their research and make sure that emergency medical services are available at their clinic of choice (see Sec. 6, Ch. 4, Medical Tourism ).
The following authors contributed to the previous version of this chapter: Joanna Gaines, Ana Carolina Faria e Silva Santelli
Bibliography
Hamer DH, Angelo K, Caumes E, van Genderen PJJ, Florescu SA, Popescu CP, et al. Fatal yellow fever in travelers to Brazil, 2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(11):340–1.
Malaria Atlas Project. Country profile: Brazil. Available from: https://malariaatlas.org/trends/country/BRA .
Melo CFCAE, Vasconcelos PFDC, Alcantara LCJ, Araujo WN. The obscurance of the greatest sylvatic yellow fever epidemic and the cooperation of the Pan American Health Organization during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020;53:e20200787.
Ministry of Health. Epidemiological bulletin: special issue. Chagas disease World Day, 14 April; year 2 [in Portuguese]. Brasilia: The Ministry; 2021. Available from: www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/boletins/boletins-epidemiologicos/especiais/2021/boletim_especial_chagas_14abr21_b.pdf .
Ministry of Health. Ministry of Health. Epidemiological bulletin 41. Monitoring of cases of urban arboviruses transmitted by Aedes aegypti (dengue, chikungunya and Zika), epidemiological weeks 01 to 52 [in Portuguese]. Brasilia: The Ministry; 2020. Available from: www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/boletins/boletins-epidemiologicos/edicoes/2020/boletim_epidemiologico_svs_41.pdf .
Nobrega AA, Garcia MH, Tatto E, Obara MT, Costa E, Sobel J, et al. Oral transmission of Chagas disease by consumption of acai palm fruit, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15(4):653–5.
Petersen E, Wilson ME, Touch S, McCloskey B, Mwaba P, Bates M, et al. Rapid spread of Zika virus in the Americas—implications for public health preparedness for mass gatherings at the 2016 Brazil Olympic Games. Int J Infect Dis. 2016;44:11–5.
Possas C, Lourenço-de-Oliveira R, Tauil PL, Pinheiro FP, Pissinatti A, Cunha RVD, et al. Yellow fever outbreak in Brazil: the puzzle of rapid viral spread and challenges for immunisation. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2018;113(10):e180278.
Sabino EC, Buss LF, Carvalho MPS, Prete CA Jr, Crispim MAE, Fraiji NA, et al. Resurgence of COVID-19 in Manaus, Brazil, despite high seroprevalence. Lancet. 2021;397(10273):452–5.
Silva MMO, Tauro LB, Kikuti M, Anjos RO, Santos VC, Gonçalves TSF, et al. Concomitant transmission of dengue, chikungunya, and Zika viruses in Brazil: clinical and epidemiological findings from surveillance for acute febrile illness. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;69(8):1353–9.
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Entry requirements
This advice reflects the UK government’s understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK, for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Brazil set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Brazilian Embassy in the UK .
COVID-19 rules
There are no COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements for travellers entering Brazil.
Passport validity requirements
To enter Brazil, your passport must have an ‘expiry date’ at least 6 months after the date you arrive.
Check with your travel provider that your passport and other travel documents meet requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.
You will be denied entry if you do not have a valid travel document or try to use a passport that has been reported lost or stolen.
Visa requirements
You can visit Brazil without a visa for up to 90 days for tourism.
If you want to extend your tourist visa, contact the Federal Police (in Portuguese) before your visa expires.
For more information about visas, contact the Brazilian Consulate in London .
If you overstay your visa, you’ll face a daily fine. You have the option to pay this fine either when you leave Brazil or during your next visit. You will not be allowed to re-enter Brazil if you do not pay the fine. Overstaying your visa will result in a 6-month ban from re-entering the country.
Make sure you get your passport stamped.
Make sure the border control officer puts a stamp in your passport. If it is not stamped, you may be fined when you leave.
Read about passport stamping if you live in Brazil (in Portuguese).
At Brazil border control, you must be able to show:
- information about the purpose of your visit
- evidence you have enough money for your whole stay
- details of your accommodation
- evidence of return or onward travel
British-Brazilian dual nationals
Brazilian immigration authorities often require dual British-Brazilian nationals visiting Brazil to travel on Brazilian (rather than British) passports.
Travelling with children
Children with dual british-brazilian citizenship.
British-Brazilian dual nationals under the age of 18 who are travelling without all parents or legal guardians need authorisation from all parents or legal guardians to travel in Brazil or leave the country.
If they travel with only one parent (or guardian) or without any parent, they must have 2 original written authorisations from all parents or guardians. Read more about the formal travel authorisation process for Brazilian minors and the frequently asked questions .
You must show this permission when the under-18 leaves Brazil. One copy will be kept by the Federal Police inspection agent, together with a copy of the under-18’s identification document, and the other must stay with the under-18 or the adult accompanying them on the trip.
Children who are not dual British-Brazilian nationals
The Federal Police have sometimes delayed the travel of non-Brazilian under-18s who travel without authorisation from both parents. Families of non-Brazilian under-18s travelling through Brazil without one or both parents should follow the instructions for dual British-Brazilian under-18s. Make sure the under-18 or their travelling companion also carries the original or notarised copy of the under-18’s birth certificate. Contact the Brazilian Consulate in London for more information.
Vaccination requirements
At least 8 weeks before your trip, check the vaccinations and certificates you need in TravelHealthPro’s Brazil guide . Depending on your circumstances, this may include a yellow fever vaccine.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
- Travel Tips Brazil for planning and on the go
Book your individual trip , stress-free with local travel experts
Select Month
- roughguides.com
- South America
- travel-advice
- Travel guide
- Itineraries
- Local Experts
- Travel Advice
- Accommodation
Plan your tailor-made trip with a local expert
Book securely with money-back guarantee
Travel stress-free with local assistance and 24/7 support
Just wanted to say that it was incredible. Trip Provider was also incredibly good, and really made their best effort to solve any problems. We were very im...
More travel information for Brazil
From travel safety to visa requirements, discover the best tips for traveling to Brazil
- Eating and drinking in Brazil
- How to get to Brazil
- Getting around Brazil: Transportation Tips
- Electricity
Electricity supplies vary – sometimes 110V and sometimes 220V – so check before plugging anything in. Plugs have two round pins, as in continental Europe.
Gay and lesbian travel
Opening hours and public holidays, tourist information, travellers with disabilities, costs and money in brazil, crime and safety in brazil, health advice for brazil, the media in brazil, travelling with children in brazil, travel ideas for brazil, created by local experts.

9 days / from 2042 USD
Brazilian Beaches: Copacabana, Botafogo and more
Begin at Foz do Iguaçu, where you will stand in awe of the huge Iguaçu Falls. Next up, we'll head to the lively city of Rio de Janeiro, home of the legendary Copacabana, Botafogo and Flamengo beaches, and of course, Sugar Loaf Mountain and the iconic Christ the Redeemer statue.

10 days / from 1700 USD
Blissful Brazil
Welcome to a lavish journey that marries adventure with style, featuring stays in carefully chosen four-star hotels. This reinvigorating trip will have you sightseeing in São Paulo, gazing at the spectacular Foz do Iguaçu falls and relaxing on Rio's finest beaches before you know it.

10 days / from 2683 USD
Breathtaking Brazil: Rio, Beaches and Waterfalls
Explore the lively city of Rio de Janeiro, home to Ipanema and Copacabana beaches; experience the stunning Foz do Iguaçu National Park and see the world’s largest waterfalls system; immerse yourself in cultural Salvador, the magnificent former capital of Portugal’s New World colony.
Gay life in Brazil thrives, especially in the large cities, Rio in particular being one of the great gay cities of the world. In general, the scene benefits from Brazil’s hedonistically relaxed attitudes towards sexuality in general, and the divide between gay and straight nightlife is often very blurred.
Attitudes vary from region to region. The two most popular gay destinations are Rio and Salvador. Rural areas and small towns, especially in Minas Gerais, the Northeast and the South, are conservative; the medium-sized and larger cities less so. A useful resource to consult before your trip is w www.guiagaybrasil.com.br ; although the text is in Portuguese, there are enough English indicators to allow non-Portuguese speakers to navigate easily through it and benefit from the listings and tips.
Prior to travelling, you should take out an insurance policy to cover against theft, loss and illness or injury. Before paying for a new policy, however, it’s worth checking whether you already have some degree of coverage – credit-card companies, home-insurance policies and private medical plans sometimes cover you and your belongings when you’re abroad. Most travel agents, tour operators, banks and insurance brokers will be able to help you. Remember that when securing baggage insurance, make sure that the per-article limit – typically under £500 equivalent – will cover your most valuable possession.
Even the humblest hotel has a lavadeira , who will wash and iron your clothes. Agree on a price beforehand, but don’t be too hard – livelihoods are at stake. Larger hotels have set prices for laundry services – usually, surprisingly expensive. Very common in larger cities are lavandarías , which operate a very useful por peso system – the clothes are weighed at the entrance, you pay per kilo, and pick them up washed and folded the next day for a couple of dollars per kilo. Ironing ( passar ) costs a little more.
A post office is called a correio , identifiable by their bright yellow postboxes and signs. An imposing Correios e Telégrafos building will always be found in the centre of a city of any size, but there are also small offices and kiosks scattered around that only deal with mail. Queues are often a problem, but you can save time by using one of their franking machines for stamps; the lines move much more quickly. Stamps ( selos ) are most commonly available in two varieties, either for mailing within Brazil or abroad. A foreign postage stamp costs around R$1.70 for either a postcard or a letter up to 10g. It is expensive to send parcels abroad.
Mail within Brazil takes three or four days, longer in the North and Northeast, while airmail letters to Europe and North America usually take about a week. Surface mail takes about a month to North America, and two to Europe. Although the postal system is generally very reliable, it is not advisable to send valuables through the mail.
We’ve provided maps of all the major towns and cities and various other regions. More detailed maps are surprisingly hard to get hold of outside Brazil and are rarely very good: there are plenty of maps of South America, but the only widely available one that is specifically of Brazil is the Bartholomew Brazil & Bolivia (1:5,000,000), which is not very easy to read. Much better are the six regional maps in the Mapa Rodoviário Touring series (1:2,500,000), which clearly mark all the major routes, although these, even in Brazil, are difficult to find.
A useful compendium of city maps and main road networks is published by Guias Quatro Rodas, a Brazilian motoring organization, which also has maps to Rio, São Paulo and other cities, states and regions. These are easy to find in bookstores, newsagents and magazine stalls. Very clear 1:960,000 maps of individual states are published by On Line Editora, and are usually available in Brazilian bookstores and newspaper kiosks; topographical and hiking maps are difficult to come by, though very occasionally they are available from municipal tourist offices or national parks in Brazil, or from local trekking equipment shops or tour operators.
Basic hours for most stores and businesses are from Monday to Friday 9am to 6pm and Saturday 9am to noon, with an extended lunch hour from around noon to 2pm. Shops in malls stay open until late Saturday night. Banks open at 10am, and stay open all day, but usually stop changing money at either 2pm or 3pm; except for those at major airports, they’re closed at weekends and on public holidays. Museums and monuments more or less follow office hours but many are closed on Monday.
Phones are operated by phonecards ( cart ã o telefônico ), which are on sale everywhere – from newspaper stands, street sellers’ trays and most cafés. For local calls, a 5- real card will last for several conversations; for long-distance or international calls, higher-value phonecards come in 10, 20, 50 or 100 real denominations. Calls to the US or Europe cost about US$1.50 per minute. Before dialling direct, lift the phone from the hook, insert the phonecard and listen for a dialling tone. Note that long-distance calls are cheaper after 8pm.
The dialling tone is a single continuous note, engaged is rapid pips, and the ringing tone is regular peals, as in the US. The phone system in Brazil is continually overloaded. If you get an engaged tone, keep trying – nine times out of ten, the phone is not actually engaged and you get through after seven or eight attempts. The smaller the place, the more often you need to try.
Long-distance and international calls can also be made from a posto telefônico , which all operate in the same way: you ask at the counter for a chave , are given a numbered key, go to the booth, insert the key and turn it to the right, and can then make up to three completed calls. You are billed when you return the key. To make a call between cities, you need to dial the trunk code, the código DDD (pronounced “daydayday”), listed at the front of phone directories. For international calls, ask for chamada internacional ; a reverse-charge call is a chamada a cobrar . Reversing the charges costs about twice as much as paying locally, and it is much cheaper to use a telephone charge-card from home. Except in the most remote parts of Amazônia and the Northeast, everything from a small town upwards has a posto , though note that outside large cities they shut at 10pm.
Long-distance telephone access codes
The privatization of Brazil’s telephone system has led to a proliferation of new telephone companies and increased competition. Before making a national or international call you must now select the telephone company you wish to use by inserting a two-digit code between the zero and the area code or country code of the number you are calling. To call Rio, for example, from anywhere else in the country, you would dial zero + phone company code + city code followed by the seven-digit number. For local calls, you simply dial the seven- or eight-digit number.
As different phone companies predominate in different areas of the country, pay phones will display which company code should be used from that particular phone, or the hotel receptionist will let you know the correct code to be used if calling from your hotel. The commonest codes are 21, 23 and 14. If you want to reverse the charges, dial 90 and then the number with company code as above. To reverse the charges on an international call, dial 00080 followed by the country code. As ever, the simplest option to make international calls is a phonecard bought before you leave.
Most of Brazil is three hours behind GMT, but the states of Amazonas, Acre, Rondônia, Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul are four hours behind – that includes the cities of Manaus, Corumbá, Rio Branco, Porto Velho, Cuiabá and Campo Grande.
Bills usually come with ten percent taxa de serviço included, in which case you don’t have to tip – ten percent is about right if it is not included. Waiters and some hotel employees depend on tips. You don’t have to tip taxi drivers (though they won’t say no), but you are expected to tip barbers, hairdressers, shoeshine kids, self-appointed guides and porters. It’s useful to keep change handy for them – and for beggars.
You’ll find tourist information fairly easy to come by once in Brazil, and there are some sources to be tapped before you leave home. Brazil’s embassies or larger consulates have tourist sections, where you can pick up brochure information and advice.
Popular destinations such as Rio, Salvador, the Northeast beach resorts, and towns throughout the South have efficient and helpful tourist offices , but anywhere off the beaten track has nothing at all – only Manaus, Belém and Porto Velho have offices in the Amazon region, for example.
Most state capitals have tourist information offices, which are announced by signs saying Informações Turísticas . Many of these provide free city maps and booklets, but they are usually all in Portuguese. As a rule, only the airport tourist offices have hotel-booking services , and none of them is very good on advising about budget accommodation. Tourist offices are run by the different state and municipal governments, so you have to learn a new acronym every time you cross a state line. In Rio, for example, you’ll find TurisRio, which advises on the state, and Riotur, which provides information on the city. There’s also EMBRATUR , the national tourist organization, but it doesn’t have direct dealings with the general public apart from its excellent website.
Travelling in Brazil for people with disabilities is likely to be difficult if special facilities are required. For example, access even to recently constructed buildings may be impossible, as lifts are often too narrow to accept wheelchairs or there may be no lift at all. In general, though, you’ll find that hotel and restaurant staff are helpful and will do their utmost to be of assistance to try to make up for the deficiencies in access and facilities.
Buses in cities are really only suitable for the agile; taxis , however, are plentiful, and most can accommodate wheelchairs. Long-distance buses are generally quite comfortable, with the special leito services offering fully reclining seats. Internal airlines are helpful, and wheelchairs are available at all the main airports.
The cost of living in Brazil is low outside the main tourist spots, and even within them shopping around can lower costs a lot. Europeans will mostly think Brazil cheap, North Americans a little less so but still comparing favourably with the US for most things. Particularly reasonable are hotels (except in Rio), foodstuffs (including eating out) and bus travel, while most museums are free. The exception is internal plane tickets, which a near-monopoly between TAM and Gol make expensive, unless you have an airpass. Other relatively expensive things are sunblock, good-quality clothing, cameras and anything to do with computers (except internet cafés, which are very cheap).
On the whole, Brazil is very much a viable destination for the budget traveller. The cheapness of food and budget hotels – and the fact that the best attractions, such as the beaches, are free – still make it possible to have an enjoyable time on a budget of less than R$125 a day. Staying in good hotels, travelling by comfortable buses or planes and not stinting on the extras is likely to cost you around R$400 a day.
The Brazilian currency is the real (pronounced “hey-al”); its plural is reís (pronounced “hey-ice”), written R$. The real is made up of one hundred centavos, written ¢. The rather pleasing notes, themed after Brazilian wildlife and all the same size but different colours, are for 2, 5, 10, 20, 50 and 100 reís; coins are 1, 5, 10, 25, 50 centavos and the 1 real. You will occasionally see a tattered R$1 note but these are being phased out, although they are legal tender. Throughout the Guide, all prices are given in Brazilian reís unless otherwise noted. However, US dollars and euros are easy enough to change in banks and exchange offices anywhere, and are also readily accepted by luxury hotels, tour companies and souvenir shops in the big cities.
Changing money in Brazil is simple; just take your bank or credit card with PIN (Personal Identification Number, which you must set up with your bank before your trip), and use ATMs – they are now ubiquitous in Brazil, to be found in most supermarkets, many pharmacies and all airports, as well as banks. Only Visa cards can be used to withdraw cash advances at the ATMs of Banco do Brasil and Banco Bradesco; only MasterCard at HSBC, Itaú and Banco Mercantil. Increasing numbers of Brazilian banks are linking their cash dispensers to the Cirrus and Maestro networks; the most reliable and widespread is the Banco 24 Horas network and HSBC. One important thing to note is that for security reasons most bank ATMs stop dispensing cash after 8pm, although Banco 24 Horas in large supermarkets will dispense until 10pm. Airport ATMs are the only ones that dispense cash all hours.
The main credit cards are widely accepted by shops, hotels and restaurants throughout Brazil, even in rural areas. MasterCard and Visa are the most prevalent, with Diners Club and American Express also widespread. It’s a good idea to inform your credit-card issuer about your trip before you leave so that the card isn’t stopped for uncharacteristic use.
Given the ease of using plastic, traveller’s cheques are not recommended, unless you want a small emergency reserve. Only the head offices of major banks (Banco do Brasil, HSBC, Banco Itaú, Banespa) will have an exchange department (ask for câmbio); whether changing cash or traveller’s cheques, you’ll need your passport. You can also change cash and traveller’s cheques in smart hotels and in some large travel agencies. Airport banks are open seven days a week, others only Monday to Friday.
Exchange rates were stable in the US$1.80–2.20 range for years but rose against the dollar with the financial crisis of late 2008, making Brazil cheaper for North Americans but more expensive for Europeans, especially Britons. But since Brazil’s newfound economic stability means it is now well placed to weather crises, exchange-rate turbulence is unlikely to be a feature of your stay. You will see two rates quoted in hotels: the oficial, or interbank rate, which you will be able to get in a casa de câmbio, an exchange counter in a travel agency or specialized exchange dealer (although these are now thin on the ground), and the turismo, a few cents less – more in hotels, where they bank on the ignorance of the clientele. Rates out of ATMs are usually the oficial, making plastic an even better option.
Brazil has a reputation as a rather dangerous place, and while it’s not entirely undeserved, it is often overblown and you should not let fear overshadow your stay. If you take the precautions outlined below, you are extremely unlikely to come to any harm – although you might still have something stolen somewhere along the way. The tips in this section apply everywhere, but be particularly alert in Rio, Salvador and Recife.
Criminals know that any injury to a foreign tourist is going to mean a heavy clampdown, which in turn means no pickings for a while. So unless you resist during an incident, nothing is likely to happen to you. That said, having a knife or a gun held on you is something of a shock: it’s very difficult to think rationally. But if you are unlucky enough to be the victim of an assalto (a hold-up), try to remember that it’s your possessions rather than you that are the target. Your money and anything you’re carrying will be snatched, your watch will get pulled off your wrist, but within a couple of seconds it will be over. On no account resist: it isn’t worth the risk.
Taking precautions
As a rule, assaltos are most common in the larger cities, and are rare in the countryside and towns. Most assaltos take place at night, in backstreets with few people around, so stick to busy, well-lit streets; in a city, it’s always a lot safer to take a taxi than walk. Also, prepare for the worst by locking your money and passport in the hotel safe – the one in your room is more secure than the one at reception. If you must carry them, make sure they’re in a moneybelt or a concealed internal pocket. Do not carry your valuables in a pouch hanging from your neck. Only take along as much money as you’ll need for the day, but do take at least some money, as the average assaltante won’t believe a gringo could be out of money, and might get rough. Don’t wear an expensive watch or jewellery: if you need a watch you can always buy a cheap plastic digital one on a street corner. And keep wallets and purses out of sight – pockets with buttons or zips are best.
You need to take special care when carrying a laptop – around business-oriented airports, like Congonhas in São Paulo and Santos Dumont in Rio, laptop stealing has become epidemic. Scouts wait at exits and phone ahead to thieves on motorbikes, who pull alongside your taxi when it is stuck in traffic and tap on the window with a revolver. Conceal laptops inside bags that do not look like computer bags, and try to avoid looking like a businessperson even if you are one.
More common than an assalto is a simple theft, a furto. Brand-new, designer-label bags are an obvious target, so go for the downmarket look. You’re at your most vulnerable when travelling and though the luggage compartments of buses are pretty safe – remember to get a baggage check from the person putting them in and don’t throw it away – the overhead racks inside are less safe; keep an eye on things you stash there, especially on night journeys. On a city beach, never leave things unattended while you take a dip: any beachside bar will stow things for you. Most hotels (even the cheaper ones) will have a safe, a caixa, and unless you have serious doubts about the place you should lock away your most valuable things: the better the hotel, the more secure it’s likely to be. In cheaper hotels, where rooms are shared, the risks are obviously greater – some people take along a small padlock for extra security and many wardrobes in cheaper hotels have latches fitted for this very purpose. Finally, take care at Carnaval as it’s a notorious time for pickpockets and thieves.
At international airports, particularly Rio and São Paulo, certain scams operate; for instance, well-dressed and official-looking men target tourists arriving off international flights in the arrivals lounge, identify themselves as policemen, often flashing a card, and tell the tourists to go with them. The tourists are then pushed into a car outside and robbed. If anyone, no matter how polite or well dressed they are, or how good their English is, identifies themselves as a policeman to you, be instantly on your guard – real policemen generally leave foreigners well alone. They won’t try anything actually inside a terminal building, so go to any airline desk or grab one of the security guards, and on no account leave the terminal building with them or leave any luggage in their hands.
If you are robbed or held up, it’s not necessarily a good idea to go to the police. Except with something like a theft from a hotel room, they’re very unlikely to be able to do anything, and reporting something can take hours even without the language barrier. You may have to do it for insurance purposes, when you’ll need a local police report: this could take an entire, and very frustrating, day to get, so think first about how badly you want to be reimbursed. If your passport is stolen, go to your consulate and they’ll smooth the path.
If you have to deal with the police, there are various kinds. The best are usually the Polícia de Turismo, or tourist police, who are used to tourists and their problems and often speak some English, but they’re thin on the ground outside Rio. In a city, their number should be displayed on or near the desk of all hotels. The most efficient police by far are the Polícia Federal, the Brazilian equivalent of the American FBI, who deal with visas and their extension; they have offices at frontier posts, airports and ports and in state capitals. The ones you see on every street corner are the Polícia Militar, with blue or green uniforms and caps. They look mean – and very often are – but, apart from at highway road blocks, they generally leave gringos alone. There is also a plain-clothes Polícia Civil, to whom thefts are reported if there is no tourist police post around – they are overworked, underpaid and extremely slow. If you decide to go to the police in a city where there is a consulate, get in touch with the consulate first and do as they tell you.
The drug wars in the favelas that you will have heard about and may well see on local TV during your stay are very localized and unlikely to have any impact on foreign tourists. But you should be extremely careful about using drugs in Brazil. Marijuana – maconha – is common, but you are in trouble if the police find any on you. You’ll be able to bribe your way out of it, but it will cost you the daily withdrawal limit on whatever plastic you have. Foreigners sometimes get targeted for a shakedown and have drugs planted on them – the area around the Bolivian border has a bad reputation for this – in order to get a bribe out of them. If this happens to you, deny everything, refuse to pay and insist on seeing a superior officer and telephoning the nearest consulate – though this approach is only for the patient.
Cocaine is not as common as you might think, as most of it simply passes through Brazil from Bolivia or Colombia bound for Europe. Nevertheless, the home market has grown in recent years, controlled by young and vicious gang-leaders from the favelas of the major cities.
Be careful about taking anything illegal on buses: they are sometimes stopped and searched at state lines. The stupidest thing you could do would be to take anything illegal anywhere near Bolivia, as buses heading to or from that direction get vigorously searched by the federais. Much the same can be said of smuggling along the rivers into Peru and Colombia: don’t even think about it.
There are no compulsory vaccinations required to enter the country from Europe or North America (although you may need a yellow fever certificate entering from another South American country), but certain precautions should be taken, especially if you’re staying for any length of time or visiting more remote regions. Taking out travel insurance is vital, and you should be especially aware of HIV and dengue fever, a significant problem in Rio during the Brazilian summer (Dec–April). But you should not let health issues make you unduly paranoid – if you need it, good medical care is available cheaply for all but the most serious of problems.
Pharmacies and medical treatment
Most standard drugs are available in pharmacies (farmácias), which you’ll find everywhere – no prescriptions are necessary. A pharmacy will also give injections (unless you’ve already had one, you’ll need a tetanus jab if you get bitten by a dog) and free medical advice, and they’re a good first line of defence if you fall ill.
If you are unlucky enough to need medical treatment in Brazil, forget about the public hospitals – as a foreigner, you have virtually no chance of getting a bed unless you have an infectious disease, and the level of health care offered by most is appalling. You can get good medical and dental care privately: North Americans will think it fairly inexpensive, Europeans used to state-subsidized health care will not. A doctor’s visit will cost on average US$40–75; drugs are relatively cheap. Hotels in big cities will have lists of English-speaking doctors; ask for a médico. Outside the larger centres, you will probably have to try out your Portuguese. Any Brazilian doctor will also understand – although not necessarily speak – Spanish.
Food and water
Many diseases are directly or indirectly related to impure water and contaminated food, and care should be taken in choosing what to eat and drink.
You should, of course, take particular care with seafood, especially shellfish – don’t eat anything that’s at all suspicious. Fruit and salad ingredients should be washed in bottled or purified water or, preferably, peeled. Ultimately, you are going to run some risks with food, so if you’re going to enjoy your stay to the full, you can’t be too paranoid.
Even in the most remote towns and villages mineral water (água mineral), either sparkling (com gás) or still (sem gás), is easily available and cheap. To avoid dehydration be sure to drink plenty of non-alcoholic liquids, always carry a bottle of water on long trips, and check that the seal on any bottled water you use is intact.
As with food, it’s difficult to be on guard all the time whilst drinking; fruit juices are often diluted with water, and ice is rarely made with filtered water outside a smart hotel. It is not realistic to restrict all water intake to mineral water, but if you are sensible you can at least minimize risk.
Chagas’ disease
A serious disease you should guard against is Chagas’ disease, which is endemic in parts of the Northeast and the Amazon. Although it is difficult to catch, it can lead to serious heart and kidney problems that appear up to twenty years after infection. The disease is carried in the faeces of beetles that live in the cracks of adobe walls, so if sleeping in an adobe hut, make sure nothing can crawl into your hammock; either use a mosquito net or sling the hammock as far from walls as you can. The beetle bites and then defecates next to the spot: scratching of the bite will rub in the infected faeces, so before scratching a bite that you know wasn’t caused by a mosquito, bathe it in alcohol. If you are infected, you will have a fever for a few days that will then clear up as if nothing untoward happened. Though the disease can be treated in its early stages, it becomes incurable once established. If you travel through a Chagas area and get an undiagnosed fever, have a blood test as soon as possible afterwards.
Dengue fever
Dengue fever, a viral disease transmitted by mosquito bites, is increasingly common in all Brazilian cities save the extreme south of the country. Rio has been particularly badly affected in recent years, as the spectacular incompetence of its city government has allowed the mosquito problem to get out of hand. It is highly seasonal, peaking in the southern hemisphere summer (Dec–April). The symptoms are debilitating rather than dangerous: light but persistent fever, tiredness, muscle and joint pains, especially in the fingers, and nausea and vomiting. It is easily treatable, but you will feel pretty grim for a week or so. It is much more widespread than any other disease in urban areas, and is currently the focus of much educational and preventive work by the Brazilian government. The same precautions against mosquito bites outlined in the section on malaria above apply here. The difference is that the dengue mosquito comes out during the day rather than at night. Be cautious in urban environments around anything that could act as a water retainer and thus as a mosquito breeding ground: drainage channels, old oil drums and tyres, abandoned lots, swampy areas in general.
There is one dangerous form of dengue, hemorraghic dengue, which kills hundreds of people a year in Brazil. Tourists tend not to get it, since you almost always need to have had a previous attack of dengue to be vulnerable to it. It is particularly dangerous to children. The body’s immune system is provoked to attack itself by the dengue virus, resulting in internal bleeding that can quickly get out of hand. If dengue-like symptoms are accompanied by bleeding from the nose and ears or highly bloodshot eyes, get yourself to a private hospital fast. Even if you are unlucky enough to get it, in the vast majority of cases getting timely treatment will mean a few days in hospital is all that’s needed for complete recovery. You will feel very weak and should take things easy for a couple of weeks after you leave hospital, however.
Diarrhoea, dysentery and giardia
Diarrhoea is something everybody gets at some stage, and there’s little to be done except drink a lot (but not alcohol) and bide your time. You should also replace salts either by taking oral rehydration salts or by mixing a teaspoon of salt and eight of sugar in a litre of purified water. You can minimize the risk by being sensible about what you eat, and by not drinking tap water anywhere. This isn’t difficult, given the extreme cheapness and universal availability of soft drinks and água mineral, while Brazilians are great believers in herbal teas, which often help alleviate cramps.
If your diarrhoea contains blood or mucus, the cause may be dysentery or giardia. With a fever, it could well be caused by bacillic dysentery and may clear up without treatment. If you’re sure you need it, a course of antibiotics such as tetracyclin or ampicillin (travel with a supply if you are going off the beaten track for a while) should sort you out, but they also destroy “gut flora” that help protect you. Similar symptoms without fever indicate amoebic dysentery, which is much more serious, and can damage your gut if untreated. The usual cure is a course of metronidazole (Flagyl), an antibiotic that may itself make you feel ill, and should not be taken with alcohol. Similar symptoms, plus rotten-egg belches and farts, indicate giardia, for which the treatment is again metronidazole. If you suspect you have any of these, seek medical help, and only start on the metronidazole (750mg three times daily for a week for adults) if there is definitely blood in your diarrhoea and it is impossible to see a doctor.
Hepatitis A
Wherever you go, protection against hepatitis A is a sensible precaution. The disease is transmitted through contaminated water and food, resulting in fever and diarrhoea, and it can also cause liver damage. Gammaglobulin injections, one before you go and boosters every six months, are the standard protection. If you plan to spend much time in Amazônia or the Northeast, or if you know that you will be travelling rough, it’s well worth protecting yourself. If you have had jaundice, you may well have immunity and should have a blood test to see if you need the injections. A newer vaccine – Havrix – is very effective and lasts for up to ten years.
HIV and AIDS
Brazil has a relatively high number of people with AIDS and HIV. There are many reasons for this: a scandalous lack of screening of either blood donors or supplies in the 1980s; the level of gay sex between Brazilian men, among whom bisexuality is common; the popularity of anal sex, not least among heterosexual couples; and the sharing of needles among drug users in large cities. But Brazil has been a world leader in dealing with the epidemic. It faced down international drug companies in the late 1990s with the threat that they would independently manufacture AIDS drugs – with the result that all HIV-positive Brazilians now receive free anti-retroviral medicines in a programme that has become a global model for developing countries. Brazil also has some of the funniest and most imaginative safe-sex campaigns anywhere, particularly in evidence during Carnaval.
A straightforward understanding of the disease and how it is transmitted is the best defence. Firstly, HIV is not evenly distributed throughout Brazil. A majority of HIV carriers are concentrated in the big cities. As anywhere else, sex with a prostitute is a high-risk activity. The situation with blood and blood products has now improved enormously, but in remoter parts of the country, especially the Amazon, make sure that if you have an injection it is with a needle you see being removed from its packaging. Finally, use a condom. Only a tiny minority of sexually active Brazilian men carry them as a matter of course. They are widely available in pharmacies, where you should ask for a camisinha.
Malaria is endemic in northern Brazil, and anyone intending to travel in Amazônia should take precautions very seriously. You are safe if you are only visiting cities and towns, where intensive campaigns keep malarial mosquitoes at a distance, and if your visit will be restricted to Manaus, Santarém and Belém you can forego prophylaxis. Mosquitoes are also not a problem on river journeys, since the breezes keep them off, and they are much less common in black-water river systems – such as the River Negro, where jungle lodges around Manaus are concentrated – where malaria is rare.
If you will be sleeping in a rural area anywhere else in the Amazon, however, it is a good idea to take precautions. In recent years, rates have climbed as mosquitoes have become more resistant to insecticides and drugs, and a few unwary tourists die avoidably every year. Southern Pará state and much of rural Rondônia state are the riskiest areas for malaria. However, with simple precautions you can minimize the chances of getting it even in highly malarial areas, and, properly treated, a dose of malaria should be no worse than a severe bout of flu. But make no mistake – unless you follow the precautions outlined here, and take malaria prophylaxis when appropriate, malaria can kill.
There are two kinds of malaria in Brazil: falciparum, which is more serious but less common, and vivax. Both are transmitted by anopheles mosquitoes, which are most active at sunrise and for an hour or so before sunset. Even in very malarial areas, only around five percent of anopheles are infected with malarial parasites, so the more you minimize mosquito bites, the less likely you are to catch it. Use insect repellent: the most commonly used in Brazil is Autan, often in combination with Johnson’s Baby Oil to minimize skin irritation. The most effective mosquito repellents – worth looking out for before you leave home – contain DEET (diethyl toluamide). DEET is strong stuff, so follow the manufacturers’ instructions, particularly with use on children. If you have sensitive skin, a natural alternative is citronella or, in the UK, Mosi-guard Natural, made from a blend of eucalyptus oils (though still use DEET on clothes and nets). Wear long-sleeved shirts and trousers, shoes and socks during the times of day when mosquitoes are most active. Sleep under a sheet and, crucially, use a mosquito net. Nets for hammocks (mosqueteiro para rede) are reasonable and easily available in Amazonian cities and towns. Mosquito coils also help keep the insects at bay.
When taking preventive tablets it’s important to keep a routine and cover the period before and after your trip with doses. Doctors can advise on which kind to take. As resistance to chloroquin-based drugs increases, mefloquin, which goes under the brand name of Lariam, has become the recommended prophylactic for most travellers to Brazil. This has very strong side effects, and its use is controversial.
Malaria has an incubation period of around two weeks. The first signs of malaria are remarkably similar to flu – muscle pains, weakness and pain in the joints, which will last for a day or two before the onset of malaria fever proper – and may take months to appear: if you suspect anything go to a hospital or clinic immediately. You need immediate treatment and a blood test to identify the strain. Malaria treatment is one public-health area where Brazil can take some credit. Dotted in malarial parts of the Amazon are small malaria control posts and clinics, run by the anti-malaria agency SUCAM – ask for the posto da SUCAM. They may not look like much, but the people who staff them are very experienced and know their local strains better than any city specialist. Treatment in a posto is free, and if you do catch malaria you should get yourself taken to one as quickly as possible; don’t shiver in your hammock and wait for it to pass. It often does, but it can also kill. If in a city and you get the same symptoms (a fever and the shakes), make sure you get a blood test right away; you’ll get your results in a few hours, and quick diagnosis is vital. Remember that the incubation period means that the symptoms may only appear after you return home – make sure to tell your doctor where you’ve been if you get a fever shortly after your return home.
Malaria is a much more serious issue for a child. We specifically recommend avoiding the state of Rondônia other than Porto Velho, rural Acre and Amapá and southern Pará if you are travelling with children.
Yellow fever
Getting a yellow fever vaccination, which offers protection for ten years, is recommended if you’re going to Amazônia, Goiás or Mato Grosso. This viral disease is transmitted by mosquitoes and can be fatal, but is extremely rare even in places where it is endemic. Symptoms include headache, fever, abdominal pain and vomiting, and though victims may appear to recover, without medical help they may suffer from bleeding, shock and kidney and liver failure. While you’re waiting for help, it is important to keep the fever as low as possible and prevent dehydration.
In the Amazon
Given the remoteness of many parts of the Amazon and the prevalence of insects and snakes, health care takes on a special significance. If you are trekking through forest or savanna, long trousers are a good idea, and it is vital to wear good boots that protect your ankles from snake bites, chiggers (mites) and scorpions. You should never trek alone.
Snakes are timid and, unless you’re unlucky, only attack if you step on them. Many of the most poisonous snakes are tiny, easily able to snuggle inside a shoe or a rucksack pocket. Always shake out your hammock and clothes, keep rucksack pockets tightly closed and take special care when it rains, as snakes, scorpions and other nasty beasties quite sensibly head for shelter in huts. If you do get bitten by a snake, try to kill it for identification – but only if this can easily be done. Use a shoelace or a torn piece of shirt wound round the limb with a stick as a tourniquet, which you should repeatedly tighten for twenty seconds and then release for a minute, to slow down the action of the poison. Contrary to popular belief, cutting yourself and sucking out blood will do you more harm than good. It goes without saying that you should get yourself to a doctor as soon as possible. If you are well off the beaten track, health posts in the nearest town may have serum, but you must know the type of snake involved.
Due to the humidity, any cut or wound gets infected very easily. Always clean cuts or bites with alcohol or purified water before dressing. As a general rule, leave all insects alone and never handle them. Even the smallest ants, caterpillars and bees can give you nasty stings and bites, and scorpions, large soldier ants and some species of bee will give you a fever for a day or two as well.
As in the US, Brazil has a regional press rather than a national one. Even the top Rio and São Paulo papers are a little parochial; elsewhere, newspapers are at best mediocre but are always valuable for listings of local events. Brazil also boasts a lurid but entertaining yellow press, specializing in gruesome murders, political scandals and football.
Newspapers and magazines
The top newspapers are the slightly left-of-centre Folha de São Paulo and the Rio-based, right-of-centre O Globo, usually available, a day late, in large cities throughout the country. Both are independent and have extensive international news, cultural coverage and entertainment listings, but are respectable rather than exciting. Even stodgier but reasonable is the right-wing Estado de São Paulo, while the Gazeta Mercantil and Valor Econômico are high-quality equivalents of the Financial Times or Wall Street Journal. The most enjoyable of the yellow press is Rio’s Última Hora, especially good for beginners in Portuguese, with a limited vocabulary and lots of pictures, but all major cities have similar local tabloids.
There are also two good weekly current-affairs magazines: Veja and Isto É. They are expensive, around US$5, since their readership is exclusively middle class. You will find Brazilian editions of most major fashion and women’s magazines. The weekly Placar is essential for anyone wanting to get to serious grips with Brazilian football. Vogue Brasil, edited in São Paulo and published by Condé Nast, is a quality magazine offering great insight into the style of the Brazilian elite, while Plástica is a glossy monthly magazine that sheds light on Brazil’s apparent obsession with plastic surgery.
Apart from in airports, Rio and São Paulo, where you can find the International Herald Tribune and the Economist, English-language newspapers and magazines are very difficult to find in Brazil. The exceptions are Time and Newsweek, which are widely available in newspaper kiosks in big cities, albeit often weeks old.
Radio is always worth listening to if only for the music. FM stations abound everywhere, and you should always be able to find a station that plays local music. Shortwave reception for the BBC World Service is good in Brazil.
Brazilian TV is ghastly, the worst you are ever likely to see, and therefore compulsive viewing even if you don’t understand a word of Portuguese. There are several national channels, of which the most dominant is TV Globo, the centrepiece of the Globo empire, Latin America’s largest media conglomerate. The empire was built up by Brazil’s answer to Rupert Murdoch, Roberto Marinho, who died in 2003. One of the most powerful men in Brazil, Marinho was very cosy with the military regime and prone to use his papers and TV channels as platforms for his ultra-conservative views. The other major national channels are Manchete, TV Bandeirantes, SBT and Record.
The channels are dominated by telenovelas, glossy soap operas that have massive audiences in the evenings. Football coverage is also worth paying attention to, a gabbling, incomprehensible stream of commentary, punctuated by remarkably elongated shouts of “Gooooool” whenever anyone scores – which is often, Brazilian defenses being what they are. However, there are a few genuine highlights, notably Jô Soares, the funniest and cleverest of Brazilian comedians, who hosts a very civilized late-night chat show on Globo every weekday.
Brazilian has the highest number of computers with internet access in South America and all things online are highly developed, with internet cafés on every corner, and much of what used to be tediously queued up for – banking, cinema-going, buying plane tickets – now done online as a matter of course.
Travelling with children is relatively easy in Brazil. They are made to feel welcome in hotels and restaurants in a way that’s not always so in Europe or North America. In fact, it is also more secure: even thieves and assaltantes seem to respect families with children and leave them alone.
Travelling around Brazil takes time, so try not to be too ambitious in terms of how much you aim to cover. Because of frequent scheduled stops and unscheduled delays it can take all day to fly from one part of the country to another. Long bus journeys are scheduled overnight and can be exhausting. Children pay full fare on buses if they take up a seat, ten percent on planes if under 2 years old, half-fare between 2 and 12, and full fare thereafter. Newer airports have a nursery (berçário) where you can change or nurse your baby and where an attendant will run your baby a bath, great on a hot day or if your plane’s delayed. If you plan on renting a car, bring your own child or baby seat as rental companies never supply them and they are very expensive in Brazil. Cars are fitted with three-point shoulder seatbelts in the front, but many only have lap seatbelts in the back.
In hotels, kids are generally free up to the age of 5, and rooms often include both a double and a single bed; a baby’s cot may be available, but don’t count on it. It’s rare that a room will sleep more than three, but larger hotels sometimes have rooms with an interlinking door. Hotels will sometimes offer discounts, especially if children share rooms and even beds with siblings or parents; the lower- to mid-range hotels are probably the most flexible in this regard. If you’re planning on staying more than a few days in a city, you may find it cheaper and more convenient to stay in an apartment-hotel, which will sleep several people and comes with basic cooking facilities. Baths are rare in Brazil, so get your kids used to showers before leaving home. Occasionally, a hotel will provide a plastic baby bath, but bring along a travel plug, as shower pans are often just about deep enough to create a bath.
Many of the mid- and upper-range hotels have TV lounges, TVs in rooms, swimming pools, gardens and even games rooms, which are often useful in entertaining kids. Most large towns also have cinemas, the best often being the new multiplexes found in shopping centres.
Food shouldn’t be a problem as, even if your kids aren’t adventurous eaters, familiar dishes are always available and there’s also the ubiquitous comida por kilo option. Portions tend to be huge, often sufficient for two large appetites, and it’s perfectly acceptable to request additional plates and cutlery. Most hotels and restaurants provide high chairs (cadeira alta) as well. Commercial baby food is sold in Brazilian supermarkets. Remember to avoid tap water and use only mineral water when preparing formula and washing out bottles. Mid-range hotels and upwards have a minibar (frigobar) in the rooms where you can store bottles and baby food, but where there isn’t one you will be able to store things in the hotel’s refrigerator. A small cooler box or insulated bag is a good idea and, while ice compartments of frigobars are useless, you can always place your freezer blocks in the hotel’s freezer (congelador).
In general, Brazilian infants don’t use disposable nappies/diapers (fraldas), due to the cost, around R$12 for twenty – very expensive for most Brazilians. As brands such as Pampers are sold in pharmacies and supermarkets, it’s worth only bringing a minimum with you until you can make it to a shop.
Health shouldn’t be a problem, but before planning your itinerary check which areas entail taking anti-malarial tablets (the state of Rondônia other than Porto Velho, rural Acre and Amapá and southern Pará is rife with malaria and should be avoided), and make enquiries as to whether the vaccines recommended or required in some parts of Brazil (in particular the Amazon) are likely to have any unpleasant side effects for babies or young children. For most of Brazil, the only likely problem will be the strength of the tropical sun and the viciousness of the mosquitoes: bring plenty of sunscreen (at least factor 20 for babies and factor 15 for young children) and an easy-to-apply non-toxic insect repellent.
The Rough Guides to Brazil and related travel guides
In-depth, easy-to-use travel guides filled with expert advice.

Travel advice for Brazil
Find even more inspiration here.

Ready to travel and discover Brazil?
Get support from our local experts for stress-free planning & worry-free travels.
- Where to stay
- Travel advice
Keeping safe while traveling in Brazil
Brazil is a safe destination for tourists.
Often, Brazil´s reputation is exaggerated in the media and by the public, especially when it comes to crime and the safety of foreigners and tourists. Parts of Brazil do have high crime rates, but in general, if you stick to good travel advice for Brazil , you should have no more problems with personal safety in Brazil, than you would have in other tourist destinations. On most occasions, tourists will not encounter any crime, even if they do, in most cases it is petty crime like pickpocketing.
Personal Safety in Brazil
Check the Area
Firstly, if you decide to go exploring you should be aware of what kind of area you are in/going to. Most serious crime is concentrated in the outskirts of the big cities, namely Sáo Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Recife and does not affect the level of travel safety in Brazil because tourists do not frequent these areas as part of their tours.
In the outskirts and “favelas”, poverty is rife so naturally there is more crime. It can sometimes be deceiving to rely on metrics such as city crime rates. Certain areas can inflate the figure of the entire city. We advise that you do not venture into these areas alone, or without a local person or guide.
You may come across some tourist organizations that advertise “favela tours”, where they will take you into one of these favelas to show you around. You should be weary of who these people are and try to check their credibility. If in doubt, check with Brazil Selection (Contact) or your tour operator. It can also be thoughtful to ask the guides whether they are local people or not. If you do decide to take one of these tours, remember, some of these places may be beautiful, interesting and full of life but they are also family homes and everyone should respect this. It is unsavory to enter any residential area with the intention of looking “ at” people. Instead be open and you will be welcomed!
In the favelas around Rio de Janeiro, (where tourists are most likely to want to explore them) security can be uncertain. There are favelas located in almost every area of the city, including close to the “Zona Sul” where most of the tourist activity is. You can check this map to see where they are. If you are exploring the city alone, it is advisable to be aware of where the favelas are located so you do not wander into one without realizing. If you do, more often than not, the locals will be happy to help you find your way again! It is just that getting lost in a favela can be intimidating for tourists because the narrow, mazelike streets can be complicated to navigate. It is common for tourists to accidentally wonder into favelas and get lost while using GPS navigation. Again, if you are in doubt about the route you are taking, check it out with your tour operator or hotel.
Criminals sometimes like to target both locals and tourists at airports. Because of heavy police and security presence, these are normally petty scam artists . Don´t leave your luggage unattended and use registered taxis to avoid risk of being scammed/overcharged.
It can be quite tempting to wonder onto a deserted part of the beach at night, but this is uncommon in Brazil and not even the locals do it. Unless you are certain that there is a low risk of crime (as is the case in some areas) it is best to avoid doing this. Instead, look for an area where there are plenty of other people, or open bars or clubs. When going to the beach, try to limit the valuables you bring with you and keep your possessions close by, they can be a favorite spot for pickpockets, especially in Rio de Janeiro.
Common areas for pickpockets
In terms of pickpocketing, you should be a little more careful in the following areas. In Rio de Janeiro pickpocketing is more common in areas such as Copacabana Beach, Ipanema Beach , Santa Theresa and Lapa . In São Paulo , the Avenida Paulista, Rua Augusta and Praça Republica are pickpocket hotspots. In the Northeastern cities such as Fortaleza , pickpockets may target any tourist area like Beira Mar , just be careful and follow the guidelines outlined on this page.
Be wary of the time
The time of day is important as regards your safety in Brazil. If you are planning activities or exploring an area, be sure to check what time you will be in which areas. In general, if you plan on going out at night, stick to the busier areas where there is more footfall. Avoid going to darker and quieter locations, if you are alone. Your tour guide will let you know the best places to enjoy at night! If in doubt, you can always check with the hotel. In general, anywhere with high tourist presence will also have high police presence at night and during the day. It is advisable to take a taxi to your location and avoid walking too much between different areas at nighttime, especially after having had something to drink. Be careful on public transport at night if you have any valuables, usually everything is fine but it´s much better to get a taxi instead; they are much faster and more reliable, especially in Brazil!
Swimming in Brazil
Many of Brazil´s beaches offer the chance for a fantastic swim in beautiful scenery and this is certainly something you cannot miss on your holiday. However, some beaches in Brazil have strong rip currents that can be quite hard to spot. It is advisable that you pay close attention to the signs in the area and advice from locals and the hotel you are staying at. If in doubt, swim only where there is a lifeguard or other swimmers. If you plan on taking watersports lessons, make sure the school you are with is certified by the proper organization, this would be IKO for kitesurfing for example. Sharks are not common, but have been known to appear especially off the coast of Recife, be wary of where you are swimming here and if in doubt seek local advice. Lastly, remember that the power of the Brazilian sun is multiplied in the salt water. If you plan to spend a long time swimming, consider using a zinc based, waterproof sunscreen to protect you from sunburn.
Driving in Brazil
U.K and U.S citizens can drive in Brazil for up to 180 days provided they carry their original driving license. An international driving permit is useful as well. Brazilian driving standards may be poor compared to what you are used to. Be extra vigilant on the roads and avoid stopping at the roadside at night, if you need to do so, look for a petrol station or a well – lit public area. In some areas, you may drive through red lights after 11pm. Be careful with people approaching you to ask for directions and try to use the middle lane where possible. In the cities there may be a lot of cyclists on the road, take extra care in looking out for them!
Practical Advice for Personal Safety in Brazil
Pickpocketing is common in tourist areas, especially during festivities like carnaval ; do not keep valuables in a pouch around your neck or in your back pocket. In the busier areas, there may be more “snatch and run” kind of crimes, but these are uncommon in tourist areas where police presence is always high.
You can greatly reduce the risk of falling victim to crime by following these guidelines to personal safety in Brazil.
- Make sure you lock your passport in the hotel safe as well as any other important documents and money.
- If you bring your driving license as a form of ID, keep it in a concealed pocket or in a money belt.
- Don´t bother wearing flashy or expensive jewellery when going to walk the streets.
- Keep just the right amount of cash you need for the day and avoid leaving your accommodation without any money.
- Make a copy of all your documents and send them to us before coming to Brazil!
- When not in use, it is better to keep cameras and mobile phones out of sight.
- Avoid unnecessary trips into dark, deserted or poverty – stricken areas alone.
- Travel home at night by taxi.
Brazilian Emergency Service Numbers
Emergencies – Military Police (Policia Militar) – 190
Ambulance (Ambulância) – 192
Fire Brigade (Corpo de Bombeiros) – 193
Overall, Brazil is absolutely a safe destination for tourists!
In summary, there are certainly some things to look out for as regards personal and travel safety in Brazil. However, Brazil is no more dangerous for tourists than other common holiday destinations. The punishment for causing trouble to a foreigner in Brazil is severe and almost not worth the time of any criminal. All you have to do is exercise common sense to avoid putting yourself in a risky situation. Remember, Brazilian people are some of the happiest, most welcoming and friendly people in the world! Enjoy your time here and don´t be hesitant to interact with the locals!
Other Pages of Essential Information on Brazil
Doing business in brazil, brazilian currency, vaccines for brazil, police and emergency services in brazil, language spoken in brazil, passports and visas, brazilian norms, brazilian standards, clothing and luggage.
Exploring The Weather Conditions While Traveling East On I-20
- Last updated May 28, 2024
- Difficulty Intemediate
- Category Travel

As you embark on a journey across the vast expanse of I-20, one cannot help but wonder about the ever-changing weather conditions that lie in wait. From the arid plains of West Texas to the humid swamps of Louisiana, this interstate takes travelers on a whirlwind adventure through a variety of climates and landscapes. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of weather along I-20, exploring the dramatic shifts in temperature, precipitation, and atmospheric conditions that make this route an unpredictable and thrilling experience for any road trip enthusiast. Buckle up and prepare to witness the bewildering beauty of nature at its most capricious while traveling east on I-20.
What You'll Learn
Introduction to traveling on i-20 east and weather conditions, weather patterns and climate along the i-20 east route, tips for preparing for and navigating different weather conditions, safety precautions and resources for staying informed about the weather.

If you are planning a trip on I-20 East, it is essential to understand the weather conditions you may encounter along the way. I-20 East stretches across several states, and the weather can vary significantly depending on your location and the time of year. To ensure a safe and enjoyable journey, it is crucial to be prepared for any potential weather hazards you might encounter. In this blog post, we will provide an overview of the different weather conditions you might experience while traveling on I-20 East and offer tips on how to stay safe on the road.
Spring and Summer Weather
During the spring and summer months, the weather along I-20 East can be quite unpredictable. Thunderstorms, heavy rainfall, and high temperatures are common during this time of year. It is essential to keep an eye on the weather forecast before hitting the road, as severe thunderstorms can bring strong winds, hail, and even tornadoes.
If you are traveling during the spring and summer, make sure to pack the necessary essentials such as rain gear, an emergency kit, and plenty of water. Additionally, it is advisable to have a weather monitoring app on your phone to receive updates on any severe weather alerts in your area.
Fall Weather
Fall is generally considered to be a more pleasant time of year to travel on I-20 East. The temperatures begin to cool down, and the risk of severe storms decreases. However, it is still important to be prepared for sudden weather changes, as temperature fluctuations can occur.
When traveling during the fall, it is a good idea to dress in layers and have a lightweight jacket or sweater with you. Additionally, be aware of foggy conditions that may occur in the mornings and evenings, particularly in areas surrounded by lakes or bodies of water.
Winter Weather
If you are traveling on I-20 East during the winter months, you need to be prepared for potentially hazardous weather conditions. Snow and ice can be significant problems in certain areas, especially in states like Georgia and Alabama, where winter storms are more common.
Before embarking on your journey during the winter months, check the weather forecast and road conditions along your route. If there is a storm warning or icy road conditions, it would be best to delay your trip or choose an alternative route if possible.
It is essential to have winter supplies in your car, including warm clothing, blankets, and an ice scraper. Additionally, make sure to check your tire pressure and ensure that your vehicle is in good condition before traveling on I-20 East during the winter months.
Traveling on I-20 East can be an exciting adventure, but it is crucial to be aware of the weather conditions you might encounter along the way. Whether you are facing thunderstorms in the spring, fog in the fall, or winter storms in the colder months, being prepared is the key to a safe and enjoyable trip.
Always check the weather forecast before you set off, and be ready to adjust your plans if necessary. Pack the essential items you may need, such as rain gear, warm clothing, and an emergency kit. By taking these precautions, you can ensure a smooth journey on I-20 East, regardless of the weather.
The Transformation of Travel: How VR is Revolutionizing the Way We Explore
You may want to see also
The weather patterns and climate along the I-20 East route can vary significantly depending on the time of year and the specific location. It is important to be aware of these variations when planning your travel and to be prepared for any potential weather conditions you may encounter.
Starting in West Texas, the I-20 East route passes through a region known for its dry and arid climate. Summers in this area can be scorching hot, with temperatures often exceeding 100 degrees Fahrenheit. It is important to stay hydrated and to use appropriate sun protection when traveling through this region during the summer months. In the winter, temperatures can drop below freezing, and there may be occasional snowfall. Make sure to check the weather forecast and road conditions before embarking on your journey, and take appropriate precautions if winter weather is expected.
As you continue further east into central Texas, the climate begins to transition to a more humid subtropical climate. Summers in this region can still be hot, but the humidity can make the temperatures feel even more oppressive. Thunderstorms and heavy rainfall are common during the summer months, so be prepared for potential delays or road closures due to inclement weather. Winters in central Texas are generally mild, with temperatures rarely dropping below freezing. However, there can still be occasional cold fronts that bring colder temperatures and the possibility of freezing rain or sleet.
Moving into Louisiana, the climate remains humid and subtropical. Summers in this state can be hot and muggy, with frequent thunderstorms and the potential for tropical storms or hurricanes. It is important to stay updated on any potential severe weather alerts and to have a plan in place in case evacuation becomes necessary. Winters in Louisiana are generally mild, with temperatures rarely dropping below freezing. However, there can still be occasional cold snaps, so it is wise to have warm clothing available.
As you travel further east into Mississippi, the climate remains humid and subtropical. Summers in Mississippi are hot and humid, with frequent thunderstorms. Hurricanes are also a potential threat in this region, so it is important to be aware of any tropical weather systems that may be active during your travel dates. Winters in Mississippi are also generally mild, with temperatures rarely dropping below freezing.
Finally, as you approach the easternmost portion of the I-20 East route and enter Alabama, you will continue to experience a humid subtropical climate. Summers in this state are hot and humid, with frequent thunderstorms. Winters are generally mild, but there can still be occasional cold snaps with freezing temperatures.
In conclusion, the weather patterns and climate along the I-20 East route can vary significantly depending on the specific location and time of year. It is important to be prepared for a wide range of weather conditions, from extreme heat to severe thunderstorms and the potential for tropical weather systems. Stay updated on the weather forecast and road conditions, and be sure to pack appropriate clothing and supplies for any potential weather scenarios.
Navigating the Process: A Step-By-Step Guide to Applying for a Travel Visa to Vietnam
When traveling on Interstate 20 East, depending on the time of year and location, you may encounter a variety of weather conditions. It is essential to be prepared and know how to navigate different weather conditions to ensure a safe and enjoyable trip. Here are some tips to help you prepare for and handle changing weather while traveling on I-20 East.
Check the Weather Forecast:
Before your trip, check the weather forecast along your route and at your destination. This will give you an idea of the conditions you may encounter and help you plan accordingly. Pay attention to any severe weather warnings or advisories issued by the National Weather Service.
Pack Essential Items:
Regardless of the weather conditions, there are a few items you should always have in your vehicle. These include:
- An emergency kit with a flashlight, first aid supplies, extra batteries, and a basic tool kit.
- Warm clothing and blankets, especially if traveling during the winter months.
- A fully charged cell phone and a car charger.
- Extra food and water in case of unexpected delays.
- An ice scraper and snow brush if traveling in snowy conditions.
Understand Road Conditions:
Different weather conditions can affect the road surface differently, making it important to understand road conditions and adjust your driving accordingly. Here are a few examples:
- Rain: Reduce your speed and increase the following distance between you and the vehicle ahead. Avoid sudden movements and be cautious of hydroplaning.
- Snow and Ice: Drive slowly, use your brakes and accelerator gently, and allow extra time for braking. Be cautious of black ice, which can be difficult to see.
- Fog: Reduce your speed and use low beam headlights or fog lights to improve visibility. Use caution when passing other vehicles and keep a safe distance.
Monitor Traffic Updates:
Weather conditions can cause traffic delays and accidents. Stay updated on traffic conditions by tuning into local radio stations or using a GPS with real-time traffic updates. If you encounter heavy traffic or an accident, remain patient, and follow any detour signs or instructions from law enforcement.
Adjust Your Travel Plans:
In severe weather conditions, such as blizzards, hurricanes, or thunderstorms, it may be advisable to adjust your travel plans. Consider delaying your trip or finding alternative routes if possible. Safety should always be a top priority when traveling, and it's better to arrive a little late than risk getting stuck or involved in a dangerous situation.
Stay Informed During Your Trip:
While on the road, continue monitoring weather forecasts and road conditions. This will help you anticipate any changes in weather and adjust your driving accordingly. Additionally, use smartphone apps or websites to receive real-time updates on weather conditions or any emergencies along your route.
Remember, weather conditions can change quickly, especially when traveling long distances. Always be prepared and stay alert to ensure a safe and enjoyable journey on Interstate 20 East.
Does Traveling from the US to Brazil Require a Visa?
When traveling, it is important to stay informed about the current weather conditions to ensure your safety. This is particularly crucial when traveling on a major interstate like I-20 East, as the weather can quickly change and impact road conditions. To help you stay safe, here are some safety precautions and resources to consider:
- Check the Weather Forecast: Before starting your journey on I-20 East, it is essential to know the weather conditions you may encounter along the way. Check the weather forecast for your departure point, destination, and the areas you will be passing through. This will give you an idea of what to expect and help you plan accordingly.
- Pack Emergency Supplies: It is always a wise decision to pack some emergency supplies when traveling. These may include a first aid kit, blankets, non-perishable food, and water. Additionally, keep a flashlight, extra batteries, and a portable phone charger in your vehicle. These supplies will be useful in case you encounter unexpected weather conditions or delays.
- Monitor Road Conditions: Keep an eye on the road conditions along your route. Check for any closures, accidents, or construction zones that may affect your travel on I-20 East. Consider using traffic and navigation apps that provide real-time updates on road conditions, such as Google Maps or Waze.
- Stay Connected: It is crucial to stay connected and informed about any weather updates or alerts. Make sure your mobile phone is fully charged and enable emergency weather alerts. Many weather apps allow you to set notifications for severe weather conditions, such as thunderstorms or high winds. This will help you stay aware of any changes in the weather as you travel.
- Listen to Local Radio Stations: Local radio stations often provide updates on traffic conditions and weather advisories. Tune in to a reliable station along your route to stay informed about any weather-related issues. The radio can be a valuable resource, especially if you encounter areas with limited cellular coverage.
- Take Breaks if Necessary: If you encounter adverse weather conditions while traveling on I-20 East, it is essential to prioritize your safety. If the weather becomes challenging to handle, consider taking breaks at rest stops, gas stations, or other safe locations until conditions improve. Use this time to reassess your travel plans and determine if it is safe to continue.
- Follow Recommended Safety Measures: When traveling on I-20 East, it is crucial to follow recommended safety measures during adverse weather conditions. Reduce your speed, maintain a safe following distance, and use your headlights when visibility is reduced. Be cautious of changing road conditions, such as black ice or flooded areas, which can make driving hazardous.
Remember, your safety is paramount when traveling on I-20 East or any other interstate. By staying informed about the weather, packing emergency supplies, and following safety precautions, you can have a safer and more enjoyable journey. Pay attention to weather updates, use reliable resources, and make smart decisions to ensure a smooth and worry-free trip.
What Qualifies as Eligible Travel Purchases for the Costco Visa?
Frequently asked questions.

- Duke Trotter Author Editor Reviewer Traveller

- Karli Trujillo Author Editor Reviewer
It is awesome. Thank you for your feedback!
We are sorry. Plesae let us know what went wrong?
We will update our content. Thank you for your feedback!
Leave a comment
Travel photos, related posts.

The Ultimate Guide to Keeping HGH Cool While Traveling
- May 11, 2024

Exploring America on Wheels: A Comprehensive Guide to Traveling with an RV
- May 22, 2024

Unraveling the Dynamics: Does Heizou Like the Traveler?
- May 26, 2024

Is Travel Brand Luggage Worth the Money?
- May 13, 2024

Exploring the Beautiful Bahamas: Can You Travel with a US Visa?
- Mar 28, 2024

Who Covers the Cost of Obama's Travel When Campaigning for Hillary?
- May 15, 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Brazil Travel Advisory. Reissued with updates to Country Summary. Exercise increased caution in Brazil due to crime. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory. Do not travel to: Any areas within 150 km/100 miles of Brazil's land borders with Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and ...
OVERALL RISK: MEDIUM. Brazil is somewhat safe but you should take precaution on the streets of major cities, and after dark. Be wary of pickpockets and bag snatching and keep your valuables safely by your side. Never carry all your money in one place or leave your valuables in plain sight in a car or at a beach when swimming.
FCDO travel advice for Brazil. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences. ... There is a limited railway infrastructure in Brazil, and there have been ...
Road safety. Brazil has one of the highest road accident rates in the world. ... Avoid non-essential travel. Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. ...
If your travel plans in Brazil include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip. Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe. Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
Safety. The wet season is from November to July, however heavy rainfall can occur all year, depending on the region. Landslides and flooding can occur, and severe storms often delay flights. Be prepared to change your travel plans. Large scale protests can occur at any time in Brazil. Monitor the media.
FCDO travel advice for Brazil. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
Safety. Brazil has increasingly invested in public safety. The country has been strengthening security in tourist destinations so tourists who intend to visit the country can feel safe when traveling to Brazil. ... Citizens of other countries wishing to obtain a visa to travel to Brazil should contact Brazilian consular offices abroad for more ...
FCDO travel advice for Brazil. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
The basics. Brazil has been one of the hardest hit countries by the pandemic. The country holds the second highest Covid-19 death toll in the world, second only to the United States. Ad Feedback ...
Be mindful of this and other common travel scam. Always stay vigilant when other people approach you and stay on your guard in crowds. 11. Don't walk around at night alone - If you have to, avoid city beaches, parks, and empty streets. Generally, even local Brazilians don't walk around much at night.
Brazil Healthy Travel Packing List. Pack items for your health and safety. You may not be able to purchase and pack all of these items, and some may not be relevant to you and your travel plans. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you. ... Personal safety equipment Examples: child safety seats, bicycle helmets; Earplugs ...
Rio is also home to a travelers' bucket-list mainstay: the massive, art deco-style Christ the Redeemer statue atop Mount Corcovado. But is Rio de Janeiro safe to visit? Unfortunately, the Rio ...
Yet, I'm not blind to Brazil's safety concerns. There is huge socio-economic disparity and it trickles down into every facet of local life, from education and employment to housing and healthcare. Brazil ranked 7th on Forbes' Billionaires List for 2020, yet minimum wage in the country remains less than US $0.90 per hour.
Brazil's metro and subway. The metro is one of the easiest ways to get around major cities like Rio and São Paulo. Fares are around R$3.50 - R$3.80. If you plan to use the metro often, there are rechargeable travel cards you can purchase. The metros are generally cleaner and safer than traveling by local bus.
Or more specifically, did I feel safe as a solo female traveler in Brazil. Both are fair questions, and my answer is…it's complicated. In short, yes, Brazil is safe enough to travel to - but read my more in-depth response here. My personal experience is that I had no negative incidents involving safety or theft while in Brazil and I loved ...
Safety & Security Crime. Travel in Brazil is generally safe, although crime remains a problem in urban areas and has spread to rural areas. The incidence of crime against tourists is greater in areas surrounding beaches, hotels, nightclubs, and other tourist destinations (see Sec. 4, Ch. 11, Safety & Security Overseas). Drug-related violence ...
FCDO travel advice for Brazil. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
4. Take a Travel Water Bottle. It comes as no surprise to many that Brazil is a seriously hot country. Therefore, travellers will need to make the effort to stay hydrated. Although tap water in Brazil is officially safe to drink, this is disputed by locals and travellers alike - especially in locations near the coast!
For most of Brazil, the only likely problem will be the strength of the tropical sun and the viciousness of the mosquitoes: bring plenty of sunscreen (at least factor 20 for babies and factor 15 for young children) and an easy-to-apply non-toxic insect repellent. The Rough Guides to Brazil and related travel guides.
Often, Brazil´s reputation is exaggerated in the media and by the public, especially when it comes to crime and the safety of foreigners and tourists. Parts of Brazil do have high crime rates, but in general, if you stick to good travel advice for Brazil, you should have no more problems with personal safety in Brazil, than you would have in ...
Staying Safe in Rio: 8 Essential Tips for Travelers. Despite growing concern about safety in Rio, travelers continue to flock to this incredible seaside city. Here's everything you need to know to stay safe. Is Brazil safe for travelers? Here's our help, advice and support for planning a successful trip and traveling safely in Brazil.
Use this time to reassess your travel plans and determine if it is safe to continue. Follow Recommended Safety Measures: When traveling on I-20 East, it is crucial to follow recommended safety measures during adverse weather conditions. Reduce your speed, maintain a safe following distance, and use your headlights when visibility is reduced.
Women's safety in Brazil's forests. We were conducting fieldwork in Tijuca National Park in Brazil's Atlantic Forest when we saw a police car pull up. Within minutes, two police officers were crouching down, rifles in hand, entering the bush and moving in our direction. We shouted that we were biologists, and—to our relief—they ...