- GTA 5 Cheats
- What is Discord?
- Find a Lost Phone
- Upcoming Movies
- Nintendo Switch 2
- Best YouTube TV Alternatives
- How to Recall an Email in Outlook

Tesla Autopilot vs. full self-driving: What’s the difference?
It’s no longer the only company with self-driving cars on the road, but Tesla was one of the first brands to make this innovative functionality available to the public. Thanks to an array of cameras, sensors, and AI technology, most Telsa vehicles are capable of driving themselves to some degree. However, this doesn’t mean drivers can take a nap behind the wheel. In fact, none can be used without driver supervision — and there are some serious limitations to the tech.
Tesla Autopilot
Tesla enhanced autopilot, tesla full self-driving (fsd), tesla autopilot controversies.
Tesla currently offers features known as Tesla Autopilot and Full Self-Driving. But what’s the difference between the two? And is one more reliable than the other? Here’s everything you need to know about Tesla’s Autopilot and Full Self-Driving technology.
Tesla Autopilot was the company’s first autonomous mode, and was introduced in 2014. It’s still the least advanced of the options, but it’s also included for free with all new Tesla cars — so it’s kind of like an added bonus.
- Is your check engine light on? Here are 10 possible reasons why
- Tesla Destination Chargers vs. Superchargers: What’s the difference?
- Tesla pulls latest Full Self-Driving beta less than a day after release
Autopilot is designed to be used with full driver supervision, and is essentially an advanced version of cruise control. It has lane-centering and adaptive cruise control, meaning the car can both stay in the center of a lane and can slow down and speed up depending on what’s in front of it.
These are features that aren’t necessarily exclusive to Tesla. Together, they’re basically an advanced cruise control, which is on offer by other cars.
Tesla Enhanced Autopilot adds some features that other cars don’t have. It’s also not free — it costs $6,000.
Enhanced Autopilot allows the car to park on its own, and also has features like auto lane change, meaning the car can change lanes as it sees fit. This feature also ties into the “Navigate on Autopilot” feature, which allows the car to drive from a highway’s on-ramp to its off-ramp, theoretically without the driver’s input — though the driver should still stay aware.
It also includes Summon and Smart Summon, which allow the car to drive to you in a parking lot — no remote control necessary.
Some of these are features that you can’t really find anywhere else — though features like lane changing are set to become more common.
Last but not least is Tesla Full Self-Driving (FSD). It’s the most advanced option, but Tesla has labeled it as a “beta,” suggesting that it’s more of a way to test the feature with real-world drivers. Tesla debuted FSD in 2020, and has been periodically improving it ever since.
It’s the most expensive option on Tesla’s menu — it costs a hefty $15,000 upfront, or $200 per month if you prefer to pay for it as a subscription. For that money, it adds a major feature: the ability to start and stop at traffic lights and stop signs.
Tesla sees FSD as the eventual car-to-door feature, unlocking the ability to fully drive an individual from point A to point B. But it’s not quite there yet. You should still remain alert and ready to take control while using Full Self-Driving — the name is pretty misleading, as the car still can’t actually fully drive itself, and you shouldn’t expect it to.
So which mode lets you nap behind the wheel? Sorry, none of them. But that hasn’t stopped sleepy drivers from trying .
The self-driving capabilities of Tesla have been the subject of much scrutiny. For one, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) began investigating the use of Autopilot in 2021 due to several accidents in which the feature was involved. The results of the investigation eventually led to a recall of over 360,000 Tesla vehicles using the Full Self-Driving beta. According to the official report, the NHTSA found that the system could cause vehicles to “act unsafe” when approaching intersections and some failed to stop appropriately.
Aside from the recall, it’s important to note that Tesla itself does not claim that any of its self-driving features can be used without a “fully attentive driver.” According to its owner manual , the company says drivers should “never depend on Autosteer to determine an appropriate driving path” and that Autosteer is a “hands-on feature.” Whether or not drivers follow those guidelines is another story — but it’s clear that no Tesla is ready to drive you from point A to point B while you take a nap.
Editors' Recommendations
- How to add Bluetooth to an older car
- Is Tesla Full Self-Driving worth it?
- Tesla hopes full self-driving beta will be out globally by the end of 2022
- Tesla issues stark warning to drivers using its Full Self-Driving mode
- Elon Musk suggests Autopilot was off in fatal Texas Tesla crash

Don't let the name Autopilot fool you: None of the cars in Tesla's current range are capable of driving themselves. Instead, Autopilot is a partially automated system that is regularly improved via over-the-air software updates. It relies on eight surround-view cameras that give the car 360-degree visibility for up to 820 feet, 12 ultrasonic sensors, and a forward-facing radar. Tesla has regularly stressed that, unlike its rivals, it doesn't believe in lidar technology.
The data gathered by Autopilot's hardware allows the car to steer, accelerate, and brake automatically within its lane, commonly called adaptive cruise control, though the company warns the system requires active driver supervision. In other words, even if your Model S can steer itself around a bend, you shouldn't be watching a movie while you cruise down I-80 at 75 mph. There are many circumstances Autopilot can't handle on its own, and the driver could be asked to take over without notice.
Autonomous car company Waymo says it will stop using the term “self-driving” in a move that many will see as a swipe at Tesla.
Alphabet-owned Waymo said that starting this year it will refer to its driving technology as “fully autonomous.”
A Tesla enthusiast has posted a video showing a Model 3 Performance vehicle traveling from San Francisco to Los Angeles, California in Full Self-Driving (FSD) beta mode, with almost no human intervention necessary during the entire trip.
The video (above), spotted by Teslarati, has been sped up to compress the 380-mile journey int0 15 minutes of footage, though it’s still easy to see the vehicle’s driving decisions play out on its touchscreen display.
How to use Tesla Autopilot: let your car take the strain
Understanding how Tesla's driver assistance system works

Autopilot is one of the best known driver assistance systems, and has been available on Tesla cars since the end of 2015. The hardware and software used to run Autopilot has been upgraded over the years, and the system is now capable of performing a range of semi-autonomous functions.
These functions include traffic-aware cruise control, automated steering, an automatic parking system, driverless lane-changes, and even a function called Smart Summon, where a Tesla can navigate its way across a car park to wherever you are standing.
But, despite Autopilot being able to handle the steering, accelerator and brake in many situations, the system isn't foolproof and the driver remains fully responsible for their car at all times.
- EV charging connectors : what they are and how they compare
- How to charge a Tesla
- How to find a Tesla Supercharger
What is on offer with Autopilot?
There are currently two tiers of Autopilot on new Tesla electric carss. As standard, every model comes with the Autopilot functions of Traffic-Aware Cruise Control and Autosteer.
The former works just like the radar cruise control of other cars, keeping a safe distance from the vehicle ahead. The latter activates the steering to stay in lane when road markings are visible and cruise control is activated.
Next, and for a fee of $10,000 / £6,800 / AU$10,100, there is Full Self-Driving Capability, known as FSD.
This includes extra Autopilot features and, Tesla hopes, will mean fully autonomous driving. For now, FSD includes a beta version of Navigate on Autopilot, Auto Lane Change, Autopark, Summon, Smart Summon and a beta version of Traffic and Stop Sign Control.
Get daily insight, inspiration and deals in your inbox
Get the hottest deals available in your inbox plus news, reviews, opinion, analysis and more from the TechRadar team.
A further feature called Autosteer on City Streets is coming soon (as of July 2021).
A recent change to how Autopilot is sold in the UK saw the introduction of Enhanced Autopilot, which is a £3,400 upgrade to the standard car and includes Navigate on Autopilot, Auto Lane Change, Autopark, Summon and Smart Summon.
On top of this, FSD costs £6,800 and adds Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control, plus Autosteer on city streets once Tesla makes it available.
How to enable Tesla Autopilot
Enabling Autopilot depends on what type of Tesla you have. For the Model S and Model X, cruise control is switched on by pulling down once on the cruise control stalk. In the Model 3 and Model Y, it is enabled by pulling down once on the gear selector stalk.
To enable Autosteer, pull the aforementioned stalks twice instead of once. To help you know when Autosteer is available, a grey steering wheel icon appears next to the speedometer.
This icon turns blue when Autosteer is engaged with two pulls of the gear selector or cruise control stalk.
Several of the more advanced Autopilot functions first need enabling in the settings menu before they are activated with two pulls of the stalk.
For example, Navigate on Autopilot is enabled by going to Controls > Autopilot > Autosteer.
Camera calibration is then required and the latest version of Navigation maps must be downloaded via Wi-Fi. Once you have done all that, there will be an option to navigate using Autopilot the next time you enter a destination into the navigation system.

How to enable Full Self-Driving Tesla Autopilot features
Navigate on Autopilot is switched on by pulling down twice on the gear selector/cruise control stalk, providing it has previously been enabled in the settings menu.
Similarly, Auto Lane Change is enabled by going to the Autopilot settings menu. After that, once in Autosteer mode (two downward pulls on the stalk), engaging the indicator will prompt the car to change lanes.
Autopark automatically scans for potential parking spaces when you are driving slowly. Parallel parking locations are indicated when driving below 15mph and perpendicular spaces are indicated below 10mph.
A grey P icon appears on the left or right side of the instrument panel to show a suitable space has been found. To park, press the brake and shift to reverse, then tap the Start Autopark button that appears on the touchscreen and release the brake and steering wheel.
Once complete, the system will shift into park. You can stop the maneuver at any time by taking control of the steering wheel or pressing the brake.
Summon can be used to get your Tesla out of a tight parking spot while standing outside. To do this, open the Tesla smartphone app and tap on Summon, then press the forward or reverse buttons.
You can watch Summon in action in the video below
Model S and Model X owners can instead use the key fob, by holding the center of the fob for three seconds until the car's hazard lights come on. Then press the trunk or frunk (boot or front boot) buttons to move the car backwards or forwards.
Smart Summon lets your car drive further, potentially all the way across a parking lot, while navigating around objects. This can only be used on private land and driveways.
To use the feature, open the Tesla app, tap on Summon then select the Smart Summon icon. Now press and hold the Come To Me button, or tap on the target icon and set a destination for your car to drive itself to and press the Go To Target button.
Releasing either button immediately stops the car. You need to be within 200 feet of the vehicle to use Smart Summon.
Lastly, the beta of Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control is enabled by navigating (while parked) to Controls > Autopilot > Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control (Beta), then engaging Autopilot with two pulls of the gear or cruise control stalk.
The car will then slow when approaching every stop sign and traffic light, even if the light is green. If it is safe to proceed, tap the accelerator to tell the car to carry on instead of stopping.
- Tesla to open Supercharger network to other electric cars later this year

Alistair Charlton is a freelance technology and automotive journalist based in London. His career began with a stint of work experience at TechRadar back in 2010, before gaining a journalism degree and working in the industry ever since. A lifelong car and tech enthusiast, Alistair writes for a wide range of publications across the consumer technology and automotive sectors. As well as reviewing dash cams for TechRadar, he also has bylines at Wired, T3, Forbes, Stuff, The Independent, SlashGear and Grand Designs Magazine, among others.
This Game Boy-styled MagSafe stand just tickled my retro-gaming synapse – now all I need is a matching controller for Nintendo emulators
AI Explorer could revolutionize Windows 11, but can your PC run it? Here's how to check
Netflix's Wednesday season 2 cast clicks into gear with Westworld star addition as Apple's Neuromancer series finds its lead
Most Popular
- 2 New Deadpool and Wolverine trailer is packed with Marvel Easter eggs – here are 6 of the best
- 3 Sony’s wearable air conditioner is the first step towards a real Dune stillsuit
- 4 Samsung's S90C OLED is our best-rated TV, and it just crashed to a new record-low price
- 5 This Android phone for audiophiles offers a hi-res DAC, balanced output and 3.5mm jack – plus a cool cyberpunk look that puts Google and OnePlus to shame
- 2 Sony dropped OLED for its flagship 2024 TV – here's why
- 3 Today's Wordle answer is the hardest this year, with an average score of 5.4, and 'Wordle 1037 X' is trending on Twitter – here's why it's so tough and what to do in future
- 4 Missed out on the Fujifilm X100VI? New leak suggests the next best thing could land soon
- 5 New Deadpool and Wolverine trailer is packed with Marvel Easter eggs – here are 6 of the best
Pocket-lint
What is tesla autopilot and how does it work.
Tesla vehicles have some self-driving or autonomous capabilities through a feature bundle called Autopilot.
Key Takeaways
- Tesla's Autopilot is an optional driver assistance system that includes features like Traffic-Aware Cruise Control and Autosteer.
- Enhanced Autopilot, available as an add-on purchase, includes additional features like Navigate on Autopilot and Autopark.
- Full Self-Driving, currently in beta, is a higher-tier add-on that includes everything in Autopilot and Enhanced Autopilot, along with capabilities like Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control.
Tesla vehicles have some self-driving or autonomous capabilities through a bundle of features, called Autopilot, which should only be used with a fully attentive driver. If you want to get Autopilot for your Tesla vehicle or want to learn more, including how it works, bookmark this guide.
What is Tesla Autopilot?
Tesla's Autopilot is an optional driver assistance system that's available in all Tesla vehicles . There are three different tiers: Autopilot, Enhanced Autopilot and Full Self-Driving. The core Autopilot features include Traffic-Aware Cruise Control and Autosteer.
Enhanced Autopilot is available as an add-on purchase, currently priced at $6,000, and it includes Navigate on Autopilot, Auto Lane Change, Autopark, Summon and Smart Summon. Full Self-Driving, currently in beta , is a $15,000 add-on purchase that includes everything in Autopilot and Enhanced Autopilot, along with Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control, and Autosteer on City Streets.
All of those features mean your Tesla can steer, turn, accelerate, and brake - all autonomously and automatically, either within a given lane, or from a starting point to your final destination, depending on which level of Autopilot you have access to and are currently using.
The Autopilot name is a little misleading, as it requires driver supervision and does not make your vehicle "fully" autonomous . Tesla monitors whether or not your paying attention with a camera located above the rearview mirror, as well as monitors for pressure on the steering wheel to ensure your hands are on the wheel at all times.
Tesla regularly releases over-the-air software updates to improve and evolve the Autopilot and Full Self-Driving over time.
Which vehicles have Autopilot?
Any Tesla built in 2016 or later has all the necessary hardware required by Autopilot. From 2016 until late 2021, that means the car includes 8 cameras, 12 ultrasonic sensors, vision processing tools, an onboard computer, and more.
Starting in 2021, Tesla began removing ultrasonic sensors from the Model 3 and Model Y , and in 2022 the transition away from the sensors was completed by removing them from the Model X and Model S . Instead of using the radar-like sensors, Tesla is relying completely on the cars' cameras to measure distance. Even without the ultrasonic sensors, you're still able to use Tesla's Autopilot features, up to an including Full Self-Driving.
How much is Autopilot?
Autopilot is included with the purchase of any new Tesla, with optional add-ons for Enhanced Autopilot or Full Self-Driving. Their prices are as follows:
Price : Included in the purchase price of new Teslas. If you're buying a used Tesla that lacks Autopilot, the price will vary.
Enhanced Autopilot
Price : $6,000 add-on at the time of vehicle purchase or after purchase.
Full Self-Driving capability
Price : $15,000 add-on at the time of vehicle purchase. Alternatively, you can sign up for a month-to-month subscription to enable Full Self-Driving for $99 a month if you have Enhanced Autopilot, or $199 if you have access to basic Autopilot. The subscription can be started and stopped as often as you'd like.
What features are included with Autopilot, Enhanced Autopilot and FSD?
Here are the main features for each of the two add-on Autopilot packages you can purchase for your Tesla vehicle. Keep in mind, these features are in addition to the standard Autopilot features of:
Traffic-Aware Cruise Control : Matches the speed of your Tesla vehicle with traffic.
Autosteer : Assists in steering and keeping your car within a lane. Used in combination with traffic-aware cruise control.
Navigate on Autopilot : Actively guides your Tesla vehicle from a highway's on-ramp to off-ramp, including suggesting and making lane changes, navigating interchanges, automatically engaging the turn signal, and taking the exit.
Auto Lane Change : Assists in moving to an adjacent lane on the highway when Autosteer is engaged.
Autopark : Helps automatically parallel or perpendicular park your Tesla vehicle.
Summon : Moves your Tesla vehicle in and out of a tight space using the app.
Smart Summon : You can summon your Tesla to pick you up at a store's entryway. The car will navigate the parking lot on its own.
Traffic and Stop Sign Control (Beta) : Identifies stop signs and traffic lights and slows your Tesla vehicle to a stop on approach, with your active supervision.
Autosteer on City Streets : This feature is listed as coming soon on Tesla's website, but anyone who paid for Full Self-Driving can use a beta version of the feature. Once enabled, your Tesla will autonomously navigate all streets, stop signs and stop lights, including making turns, and lane changes to take you from point A to point B.
How do you buy Tesla Autopilot?
You can purchase Autopilot at any time through your Tesla account, either on the website or via the mobile app. Once the purchase is complete, you may need to install a software on your car to enable the unlocked features. Otherwise, the features will be available shortly after purchase.
How do you operate Autopilot?
We recommend you read your vehicle's owner manual for detailed information. But we've outlined how to turn on some of Autopilot's core features below.
Enable Autopilot
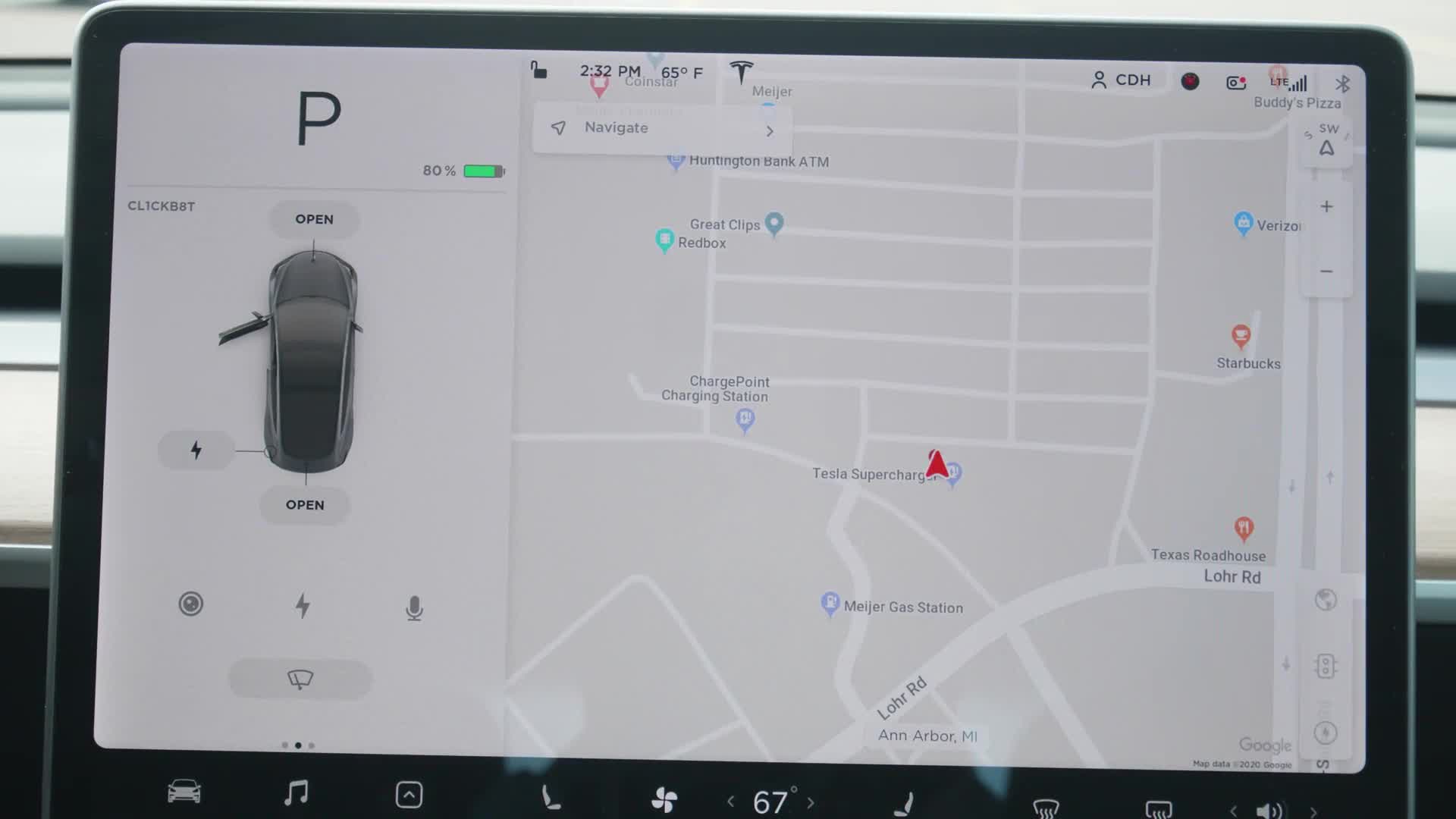
The only Autopilot feature that's enabled for each driver profile on a Tesla is Traffic-Aware Cruise Control. You'll need to manually enable each feature and agree to Tesla's terms before you can use them. You can find the Autopilot settings by tapping on the vehicle icon in your Tesla's screens taskbar, followed by selecting Autopilot from the menu.
When you enable features like Autosteer and Full Self-Driving you will need to agree to Tesla's sternly worded warning that reminds you're expected to keep your hands on the steering wheel at all times and to be prepared to take over at any time.
Traffic-Aware Cruise Control
To use Traffic-Aware Cruise Control in a Model 3 or Model Y, pull down once on the drive stalk located on the right side of the steering wheel. For the Model S and Model X, pull down once on the cruise control stalk on the left of the steering column.
To use Autosteer in Model S and Model X, pull toward you twice on the cruise control stalk on the steering column. In Model 3 and Model Y, pull down twice on the gear selector stalk on the right of the steering column.
Note: A steering wheel icon will appear on your display when Autosteer is available. A blue steering wheel icon will appear when it is engaged.
Navigate on Autopilot
To start using this feature, you must first enable Autosteer ( Controls > Autopilot > Autosteer ) and then enable the Navigate on Autopilot feature. You'll need to enter a destination in order for Navigate on Autopilot to be available. You can then either press the Navigate on Autopilot button in your Navigation Turn List, or set Navigate on Autopilot to automatically turn on when it's available.
On Model 3 and Model Y, Navigate on Autopilot can be used on most highways by moving the gear lever twice downward. On Model S and Model X, Navigate on Autopilot can be engaged on most highways by pulling the cruise stalk toward you twice.
Auto Lane Change
To initiate an automated lane change, you must enable Auto Lane Changes through the Autopilot menu. Then, when the car is driving in Autosteer mode, you can press the turn signal up or down to turn on your blinker, and the car will make a lane change once it's clear.
When your Tesla is moving slow enough and it detects a parking spot, you'll see a grey P icon will appear on your instrument panel.
To use Autopark, press on the brake, shift the gear selector into Reverse, and keep your foot on the brake. Start Autopark will appear in blue text on your touchscreen. Press it to start, which will then prompt you to release the brake and loosen your grip on the steering wheel.
Autopark will begin to control the vehicle. Once Autopark is complete, the car will let you know it is done and shift into Park.
You can override Autopark at any time by taking control of the steering wheel.
To use Summon, open the Tesla app. Press Summon and then press the forward or reverse buttons. Model S and Model X owners can use Summon with their key fob by holding the center of the key fob for 3 seconds until the car's hazard lights come on and then pressing either the frunk or trunk button on the fob to Summon forward and backward.
Smart Summon
Smart Summon is designed to allow your car to drive to you or a location of your choosing. It is only intended for use in private parking lots and driveways.
To use Smart Summon, open your Tesla app, then tap Summon, and select the Smart Summon icon. To actually activate the feature, press and hold the Go to Target button. Or, tap the target icon, then set the target destination of your choice by adjusting the map, and press and hold the Go to Target button.
Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control (Beta)
Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control identifies stop signs and traffic lights and slows your car to a stop. To enable it, shift your car into Park and tap Controls > Autopilot > Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control (Beta) . Then, whenever you engage Traffic-Aware Cruise Control or Autosteer, the car will stop for lights and signs.
Can you try Autopilot before purchasing?
Yes. You can experience Autopilot on a test drive at one of Tesla's store locations.
Want to know more?
We recommend checking out these Tesla webpages for more information:
- Tesla Autopilot
- Tesla Full Self-Driving
- What's My Car Worth?
- Buyer's Guide
Tesla Model 3: The Complete Guide
Driving a Tesla for the first time can be daunting, so we've explained everything you need to know about operating a Model 3.

Getting Started
Our Tesla Model 3 has three keys: a Tesla key card; a key fob, which is a $150 accessory; and your phone, which you can set up through the Tesla mobile app to work as a key. To unlock the car with the key card, swipe the card on the B-pillar, and the door will unlock or lock. With the key fob or phone as a key, simply approach the car, push in the right side of the door handle, and pull the door open. The car will lock automatically once the phone or key fob is about five feet away from the car. You can also unlock or lock the car remotely via the Tesla mobile app or simply push on the roof of the car-shaped Tesla key fob.

There's No Ignition
You don't really turn on the car, either. Simply depress the brake pedal, push the right stalk on the steering column—it goes up for reverse and down for drive—and you're off. To engage neutral, gently push up to the first stopping point on the right stalk for about two seconds. When you're done driving, put the car in park by pushing the button on the side of the right stalk.
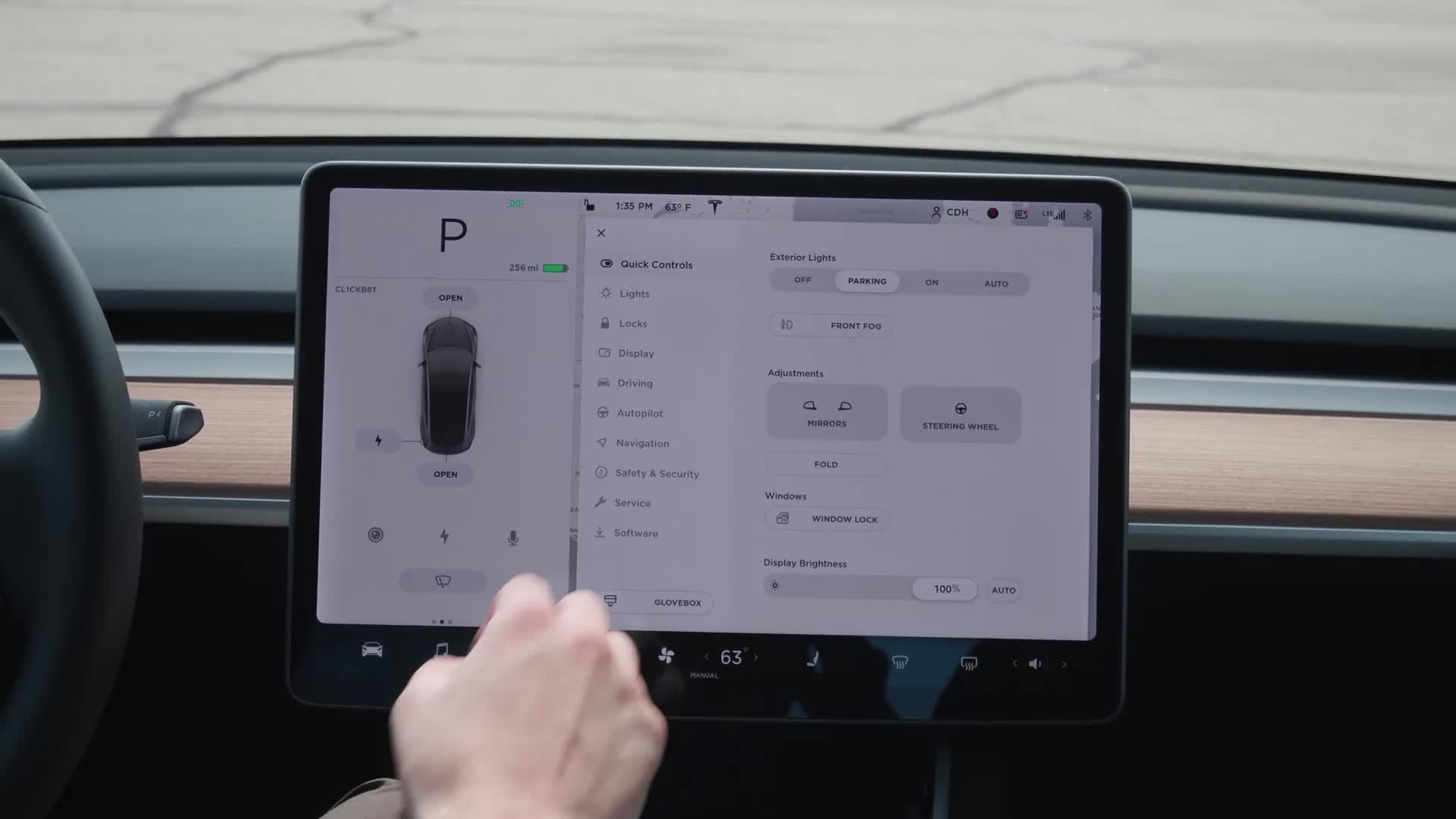
Making Adjustments
To adjust the steering wheel and mirrors, touch the front-facing car icon at the bottom left of the central touchscreen. This will bring up all of the vehicle's settings menus. Make sure you're under Quick Controls. This will allow you to adjust the steering wheel and mirrors via the two buttons and spin wheels on the steering wheel. Here, you can also turn the lights on or off, fold the mirrors inward, lock the windows, and adjust the screen's brightness. Adjustments, including the driver's seating position, can be saved on up to 10 driver profiles that can be chosen at the top right of the screen.
Driving, Cruise Control, and Autopilot
Driving an electric car isn't that much different from driving a gasoline-powered car—other than that they make almost no noise at all. As we said earlier, you never really start the car. You just put it in gear and silently creep away. Fair warning: the instant torque during hard acceleration might frighten you at first, but trust us, it can get a bit addicting. Reverse is different, though, because the car emits a high-pitched humming sound when in reverse—this definitely gets a lot of raised eyebrows from onlookers.

The Driving Graphic
On the left side of the Model 3's center-mounted 15-inch touchscreen, there is a driving graphic that displays your car, lanes in the road, bike lanes, railroad crossings, road arrows, stop signs, stoplights, pedestrians, and other cars (it even differentiates among cars, trucks, and SUVs). There isn't a typical gauge cluster in front of the Model 3's steering wheel as there is in most gas-powered cars. Instead, the Model 3's speed is displayed above the driving graphic. That's also where the blinkers flash.
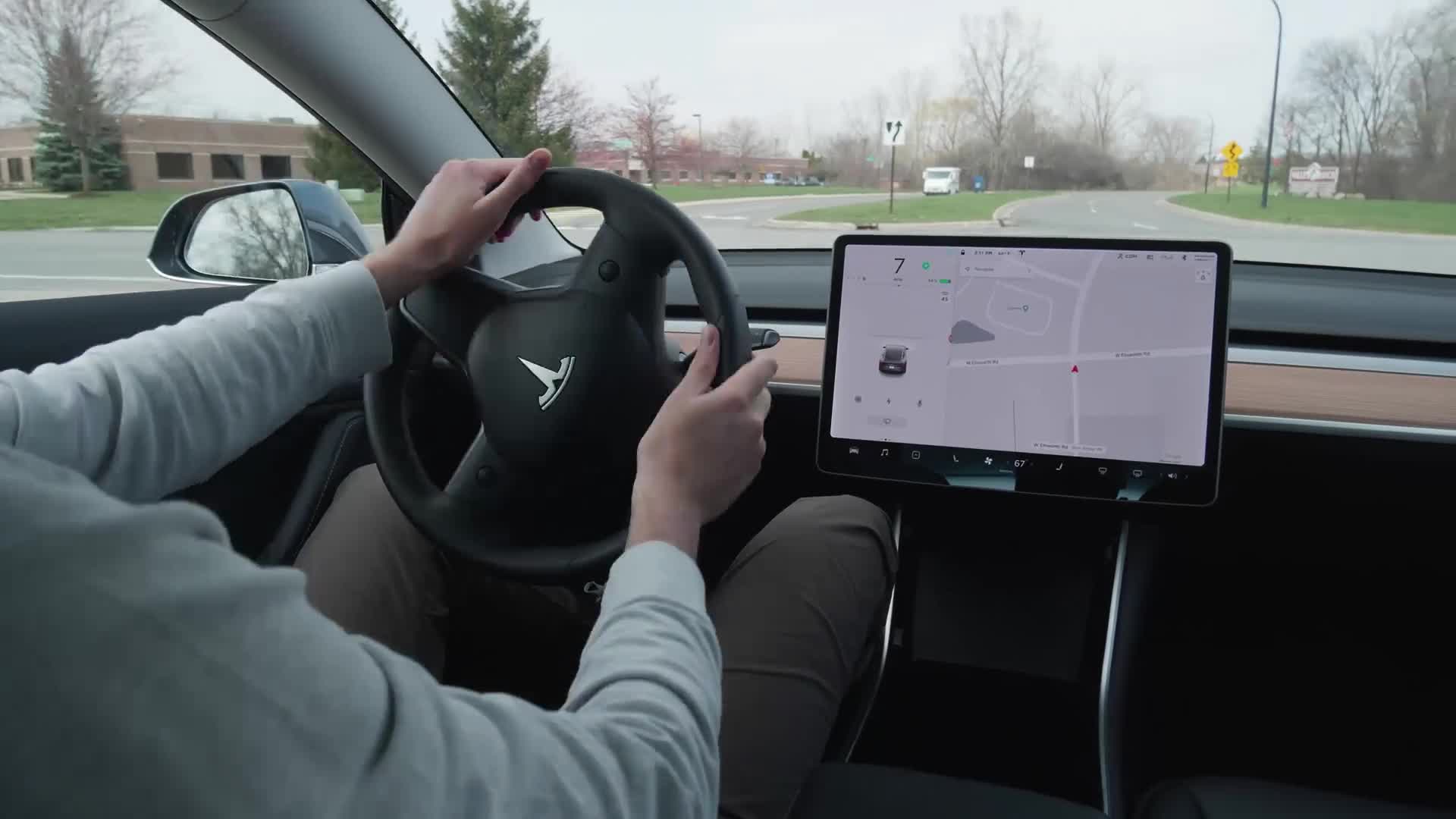
How to Use Cruise Control
Under the speedometer are the cruise-control speed settings. To engage cruise control, press down once on the right stalk while in drive. The Model 3 is equipped with adaptive cruise control, meaning cameras on the outside of the car detect its surroundings and decelerate or accelerate to maintain following distances. To adjust the speed, there are + and - symbols next to the speed or you can use the right wheel on the steering wheel to speed up or slow down.
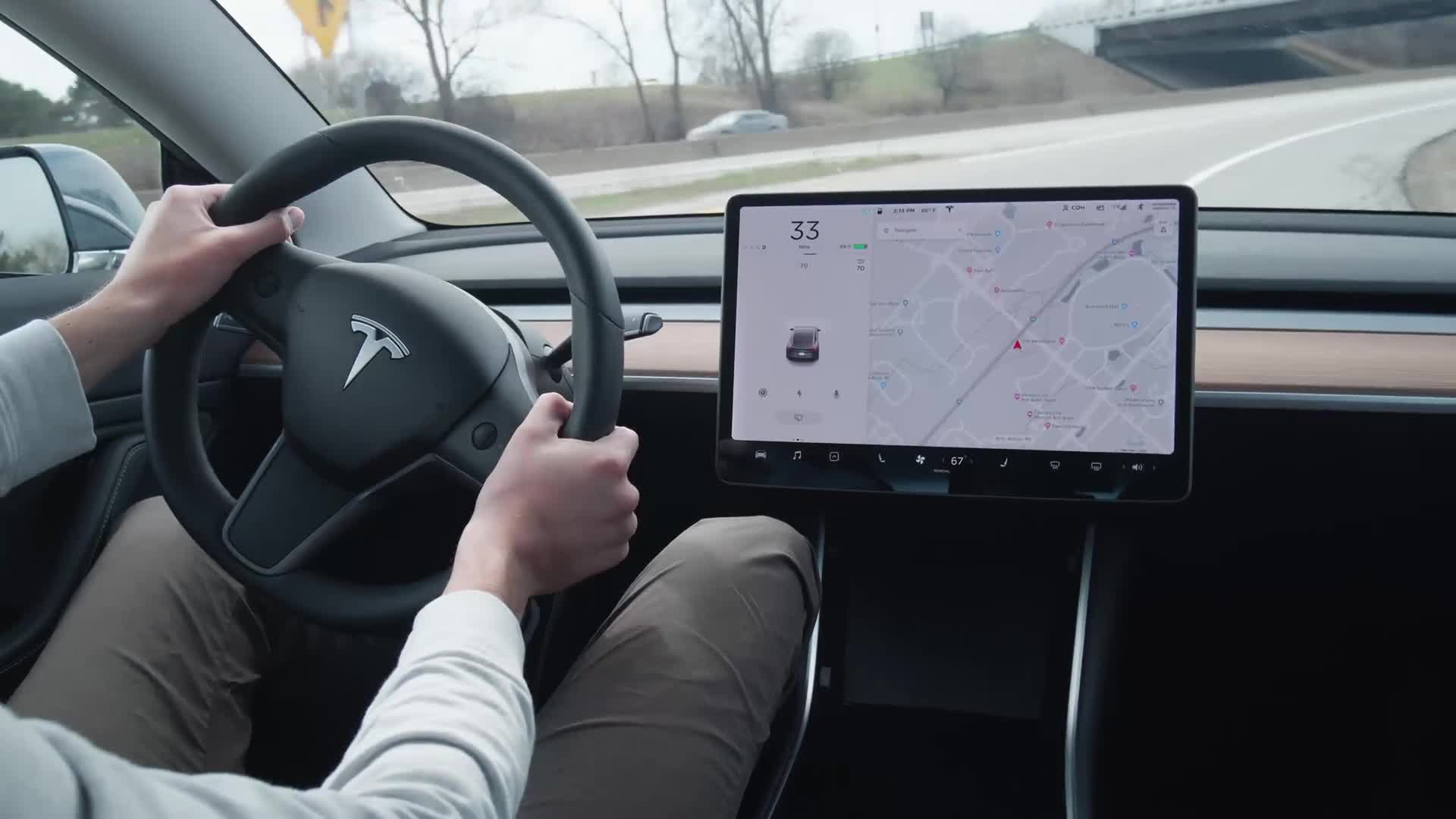
How to Engage Autopilot
To use the Model 3's Autopilot, press down on the right stalk twice. You'll hear a chime, and the lanes on the driving graphic will turn blue, indicating that the car will stay in that lane. Once Autopilot is engaged, the car will continue to slow down and accelerate based on the set cruise control speed, and also take gradual turns.
In a car equipped with the Full Self Driving option, Autopilot can change lanes, too. Simply hit the blinker and the car will switch lanes for you. If there's a vehicle in the way, the exterior cameras will detect it and wait for the way to be clear.

Bring the Car to You Remotely with Summon and Smart Summon
Autopilot and Summon are standard on Model 3s. C/D’ s long-term test car has the Full Self Driving option, which includes automatic lane changing and Smart Summon. You have to be within approximately 200 feet of your car to use Smart Summon. Both Summon and Smart Summon work through the Tesla mobile app. Summon will move the car forward or reverse, while Smart Summon can bring your parked car to your location without a driver. In the app, use the crosshair-like icon to show your location, and hold the Summon icon to bring the car to you.
One-Pedal Driving
The Model 3 has full one-pedal driving due to regenerative braking. Simply put, regenerative braking means that when you let off the throttle, the car automatically starts slowing by using the electric motor in reverse, which also serves to send energy back to the battery. If the car's charge is full, though, regenerative braking will be reduced, and the car will not stop itself. Regenerative braking is most apparent when the car is on a lower state of charge, therefore reserving the battery's charge.
The 15-Inch Touchscreen
The Tesla Model 3's interior is very minimalistic, meaning there aren't many buttons or knobs. There's just one large 15-inch touchscreen in the middle of the dashboard where the majority of the controls are, as well as two scrollable buttons on each side of the steering wheel. Normal things you expect to see in a car like a radio, air conditioning, and controls to adjust the mirrors or the steering wheel are all controlled on the central touchscreen.
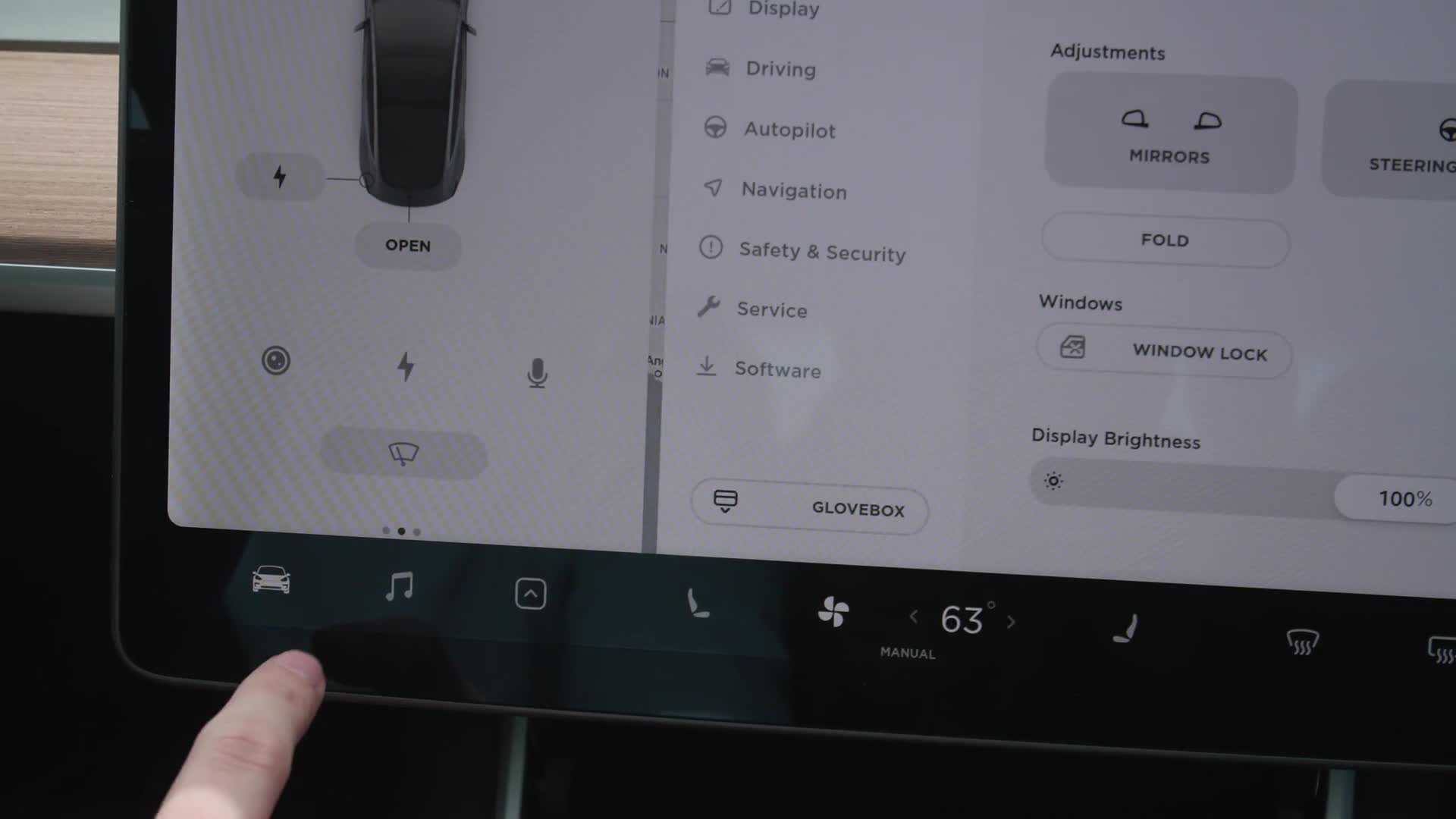
Open the Glovebox via the Touchscreen
Yes, in the Model 3, even the glovebox opens via touchscreen. Hit the car icon at the bottom right of the screen to open up the settings menu, and on the left under the system menus, there is a button to open the glovebox. It closes manually.
How to Use the Climate Controls
The climate-control settings are also integrated in the central touchscreen. Select the fan icon at the bottom of the screen, and the climate control settings pop up. In the Model 3, the air blows out of a vent that sprawls across the entire dash—just above the wood paneling in our long-term test car. Our Model 3 also has heated seats, which can be controlled in this menu, too. We can choose which seat is heated, even the middle back seat, and how much heat comes out in three levels.
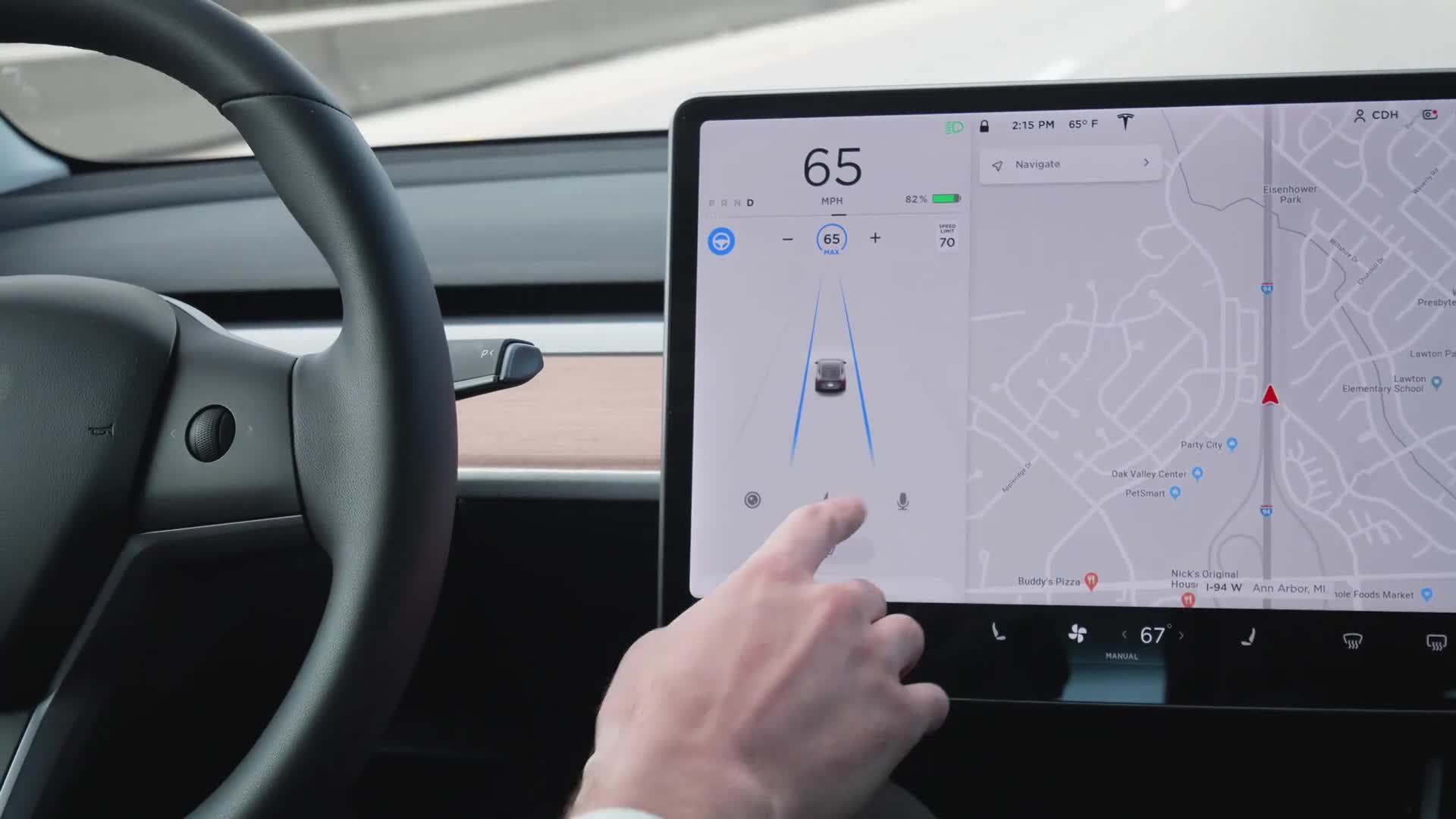
Ask Anything with Voice Command
Below the driving graphic, there is a microphone icon that's used to bring up voice command. You can also press the right scroll button on the steering wheel to activate voice commands. There will be an activation tone, and then you can speak commands such as "show me Superchargers," "lock the doors," or "text Connor."
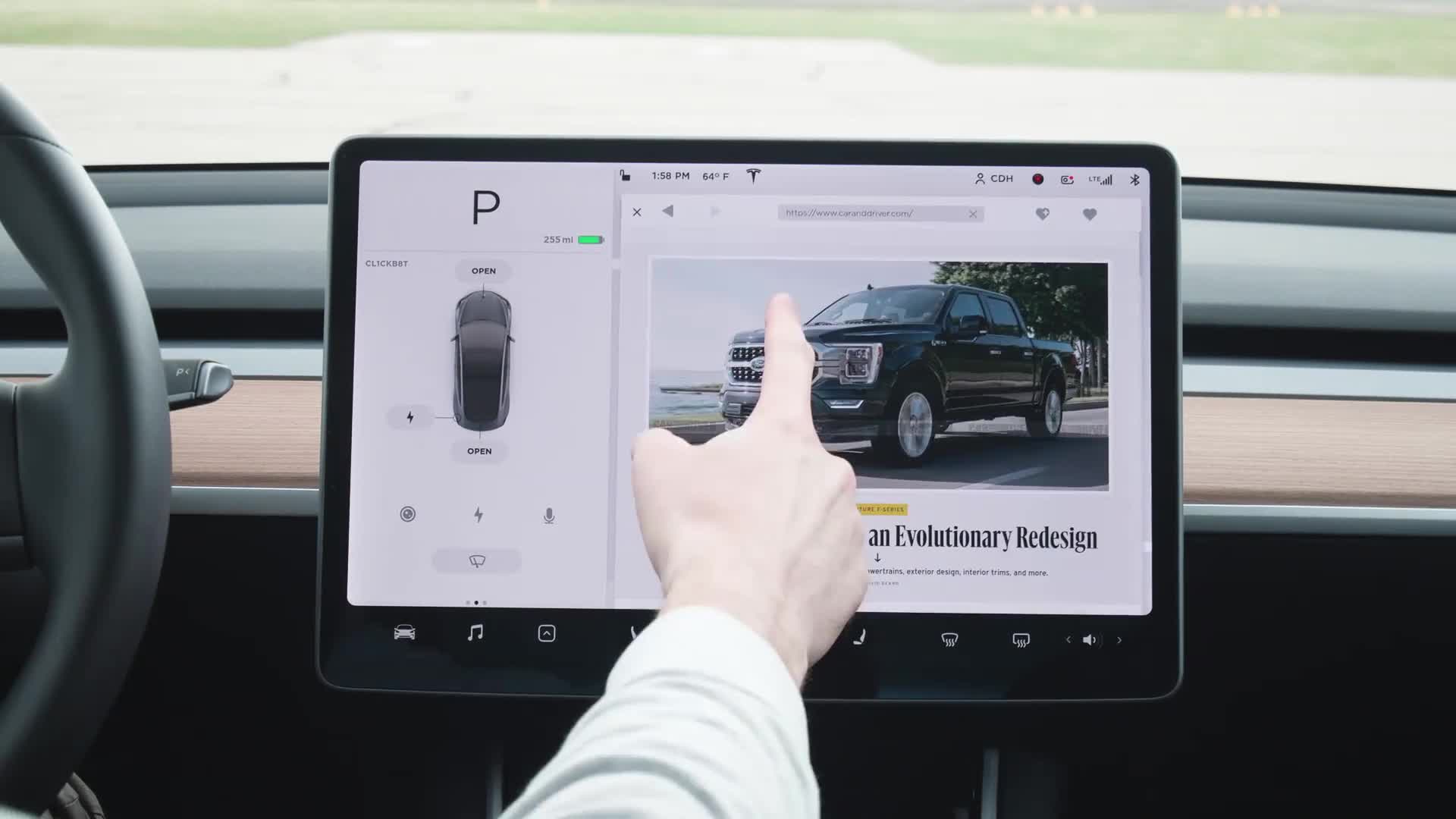
Stay Entertained
To help you kill time at charging stations, Netflix, Hulu, Twitch, and YouTube are integrated into the Model 3's entertainment menu. On the Model 3 they work like any other streaming device, but they can only be used while the car is in park. The entertainment menu is also loaded with games. Our favorite is a Mario Kart-like racing game where the Model 3's brake pedal and steering wheel are used to control the car in-game. In addition to streaming apps and games, Tesla owners can browse the web directly from the car's touchscreen. Owners can also log into their Spotify account to stream their music in the car or they can connect a Bluetooth device, listen to the radio, or search for podcasts.
Charging Tesla Model 3 at Home
All Teslas come out of the box with a mobile connector that has a 20-foot cable that can charge the car from different wall outlets at medium to low speeds. The mobile connector kit includes an adapter for standard 120-volt household outlets that will charge the Model 3 and Model S at around three miles of range per hour, and the Model X at around two miles of range per hour. Other adapters for different outlets can be purchased directly through Tesla.
However, the majority of Tesla owners have charging units installed at their homes. Wall connectors can work with almost any home power supply and are purchased from Tesla for $500. Through Tesla's website, a local electrician who has been trained to install Tesla charging equipment can be found to install the wall connector either indoors or out. Tesla's own installation services are also available, but only in certain areas. Connected to a wall charger, the Model 3 can charge up to 44 miles of range per hour of charge at an 11.5-kW or 48-amp output.
Customers can also get Tesla's Powerwall, which starts at $6500. It's essentially a giant battery plugged into the wall. Powerwall gives homeowners the ability to store power produced either by solar panels or during off-peak times to be used later to power their home or charge their Tesla. Like the wall charger and other Tesla accessories, the Powerwall can be ordered directly from the Tesla website.
Charging Tesla Model 3 on the Road
On the road, Teslas can be charged at one of its 1870 Supercharger stations across the world. They either provide 150 or 250 kW of electric power, and there are also urban chargers that supply 72 kW of power. To plug in, simply back into the parking space—each Supercharger station typically has around eight stalls—and plug in. Payment is processed through the credit card associated with the driver's Tesla account and typically costs between $5 and $15, depending on the state of charge. When charging is complete, hang up the charging cable, and you're off.
In addition to the Superchargers, Tesla also has destination chargers across the country at hotels, restaurants, and shopping centers. They're free and can be used by any Tesla owner to charge the car for a few hours or even overnight. Third-party charging stations can be located through Plugshare.com . The Tesla mobile connector bundle that comes with every car includes J1772, 120v, and 240v adapters.

Tesla Performance
Our long-term Dual Motor Tesla Model 3 Long Range weighed in at 4038 pounds and launched from zero to 60 mph in 4.1 seconds. That acceleration hits hard, due to the instant torque provided from the electric motors, and in the higher-performance Tesla models, there's even more oomph. The Model 3 Performance can do 60 mph in 3.5 seconds , and when we tested the larger Model S Performance, we reached that speed a full second quicker, in 2.5 seconds. But that incredible number isn't even the best time we've measured with an EV. A Porsche Taycan Turbo S to 60 mph in 2.4 seconds, making it the third-quickest car we’ve ever tested. Electric cars don't have to be slow.
How Much Teslas Cost
If you're going to get behind the wheel of a Tesla, you're going to have to get one first. But how much does a Tesla cost? Like any other car, it varies depending on model, trim level, and options. Currently the entry-level, let's say least expensive, Tesla is the Model Y compact crossover. It's almost identical to the Model 3, and it starts at $40,200, but that's for the Standard Range battery, which provides about 230 miles of driving range. They can cost you more than $62,200 for the Model Y Performance. On the highest end of the spectrum, the Model X SUV reaches prices around $106,000 for the Performance model, which Tesla claims can hit 60 mph from a stop in less than three seconds.

Order Online or in Person
You can order a Tesla online through Tesla's website or its in person showrooms. But Tesla's stores aren't like typical car dealerships because you're buying directly from Tesla. In some states, you might have to cross state lines to purchase one. And sometimes, as in our case here in Michigan, the Tesla service center is at a separate location. When our long-term Model 3 suffered a catastrophic battery failure , we had to send the car across the border to a service center in Toledo, Ohio.
Sitting on the floor of the library and poring over issues of Car and Driver is one of Connor Hoffman's earliest memories. Choosing to attend the nation's top-ranked journalism school at the University of Missouri and graduating with a magazine writing emphasis was all part of chasing his dream of writing for Car and Driver. When he's not bragging about Mizzou having the best journalism program in the country, he's probably on a rant about Toyota trucks.
.css-1updq97:before{background-color:#000000;color:#fff;left:0;width:50%;border:0 solid transparent;bottom:48%;height:0.125rem;content:'';position:absolute;z-index:-2000000;} Reviews .css-1e2ieb7:after{background-color:#000000;color:#fff;right:0;width:50%;border:0 solid transparent;bottom:48%;height:0.125rem;content:'';position:absolute;z-index:-2000000;}

Tested: Maybach S680 Is a Relative Bargain

2024 Porsche Macan EV Isn't Just Quick

2024 Toyota Tacoma Hybrid Is a Spicier Taco

1975 Volkswagen Rabbit: A Whole Different VW

Tested: 2024 Maserati GranTurismo Trofeo

2025 Ski-Doo MXZ X-RS 850 Turbo R: Peak Snowmobile

1996 Chevrolet Corvette vs. Malibu Corvette Boat

Comparison Test: Kia Sportage vs. Nissan Rogue

2024 Mercedes-Benz CLE Cabriolet: Sunset Cruiser

2025 Toyota Camry Carefully Evolves

1975 Toyota Corolla SR-5 Archive Test
- Car Companies

- AutoPilot Tech
Tesla Autopilot – What Does It Do and How Does it Work?

Tesla has one of the most advanced self-driving cars on the market that’s included with every new car sold and can be activated through software updates. Tesla has different versions of Autopilot which we’ll break down below. In essence, there’s “Autopilot” (comes standard) and “Full Self-Driving” which contains more advanced autonomous features and is a paid option. There’s also another variant in between the two called “Enhanced Autopilot” that Tesla has occasionally offers. All of these options still require a human driver to be attentive on public streets, analogous to Level 2 driving ( what do Levels mean? ) but making overall everyday freeway and stop-and-go traffic a much safer and enjoyable experience.
If you’re considering a Tesla and trying to decide whether Full Self-Driving ($15,000) is worth it, you’ll also want to check out our Autopilot vs Full Self-Driving: Is it Worth it? article for a quick read.
Table of Contents
- What Makes Tesla Different
Tesla Autopilot Overview
Standard autopilot capabilities.
- Full Self-Driving Capabilities
- Standard Safety Features
- Autopilot FAQs
What Makes Tesla’s Autopilot Different
Tesla vs other auto manufacturers.
While Tesla has enjoyed a headstart in the market and arguably employs the most sophisticated hardware of any consumer-grade vehicle currently, other car manufacturers are slowly catching up. Most notably are those car manufacturers who employ the Mobileye system. This was the same system Tesla originally utilized in Autopilot Hardware 1 (AP1) until 2016 when Tesla decided to build its own system. Manufacturers using the Mobileye EyeQ 3 (as used in AP1), include GM with Super Cruise, Nissan / Infinity with ProPilot and Volvo with Pilot Assist. GM’s Super Cruise is considered the closest to Tesla currently, but can only be used on certain, highly mapped roads. See our Cars with Autopilot article for more.
In 2019, Mobileye released its EyeQ 4 system to manufacturers which will be much closer to what Tesla offers. For example, a fully-optioned 2019 BMW X5 is one of the first non-Tesla vehicles to offer automatic lane changes besides Mercedes. That said, no other manufacturer has been as aggressive in pursuing self-driving technology as Tesla and building powerful hardware into every car, creating legions of fans eagerly anticipating each new software release.
So what can you expect if you purchase a Tesla today? Read on as we break down all the Autopilot and Full Self-Driving features.
Continuous Advances via Software Updates
Tesla has already disrupted the traditional automaker model by including all the hardware necessary for self-driving as part of every vehicle sold. Tesla owners who wish to “upgrade” to self-driving can do so “over-the-air” as part of a software update. These over-the-air software updates are partly what makes Tesla so unique as an auto manufacturer, in many ways similar to the way phone manufacturers upgrade their phone software, continuously over time, so customers always have the latest software for their phone. While others are now slowly also providing over the air updates, most do not allow as much of the vehicle to be updated as Tesla provides.
Autopilot continually improves as new updates are released (generally every month or two), oftentimes with major improvements.
The term Autopilot is an umbrella term used by Tesla to describe its semi-automatic driving features, including standard, included “Autopilot” and the optional “Full Self-Driving” package. Here’s how it all works.
Let’s begin with the hardware. Here’s where Tesla has a big advantage over other auto manufacturers. All new Teslas sold today have the necessary hardware required to eventually drive themselves, according to CEO Elon Musk (and he’ll upgrade it, if not). The Tesla Autopilot driving system relies primarily on cameras ( vs. Lidar – see article ), ultrasonic sensors and forward-facing radar to navigate the roads, a setup which Elon Musk believes is more practical for consumer cars than the more expensive and bulky Lidar setups used in many other autonomous cars being tested.
The Tesla Autopilot system employs 8 cameras that provide a 360 view for the system around the car, plus a front-facing radar to help see through rain, fog and snow, in addition to long-range ultrasonic sensors (e.g. parking sensors). In addition, Teslas come loaded with powerful computing hardware from manufacturers like NVIDIA, that allow the vehicles to process the enormous amounts of data using AI, neural nets, and machine learning to react to conditions in real-time.

Autopilot Hardware Revisions (AP1 vs AP2 vs AP3, etc.)
The current hardware suite seen on Tesla’s today wasn’t always the case. The advanced features included in the “Full Self-Driving” package for Tesla vehicles is only available for those vehicles manufactured with Autopilot 2.0 (AP2) hardware, beginning in Q4 of 2016. How can you tell if a vehicle is Tesla Autopilot 2 or greater? The easiest is whether is has cameras mounted on the side of the vehicle, embedded in the side blinkers (#5 in the diagram above).
Autopilot 2.0 Hardware Visual Giveaway:

The original Autopilot 1.0 (AP1) hardware (see AP1 vs AP2 ) included in early Tesla models starting in Q4 2014 (no side cameras in the front fender signal) was provided by a third-party supplier called Mobileye. While it was a very capable system, Tesla decided to part ways with Mobileye in Autopilot 2.0 in order to more rapidly advance full self-driving capabilities. That means that certain features, such as Navigate on Autopilot included with Full Self-Driving, aren’t available for AP1 vehicles and future self-driving features also likely won’t rollout out to older AP1 cars.
For more on the hardware differences on older Tesla vehicles see Tesla AP1 vs AP2 vs Hardware 3 .
Autopilot vs. Full Self-Driving Option
Tesla has three tiers of autonomous driving – “Autopilot” (standard), “Enhanced Autopilot” (limited availability – paid option), and “Full Self-Driving” (FSD – paid option). See Autopilot vs Enhanced Autopilot and Enhanced Autopilot vs Full Self-Driving or more. Tesla “Autopilot” is standard and is essentially an adaptive cruise-control plus automatic steering (lane keeping) system while the paid options of Enhanced Autopilot and Full Self-Driving contain more autonomous driving-like features like automatic lane changes, Navigate-on-Autopilot, Summon and Autopark.
Here’s the lineup:
- Autopilot – offers full stop-and-go adaptive cruise control with automatic steering. It’s included with all vehicles.
- Enhanced Autopilot [not currently offered] – in the past, this was a limited-availability paid option (usually as a post-purchase upgrade) that offered automated lane changes and advanced autonomous driving features such as Navigate-on-Autopilot (freeway on-ramp to off-ramp), Smart Summon and Autopark. It was a $4,000 option and only available via in-app upgrades.
- Full Self-Driving (FSD) – is a paid option that includes all the Enhanced Autopilot features plus Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control , allowing safer Cruise Control and Autosteer on city streets and divided Highways. It also promises an improved future Autosteer on City Streets, allowing the vehicle to make sharper turns, such as at intersections. As of this writing, it’s a $8,000 option (or $99/mo) that can be added at the of the vehicle purchase.
In this article, we’ll be reviewing the currently available features of both Autopilot, Enhanced and Full Self-Driving. However, you can get a glimpse of the future by watching the Tesla Autonomy Day video where they review what’s coming down the road and the Full Self-Driving Beta that is currently in limited release.
That said, these features require driver attentiveness and are Level 2 in nature (see what do Levels mean ?). Not paying attention with autonomous cars can result in accidents , but even so, the NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration) praised the Autopilot software with helping mitigate crashes overall. With the release of Navigate on Autopilot in the Version 9 software update in Q4 of 2018, Tesla vehicles are starting to get some new features that are more autonomous in nature, like the ability to automatically drive and navigate from freeway on-ramp to exit.
Any Standard Safety Features?
What is included outside of Tesla Autopilot or Full Self-Driving Options? Your Tesla comes default with standard active safety features which include automated safety systems as outlined below, including Lane Assist, Lane Departure Avoidance, Collision Avoidance Assist and Speed Assist. You can always purchase more advanced features included in Full Self-Driving later, albeit for a higher price.
Autopilot is included with Tesla vehicles currently (except the “off the menu” Model 3 Standard Range). The Autopilot feature Tesla currently provides on its vehicles is Level 2 autonomy ( what do Levels mean? ) – partial automation where the driver must still be attentive and be able to take over at any moment.
The key features of standard Autopilot include:
- Automated Cruise Control (ACC or TACC)
- Automated Steering (Level 2), combined with ACC above
- Ability to work in stop-and-go traffic
Adaptive Cruise Control with Stop & Go
Like many car manufacturers offer today, Tesla allows you to set the cruise control to a certain speed and have the car automatically slow down as vehicles in front of you decrease their speed. This is typically referred to as Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) or Dynamic Cruise Control, but Tesla calls it Traffic-Aware Cruise Control (TACC). Once activated and you’ve set your speed, you have the ability to adjust the following distance and the TACC will slow down all the way to stop, depending on traffic, and then automatically resume without any driver intervention. This is works in both highway and city traffic and does wonders for reducing the stress and cognitive load on the driver that comes with busy traffic environments (in addition to reducing the risk of accidents and rear-end collisions).
How to Use It:
- Model 3 – Push down once on the gear lever while in Drive mode. Use the Touchscreen to adjust follow distance. Note that pushing down once on the gear lever just initiates distance cruise control (TACC), but not Autosteer. Pushing down twice will enact both TACC and Autosteer (see below).

- Model S and X – Pull back once on the cruise control lever on the left side of the steering wheel. Adjust the desired speed by moving the cruise control lever up or down and releasing. To change the following distance, rotate the cruise control lever.

Limitations: Works from 18 to 90mph in generally clear visibility and straight roads. Note that when TACC is active over 50 MPH, Automatic Emergency Braking for stationary objects is limited (to avoid false positives / sudden braking on the freeway, which could cause accidents). That means you must pay attention at all times when driving at freeway speeds. From the Owner’s Manual:
“Traffic-Aware Cruise Control cannot detect all objects and may not brake/decelerate for stationary vehicles, especially in situations when you are driving over 50 mph (80 km/h) and a vehicle you are following moves out of your driving path and a stationary vehicle or object is in front of you instead.”
Compared to Others: The Tesla Traffic-Aware Cruise Control system compares very favorably to other ACC implementations in that it works in a wide variety of conditions and handles stop-and-go traffic very well. By comparison, Volvo requires driver intervention if the car has been stopped for too long.
Autosteer (with Cruise Control)
The Autosteer capability works in conjunction with the Traffic-Aware Cruise Control (TACC) and will keep the vehicle centered in the lane (i.e. Lane Centering). It works under multiple conditions, both on the highway and in city driving as long as the vehicle can accurately detect the lanes and/or road boundaries. In essence, it steers itself – within limits. It can’t handle sharp turns on winding roads and requires you keep your hands on the steering wheel and will disengage the system if you don’t.
By using Autosteer in conjunction with TACC, you are effectively driving at autonomous Level 2.

How to Use It: Before you can use Autosteer, you must turn it on in Settings. Once you’re driving and the vehicle has detected the lanes and feels confident enough that it can safely enable Autosteer, it will display a grey steering wheel icon. Once you engage Autopilot the steering wheel turns blue (as shown in the above image, upper left).
- Tesla Model 3 – push down the gear lever twice to enable. You will hear a positive tone, letting you know it’s active.
- Tesla Model S or X – Pull the cruise control lever towards you twice.
Limitations:
- Highways and freeways – Autosteer should only be used on active highways and freeways with no cross traffic. Autosteer will not respond to stoplights or stop signs and while it can be used in city traffic, it is dangerous as the driver may become complacent and inadvertently drive through stoplights and stop signs (although warnings are now issued).
- Hands-on – Hands must be on the steering wheel. If hands are off the steering wheel for an certain period of time (under a minute), the car will warn you to put your hands back on the wheel. If you do not, it will stop the car and no longer allow the use of Autosteer until the next trip.
- Speed restrictions – in situations where the speed limit cannot be detected, Autosteer is limited to 45mph. Where the speed limit is detected, the maximum speed is set to +5mph above the speed limit.
Compared to Others: Because Tesla uses its own powerful camera AI system, it’s able to handle a greater variety of roads and conditions than most other manufacturer’s systems. The closest competitor is GM’s Super Cruise, but it’s limited to roads where GM has done extensive mapping ahead of time. Other systems such as Nissan’s ProPilot and Volvo’s Pilot Assist aren’t nearly as good as Tesla (or GM) in keeping centered within lanes. BMW released a slightly better version with the 2019 X5, but again, fairly rudimentary. See Cars with Autopilot for more.
Full Self-Driving Features & Capabilities
Beyond the standard Autopilot outlined above, Tesla also offers an Autopilot tier called “Full Self-Driving” (FSD), for an extra $12,000 (see “ Is Full Self-Driving Worth It? “). While the name would imply that the vehicle could completely drive itself, that’s far from the truth, despite Tesla’s bold ambitions for autonomy . In truth, both standard Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD) are both Level 2 vehicles, which require an attentive and responsible driver at all times.
That said, the Full Self-Driving package does have some practical semi-automated features, like automated lane changes plus more futuristic features like Navigate-on-Autopilot, Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control for city streets, and Smart Summon, that while cool, aren’t quite yet fully autonomous yet but certainly hints of the future.
Outlined below are the features currently offered with FSD:
Assisted Auto Lane Change
Here’s a feature that few other car manufacturers currently offer to general consumers – the ability to automatically and safely change (one) lane while in ACC+Auto-Steering mode. This makes it convenient to change lanes to avoid slower traffic, when required, without having to disengage Autopilot and then re-engage it. It works, but on rare occasions, it can quickly abort and go back into the original lane which can be somewhat unnerving, so it’s best to only use this function once you have thoroughly checked your surroundings and have your hands on the wheel during the maneuver.
How to Use It: First, enable Auto Lane Change in Settings. Then, with Autosteer active, simply apply the turn signal (half-press on Model S and X) to the desired direction and the vehicle will change lanes when it’s safe to do so. Once the lane change has completed, the signal will automatically turn off. You may cancel Auto Lane Change by manually steering, applying the brake or canceling the turn signal if pressed fully (on the Model S and X).
Limitations: It only changes one lane at a time, the adjacent lane must be clear of obstacles and the vehicle must detect the outside of the target lane halfway through the lane change or it will cancel the maneuver.
Compared to Others: Only certain BMWs and high-end Mercedes something similar.
Navigate on Autopilot
Navigate on Autopilot is arguably the most exciting Autopilot feature released in years and provides a glimpse of what autonomous driving is capable of. Navigate on Autopilot is a freeway-only function, allowing the vehicle to navigate itself autonomously towards a destination from a freeway on-ramp to exit, changing lanes and switching freeways as required. It will also automatically changes lanes to avoid slow traffic, as needed. This system effectively combines Traffic Aware Cruise Control (TACC), Autosteer and Auto Lane Change capabilities to provide an almost fully automated driving solution.
How to Use It: To use Navigate on Autopilot you must enable it in Settings, under Autopilot. When you’re ready to use it, enter your destination into the navigation system. If the route uses freeways, then you’ll see a “Navigate on Autopilot” button in the navigation system, press it to activate it. You can also set it to automatically activate for destinations that use compatible roads and opt to forgo lane change confirmations and more.
Once on the freeway, enable Autosteer (see above) and you’re all set. The system will show on the screen a suggested lane change on the screen (for either a faster lane or for lane changes required to make the destination) and will also provide an audible prompt if the lane change is required for the destination. If you’ve set it to automatically change lanes without confirmation, it will do so (it must detect your hands on the wheel during the change), although you can have it notify you of upcoming lane changes with an audible alert as well.
It will also automatically exit the freeway (by turning on the blinker and changing lanes), if the exit is directly off the freeway. In addition, it will come to a stop at the first intersection from the off-ramp.
Limitations: Navigate on Autopilot only works with current vehicles ( AP2 or greater hardware ), on freeways and requires that the driver’s hands are on the steering wheel if lane confirmations are turned off in settings.
Compared to Others: No other system currently has something this advanced on the road for consumers today and it’s really an early glimpse of future autonomous driving.
Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control
One of the more sophisticated features of the Full Self-Driving package is the Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control feature which allows you to use Auto Steer with Cruise Control on city streets and automatically respond to stoplights and stop signs.
It does come with some current limitations, however. For example, if there is a lead car in front of you, your vehicle will continue through a stoplight if it’s green. However, if there is no lead car in front of you, the vehicle will automatically slow down regardless of the light’s color until you confirm it’s safe, only then will the vehicle continue through the intersection if it’s green.
How to Use It: Simply engage Auto Steer and the vehicle will drive along the current road until it approaches an intersection with a traffic control. For red stoplights or stop signs, the vehicle will stop, requiring you to press down on the gear lever or accelerator to continue. At green stoplights, if there is a lead car, the vehicle will continue. If there is no lead car, the car will slow down even if the light is green, however, you can press gear lever or accelerator to continue.
Limitations: This is a BETA feature and may or may not accurately detect traffic controls. It’s up to the driver to pay close attention to the road when using this feature.
Compared to Others: No other vehicle has this feature – it’s truly a glimpse into the future of Full Self-Driving.
One of the most challenging and stressful aspects of everyday driving can be parking, especially parallel parking. More and more car manufacturers are now offering assisted parking technology for both in parallel and perpendicular spots. One advantage electric vehicles have in this area over traditional cars is that electric vehicles can fully drive the car into the spot, automatically switching between forward and reverse and applying the brakes. Transitional gas-powered vehicles with transmissions, such as the Volvo XC90 will automatically steer the car, but require the user to apply the gas and brake – potentially causing issues if the driver is paying attention to the parking guidance system.
How to Use: Drive slowly by potential spaces. If the car detects a suitable space a parking icon will display on the screen. Remove hands from the steering wheel and put the car into reverse. Press “Start Autopark” on the screen.

Limitations: Autopark requires cars parked on each side of the space to operate.
Compared to Others: Tesla’s system is generally very good and can handle both parallel and perpendicular spots. However, it requires there be cars in the adjacent spaces in order to detect the parking spot. In contrast, Nissan’s new ProPilot system doesn’t require cars be in adjacent spots and also provides a useful top-down 360 view of the surrounding area to better visualize the surrounding environment.
Summon and ‘Smart Summon’
One of the most interesting self-driving features provided by Tesla is the Summon feature. It allows you to “summon” your Tesla from a garage remotely, for example to a clear space where passengers and cargo can easily be loaded or unloaded. This is very helpful in situations where the car is parked in a tight space, making entry and exit difficult (like apartment spots or tight garage spots). In addition, it can automatically open and close garage doors!

In addition, Tesla has released “Smart Summon”, a beta feature allows a vehicle to automatically navigate to you on private property, such as parking lots.
How to Use: For normal Summon (not Smart Summon), enable the Summon feature in Settings, then Customize to adjust details such as Side Clearance, auto HomeLink, etc. Then position the vehicle for parking so it only has to move in forward or reverse. Finally, operate Summon by either using the Tesla App or the car key.
For the Smart Summon beta feature, click Summon and then the Smart Summon icon. You must be within 200 feet of the car and should be able to see it at all times. Hold down Go To Target button to begin and release at any time to stop.
Limitations: Normal Summon only drives forward and reverse in a straight line and will not work with raised edges higher than one inch. Smart Summon is available to those who have purchased Full Self-Driving Capability or Enhanced Autopilot and only works within line-of-sight.
Compared to Others: Other manufacturers such as BMW and Mercedes have a similar feature to the basic Summon in their higher end models, but no manufacturer has anything like Smart Summon.
Future Full Self-Driving Capabilities
The Full Self-Driving Beta (aka Supervised) is now fully available for anyone to purchase if you have the hardware, which is standard on all new Tesla vehicles being sold.
Standard Automated Safety Features
In addition to true autonomous and self-driving features, Tesla includes many intelligent safety systems as standard equipment designed to help support the driver.
Lane Assist (LA, aka LKA)
Lane Assist, commonly known as Lane Keeping Assist (LKA), helps ensure you stay in your lane and don’t accidentally drift or drive into adjacent lanes or vehicles. It acts a bit like a Blind Spot Warning (BSW) system in that it will alert you visually (via the instrument cluster on the Model X and S) if there are cars or objects next to the car.
We found LKA to be far better than others. With other systems, if you are too close to a lane marker they often trigger false alerts by shaking the wheel. However, with Tesla’s version, it seems to only shake the wheel when it realizes you’ve erroneously drifted too far (perhaps by using the neural network technology). Because of that, it’s the only LKA system I’d actually keep on at all times.
It has the following features:
- Visual warning on the X and S instrument cluster
- Steering wheel vibration when drifting from the lane
- Steering intervention if drifting into an adjacent lane
- Lane Departure Avoidance to actively bring you back into the lane

How to Use: Automatically engaged. However, certain features can be controlled in Autopilot settings, such as steering wheel vibration and Land Departure Avoidance (Lane Departure Emergency Avoidance is turned on each time automatically).
Limitations: Generally 25 to 90 mph on highways with clear markings
Compared to Others: Generally good compared to others, however, systems like those on Volvo more clearly alert the driver directly on the side rearview mirrors (something found on many other cars but missing from Tesla vehicles, unfortunately).
Collision Avoidance Assist (CAA)
Collision Avoidance Assist (CAA) is composed of two systems designed to avoid frontal collisions:
- Frontal Collision Warning – an audible and visual (in Model X and S instrument clusters) warning if the system detects an imminent collision

- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) – as is standard on many cars today, Tesla includes AEB to avoid accidents if it feels a collision is unavoidable if no action is taken. It will automatically apply the brakes and continue to apply them until the car has stopped, the threat is gone or the driver pumps the brakes or turns sharply.
How to Use: Both systems are on by default but can be adjusted or even turned off within the system settings.
Limitations: Both systems work between 7 and 90mph. If the driver intervenes by turning sharply or applying the brakes (and releasing in the case of AEB), the system will disengage. Note: AEB may NOT work in all cases if you have Traffic Aware Cruise Control (TACC) activated (see TACC section above).
Compared to Others: Tesla’s system is generally good, but Volvo is considered to be the leader in this area and has spent considerable resources on additional features such as large animal detection and avoidance.
Speed Assist
Speed Assist is designed to help you understand the current speed limit and warn you if you are going over a designated limit. It works by reading traffic speed signs and by using GPS position to determine what the speed limit should be. It provides both visual warnings on the instrument cluster (X and S) as well as visual chimes, if desired. You can adjust the threshold at which point you’d like to be warned (absolute, relative, etc.).

How to Use: Warnings can be turned on and of and adjusted in the system settings (for example no warnings, visual only, visual + chime, etc).
Limitations: Poor visibility and/or GPS signal may hinder the ability of the system to determine the speed limit.
Compared to Others: This is a typical function now available in most luxury cars and is generally comparable.
Tesla Autopilot FAQs
Note, when we use the term Autopilot below, we’re referring to both standard Autopilot and Full Self-Driving unless otherwise indicated.
The basic Tesla Autopilot functionality that comes standard with Tesla vehicles is called “Autopilot.” The more advanced option that includes the ability to change lanes and automated point-to-point navigation is called “Full Self-Driving”. Both of these still require an attentive driver at all times.
In a nutshell, Tesla Autopilot is a driver assistance feature that helps steer the vehicle and automatically keep distance from other cars (adaptive cruise control). A paid option, called Full Self-Driving (FSD) is more advanced but still requires an attentive driver. It allows for automated lane changes, point-to-point freeway navigation and more. See our Is Full Self-Driving Worth It? article for more.
Tesla’s standard Autopilot and the paid Full Self-Driving option are not fully autonomous driving, known as Level 5 (see What Are Self-Driving Levels for more). They are driver assistance features and require an attentive driver with hands on the steering wheel.
All current Tesla vehicles come standard with basic Autopilot. This includes stop-and-go Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) and Automated Steering. Tesla offers a “Full Self-Driving” package for $15,000, that despite the name, isn’t really autonomous driving, but does offer things like automated lane changes and point-to-point freeway navigation. See Is Full Self-Driving Worth It? for more.
The standard Autopilot that is included with new vehicles does not automatically stop at red lights. However, the optional Full Self-Driving package does automatically stop at red lights and stop signs (see the Full Self-Driving article).
You can tell if a Tesla has Full Self-Driving (FSD) by checking the menu under Autopilot (Controls > Autopilot) and seeing if Navigate on Autopilot is available. If you’re wondering whether the vehicle has the Full Self-Driving computer (Hardware 3) needed for Full Self-Driving, you can check that by going into the settings under Control > Software and then “Additional Information”. See our Tesla Autopilot AP1 vs AP2 vs AP3 article for more.
Autopilot will work on most roads with clear lane markings.
Currently Autopilot does not handle these situations gracefully and is one of the many reasons it’s incredibly important to pay attention at all times. Per the manual, it will also not stop for stationary objects at high speeds (see Tesla Autopilot Crashes and Causes for more).
Tesla has changed its Autopilot offering lineup several times over the last few years and one of the tiers that has come and gone, but then reappeared on occasion is one called “Enhanced Autopilot”. See our Autopilot vs Enhanced Autopilot article for the history and latest information.
Yes, and the Full Self-Driving package will recognize traffic controls, such as stoplights and stop signs. However, it is somewhat dangerous to use unless you are really paying attention due to the many unexpected hazards that can present themselves. Autopilot and FSD are best used on long stretches of highway or unpopulated, clearly marked roads. The driver must still pay attention at all times. In the future, the Full Self-Driving package will be able to handle turns on city streets, as demonstrated in the Full Self-Driving Beta in limited release.
The Full Self-Driving package will stop at intersections with traffic controls. Standard Autopilot will not. Note that using Autopilot in city environments requires extreme vigilance.
While Autopilot does technically detect them, it’s not always perfect and may not act appropriately in all circumstances. This is one of the many reasons to avoid using Autopilot in dense city traffic environments
That’s the $10,000 question! Elon Musk said Tesla vehicles should be fully autonomous in 2021 . However, Tesla has a habit of announcing overly aggressive timelines and not meeting them. Our guess and from we’ve seen from the Full Self-Driving Beta is that we’ll see helpful city driving features make their way into Tesla vehicles later in 2021 or 2022, depending on regulations, but nothing like what was promised at Tesla Autonomy Day , that is Level 4 or 5 capabilities.
Tesla requires your hand on the wheel and we strongly recommend it so you can immediately tell if the car wants to do something it’s not supposed to and you can quickly correct it. While many people try to fake having a hand on the wheel, this is a sure-fire way to get in an accident. Autopilot is meant to relieve driver stress and allow the driver to better pay attention to surroundings, not less.
Tesla has the most advanced self-driving capabilities on the market for consumers, bar none. It handily beats other systems including GM’s Super Cruise, Nissan / Infinity’s ProPilot and Volvo’s Pilot Assist. That said, it’s a powerful and sophisticated system that requires driver attention and an understanding of its limitations. By contrast, GM’s Super Cruise does a better job of ensuring driver attentiveness (via eye tracking) and by restricting the roads where it can be used (limited to ones they mapped thoroughly).
If you’re the type of person who wants the latest-and-greatest, Tesla can’t be beat. On the other hand, if you want a relatively conservative system with the highest level of safety, GM’s Super Cruise is likely a better choice since it’s more restrictive and can only be used on certain roads and ensures the driver is paying attention. See Cars with Autopilot for more.
What we like:
- Excellent ability to stay within the lane and keep distance to cars
- Ability to use on almost any road
- Lane changing capabilities (FSD package)
- Navigate-on-Autopilot (on-ramp to off-ramp autonomy, FSD package)
What could be better:
- Smoother acceleration and deceleration
- Only initiating an automated lane change when clear (FSD)
- Turn on Autopilot automatically after manual lane change (standard Autopilot)
- Merging with other cars more confidently
- Recognizing turn signals from other cars and slowing down to let them in.
- Improved Autopark without needing surrounding cars
- Improved Smart Summon with better reliability
On our wish list:
- Audible warning if there is a stopped car/object above 50 MPH with TACC active.
- Avoid driving in other car’s blind spots when possible by adjusting speed
- Veer slightly out of the way for passing motorcycles, if possible.
- Automatically turn on the rear-view camera when changing lanes (and keep on top).
Is the Full Self-Driving package worth an extra $12,000? It frankly depends on how much you believe Tesla will actually roll out autonomous features in addition to the ones already currently available in the package.
See our Future Autopilot Updates article and the Tesla Autonomy Day video for more.
Considering a Tesla?
If you’re in the market for a new Tesla vehicle, be sure to take advantage of the Free Supercharging referral code program.
RELATED ARTICLES
Tesla fsd v12.3.5 rolling out. now $99/mo. or $8k to purchase, latest tesla autopilot software updates, tesla autopilot vs enhanced autopilot – what’s the difference, most popular, tesla referral program code for free supercharging & more, tesla autopilot vs full self-driving (fsd) – worth it, cars with autopilot in 2024.
© AutoPilot Review

Tesla Cruise Control vs. Autopilot (Detailed Comparison)
If you are going to purchase a Tesla vehicle you must be familiar with Tesla Cruise Control as well as Tesla Autopilot. Cruise Control will provide you with many features. While the Autopilot feature set adds a new capability to your Tesla that makes driving safer and less stressful.
In this article, I will discuss the main features and comparison between Tesla Cruise Control and Tesla Autopilot.
Let’s Get Started…!!!
Table of Contents
What is Tesla Cruise Control?
When you are enjoying the Tesla cruise control feature your vehicle may automatically change its speed to keep a safe following distance from the car in front of it. By using sensors, cameras, and radar it can detect the speed of the vehicle in front of you. In this way, it can modify the speed of your vehicle appropriately.
Cruise control helps you to keep a safe following distance, and allows your Tesla to automatically slow down or accelerate up. It will help you to detect a car which is in your same lane. It will allow your vehicle to keep moving at a predetermined speed.
While driving and enjoying the Tesla cruise control feature you have to keep an eye in front of you and manually apply the brakes when necessary.
What is Tesla Autopilot?
The complete semi-autonomous driving functions present in your Tesla vehicle are referred to as “Autopilot”. Tesla Autopilot is one of Tesla’s most ambiguous properties. There are four distinct hardware variants and four distinct software packages that have been introduced throughout the years.
Every component present in your Tesla autopilot will perform a particular function, for example maintaining speed, steering, or parking of your Tesla vehicle. There are a total of four distinct Autopilot software packages that combine these elements in various ways.
The main thing that you must keep in mind is that Tesla’s Autopilot is not autonomous, so you must maintain concentration, keep your hands on the wheel, and be prepared to take over at any moment.
To monitor your participation, Tesla has put in place several safety mechanisms for you. If Autopilot is used improperly, it may be warned about or its functionality may be restricted.
Following are some advanced features offered by Tesla Autopilot:
1) Tesla Autopilot includes the Traffic Aware Cruise Control to lock on to and match the speed of the car in front of it. It will completely stop and restart your Tesla vehicle without the need for your action as compared to Tesla cruise control.
2) The autopilot helps you to monitor lane markings. Your vehicle will make the appropriate steering adjustments. Tesla steers proactively to handle reasonably major curves in the road.
3) You can automatically change the lane by using Auto Lane Change. When you begin to change lanes, you must have to use the turn signal to signal the chosen lane. When Tesla autopilot is confirmed, your car will automatically move over.
4) The most advanced feature of your Tesla Autopilot is Stop Sign and Traffic Light Control (beta). With this function, your Tesla vehicles can view and react to stop signs and traffic signals.
Your automobile will slow down at stop signals even if it’s green. You have to give a confirmation tap on the accelerator pad to proceed with your vehicle again.
5) Tesla autopilot provides you with two different kinds of summons named Basic Summon and Smart Summon. This summons will allow you to move your vehicle without your presence.
When you are using the basic summon feature you can only move forward and backward. Smart Summon will help your Tesla to independently find its way to the driver in a parking lot.
6) On the highway by using navigate on autopilot (beta) semi-autonomous driving and navigation is possible. When you are travelling on a highway the option to navigate on Autopilot will be available.
This will help your Tesla vehicle to change lanes to pass other vehicles, move out of the passing lane, make exits, and navigate through highway interchanges.
Tesla Cruise Control vs. Autopilot
1) Cruise control in your Tesla vehicle is similar to the cruise control present in many other automobiles. When you activate the cruise control feature, it will enable your vehicle to keep the specified constant speed.
Advanced driving assistance systems like Tesla’s Autopilot provide cutting-edge features as compared to standard cruise control.
2) Your Tesla cruise control is not able to change the speed of your car in response to traffic ahead. In contrast, Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC), which is one of the elements of Autopilot, can change your vehicle’s speed according to traffic conditions. By using this feature, you can completely halt your vehicle and then start moving again if the flow of traffic permits.
3) Tesla cruise control does not offer you any aid with steering or lane-keeping. But, your Tesla autopilot will offer you some self-steering capabilities along with auto steering. Your vehicle will be in its lane when your Tesla vehicles use the autopilot feature.

Which option should be considered in the future?
When you talk about Tesla cruise control you should keep in your mind that your Tesla cannot have cruise control without the driver-assist technology package Autopilot installed.
The Traffic-Aware Cruise Control feature of your Tesla Autopilot package allows your Tesla to keep its cruising speed while the road in front of you is clear. It will also slow your vehicle according to the behavior of the car that is in front of you.
While using cruise control, you must always maintain your hands on the wheel and be ready to brake or take control of the car at any time.
You can avail the autopilot package as a subscription for $99 per month or you may also enjoy the Enhanced Autopilot package for $199 per month. To subscribe to these packages, you can use your Tesla app or Tesla account.
The following points should be kept in mind:
1) The top cruising speed is 150 km/h or 90 mph. You must maintain a safe speed according to the posted speed limit.
2) Always keep an eye on the road in front of you. You should be ready to make adjustments whenever necessary.
3) When you are using Tesla cruise control you should be careful about your routes. Avoid using the feature during harsh weather conditions.
4) You should clean your Tesla cameras and sensors from any type of debris before activating the Autopilot features.
5) You must get familiar with Autopilot’s restrictions and the circumstances that can call for driver intervention.
Final Thoughts
So far, I have discussed all the features related to your Tesla cruise control and Tesla autopilot along with their comparison. The difference may include:
- Cruise control will provide you with a specified speed while Autopilot will give you more advanced features.
- As compared to Tesla Autopilot, cruise control will not be able to change the speed.
- Steering and Lane keeping features are not present in cruise control.
We went over in detail each of these and answered some quires that you might have in your mind.
If you have some information to share with us about this topic, feel free to contact us. We would love to hear from you.
What Happens If A Tesla Goes Into Water?
Tesla Model X Seat Stuck
Tesla EAP vs. FSD (Detailed Comparison)
Howdy, I’m Nabeel, and for the past 10 years, my automotive passion has been charged up with a focus on cars and Jeeps, with a special love for Teslas. From the hum of the electric motor to the thrill of off-road adventures, I’ve clocked countless miles and experiences. Join me as I delve into the electrifying world of Tesla and share a decade’s worth of automotive adventures, one ride at a time. Let’s hit the road!
Related Posts


Tesla Window Keeps Rolling Down (7 Ways To Fix)

Tesla Alarm Keeps Going Off (15 Ways To Fix)
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Tesla Enhanced Autopilot vs Full Self Driving: which one should you buy?
If you're paying for a better Tesla Autopilot, which option should you take?

Every Tesla you can buy comes with Basic Autopilot as standard. That means you can enjoy the company’s simplest autonomous features without having to pay any more money. But basic also means limited, and Tesla offers two additional tiers of Autopilot — so long as you’re willing to pay for them.
Teslas are also capable of coming with Enhanced Autopilot and Full Self Driving . By parting with several thousand dollars, you can ensure your car can do more things without (much) intervention from the driver. But both tiers do different things and, crucially, cost different amounts. So if you can afford better Autopilot on your Tesla, should you buy Enhanced Autopilot or Full Self Driving?
Enhanced Autopilot vs Full Self Driving: Price
The crucial difference between the two Autopilot tiers is the price. Enhanced Autopilot will set you back $6,000, while Full Self Driving costs $15,000 — two and a half times as much.
Full Self Driving is also available in subscription form. It costs $199 a month for drivers with Basic Autopilot to upgrade to Full Self Driving, or $99 for drivers that already have Enhanced Autopilot. The subscription is a rolling monthly contract, and drivers are able to cancel at any time without penalty.
It’s not currently possible to upgrade to Enhanced Autopilot with a subscription.
Enhanced Autopilot vs Full Self Driving: Basic Autopilot Features

Basic by name, basic by nature, relatively speaking. Basic Autopilot comprises four key features: blind-spot monitoring, emergency braking, adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assistance. Crucially these features can work at the same time, meaning a Tesla can control steering and acceleration when Autopilot is engaged.
In short, this means Autopilot can keep your Tesla centered within a clear lane and can alter its own speed based on traffic ahead.
Enhanced Autopilot vs Full Self Driving: Enhanced Autopilot Features

Enhanced Autopilot has all the same features as Basic Autopilot, plus a bunch more. The most useful is the Auto Lane Change feature, which allows the car to switch lanes depending on surrounding traffic. That way it can overtake slow cars, and prepare for merges and exits that may be occurring ahead.
That last part ties into Enhanced Autopilot’s ‘Navigate on Autopilot’ feature. Using the Tesla navigation system built into the car, this feature is able to navigate on highways “from on-ramp to off-ramp." In other words you just need to sit back and be ready in case the car does something stupid, which can and does happen from time to time.
Enhanced Autopilot also comes with autonomous parking features as well. Autopark is capable of pulling into parallel and perpendicular parking spaces by itself. This feature will also check for empty parking spaces around you, just in case you’re really struggling to find a spot.
Finally, Smart Summon does the complete opposite. This feature prompts the car to pull out of a parking space, and navigate the parking lot towards you. Which is helpful if you’re parked in a tight space, or straight-up forgot where you left your car.
Enhanced Autopilot vs Full Self Driving: Full Self Driving Features
Despite its name, Tesla’s Full Self-Driving Autopilot does not mean your car is capable of driving itself. It’s something that has got Tesla in legal trouble more than once, notably in Germany and California . CEO Elon Musk has been promising various deadlines for true self driving for a few years now, but so far he hasn’t been able to put his money where his mouth is.
At the time of writing Full Self Driving offers all the same functionality as Basic and Enhanced Autopilot tiers. The only exclusive feature included in the public release of FSD is traffic light and stop sign control. Autosteer on city streets is listed as “coming soon," but is currently only available as part of the Full Self Driving Beta.
Tesla drivers can express their interest to join the FSD beta from their car’s infotainment screen, but the company is picky about who is allowed to take part. The bare essentials include owning a car with Full Self Driving, whether it's permanent or a subscription, and a Tesla Safety Score (visible in the app) of 95 or above. But even then it’s not guaranteed.
Tesla isn’t continually adding beta testers, so you need to be able to wait several weeks or months for the next intake — assuming Tesla even chooses you to take part. You’ll need to maintain your safety score throughout, and Tesla reserves the right to kick you out of the beta if your driving ability deteriorates.
Enhanced Autopilot vs Full Self Driving: Which should you buy?

To put it simply, Full Self Driving is incredibly expensive. $9,000 more than Enhanced Autopilot, as of the last price hike. And for that price you get traffic light and stop sign control, alongside a chance to join Tesla’s FSD beta; not a guarantee, a chance.
In the past, things were different. Until earlier this year Tesla drivers could only choose between Basic Autopilot and Full Self Driving. That made the cost of upgrading a little bit more justifiable, since you actually had something to show for it.
These days, now that Enhanced Autopilot is officially back as an option, you only have the promise of what could be, rather than what is actually available today.
Things could change, especially if Autosteer on City Streets is added to the public version of Full Self Driving. But right now we only have a promise from Elon Musk that it will happen in the near future. I know I wouldn’t want to bet $9,000 on Musk keeping his promises, given his history of doing the exact opposite .
Of course. Full Self Driving is only going to go up in price. Musk himself admitted that, and the cost has already risen in price multiple times since it launched. Originally costing $8,000, the price later rose to $10,000 in 2021, $12,000 in January 2022 and finally $15,000 in September.
By paying for FSD now, you’re essentially locking in the price now and betting that it’ll be worth it in the future. But right now, if you’re asking me, I’d stick with Enhanced Autopilot and save that $9,000 for something else.
Next: How do self-driving cars work? Everything you need to know .
Sign up to get the BEST of Tom’s Guide direct to your inbox.
Upgrade your life with a daily dose of the biggest tech news, lifestyle hacks and our curated analysis. Be the first to know about cutting-edge gadgets and the hottest deals.

Tom is the Tom's Guide's UK Phones Editor, tackling the latest smartphone news and vocally expressing his opinions about upcoming features or changes. It's long way from his days as editor of Gizmodo UK, when pretty much everything was on the table. He’s usually found trying to squeeze another giant Lego set onto the shelf, draining very large cups of coffee, or complaining about how terrible his Smart TV is.
Tesla just recalled every Cybertruck over dangerous accelerator pedal flaw — what you need to know
5 coolest cars we saw at the New York Auto Show 2024
5 Hulu shows to watch now with 100% on Rotten Tomatoes April 2024
Most Popular
- 2 Apple reportedly slicing Vision Pro shipments in half due to weakening demand
- 3 Razer's new Viper V3 Pro gaming mouse boasts an obscene 8000Hz polling rate
- 4 Ray-Ban Meta smart glasses just got a ton of upgrades, including new AI features and video calling
- 5 New 4K Chromecast with Google TV reportedly on the way — what we know
Ad-free. Influence-free. Powered by consumers.
The payment for your account couldn't be processed or you've canceled your account with us.
We don’t recognize that sign in. Your username maybe be your email address. Passwords are 6-20 characters with at least one number and letter.
We still don’t recognize that sign in. Retrieve your username. Reset your password.
Forgot your username or password ?
Don’t have an account?
- Account Settings
- My Benefits
- My Products
- Donate Donate
Save products you love, products you own and much more!
Other Membership Benefits:
Suggested Searches
- Become a Member
Car Ratings & Reviews
2024 Top Picks
Car Buying & Pricing
Which Car Brands Make the Best Vehicles?
Car Maintenance & Repair
Car Reliability Guide
Key Topics & News
Listen to the Talking Cars Podcast
Home & Garden
Bed & Bath
Top Picks From CR
Best Mattresses
Lawn & Garden
TOP PICKS FROM CR
Best Lawn Mowers and Tractors
Home Improvement
Home Improvement Essential
Best Wood Stains
Home Safety & Security
HOME SAFETY
Best DIY Home Security Systems
REPAIR OR REPLACE?
What to Do With a Broken Appliance
Small Appliances
Best Small Kitchen Appliances
Laundry & Cleaning
Best Washing Machines
Heating, Cooling & Air
Most Reliable Central Air-Conditioning Systems
Electronics
Home Entertainment
FIND YOUR NEW TV
Home Office
Cheapest Printers for Ink Costs
Smartphones & Wearables
BEST SMARTPHONES
Find the Right Phone for You
Digital Security & Privacy
MEMBER BENEFIT
CR Security Planner
Take Action
Ford’s BlueCruise Remains CR’s Top-Rated Active Driving Assistance System
Systems from Jaguar/Land Rover, Lucid, and Subaru are new to our rankings, and we also tested updated versions from Hyundai and Nissan
It’s equal parts eerie and amazing to experience Ford ’s BlueCruise hands-free driving feature as it takes over your car’s steering, braking, and acceleration while you travel down the highway.
The eerie part is watching the steering wheel turn back and forth on its own, making micro-adjustments to keep the car in the center of its lane, while the system also slows down or speeds up to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead. The amazement soon follows: With your hands off the wheel and relaxing on the armrests as the automated systems take charge, you might start to believe that the age of the self-driving car is finally upon us.
But while BlueCruise’s capabilities are impressive and can make driving more relaxing, cars that can truly and safely drive themselves remain a long way off.
BlueCruise is what’s known as an active driving assistance (ADA) system. In the simplest terms, ADA is the simultaneous use of a car’s adaptive cruise control (ACC) to control speed and lane centering assistance (LCA) to control steering. ACC is an advanced form of cruise control that brakes or accelerates to keep the car a set distance from vehicles traveling ahead of you in your lane. LCA provides steering support to keep the vehicle at or near the center of the lane.
“Systems like BlueCruise are an important advancement that can help make driving easier and less stressful,” says Jake Fisher, CR’s senior director of auto testing. For instance, it can allow drivers to relax their grip and even periodically let go of the steering wheel, while the car maintains a safe distance from other vehicles when driving on a straight, boring section of highway or when stuck in a traffic jam. ADA systems can also have safety benefits, such as potentially keeping you from crossing over a lane line into opposing traffic during a moment of inattention.
“But they don’t make a car self-driving at all,” Fisher says. “Instead, they create a new way of collaboratively driving with the computers in your car. When automakers do it the right way, it can make driving safer and more convenient. When they do it the wrong way, it can be dangerous.”
Though still relatively new, ADA systems are already available on more than 50 percent of 2023 model-year vehicles, according to CR’s data. So it’s likely that the next new car you buy will come with an ADA system as an option, if not as a standard feature.
Since our last test in late 2022, we’ve added systems from three other automakers into the mix— Jaguar / Land Rover , Lucid , and Subaru —that previously weren’t included. We also tested updated systems from Hyundai and Nissan . Still, even with the additional competition, and now a total of 17 tested systems, Ford’s BlueCruise remains CR’s top-rated ADA system, followed by Cadillac Super Cruise and Mercedes-Benz Driver Assistance. Tesla , once an innovator in ADA with its Autopilot system, remains in about the middle of the pack. (The new Nissan ProPILOT Assist 2.0 has leapfrogged above Tesla.) That’s because Tesla hasn’t changed Autopilot’s basic functionality much since it first came out, instead just adding more features to it, says Fisher: “After all this time, Autopilot still doesn’t allow collaborative steering and doesn’t have an effective driver monitoring system . While other automakers have evolved their ACC and LCA systems, Tesla has simply fallen behind.”
Our testers saw significant improvements with Hyundai’s Highway Driving Assist 2, which scored 12 points higher than the original system. This is mainly because the updated version’s LCA system does a much better job of keeping the vehicle near the center of the lane, rather than allowing it to ping-pong back and forth between the lane lines. While the original system still scores last of the 17 systems we’ve tested, Highway Driving Assist 2 ranks 11th.
Photo: John Powers/Consumer Reports Photo: John Powers/Consumer Reports
Systems to Help Keep the Driver Safe
Not all ADA systems are created equal. Fisher and other safety experts say that many of them are designed in a way that may lull drivers into complacency, giving them a false impression that the car is handling everything on their behalf. That can be dangerous if the ADA system encounters something it can’t handle, such as road construction or an emergency vehicle, and the driver is not prepared to take back control of the car quickly. In order for any ADA system to be used safely, the driver always needs to remain attentive.
Pnina Gershon, a research scientist at the MIT AgeLab and the MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics , points to data showing that drivers often develop overreliance on driving assistance systems after a relatively short period of use. “We observe frequent situations where the level of attention placed on the road is below what one would traditionally expect a driver to have, especially with the known limitations of these systems, which require drivers to be ready to regain control in a safe and timely manner,” Gershon says. The data also shows that distracted driving is more common when using driving automation systems. “Automation aims to free resources and, not surprisingly, drivers use these ‘freed-up’ resources to do other things than driving.”
The two ADA systems that CR rates highest, the Ford/Lincoln BlueCruise and General Motors’ Super Cruise (Chevrolet/Cadillac/GMC), use direct driver monitoring systems (DDMS) that require drivers to keep their eyes on the road even while the systems are automating steering, acceleration, and braking. Both point infrared cameras at the driver’s face and sound an alert if he or she stops paying attention to the road, even if just for a few seconds. If drivers don’t turn their eyes back to the road, the system soon begins to slow the car.
CR safety experts say that this type of DDMS is key to the safety of any ADA system—and, in fact, CR awards extra points to the Overall Score of tested models whose ADA systems are adequately equipped. Starting with 2024 model-year vehicles, we will deduct points if an ADA system doesn’t have adequate DDMS. Right now, only Ford and GM’s systems meet our criteria for earning additional points, but others could be available soon.
Most ADA systems, however, do not adequately monitor drivers. Instead, they simply require occasional hand pressure on the steering wheel to indicate that the driver is paying attention. This makes it too easy to just give the steering wheel a quick tug without actually looking out at the road. “If an automaker is going to equip a car with an ADA system, they should put in adequate safeguards—or not include both lane centering assistance and adaptive cruise control at all,” says Kelly Funkhouser , CR’s manager of vehicle technology.
Also of concern to CR’s safety experts are the ADA systems from some automakers that allow their vehicles to be driven for an inordinately long amount of time without requiring the driver to apply any pressure to the steering wheel, let alone make sure they are actually paying attention to the road. In our tests, both Mercedes-Benz and Tesla allowed the vehicle to drive down the highway hands-free for about 30 seconds before the first audible alert was given to the driver to put a hand back on the steering wheel. “That means the car could travel more than half a mile on a highway with hands off the wheel and the driver not paying attention at all—that’s a risky situation,” Funkhouser says.
But Hyundai’s latest Highway Driving Assist 2 is even worse. In our testing, the system consistently allowed our drivers to keep their hands fully off the steering wheel for 2 minutes and 15 seconds before the first audible warning was given to put their hands back on the wheel. “That’s simply irresponsible on the part of the automaker,” Funkhouser says.
What We Tested
We only included vehicles in our testing that were equipped with a system that allows for the simultaneous use of ACC and LCA at highway speeds. Models from Mazda , Porsche , Stellantis ( Alfa Romeo , Chrysler , Dodge , Fiat , Jeep , Ram ) were not included because we didn’t have a vehicle equipped with these features in our fleet when the tests were conducted.
How We Rated the Systems
The 17 active driving assistance systems we tested were put through their paces around the track at our 327-acre Auto Test Center in Connecticut and on a 50-mile loop on public roads between September and December 2022, and between June and August 2023. Each system was rated for its performance in 40 separate tests, such as steering the car, controlling the speed, and keeping the driver safe and engaged with the act of driving. Additional features such as automatic lane changes or reacting to traffic lights were not evaluated in these tests. (Take a tour of Consumer Reports’ $1 million ADAS test loop .)
The specific vehicles we tested generally reflect the performance of other models within each automaker’s lineup equipped with the same systems, but there can be differences among models, model years, and packages that could affect some parameters of how the system operates.
CR testers evaluated the way each of the 17 systems performed within five specific categories: capabilities and performance , keeping the driver engaged , ease of use , clear when safe to use , and unresponsive driver .
Capabilities and Performance
Keeping Driver Engaged
Ease of Use
Clear when safe to use.
Unresponsive Driver
Consumer Reports' ADAS Loop
CR expands the tract at its Auto Test Center to help evaluate advanced auto technology.
Unlike active safety systems , such as automatic emergency braking (AEB), that intervene only momentarily when necessary to help prevent a collision, active driving assistance systems provide continuous support intended to make driving easier—for instance, when you’re on a long, boring highway drive or when you get stuck in a slow-moving traffic jam. For this category, we judged how well each system’s lane centering assistance (LCA) kept the vehicle in the center of the lane, as well as how smoothly and intuitively the adaptive cruise control (ACC) could adjust its speed behind other cars.
When it comes to LCA, the systems from Ford, Mercedes-Benz, and Tesla all gave smooth steering inputs and did a good job of keeping the car at or near the center of the lane on both straight and curvy roads. This type of performance gives confidence to the driver that these systems are highly capable.
The previous version of the Hyundai / Kia / Genesis Highway Driving Assist system was dinged for its less capable steering assistance, which caused the vehicle to ping-pong back and forth between the lane lines—even though it’s intended to stay near the center of the lane. At times it also moved uncomfortably close to a vehicle in an adjacent lane, and our testers noted that occasionally the system was incapable of keeping the vehicle within the lane through curves. The updated Hyundai/Kia/Genesis system—called Highway Driving Assist 2 (evaluated on a Hyundai Ioniq 6 )—performed much better thanks to its substantially improved LCA system, which no longer struggles to keep the vehicle near the center of the lane.
The Jaguar/Land Rover Adaptive Cruise w/Steer Assist (tested on a Land Rover Range Rover Sport ) performed the worst of any system at keeping the vehicle centered, or even within the lane, on city streets. There were many times the system would suddenly go into a “standby” mode and stop giving steering assistance, and then depart the lane. Other times the steering-assistance remained engaged but the driver still had to intervene to keep the vehicle from crossing over a lane line. It faired much better on the highway—in fact, it almost felt like an entirely different system.
Volvo/Polestar’s Pilot Assist system lost points because it frequently goes into “standby” mode—which is when the system is not giving steering assistance—without a clear warning to the driver. The periodic mode changes create uncertainty as to whether the system is actively providing steering assistance or not, resulting in the driver frequently looking at the instrument panel for verification rather than keeping their eyes on the road.
The Mercedes and Lexus / Toyota ACC systems scored top marks for their well-tuned following-gap distance settings. Our testers found the closest setting to be comfortable in high-traffic areas while still not allowing so much space that other vehicles would continually cut in ahead. We also like that the Mercedes and Subaru ACC systems have settings that allow the driver to adjust the deceleration and acceleration force with which it slows down and speeds back up for traffic ahead.
BMW ’s Driving Assistance Professional and GM’s Super Cruise have a driver monitoring camera that ensures the operator is looking at the road ahead when the ACC system brings the vehicle to a full stop, for up to 30 seconds. This provides the convenience of a stop-and-go feature in most traffic jam situations, without the hassle of having to re-engage ACC once traffic ahead starts moving forward again. The camera is there as a safeguard to ensure that drivers are watching the roadway. Most of the other systems change the ACC mode to standby after the vehicle has been stopped for just a few seconds, which eliminates the benefits of using ACC in stop-and-go traffic.
The ACC function of Tesla’s Autopilot system is capable of stopping the car, such as at a red light behind another vehicle, for an unlimited amount of time before resuming again. But without an adequate driver monitoring camera, this is potentially unsafe as there’s no way to know whether the driver is still paying attention when the vehicle starts moving again.
Manager of vehicle technology for Consumer Reports
Illustration: Chris Griggs/Consumer Reports Illustration: Chris Griggs/Consumer Reports
Keeping the Driver Engaged
When a system is controlling a car’s speed and steering, there’s a risk that its driver might feel more free to pick up a cell phone, eat a messy burger, or engage in other reckless, distracting behavior. That’s why we think it’s essential that ADA systems use direct driver monitoring systems (DDMS) to make sure the driver is paying attention to the road. A good system will encourage the driver to stay actively engaged, such as by allowing the driver to give steering inputs without fear of the LCA function shutting off.
A camera-based driver monitoring system that uses head- and eye-tracking technology checks to see whether the driver is looking at the road, and that’s why Ford’s BlueCruise and GM’s Super Cruise are far above the competition when it comes to keeping the driver engaged. While some other systems do have cameras, we found that they will still function even if their cameras are covered, and in some cases the cameras can actually be turned off—neither of which is the case with BlueCruise or Super Cruise. The systems without driver-monitoring cameras require only that the driver place their hands on the wheel every once in a while, which doesn’t necessarily mean the driver is looking at the road ahead.
Ford’s BlueCruise sets a high standard among ADA systems, aided by an infrared camera that monitors the driver’s eyes to determine whether they are looking at the road. If the driver glances away from the road for more than about 5 seconds—whether to look at their cell phone or fiddle with the infotainment screen, or because they fell asleep—the system will give the driver a visual warning and an audible chime. When operating on pre-mapped highways that allow for hands-free operation, BlueCruise prompts the driver in advance of risky scenarios, such as lane merges or curves, to place their hands back on the wheel. This feature encourages drivers to be ready to steer if needed and doesn’t turn the LCA system off when they do.
Both Lucid’s Highway Assist and Nissan’s ProPILOT Assist 2.0 have driver-monitoring camera hardware already in the vehicle. However, in both systems the camera can be toggled “off” within a settings menu, yet the ADA system can still be used. When we asked Nissan the reasoning behind giving drivers the ability to use the new Ariya EV’s ADA system without having to also use the driver-monitoring camera, a spokesperson told us that the automaker would “... continue to monitor the landscape of this emerging technology along with customer feedback and regulatory requirements but (we have) no plans at this time to remove that option on ProPilot Assist for our customers.”
“It’s disappointing that both Lucid and Nissan have this equipment in their vehicles, yet they aren’t using it to the fullest, safest potential,” Funkhouser says.
CR reached out to automakers that have an ADA system but that don’t have a camera-based driver-monitoring system, seeking comment and information on their plans. Several automakers did not respond, while others declined to provide further details, saying the information is proprietary. Of those that did respond, Polestar (Volvo’s EV sub-brand) said DDMS will be included as a standard feature in its upcoming 2024 Polestar 3 SUV . Audi told us that DDMS “is not available at this time.” Rivian acknowledged that its camera is turned off in most vehicles while its Highway Assist system is active, and said it would keep CR posted on its plans for adding DDMS. Mercedes equips some models, like the EQS and S-Class , with a driver-facing camera to detect inattention, but the ADA system continues to operate even if the system deems the driver to be inattentive. And the driver-monitoring camera can be switched off, even when using ADA.
When there’s a seamless collaboration between the lane centering assistance system and the driver’s own steering inputs, it encourages the driver to stay alert and in control.
BMW and Mercedes ranked at the top when it comes to allowing the driver to give their own steering inputs (known as “collaborative driving”), for example, if you need to swerve out of the lane to avoid a pothole or give some berth to a cyclist. BlueCruise also allows for collaborative driving, and here it distances itself from Super Cruise, Autopilot, Lucid’s Highway Assist, and Rivian’s Highway Assist, all of which immediately disengage the LCA if the driver turns the steering wheel, which—annoyingly—forces the driver to re-engage the system afterward each time. This tells the driver that either the system is steering or the driver, but you can’t have it both ways.
For many people, the next new car they buy will be their first experience with an active driving assistance system. Because these systems are still so new, it’s important for auto manufacturers to make them as easy to use as possible, with simple controls, clear displays, and good feedback regarding the system’s status so that a driver will know what the system is doing and why it’s operating in a certain way.
Our testers evaluated how easy it was for drivers to engage the systems and make adjustments to the settings. They also reviewed the types and amount of information displayed to drivers, and how easy it was to know and understand what the system was doing.
The Highway Driving Assist and Highway Driving Assist 2 systems found in Hyundai/Kia/Genesis models were the top-rated systems in terms of ease of use (the controls are essentially identical between the two systems), due in large part to a strong showing in the “controls” category. Both the Hyundai/Kia/Genesis systems and Honda Sensing/ Acura Watch have separate controls on the steering wheel enabling the driver to activate ACC and LCA independently, which allows drivers to experience and understand each feature on its own. This makes it possible, for example, for the driver to use LCA without ACC if they want. And it prevents the potential confusion of, say, the LCA automatically engaging when the driver activates ACC.
There should be distinct, independent controls for ACC and LCA activation. Combining them into either a single control or a multistep activation removes the freedom for drivers to use each feature on its own. It also implies that the system is more capable than the sum of the two features alone.
Rivian, BMW, and Mercedes scored very well in “displays.” That’s because the driver’s instrument panel in these vehicles provides detailed information regarding lane lines, showing, for example, how close your vehicle is to the lines and to the surrounding traffic. This helps drivers understand what the system is “seeing,” and thus why the system is behaving the way it is.
By contrast, Nissan/Infiniti’s confusing and poorly labeled symbols on the steering wheel make ProPILOT Assist and the updated ProPILOT Assist 2.0 unintuitive to use and hurt its “ease of use” score.
GM’s Super Cruise would have scored the lowest for “displays” if it weren’t for the bright green LED indicator on the top of the steering wheel rim, which makes it clear when the system is engaged. Beyond that, Super Cruise offers little information in the instrument panel beyond a small, steering wheel icon that indicates the system is active. It doesn’t, for example, show a display of the car, lane lines, or the car ahead, as other systems do.
The latest ADA systems are safest to use either on long highway drives or when you’re stuck in a traffic jam—situations in which they can best reduce driver fatigue and stress. On the other hand, using these systems on narrow, curvy roads or around pedestrians can be dangerous and stressful for drivers.
We evaluated the systems in terms of how clearly they communicate in real time about when drivers should—and should not—be using the technology. We also looked at how well they "explain" themselves in instances when the system won’t engage or suddenly turns itself off.
While ADA systems are generally not designed for narrow, curvy roads, most systems do allow drivers to use them in those environments. We think it’s smart that GM’s Super Cruise, Lucid’s Highway Assist, and Rivian’s Highway Assist use GPS-based geofencing to ensure operation within relatively safe driving environments, such as divided highways.
A big difference between Ford’s BlueCruise, compared with GM’s Super Cruise and Lucid’s Highway Assist, is that BlueCruise can be used even when you’re not driving on the highway, while Super Cruise and Highway Assist cannot. Ford is able to incorporate LCA on regular, nonhighway roads because the system requires not just eyes on the road (via the DDMS) but also hands on the steering wheel in certain situations. We also like that even when driving on pre-mapped divided highways that are theoretically “hands-free zones,” BlueCruise requires drivers to place their hands back on the wheel in advance of risky upcoming scenarios, such as sharp curves or lane merges.
Jaguar/Land Rover, Lexus/Toyota, Tesla, and Volvo rank toward the bottom of the chart in terms of making it clear when they are (and are not) safe to use. Tesla’s Autopilot and Lexus’ Safety System+ 3.0 are both capable of being used even when there’s only a single lane line down the middle of the road, which can lead to the driver using them in an unsafe situation. The systems try to create a “center” of the lane but often end up steering too close to the unlined edge of the road.
We were disappointed with Volvo/Polestar’s Pilot Assist system for numerous reasons, including that we found too many instances where the system switched itself into standby mode—meaning the ACC is still controlling the car’s speed, but the LCA is no longer giving any steering assistance—for no apparent reason. “The result is that Pilot Assist isn’t all that helpful to the driver. Much of this could have been solved had Volvo simply installed a driver-facing camera,” Funkhouser says. We plan to evaluate the Polestar 3 when it comes out with a DDMS.
Other than BlueCruise and Super Cruise, the ADA systems we tested don’t make it clear to drivers when they are safe to use. Plus, we find that most vehicle owner’s manuals are overly vague, making the systems seem more like tools used to reduce manufacturer liability rather than to help drivers fully understand, and use, these high-tech features.
An Unresponsive Driver
Systems that are capable of controlling the steering and speed of a vehicle should also be designed to help the driver at moments of greatest need, such as an incapacitating health emergency or if the driver falls asleep at the wheel. We evaluated how effectively the systems escalate driver warnings and assume steering and speed control in such scenarios, paying particular attention to how long it takes before the first audible warning sounds (because an inattentive or sleeping driver probably would not see a visual warning).
Although most vehicles in our testing can’t monitor the driver’s eyes, most do have a system that will signal an alert if the system deems the driver to be inattentive for a sustained period and then bring the car to a stop (with hazard lights on) and even call for outside help.
Ford’s BlueCruise is the best at discerning when a driver is being inattentive, thanks to its DDMS. If the system detects that the driver isn’t looking forward for 4 to 5 seconds, an audible warning alerts him or her to watch the road.
If the driver is unresponsive, however, BlueCruise merely slows the vehicle to 6 mph and continues driving in the same lane indefinitely. It doesn’t bring the car to a complete stop, put on the emergency flashers, or call for help. By contrast, with GM’s Super Cruise and Mercedes’ Driver Assistance, if the driver doesn’t respond to prompts from the system to re-engage, the car will turn on the emergency flashers, bring the car to a full stop (in whatever lane it’s currently traveling), and call for help. We think that’s the smarter response.
It’s alarming that, with the Honda and Kia systems, if a driver becomes unresponsive to warnings to put their hands on the steering wheel, the ADA systems will shut off before bringing the vehicle to a stop. This means that if the driver is distracted or medically impaired, the vehicle will just continue to roll forward—potentially off the road at speed—without any steering assistance or speed control, until it eventually rolls to a stop or runs into something.
Hyundai’s newer system—Highway Driving Assist 2—isn’t any better than the original system in this regard. In fact, in some ways it’s worse. Once Highway Driving Assist 2 determines that the driver is unresponsive, the system deactivates the LCA aspect, but the ACC will maintain the vehicle at a speed of 40 mph, without steering assistance, rather than letting the vehicle roll to a stop. Similarly, Subaru’s system also shuts off the LCA but keeps ACC on at the set speed without slowing.
Other than BlueCruise and Super Cruise, none of the systems we tested will alert the driver to pay attention if they are merely resting a hand on the steering wheel with a light amount of pressure, despite the fact that the driver may not be looking at the road and could even be asleep.
Test-Drive Before You Buy
When shopping for a new car, be sure to have the salesperson walk you through the details of how these advanced technologies work and how to adjust any specific settings.
As these systems become available on more new cars, it’s important that consumers understand their limitations. No matter what the automakers might imply in their marketing, none of the systems we tested here are capable of doing the driving for you.
“Automakers also need to realize that the more capable they develop a system in terms of driver assistance, the greater the chances are that the driver might tune out and try to leave the driving to the car,” Funkhouser says. “That’s why camera-based, direct driver monitoring is so critical and should be an essential tool of any good active driving assistance system going forward.”
Active Driving Assistance Systems in Action
Active Driving Assistance systems rely on several of a car’s high-tech features working together. Watch the videos below, created using CR’s fleet of test vehicles, to learn the difference among lane centering assistance, lane departure warning, and lane keeping assistance; how adaptive cruise control works; what makes for an effective direct driver monitoring system; and which ADA systems performed best in our overall tests.
More on ADAS Systems

Mike Monticello
Mike Monticello is the manager of road tests and reviews for the autos team at Consumer Reports. He has been with CR since 2016. Mike has been evaluating and writing about cars for nearly 25 years, having previously worked at Road & Track magazine and Edmunds.com. On the weekends, he usually switches from four wheels to two, riding one of his mountain bikes or motorcycles. Follow him on Twitter @MikeMonticello .
Sharing is Nice
We respect your privacy . All email addresses you provide will be used just for sending this story.
Trending in Car Safety
Popular Cars to Avoid and What to Buy Instead
Best Cars of the Year: 10 Top Picks of 2024
Safest New Cars of 2024, According to the IIHS
Best Used Cars for You
Free Shipping Over $100

Forgot your password?
March 01, 2023
Understanding Tesla's different Autopilot software packages
Guest post: Blane Erwin, Current Automotive
It might not be robotaxi-ready yet, but Autopilot is already one of the leading semi-autonomous driving software suites available today. It has tons of features, is constantly being improved upon, and is the single biggest option most consider when considering a Tesla.
Source: Tesla
It’s also one of the most confusing features from Tesla. With four different hardware versions and four different software packages released over the years, it’s tough to keep track of what was available when, and what each system can do. It’s easier to understand the software once you know about the hardware that makes it all work. For a quick refresher, check out our comprehensive overview of Tesla's Autopilot Hardware .
In short, Autopilot is really just a catch-all term that refers to Tesla’s entire suite of semi-autonomous driving features. Each feature has a specific task, such as maintaining speed, steering, or parking. Over the years, Tesla has sold four different Autopilot software packages that bundle these features together in different ways.
Tesla Autopilot Features
Traffic Aware Cruise Control uses the Tesla’s radar to lock-on to the vehicle in front of it and match its speed. Unlike many other automaker’s adaptive cruise control systems, Traffic Aware Cruise Control will bring Tesla all the way down to a stop and back up to speed again with no driver input required.
Autosteer uses the Tesla’s cameras to track lane lines. The car will then provide steering input necessary to keep a Tesla centered in its lane. While many other automakers use reactive “lane keep assist” systems that will bounce the car off of lane lines, Tesla actually steers proactively to handle relatively significant curves in the road. It cannot currently handle turns at intersections, and Tesla requires the driver to keep their hands on the wheel for the ability to make fast corrections as needed.
Auto Lane Change will automatically make a lane change. Initiate the lane change with the turn signal, indicating the desired lane. Autopilot will verify (or wait) for that lane to clear, then move the car over on its own.
Autopark will park the Tesla autonomously – hands off, for real. Drive at low speeds along parking spots, waiting for the screen to indicate that it sees a parking spot. The spot needs to be near other vehicles, as the car uses its sonar sensors to look for the space – it can’t see the painted lines. When it does find a suitable spot, put the car in reverse and click “Begin” on the Autopark prompt on the center screen. Autopark can park in both parallel and perpendicular parking spots.
Youtube: Current Automotive
Summon allows the car to move without anyone inside of it, and it comes in two flavors: Basic Summon and Smart Summon. Basic Summon only allows straight forward and backwards movement while the driver pushes a button on the Tesla App. Smart Summon will enable the Tesla to autonomously navigate its way to the driver in a parking lot.
Navigate on Autopilot (beta) allows semi-autonomous driving and navigation from on-ramp to off-ramp on the highway. If the driver enters a destination that requires highway driving into the navigation system, an option for Navigate on Autopilot will appear. Navigate on Autopilot will make lane changes to overtake traffic, move out of the passing lane, make exits, and will travel through highway interchanges with no driver input required.
Stop Sign and Traffic Light Control (beta) is the first feature meant for use on city streets. Tesla vehicles with this feature can see and respond to stop signs and traffic signals. As of right now, the car will slow down for all signals (even if they’re green). The driver must give a confirmation tap on the drive selector stalk or accelerator pedal for the car to continue through an intersection.
Autosteer on City Streets (unreleased) is still unknown in scope. Based on the name, a reasonable expectation might be that it will be able to handle sharper turns typical of city streets and turn through intersections after the driver indicates the turn with the stalk.
Tesla Autopilot Software Packages
The above features have been bundled in four different ways over the years, as laid out in the chart below. Please note that this chart reflects the historical price for Enhanced Autopilot, not the upgrade Tesla suddenly made available from September 19 to September 30, 2020. During this brief time period, vehicles with base Autopilot will be eligible to upgrade to Enhanced Autopilot for $4,000. Full Self Driving remains a $5,000 upgrade for vehicles with Enhanced Autopilot, so it will be cheaper for vehicles with Autopilot to go straight to Full Self Driving – a total of $8,000 – than it would for them to first upgrade to Enhanced Autopilot, then upgrade again to Full Self Driving – a total of $9,000.
Source: Current Automotive
Full Self Driving is listed twice because it has been sold during two distinct time periods. Any car with Full Self Driving will have the same features, but the price paid for FSD may have differed depending on the time it was purchased.
Upgrade paths are available for all vehicles with any version of Autopilot Hardware. Tesla vehicles with Autopilot Hardware 1.0 but without Autopilot 1 software can still upgrade today, even though Autopilot 1 hasn’t been available new since 2016.
Vehicles with Autopilot Hardware 2.0 or greater can upgrade to basic Autopilot for $3,000, and cars with Basic Autopilot or Enhanced Autopilot can upgrade to Full Self Driving for $8,000 and $5,000 respectively.
Tesla has slowly been raising the price of Full Self Driving and may continue to do so in the future. The company has also said plans are in place to offer subscription options by the end of the year.
This story is an excerpt from an earlier article via Current Automotive ; Editor's Note: Current Automotive is the first-ever U.S. car retailer focused exclusively on used electric cars launched by two former Tesla employees.
- Autonomous Vehicle
- self-driving cars
- Tesla Autopilot
- Previous post
In same blog

Tesla is Leading the Pack in Long-Term Maintenance Costs

The Electric Vehicle Revolution: Charging Infrastructure Expansion in the U.S.

Tesla Recalls All Cybertrucks Due to Accelerator Pedal Issue
What's new.

- Best Sellers
- Wheels & Accessories
- Maintenance
- Cleaning & Detailing
- Garage & Tools
- Roadside Emergency
- Gifts & Apparel
- Shop by Brand
- Evannex Sales
- Clearance Items
- In The News
- Testimonials
- Improve Your Tesla
- Learn About Tesla
- choosing a selection results in a full page refresh
Cars for sale
Sell my car, car research, sign in, tesla autopilot and full self-driving vs. gm super cruise vs. ford bluecruise, tesla took an early lead in the race to automate driving tasks, but gm and ford have beaten the start-up to delivering hands-free driving..

Article QuickTakes
Tesla Autopilot
Tesla full self-driving capability, general motors super cruise, ford bluecruise.
The past decade has seen a sharp rise in the availability and capability of advanced driver-assistance systems. Many mainstream vehicles now have blind-spot monitoring, which informs you when traffic is lurking next to your rear-quarter panel, and automated emergency braking, which slows the vehicle to mitigate or prevent an imminent rear-end collision. Cruise control has evolved into adaptive cruise control, which uses radar, cameras, and/or laser to track and match the speed of the vehicle ahead of you.
On the cutting edge of driver-assistance technology, a few automakers have even released technologies that make it possible for you to remove your hands from the steering wheel in certain circumstances. General Motors is one of them, with its highway-limited Super Cruise system, and Ford is another, with its similarly capable BlueCruise. And then there’s Tesla. Its Autopilot and Full Self-Driving Capability tech doesn’t allow for hands-free motoring, but it can control the vehicle and negotiate traffic with a driver loosely holding the steering wheel.
If you’re interested in a vehicle with this kind of advanced driver-assistance technology, this primer will help you understand how GM’s, Ford’s, and Tesla’s systems compare.
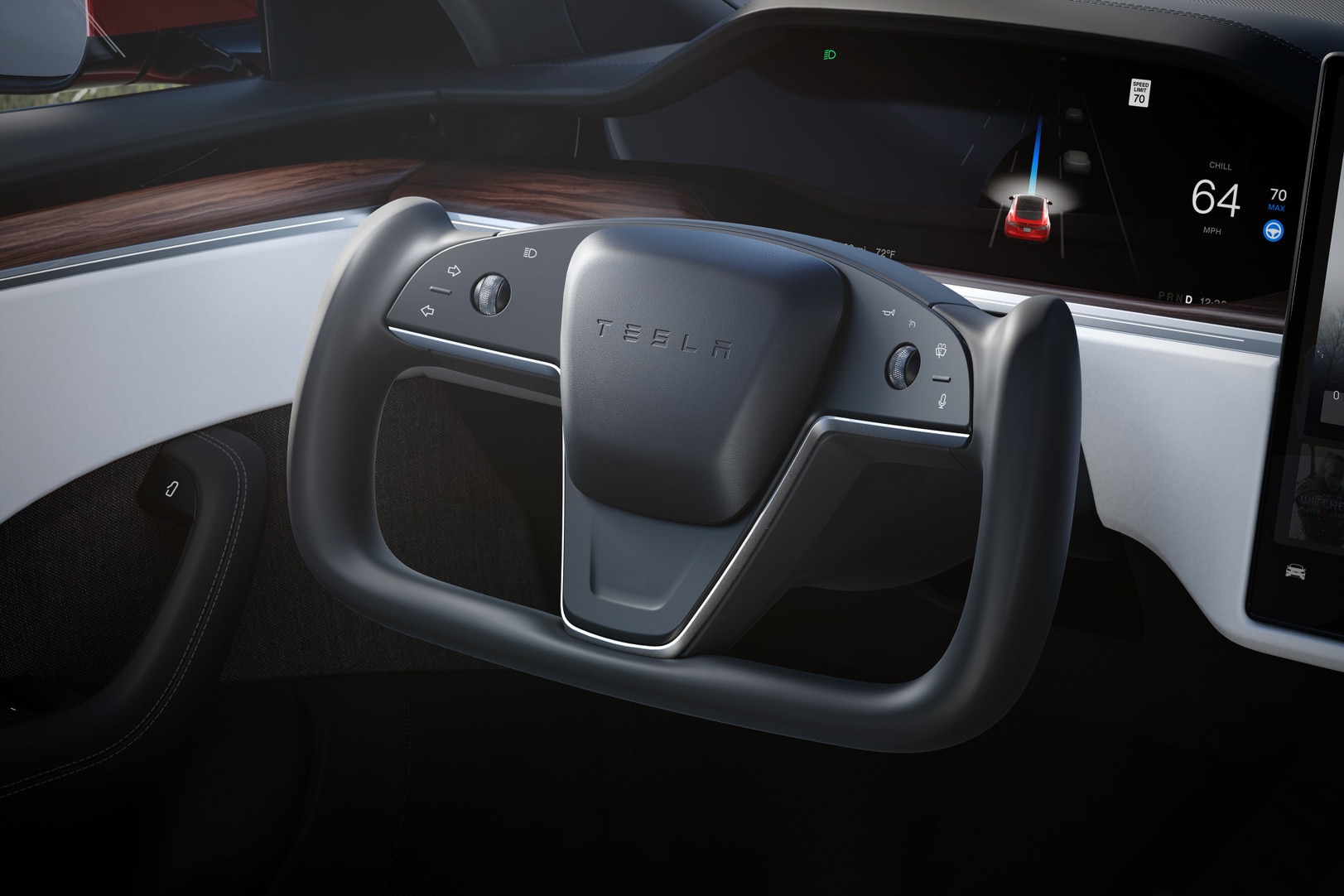

Released in 2015, Tesla’s Autopilot captivated consumers, investors, and the auto industry with its ability to accelerate, brake, and steer the vehicle. It gave the impression that the car was capable of driving itself, even if it was designed to be used by an attentive driver with hands on the wheel and ready to take control at any moment.
As other automakers have upgraded from lane-departure warning to lane-keeping assistance systems to lane-centering systems, the Tesla technology that once seemed so futuristic is now common. Currently, the Autopilot tech suite consists of adaptive cruise control and Autosteer, Tesla’s lane-centering system. Competitors’ products, such as Honda Sensing Suite and Kia Highway Driving Assist, have the same capabilities as Autopilot.
Autopilot is standard on every new Tesla on sale today: the Model 3, Model S, Model Y, and Model X. Depending on the model and age of the vehicle, Autopilot uses radar, ultrasonic sensors, and/or cameras to track lane markings and vehicles around them. And while this wasn’t always the case, Tesla now monitors driver engagement, using a torque sensor to detect that the driver has a hand on the steering wheel and, in certain new models, a camera above the rearview mirror to ensure drivers are alert. If a driver removes their hands from the wheel and their eyes from the road, the system will audibly warn them to act. If they continue to disobey the car’s orders, Autopilot will shut down and the vehicle will slow to a stop.
Tesla, believing it can achieve autonomy using just cameras and ultrasonic sensors, no longer equips the Model 3 and Model Y with radar. (The Model S and Model X will likely lose radar, too, at some point.) The reliance on cameras makes Autopilot and FSD more susceptible to perception issues in rain, snow, and fog. Faded lane markings and abrupt road changes in construction zones can also trip up the system.

Tesla’s more advanced, extra-cost driver-assistance system is called Full Self-Driving Capability (FSD), but don’t let the name fool you: FSD is not capable of autonomous driving, wherein the driver can simply punch in a destination and let the car do the rest. The driver still must keep his or her hands on the wheel and eyes on the road when using FSD.
The FSD package builds on Autopilot with additional capabilities, including some “beta” features that are still under development and should be used with caution. One of those features, called Navigate on Autopilot, uses the destination typed into the navigation system and, working in conjunction with Autopilot, seeks to handle the highway portion of your trip. When operating properly, it should guide your vehicle from on-ramp to off-ramp, even automatically changing lanes to pass slower vehicles or to navigate an interchange. As with Autopilot, the driver must remain alert with hands on the wheel and eyes on the road while the car does this.
When Autopilot is enabled but there’s no destination in the navigation system, FSD’s Auto Lane Change can move the vehicle into an adjacent lane to pass slower traffic. The other beta feature, called Traffic and Stop Sign Control, reads stop signs and traffic signals and tells the car to behave accordingly. This technology similarly requires active supervision.
FSD also adds a host of parking assistance features. Summon allows the driver to exit the car and move their Tesla forward or backward in and out of a tight parking spot via a mobile app. Using Smart Summon, the car will exit a parking spot and maneuver around a parking lot to come pick the driver up. FSD will also parallel-park for you (with a driver behind the wheel) at the push of a button.
Autopilot and FSD can be activated nearly everywhere, and that gives Tesla a huge bragging point over the competition, although that doesn’t mean drivers should use them everywhere. The real-world capabilities of these systems vary based on a variety of factors. In many city and suburban settings, the Tesla systems are unpredictable and unreliable, and using them is a nuisance. Users have noted that they may swerve suddenly or may not detect major obstacles. Teslas using Autopilot have also been known to collide with stationary emergency vehicles, most often at night. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration recently opened an investigation in hopes of understanding why those crashes occurred.
The Model 3, Model S, Model Y, and Model X are all available with FSD at a cost of $10,000. For those who can’t afford or justify such a high premium, the automaker offers a FSD subscription plan to owners. The monthly cost is either $99 or $199, depending on what hardware a vehicle has, which determines what FSD features will be activated. Used Teslas with the necessary hardware (specifically version 3.0 or newer) are also compatible with FSD. Vehicles equipped with older technology can be retrofitted with this equipment for $1,500.
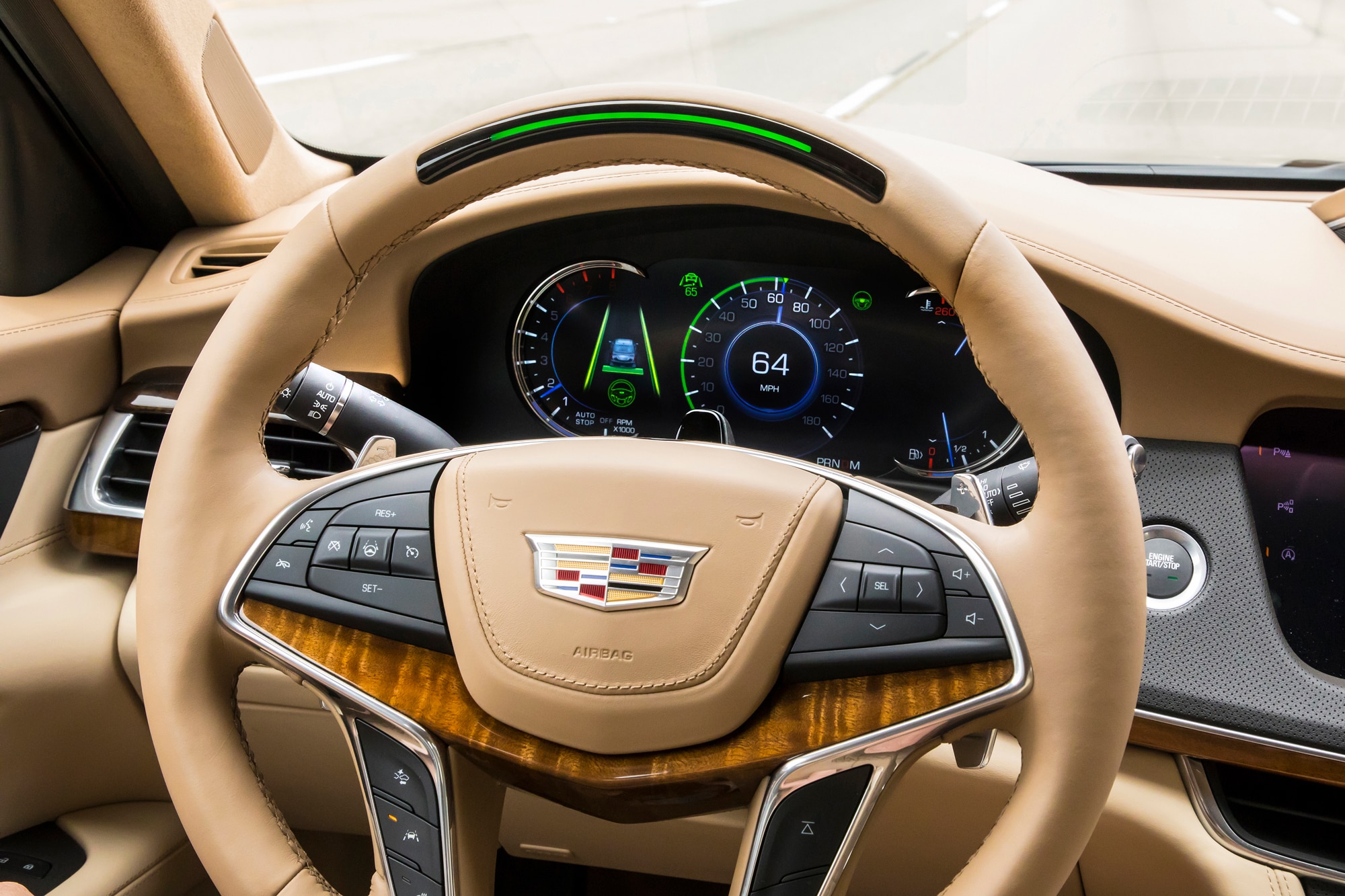

In addition to lane-keeping assistance and adaptive cruise control, Super Cruise allows for hands-free operation on 200,000 miles of select, pre-mapped divided highways in North America. Introduced in 2017 on the Cadillac CT6 as the first hands-free driver-assistance system available on a production car in the U.S., it has since trickled down to other brands and vehicles under the GM umbrella.
The latest version supports automatic lane changes to keep the vehicle at an optimal speed and, on certain trucks and SUVs, a trailering feature. The latter takes into account the weight of a trailer and how it affects the vehicle’s driving dynamics and then determines the best following distance. It will also make steering adjustments to keep the trailer in line.
Super Cruise uses a combination of high-definition maps, GPS, radar, and cameras to monitor the road and other vehicles. The mapping data informs the system of what’s coming up, giving the car time to anticipate, say, a tight curve by slowing down in advance. The maps are also frequently updated so that the system can hand control back to a driver as the vehicle approaches a construction zone.
In addition to audio and dashboard alerts, a light bar on the steering wheel changes color to signify when Super Cruise is active. A camera mounted on the steering column makes sure the driver continues to pay attention, and capacitive sensors in the steering wheel let the car know when the driver has resumed control.
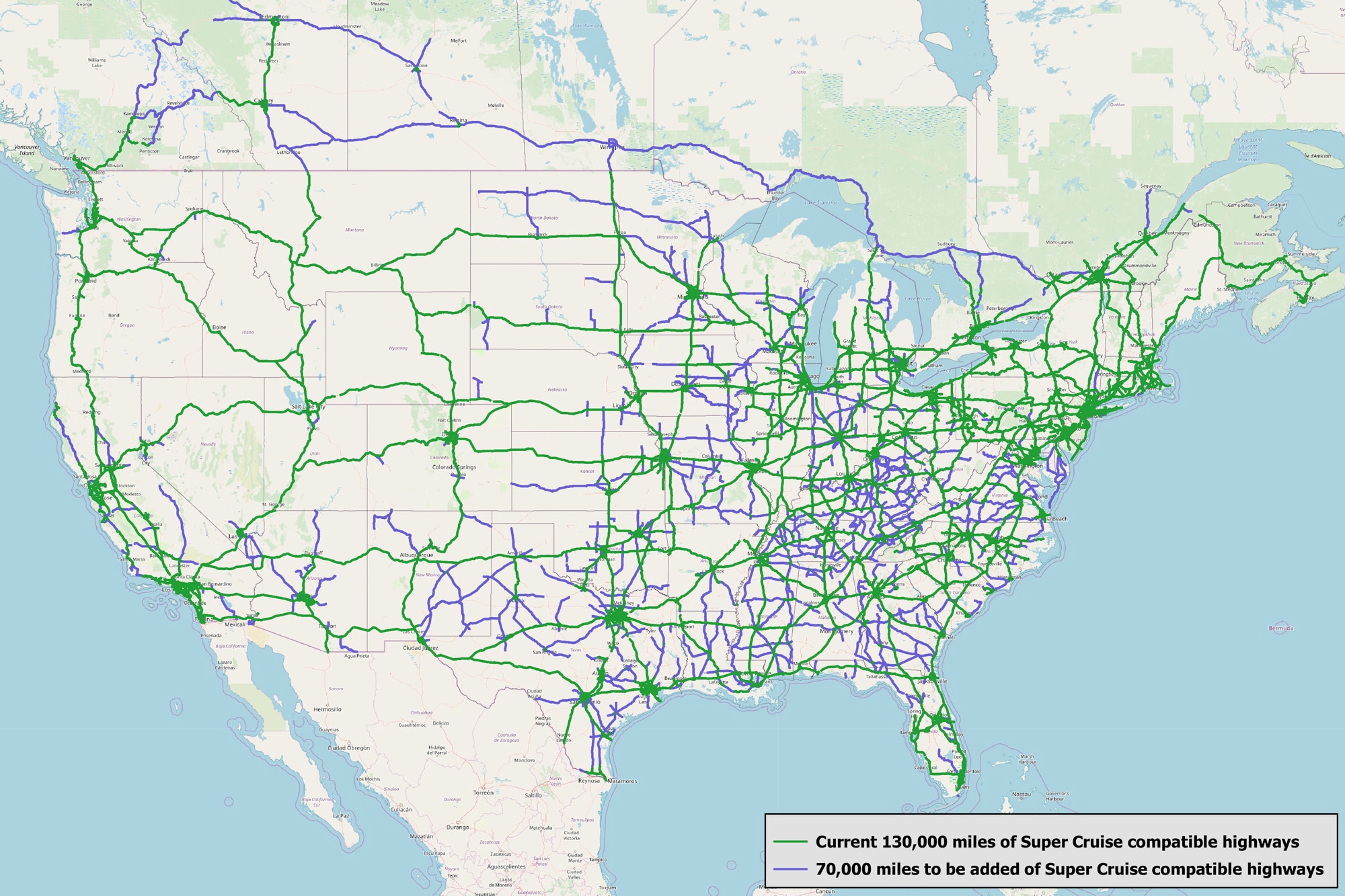
As the first hands-free driver-assistance feature to reach the market, Super Cruise has enjoyed several years of real-world testing, allowing GM to examine and improve the feature set as well as expand its system's coverage area while the competition rushes to catch up. But as we mentioned earlier, Super Cruise works only on divided highways, and it can’t navigate every situation. Road construction and faded lane markings may cause it to disengage. On the plus side, when that does happen, the driver knows right away via the highly visible light bar in the steering-wheel rim. Fail to take charge and the vehicle will prompt you with beeps and a voice command before coasting to a stop (at which point, you won't be able to re-engage the system until the next ignition cycle).
For 2022, GM intended to offer Super Cruise in the Cadillac Escalade, CT4, CT5, and XT6, the GMC Sierra and Hummer EV, and the Chevrolet Silverado and Bolt EUV. Unfortunately, the chip shortage delayed those plans, and currently only the Chevy Bolt EUV offers the tech, to the tune of $2,200.
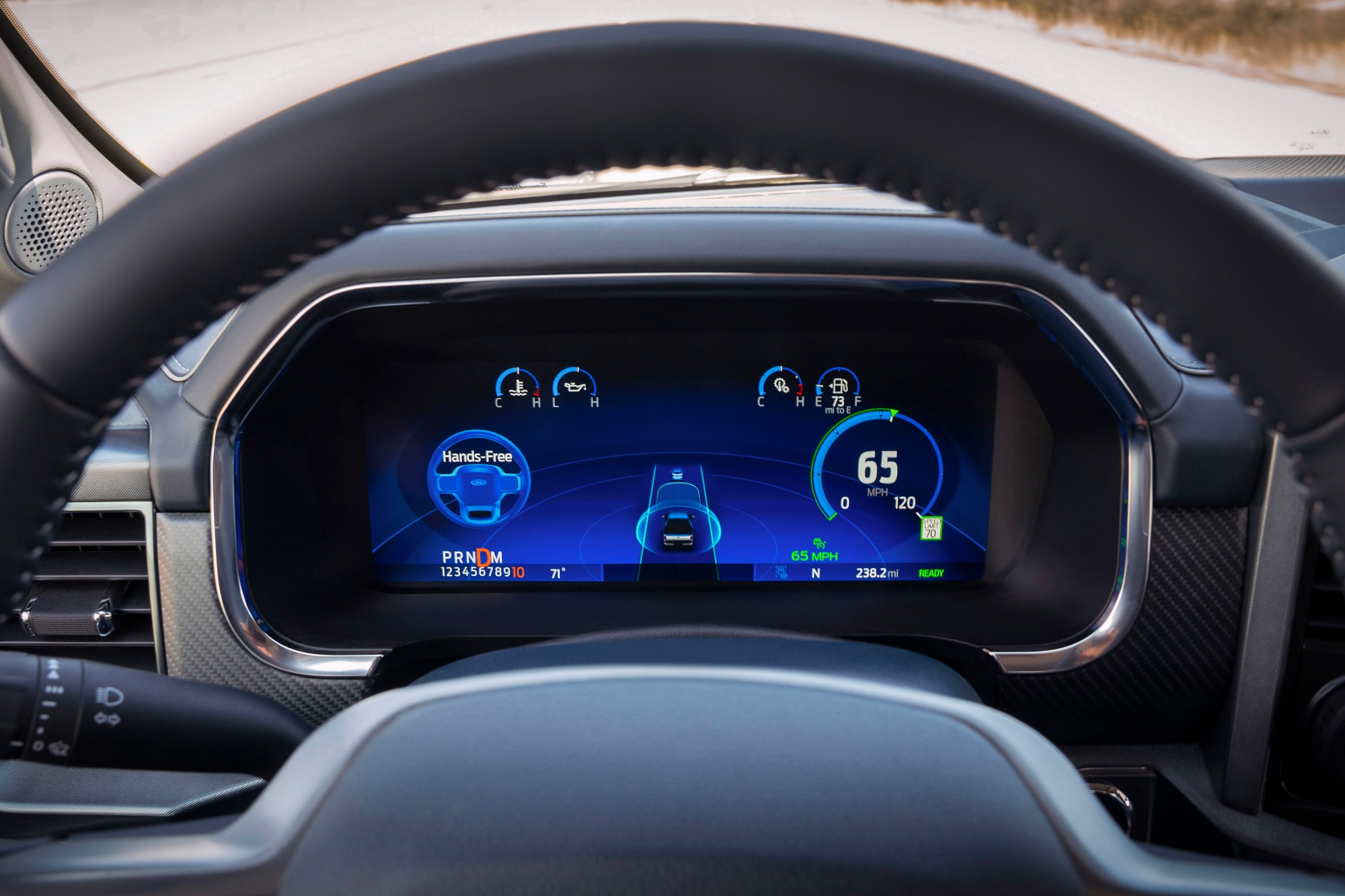

BlueCruise is the new kid on the block. Like GM’s offering, Ford’s system allows the driver to remove their hands from the wheel on pre-mapped divided highways (called Blue Zones) and uses GPS, high-definition maps, radar, and cameras to enable lane centering and adaptive cruise control, keeping the vehicle where it should be.
BlueCruise currently works on more than 100,000 miles of road in the U.S. and Canada, or about half of what GM’s system covers at the time of this writing. BlueCruise also lacks the lane-changing assistance of Super Cruise and FSD, but Ford plans to retroactively add this capability to current models via an over-the-air update in the future.
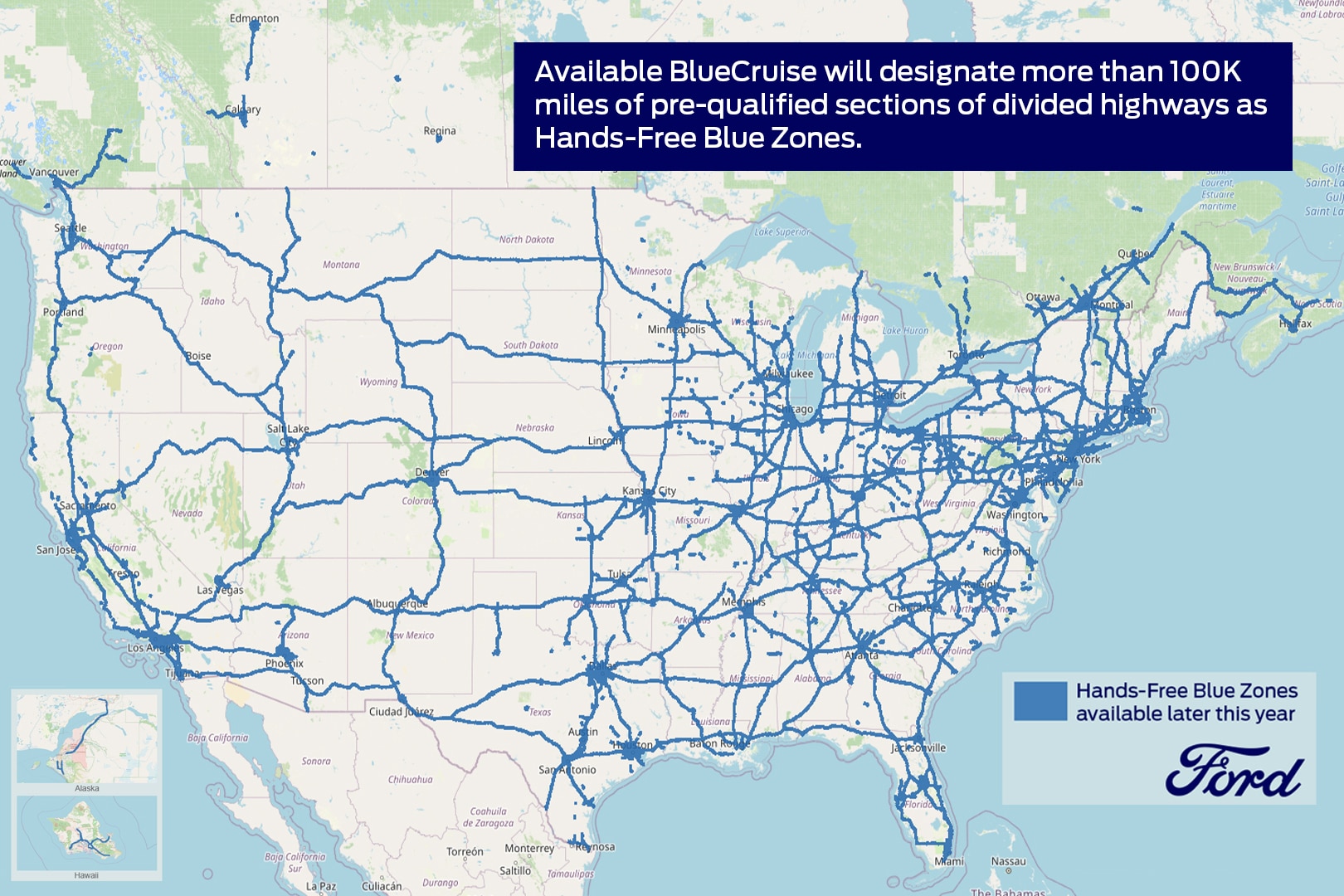
A camera in the instrument cluster tracks the driver’s eyes, and a torque sensor in the steering wheel determines if the driver has command of the helm. Unlike Super Cruise, BlueCruise doesn’t use a steering-wheel light bar to relay information, but rather sticks to just visual alerts in the dash cluster and audible warnings. If the driver fails to act, the vehicle will slow to a crawl.
BlueCruise is available on the 2021 F-150 and Mustang Mach-E. For the F-150, it comes standard on the top-spec Limited trim. Buyers of the Lariat, King Ranch, and Platinum models can get it by opting for the $1,595 Ford Co-Pilot 360 Active 2.0 package. As for the Mach-E electric crossover, the CA Route 1, Premium, and First Edition trim levels include BlueCruise at no additional charge, while the Select model offers it only as part of the $3,200 Comfort and Technology package.

Related Articles

Proceed with caution: Financial woes put the electric SUV in dangerous waters.

From mountains to private racetracks, car manufacturers have some awesome test beds.

An off-road test drive reveals Toyota's new Cruiser is capable of tackling trails too tough for a crossover SUV.

Reservations
Insurance replacement, buying a car, about car sales, car rental locations, more locations, top us locations, loyalty program, redeem points & perks, customer support, how to use autopilot.
Autopilot combines cruise control and autosteer in Tesla vehicles. While not a self-driving setting, it helps drivers keep a safe distance from cars in front and remain in their lane.
Both Traffic Aware Cruise Control (TACC) and Autosteer are controlled using the touchscreen, gear selector stalk and right-hand steering wheel scroll. However, the driver remains responsible for steering and braking at all times .
Switch off either setting by pushing the gear selector stalk upwards or lightly pressing the brake pedal.
What is Autopilot?
Autopilot includes two features: Traffic-Aware Cruise Control (TACC) and Autosteer. TACC matches the speed of your car to that of the surrounding traffic while Autosteer assists with steering within a clearly marked lane while TACC is engaged.
How Do I Engage Traffic-Aware Cruise Control?
When TACC is available, a gray circle with a speed-limit number in it appears to the right of the speedometer. To engage, push down once on the gear selector stalk. The associated circle will turn blue when TACC is engaged. Adjust your speed via the touchscreen or right-hand scroll on the steering wheel. Push the stalk up once or lightly touch the brake pedal to disengage TACC.
How Do I Engage Autosteer?
When Autosteer is available, a gray steering wheel icon will appear next to the TACC circle on the touchscreen. To engage, push down twice on the gear selector stalk. The steering wheel icon will turn blue when Autosteer is engaged. Push the stalk up once or lightly touch the brake pedal to disengage Autosteer. However, the driver remains responsible for steering at all times.
Can I Set A Following Distance When Using Tacc?
While TACC is engaged, push the right-hand scroll on the steering wheel to the right or left to set your preferred following distance. As traffic slows, TACC will maintain the programmed following distance between the Tesla and the car in front of you, helping prevent rear-end collisions.
Will Tesla models brake automatically?
To maintain the programmed following distance when using TACC, Tesla models will brake automatically. Additionally, regen braking automatically applies the brakes when you take your foot off the gas and Tesla models includes an Automatic Emergency Braking feature. However, the driver remains responsible for braking at all times.
EDUCATIONAL SERIES
Explore other topics
Your first drive, charging a tesla, making adjustments, safety & security, voice command, features & storage, get the most out of your electric car rental., touchscreen | driving information.
Courtesy of Tesla, Inc.
Regenerative Braking
Plugging in.

Robotics & Automation News
Market trends and business perspectives

Autopilots in cars. What does the future hold for us?
In modern life, a car is one of the most necessary things in our life, because it gives a sense of freedom and choice, which is so necessary for a sense of personal security and importance.
Therefore, car manufacturers are constantly trying to surprise their customers by adding new functions and technologies to their cars. Thus, the autopilot system begins to flood the car market, making the life of drivers much easier.
Among the main players in the self-driving car market are such popular manufacturers as Tesla, Waymo, General Motors, Ford, and BMW. Each of them is actively working on the modernization and improvement of autopilot systems in order to meet the needs of consumers as efficiently as possible.
The use of artificial intelligence, sensor systems, as well as advanced technologies that improve the experience of using the autopilot help in building trust and a better image among competitors.
For example, Tesla is considered one of the best sellers for its Autopilot system, which can currently perform many functions of driving on Autopilot both on highways and in city conditions.
The management of the company makes big bets on the development of this system and constantly improves its operation, thanks to which it is possible to obtain an even higher level of safety and work efficiency.
Their competitors, General Motors, are also actively working on the development of an autopilot system, namely Super Cruise, which allows drivers to hand over control on autobahns and in limited areas of the city. Because the safety of the driver and other road users is first of all important.
BMW took a slightly different route and is working on introducing artificial intelligence into its autopilot system so that the car not only follows instructions on its own, but can also analyze its surroundings.
And although this technology is still in the development stage and works perfectly, I am sure that it will continue to be popularized all over the world.
Therefore, if you want to try the autopilot system in action, but not for all the money in the world, then auction cars denver is exactly what you need.
However, currently the main problem with the autopilot system turns out to be that it is simply a programmed function in the car itself, which can stop working at the most inopportune moment, so it requires constant checking and control by the driver.
How to choose a car with autopilot? What you should pay attention to when choosing
If you want to try driving a car with the autopilot system, we recommend that you pay attention to the following extremely important factors:
First, the system can have different levels of autonomy. Some may only offer you a lane keeping system or adaptive cruise control, while more technologically advanced cars allow you to drive the car using autopilot only in certain situations. Therefore, when choosing, focus on your needs and wishes.
Of course, the cost of the car depends on this factor, so if you have certain price restrictions, take this into account when choosing. Also, make sure in advance that you can service this car. Well, the most important factor is the level of security.
Make sure that the car and its autopilot system has high levels of safety, allows you to react effectively to traffic, road situations and minimizes the risk of accidents as a whole. Some cars have an additional automatic braking system to prevent collisions.
Although the future development of technology and human capabilities looks attractive, it is worth being prepared for the dangers that may be associated with this technology.
When starting your journey, be sure to check all systems and periodically monitor the movement of your vehicle to prevent trouble.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- The Inventory
Tesla Driver Charged With Killing Motorcyclist After Turning on Autopilot and Browsing His Phone
Your tesla is not a "self driving car" no matter how hard you want to believe it..

A 28-year-old motorcyclist died in Washington State on Friday afternoon because a dipshit Tesla driver rear-ended him at speed . A Snohomish man, 56, was commuting in his 2022 Tesla Model S when he activated the car’s camera-based advanced driver assist system and according to his statements to police , began looking through his phone . With nobody paying attention to the car’s actions , the Tesla software ignored Jeffrey Nissen on his motorcycle and continued on at speed. The car rear-ended the two-wheeler , Nissen was flung from the bike, and his life ended pinned underneath the electric car, where he was still lodged when police arrived to the scene.
Related Content
The Tesla driver, who told police he was “putting the trust in the machine to drive for him,” was inattentive to the road in front of him, and was only brought back to reality when he “heard a bang as the car lurched forward.” The driver was not impaired by drugs or alcohol, though he admitted to having an alcoholic beverage prior to the 3:54 p.m. crash.
Local news reports say the driver was using “Autopilot” rather than “Full Self-Driving” though the two systems are often conflated. The current FSD software requires drivers to keep their eyes up on the road for the system to remain active, where Autopilot doesn’t seem to require this. Autopilot is little more than lane keep assist paired with a camera-based cruise control system.
Tesla will claim that it isn’t culpable for the incident, as the official line is that its so-called Autopilot and Full Self-Driving software are “intended for use with a fully attentive driver, who has their hands on the wheel and are prepared to take over at any moment.” The company and its CEO, however, have knowingly engaged in public discussion describing the cars as “driving themselves” and the people buying these cars believe them. This isn’t even the first time a “self-driving” Tesla has run over a motorcyclist .
The Tesla driver, who is not named, was booked into the Snohomish County Jail with a charge of Vehicular Homicide. He posted a $100,000 bail on Sunday.
According to a survey by Forbes , 93 percent of Americans have concerns about self-driving car safety, and 61 percent say they wouldn’t trust a self-driving car. But when it comes to Tesla “beta testing” this half-baked software on our public streets, we don’t get the legal opportunity to challenge it. Some Tesla drivers get to risk the lives of everyone around them because they paid for the privilege. The system can’t even see a fucking motorcyclist.
This article originally appeared on Jalopnik .
Advertisement
Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications
Releases: PX4/PX4-Autopilot
V1.15.0 beta 1.
- 👍 1 reaction
- ❤️ 1 reaction
- 🚀 7 reactions
Stable Release v1.14.0
Major changes, dynamic control allocation.
- Improved Preflight Failure Check Reporting
- Failsafe Simplification and Simulation
- Default Simulation is now New Gazebo
- Improved ROS 2 Interface thanks to uXRCE-DDS
Read Before Upgrading
The v1.14 release includes a few breaking changes for users upgrading from previous versions, in particular we are moving away from using mixer files to define the vehicle geometry, motor mappings and actuators.
Additionally, we deprecated the Fast-RTPS interface used by ROS 2 in favor of a much cleaner solution that doesn't require a custom build target, and goes away with the additional message generation step.
Please see our detailed upgrade instructions on our docs.
We are very excited to enable the new dynamic control allocation by default; it allows users to define vehicle configurations at runtime without needing a mixer file, thanks to the new vehicle setup dashboard in QGroundControl.
Improved Preflight Failure Check Reporting (QGC Arming Checks UI)
PX4 v1.14 adds much improved preflight failure reporting through the events interface . If the vehicle won't arm, you can more easily find out why in the QGC Arming Checks UI (opens new window) . No more wondering if it's a problem with the safety switch, a poor calibration, or something in the internals of the estimator!
As part of this change, it is now possible to switch to any mode when disarmed (previously you could not switch to a mode that required GPS if you didn't have a good position estimate). PX4 will only allow you to arm when the conditions for the current mode are met, and will report failure checks that are not relevant to the current mode as warnings.
Failsafe Simplification
Safety Failsafe handling has been simplified, in particular with respect to what happens if a failsafe is triggered when another failsafe is already in progress.
There is now a hold delay before the action is performed, giving the user time to override the failsafe if needed. If multiple failsafes are triggered, the more severe action is taken. For example if both RC and GPS are lost, and manual control loss is set to Return mode and GCS link loss to Land, Land is executed. The new Failsafe State Machine Simulation allows you to test failsafe behaviour under all possible configurations and conditions.
Given the recent changes (opens new window) by the Open Robotics simulation team, we are introducing name changes for our gazebo simulations, mirroring Open Robotics naming scheme, starting with v1.14:
Ignition Gazebo (opens new window) to Gazebo Gazebo (opens new window) to Gazebo Classic . Most importantly this affects the PX4 build target names as well:
Gazebo targets are prefixed with gz_ (e.g. make px4_sitl gz_x500). Gazebo Classic make targets are now prefixed with gazebo-classic_ (e.g., make px4_sitl gazebo-classic_cloudship).
Improved ROS 2 Interface via uXRCE-DDS
We updated the ROS 2 interface, replacing Fast-RTPS (opens new window) with uXRCE-DDS , resulting in an improved experience across the board. The change also avoids the need for _rtps build targets, enabling the interface on even more targets by default.
Full changelog available here
- 👍 8 reactions
- 🎉 15 reactions
- ❤️ 8 reactions
- 🚀 12 reactions
v1.14.0-rc1
Release Candidate v1.14.0
What's Changed
- [New] Dynamic Control Allocation
- [New] Default simulation is now New Gazebo
- [New] Improved ROS 2 Interface thanks to uXRCE-DDS
The v1.14 release includes a few breaking changes for users upgrading from previous versions. In particular, we are moving away from using mixer files to define the vehicle geometry, motor mappings, and actuators.
Additionally, we deprecated the Fast-RTPS interface in favor of a much cleaner solution that doesn't require a custom build target and goes away with the additional message generation step.
Please read the full release notes for recommended steps for upgrading users.
Changes between releases
Since beta2 ~ rc1.
v1.14.0-beta2...v1.14.0-rc1
- FWPositionControl: navigateWaypoints: fix logic if already past waypo… - PX4-Autopilot#21642
- Geofence: Disable pre-emptive geofence predictor by default - PX4-Autopilot#21657
- VTOL mission item resets and QC rework - PX4-Autopilot#21665
- RTCM Fixes - PX4-Autopilot#21666
- FW/VTOL: open up a couple of param constraints - PX4-Autopilot#21671
- netman: update module description ( #21664 ) - PX4-Autopilot#21673
- lights: Add LP5562 RGBLED driver - PX4-Autopilot#21685
- rc_update: throttle trim centering fix for reverse channel - PX4-Autopilot#21692
- Fix Rover Thrust Normalization - PX4-Autopilot#21722
- FW Rate Controller: fix saturation logic for VTOLs with differential thrust enabled - PX4-Autopilot#21725
- Fix PWM/Oneshot calibration - PX4-Autopilot#21726
- icp201: increase startup delay (FMUv6X) - PX4-Autopilot#21766
- SITL Tailsitter tuning fixes and add quadtailsitter - PX4-Autopilot#21773
- FMUv6X: Enable ADS1115 - PX4-Autopilot#21794
- Navigator: Loiter: always establish new Loiter with center at current… - PX4-Autopilot#21798
- Default motor PWM configuration - PX4-Autopilot#21800
- rc_update: fix on-off-switch with negative threshold values - PX4-Autopilot#21801
- ROMFS: auto try RGBLED is31fl3195 - PX4-Autopilot#21804
- netman line too long - PX4-Autopilot#21829
- icp201: increase startup delay (FMUv6X) - PX4-Autopilot#21834
- mag_cal: fix mag bias estimate to mag cal - PX4-Autopilot#21835
- airframes/x500_v2: move motors from AUX to MAIN - PX4-Autopilot#21841
- Opt flow fixes - PX4-Autopilot#21844
- Jenkinsfile-compile board updates - PX4-Autopilot#21860
Changelog since v1.13.3
v1.13.3...v1.14.0-rc1
- 👍 6 reactions
- ❤️ 19 reactions
- 🚀 6 reactions
- 👀 4 reactions
Stable Release v1.13.3
- [New] CUAV Pixhawk V6X #21221
- [New] Holybro Pixhawk 6C Mini #21227
- [New] ARK PAB Carrier #21104
- [Fix] Cube Orange: enable mavlink_shell #20868
- [Fix] mRo Pixracer Pro: Configure FRAM for mRo PixracerPro. #21161
- [Fix] mRo Pixracer Pro: fix voltage/current monitoring #19757
- [Fix] Add support for ROS2 Humble for the microRTPS bridge #20968
Full Changelog : v1.13.2...v1.13.3
- 👍 19 reactions
Stable Release v1.13.2
- Navigator: fix init of _mission_item by @sfuhrer in #20496
- Holybro PX4Vision: Don't use IO by @julianoes in #20534
- px4_fmu-v6: Add Revision 1 to manifest to note I2C4 is only internal by @julianoes in #20526
- VTOL takeoff problem hotfix by @MaEtUgR in #20568
- EKF2: ZVU improvements by @bresch in #20613
- fmu-v2: make optional sensor startup quiet by @julianoes in #20384
Full Changelog : v1.13.1...v1.13.2
Contributors
- 👍 11 reactions
- 🎉 8 reactions
Stable Release v1.13.1
- [BACKPORT v1.13] drivers/imu/invensense/icm42670p: cleanup and small fixes by @julianoes in #20165
- [BACKPORT v1.13] px4_fmu-v6x:HB Mini add Ver 3, Ver 4 init by @julianoes in #20166
- standard: fixed pusher assist in hover by @sfuhrer in #20220
- V1.13.0 ARKV6X Backport by @AlexKlimaj in #20253
- [BACKPORT v1.13] Pixhawk 6C external bus hack by @julianoes in #20250
- [BACKPORT v1.13] Add PX4 vision v1.5 Airframe by @julianoes in #20244
- Backport Add BMP390 to BMP388 driver by @AlexKlimaj in #20261
- [v1.13] boards/platform: remove confusing override by @julianoes in #20264
- [BACKPORT v1.13] Add Holybro Pixhawk Pi CM4 Baseboard Support by @julianoes in #20182
- [BACKPORT v1.13] libuavcan: update submodule by @julianoes in #20314
- [v1.13] Fix RTK by @julianoes in #20310
- 1.13 Backport Fix ARKV6X control allocator with base boards by @AlexKlimaj in #20315
- [BACKPORT v1.13] ms5611: ignore reading 0 by @julianoes in #20351
Full Changelog : v1.13.0...v1.13.1
- 👍 7 reactions
Stable Release v1.13.0
This is the v1.13 stable release, which brings a number of significant improvements to PX4:
The full release notes are here: https://docs.px4.io/master/en/releases/1.13.html
- Control Allocation Beta ( PR#18776 )
- Autotune for fixedwing and multicopter
- Explicitly allow just one source
- Fall back to other source in air
- Disable stick input completely
- Configuration parameter: COM_RC_IN_MODE
- Remaining flight time based on low battery ( PR#17828 )
- Remaining flight time based low battery RTL ( PR#18646 )
- Improved default battery estimation parameters ( PR#19429 , PR#19700 )
- Autonomous gentle touch down using distance sensor ( PR#19126 )
- Orbit Flight Mode Improvements ( approach smoothness , radius limiting , and stick input with heading not to the center )
- Goertek SPL06 ( PR#19229 )
- TDK ICP10100 & ICP10111 ( PR#18451 )
- Maiertek MPC2520 ( PR#17910 )
- TE MS5837 ( PR#19183 )
- Sensirion SHT3X ( PR#18910 )
- TDK ICM42670p ( PR#18141 )
- BMI088 I2C (Support Improved) ( PR#17467 )
- Pixart PAA3905 ( PR#19461 )
- TI INA228 ( PR#19461 )
- TI INA238 ( PR#18260 )
- GPS PPS Input Capture ( PR#18849 )
- NXP Ultra Wide Band (UWB) SR150 ( PR#14474 )
- ARK CAN RTK GPS ( PR#18412 )
- ATL Mantis EDU ( PR#17910 )
- Diatone Mamba f405 mk2 ( PR#18402 )
- Holybro Kakute H7 ( PR#19019 )
- Matek GNSS-M9N-F4 ( PR#19061 )
- Matek H743-slim ( PR#18544 )
- mRo Control Zero Classic ( PR#19593 )
- Pixhawk FMUv6C ( PR#19544 )
- Raspberry Pi Pico ( PR#18083 )
- Sky Drones SmartAP Airlink ( PR#19529 )
- MAVLink triggered parachute system support ( PR#18589 )
- EKF2 barometer bias estimator
- EKF2 range finder kinematic consistency check
- EKF2 propeller momentum drag coefficient used for multi-rotor wind estimation.
- incremental accel and gyro auto-calibration
- dedicated magnetometer bias estimator for easy preflight calibration
- Disabled by default, see usage instructions to get started
- Easy and flexible actuator configuration
- Support for more hardware setups without manual mixer file adjustments
- Possibility to dynamically adjust allocation in flight e.g. rotor loss
- UAVCANv1 aka OpenCyphal
- Battery Support
- Hygrometer Support
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE)
- Log message handling from CAN nodes
Full Changelog :
Full Changelog : v1.12.0...v1.13.0
- 🎉 22 reactions
- 🚀 5 reactions
v1.13.0-rc1
PX4 stable v1.13.0 first release candidate
- 👍 4 reactions
- 🎉 12 reactions
- ❤️ 12 reactions
v1.13.0 Beta 1
- 👍 18 reactions
- 🚀 19 reactions
Stable Release v1.12.3
- Enable Cube Orange built in ADS-B receiver by default: #18188
- fixed flash overflow on px4_fmu-v2_default and px4_fmu-v5_optimized
- 👍 26 reactions
- 👀 15 reactions
Genesis unveils new G80 EV Magma concept teasing latest Tesla Model S Plaid rival
A new sporty Genesis electric car is poised to compete with Tesla’s Model S Plaid. Genesis revealed the G80 EV Magma Concept alongside its newly designed Electrified G80 at the Beijing Auto Show. Can the high-performance Genesis compete with Tesla’s Model S Plaid?
Genesis is quickly making its presence known in the new electric era. The luxury automaker’s sales have grown in the US, its second-largest market, from 7,000 in 2016 to over 69,000 last year.
With sales surging, Genesis overtook Infiniti in US sales as it closes in on luxury rivals Porsche, which sold 75,415 vehicles in the US, Land Rover (71,727), and Volvo (128,350). Genesis’ EV sales quadrupled in the US last year, outpacing Lexus and Lucid.
Like most automakers, Genesis aims to grow the brand in the world’s largest EV market. China’s domestic automakers like BYD and NIO dominate the market as foreign brands are being squeezed out.
Genesis reaffirmed its commitment to the region at the Beijing Auto Show, debuting the new G80 EV Magma Concept alongside the new Electrified G80 and several other high-performance cars.

Meet the Genesis G80 EV Magma Concept
The G80 EV Magma is the second all-electric vehicle in the brand’s new high-performance unit.
Genesis introduced the GV60 Magma last month after teaming up with legendary racer Jacky Ickx. Magma is “the brand’s expansion into the realm of high-performance vehicles.
The GV60 Magma takes Genesis’ first EV, the GV60, and fuses a sporty design with a lower center of gravity for enhanced control and performance.

Meanwhile, the G80 EV looks to be the brand’s answer to the Tesla Model S Plaid . The electric car builds on the Electrified G80 with a more athletic design fused with added performance and style.
One of the first things you will notice is the redesigned front grille. The G80 EV Magma also features wider fenders and a new bumper reminiscent of iconic race cars. Like the GV60 Magma, the new EV is lowered for better handling.
According to Genesis, an advanced suspension, high-performance wheels, and added ventilation significantly upgrade the vehicle’s capabilities.

The G80 EV Magma was introduced alongside a newly designed Electrified G80, X Gran Berlinetta Concept, and GV60 Magma Concept.
Genesis also recently revealed the Neolum concept, previewing its first full-size electric SUV. It will spearhead the brand’s new tech and design offensive.
FTC: We use income earning auto affiliate links. More.


Peter Johnson is covering the auto industry’s step-by-step transformation to electric vehicles. He is an experienced investor, financial writer, and EV enthusiast. His enthusiasm for electric vehicles, primarily Tesla, is a significant reason he pursued a career in investments. If he isn’t telling you about his latest 10K findings, you can find him enjoying the outdoors or exercising
Investigation Update on the Radiance of the Seas
Cruise Line : Royal Caribbean International
Cruise Ship : Radiance of the Seas
Voyage Dates : April 8–April 22, 2024
Voyage number: 20095
Number of passengers who reported being ill during the voyage out of total number of passengers onboard : 67 of 1,993 (3.36%)
Number of crew who reported being ill during the voyage out of total number of crew onboard : 2 of 924 (0.22%)
Predominant symptom : diarrhea and vomiting
Causative agent : norovirus
Actions : In response to the outbreak, Royal Caribbean Cruises and the crew aboard the ship reported the following actions:
- Collected stool specimens from gastrointestinal illness cases for testing.
- Isolated ill passengers and crew.
- Increased cleaning and disinfection procedures according to the ship’s outbreak prevention and response plan.
VSP conducted an environmental assessment and outbreak investigation to assist the ship in controlling the outbreak.
Note : The gastrointestinal illness cases reported are totals for the entire voyage and do not represent the number of active (symptomatic) gastrointestinal cases at any given port of call or at disembarkation.
Learn how passengers can protect themselves with these tips for healthy cruising .
- Inspection Reports
- About Inspections
- Cruise Ship Outbreak Updates
- About Noroviruses on Cruise Ships
- VSP Operations Manual [PDF – 5 MB]
- VSP Construction Guidelines [PDF – 4 MB]
- Illness Prevention Information
- Publications
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

Out-of-control 700ft cruise ship crunches into dock at Turkish port
This is the moment a 700ft cruise ship crunched into a dock at a Turkish port after desperately trying to slow down.
The Celestyal Journey cruise ship was making a routine arrival into the port in Kusadasi, Turkey last week when it hit the concrete pier with its bow bulb.
The crew miscalculated the speed and approached the pier too quickly, resulting in the collision, Cruise Hive reported.
Members of the vessel's 597-person crew reportedly lowered the anchor in a bid to slow the approach, but despite their efforts the ship still crashed into the pier.
The collision caused only minimal damage to the ship and pier. No injuries were reported onboard or on the shore.
The Celestyal Journey struck a pier at Kusadasi Cruise Port on Monday last week at 12pm local time while crew were trying to dock.
Passengers were still able to enjoy their day in Kusadasi, one of the most well-preserved Greco-Roman cities in the world, as planned, according to Cruise Hive.
The port, which has eight berths for large ships, is the most popular cruise port in Turkey. Officials say the incident has not negatively impacted operations.
Celestyal Cruises, which operates the vessel and two other ships, did not have to alter any routes following the incident.
The Celestyal Journey entered service in 1994 and initially sailed for Holland America Line as Ryndam. Celestyal Cruises acquired the cruise ship last year.
The cruise liner has 630 cabins, including 149 that feature balconies, and offers guests access to seven exclusive restaurants, and eight bars and lounges, Haber7.com reported.
Celestyal Journey is currently sailing seven-night cruises in the Aegean Sea region until late October 2024.
However, unlike a typical closed-loop route, the Celestyal Journey's round-trip sailings overlap, allowing guests to embark and debark in Kusadasi, as well as various cities in Greece.
Travellers can start their voyage in Heraklion, Crete Greece; Piraeus-Athens, Greece; or Thessaloniki, Greece.
The ship's final journey in the Aegean Sea will embark on October 19 this year. It will be followed by a 14-day repositioning cruise from Athens to Doha, Qatar.
Once it arrives in its new homeport in Doha, the Celestyal Journey will offer seven-night roundtrip sailings to the United Arab Emirates.

Autopilot and Full Self-Driving Capability
Autopilot is an advanced driver assistance system that enhances safety and convenience behind the wheel. When used properly, Autopilot reduces your overall workload as a driver. Each new Tesla vehicle is equipped with eight external cameras and powerful vision processing to provide an additional layer of safety. Model 3 and Model Y built for the European and Middle Eastern markets will now utilise our camera-based Tesla Vision, which are not equipped with radar and instead rely on Tesla’s advanced suite of cameras and neural net processing to deliver Autopilot and related features.
Autopilot comes standard on every new Tesla. For owners who took delivery of their vehicle without Autopilot, there are two Autopilot packages available for purchase, depending on when your vehicle was built: Enhanced Autopilot and Full Self-Driving capability.
Autopilot, Enhanced Autopilot and Full Self-Driving capability are intended for use with a fully attentive driver, who has their hands on the wheel and is prepared to take over at any moment. While these features are designed to become more capable over time, the currently enabled features do not make the vehicle autonomous.
Autopilot is a suite of driver assistance features that comes standard with the purchase of a new vehicle or can be purchased after delivery, and brings new functionality to your Tesla that makes driving safer and less stressful. Available packages include:
- Traffic-Aware Cruise Control: Matches the speed of your vehicle to that of the surrounding traffic
- Autosteer: Assists in steering within a clearly marked lane, and uses traffic-aware cruise control
Enhanced Autopilot
- Auto Lane Change: Assists in moving to an adjacent lane on the motorway when indicator is engaged by driver
- Navigate on Autopilot (Beta): Actively augments Auto Lane Change by providing guidance to the driver to transit motorway’s on-ramp to off-ramp, including suggesting lane changes and navigating interchanges
- Autopark: Helps parallel or perpendicular park your vehicle, with a single touch
- Summon: Moves your vehicle in and out of a tight space using the mobile app
- Smart Summon: Your vehicle will navigate more complex environments and parking spaces, manoeuvring around objects as necessary to come find you in a car park within your direct vicinity.
Full Self-Driving Capability
- All functionality of Basic Autopilot and Enhanced Autopilot
- Traffic and Stop Sign Control (Beta): Identifies stop signs and traffic lights and slows your vehicle to a stop on approach, with your active supervision.
- Autosteer on city streets
The currently enabled Autopilot, Enhanced Autopilot and Full Self-Driving features require active driver supervision and do not make the vehicle autonomous. Full autonomy will be dependent on achieving reliability far in excess of human drivers as demonstrated by billions of miles of experience, as well as regulatory approval, which may take longer in some jurisdictions. As Tesla’s Autopilot, Enhanced Autopilot and Full Self-Driving capabilities evolve, your vehicle will be continuously upgraded through over-the-air software updates.
Before using Autopilot, read your Owner's Manual for instructions and more safety information. While using Autopilot, it is your responsibility to stay alert, keep your hands on the steering wheel at all times and maintain control of your vehicle. Many of our Autopilot features, like Autosteer, Navigate on Autopilot and Summon, are disabled by default. To enable them, you must go to the Autopilot Controls menu within the Settings tab and turn them on.
Before enabling Autopilot, the driver first needs to agree to “keep your hands on the steering wheel at all times” and to always “maintain control and responsibility for your vehicle.” Subsequently, every time the driver engages Autopilot, they are shown a visual reminder to “keep your hands on the wheel."
Traffic-Aware Cruise Control
To engage Traffic-Aware Cruise Control in Model S and Model X, pull the cruise control stalk on the left of the steering column towards you once. In Model 3 and Model Y, pull down once on the gear selector stalk on the right of the steering column.
To engage Autosteer in Model S and Model X, pull towards you twice on the cruise control stalk on the left of the steering column. In Model 3 and Model Y, pull down twice on the gear selector stalk on the right of the steering column. A grey steering wheel icon will appear on your display, next to the speedometer, when the system is available to engage. A blue steering wheel icon will appear on your display, next to the speedometer, when Autosteer is engaged.
When Autosteer is in use, it measures the amount of torque that you apply to the steering wheel and, if insufficient torque is applied, an escalating series of audible and visual alerts again reminds you to place your hands on the wheel. This helps ensure you are attentive and trains good driving habits. If you repeatedly ignore these warnings, then you will be locked out from using Autopilot for the duration of that trip.
Auto Lane Change
To initiate an assisted lane change, Autosteer needs to be active and the driver must be holding the steering wheel. The assisted lane change must be confirmed by the driver by engaging the indicator in the direction you would like to move.
Navigate on Autopilot
Navigate on Autopilot is designed to get you to your destination more efficiently by actively guiding you from on-ramp to off-ramp, including suggesting lane changes, navigating motorway interchanges, and assist in taking exits. It’s designed to make finding and following the most efficient path to your destination even easier on the motorway when Autopilot is in use.
To engage this feature, you must first enable Autosteer by going to Controls > Autopilot > Autosteer - then enable the Navigate on Autopilot feature. Camera calibration will be required and the latest version of Navigation maps must be downloaded via Wi-Fi.
For each route where Navigate on Autopilot is available, you will have the option to activate it by pressing the NAVIGATE ON AUTOPILOT button located in your Navigation Turn List. You can also activate Navigate on Autopilot any time a destination is entered and Autopilot is engaged by adjusting your Navigate on Autopilot settings from Controls > Autopilot > Customize Navigate on Autopilot.
On Model 3, Navigate on Autopilot can be engaged on most motorways by moving the gear lever twice downwards, in quick succession.
On Model S and Model X, Navigate on Autopilot can be engaged on most motorways by pulling the cruise stalk toward you, twice in quick succession.
If your vehicle sees a parking spot, a grey 'P' icon will appear on the left or right hand side of your instrument panel, depending on the location of the space. Autopark detects parallel parking locations when driving below 24kph and perpendicular parking locations when driving below 16kph.
To use Autopark at that time, press on the brake and shift the gear selector into ‘Reverse.’ Keep your foot on the brake. ‘Start Autopark’ will appear in blue text on your touchscreen – press this to start the feature and release the brake and steering wheel. Autopark will then begin to maneuver the vehicle into the parking space by controlling your vehicle’s speed, gear changes and steering angle, but you should remember to be alert and monitor the backup camera view to check for obstacles.
Once Autopark is complete, the vehicle will let you know it is complete and shift into ‘Park.’ You can override Autopark at any time by taking control of the steering wheel.
To use Summon, open the Tesla app. Press Summon and then press and hold the forward or reverse buttons. Summon also integrates with HomeLink and will open your garage door to pull your vehicle out of the garage.
Smart Summon
Smart Summon is designed to allow your vehicle to drive to you or a location of your choosing, manoeuvring around and stopping for objects as necessary, while under your supervision. Like Summon, Smart Summon is only intended for use in private parking lots and driveways. You are still responsible for your vehicle and must monitor it and its surroundings at all times and be within your line of sight because it may not detect all obstacles. Be especially careful around quick moving people, bicycles and vehicles.
To use Smart Summon, open your Tesla app, tap Summon and then select the Smart Summon icon. To activate the feature, press and hold the COME TO ME button. Alternatively, tap the target icon, set the target destination of your choice by adjusting the map, and then press and hold the GO TO TARGET button. You can stop your vehicle from driving at any time by releasing the button.
Smart Summon works with your Tesla app and your phone’s GPS to operate. You must be within approximately 6 metres of your vehicle to use for a total travel distance of 20 metres. Smart Summon requires the latest version of the Tesla mobile app (3.10.0 or later). Please refer to the Owner’s Manual for additional details about this feature.
Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control (Beta)
Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control (Beta) identifies stop signs and traffic lights and automatically slows your vehicle to a stop upon approach while using Autopilot, with your active supervision. To enable, shift your vehicle into PARK and tap Controls > Autopilot > Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control (Beta), then engage Traffic-Aware Cruise Control or Autosteer.
When Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control (Beta) is enabled, the driving visualisation displays upcoming traffic lights, stop signs or road markings at intersections where your vehicle may need to stop. As you approach an intersection, even if the traffic light is green, your vehicle will display a red line to indicate where the vehicle will stop and the vehicle will begin to slow. To continue through the stop line, pull the Autopilot stalk or briefly tap the accelerator pedal to confirm that it is safe to proceed. At this time, Traffic Light and Stop Sign Control does not turn the vehicle, whether you are in a turn lane or have your indicator on.
Notifications on the touchscreen will provide a stop reason (stop sign, traffic light or junction) and will also provide an estimated distance to when your vehicle will stop. If the Traffic Light notification does not indicate a light colour, your vehicle has not confirmed the traffic control state.
As with all Autopilot features, you must be in control of your vehicle, pay attention to its surroundings and be ready to take immediate action including braking. This feature is in Beta and may not stop for all traffic controls. While Traffic and Stop Sign Control is enabled on surface streets with Autosteer active, your speed will be confined to the noted limit. Please review the Owner’s Manual for additional information, instructions for use and warnings.
Active safety features come standard on all Tesla vehicles made after September 2014 for elevated protection at all times. These features are made possible by our Autopilot hardware and software system and include:
- Automatic Emergency Braking: Detects cars or obstacles that the vehicle may impact and applies the brakes accordingly
- Forward Collision Warning: Warns of impending collisions with slower moving or stationary vehicles
- Side Collision Warning: Warns of potential collisions with obstacles alongside the vehicle
- Obstacle Aware Acceleration: Reduces acceleration when an obstacle is detected in front of your vehicle while driving at low speeds
- Blind Spot Monitoring: Warns when a vehicle or obstacle is detected when changing lanes
- Lane Departure Avoidance: Applies corrective steering to keep your vehicle in the intended lane
- Emergency Lane Departure Avoidance: Steers your vehicle back into the driving lane when it detects that your vehicle is departing its lane and there could be a collision
Active safety features are designed to assist drivers, but cannot respond in every situation. It is your responsibility to stay alert, drive safely and be in control of your vehicle at all times.
As of April 2019, all new Tesla vehicles come standard with Autopilot*, which includes Traffic-Aware Cruise Control and Autosteer.
For vehicles without Autopilot software, but are equipped with the necessary hardware, you can purchase Autopilot, Enhanced Autopilot or Full Self-Driving capability at any time through your Tesla Account – and the Autopilot software required will be added to your vehicle.
*Exceptions may apply. You can verify which Autopilot package applies to your vehicle through the onboard infotainment system.
You can experience Autopilot, Enhanced Autopilot or Full Self-Driving capability on a test drive at one of our Tesla store locations.
You can purchase Autopilot, Enhanced Autopilot or Full Self-Driving capability at any time through your Tesla Account – and the Autopilot software required will be added to your vehicle.
Tesla vehicles built between September 2014 and October 2016 include first generation Autopilot hardware: one camera, a first-generation radar and ultrasonic sensors.
These vehicles are ineligible for retrofits to the latest Autopilot hardware.
Check your configuration from your touchscreen. Select ‘Controls’ > ‘Software’ and confirm Autopilot computer type. Then press ‘Additional Vehicle Information.’
As of April 2022, Model 3 and Model Y built for the European and Middle Eastern markets will feature Tesla Vision, which utilises Tesla’s advanced suite of cameras and neural net processing to deliver Autopilot and related features. This camera suite provides occupants with an awareness of their surroundings that a driver alone would not otherwise have. A powerful onboard computer processes these inputs in a matter of milliseconds to help make driving safer and less stressful.
Yes. Autopilot is a hands-on driver assistance system that is intended to be used only with a fully attentive driver. It does not turn a Tesla into a self-driving vehicle nor does it make a vehicle autonomous.
Before enabling Autopilot, you must agree to “keep your hands on the steering wheel at all times” and to always “maintain control and responsibility for your vehicle.” Once engaged, Autopilot will also deliver an escalating series of visual and audio warnings, reminding you to place your hands on the wheel if insufficient torque is applied. If you repeatedly ignore these warnings, you will be locked out from using Autopilot during that trip.
You can override any of Autopilot’s features at any time by steering, applying the brakes, or using the cruise control stalk to deactivate.
If you repeatedly ignore the inattentive driver warnings, Autosteer will be disengaged for that trip. If you receive several ‘Forced Autopilot Disengagements’ (three times for vehicles without a cabin camera and five times for vehicles with a cabin camera), Autosteer and all features that use Autosteer will be temporarily removed for approximately one week.
There is no way to manually clear a Forced Autopilot Disengagement or suspension. After approximately one week, you will be able to use Autosteer again.
Many factors can impact the performance of Autopilot, causing the system to be unable to function as intended. These include, but are not limited to: poor visibility (due to heavy rain, snow, fog, etc.), bright light (due to oncoming headlights, direct sunlight, etc.), mud, ice, snow, interference or obstruction by objects mounted onto the vehicle (such as a bike rack), obstruction caused by applying excessive paint or adhesive products (such as wraps, stickers, rubber coating, etc.) onto the vehicle; narrow, high curvature or winding roads, a damaged or misaligned bumper and extremely hot or cold temperatures.
To ensure the Autopilot hardware can provide information that is as accurate as possible, keep the cameras and sensors clean and free of obstructions or damage. Occasionally remove any buildup of dirt by wiping the cameras and sensors with a soft cloth dampened with warm water.
Before using Autopilot, please read your Owner's Manual for instructions and more safety information. While using Autopilot features, it is your responsibility to stay alert, drive safely and be in control of your vehicle at all times.
Activating Autopilot in Model S and Model X
Activating Autopilot in Model 3 and Model Y
Before Autopilot features can be used for the first time, cameras must complete a self-calibration process. Calibration typically completes after driving 32-40 km, but the distance varies depending on road and environmental conditions. Contact Tesla if your vehicle has not completed the calibration process after driving 160 km.
To improve safety and increase confidence when changing lanes, vehicles built since October 2016 will display a red lane line when your indicator is engaged and a vehicle or obstacle is detected in your target lane. This includes improved blind spot monitoring on the instrument panel which reflects the type of vehicle in your blind spot, supplementing an already attentive driver.
Back to Top

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Navigate on Autopilot: Navigate on Autopilot builds on the features of Traffic-Aware Cruise Control and Autosteer. While Autosteer is active, Navigate on Autopilot allows Model Y to suggest and, if configured, automatically change lanes to pass other vehicles and follow the navigation route (see Navigate on Autopilot ). Informational Purposes.
To engage Traffic-Aware Cruise Control in Model S and Model X, pull down once on the cruise control stalk on the left of the steering column. In Model 3 and Model Y, pull down once on the gear selector stalk on the right of the steering column. ... As with all Autopilot features, you must be in control of your vehicle, pay attention to its ...
Autopilot is designed to be used with full driver supervision, and is essentially an advanced version of cruise control. It has lane-centering and adaptive cruise control, meaning the car can both ...
As standard, every model comes with the Autopilot functions of Traffic-Aware Cruise Control and Autosteer. The former works just like the radar cruise control of other cars, keeping a safe ...
1. Open the Tesla app. 2. Press "Summon" followed by the forward or reverse buttons, depending on how your car needs to pull out. Model S or Model X owners can also achieve this by holding the ...
Tesla's Autopilot is an optional driver assistance system that includes features like Traffic-Aware Cruise Control and Autosteer. Enhanced Autopilot, available as an add-on purchase, includes ...
Once Autopilot is engaged, the car will continue to slow down and accelerate based on the set cruise control speed, and also take gradual turns. In a car equipped with the Full Self Driving option ...
Tesla "Autopilot" is standard and is essentially an adaptive cruise-control plus automatic steering (lane keeping) system while the paid options of Enhanced Autopilot and Full Self-Driving contain more autonomous driving-like features like automatic lane changes, Navigate-on-Autopilot, Summon and Autopark.
The difference may include: Cruise control will provide you with a specified speed while Autopilot will give you more advanced features. As compared to Tesla Autopilot, cruise control will not be able to change the speed. Steering and Lane keeping features are not present in cruise control.
Basic Autopilot comprises four key features: blind-spot monitoring, emergency braking, adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assistance. Crucially these features can work at the same time ...
Jimt29 said: I know of two. Right Stalk: One press = cruise control. Two presses = auto pilot. If you care to make it more complicated than that, I defer to your wisdom. What you are calling "Autopilot" is Autosteer. Autopilot is a collection of features, mainly traffic-aware cruise control and autosteer.
I am confused about the differences between "Cruise Control", Basic Autopilot and Enhanced Autopilot - likely from watching too many videos in preparation for delivery (and with potentially mistaken or out-of-date information in one or more videos). ... I wish there was a "basic" cruise control setting under the level of TACC - this might have ...
BlueCruise is what's known as an active driving assistance (ADA) system. In the simplest terms, ADA is the simultaneous use of a car's adaptive cruise control (ACC) to control speed and lane ...
Tesla Autopilot Features Traffic Aware Cruise Control uses the Tesla's radar to lock-on to the vehicle in front of it and match its speed. Unlike many other automaker's adaptive cruise control systems, Traffic Aware Cruise Control will bring Tesla all the way down to a stop and back up to speed again with no driver input required.
Basic Autopilot includes Traffic-Aware Cruise Control and Autosteer. Traffic-Aware Cruise Control: Maintains your speed and an adjustable following distance from the vehicle in front of you, if there is one (see Traffic-Aware Cruise Control). Autosteer: Maintains your speed and distance from a leading vehicle while also intelligently keeping Model 3 in its lane (see Autosteer).
Currently, the Autopilot tech suite consists of adaptive cruise control and Autosteer, Tesla's lane-centering system. Competitors' products, such as Honda Sensing Suite and Kia Highway Driving Assist, have the same capabilities as Autopilot.
Autopilot combines cruise control and autosteer in Tesla vehicles.While not a self-driving setting, it helps drivers keep a safe distance from cars in front and remain in their lane.. Both Traffic Aware Cruise Control (TACC) and Autosteer are controlled using the touchscreen, gear selector stalk and right-hand steering wheel scroll.However, the driver remains responsible for steering and ...
In addition to the $600 option (that Ford lists as software-specific), BlueCruise requires the Co-Pilot 360 Active 2.0 package on the F-150, which is $1,595 all total (including the $600 software ...
"Traffic-Aware Cruise Control may occasionally brake Model S when not required," cautioned the 2015 Model S owner's manual. A similar warning remains in the latest Tesla owners' manuals.
First, the system can have different levels of autonomy. Some may only offer you a lane keeping system or adaptive cruise control, while more technologically advanced cars allow you to drive the car using autopilot only in certain situations. Therefore, when choosing, focus on your needs and wishes.
But one of the biggest issues is how they've approached marketing the brand's adaptive cruise control system "Autopilot." Brandished as autonomous numerous times, the feature is slightly more ...
Autopilot is little more than lane keep assist paired with a camera-based cruise control system. Advertisement.
Navigate on Autopilot: Navigate on Autopilot builds on the features of Traffic-Aware Cruise Control and Autosteer. While Autosteer is active, Navigate on Autopilot allows Model 3 to suggest and, if configured, automatically change lanes to pass other vehicles and follow the navigation route (see Navigate on Autopilot ). Informational Purposes.
Contribute to PX4/PX4-Autopilot development by creating an account on GitHub. PX4 Autopilot Software. Contribute to PX4/PX4-Autopilot development by creating an account on GitHub. ... and manual control loss is set to Return mode and GCS link loss to Land, Land is executed. The new Failsafe State Machine Simulation allows you to test failsafe ...
Tesla models produced and equipped with any version of its Autopilot system, which Tesla described as an SAE Level 2 (L2) Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS). Autopilot is the simultaneous engagement of Tesla's Traffic-Aware Cruise Control (TACC) and Autosteer. In describing the safety defect, Tesla's Defect
The Federal Aviation Administration and United Airlines are investigating after a video surfaced showing an unauthorized person in the pilot's seat during a flight charted by the Colorado ...
The GV60 Magma takes Genesis' first EV, the GV60, and fuses a sporty design with a lower center of gravity for enhanced control and performance. Genesis G80 EV Magma Concept (Source: Genesis)
Cruise Line: Royal Caribbean International. Cruise Ship: Radiance of the Seas. Voyage Dates: April 8-April 22, 2024. Voyage number: 20095 Number of passengers who reported being ill during the voyage out of total number of passengers onboard: 67 of 1,993 (3.36%). Number of crew who reported being ill during the voyage out of total number of crew onboard: 2 of 924 (0.22%)
Celestyal Cruises acquired the cruise ship last year. The cruise liner has 630 cabins, including 149 that feature balconies, and offers guests access to seven exclusive restaurants, and eight bars ...
As of April 2019, all new Tesla vehicles come standard with Autopilot*, which includes Traffic-Aware Cruise Control and Autosteer. For vehicles without Autopilot software, but are equipped with the necessary hardware, you can purchase Autopilot, Enhanced Autopilot or Full Self-Driving Capability at any time through your Tesla Account - and ...