- Getting Pregnant
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
- Birth Clubs
- See all in Community
- Ovulation Calculator
- How To Get Pregnant
- How To Get Pregnant Fast
- Ovulation Discharge
- Implantation Bleeding
- Ovulation Symptoms
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Am I Pregnant?
- Pregnancy Tests
- See all in Getting Pregnant
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Pregnant Sex
- Weight Gain Tracker
- Signs of Labor
- Morning Sickness
- COVID Vaccine and Pregnancy
- Fetal Weight Chart
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy Discharge
- Find Out Baby Gender
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- See all in Pregnancy
- Baby Name Generator
- Top Baby Names 2023
- Top Baby Names 2024
- How to Pick a Baby Name
- Most Popular Baby Names
- Baby Names by Letter
- Gender Neutral Names
- Unique Boy Names
- Unique Girl Names
- Top baby names by year
- See all in Baby Names
- Baby Development
- Baby Feeding Guide
- Newborn Sleep
- When Babies Roll Over
- First-Year Baby Costs Calculator
- Postpartum Health
- Baby Poop Chart
- See all in Baby
- Average Weight & Height
- Autism Signs
- Child Growth Chart
- Night Terrors
- Moving from Crib to Bed
- Toddler Feeding Guide
- Potty Training
- Bathing and Grooming
- See all in Toddler
- Height Predictor
- Potty Training: Boys
- Potty training: Girls
- How Much Sleep? (Ages 3+)
- Ready for Preschool?
- Thumb-Sucking
- Gross Motor Skills
- Napping (Ages 2 to 3)
- See all in Child
- Photos: Rashes & Skin Conditions
- Symptom Checker
- Vaccine Scheduler
- Reducing a Fever
- Acetaminophen Dosage Chart
- Constipation in Babies
- Ear Infection Symptoms
- Head Lice 101
- See all in Health
- Second Pregnancy
- Daycare Costs
- Family Finance
- Stay-At-Home Parents
- Breastfeeding Positions
- See all in Family
- Baby Sleep Training
- Preparing For Baby
- My Custom Checklist
- My Registries
- Take the Quiz
- Best Baby Products
- Best Breast Pump
- Best Convertible Car Seat
- Best Infant Car Seat
- Best Baby Bottle
- Best Baby Monitor
- Best Stroller
- Best Diapers
- Best Baby Carrier
- Best Diaper Bag
- Best Highchair
- See all in Baby Products
- Why Pregnant Belly Feels Tight
- Early Signs of Twins
- Teas During Pregnancy
- Baby Head Circumference Chart
- How Many Months Pregnant Am I
- What is a Rainbow Baby
- Braxton Hicks Contractions
- HCG Levels By Week
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Am I Pregnant
- Why is Poop Green
- Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp
- Insemination
- UTI During Pregnancy
- Vitamin D Drops
- Best Baby Forumla
- Postpartum Depression
- Low Progesterone During Pregnancy
- Baby Shower
- Baby Shower Games

Your baby's checkup schedule: What to expect at doctor visits
There are a lot of doctor visits in your baby's first few years, and they're all important! Your baby's pediatrician will monitor their growth and development, stay on top of their vaccinations, and answer your questions and concerns.

It can seem like you're always headed to the doctor, even when all is well with your baby. But there's good reason for all those appointments.
"There's so much that happens in the first year of life that it's important that nothing gets missed!" explains Chandani DeZure, M.D., a neonatal and pediatric hospitalist at Lucile Packard Children's Hospital/Stanford University Opens a new window in Palo Alto, California and member of the BabyCenter Medical Advisory Board .
"Babies need to be developing and growing appropriately, eating well, and getting vaccinated to protect against diseases so they can thrive as they get older and be as healthy as possible. All this and more happens at regular well-baby checkups," says Dr. DeZure.
Checkups are also the perfect time to ask questions and raise concerns about your baby's sleep habits , crying , poop , breastfeeding , formula feeding , development milestones , and more.
Learn how to find a pediatrician for your baby .
What newborn doctor visits will my baby have?
In the first week, the doctor will want to check your newborn to make sure they're doing well. Then you'll have scheduled visits at 1 and 2 months.
A lot happens right after birth and while you're still at the hospital with your newborn . At birth, the medical team will assess your baby's health and assign an Apgar score – which evaluates your baby's heart rate, breathing, muscle tone, reflex response, and color.
They'll weigh your baby and measure your baby's length and head circumference . These numbers will be recorded on a growth chart , which will be used to keep track of your baby's growth at all future doctor's visits.
Your baby's progress along the growth chart is just one way to evaluate their health. "Growth charts are not intended to be used as a sole diagnostic instrument," explains the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Opens a new window (CDC). "Instead, growth charts are tools that contribute to forming an overall health picture for the child being measured."
At the hospital, your baby will get antibiotic eye ointment (to prevent dangerous eye infections) and a vitamin K shot (to help their blood clot normally and protect them from a rare but dangerous bleeding disorder). They'll also receive their first hepatitis B shot .
Your pediatrician or a pediatric hospitalist will give your newborn a complete physical at the hospital within 24 hours of birth. They'll examine your baby head to toe, checking their skin tone, reflexes, alertness, heart, lungs, and skin (for rashes and jaundice ).
If you're having your baby circumcised , that will be done a day or two after birth.
Your baby will also receive screening tests while at the hospital. These include tests for hearing loss , congenital heart defects , and metabolic disorders (such as PKU and sickle cell disease ). Screening tests are usually done between 24 hours and 48 hours after birth.
Read more about what happens to your baby right after birth .
Your baby's checkup schedule
Some pediatricians' schedules vary slightly, but the American Academy of Pediatrics Opens a new window (AAP) recommends babies get checkups at birth, 3 to 5 days after birth, and then at 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. (Once your baby is a toddler and child, they'll have routine checkups at 30 months, 3 years, and annually after that.)
If you've gotten behind, talk with your child's doctor about a catch-up schedule. "It's particularly important for parents to work with their child's doctor or nurse to make sure they get caught up on missed well-child visits and recommended vaccines," says the CDC Opens a new window . "Making sure that your child sees their doctor for well-child visits and recommended vaccines is one of the best things you can do to protect your child and community from serious diseases that are easily spread."
At each visit, your baby's doctor will:
- Do a complete physical examination, checking your baby's eyes and ears, heart and lungs, head, body, belly, genitals, and hips and legs
- Weigh your baby and take their measurements (length and head circumference). The doctor will chart these numbers on your baby's growth chart and let you know how they're progressing.
- Ask about your baby's eating habits and number of wet and poopy diapers
- Ask about your baby's sleeping habits
- Watch how your baby responds to movement. They'll ask you if you've noticed anything unusual about your baby's eyes or the way they look at things.
- Watch how your baby responds to sounds. The doctor will ask if your baby responds to your voice and other sounds by turning in the direction of the sound.
- Run any appropriate tests (screening and diagnostic), depending on your baby's needs
- Give needed vaccinations
- Chat about your baby's developmental skills, including gross motor skills and fine motor skills , social skills , and language skills
- Answer your questions and concerns
Follow the links below for more detailed information about what to expect at each visit, but here are some highlights:
1-month doctor appointment
At the 1-month checkup , the doctor will check your baby's soft spots (fontanels) and the shape of your baby's head. They'll also review the results of your baby's newborn screening tests.
Your baby may also get their second hepatitis B shot. The first was probably given at birth, and the second shot can be given at the 1- or 2-month visit.
The doctor may also ask about your baby's head control and cooing. They'll also ask how you're doing and ask you some screening questions for postpartum depression . (They'll continue to monitor you for postpartum depression through your baby's 6-month checkup.)
2-month doctor appointment
At the 2-month visit , your baby will receive their first shots of DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis), Hib (haemophilus influenzae type B), IPV ( polio ), and PCV (pneumococcal disease), along with an oral vaccine for RV ( rotavirus ).
The doctor will check your baby's posture and may ask about their head control, ability to push up , and whether they're smiling voluntarily yet.
4-month doctor appointment
Your baby's 4-month checkup will include another oral dose of the rotavirus vaccine and a second DTaP vaccine. They'll also receive the second dose of the IPV, Hib, and PCV vaccines. (Some offices have combination vaccines, so your baby may receive less pokes than they would if each vaccine were given individually.)
The doctor will screen your baby for iron-deficiency anemia and lead poisoning (by asking you questions about breast milk or formula intake and environmental exposures) and test for these if necessary. They may ask what sounds your baby's making and whether they're reaching for and grabbing things . And they'll check your baby's gums and refer you to a dentist to establish dental care whenever the first tooth erupts .
6-month doctor appointment
At the 6-month checkup , the doctor may talk with you about your baby's readiness to start solids and other developmental strides, such as rolling over and babbling.
The third hepatitis B, DTaP, Hib, PCV, and IPV vaccines are typically given at 6 months, along with an oral rotavirus vaccine. Your baby can also get their first COVID vaccine now and, if it's flu season, they'll also get a flu shot . Your baby will need a second dose of the flu shot 4 weeks later.
9-month doctor appointment
At their 9-month checkup , your baby will catch up on any missed vaccinations (including a flu shot if it's flu season).
The doctor will check for any new teeth and ask you if your baby is crawling or scooting around, if they know any words , and if they can pick up objects with their thumb and forefinger.
They may remind you of the importance of babyproofing your home now that your baby is mobile.
12-month doctor appointment
At your baby's 12-month checkup , your baby's doctor will order tests to rule out iron-deficiency anemia. Depending on risk factors, they may also offer tests for tuberculosis and lead exposure , if your baby is at risk. And they may ask you if your baby points at things , says words, and stands on their own .
Your baby will also get a handful of vaccines:
- COVID, if the timing is right based on when your baby got their first shot
- Flu, if it's flu season and your baby hasn't been immunized yet.
- MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella), which can be given between 12 and 15 months and again between 4 and 6 years
- Varicella (chickenpox), given between 12 and 15 months and again between 4 and 6 years
- Hepatitis A (HepA), which they can receive between 12 months and 23 months, with a second dose at least 6 months later)
- Hib vaccine. The fourth dose can be given now or anytime between 12 and 15 months.
- PCV. The fourth dose can be given between 12 and 15 months.
Some of these shots will be combined. And your baby's doctor may spread them out between this visit and your baby's 15-month visit.
15-month doctor appointment
Your child's doctor will give your baby a fourth dose of the DTaP vaccine (given between now and 18 months), and – if they haven't already had them – your baby may now get their Hib, PCV, MMR, hepA, and varicella immunizations.
Your child may also get a flu vaccine, if it's flu season, and/or a COVID vaccine, if appropriate.
The doctor may check your baby for new teeth and apply fluoride unless you have a dentist taking care of this. And they may check your child's blood pressure, hearing, and vision.
18-month doctor appointment
At the 18-month check-up , your child's doctor will make sure your toddler is caught up on any missed immunizations and give them another round of DTaP and hepatitis A vaccines. If your child has risk factors for anemia or lead poisoning, the doctor will screen for those.
And they'll ask about your toddler's sleeping, eating, potty-training readiness , walking , and ability to follow simple commands .
24 month doctor appointment
Your toddler's 2-year checkup is a good time to make up any missed immunizations and screen for anemia and/or lead poisoning if your child has risk factors. The doctor will probably ask your child to walk so they can check their gait and coordination.
Your child's doctor may ask about potty training and temper tantrums , and they may encourage you to take your child for a dental checkup if you haven't done so yet.
How can I prepare for my baby's doctor appointments?
Here are some tips:
Consider timing
If possible, schedule your visit at a time when your baby is usually happy (fed, and not on the verge of needing a nap ). If this time coincides with a time when the office isn't usually very busy, even better! This isn't always practical – doctor's offices don't always have appointment times that coincide with your preferences, and your baby may not be on enough of a schedule to make even an educated guess at the best time for them. But it's worth a try.
Dress (both of you) comfortably
Your baby will need to be undressed for their exam, so dress them in something that's easy off/easy on. (Practicality over cuteness today!) Make sure you're dressed for the appointment, too – in something comfortable and that you can easily nurse in, if you're breastfeeding . Bring a sweater for you and your child (or a blanket for your baby), in case the office is chilly (doctor's offices often are).
Pack thoughtfully
Before your appointment, make sure your diaper bag is stocked with everything you might need. This includes diapering supplies ( diapers , wipes , a change of clothes) and feeding supplies (a bottle if you're bottle feeding and snacks if your baby is eating solids), a blankie or other lovey , burp cloths , and a pacifier if your baby uses one. Bring your current insurance information and any other paperwork, too.
Jot things down
The doctor will ask you about your baby: the number of wet and soiled diapers they have each day, how many hours they sleep, and how much and often they eat. They'll ask about motor and language skills, too. When did your baby start rolling over, sitting up, and crawling? Are they babbling yet? It's a good idea to keep ongoing notes about these things, or jot them down before your visit.
Importantly, bring a list of questions you have. These visits are the perfect time to get them answered!
Make sure you tell the doctor about any concerns, too, no matter how small they seem. Do you wonder if your baby sometimes doesn't hear you or if they favor one side of their body when they crawl across the floor? Are you worried that your baby should be walking or talking by now or that they often wake up screaming ?
Remember that you and the doctor are partners in managing your baby's health. Don't hesitate to give your perspective, and make sure your questions are addressed.
Learn more:
- Everything you need to know about baby poop
- How your baby's skull, skeleton, and bones develop after birth
- The importance of tummy time for your baby
- How to make shots less painful for your baby
Was this article helpful?
Vaccine schedule for babies and kids

Baby's doctor visits: The 1-month checkup

Postpartum depression screening for new moms

The pneumococcal vaccine

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
AAP. 2023. AAP schedule of well-child care visits. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/family-life/health-management/Pages/Well-Child-Care-A-Check-Up-for-Success.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
AAP. 2023. All about the recommended immunization schedules. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/immunizations/Pages/Recommended-Immunization-Schedules.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
AAP. 2023. Recommended childhood and adolescent immunization schedule for 2023. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/news/Pages/recommended-childhood-and-adolescent-immunization-schedule-for-2023.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
AAP. 2023.Vaccines Opens a new window your child needs by age 6. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/immunizations/Pages/Your-Babys-First-Vaccines.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
AAP. 2022. Why your newborn needs a vitamin K shot. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/prenatal/delivery-beyond/Pages/Where-We-Stand-Administration-of-Vitamin-K.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
AAP. 2022. Your child's checkups. The American Academy of Pediatrics. https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/Your-Childs-Checkups/Pages/default.aspx Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
CDC. 2022. Growth charts. National Center for Health Statistics. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/index.htm Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
CDC. 2023. Stay up to date with COVID-19 vaccines. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/stay-up-to-date.html Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]
Nemours KidsHealth. 2022. Your child's checkup: 1 month. https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/checkup-1mo.html Opens a new window [Accessed June 2023]

Where to go next


Personalize Your Experience
Log in or create an account for a personalized experience based on your selected interests.
Already have an account? Log In
Free standard shipping is valid on orders of $45 or more (after promotions and discounts are applied, regular shipping rates do not qualify as part of the $45 or more) shipped to US addresses only. Not valid on previous purchases or when combined with any other promotional offers.
Register for an enhanced, personalized experience.
Receive free access to exclusive content, a personalized homepage based on your interests, and a weekly newsletter with topics of your choice.
Home / Parenting, Kids & Teens / Quick guide to your infant’s first pediatrician visits
Quick guide to your infant’s first pediatrician visits
Please login to bookmark.

Frequent checkups with a health care provider are an important part of your baby’s first few years. These checkups — often called well-child visits — are a way for you and your child’s health care provider to keep tabs on your child’s health and development, as well as spot any potential problems. Well-child visits also give you a chance to discuss any questions or concerns you might have and get advice from a trusted source on how to provide the best possible care for your child.
The benefit of seeing your child’s provider regularly is that each visit adds critical information to your child’s health history. Over time, you and the provider will get a good idea of your child’s overall health and development.
In general, the provider will be more attentive to your child’s pattern of growth over time, rather than to specific one-time measurements. Typically what you’ll see is a smooth curve that arcs upward as the years go by. Regularly reviewing your child’s growth chart can also alert you and the provider to unexpected delays in growth or changes in weight that may suggest the need for additional monitoring.
Each health care provider does things a bit differently, but here’s what will generally be on the agenda during your first well-child exams.
Body measurements
Checkups usually begin with measurements. During first-year visits, a nurse or your baby’s health care provider will measure and record your baby’s length, head circumference and weight.
Your child’s measurements will be plotted on his or her growth chart. This will help you and the provider see how your child’s size compares with that of other children the same age. Try not to fixate on the percentages too much, though. All kids grow and develop at different rates. In addition, babies who take breast milk gain weight at a different rate than do babies who are formula-fed.
Keep in mind that a child who’s in the 95th percentile for height and weight isn’t necessarily healthier than a child who’s in the fifth percentile. What’s most important is steady growth from one visit to the next. If you have questions or concerns about your child’s growth rate, discuss them with your child’s provider.
Physical exam
Your child’s health care provider will give your child a thorough physical exam and check his or her reflexes and muscle tone. Be sure to mention any concerns you have or specific areas you want the doctor to check out.
Here are the basics of what providers commonly check for during an exam:
- Head — In the beginning, your child’s health care provider will likely check the soft spots (fontanels) on your baby’s head. These gaps between the skull bones give your baby’s brain plenty of room to grow in the coming months. They’re safe to touch and typically disappear within two years, when the skull bones fuse together. The health care provider may also check baby’s head for flat spots. A baby’s skull is soft and made up of several movable plates. If his or her head is left in the same position for long periods of time, the skull plates might move in a way that creates a flat spot.
- Ears — Using an instrument called an otoscope, the health care provider can see in your child’s ears to check for fluid or infection in the ears. The provider may observe your child’s response to various sounds, including your voice. Be sure to tell the provider if you have any concerns about your son’s or daughter’s ability to hear or if there’s a history of childhood deafness in your family. Unless there’s cause for concern, a formal hearing evaluation isn’t usually needed at a well-child exam.
- Eyes — Your child’s health care provider may use a flashlight to catch your child’s attention and then track his or her eye movements. The provider may also check for blocked tear ducts and eye discharge and look inside your child’s eyes with a lighted instrument called an ophthalmoscope. Be sure to tell the provider if you’ve noticed that your child is having any unusual eye movements, especially if they continue beyond the first few months of life.
- Mouth — A look inside your baby’s mouth may reveal signs of oral thrush, a common, and easily treated, yeast infection. The health care provider might also check your baby’s mouth for signs of tongue-tie (ankyloglossia), a condition that affects the tongue’s range of motion and can interfere with a baby’s oral development as well as his or her ability to breast-feed.
- Skin — Various skin conditions may be identified during the exam, including birthmarks, rashes, and jaundice, a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes. Mild jaundice that develops soon after birth often disappears on its own within a week or two. Cases that are more severe may need treatment.
- Heart and lungs — Using a stethoscope, your child’s health care provider can listen to your child’s heart and lungs to check for abnormal heart sounds or rhythms or breathing difficulties.
- Abdomen, hips and legs — By gently pressing a child’s abdomen, a health care provider can detect tenderness, enlarged organs, or an umbilical hernia, which occurs when a bit of intestine or fatty tissue near the navel breaks through the muscular wall of the abdomen. Most umbilical hernias heal by the toddler years without intervention. The provider may also move your child’s legs to check for dislocation or other problems with the hip joints, such as dysplasia of the hip joint.
- Genitalia — Your child’s care provider will likely inspect your son’s or daughter’s genitalia for tenderness, lumps or other signs of infection. The provider may also check for an inguinal hernia, which results from a weakness in the abdominal wall.
For girls, the doctor may ask about vaginal discharge. For boys, the provider will make sure a circumcised penis is healing well during early visits. The provider may also check to see that both testes have descended into the scrotum and that there’s no fluid-filled sac around the testes, a condition called hydrocele.
Your child’s provider will likely ask you about your child’s eating habits. If you’re breastfeeding, the provider may want to know how often you’re feeding your baby during the day and night and whether you’re having any problems. If you’re pumping, the provider may offer suggestions for managing pumping frequency and storing breast milk. If you’re formula-feeding, the provider will likely want to know how often you feed and how many ounces of formula your baby takes at each feeding. In addition, the provider may discuss with you your baby’s need for vitamin D and iron supplements.
Bowel and bladder function
In the first few visits, your child’s health care provider will likely also ask how many wet diapers and bowel movements your baby produces a day. This information offers clues as to whether your baby is getting enough to eat.
Sleeping status
Your child’s health care provider may ask you questions about your child’s sleep habits, such as your regular bedtime routine and how many hours your child is sleeping during the day and night. Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns you may have about your child’s sleep, such as getting your baby to sleep through the night. Your child’s provider may also help you figure out how to find rest for yourself, especially in the early baby months.
Development
Your child’s development is important, too. The health care provider will monitor your child’s development in the following five main areas.
- Gross motor skills — These skills, such as sitting, walking and climbing, involve the movement of large muscles. Your child’s health care provider may ask you how well your baby can control his or her head. Is your baby attempting to roll over? Is your baby trying to sit on his or her own? Is your child starting to walk or throw a ball? Can your toddler walk up and down steps?
- Fine motor skills — These skills involve the use of small muscles in the hand. Does your baby reach for objects and bring them to his or her mouth? Is your baby using individual fingers to pick up small objects?
- Personal and social skills — These skills enable a child to interact and respond to his or her surroundings. Your child’s health care provider may ask if your baby is smiling. Does your baby relate to you with joy and enthusiasm? Does he or she play peekaboo?
- Language skills — These skills include hearing, understanding and use of language. The health care provider may ask if your baby turns his or her head toward voices or other sounds. Does your baby laugh? Is he or she responding to his or her name?
- Cognitive skills — These skills allow a child to think, reason, solve problems and understand his or her surroundings. Your child’s provider might ask if your baby can bang together two cubes or search for a toy after seeing you hide it.
Vaccinations
Your baby will need a number of scheduled vaccinations during his or her first years. The health care provider or a nurse will explain to you how to hold your baby as he or she is given each shot. Be prepared for possible tears. Keep in mind, however, that the pain caused by a shot is typically short-lived but the benefits are long lasting.
Your child’s provider may talk to you about safety issues, such as the importance of placing your baby to sleep on his or her back and using a rear-facing infant car seat as long as possible.
Questions and concerns
During your son’s or daughter’s checkups, it’s likely that you’ll have questions, too. Ask away! Nothing is too trivial when it comes to caring for your baby. Write down questions as they arise between appointments so that you’ll be less likely to forget them when you’re at your child’s checkup.
Also, don’t forget your own health. If you’re feeling depressed, stressed-out, run-down or overwhelmed, describe what’s happening. Your child’s provider is there to help you, too.
Before you leave the health care provider’s office, make sure you know when to schedule your child’s next appointment. If possible, set the next appointment before you leave the provider’s office. If you don’t already know, ask how to reach your child’s provider in between appointments. You might also ask if the provider has a 24-hour nurse information service. Knowing that help is available when you need it can offer peace of mind.

Relevant reading
Medical Robotics Breakthroughs
From laboratory robots to robotic prosthetics, this exploration of scientific inquiry celebrates the greatest developments to date in medical robotics. Get to know the physicians, scientists, and other researchers responsible for these breakthroughs in medicine, and explore the ups, the downs, and the eureka moments that are science in action.…

Discover more Parenting, Kids & Teens content from articles, podcasts, to videos.
Want more children’s health and parenting information? Sign up for free to our email list.
Children’s health information and parenting tips to your inbox.
Sign-up to get Mayo Clinic’s trusted health content sent to your email. Receive a bonus guide on ways to manage your child’s health just for subscribing.
You May Also Enjoy

Privacy Policy
We've made some updates to our Privacy Policy. Please take a moment to review.
What To Expect From Baby's First Pediatrician Visit
Pediatricians may be the next best thing to a handbook for newborns., by sharon brandwein.

Whether it’s your first baby or your third, bringing a new life into the world is no easy feat. The parenting journey is long, and having your own little “village” will help you navigate any bumps in the road. But with everything that your support network of friends and family can do, they can’t do it all.
Babies may not come with handbooks, so that’s where your pediatrician comes in. Not only can they, too, offer the support you need, but they’re also there to answer questions about whether or not a poop is normal and crayons in noses (it happens, folks).
Every parent wants to give their baby a healthy start in life, and doing so begins with your baby’s first pediatrician visit, also known as a well baby visit. In what will be the first of many, your baby’s doctor will check in on your little one soon after they’re discharged from the hospital to ensure everything is on track. During this visit, the doctor will not only examine your baby from tip to toe, but they’ll also take the time to answer questions, dispense some sage advice and allay any lingering fears you may have.
When Do Newborns Have Their First Doctor Appointment?
“Your newborn’s appointment should be within 1-2 days after discharge from the hospital,” says Dr. Emily Wisniewski, a pediatrician with Mercy Family Care Physicians . “Some babies can wait a little bit longer, 3-5 days even, provided there were no concerns about feeding, significant weight loss, or jaundice. But otherwise, you [and your baby] should be checked on soon after discharge to make sure your baby is growing and feeding well.”
It’s worth noting that after your baby’s initial visit to the pediatrician, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends well-baby visits at the following intervals for the first two years of your baby’s life.
How Far in Advance Do I Need to Schedule the First Baby Checkup?
Schedules can vary widely from doctor to doctor. If you’re concerned about getting an appointment, consider calling ahead (before your due date) to get a better idea of how busy your preferred pediatrician will be. There’s no harm in being proactive and scheduling your appointment in advance.
What Will Happen During My Newborn’s First Doctor Appointment?
Wisniewski tells Babylist that doctors and nurses cover a lot of ground during the first visit to the pediatrician.
“We get to know the family—especially if they are new to the practice or a first-time parent—and ask questions about feeding, peeing and pooping, safety in the home—regarding safe sleep, smoke detectors/guns in the home and other family members in the home,” she says. “We also will do a postpartum depression screening to check in on parents as well as baby.” In addition to the baby’s physical exam, Wisniewski says doctors will often leave time to “address any questions or concerns the parents have.”
What Will My Baby’s First Physical Exam Look Like?
Once you’ve filled out any required paperwork, the nurse will probably be the next person you see. Ahead of the doctor’s exam, the nurse will weigh and measure your baby. He or she will then chart your baby’s measurements on a growth chart that shows what percentile your baby is measuring. Beyond length and weight, the nurse will also measure the circumference of your baby’s head.
Incidentally, your baby will need to be naked to get the most accurate measurements. So, you’ll want to bring an extra diaper —but more on that later.
After the nurse has all the measurements and numbers plotted, the pediatrician will examine your little one from head to toe. This includes:
Checking Your Baby’s Head: Your doctor will palm your baby’s head to check for a still-soft fontanel, which you may know as the soft spot. Your baby’s head circumference should increase by about 4 inches within their first year, and the soft spots on their skull are designed to accommodate that growth. However, if they close up too quickly, that could be cause for concern.
Checking Their Neck and Collarbone: The doctor will feel your baby’s bones along the neck and collarbone to check for any breaks or fractures that occurred during delivery.
Rolling Your Baby’s Hips: Pediatricians often roll babies’ hips to look for any signs of hip dysplasia. Incidentally, they will do this at every well-baby visit until your little one takes their first steps.
Testing Your Baby’s Reflexes: During this visit and four to follow, your pediatrician will assess your baby’s Moro reflex (also known as the startle reflex). Typically, the Moro reflex test simulates falling. It involves placing the baby face up on a soft padded surface, lifting their head slightly above their body, then gently letting it fall into the doctor’s hand. The doctor is looking for your baby to extend their arms and draw them back quickly (what all of us do when we feel like we’re falling).
In addition to the Moro reflex, your pediatrician will also check your baby’s rooting reflex as well as their sucking reflex. To check the rooting reflex, they will touch or stroke your baby’s cheek to gauge whether or not baby automatically turns their head to that side and opens their mouth. To check the sucking reflex, the doctor will place a gloved finger in your baby’s mouth to see whether they start sucking.
Checking Their Femoral Pulse: Pediatricians typically check the baby’s pulse via the femoral artery. A weak femoral artery pulse could be a sign of a heart condition.
Checking Genitalia: During your baby’s first trip to the pediatrician (and every visit that follows), your pediatrician will check on the development of your baby’s genitalia. In this case, they’re looking for signs of infection from circumcisions, following up on undescended scrotums or labial adhesions.
Examining the Umbilical Stump: Doctors will also check on how the umbilical stump is healing and offer some guidance for care until it falls off on its own—usually within 1-3 weeks after birth.
What Questions Will the Pediatrician Ask?
Throughout the physical exam, your baby’s doctor will ask questions about your child’s feeding patterns, elimination and sleep schedule. Their questions will likely focus on the following topics:
- Feeding Patterns/Schedule: While you don’t necessarily need to keep a food diary, you should be prepared to communicate how often and how well your baby eats. This is also a good opportunity to share any questions or concerns you have about feeding baby.
- Baby’s Digestive System: Peeing and pooping are indicators of overall health so expect your provider to ask questions about baby’s digestive system. They’ll want to know how many wet diapers your baby has each day, how often they’re pooping, as well as the color and consistency of their poop.
- Sleeping Patterns: Your baby’s doctor will also check in on how your baby is sleeping , and they’ll likely go over safe sleeping guidelines.
Will My Baby Be Vaccinated During Their First Visit to the Pediatrician?
Baby’s first official checkup and first immunization will take place at the hospital. Typically, baby won’t get any shots during their first visit to the pediatrician, but Wisniewski notes, “If your baby did not receive the Hepatitis B vaccine in the hospital (usually given prior to discharge), then your infant should receive this at their first pediatrician appointment.”
What Should I Bring With Me to the First Checkup?
The short answer here is simply to bring your diaper bag . Remember that you’ll need to remove baby’s clothing and diaper for the nurse to take their measurements and get an accurate weight. So, it’s a good idea to bring along a blanket and a fresh diaper.
Wisniewski also suggests bringing the discharge summary of your baby’s hospital stay. “It helps the doctor know what happened in the hospital and if any follow-up is needed (like checking for jaundice),” she says.
What Questions Should I Ask the Doctor at My Baby’s First Appointment?
While your baby’s pediatrician will ask plenty of questions about your baby’s general health, this is also the time for you to ask any and all questions you may have about your newborn.
Common questions that new parents often have include:
- How do I know if my baby ate enough ?
- What should I do if my baby is not drinking enough breast milk ?
- Should I give supplements to my baby?
- How can I store my breast milk?
- How can I help my baby latch on to my breast?
- What’s the best way to soothe or care for sore nipples?
- How many naps should my baby take?
- How many hours a day should my baby sleep ?
- Is it okay if I wake up my baby to eat?
- How can I help my baby to stay asleep?
- Is it safe for my baby to s leep on their back ?
- How can I try to avoid sudden infant death syndrome?
- Where should my baby sleep?
- When will my baby sleep through the night?
Helpful hint: Keep a digital note or write down all the questions you have for your baby’s doctor. There’s a lot of ground to cover on your baby’s first visit to the doctor, and if your little one is fussing or crying for the duration, you can easily become flustered and forget your questions. Keeping an actual note is the best way to ensure you walk out of the appointment with all your questions answered. But don’t worry! This is a routine visit, and your pediatrician is here to guide you through it all.

Sharon Brandwein
Sharon Brandwein is a Certified Sleep Science Coach and a freelance writer. She specializes in parenting, health, and of course, all things sleep. Sharon’s work has also appeared on ABC News, USAToday, Parents, and Forbes. When she’s not busy writing, you might find her somewhere curating a wardrobe for her puppy.

- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
- Newborn Care
What to Expect at Your Baby’s First Pediatrician Visit
Nervous about your baby's first pediatrician visit? Here's what to expect, from paperwork to meeting the doctor, plus tips for making the visit easier for you and your baby.
Your baby should have their first well-baby visit at the pediatrician's office three to five days after birth, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). After that, you'll be going in for checkups every few months over the course of the first year.
Since your baby's first pediatrician visit might be the first time your newborn leaves home, it's natural to feel some trepidation. But remember that this visit is often empowering and informative for new parents. Read on to learn what to expect during your baby's first pediatrician visit, from exams to vaccinations, as well as tips for timing and preparation.
There Will Be Paperwork
Be prepared to fill out paperwork when you arrive. Remember to pack the following:
- Your ID and health insurance card
- Information about your newborn's discharge weight
- Any complications during pregnancy or birth
- Your family's medical history
Knowing that your older child has asthma or your parents have diabetes, for example, focuses your pediatrician's attention on likely problems, says Christopher Pohlod, DO , assistant professor of pediatrics at Michigan State University's College of Osteopathic Medicine.
The Nurse Will Do Some Exams
A nurse will probably handle the first part of your baby's exam. They'll do the following:
- Weigh your naked baby on a scale
- Extend their limbs to measure height and width
- Use a tape measure to determine the head circumference
According to the AAP, it's normal for babies to lose weight after birth (up to 10% of their body weight). But they'll generally gain it back within a couple of weeks.
You'll Get to Know the Doctor
The pediatrician will examine your baby, educate you about their health, and answer any questions. One of the biggest components of the first pediatrician visit is developing a relationship with your child's new doctor. They will be a source of information, support, and troubleshooting in the many years to come.
They'll Check Your Baby's Neck and Collarbone
At your baby's first pediatrician visit, a health care provider will feel along your baby's neckline to check for a broken collarbone during the physical exam. That's because some babies fracture their clavicle while squeezing through the birth canal.
If your pediatrician finds a small bump, that could mean a break is starting to heal. It will mend on its own in a few weeks. In the meantime, they may suggest pinning the baby's sleeve across their chest to stabilize the arm so the collarbone doesn't hurt.
They'll Check Your Baby's Head
A pediatrician will also palm your baby's head to check for a still-soft fontanel. They will do this at every well visit for the first one to two years.
Your baby's head should grow about 4 inches in the first year, and the two soft spots on their skull are designed to accommodate that rapid growth. But if the soft spots close up too quickly, it can lead to a condition called craniosynostosis, which is when the tight quarters can curb brain development, and your child may need surgery to fix it.
They'll Check Your Baby's Hips
The doctor will roll your baby's hips to check for signs of developmental hip dysplasia, a congenital malformation of the hip joint that affects 1 in every 1,000 babies. You can expect this exam starting at your baby's first pediatrician visit and every visit until your baby can walk.
"The exam looks completely barbaric," says Vinita Seru, MD , a pediatrician in Seattle. "I tell families what I'm doing so they don't think I'm trying to hurt the baby."
If your pediatrician feels a telltale click from the hips, they'll order an ultrasound. Luckily, when dysplasia is found early, treatment is simple: The baby wears a pelvic harness for a few months.
They'll Check Your Baby's Reflexes
To check for a Moro reflex, a health care provider startles your baby. For the first 3 or 4 months, whenever something startles your infant, they'll fling their arms out as if they're falling. It's an involuntary response that shows your baby is developing normally.
This exam starts at the first pediatrician visit and continues through the first four well-child visits. A health care provider might also check whether your little one grasps a finger or fans their toes after you touch their foot.
They'll Check Your Baby's Pulse
By pressing the skin along the side of the baby's groin, a health care provider checks for your baby's pulse in the femoral artery, which runs up from your baby's thigh. Your pediatrician wants to see if the pulse is weak or hard to detect on one or both sides as that may suggest a heart condition.
You can expect this exam at the first pediatrician visit and all baby well visits. Around 1 in 125 babies are diagnosed with a heart defect every year in the US. This check is a simple way to screen for problems, says Dr. Seru: "When a heart condition is caught early, it can increase the likelihood of a good recovery."
They'll Check Your Baby's Genitalia
Starting at the first pediatrician visit and every well-baby visit after that, a health care provider will check your baby's genitals to ensure everything looks normal.
In about 1 to 3% of babies with testicles, the testicles don't descend into the scrotum before birth. While the problem usually corrects itself by 3 to 4 months of age, your doctor will keep an eye on things to see if your baby needs surgical assistance in the future. They will also check for signs of infection if your baby has been circumcised .
In babies with vulvas, it's not uncommon to find labial adhesions. Although the labia should open up over time, adhesions can shrink the vaginal opening and make your baby more prone to urinary tract infections (UTIs) . "If we know that they're there when your baby has a high fever, we look for a UTI first," says Melissa Kendall, MD , a pediatrician in Orem, Utah.
They'll Ask About Your Baby’s Feeding Patterns
The doctor will want information about your baby's feeding patterns. You don't need to keep super-detailed records, but you should have a general idea of the following:
- How often your baby is eating
- How long they feed (if nursing)
- How much they consume (if bottle-feeding)
This is an excellent time to raise concerns or questions about latching, formula brands, and other feeding issues.
They'll Check Your Baby’s Digestive System
You should have a general idea of how often you change your baby's diapers each day. If your doctor knows the consistency, frequency, and color of your baby's poop , they can better assess their digestive system and nutrient absorption.
They'll Ask About Your Baby's Sleeping Patterns
A health care provider will also probably inquire about sleeping patterns at your first pediatrician visit. They'll also make sure you're following safe sleep practices to help reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
They'll Review the Childhood Vaccination Schedule
Hospitals usually give babies their first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine shortly after birth, but if your baby was born at home or at a birth center, they might receive it at their first pediatrician visit.
Most vaccinations start when your baby is 2 months old, and a health care provider might review the vaccine schedule with you so you're prepared for the many vaccines your baby will receive in the months ahead.
There Will Be Time for Questions
You will cover a lot of ground during your baby's first pediatrician visit. Ask the doctor to slow down, repeat, or clarify information if needed. It's also wise to come prepared with any questions you have.
Here are some examples:
- Is this behavior normal?
- Is my baby eating enough?
- Should their stool look like that?
- When should I schedule the next appointment?
- What should I expect in the next few days and weeks?
When you have a written list of talking points, you won't worry about your mind going blank if your baby starts to fuss, says Dr. Pohlod.
You'll Schedule Your Next Appointment
The lineup of well-baby checkups during the first year includes at least a half dozen more pediatrician visits.
Recommended Baby Checkup Schedule
Here is a quick-glance list of what ages the AAP recommends that your child be seen for well-child pediatrician visits through their second year:
- 3 to 5 days old
- 1 month old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
- 9 months old
- 12 months old
- 15 months old
- 18 months old
- 24 months old
At first glance, the recommended number of checkups may seem like a lot. But trust the process: This schedule was designed to closely monitor your baby's growth and development to ensure their health and well-being.
The checkups, depending on the age of your baby, will include measurements, sensory screening, and developmental health, which include social, behavioral, and mental health. It will also include vaccinations, oral health, and advice for parents and caregivers.
Frequent appointments with your baby's health care provider are also the best way to get personalized expert answers to your questions about your baby. Ultimately, it's important to be comfortable with your doctor, and seeing them frequently in the first year helps you develop a relationship you may have for years to come.
When you schedule your next appointment, ask about the office's hours of operation, billing policies, and how after-hours communication works. Keep the doctor's phone number handy, and be informed of what to do and who to contact in an emergency or when you have a question.
Tips for Your Baby's First Pediatrician Visit
Leaving the house with a newborn isn't easy, and it can be especially stressful when you're on a timetable (like when you're trying to make it to a scheduled appointment). But your baby's first pediatrician visit doesn't have to be super stressful. Here are some tips for smooth sailing:
- Plan your time. Ask for an appointment during the least busy part of the day. You can also see if a health care provider has specific time slots dedicated to seeing newborns. Expect the visit to take about 25 minutes, but plan for waiting and setbacks as well.
- Bring a support person. Consider bringing your partner or another caregiver to your baby's first doctor appointment. Two people can more effectively care for the baby, remember the doctor's advice, and recall questions you plan to ask.
- Dress your baby with the exam in mind. Since the doctor will examine your baby's entire body, dress them in easy-on, easy-off clothing or even just a diaper and comfortable blanket if weather permits.
- Be prepared, but pack light. Definitely bring a change of clothes, extra diapers, wipes, pacifiers, feeding supplies, and other necessities, but try not to overpack. Ultimately, "warmth, cuddling, loving, and reassuring voices are more helpful than a stuffed animal" at a newborn exam, says Brian MacGillivray, MD, a family medicine specialist in San Antonio.
- Wait in the car, if you can. If you attend the appointment with another person, send them inside to fill out paperwork while you wait in the car with the baby. This limits your newborn's exposure to germs. Some offices even have systems in place that allow you to fill out the paperwork online, wait in your car, and receive a call or text when it's time to go in.
- Keep your distance from others. If you must sit in the waiting room, have your baby face the corner. According to Mary Ellen Renna, MD , a pediatrician from Jericho, New York, the chances of catching sickness are lower if you maintain a 3-foot radius from others.
AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits . American Academy of Pediatrics . 2023.
Weight Loss . The American Academy of Pediatrics . 2020.
Clavicular Fractures in Newborns: What Happens to One of the Commonly Injured Bones at Birth? . Cureus . 2021.
Facts About Craniosynostosis . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . 2023.
Developmental Dislocation (Dysplasia) Of the Hip (DDH) . American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons . 2022.
Moro Reflex . StatPearls . 2023.
A five (5) chamber heart (Cor Triatriatum) in Infancy: A rare congenital heart defect . Niger Med J . 2013.
Undescended Testicles: What Parents Need To Know . American Academy of Pediatrics . 2022.
Periodicity Schedule . American Academy of Pediatrics . 2023.
Related Articles
Internet Explorer Alert
It appears you are using Internet Explorer as your web browser. Please note, Internet Explorer is no longer up-to-date and can cause problems in how this website functions This site functions best using the latest versions of any of the following browsers: Edge, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, or Safari . You can find the latest versions of these browsers at https://browsehappy.com
- Publications
- HealthyChildren.org
Shopping cart
Order Subtotal
Your cart is empty.
Looks like you haven't added anything to your cart.
- Career Resources
- Philanthropy
- About the AAP
- Confidentiality in the Care of Adolescents: Policy Statement
- Confidentiality in the Care of Adolescents: Technical Report
- AAP Policy Offers Recommendations to Safeguard Teens’ Health Information
- One-on-One Time with the Pediatrician
- American Academy of Pediatrics Releases Guidance on Maintaining Confidentiality in Care of Adolescents
- News Releases
- Policy Collections
- The State of Children in 2020
- Healthy Children
- Secure Families
- Strong Communities
- A Leading Nation for Youth
- Transition Plan: Advancing Child Health in the Biden-Harris Administration
- Health Care Access & Coverage
- Immigrant Child Health
- Gun Violence Prevention
- Tobacco & E-Cigarettes
- Child Nutrition
- Assault Weapons Bans
- Childhood Immunizations
- E-Cigarette and Tobacco Products
- Children’s Health Care Coverage Fact Sheets
- Opioid Fact Sheets
- Advocacy Training Modules
- Subspecialty Advocacy Report
- AAP Washington Office Internship
- Online Courses
- Live and Virtual Activities
- National Conference and Exhibition
- Prep®- Pediatric Review and Education Programs
- Journals and Publications
- NRP LMS Login
- Patient Care
- Practice Management
- AAP Committees
- AAP Councils
- AAP Sections
- Volunteer Network
- Join a Chapter
- Chapter Websites
- Chapter Executive Directors
- District Map
- Create Account

- Materials & Tools
- Clinical Practice
- States & Communities
- Quality Improvement
- Implementation Stories
Well-Child Visits: Parent and Patient Education
The Bright Futures Parent and Patient Educational Handouts help guide anticipatory guidance and reinforce key messages (organized around the 5 priorities in each visit) for the family. Each educational handout is written in plain language to ensure the information is clear, concise, relevant, and easy to understand. Each educational handout is available in English and Spanish (in HTML and PDF format). Beginning at the 7 year visit , there is both a Parent and Patient education handout (in English and Spanish).
For the Bright Futures Parent Handouts for well-child visits up to 2 years of age , translations of 12 additional languages (PDF format) are made possible thanks to the generous support of members, staff, and businesses who donate to the AAP Friends of Children Fund . The 12 additional languages are Arabic, Bengali, Chinese, French, Haitian Creole, Hmong, Korean, Polish, Portuguese, Russian, Somali, and Vietnamese.
Reminder for Health Care Professionals: The Bright Futures Tool and Resource Kit, 2nd Edition is available as an online access product. For more detailed information about the Toolkit, visit shop.aap.org . To license the Toolkit to use the forms in practice and/or incorporate them into an Electronic Medical Record System, please contact AAP Sales .
Parent Educational Handouts
Infancy visits.

3 to 5 Day Visit

1 Month Visit

2 Month Visit
4 Month Visit

6 Month Visit

9 Month Visit
Early childhood visits.

12 Month Visit

15 Month Visit
18 Month Visit

2 Year Visit

2.5 Year Visit

3 Year Visit

4 Year Visit
Parent and patient educational handouts, middle childhood visits.

5-6 Year Visit

7-8 Year Visit

7-8 Year Visit - For Patients

9-10 Year Visit

9-10 Year Visit - For Patients
Adolescent visits.

11-14 Year Visit

11-14 Year Visit - For Patients

15-17 Year Visit

15-17 Year Visit - For Patients

18-21 Year Visit - For Patients
Last updated.
American Academy of Pediatrics
Preventive Health Care Visits in Infants
Healthy infants should be seen by their doctor often during the first year of life. Preventive health care visits (also called well-child visits) typically take place within a few days after birth or by 2 weeks of age and at 1, 2, 4, 6, and 9 months of age. During these visits, the doctor uses age-specific guidelines to monitor the infant's growth and development and asks the parents questions about various developmental milestones (see table Developmental Milestones From Birth to Age 12 Months ). Tests are sometimes done, and during many visits, the doctor vaccinates the infant against various illnesses (see Childhood Vaccination Schedule ).
Health care visits also allow the doctor to educate the parents about eating, sleeping, behavior, child safety, nutrition, exercise, and good health habits. In addition, the doctor advises the parents what developmental changes to expect in their infant by the next visit.

Examination
The infant's length and height , weight , and head circumference are measured at every visit. The doctor examines the infant for various abnormalities, including signs of hereditary disorders or birth defects .
The eyes are examined, and vision is tested. Infants who were born very prematurely (before the completion of 32 weeks of development in the uterus) usually need more frequent eye examinations by an eye specialist to look for retinopathy of prematurity , which is an eye disease that occurs when infants are born before the blood vessels in their eyes are fully developed and may result in blindness, and for the development of refractive errors , which result in blurring of vision. These disorders are more common among infants who were born very prematurely.
The doctor checks the infant’s hips for signs that the hip joints are loose or dislocated ( developmental dysplasia of the hip ). The doctor checks the infant's teeth , if they are present, for cavities and the mouth for thrush , which is a common yeast infection among infants.
The doctor also examines the heart, lungs, abdomen, arms and legs, and genitals.
Screening tests are done to assess whether infants are at risk of certain disorders.
Blood tests are done to detect anemia , sickle cell disease , and exposure to lead .
Hearing tests are done shortly after birth to determine whether an infant has a hearing disorder or hearing loss (see Newborn Screening Tests ) and are repeated later if new concerns about the infant's hearing develop (see also Hearing Impairment in Children ).
Infants are screened for tuberculosis (TB) risk factors with a questionnaire at all well-child visits, usually beginning in infancy. Risk factors include exposure to TB, being born in or having traveled to areas of the world where TB is common (countries other than the United States, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand and Western and North European countries), having a family member with TB, and having parents or close contacts who are recent immigrants from an area where TB is common or who have recently been in jail. Those with risk factors usually have tuberculosis screening tests done.
At these visits, the doctor gives parents age-appropriate safety guidelines.
The following safety guidelines apply to infants from birth to age 12 months:
Use a rear-facing car seat and place it in the back seat of the vehicle.
Set the hot water heater to 120° F or less.
Prevent falls from changing tables and around stairs.
Place infants on their back to sleep on a firm, flat mattress for every sleep, do not share a bed, and do not place pillows, bumper pads, nonfitted sheets, stuffed animals or other toys, quilts, comforters, or weighted or loose blankets in the crib. (See also sidebar Safe to Sleep: Reducing the Risk of SIDS .)
Do not give infants foods and objects that can cause choking or be inhaled into the lungs.
Do not use baby walkers.
Place safety latches on cabinets and cover electrical outlets.
Remain alert when watching infants in the bathtub or near a pool or any body of water and when they are learning to walk.
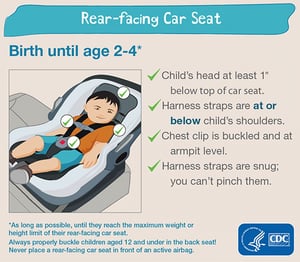
Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), National Center for Injury Prevention and Control ( Transportation Safety Resources ). This guidance from the CDC is for the United States, and regulations may differ in other countries.

Nutrition and exercise
For infants, recommendations for nutrition are based on age. The doctor can help parents weigh the benefits of breastfeeding versus formula-feeding and give guidance regarding solid foods .
Parents should provide infants with a safe environment they can roam in and explore. Outdoor play should be encouraged from infancy.
Screen time (for example, television, video games, cell phones and other handheld devices, and noneducational computer time) may result in inactivity and obesity. Limits on the time a child spends using devices with screens should start at birth and be maintained throughout adolescence.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
- Pregnancy Weeks
- Nursery Design
- Toddler Sleep
- White Noise
What to Expect at Well-Child Visits
On This Page
Well-child visit schedule.
- Newborn Well-Child Visit
- Baby Well-Child Visits
1-Month Well-Child Visit
2-month well-child visit, 4-month well-child visit, 6-month well-child visit, 9-month well-child visit, 12-month well-child visit, toddler well-child visits, 15-month well-child visit, 18-month well-child visit, 24-month well-child visit, 30-month well-child visit, 3-year well-child visit.
- Vaccines Schedule From 0-2 Years
While it’s a no-brainer that you take your baby or toddler to the doctor when they’re sick, it’s also important to bring your child to the pediatrician for regularly scheduled visits when they are feeling just fine! Enter: The well-child visit. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that each kiddo goes to the doctor within days of birth, then almost monthly, then annually for must-have screenings and assessments. Here’s what to expect at childhood checkups—and when to expect them .
In the first few years of life, you’ll get to know your child’s healthcare provider very well.
Typical child well visit schedule:
- Within 3 to 5 days of birth
- Annually after 3 years
What to Expect at the Newborn Well-Child Visit
Congrats! You just brought your baby home from the hospital…now pack up the diaper bag and head to their very first visit to the pediatrician! (Still haven’t secured your baby’s pediatrician? Use our guide to help you find the perfect doc .) All newborns need a first-week checkup within 3 to 5 days from birth.
What to bring to Newborn Well-Child Visit
Beyond your sweet babe, you may need to bring all your hospital paperwork, which should contain info about your baby’s discharge weight and/or any possible complications that occurred during pregnancy or birth. Some hospitals and practices use online charts that multiple providers can access, but if yours doesn’t, you’ll want to have that information on hand. (If you’re unsure, just ask!)
Newborn Well-Child Visit Vaccines
If your little one did not receive the Hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine while at the hospital, they should receive the first HepB vaccine dose now.
Newborn Well-Child Visit Screenings
Your baby’s pediatrician will likely tackle the following screening measure and exams:
Your baby will be measured and weighed to ensure they’re growing as expected.
Baby’s head, ears, eyes, and mouth will be examined.
Baby’s skin will be looked at for birthmarks or rashes.
The doctor will review the results of two newborn screenings your baby received shortly after birth: hearing and blood test results. (Rescreening may be done.)
If your baby did not have their hearing screened at the hospital—or if they were born at home or a birthing center, their hearing will be screened .
The pediatrician will press gently on your baby’s tummy to check organs and for an umbilical hernia.
They’ll also move your baby’s legs to check for dislocation or other issues with their hip joints.
Your baby’s genitalia will be examined for signs of infection, such as tenderness or lumps.
What to Expect at Baby Well-Child Visits
During the first year of your baby’s life, they will visit the pediatrician every month or so for a well-child checkup. All first-year well-visits entail the following:
Baby’s weight and height will be recorded.
The pediatrician will check on your baby’s developmental milestones.
Baby’s heart rate and breathing will be checked.
The doctor will examine your baby’s skin.
They’ll also press on Baby’s belly to detect enlarged organs or an umbilical hernia.
Baby’s legs and hips will be checked for dislocation or other joint problems.
Baby’s genitalia will be inspected for signs of infection.
Beyond the screenings listed above, you can also expect:
Your little one may receive the HepB vaccine, though sometimes this occurs at Baby’s two-month checkup.
Mom will be screened for postpartum depression. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends moms be screened for postpartum depression (PPD) during well-child visits at 1, 2, 4, and 6 months of age.
If your baby is breastfeeding or consuming less than 27 ounces a day of vitamin-D containing baby formula, the pediatrician will offer advice about vitamin D supplementation .
Possible questions about feeding, sleep, number of wet and dirty diapers, and other 1-month milestones
Beyond the screenings listed above, you can expect:
Baby is set to receive the following vaccinations: RV, DTap, Hib, PCV13, and IPV.
Mom will be screened for postpartum depression .
Possible questions about feeding, sleep, number of wet and dirty diapers, tummy time , and other 2-month milestones
Your bub will likely receive the following vaccinations: RV, DTap, Hib, PCV13, and IPV.
Mom will be screened for postpartum depression.
Blood may be drawn to screen for anemia , which is a condition marked by a low supply of healthy red blood cells.
If your baby is partially or completely breastfed, the doctor will offer advice about introducing an iron supplement .
Possible questions about sleep regression , babbling, Baby’s gums, teething, starting solids soon, when/how to introduce allergens , and other 4-month milestones
Your baby will likely get the following vaccinations: DTap, Hib, and PCV13. If your bub received the PedvaxHIB vaccine, they don’t require a 6-month Hib shot. If your Baby received the RotaTeq (RV5) vaccine, they’ll get their third dose now.
If your baby’s 6-month well-visit falls during flu season, they should get the recommended flu shot —with the second dose four weeks later. If it’s not flu season, your pediatrician will advise you when to return to get this important vaccine.
Fluoride varnish may be applied if your bub’s first tooth has popped through (most babies start cutting teeth around this age).
Possible questions about starting solids, introducing nuts , teething, and sleep, and other 6-month baby milestones
If your baby hasn’t yet received their third HepB and IPV shots, they may get them now. Technically, babies can get either of these vaccines between 6 and 18 months, and many doctors opt to give them during the 9-month checkup.
Your baby’s pediatrician will conduct a more formal developmental screening than usual, asking several questions about your little one’s growth and behavior. The doc may even ask if they can observe you and your little one playing together. All of this is to see whether your baby is developing at an expected rate or further testing is needed.
Possible questions about pointing, babyproofing , sippy cups, constipation, and other 9-month baby milestones
Baby will likely receive the following vaccinations: Hib, PCV13, MMR, VAR, HepA (second dose around 6 months later). Your little is eligible for all these vaccines at their one-year checkup, but that doesn’t mean they’ll occur all at once. For example, babies should receive Hib, PCV13, MMR, VAR vaccines between 12 and 15 months. And you have until 23 months to tick the HepA shot off your list.
Your baby may be screened for anemia .
Based on your little one’s risk, their hearing, vision, blood pressure, and/or their blood lead levels may be tested.
Possible questions about crawling, walking, talking, transitioning to whole milk , and other first-year baby milestones
During Baby’s first year, doctor appointments were coming at you in rapid succession. But now that you’ve got a toddler on your hands, the time between well-visits widens. Between 15 months old and your bub’s third birthday, you’ll be back at the pediatrician’s office just five times for checkups. Here’s what you can expect at every well visit:
Your toddler’s weight and height will be recorded.
The pediatrician will check on your tot’s developmental milestones.
Your toddler’s head, ears, eyes, and mouth will be examined.
Toddler’s heart rate and breathing will be checked.
A skin examination will likely occur.
The doctor will press on your child’s belly to feel organs and for an umbilical hernia.
Your toddler's genitalia will be looked at for signs of infection, such as tenderness or lumps.
Depending on which vaccines your child got at their 12-month visit, they may be due for Hib, PCV13, MMR, VAR, which are all recommended between 12 and 15 months.
Your toddler may be checked for anemia.
Based on specific risk factors, your toddler may have their vision, hearing, and/or blood pressure checked, too.
If your tot has already received a fluoride varnish on their teeth, a second application may occur .
Possible questions about sleep, motor skills, social skills, eating, talking, and constipation, and other 15-month milestones
Depending on which immunizations your kiddo got during their last well visit, they may be due for HepA with a second dose about 6 months later and/or DTap
Based on your child’s risk factors—or possible concerns—your tot’s pediatrician may screen for anemia or lead poisoning, do a blood pressure check, and/or conduct a hearing or vision test.
In addition to regular developmental surveillance and screening, all 18-month-olds need a formal screening for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) at their well-child visit. There are several screening tool options, but the 23-point questionnaire called the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers–Revised with follow-u (M-CHAT-R/F) is the most common screening tool used in pediatric offices.
Possible questions about sleep, eating, motor skills, play habits, potty training, tantrums, and other 18-month milestones
Once your tot is 2 years old, they can get the nasal spray version of the flu shot. (Your toddler is still too young to get their annual jab—or FluMist—at the local pharmacy.)
The AAP recommends all children get screened for autism spectrum disorder at both their 18- and 24-month well-child visits. ( Learn about early autism signs. )
Your child’s doc will likely start using BMI (body mass index) to screen for overweight and obesity in children beginning at 2 years old.
Your child’s doctor may order tests for anemia, lead, high cholesterol, and/or tuberculosis if needed.
Possible questions about sleep, potty training , motor and language development , and other 24-month milestones
Plan for all of the basic well-visit screenings at the 30-month (or two-and-a-half year) checkup. If your toddler is up to date on vaccines and feeling good, not much else happens at this checkup! But just because there’s nothing “big” happening at this well visit, doesn’t mean it’s not important. Remember, these checkups are how doctors track your child’s development. It’s a time to ask questions about your child’s 30-month milestones . And these visits ensure that your toddler is getting the care they need to stay healthy!
While visual acuity screening (seeing details of letters or symbols from a distance) is recommended to begin between the ages 4 and 5, cooperative 3-year-olds can easily be tested, too.
Your child’s blood pressure will be checked.
Again, your child may be checked for anemia, lead, and/or tuberculosis, if needed.
Possible questions about sleep, speech and language development, motor skills, and other 3-year milestones
Well-Child Visit Vaccine Schedule: Birth to 2 Years
The first two years are prime for protecting your child against numerous diseases and infections. Here’s the rundown of the recommended vaccine schedule for your little one’s earliest years:
Vaccines at 1-month checkup: HepB vaccine. Sometimes this occurs at Baby’s two-month checkup, instead.
Vaccines at 2-month checkup: RV, DTap, Hib, PCV13, and IPV
Vaccines at 4-month checkup: RV, DTap, Hib, PCV13, and IPV
Vaccines at 6-month checkup: DTap, Hib, PCV13, flu shot. While all 6-month-olds should receive their annual flu shot, your baby’s 6-month checkup may not occur during flu season. If that’s the case, your baby will receive the vaccine later. Regardless, your child may need a second dose of the flu vaccine four weeks after the first. Also, if your Baby received the RotaTeq, (RV5) vaccine, they’ll get their third dose at 6 months.
Vaccines at 9-month checkup: HepB, IPV (though they can be given as early as 6 months and as late as 18 months)
Vaccines at 12-month checkup: Hib, PCV13, MMR, VAR, HepA (second dose ~6 months later). Your baby is eligible for all these vaccines at their one-year checkup, but that doesn’t mean they will all occur at once. For example, babies should receive Hib, PCV13, MMR, VAR vaccines between 12 and 15 months. And you have until 23 months to tick the HepA shot off your list.
For a more in-depth look at the recommended vaccine schedule for children, please check out our soup-to-nuts vaccine guide .
- American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP): 1st Week Checkup Checklist: 3 to 5 days old
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Recommended Vaccinations for Infants and Children, Parent-Friendly Version
- Nemours Children’s Health: Hearing Tests
- Incorporating Recognition and Management of Perinatal Depression Into Pediatric Practice, Pediatrics, January 2019
- AAP: Where We Stand: Vitamin D & Iron Supplements for Babies
- AAP: Checkup Checklist: 4 Months Old
- AAP: Checkup Checklist: 6 Months Old
- AAP: Checkup Checklist: 9 Months Old
- AAP: Checkup Checklist: First Birthday (12 Months Old)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Important Milestones: Your Baby By Fifteen Months
- AAP: How Pediatricians Screen for Autism
- National Alliance of State Pharmacy Associations: Pharmacist Administered Vaccines, Updated August 2022, Based on NASPA Analysis of State Pharmacy Practice Laws
- CDC: About Child & Teen BMI
- Nemours Children’s Health: Your Child's Checkup: 2 Years (24 Months)
View more posts tagged, health & safety
Have questions about a Happiest Baby product? Our consultants would be happy to help! Submit your questions here.
Disclaimer: The information on our site is NOT medical advice for any specific person or condition. It is only meant as general information. If you have any medical questions and concerns about your child or yourself, please contact your health provider.
You may also like
In the 48 contiguous United States, customers will be charged $59.50 + tax for the shipment of SNOO back to Happiest Baby. Added charges will apply for shipping to and from Alaska and Hawaii.
* An additional $185 shipping fee will be applied to SNOO purchases sent to Hawaii and Alaska.
Your baby's first year of pediatrician visits, explained

Understanding baby checkups
Baby check-ups, often called “well visits” or “well baby visits”, are routine doctor visits with your child’s pediatrician. This is a designated time for the doctor to assess how your baby is doing and for parents to address any concerns they might have.
These early appointments are important because lots of things happen — like immunizations, developmental screenings, and physical exams — that are important for your child’s healthy growth and development.
When to schedule the first pediatrician visit
Technically, your child’s first pediatrician visit will happen in the hospital, birth center, or home, shortly after your baby is born. Your baby should also have their newborn hearing screening done during this time. But your child’s first trip to the ped’s office will happen 3 to 5 days after birth, unless they need to be seen sooner.
As you can imagine, things might be quite hectic then. You’ve just delivered your baby, you may have had a hospital stay, and then you’re discharged and off to the parenting races. It can leave you wondering: when do I actually schedule my baby’s first doctor’s appointment?
Usually, you’ll want to schedule your baby’s first pediatrician visit after they are born, but this means you should already have chosen your child’s pediatrician. You, or a designated support person, can make the call to schedule the appointment shortly after birth.
What happens at the first pediatrician visit
Here’s what typically happens at a newborn’s first doctor appointment.
- Completing paperwork. Yes, more paperwork. This is one reason why it can be helpful to bring a support person along, if possible. That way, one person can focus on completing the paperwork while the other can tend to the baby.
- Reviewing medical history. It’s important for your child’s doctor to know about your family’s medical history because this lets them know whether there may be any concerns to watch out for when it comes to your baby’s health.
- Assessing baby’s growth, sleep, and eating habits. The pediatrician will likely ask you many questions about how your baby has been sleeping and eating, as well as how many wet and poop-y diapers they make per day. This information helps the pediatrician determine how well your baby is growing. They will also weigh your baby on a scale without clothes, and measure their length and the size of their head. They will tell you what percentile your baby is in for each of these measurements, giving you an indication of their size in comparison to other children the same age.
- Performing a physical exam. A physical exam for newborns is especially important to see whether the baby might have any injuries from birth. Doctors will check your baby’s head for soft spots, or fontanelles, on top, and talk with you about the soft spots. They will also check your baby’s neck, hips, and umbilical cord, and should give you information on how to keep the area clean until it falls off later. The pediatrician will also check your baby's newborn reflexes and look for signs of jaundice, like yellowing of the eyes or skin.
Preparing for the first pediatrician visit
During this well visit, you'll also get the chance to ask questions. So a great way to prepare for your baby’s first doctor visit is to prepare a list of questions you want to ask in advance. For example:
- How can I help my baby regain any birth weight they lose?
- How do I care for my baby's umbilical cord, and when will it fall off?
- (If you have a baby who was circumcised) How can I help my child's circumcision heal well?
- (If you have a baby who was not circumcised) How do I clean my child's penis properly?
- How can I help my baby reach their developmental milestones?
- Does my baby show any signs of developmental delays?
- What should I do if my baby gets sick?
- Are there any resources you recommend for postpartum support?
A few practical tips for the first pediatrician visit
Emotionally, the first pediatrician visit can be tough for the family. Your baby may cry because they’re outside their comfort zone, and it can be hard to see your baby upset, even though it's for their own good.
Being prepared with all the supplies and information you need can help make the first well visit easier. Here’s a list of helpful items to bring along:
- Extra diapers and wipes
- Extra milk, if needed
- Extra baby clothes and burp cloths
- A blanket (it can be cold in doctor’s offices)
- A pacifier if your baby uses one
- Your ID and health insurance card
- Any helpful notes about complications you may have had during pregnancy or birth
- Notes about family medical history
- Paperwork you completed from the hospital
Older infant-checkup schedule
After the first pediatrician visit, well baby checkups will probably happen according to this American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)-recommended infant checkup schedule :
After 12 months, when your baby officially becomes a toddler, checkups will likely happen at 15 months, 18 months, 24 months, and 30 months. From 3 years old onward, child checkups will happen once a year.
What happens at later well-baby visits
Most well baby visits include a standard set of activities, including:
- A growth assessment of weight, length or height, and head size
- Vaccinations
- A physical exam, including checking for jaundice during the first few visits
- Evaluating developmental milestones progress
- Talking about sleep and nutrition
Questions to ask your pediatrician at well visits
Open communication between parents and their child’s pediatrician is important, since the common goal is to make sure your baby is healthy and growing well. These common questions may help you feel empowered and informed about your baby’s well-being:
- What vaccinations are recommended for my child at this age?
- Is my child’s growth on track?
- Is my child meeting their developmental milestones for this age?
- What should my child be eating and/or drinking at this age?
- Do you recommend any medications or vitamins for my baby at this age? What are the potential risks and benefits?
What to do between pediatrician appointments
Of course, if there are any other questions, concerns you have, or ideas you want to run by your child’s doctor, well visits are the perfect time to bring them up. But between pediatrician visits, it can be helpful to have a trusted source you can go to for support. Summer Health’s doctors and specialists are available for all your child's primary care and urgent care needs.
There are several ways Summer Health pediatricians and specialists can support you and your family between pediatrician appointments, like:
- Answering questions you have about your baby’s sleep, eating habits, growth, development, or behavior
- Providing you with breastfeeding tips and recommendations if you run into any issues
- Helping you care for your baby if they get sick (You can even send us a photo or video of your baby if there are certain symptoms you’d like us to see or hear.)
With a trusted pediatrician your child can see in-person regularly, and the support of the caring providers at Summer Health, you can ensure your child has the best care team during their first year of life.
American Academy of Pediatrics. Recommendations for Preventive Pediatric Health Care. https://downloads.aap.org/AAP/PDF/periodicity_schedule.pdf
Related posts
Baby cries and colic: a guide for worried parents.
Trying to figure out why your baby is crying can feel like trying to solve a logic puzzle. Sometimes there’s an easy fix. Other times, the odds aren’t quite in your favor. It can be especially frustrating when your baby is fussy or crying right after you've tried to solve a core problem, like feeding them if you think they’re hungry. And if you have a colicky baby who cries more than most, your child may seem inconsolable. Knowing these can be stressful times for parents, here are some ways you can try to solve the unpredictable puzzle of baby’s cries.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Suspendisse varius enim in eros elementum tristique. Duis cursus, mi quis viverra ornare, eros dolor interdum nulla, ut commodo diam libero vitae erat. Aenean faucibus nibh et justo cursus id rutrum lorem imperdiet. Nunc ut sem vitae risus tristique posuere.
When can babies start to swim
Is there anything cuter than a little tot smiling as he/she splashes away in the water on a sunny day? One of your priorities as a parent might be keeping that smile on your little one’s face, but your top priority is probably keeping them safe in the water. Consider this deep-dive into introducing swimming to newborns and infants a helpful start to a lifelong love of and respect for water.

Tips for traveling with a newborn baby
Whether you're daydreaming about a family getaway or already have one in the works, preparing for travel with a newborn is a big deal. Between packing, sorting out travel details, and wondering how on earth you'll keep your baby happy during the journey, there’s a lot to consider. Traveling with a newborn should be fun and it’s a wonderful opportunity to start building precious family memories. But before you jump into planning, let's go over some key family travel tips to make sure your adventure is a smooth and enjoyable one for everyone involved.
Newborn to toddler: a complete guide on baby milestones
So many words we use to describe babies and small children are used interchangeably. So before we hop into developmental milestones, let’s clarify when your child is considered a newborn, an infant, or a toddler.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.
Block quote
Ordered list
Unordered list
Superscript
The 2-Year-Old Checkup
Medical review policy, latest update:.
Medically reviewed to ensure accuracy.
The physical checkup
Developmental milestones, more about your toddler, 2-year-old vaccines, questions to ask your doctor.
Believe it or not, the time of frequent well-baby visits is coming to an end. After taking your child for another appointment around her half birthday (when she's 30 months old), you'll book a 3-year checkup . Trusted Source American Academy of Pediatrics AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits See All Sources [3] From then on, it’s just a single yearly visit.
Updates history
Go to your toddler's month, trending on what to expect, is your toddler being disrespectful here's why and what to do, here’s why your toddler is taking off his clothes and what to do about it, ⚠️ you can't see this cool content because you have ad block enabled., using positive reinforcement on your toddler, what to do if your toddler keeps running away, 11 tips to make flying with a toddler go more smoothly.
Doctor Visits
Make the Most of Your Baby’s Visit to the Doctor (Ages 0 to 11 Months)

Take Action
Babies need to go to the doctor or nurse for a “well-baby visit” 6 times before their first birthday.
A well-baby visit is when you take your baby to the doctor to make sure they’re healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury.
At a well-baby visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch any problems early, when they may be easier to treat. You’ll also have a chance to ask any questions you have about caring for your baby.
Learn what to expect so you can make the most of each well-baby visit.
Well-Baby Visits
How often do i need to take my baby for well-baby visits.
Babies need to see the doctor or nurse 6 times before their first birthday. Your baby is growing and changing quickly, so regular visits are important.
The first well-baby visit is 2 to 3 days after coming home from the hospital, when the baby is about 3 to 5 days old. After that first visit, babies need to see the doctor or nurse when they’re:
- 1 month old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
- 9 months old
If you’re worried about your baby’s health, don’t wait until the next scheduled visit — call the doctor or nurse right away.
Child Development
How do i know if my baby is growing and developing on schedule.
Your baby’s doctor or nurse can help you understand how your baby is developing and learning to do new things — like smile or turn their head to hear your voice. These are sometimes called “developmental milestones.”
At each visit, the doctor or nurse will ask you how you’re doing as a parent and what new things your baby is learning to do.
By age 2 months, most babies:
- Lift their head when lying on their stomach
- Look at your face
- Smile when you talk to them
- React to loud sounds
See a complete list of milestones for kids age 2 months .
By age 4 months, most babies:
- Bring their hands to their mouth
- Make cooing sounds
- Hold toys that you put in their hand
- Turn their head to the sound of your voice
- Make sounds when you talk to them
See a complete list of milestones for kids age 4 months .
By age 6 months, most babies:
- Lean on their hands for support when sitting
- Roll over from their stomach to their back
- Show interest in and reach for objects
- Recognize familiar people
- Like to look at themselves in a mirror
See a complete list of milestones for kids age 6 months .
By age 9 months, most babies:
- Make different sounds like “mamamama” and “bababababa”
- Smile or laugh when you play peek-a-boo
- Look at you when you say their name
- Sit without support
See a complete list of milestones for kids age 9 months .
What if I'm worried about my baby's development?
Remember, every baby develops a little differently. But if you’re concerned about your child’s growth and development, talk to your baby’s doctor or nurse.
Learn more about newborn and infant development .
Take these steps to help you and your baby get the most out of well-baby visits.
Gather important information.
Take any medical records you have to the appointment, including a record of vaccines (shots) your baby has received and results from newborn screenings . Read about newborn screenings .
Make a list of any important changes in your baby’s life since the last doctor’s visit, like:
- Falling or getting injured
- Starting daycare or getting a new caregiver
Use this tool to keep track of your baby’s family health history .
What about cost?
Under the Affordable Care Act, insurance plans must cover well-child visits. Depending on your insurance plan, you may be able to get well-child visits at no cost to you. Check with your insurance company to find out more.
Your child may also qualify for free or low-cost health insurance through Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP). Learn about coverage options for your family.
If you don’t have insurance, you may still be able to get free or low-cost well-child visits. Find a health center near you and ask about well-child visits.
To learn more, check out these resources:
- Free preventive care for children covered by the Affordable Care Act
- How the Affordable Care Act protects you and your family
- Understanding your health insurance and how to use it [PDF - 698 KB]
Ask Questions
Make a list of questions to ask the doctor..
Before the well-baby visit, write down 3 to 5 questions you have. Each well-baby visit is a great time to ask the doctor or nurse any questions about:
- How your baby is growing and developing
- How your baby is sleeping
- Breastfeeding your baby
- When and how to start giving your baby solid foods
- What changes and behaviors to expect in the coming months
- How to make sure your home is safe for a growing baby
Here are some questions you may want to ask:
- Is my baby up to date on vaccines?
- How can I make sure my baby is getting enough to eat?
- Is my baby at a healthy weight?
- How can I make sure my baby is sleeping safely — and getting enough sleep?
- How can I help my baby develop speech and language skills?
- Is it okay for my baby to have screen time?
- How do I clean my baby's teeth?
Take a notepad, smartphone, or tablet and write down the answers so you can remember them later.
Ask what to do if your baby gets sick.
Make sure you know how to get in touch with a doctor or nurse when the office is closed. Ask how to reach the doctor on call, or if there's a nurse information service you can call at night or on the weekend.
What to Expect
Know what to expect..
During each well-baby visit, the doctor or nurse will ask you about your baby and do a physical exam. The doctor or nurse will then update your baby’s medical history with all of this information.
The doctor or nurse will ask questions about your baby.
The doctor or nurse may ask about:
- Behavior — Does your baby copy your movements and sounds?
- Health — How many diapers does your baby wet each day? Does your baby spend time around people who are smoking or using e-cigarettes (vaping)?
- Safety — If you live in an older home, has it been inspected for lead? Do you have a safe car seat for your baby?
- Activities — Does your baby try to roll over? How often do you read to your baby?
- Eating habits — How often does your baby eat each day? How are you feeding your baby?
- Family — Do you have any worries about being a parent? Who can you count on to help you take care of your baby?
Your answers to questions like these will help the doctor or nurse make sure your baby is healthy, safe, and developing normally.
Physical Exam
The doctor or nurse will also check your baby’s body..
To check your baby’s body, the doctor or nurse will:
- Measure height, weight, and the size of your baby’s head
- Take your baby’s temperature
- Check your baby’s eyes and hearing
- Check your baby’s body parts (this is called a physical exam)
- Give your baby shots they need
Learn more about your baby’s health care:
- Read about what to expect at your baby’s first checkups
- Find out how to get your baby’s shots on schedule
Content last updated March 30, 2023
Reviewer Information
This information on well-baby visits was adapted from materials from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institutes of Health.
Reviewed by: Sara Kinsman, M.D., Ph.D. Director, Division of Child, Adolescent, and Family Health Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
Bethany Miller, M.S.W. Chief, Adolescent Health Branch Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
Diane Pilkey, R.N., M.P.H. Nursing Consultant, Division of Child, Adolescent, and Family Health Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
September 2021
You may also be interested in:

Breastfeed Your Baby

Take Care of Your Child's Teeth

Eat Healthy During Pregnancy: Quick Tips
The office of disease prevention and health promotion (odphp) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website..
Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by ODPHP or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.

KATHERINE TURNER, MD
Am Fam Physician. 2018;98(6):347-353
Related letter: Well-Child Visits Provide Physicians Opportunity to Deliver Interconception Care to Mothers
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
The well-child visit allows for comprehensive assessment of a child and the opportunity for further evaluation if abnormalities are detected. A complete history during the well-child visit includes information about birth history; prior screenings; diet; sleep; dental care; and medical, surgical, family, and social histories. A head-to-toe examination should be performed, including a review of growth. Immunizations should be reviewed and updated as appropriate. Screening for postpartum depression in mothers of infants up to six months of age is recommended. Based on expert opinion, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends developmental surveillance at each visit, with formal developmental screening at nine, 18, and 30 months and autism-specific screening at 18 and 24 months; the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force found insufficient evidence to make a recommendation. Well-child visits provide the opportunity to answer parents' or caregivers' questions and to provide age-appropriate guidance. Car seats should remain rear facing until two years of age or until the height or weight limit for the seat is reached. Fluoride use, limiting or avoiding juice, and weaning to a cup by 12 months of age may improve dental health. A one-time vision screening between three and five years of age is recommended by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force to detect amblyopia. The American Academy of Pediatrics guideline based on expert opinion recommends that screen time be avoided, with the exception of video chatting, in children younger than 18 months and limited to one hour per day for children two to five years of age. Cessation of breastfeeding before six months and transition to solid foods before six months are associated with childhood obesity. Juice and sugar-sweetened beverages should be avoided before one year of age and provided only in limited quantities for children older than one year.
Well-child visits for infants and young children (up to five years) provide opportunities for physicians to screen for medical problems (including psychosocial concerns), to provide anticipatory guidance, and to promote good health. The visits also allow the family physician to establish a relationship with the parents or caregivers. This article reviews the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines for screenings and recommendations for infants and young children. Family physicians should prioritize interventions with the strongest evidence for patient-oriented outcomes, such as immunizations, postpartum depression screening, and vision screening.
Clinical Examination
The history should include a brief review of birth history; prematurity can be associated with complex medical conditions. 1 Evaluate breastfed infants for any feeding problems, 2 and assess formula-fed infants for type and quantity of iron-fortified formula being given. 3 For children eating solid foods, feeding history should include everything the child eats and drinks. Sleep, urination, defecation, nutrition, dental care, and child safety should be reviewed. Medical, surgical, family, and social histories should be reviewed and updated. For newborns, review the results of all newborn screening tests ( Table 1 4 – 7 ) and schedule follow-up visits as necessary. 2
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
A comprehensive head-to-toe examination should be completed at each well-child visit. Interval growth should be reviewed by using appropriate age, sex, and gestational age growth charts for height, weight, head circumference, and body mass index if 24 months or older. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)-recommended growth charts can be found at https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/who_charts.htm#The%20WHO%20Growth%20Charts . Percentiles and observations of changes along the chart's curve should be assessed at every visit. Include assessment of parent/caregiver-child interactions and potential signs of abuse such as bruises on uncommonly injured areas, burns, human bite marks, bruises on nonmobile infants, or multiple injuries at different healing stages. 8
The USPSTF and AAP screening recommendations are outlined in Table 2 . 3 , 9 – 27 A summary of AAP recommendations can be found at https://www.aap.org/en-us/Documents/periodicity_schedule.pdf . The American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) generally adheres to USPSTF recommendations. 28
MATERNAL DEPRESSION
Prevalence of postpartum depression is around 12%, 22 and its presence can impair infant development. The USPSTF and AAP recommend using the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (available at https://www.aafp.org/afp/2010/1015/p926.html#afp20101015p926-f1 ) or the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (available at https://www.aafp.org/afp/2012/0115/p139.html#afp20120115p139-t3 ) to screen for maternal depression. The USPSTF does not specify a screening schedule; however, based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends screening mothers at the one-, two-, four-, and six-month well-child visits, with further evaluation for positive results. 23 There are no recommendations to screen other caregivers if the mother is not present at the well-child visit.
PSYCHOSOCIAL
With nearly one-half of children in the United States living at or near the poverty level, assessing home safety, food security, and access to safe drinking water can improve awareness of psychosocial problems, with referrals to appropriate agencies for those with positive results. 29 The prevalence of mental health disorders (i.e., primarily anxiety, depression, behavioral disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder) in preschool-aged children is around 6%. 30 Risk factors for these disorders include having a lower socioeconomic status, being a member of an ethnic minority, and having a non–English-speaking parent or primary caregiver. 25 The USPSTF found insufficient evidence regarding screening for depression in children up to 11 years of age. 24 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends that physicians consider screening, although screening in young children has not been validated or standardized. 25
DEVELOPMENT AND SURVEILLANCE
Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends early identification of developmental delays 14 and autism 10 ; however, the USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend formal developmental screening 13 or autism-specific screening 9 if the parents/caregivers or physician have no concerns. If physicians choose to screen, developmental surveillance of language, communication, gross and fine movements, social/emotional development, and cognitive/problem-solving skills should occur at each visit by eliciting parental or caregiver concerns, obtaining interval developmental history, and observing the child. Any area of concern should be evaluated with a formal developmental screening tool, such as Ages and Stages Questionnaire, Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status, Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status-Developmental Milestones, or Survey of Well-Being of Young Children. These tools can be found at https://www.aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/aap-health-initiatives/Screening/Pages/Screening-Tools.aspx . If results are abnormal, consider intervention or referral to early intervention services. The AAP recommends completing the previously mentioned formal screening tools at nine-, 18-, and 30-month well-child visits. 14
The AAP also recommends autism-specific screening at 18 and 24 months. 10 The USPSTF recommends using the two-step Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) screening tool (available at https://m-chat.org/ ) if a physician chooses to screen a patient for autism. 10 The M-CHAT can be incorporated into the electronic medical record, with the possibility of the parent or caregiver completing the questionnaire through the patient portal before the office visit.
IRON DEFICIENCY
Multiple reports have associated iron deficiency with impaired neurodevelopment. Therefore, it is essential to ensure adequate iron intake. Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends supplements for preterm infants beginning at one month of age and exclusively breastfed term infants at six months of age. 3 The USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend screening for iron deficiency in infants. 19 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends measuring a child's hemoglobin level at 12 months of age. 3
Lead poisoning and elevated lead blood levels are prevalent in young children. The AAP and CDC recommend a targeted screening approach. The AAP recommends screening for serum lead levels between six months and six years in high-risk children; high-risk children are identified by location-specific risk recommendations, enrollment in Medicaid, being foreign born, or personal screening. 21 The USPSTF does not recommend screening for lead poisoning in children at average risk who are asymptomatic. 20
The USPSTF recommends at least one vision screening to detect amblyopia between three and five years of age. Testing options include visual acuity, ocular alignment test, stereoacuity test, photoscreening, and autorefractors. The USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend screening before three years of age. 26 The AAP, American Academy of Ophthalmology, and the American Academy of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus recommend the use of an instrument-based screening (photoscreening or autorefractors) between 12 months and three years of age and annual visual acuity screening beginning at four years of age. 31
IMMUNIZATIONS
The AAFP recommends that all children be immunized. 32 Recommended vaccination schedules, endorsed by the AAP, the AAFP, and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, are found at https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/child-adolescent.html . Immunizations are usually administered at the two-, four-, six-, 12-, and 15- to 18-month well-child visits; the four- to six-year well-child visit; and annually during influenza season. Additional vaccinations may be necessary based on medical history. 33 Immunization history should be reviewed at each wellness visit.
Anticipatory Guidance
Injuries remain the leading cause of death among children, 34 and the AAP has made several recommendations to decrease the risk of injuries. 35 – 42 Appropriate use of child restraints minimizes morbidity and mortality associated with motor vehicle collisions. Infants need a rear-facing car safety seat until two years of age or until they reach the height or weight limit for the specific car seat. Children should then switch to a forward-facing car seat for as long as the seat allows, usually 65 to 80 lb (30 to 36 kg). 35 Children should never be unsupervised around cars, driveways, and streets. Young children should wear bicycle helmets while riding tricycles or bicycles. 37
Having functioning smoke detectors and an escape plan decreases the risk of fire- and smoke-related deaths. 36 Water heaters should be set to a maximum of 120°F (49°C) to prevent scald burns. 37 Infants and young children should be watched closely around any body of water, including water in bathtubs and toilets, to prevent drowning. Swimming pools and spas should be completely fenced with a self-closing, self-latching gate. 38
Infants should not be left alone on any high surface, and stairs should be secured by gates. 43 Infant walkers should be discouraged because they provide no benefit and they increase falls down stairs, even if stair gates are installed. 39 Window locks, screens, or limited-opening windows decrease injury and death from falling. 40 Parents or caregivers should also anchor furniture to a wall to prevent heavy pieces from toppling over. Firearms should be kept unloaded and locked. 41
Young children should be closely supervised at all times. Small objects are a choking hazard, especially for children younger than three years. Latex balloons, round objects, and food can cause life-threatening airway obstruction. 42 Long strings and cords can strangle children. 37
DENTAL CARE
Infants should never have a bottle in bed, and babies should be weaned to a cup by 12 months of age. 44 Juices should be avoided in infants younger than 12 months. 45 Fluoride use inhibits tooth demineralization and bacterial enzymes and also enhances remineralization. 11 The AAP and USPSTF recommend fluoride supplementation and the application of fluoride varnish for teeth if the water supply is insufficient. 11 , 12 Begin brushing teeth at tooth eruption with parents or caregivers supervising brushing until mastery. Children should visit a dentist regularly, and an assessment of dental health should occur at well-child visits. 44
SCREEN TIME
Hands-on exploration of their environment is essential to development in children younger than two years. Video chatting is acceptable for children younger than 18 months; otherwise digital media should be avoided. Parents and caregivers may use educational programs and applications with children 18 to 24 months of age. If screen time is used for children two to five years of age, the AAP recommends a maximum of one hour per day that occurs at least one hour before bedtime. Longer usage can cause sleep problems and increases the risk of obesity and social-emotional delays. 46
To decrease the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), the AAP recommends that infants sleep on their backs on a firm mattress for the first year of life with no blankets or other soft objects in the crib. 45 Breastfeeding, pacifier use, and room sharing without bed sharing protect against SIDS; infant exposure to tobacco, alcohol, drugs, and sleeping in bed with parents or caregivers increases the risk of SIDS. 47
DIET AND ACTIVITY
The USPSTF, AAFP, and AAP all recommend breastfeeding until at least six months of age and ideally for the first 12 months. 48 Vitamin D 400 IU supplementation for the first year of life in exclusively breastfed infants is recommended to prevent vitamin D deficiency and rickets. 49 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends the introduction of certain foods at specific ages. Early transition to solid foods before six months is associated with higher consumption of fatty and sugary foods 50 and an increased risk of atopic disease. 51 Delayed transition to cow's milk until 12 months of age decreases the incidence of iron deficiency. 52 Introduction of highly allergenic foods, such as peanut-based foods and eggs, before one year decreases the likelihood that a child will develop food allergies. 53
With approximately 17% of children being obese, many strategies for obesity prevention have been proposed. 54 The USPSTF does not have a recommendation for screening or interventions to prevent obesity in children younger than six years. 54 The AAP has made several recommendations based on expert opinion to prevent obesity. Cessation of breastfeeding before six months and introduction of solid foods before six months are associated with childhood obesity and are not recommended. 55 Drinking juice should be avoided before one year of age, and, if given to older children, only 100% fruit juice should be provided in limited quantities: 4 ounces per day from one to three years of age and 4 to 6 ounces per day from four to six years of age. Intake of other sugar-sweetened beverages should be discouraged to help prevent obesity. 45 The AAFP and AAP recommend that children participate in at least 60 minutes of active free play per day. 55 , 56
Data Sources: Literature search was performed using the USPSTF published recommendations ( https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/BrowseRec/Index/browse-recommendations ) and the AAP Periodicity table ( https://www.aap.org/en-us/Documents/periodicity_schedule.pdf ). PubMed searches were completed using the key terms pediatric, obesity prevention, and allergy prevention with search limits of infant less than 23 months or pediatric less than 18 years. The searches included systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials, clinical trials, and position statements. Essential Evidence Plus was also reviewed. Search dates: May through October 2017.
Gauer RL, Burket J, Horowitz E. Common questions about outpatient care of premature infants. Am Fam Physician. 2014;90(4):244-251.
American Academy of Pediatrics; Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Hospital stay for healthy term newborns. Pediatrics. 2010;125(2):405-409.
Baker RD, Greer FR Committee on Nutrition, American Academy of Pediatrics. Diagnosis and prevention of iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia in infants and young children (0–3 years of age). Pediatrics. 2010;126(5):1040-1050.
Mahle WT, Martin GR, Beekman RH, Morrow WR Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery Executive Committee. Endorsement of Health and Human Services recommendation for pulse oximetry screening for critical congenital heart disease. Pediatrics. 2012;129(1):190-192.
American Academy of Pediatrics Newborn Screening Authoring Committee. Newborn screening expands: recommendations for pediatricians and medical homes—implications for the system. Pediatrics. 2008;121(1):192-217.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2007 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics. 2007;120(4):898-921.
Maisels MJ, Bhutani VK, Bogen D, Newman TB, Stark AR, Watchko JF. Hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant > or = 35 weeks' gestation: an update with clarifications. Pediatrics. 2009;124(4):1193-1198.
Christian CW Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect, American Academy of Pediatrics. The evaluation of suspected child physical abuse [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2015;136(3):583]. Pediatrics. 2015;135(5):e1337-e1354.
Siu AL, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, et al. Screening for autism spectrum disorder in young children: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2016;315(7):691-696.
Johnson CP, Myers SM American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Children with Disabilities. Identification and evaluation of children with autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics. 2007;120(5):1183-1215.
Moyer VA. Prevention of dental caries in children from birth through age 5 years: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6):1102-1111.
Clark MB, Slayton RL American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Oral Health. Fluoride use in caries prevention in the primary care setting. Pediatrics. 2014;134(3):626-633.
Siu AL. Screening for speech and language delay and disorders in children aged 5 years and younger: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2015;136(2):e474-e481.
Council on Children with Disabilities, Section on Developmental Behavioral Pediatrics, Bright Futures Steering Committee, Medical Home Initiatives for Children with Special Needs Project Advisory Committee. Identifying infants and young children with developmental disorders in the medical home: an algorithm for developmental surveillance and screening [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2006;118(4):1808–1809]. Pediatrics. 2006;118(1):405-420.
Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, Curry SJ, et al. Screening for lipid disorders in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2016;316(6):625-633.
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Expert panel on integrated guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children and adolescents. October 2012. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/sites/default/files/media/docs/peds_guidelines_full.pdf . Accessed May 9, 2018.
Moyer VA. Screening for primary hypertension in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(9):613-619.
Flynn JT, Kaelber DC, Baker-Smith CM, et al. Clinical practice guideline for screening and management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2017;140(6):e20173035]. Pediatrics. 2017;140(3):e20171904.
Siu AL. Screening for iron deficiency anemia in young children: USPSTF recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2015;136(4):746-752.
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for elevated blood lead levels in children and pregnant women. Pediatrics. 2006;118(6):2514-2518.
Screening Young Children for Lead Poisoning: Guidance for State and Local Public Health Officials . Atlanta, Ga.: U.S. Public Health Service; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; National Center for Environmental Health; 1997.
O'Connor E, Rossom RC, Henninger M, Groom HC, Burda BU. Primary care screening for and treatment of depression in pregnant and post-partum women: evidence report and systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;315(4):388-406.
Earls MF Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health, American Academy of Pediatrics. Incorporating recognition and management of perinatal and postpartum depression into pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 2010;126(5):1032-1039.
Siu AL. Screening for depression in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(5):360-366.
Weitzman C, Wegner L American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics; Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health; Council on Early Childhood; Society for Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics; American Academy of Pediatrics. Promoting optimal development: screening for behavioral and emotional problems [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2015;135(5):946]. Pediatrics. 2015;135(2):384-395.
Grossman DC, Curry SJ, Owens DK, et al. Vision screening in children aged 6 months to 5 years: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2017;318(9):836-844.
Donahue SP, Nixon CN Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on Ophthalmology, American Academy of Pediatrics; American Association of Certified Orthoptists, American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, American Academy of Ophthalmology. Visual system assessment in infants, children, and young adults by pediatricians. Pediatrics. 2016;137(1):28-30.
Lin KW. What to do at well-child visits: the AAFP's perspective. Am Fam Physician. 2015;91(6):362-364.
American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Community Pediatrics. Poverty and child health in the United States. Pediatrics. 2016;137(4):e20160339.
Lavigne JV, Lebailly SA, Hopkins J, Gouze KR, Binns HJ. The prevalence of ADHD, ODD, depression, and anxiety in a community sample of 4-year-olds. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2009;38(3):315-328.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on Ophthalmology, American Association of Certified Orthoptists, American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, American Academy of Ophthalmology. Visual system assessment of infants, children, and young adults by pediatricians. Pediatrics. 2016;137(1):28-30.
American Academy of Family Physicians. Clinical preventive service recommendation. Immunizations. http://www.aafp.org/patient-care/clinical-recommendations/all/immunizations.html . Accessed October 5, 2017.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommended immunization schedule for children and adolescents aged 18 years or younger, United States, 2018. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/child-adolescent.html . Accessed May 9, 2018.
National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. 10 leading causes of death by age group, United States—2015. https://www.cdc.gov/injury/images/lc-charts/leading_causes_of_death_age_group_2015_1050w740h.gif . Accessed April 24, 2017.
Durbin DR American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Child passenger safety. Pediatrics. 2011;127(4):788-793.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Reducing the number of deaths and injuries from residential fires. Pediatrics. 2000;105(6):1355-1357.
Gardner HG American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Office-based counseling for unintentional injury prevention. Pediatrics. 2007;119(1):202-206.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Prevention of drowning in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2003;112(2):437-439.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Injuries associated with infant walkers. Pediatrics. 2001;108(3):790-792.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Falls from heights: windows, roofs, and balconies. Pediatrics. 2001;107(5):1188-1191.
Dowd MD, Sege RD Council on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention Executive Committee; American Academy of Pediatrics. Firearm-related injuries affecting the pediatric population. Pediatrics. 2012;130(5):e1416-e1423.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Prevention of choking among children. Pediatrics. 2010;125(3):601-607.
Kendrick D, Young B, Mason-Jones AJ, et al. Home safety education and provision of safety equipment for injury prevention (review). Evid Based Child Health. 2013;8(3):761-939.
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Oral Health. Maintaining and improving the oral health of young children. Pediatrics. 2014;134(6):1224-1229.
Heyman MB, Abrams SA American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. Fruit juice in infants, children, and adolescents: current recommendations. Pediatrics. 2017;139(6):e20170967.
Council on Communications and Media. Media and young minds. Pediatrics. 2016;138(5):e20162591.
Moon RY Task Force on Sudden Infant Death Syndrome. SIDS and other sleep-related infant deaths: evidence base for 2016 updated recommendations for a safe infant sleeping environment. Pediatrics. 2016;138(5):e20162940.
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e827-e841.
Wagner CL, Greer FR American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding; Committee on Nutrition. Prevention of rickets and vitamin D deficiency in infants, children, and adolescents [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2009;123(1):197]. Pediatrics. 2008;122(5):1142-1152.
Huh SY, Rifas-Shiman SL, Taveras EM, Oken E, Gillman MW. Timing of solid food introduction and risk of obesity in preschool-aged children. Pediatrics. 2011;127(3):e544-e551.
Greer FR, Sicherer SH, Burks AW American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition; Section on Allergy and Immunology. Effects of early nutritional interventions on the development of atopic disease in infants and children: the role of maternal dietary restriction, breastfeeding, timing of introduction of complementary foods, and hydrolyzed formulas. Pediatrics. 2008;121(1):183-191.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. The use of whole cow's milk in infancy. Pediatrics. 1992;89(6 pt 1):1105-1109.
Fleischer DM, Spergel JM, Assa'ad AH, Pongracic JA. Primary prevention of allergic disease through nutritional interventions. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2013;1(1):29-36.
Grossman DC, Bibbins-Domingo K, Curry SJ, et al. Screening for obesity in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2017;317(23):2417-2426.
Daniels SR, Hassink SG Committee on Nutrition. The role of the pediatrician in primary prevention of obesity. Pediatrics. 2015;136(1):e275-e292.
American Academy of Family Physicians. Physical activity in children. https://www.aafp.org/about/policies/all/physical-activity.html . Accessed January 1, 2018.
Continue Reading

More in AFP
More in pubmed.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Academy of Family Physicians.
This content is owned by the AAFP. A person viewing it online may make one printout of the material and may use that printout only for his or her personal, non-commercial reference. This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP. See permissions for copyright questions and/or permission requests.
Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Family Physicians. All Rights Reserved.

Ages & Stages

Your Child’s Checkups
Regular checkups are an important way to keep track of your child's health and development. Your health care team will take measurements, conduct a head-to-toe examination, update immunizations, and answer questions you may have. Be sure to share your successes and milestones, any concerns about your child's development, and challenges in daily routines. These visits are a chance to learn as much as you can about the best ways to help your child grow and thrive!

- 1st Week Checkup Checklist: 3 to 5 days old
- Checkup Checklist: 1 Month Old
- Checkup Checklist: 2 Months Old
- Checkup Checklist: 4 Months Old
- Checkup Checklist: 6 Months Old
- Checkup Checklist: 9 Months Old
- Your Checkup Checklist: 15 Months Old
- Your Checkup Checklist: 18 Months Old
- Your Checkup Checklist: 2 ½ Years Old (30 Months)
- Your Checkup Checklist: 24 Months (2 Years) Old
- Your Checkup Checklist: 3 Years Old
- Your Checkup Checklist: 4 Years Old
- Your Checkup Checklist: 5 Years Old
- Your Checkup Checklist: 6 Years Old
- Your Checkup Checklist: 7 Years Old
- Your Checkup Checklist: 8 Years Old
Important Milestones: Your Child By Two Years
CDC’s milestones and parent tips have been updated and new checklist ages have been added (15 and 30 months). For more information about the updates to CDC’s developmental milestones, please review the Pediatrics journal article and these important key points .
How your child plays, learns, speaks, acts, and moves offers important clues about your child’s development. Developmental milestones are things most children (75% or more) can do by a certain age.
Check the milestones your child has reached by 2 years by completing a checklist with CDC’s free Milestone Tracker mobile app, for iOS and Android devices, using the Digital Online Checklist , or by printing the checklist [1 MB, 2 Pages, Print Only] below.
“Learn the Signs. Act Early.” materials are not a substitute for standardized, validated developmental screening tools .
What most children do by this age:
Social/emotional milestones.

Language/Communication Milestones
Close this video
Cognitive Milestones (learning, thinking, problem-solving)
Movement/physical development milestones, notices when others are hurt or upset, like pausing or looking sad when someone is crying.

Tries to use switches, knobs, or buttons on a toy

Plays with more than one toy at the same time, like putting toy food on a toy plate

Kicks a ball

Walks (not climbs) up a few stairs with or without help

Eats with a spoon

Other important things to share with the doctor…
- What are some things you and your baby do together?
- What are some things your baby likes to do?
- Is there anything your baby does or does not do that concerns you?
- Has your baby lost any skills he/she once had?
- Does your baby have any special healthcare needs or was he/she born prematurely?
Concerned About Your Child’s Development? Act Early.
You know your child best. Don’t wait. If your child is not meeting one or more milestones, has lost skills he or she once had, or you have other concerns, act early. Talk with your child’s doctor, share your concerns, and ask about developmental screening. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children be screened for general development using standardized, validated tools at 9, 18, and 30 months and for autism at 18 and 24 months or whenever a parent or provider has a concern.
If you or the doctor are still concerned:
- Ask for a referral to a specialist who can evaluate your child more; and
- Call your state or territory’s early intervention program to find out if your child can get services to help. Learn more and find the number at cdc.gov/FindEI .
For more on how to help your child, visit cdc.gov/Concerned .

As your child’s first teacher, you can help his or her learning and brain development. Try these simple tips and activities in a safe way. Talk with your child’s doctor and teachers if you have questions or for more ideas on how to help your child’s development.
- Help your child learn how words sound, even if he can’t say them clearly yet. For example, if your child says, “or nana,” say “You want more banana.”
- Watch your child closely during playdates. Children this age play next to each other, but do not know how to share and solve problems. Show your child how to deal with conflicts by helping her share, take turns, and use words when possible.
- Have your child help you get ready for mealtime, by letting him carry things to the table, such as plastic cups or napkins. Thank your child for helping.
Click here for more tips and activities
- Give your child balls to kick, roll, and throw.
- Give toys that teach your child how to make things work and how to solve problems. For example, give her toys where she can push a button and something happens.
- Let your child play dress up with grown-up clothes, such as shoes, hats, and shirts. This helps him begin to pretend play.
- Allow your child to eat as much or as little as she wants at each meal. Toddlers don’t always eat the same amount or type of food each day. Your job is to offer her healthy foods and it’s your child’s job to decide if and how much she needs to eat.
- Have steady routines for sleeping and feeding. Create a calm, quiet bedtime for your child. Put on his pajamas, brush his teeth, and read 1 or 2 books to him. Children this age need 11 to 14 hours of sleep a day (including naps). Consistent sleep times make it easier.
- Ask your child’s doctor and/or teachers about toilet training to know if your child is ready to start. Most children are not able to toilet train until 2 to 3 years old. Starting too early can cause stress and setbacks, which can cause training to take longer.
- Use positive words when your child is being a good helper. Let him help with simple chores, such as putting toys or laundry in a basket.
- Play with your child outside, by playing “ready, set, go.” For example, pull your child back in a swing. Say “Ready, set….”, then wait and say “Go” when you push the swing.
- Let your child create simple art projects with you. Give your child crayons or put some finger paint on paper and let her explore by spreading it around and making dots. Hang it on the wall or refrigerator so your child can see it.
- Use positive words and give more attention to behaviors you want to see (“wanted behaviors”), than to those you don’t want to see. For example, say “Look how well you’re eating with your spoon.”
- Let your child play with sand toys or plastic containers, spoons, or a funnel in the tub or in a sandbox.
- Help your child do simple puzzles with shapes, colors, or animals. Name each piece when your child puts it in place.
- Encourage your child’s curiosity and help her learn and explore new things. Take her to the park, take walks, or go on a bus ride.
- Sing songs, such as “Head, Shoulders, Knees, and Toes,” to teach names of body parts. After singing it a few times, see if your child sings some of the words when you touch a body part and wait.
- Limit screen time (TV, tablets, phones, etc.) to no more than 1 hour a day of a children’s program with an adult present. Children learn by talking, playing, and interacting with others.
- Encourage your child to play with blocks. Take turns building towers and knocking them down.
- Ask your child to help you open the drawer when you put away clothes or open the door when you go outside.
Special acknowledgments to the subject matter experts and others who contributed to the review of data and selection of developmental milestones, especially Paul H. Lipkin, MD, Michelle M. Macias, MD, Julie F. Pajek, PhD, Judith S. Shaw, EdD, MPH, RN, Karnesha Slaughter, MPH, Jane K. Squires, PhD, Toni M. Whitaker, MD, Lisa D. Wiggins, PhD, and Jennifer M. Zubler, MD.
Sincere gratitude to Natalia Benza, MD and José O. Rodríguez, MD, MBA for their thoughtful review of the Spanish-language translation of these milestones.
- Developmental Disabilities
- Child Development
- Positive Parenting Tips
- National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities
- Foods and Drinks for 6 to 24 Month Olds
Print Milestone Checklist

English pdf icon [1 MB, 2 Pages, Print Only] Spanish pdf icon [1 MB, 2 Pages, Print Only]
Order free materials
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

Well Child Visits in the First Two Years

Birth to 2 Years Old
In his or her first two years, your baby should have well child visits at 3-5 days, 2 weeks, 1 month, 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 9 months, 12 months, 15 months, and 18 months.
Below is information about developmental milestones and safety concerns for your child’s age as well as any developmental screenings we will complete at each visit. Please bring a completed copy of these forms to your child’s appointment!

Newborn: 3 to 5 Days after Birth
What to expect.
At your newborn’s first visit we will weigh your baby, review their feeding patterns and normal newborn care and address any questions or concerns you may have.
No Handouts
Forms to complete.
- Registration

At your newborn’s 2 week visit we will weigh your baby, review their feeding patterns and normal newborn care and address any questions or concerns you may have.
No Forms to Complete

At your Baby’s 1 month visit we will weigh your baby, review their feeding patterns, developmental milestones and normal newborn care and address any questions or concerns you have.
Your baby will be due for their hepatitis B vaccine at this visit.
We will reference the following handouts:
- Hepatitis B Vaccine VIS

2, 4, and 6 Months
At your Baby’s 2, 4 and 6 month visits we will obtain your baby’s weight, height and head circumference. At the 6 month visit we will also screen their vision.
We will then review their feeding, sleeping and developmental milestones and address any questions or concerns you have.
Your baby will be due for a rotavirus, prevnar (pneumococcal) and pentacel (DTap/Hib/Polio) combination vaccine at these visits.
- Hib Vaccine VIS
- DTaP Vaccine VIS
- Polio Vaccine VIS
- Pneumococcal Vaccine VIS
- Rotavirus Vaccine VIS

At your baby’s 9 month visit we will obtain your baby’s weight, height and head circumference. We will then review their feeding, sleeping and developmental milestones and address any questions or concerns you have.
Your baby will be due for a hepatitis B vaccine at this visit.
- 9 Month SWYC

At your baby’s 12 month visit we will obtain your baby’s weight, height and head circumference. We will also test their vision and hearing.
Your baby will have a capillary blood draw to test their hemoglobin and lead levels. We will then review their feeding, sleeping and developmental milestones and address any questions or concerns you have.
Your baby will be due for their MMR, chickenpox (varicella), hepatitis A and prevnar (pneumococcal) vaccines.
- Hepatitis A VIS
- MMR Vaccine VIS
- Varicella Vaccine VIS

At your baby’s 15 month visit we will obtain your child’s weight, height and head circumference. We will then review their feeding, sleeping and developmental milestones and address any questions or concerns you have.
Your child will be due for their hib and Dtap vaccines.

At your baby’s 18 month visit, we will obtain your child’s weight, height and head circumference. We will also test their vision.
You will complete a developmental screening called the SWYC and an autism screening form called the MCHAT.
Your child will be due for a hepatitis A vaccine.
FREE SHIPPING on ALL Training Supplies! Use Coupon Code DELIVERY0424 at checkout! Shop Now >
New 2024 Lifeguarding Program Materials are Here! Buy More, Save More with quantity discounts available! Shop Now >
The 2024 Red Cross Lifeguarding Program updates are here! Learn more >

- 0 Your Cart is Empty < Continue Shopping
Your browser's Javascript functionality is turned off. Please turn it on so that you can experience the full capabilities of this site.
Adult and Pediatric First Aid/CPR/AED Skills Session-r.21
This course is for students who have completed the Adult Child and Baby First Aid/CPR/AED online course. Upon successful completion students will receive a valid 2 year Red Cross digital certificate that is OSHA compliant and meets other workplace and regulatory requirements.
Equipment Terms & Conditions
Local classes held at convenient locations and times Participate in hands-on training Provides full certification Learn from experienced instructors
Classroom / Skills Check
- Local in-person training
- Learn from experienced instructors
- Convenient locations and times for instructor-led skills check
- Satisfies OSHA workplace safety certification requirements
The content of these reviews regarding the quality and value of this course is based on data collected across all American Red Cross classes with this title and does not reflect ratings of any specific instructor or provider.
McDonald's posts rare profit miss as customers turn picky
- Medium Text

- Q1 same-store sales, profit miss estimates
- Relative superiority on affordability declined in some markets - CEO
- Rivals Restaurant Brands, Domino's Pizza top qtrly estimates
Sign up here.
Reporting by Savyata Mishra in Bengaluru; Editing by Saumyadeb Chakrabarty
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

Fed's Williams says 2% inflation target 'critical'
The U.S. central bank's 2% target for inflation is key to achieving price stability and essential for ensuring economic prosperity, New York Federal Reserve Bank President John Williams said on Friday.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Schedule of well-child visits. The first week visit (3 to 5 days old) 1 month old; 2 months old; 4 months old; 6 months old; 9 months old; 12 months old; 15 months old; 18 months old; 2 years old (24 months) 2 ½ years old (30 months) 3 years old ... Bring your top three to five questions or concerns with you to talk with your pediatrician at ...
After that, well-baby visits are scheduled throughout the first two years at: The first week (usually a couple of days after you're discharged from the hospital) 1 month; 2 months; 4 months; 6 months; 9 months; 12 months; 15 months; 18 months; 24 months. While this schedule follows recommendations by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP ...
Your baby's checkup schedule. Some pediatricians' schedules vary slightly, but the American Academy of Pediatrics Opens a new window (AAP) recommends babies get checkups at birth, 3 to 5 days after birth, and then at 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. (Once your baby is a toddler and child, they'll have routine checkups at 30 months, 3 years, and annually after that.)
During first-year visits, a nurse or your baby's health care provider will measure and record your baby's length, head circumference and weight. Your child's measurements will be plotted on his or her growth chart. This will help you and the provider see how your child's size compares with that of other children the same age.
It's worth noting that after your baby's initial visit to the pediatrician, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends well-baby visits at the following intervals for the first two years of your baby's life. 1 month; 2 months; 4 months; 6 months; 9 months; 12 months; 15 months; 18 months; 24 months
Your pediatrician wants to see if the pulse is weak or hard to detect on one or both sides as that may suggest a heart condition. You can expect this exam at the first pediatrician visit and all ...
3- to 5-day well-baby checkup. Just a few days after birth, your baby's first checkup appointment will take place with the doctor you've chosen for them. In some cases, babies may need to be seen sooner than the recommended 3-5 days after birth. For example, if a newborn has jaundice, or weight or feeding issues, they may need to be seen ...
Schedule of Newborn Well Visits for the First Year. Lurie Children's follows the recommended schedule for visits and screenings from the American Academy of Pediatrics. After leaving the hospital (where babies get checked by a hospital pediatrician), you'll bring your baby to the pediatrician at around:
Beginning at the 7 year visit, there is both a Parent and Patient education handout (in English and Spanish). For the Bright Futures Parent Handouts for well-child visits up to 2 years of age, translations of 12 additional languages (PDF format) are made possible thanks to the generous support of members, staff, and businesses who donate to the ...
VIEW PROFESSIONAL VERSION. Healthy infants should be seen by their doctor often during the first year of life. Preventive health care visits (also called well-child visits) typically take place within a few days after birth or by 2 weeks of age and at 1, 2, 4, 6, and 9 months of age. During these visits, the doctor uses age-specific guidelines ...
Young children grow quickly, so they need to visit the doctor or nurse regularly to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. Children ages 1 to 4 need to see the doctor or nurse when they're: 12 months old. 15 months old (1 year and 3 months) 18 months old (1 year and 6 months) 24 months old (2 years) 30 months old (2 years and 6 ...
A typical schedule includes well-child checks at ages: 3 to 5 days; 2-4 weeks; 2 months; 4 months; 6 months; 9 months; 12 months; 15 months; 18 months; 2 years; 3 years
Toddler Well-Child Visits. 15-Month Well-Child Visit. 18-Month Well-Child Visit. 24-Month Well-Child Visit. 30-Month Well-Child Visit. 3-Year Well-Child Visit. Vaccines Schedule From 0-2 Years. While it's a no-brainer that you take your baby or toddler to the doctor when they're sick, it's also important to bring your child to the ...
Technically, your child's first pediatrician visit will happen in the hospital, birth center, or home, shortly after your baby is born. Your baby should also have their newborn hearing screening done during this time. But your child's first trip to the ped's office will happen 3 to 5 days after birth, unless they need to be seen sooner.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Milestones During the First 2 Years, August 2012. American Academy of Pediatrics, Movement and Coordination, August 2009. American Dental Association, Baby Teeth. KidsHealth From Nemours, Your Child's Checkup: 2 Years (24 Months), April 2022.
Babies need to see the doctor or nurse 6 times before their first birthday. Your baby is growing and changing quickly, so regular visits are important. The first well-baby visit is 2 to 3 days after coming home from the hospital, when the baby is about 3 to 5 days old. After that first visit, babies need to see the doctor or nurse when they're:
The genitalia are examined at each visit for any unusual lumps, tenderness, or signs of infection. In the first exam or two, the doctor pays special attention to a circumcised boy's penis to make sure it's healing properly. Pediatricians also check all baby boys to make certain both testes are down in the scrotum. Hips and Legs.
Immunizations are usually administered at the two-, four-, six-, 12-, and 15- to 18-month well-child visits; the four- to six-year well-child visit; and annually during influenza season ...
Your Checkup Checklist: 24 Months (2 Years) Old. . At the 24-month (2-year-old) checkup visit, your child's pediatrician will perform a complete physical exam. They will also ask about your concerns and assess language development along with progress towards other milestones. Here's what else to expect at this doctor visit. View.
The 2-month visit marks the first round of vaccines administered at the doctor's office, most of which they'll get again at the 4- and 6-month visits. "One shot gives your baby some immunity," Dr. Nicklas explains. "But it's important for them to get all recommended doses of each vaccine over the course of their first year - and ...
Developmental milestones are things most children (75% or more) can do by a certain age. Check the milestones your child has reached by 2 years by completing a checklist with CDC's free Milestone Tracker mobile app, for iOS and Android devices, using the Digital Online Checklist, or by printing the checklist [1 MB, 2 Pages, Print Only] below.
Hartford Area Pediatrics. Birth to 2 Years Old In his or her first two years, your baby should have well child visits at 3-5 days, 2 weeks, 1 month, 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 9 months, 12 months, 15 months, and 18 months. Below is information about developmental milestones and safety concerns for your child's age as well.
Details. Class IDa653o000001DqUG. This course is for students who have completed the Adult Child and Baby First Aid/CPR/AED online course. Upon successful completion students will receive a valid 2 year Red Cross digital certificate that is OSHA compliant and meets other workplace and regulatory requirements. More Details. $75.00. Product Actions.
Credit: European Commission. From May 5 to 10, China's President Xi Jinping will make state visits to France, Serbia, and Hungary - his first trip to Europe since the pandemic began. The world ...
McDonald's first-quarter same-store sales grew 2.5% in the United States, sharply lower than a 12.6% growth last year and slightly below estimates of a 2.55% growth.