
- Press Releases
- Press Enquiries
- Travel Hub / Blog
- Brand Resources
- Newsletter Sign Up
- Global Summit
- Hosting a Summit
- Upcoming Events
- Previous Events
- Event Photography
- Event Enquiries
- Our Members
- Our Associates Community
- Membership Benefits
- Enquire About Membership
- Sponsors & Partners
- Insights & Publications
- WTTC Research Hub
- Economic Impact
- Knowledge Partners
- Data Enquiries
- Hotel Sustainability Basics
- Community Conscious Travel
- SafeTravels Stamp Application
- SafeTravels: Global Protocols & Stamp
- Security & Travel Facilitation
- Sustainable Growth
- Women Empowerment
- Destination Spotlight - SLO CAL
- Vision For Nature Positive Travel and Tourism
- Governments
- Consumer Travel Blog
- ONEin330Million Campaign
- Reunite Campaign


Economic Impact Research
- In 2023, the Travel & Tourism sector contributed 9.1% to the global GDP; an increase of 23.2% from 2022 and only 4.1% below the 2019 level.
- In 2023, there were 27 million new jobs, representing a 9.1% increase compared to 2022, and only 1.4% below the 2019 level.
- Domestic visitor spending rose by 18.1% in 2023, surpassing the 2019 level.
- International visitor spending registered a 33.1% jump in 2023 but remained 14.4% below the 2019 total.
Click here for links to the different economy/country and regional reports
Why conduct research?
From the outset, our Members realised that hard economic facts were needed to help governments and policymakers truly understand the potential of Travel & Tourism. Measuring the size and growth of Travel & Tourism and its contribution to society, therefore, plays a vital part in underpinning WTTC’s work.
What research does WTTC carry out?
Each year, WTTC and Oxford Economics produce reports covering the economic contribution of our sector in 185 countries, for 26 economic and geographic regions, and for more than 70 cities. We also benchmark Travel & Tourism against other economic sectors and analyse the impact of government policies affecting the sector such as jobs and visa facilitation.
Visit our Research Hub via the button below to find all our Economic Impact Reports, as well as other reports on Travel and Tourism.


By Bastian Herre, Veronika Samborska and Max Roser
Tourism has massively increased in recent decades. Aviation has opened up travel from domestic to international. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of international visits had more than doubled since 2000.
Tourism can be important for both the travelers and the people in the countries they visit.
For visitors, traveling can increase their understanding of and appreciation for people in other countries and their cultures.
And in many countries, many people rely on tourism for their income. In some, it is one of the largest industries.
But tourism also has externalities: it contributes to global carbon emissions and can encroach on local environments and cultures.
On this page, you can find data and visualizations on the history and current state of tourism across the world.
Interactive Charts on Tourism
Cite this work.
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this topic page, please also cite the underlying data sources. This topic page can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
Reimagining the $9 trillion tourism economy—what will it take?
Tourism made up 10 percent of global GDP in 2019 and was worth almost $9 trillion, 1 See “Economic impact reports,” World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), wttc.org. making the sector nearly three times larger than agriculture. However, the tourism value chain of suppliers and intermediaries has always been fragmented, with limited coordination among the small and medium-size enterprises (SMEs) that make up a large portion of the sector. Governments have generally played a limited role in the industry, with partial oversight and light-touch management.
COVID-19 has caused an unprecedented crisis for the tourism industry. International tourist arrivals are projected to plunge by 60 to 80 percent in 2020, and tourism spending is not likely to return to precrisis levels until 2024. This puts as many as 120 million jobs at risk. 2 “International tourist numbers could fall 60-80% in 2020, UNWTO reports,” World Tourism Organization, May 7, 2020, unwto.org.
Reopening tourism-related businesses and managing their recovery in a way that is safe, attractive for tourists, and economically viable will require coordination at a level not seen before. The public sector may be best placed to oversee this process in the context of the fragmented SME ecosystem, large state-owned enterprises controlling entry points, and the increasing impact of health-related agencies. As borders start reopening and interest in leisure rebounds in some regions , governments could take the opportunity to rethink their role within tourism, thereby potentially both assisting in the sector’s recovery and strengthening it in the long term.
In this article, we suggest four ways in which governments can reimagine their role in the tourism sector in the context of COVID-19.
1. Streamlining public–private interfaces through a tourism nerve center
Before COVID-19, most tourism ministries and authorities focused on destination marketing, industry promotions, and research. Many are now dealing with a raft of new regulations, stimulus programs, and protocols. They are also dealing with uncertainty around demand forecasting, and the decisions they make around which assets—such as airports—to reopen will have a major impact on the safety of tourists and sector employees.
Coordination between the public and private sectors in tourism was already complex prior to COVID-19. In the United Kingdom, for example, tourism falls within the remit of two departments—the Department for Business, Energy, and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) and the Department for Digital, Culture, Media & Sport (DCMS)—which interact with other government agencies and the private sector at several points. Complex coordination structures often make clarity and consistency difficult. These issues are exacerbated by the degree of coordination that will be required by the tourism sector in the aftermath of the crisis, both across government agencies (for example, between the ministries responsible for transport, tourism, and health), and between the government and private-sector players (such as for implementing protocols, syncing financial aid, and reopening assets).
Concentrating crucial leadership into a central nerve center is a crisis management response many organizations have deployed in similar situations. Tourism nerve centers, which bring together public, private, and semi-private players into project teams to address five themes, could provide an active collaboration framework that is particularly suited to the diverse stakeholders within the tourism sector (Exhibit 1).
We analyzed stimulus packages across 24 economies, 3 Australia, Bahrain, Belgium, Canada, Egypt, Finland, France, Germany, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Israel, Italy, Kenya, Malaysia, New Zealand, Peru, Philippines, Singapore, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Switzerland, Thailand, and the United Kingdom. which totaled nearly $100 billion in funds dedicated directly to the tourism sector, and close to $300 billion including cross-sector packages with a heavy tourism footprint. This stimulus was generally provided by multiple entities and government departments, and few countries had a single integrated view on beneficiaries and losers. We conducted surveys on how effective the public-sector response has been and found that two-thirds of tourism players were either unaware of the measures taken by government or felt they did not have sufficient impact. Given uncertainty about the timing and speed of the tourism recovery, obtaining quick feedback and redeploying funds will be critical to ensuring that stimulus packages have maximum impact.
2. Experimenting with new financing mechanisms
Most of the $100 billion stimulus that we analyzed was structured as grants, debt relief, and aid to SMEs and airlines. New Zealand has offered an NZ $15,000 (US $10,000) grant per SME to cover wages, for example, while Singapore has instituted an 8 percent cash grant on the gross monthly wages of local employees. Japan has waived the debt of small companies where income dropped more than 20 percent. In Germany, companies can use state-sponsored work-sharing schemes for up to six months, and the government provides an income replacement rate of 60 percent.
Our forecasts indicate that it will take four to seven years for tourism demand to return to 2019 levels, which means that overcapacity will be the new normal in the medium term. This prolonged period of low demand means that the way tourism is financed needs to change. The aforementioned types of policies are expensive and will be difficult for governments to sustain over multiple years. They also might not go far enough. A recent Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) survey of SMEs in the tourism sector suggested more than half would not survive the next few months, and the failure of businesses on anything like this scale would put the recovery far behind even the most conservative forecasts. 4 See Tourism policy responses to the coronavirus (COVID-19), OECD, June 2020, oecd.org. Governments and the private sector should be investigating new, innovative financing measures.
Revenue-pooling structures for hotels
One option would be the creation of revenue-pooling structures, which could help asset owners and operators, especially SMEs, to manage variable costs and losses moving forward. Hotels competing for the same segment in the same district, such as a beach strip, could have an incentive to pool revenues and losses while operating at reduced capacity. Instead of having all hotels operating at 20 to 40 percent occupancy, a subset of hotels could operate at a higher occupancy rate and share the revenue with the remainder. This would allow hotels to optimize variable costs and reduce the need for government stimulus. Non-operating hotels could channel stimulus funds into refurbishments or other investment, which would boost the destination’s attractiveness. Governments will need to be the intermediary between businesses through auditing or escrow accounts in this model.
Joint equity funds for small and medium-size enterprises
Government-backed equity funds could also be used to deploy private capital to help ensure that tourism-related SMEs survive the crisis (Exhibit 2). This principle underpins the European Commission’s temporary framework for recapitalization of state-aided enterprises, which provided an estimated €1.9 trillion in aid to the EU economy between March and May 2020. 5 See “State aid: Commission expands temporary framework to recapitalisation and subordinated debt measures to further support the economy in the context of the coronavirus outbreak,” European Commission, May 8, 2020, ec.europa.eu. Applying such a mechanism to SMEs would require creating an appropriate equity-holding structure, or securitizing equity stakes in multiple SMEs at once, reducing the overall risk profile for the investor. In addition, developing a standardized valuation methodology would avoid lengthy due diligence processes on each asset. Governments that do not have the resources to co-invest could limit their role to setting up those structures and opening them to potential private investors.
3. Ensuring transparent, consistent communication on protocols
The return of tourism demand requires that travelers and tourism-sector employees feel—and are—safe. Although international organizations such as the International Air Transport Association (IATA), and the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC) have developed a set of guidelines to serve as a baseline, local regulators are layering additional measures on top. This leads to low levels of harmonization regarding regulations imposed by local governments.
Our surveys of traveler confidence in the United States suggests anxiety remains high, and authorities and destination managers must work to ensure travelers know about, and feel reassured by, protocols put in place for their protection. Our latest survey of traveler sentiment in China suggests a significant gap between how confident travelers would like to feel and how confident they actually feel; actual confidence in safety is much lower than the expected level asked a month before.
One reason for this low level of confidence is confusion over the safety measures that are currently in place. Communication is therefore key to bolstering demand. Experience in Europe indicates that prompt, transparent, consistent communications from public agencies have had a similar impact on traveler demand as CEO announcements have on stock prices. Clear, credible announcements regarding the removal of travel restrictions have already led to increased air-travel searches and bookings. In the week that governments announced the removal of travel bans to a number of European summer destinations, for example, outbound air travel web search volumes recently exceeded precrisis levels by more than 20 percent in some countries.
The case of Greece helps illustrate the importance of clear and consistent communication. Greece was one of the first EU countries to announce the date of, and conditions and protocols for, border reopening. Since that announcement, Greece’s disease incidence has remained steady and there have been no changes to the announced protocols. The result: our joint research with trivago shows that Greece is now among the top five summer destinations for German travelers for the first time. In July and August, Greece will reach inbound airline ticketing levels that are approximately 50 percent of that achieved in the same period last year. This exceeds the rate in most other European summer destinations, including Croatia (35 percent), Portugal (around 30 percent), and Spain (around 40 percent). 6 Based on IATA Air Travel Pulse by McKinsey. In contrast, some destinations that have had inconsistent communications around the time frame of reopening have shown net cancellations of flights for June and July. Even for the high seasons toward the end of the year, inbound air travel ticketing barely reaches 30 percent of 2019 volumes.
Digital solutions can be an effective tool to bridge communication and to create consistency on protocols between governments and the private sector. In China, the health QR code system, which reflects past travel history and contact with infected people, is being widely used during the reopening stage. Travelers have to show their green, government-issued QR code before entering airports, hotels, and attractions. The code is also required for preflight check-in and, at certain destination airports, after landing.
4. Enabling a digital and analytics transformation within the tourism sector
Data sources and forecasts have shifted, and proliferated, in the crisis. Last year’s demand prediction models are no longer relevant, leaving many destinations struggling to understand how demand will evolve, and therefore how to manage supply. Uncertainty over the speed and shape of the recovery means that segmentation and marketing budgets, historically reassessed every few years, now need to be updated every few months. The tourism sector needs to undergo an analytics transformation to enable the coordination of marketing budgets, sector promotions, and calendars of events, and to ensure that products are marketed to the right population segment at the right time.
Governments have an opportunity to reimagine their roles in providing data infrastructure and capabilities to the tourism sector, and to investigate new and innovative operating models. This was already underway in some destinations before COVID-19. Singapore, for example, made heavy investments in its data and analytics stack over the past decade through the Singapore Tourism Analytics Network (STAN), which provided tourism players with visitor arrival statistics, passenger profiling, spending data, revenue data, and extensive customer-experience surveys. During the COVID-19 pandemic, real-time data on leading travel indicators and “nowcasts” (forecasts for the coming weeks and months) could be invaluable to inform the decisions of both public-sector and private-sector entities.
This analytics transformation will also help to address the digital gap that was evident in tourism even before the crisis. Digital services are vital for travelers: in 2019, more than 40 percent of US travelers used mobile devices to book their trips. 7 Global Digital Traveler Research 2019, Travelport, marketing.cloud.travelport.com; “Mobile travel trends 2019 in the words of industry experts,” blog entry by David MacHale, December 11, 2018, blog.digital.travelport.com. In Europe and the United States, as many as 60 percent of travel bookings are digital, and online travel agents can have a market share as high as 50 percent, particularly for smaller independent hotels. 8 Sean O’Neill, “Coronavirus upheaval prompts independent hotels to look at management company startups,” Skift, May 11, 2020, skift.com. COVID-19 is likely to accelerate the shift to digital as travelers look for flexibility and booking lead times shorten: more than 90 percent of recent trips in China were booked within seven days of the trip itself. Many tourism businesses have struggled to keep pace with changing consumer preferences around digital. In particular, many tourism SMEs have not been fully able to integrate new digital capabilities in the way that larger businesses have, with barriers including language issues, and low levels of digital fluency. The commission rates on existing platforms, which range from 10 percent for larger hotel brands to 25 percent for independent hotels, also make it difficult for SMEs to compete in the digital space.
Governments are well-positioned to overcome the digital gap within the sector and to level the playing field for SMEs. The Tourism Exchange Australia (TXA) platform, which was created by the Australian government, is an example of enabling at scale. It acts as a matchmaker, connecting suppliers with distributors and intermediaries to create packages attractive to a specific segment of tourists, then uses tourist engagement to provide further analytical insights to travel intermediaries (Exhibit 3). This mechanism allows online travel agents to diversify their offerings by providing more experiences away from the beaten track, which both adds to Australia’s destination attractiveness, and gives small suppliers better access to customers.

Governments that seize the opportunity to reimagine tourism operations and oversight will be well positioned to steer their national tourism industries safely into—and set them up to thrive within—the next normal.
Download the article in Arabic (513KB)
Margaux Constantin is an associate partner in McKinsey’s Dubai office, Steve Saxon is a partner in the Shanghai office, and Jackey Yu is an associate partner in the Hong Kong office.
The authors wish to thank Hugo Espirito Santo, Urs Binggeli, Jonathan Steinbach, Yassir Zouaoui, Rebecca Stone, and Ninan Chacko for their contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Make it better, not just safer: The opportunity to reinvent travel

Hospitality and COVID-19: How long until ‘no vacancy’ for US hotels?
A new approach in tracking travel demand
An official website of the United States government
- Special Topics
Travel and Tourism
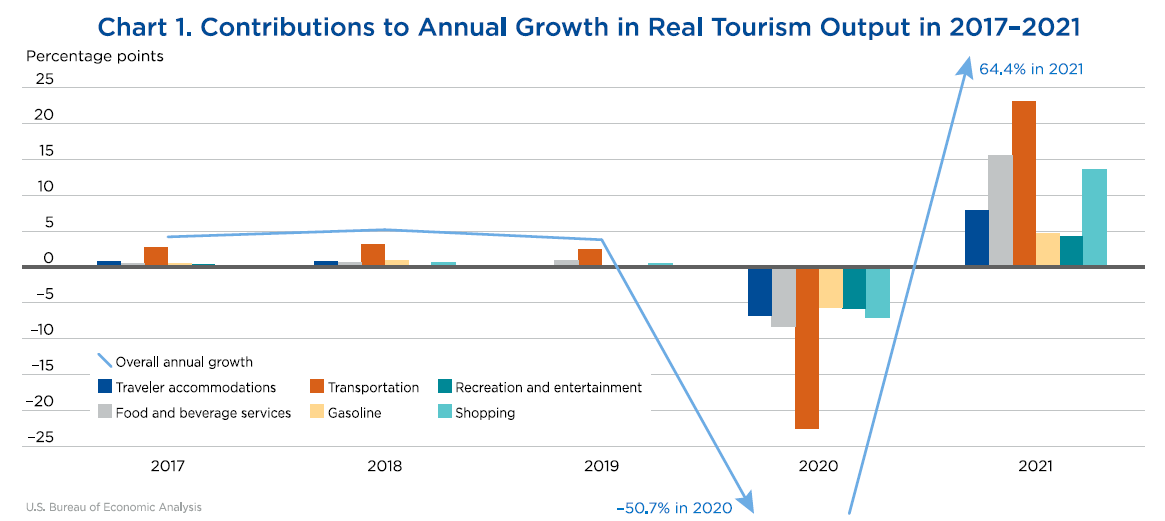
Travel and tourism satellite account for 2017-2021.
The travel and tourism industry—as measured by the real output of goods and services sold directly to visitors—increased 64.4 percent in 2021 after decreasing 50.7 percent in 2020, according to the most recent statistics from BEA’s Travel and Tourism Satellite Account.
Data & Articles
- U.S. Travel and Tourism Satellite Account for 2017–2021 By Sarah Osborne - Survey of Current Business February 2023
- "U.S. Travel and Tourism Satellite Account for 2015–2019" By Sarah Osborne - Survey of Current Business December 2020
- "U.S. Travel and Tourism Satellite Account for 2015-2017" By Sarah Osborne and Seth Markowitz - Survey of Current Business June 2018
- Tourism Satellite Accounts 1998-2019
- Tourism Satellite Accounts Data Sheets A complete set of detailed annual statistics for 2017-2021 is coming soon -->
- Article Collection
Documentation
- Product Guide
Previously Published Estimates
- Data Archive This page provides access to an archive of estimates previously published by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. Please note that this archive is provided for research only. The estimates contained in this archive include revisions to prior estimates and may not reflect the most recent revision for a particular period.
- News Release Archive
What is Travel and Tourism?
Measures how much tourists spend and the prices they pay for lodging, airfare, souvenirs, and other travel-related items. These statistics also provide a snapshot of employment in the travel and tourism industries.
What’s a Satellite Account?

- TTSA Sarah Osborne (301) 278-9459
- News Media Connie O'Connell (301) 278-9003 [email protected]
- Tourism GDP
Related topics
- Innovation and Technology
Tourism direct GDP corresponds to the part of GDP generated by all industries directly in contact with visitors. This indicator is measured as a percentage of total GDP or a percentage of GVA.
Latest publication
- Industrial production
- Tourism receipts and spending
- Tourism employment
- Tourism flows
Tourism GDP Source: Key tourism indicators
- Selected data only (.csv)
- Full indicator data (.csv)
- Add this view
- Go to pinboard
©OECD · Terms & Conditions
Perspectives
Compare variables
Highlight countries
Find a country by name
Currently highlighted
Select background.
- European Union
Show baseline: OECD
latest data available
Definition of Tourism GDP
Last published in.
Please cite this indicator as follows:
Related publications
Source database, further indicators related to industry, further publications related to industry.

Your selection for sharing:
- Snapshot of data for a fixed period (data will not change even if updated on the site)
- Latest available data for a fixed period,
- Latest available data,
Sharing options
Permanent url.
Copy the URL to open this chart with all your selections.
Use this code to embed the visualisation into your website.
Width: px Preview Embedding
- Open access
- Published: 05 January 2021
The relationship between tourism and economic growth among BRICS countries: a panel cointegration analysis
- Haroon Rasool ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0083-4553 1 ,
- Shafat Maqbool 2 &
- Md. Tarique 1
Future Business Journal volume 7 , Article number: 1 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
121k Accesses
88 Citations
13 Altmetric
Metrics details
Tourism has become the world’s third-largest export industry after fuels and chemicals, and ahead of food and automotive products. From last few years, there has been a great surge in international tourism, culminates to 7% share of World’s total exports in 2016. To this end, the study attempts to examine the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth by using the panel data over the period 1995–2015 for five BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) countries. The results of panel ARDL cointegration test indicate that tourism, financial development and economic growth are cointegrated in the long run. Further, the Granger causality analysis demonstrates that the causality between inbound tourism and economic growth is bi-directional, thus validates the ‘feedback-hypothesis’ in BRICS countries. The study suggests that BRICS countries should promote favorable tourism policies to push up the economic growth and in turn economic growth will positively contribute to international tourism.
Introduction
World Tourism Day 2015 was celebrated around the theme ‘One Billion Tourists; One Billion Opportunities’ highlighting the transformative potential of one billion tourists. With more than one billion tourists traveling to an international destination every year, tourism has become a leading economic sector, contributing 9.8% of global GDP and represents 7% of the world’s total exports [ 59 ]. According to the World Tourism Organization, the year 2013 saw more than 1.087 billion Foreign Tourist Arrivals and US $1075 billion foreign tourism receipts. The contribution of travel and tourism to gross domestic product (GDP) is expected to reach 10.8% at the end of 2026 [ 61 ]. Representing more than just economic strength, these figures exemplify the vast potential of tourism, to address some of the world´s most pressing challenges, including socio-economic growth and inclusive development.
Developing countries are emerging as the important players, and increasingly aware of their economic potential. Once essentially excluded from the tourism industry, the developing world has now become its major growth area. These countries majorly rely on tourism for their foreign exchange reserves. For the world’s forty poorest countries, tourism is the second-most important source of foreign exchange after oil [ 37 ].
The BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) countries have emerged as a potential bloc in the developing countries which caters the major tourists from developed countries. Tourism becomes major focus at BRICS Xiamen Summit 2017 held in China. These countries have robust growth rate, and are focal destinations for global tourists. During 1990 to 2014, these countries stride from 11% of the world’s GDP to almost 30% [ 17 ]. Among BRICS countries, China is ranked as an important destination followed by Brazil, Russia, India and South Africa [ 60 ].
The importance of inbound tourism has grown exponentially, because of its growing contribution to the economic growth in the long run. It enhances economic growth by augmenting the foreign exchange reserves [ 38 ], stimulating investments in new infrastructure, human capital and increases competition [ 9 ], promoting industrial development [ 34 ], creates jobs and hence to increase income [ 34 ], inbound tourism also generates positive externalities [ 1 , 14 ] and finally, as economy grows, one can argue that growth in GDP could lead to further increase in international tourism [ 11 ].
The tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) proposed by Balaguer and Cantavella-Jorda [ 3 ], states that expansion of international tourism activities exerts economic growth, hence offering a theoretical and empirical link between inbound tourism and economic growth. Theoretically, the TLGH was directly derived from the export-led growth hypothesis (ELGH) that postulates that economic growth can be generated not only by increasing the amount of labor and capital within the economy, but also by expanding exports.
The ‘new growth theory,’ developed by Balassa [ 4 ], suggests that export expansion can trigger economic growth, because it promotes specialization and raises factors productivity by increasing competition, creating positive externalities by advancing the dispersal of specialized information and abilities. Exports also enhance economic growth by increasing the level of investment. International tourism is considered as a non-standard type of export, as it indicates a source of receipts and consumption in situ. Given the difficulties in measuring tourism activity, the economic literature tends to focus on primary and manufactured product exports, hence neglecting this economic sector. Analogous to the ELGH, the TLGH analyses the possible temporal relationship between tourism and economic growth, both in the short and long run. The question is whether tourism activity leads to economic growth or, alternatively, economic expansion drives tourism growth, or indeed a bi-directional relationship exists between the two variables.
To further substantiate the nexus, the study will investigate the plausible linkages between economic growth and international tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. Financial markets are considered a key factor in producing strong economic growth, because they contribute to economic efficiency by diverting financial funds from unproductive to productive uses. The origin of this role of financial development may is traced back to the seminal work of Schumpeter [ 50 ]. In his study, Schumpeter points out that the banking system is the crucial factor for economic growth due to its role in the allocation of savings, the encouragement of innovation, and the funding of productive investments. Early works, such as Goldsmith [ 18 ], McKinnon [ 39 ] and Shaw [ 51 ] put forward considerable evidence that financial development enhances growth performance of countries. The importance of financial development in BRICS economies is reflected by the establishment of the ‘New Development Bank’ aimed at financing infrastructure and sustainable development projects in these and other developing countries. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, no attempt has been made so far to investigate the long-run relationship Footnote 1 between tourism, financial development and economic growth in case of BRICS countries. Hence, the present study is an attempt to fill the gap in the existing literature.
Review of past studies
From last few decades there has been a surge in the research related to tourism-growth nexus. The importance of growth and development and its determinants has been studied extensively both in developed and developing countries. Extant literature has recognized tourism as an important determinant of economic growth. The importance of tourism has grown exponentially, courtesy to its manifold advantages in form of employment, foreign exchange production household income and government revenues through multiplier effects, improvements in the balance of payments and growth in the number of tourism-promoted government policies [ 21 , 41 , 53 ]. Empirical findings on tourism and economic development have produced mixed finding and sometimes conflicting results despite the common choice of time series techniques as a research methodology. On empirical grounds, four hypotheses have been explored to determine the link between tourism and economic growth [ 12 ]. The first two hypotheses present an account on the unidirectional causality between the two variables, either from tourism to economic growth (Tourism-led economic growth hypothesis-TLGH) or its reserve (economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis-EDTH). The other two hypotheses support the existence of bi-directional hypothesis, (bi-directional causality hypothesis-BC) or that there is no relationship at all (no causality hypothesis-NC), respectively. According to TLEG hypothesis, tourism creates an array of benefits which spillover though multiple routes to promote the economic growth [ 55 ]. In particular, it is believed that tourism (1) increases foreign exchange earnings, which in turn can be used to finance imports [ 38 ], (2) it encourages investment and drives local firms toward greater efficiency due to the increased competition [ 3 , 31 ], (3) it alleviates unemployment, since tourism activities are heavily based on human capital [ 10 ] and (4) it leads to positive economies of scale thus, decreasing production costs for local businesses [ 1 , 14 ]. Other recent studies which find evidence in favor of the TLGH hypothesis include [ 44 , 52 ]. Even though literature is dominated by TLGH, few studies produce a result in support of EDTH [ 40 , 41 , 45 ]. Payne and Mervar [ 45 ] posit that tourism growth of a country is mobilized by the stability of well-designed economic policies, governance structures and investments in both physical and human capital. This positive and vibrant environment creates a series of development activities which proliferate and flourish the tourism. Pertaining to the readily available information, bi-directional causality could also exist between tourism income and economic growth [ 34 , 49 ]. From a policy view, a reciprocal tourism–economic growth relationship implies that government agendas should cater for promoting both areas simultaneously. Finally, there are some studies that do not offer support to any of the aforementioned hypotheses, suggesting that the impact between tourism and economic growth is insignificant [ 25 , 47 , 57 ]. There is a vast literature examining the relationship between tourism and growth as a result, only a selective literature review will be presented here.
Banday and Ismail [ 5 ] used ARDL cointegration model to test the relationship between tourism revenue and economic growth in BRICS countries from the time period of (1995–2013). The study validates the tourism-led growth hypothesis for BRICS countries, which evinces that tourism has positive influence on economic growth.
Savaş et al. [ 54 ] evaluated the tourism-led growth hypothesis in the context of Turkey. The study employed gross domestic product, real exchange rate, real total expenditure and international tourism arrivals to sketch out the causality among variables. The result reveals a unidirectional relationship between tourism and real exchange rate. The findings suggest that tourism is the driving force for economic growth, which in turn helps turkey to culminate its current account deficit.
Dhungel [ 15 ] made an effort to investigate causality between tourism and economic growth, In Nepal for the period of (1974–2012), by using Johansen’s cointegration and Error correction model. The result states that unidirectional causality exists in the long run, while in short run no causality exists between two constructs. The study emphasized that strategies should be devised to attain causality running from tourism to economic growth.
Mallick et al. [ 36 ] analyzed the nexus between economic growth and tourism in 23 Indian states over a period of 14 years (1997–2011). Using panel autoregressive distributed lag model based on three alternative estimators such as mean group estimator, pooled mean group and dynamic fixed effects, Research found that tourism exerts positive influence on economic growth in the long run.
Belloumi [ 8 ] examines the causal relationship between international tourism receipts and economic growth in Tunisia by using annual time series data for the period 1970–2007. The study uses the Johansen’s cointegration methodology to analyze the long-run relationship among the concerned variables. Granger causality based Vector error correction mechanism approach indicates that the revenues generated from tourism have a positive impact on economic growth of Tunisia. Thus, the study supports the hypothesis of tourism-driven economic growth, which is specific to developing countries that base their foreign exchange earnings on the existence of a comparative advantage in certain sectors of the economy.
Tang et al. [ 58 ] explored the dynamic Inter-relationships among tourism, economic growth and energy consumption in India for the period 1971–2012. The study employed Bounds testing approach to cointegration and generalized variance decomposition methods to analyze the relationship. The bounds testing and the Gregory-Hansen test for cointegration with structural breaks consistently reveals that energy consumption, tourism and economic growth in India are cointegrated. The study demonstrated that tourism and economic growth have positive impact on energy consumption, while tourism and economic growth are interrelated; with tourism exert significant influence on economic growth. Consequently, this study validates the tourism-led growth hypothesis in the Indian context.
Kadir and Karim [ 24 ]) examined the causal nexus between tourism and economic growth in Malaysia by applying panel time series approach for the period 1998–2005. By applying Padroni’s panel cointegration test and panel Granger causality test, the result indicated both short and long-run relationship. Further, the panel causality shows unidirectional causality directing from tourism receipts to economic growth. The result provides evidence of the significant contribution of tourism industry to Malaysia’s economic growth, thereby justifying the necessity of public intervention in providing tourism infrastructure and facilities.
Antonakakis et al. [ 2 ] test the linkage between tourism and economic growth in Europe by using a newly introduced spillover index approach. Based on monthly data for 10 European countries over the period 1995–2012, the findings suggested that the tourism–economic growth relationship is not stable over time in terms of both magnitude and direction, indicating that the tourism-led economic growth (TLEG) and the economic-driven tourism growth (EDTG) hypotheses are time-dependent. Thus, the findings of the study suggest that the same country can experience tourism-led economic growth or economic-driven tourism growth at different economic events.
Oh [ 41 ] verifies the contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy by applying Engle and Granger two-stage approach and a bivariate Vector Autoregression model. He claimed that economic expansion lures tourists in the short run only, while there is no such long-run stable relationship between international tourism and economic development in Korea.
Empirical studies have pronouncedly focused on the literature that tourism promotes economic growth. To further substantiate the nexus, the study will investigate the plausible linkages between economic growth and international tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. The inclusion of financial development in the examination of tourism-growth nexus is a unique feature of this study, which have an influencing role in economic growth as financial development has been theoretically and empirically recognized as source of comparative advantage [ 22 ].
This study employs panel ARDL cointegration approach to verify the existence of long-run association among the variables. Further, study estimated the long-run and short-run coefficients of the ARDL model. Subsequently, Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] panel Granger causality test has been employed to check the direction of causality between tourism, financial development and economic growth among BRICS countries.
Database and methodology
Data and variables.
The study is analytical and empirical in nature, which intends to establish the relationship between economic growth and inbound tourism in BRICS countries. For the BRICS countries, limited studies have been conducted depicting the present scenario. Therefore, present study tries to verify the relevance of tourism in economic growth to further enhance the understanding of economic dynamics in BRICS countries. The data used in the study are annual figures for the period stretching from 1995 to 2015, consisting of one endogenous variable (GDP per capita, a proxy for economic growth) and two exogenous variables (international tourism receipts per capita and financial development). The variables employed in the study are based on the economic growth theory, proposed by Balassa [ 4 ], which states that export expansion has a relevant contribution in economic growth. Further, this study incorporates financial development in the model to reduce model misspecification as it is considered to have an influencing role in economic growth both theoretically and empirically [ 22 , 33 ].
The annual data for all the variables have been collected from the World Development Indicators (WDI, 2016) database. The variables used in the study includes gross domestic product per capita (GDP) in constant ($US2010) used as a proxy for economic growth (EG), international tourism receipts per capita (TR) in current US$ as it is widely accepted that the most adequate proxy of inbound tourism in a country is tourism expenditure normally expressed in terms of tourism receipts [ 32 ] and financial development (FD). In line with a recent study on the relationship between financial development and economic growth by Hassan et al. [ 19 ], financial development is surrogated by the ratio of the broad money (M3) to real GDP for all BRICS countries. Here we use the broadest definition of money (M3) as a proportion of GDP– to measure the liquid liabilities of the banking system in the economy. We use M3 as a financial depth indicator, because monetary aggregates, such as M2 or M1, may be a poor proxy in economies with underdeveloped financial systems, because they ‘are more related to the ability of the financial system to provide transaction services than to the ability to channel funds from savers to borrowers’ [ 26 ]. A higher liquidity ratio means higher intensity in the banking system. The assumption here is that the size of the financial sector is positively associated with financial services [ 29 ]. All the variables have been taken into log form.
Unit root test
To verify the long-run relationship between tourism and economic growth through Bounds testing approach, it is necessary to test for stationarity of the variables. The stationarity of all the variables can be assessed by different unit root tests. The study utilizes panel unit root test proposed by Levin et al. [ 35 ] henceforth LLC and Im et al. [ 23 ] henceforth IPS based on traditional augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) test. The LLC allows for heterogeneity of the intercepts across members of the panel under the null hypothesis of presence of unit root, while IPS allows for heterogeneity in intercepts as well as in the slope coefficients [ 48 ].
Panel ARDL approach to Cointegration
After checking the stationarity of the variables the study employs panel ARDL technique for Cointegration developed by Pesaran et al. [ 23 ]. Pesaran et al. [ 23 ] have introduced the pooled mean group (PMG) approach in the panel ARDL framework. According to Pesaran et al. [ 23 ], the homogeneity in the long-run relationship can be attributed to several factors such as arbitration condition, common technologies, or the institutional development which was covered by all groups. The panel ARDL bounds test [ 46 ] is more appropriate by comparing other cointegration techniques, because it is flexible regarding unit root properties of variables. This technique is more suitable when variables are integrated at different orders but not I (2). Haug [ 20 ] has argued that panel ARDL approach to cointegration provides better results for small sample data set such as in our case. The ARDL approach to cointegration estimates both long and short-run parameters and can be applied independently of variable order integration (independent of whether repressors are purely I (0), purely I(1) or combination of both. The ARDL bounds test approach used in this study is specified as follows:
where Δ is the first-difference operator, \(\alpha_{0}\) stands for constant, t is time element, \(\omega_{1} , \omega_{2} \;\;{\text{and}}\;\; \omega_{3}\) represent the short-run parameters of the model, \(\emptyset_{1} , \emptyset_{2} ,and \emptyset_{3}\) are long-run coefficients, while \(V_{it}\) is white noise error term and lastly, it represents country at a particular time period. In the ARDL model, the bounds test is applied to determine whether the variables are cointegrated or not.
This test is based on the joint significance of F -statistic and the χ 2 statistic of the Wald test. The null hypothesis of no cointegration among the variables under study is examined by testing the joint significance of the F -statistic of \(\omega_{1} , \omega_{2} ,\omega_{3}\) .
In case series variables are cointegrated, an error correction mechanism (ECM) can be developed as Eq. ( 2 ), to assess the short-run influence of international tourism and financial development on economic growth.
where ECT is the error correction term, and \(\varPhi\) is its coefficient which shows how fast the variables attain long-term equilibrium if there is any deviation in the short run. The error correction term further confirms the existence of a stable long-run relationship among the variables.
Panel granger causality test
To examine the direction of causality Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] test is employed. Instead of pooled causality, Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] proposed a causality based on the individual Wald statistic of Granger non-causality averaged across the cross section units. Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] assert that traditional test allows for homogeneous analysis across all panel sets, thereby neglecting the specific causality across different units.
This approach allows heterogeneity in coefficients across cross section panels. The two statistics Wbar-statistics and Zbar-statistics provides standardized version of the statistics and is easier to compute. Wbar-statistic, takes an average of the test statistics, while the Zbar-statistic shows a standard (asymptotic) normal distribution.
They proposed an average Wald statistic that tests the null hypothesis of no causality in a panel subgroup against an alternative hypothesis of causality in at least one panel. Following equations will be used to check the direction of causality between the variables.
Estimation, results and Discussion
Descriptive statistics.
Table 1 presents descriptive statistics of variables selected for the period 1995–2015. The variable set includes GDP, FD and TR for all BRICS countries. Brazil tops the list with GDP per capita of 4.18, while India lagging behind all BRICS nations. In the recent economic survey by International Monetary Fund (IMF report 2016), India was ranked 126 for its per capita GDP. India’s GDP per capita went up to $7170 against all other BRICS countries which were placed in the above $10,000 bracket. China has the highest tourism receipts in comparison to other BRICS countries. China is a very popular country for foreign tourists, which ranks third after France and USA. In 2014, China invested $136.8 billion into its tourist infrastructure, a figure second only to the United States ($144.3 billion). Tourism, based on direct, indirect, and induced impact, accounted for near 10% in the GDP of China (WTTC report 2017).
Stationarity results
Primarily, we employed LLC and IPS unit root test to assess the integrated properties of the series. The results of IPS and PP tests are presented in Table 2 . Panel unit root test result evinces that FD and TR are stationary at level, while GDP per capita is integrated variable of order 1. The result exemplifies that GDP per capita, Tourism receipts and Financial Development are integrated at 1(0) and 1(1). Consequently, the panel ARDL approach to cointegration can be applied.
Cointegration test results
In view of the above results with a mixture of order integration, the panel ARDL approach to cointegration is the most appropriate technique to investigate whether there exists a long-run relationship among the variables [ 42 ]. Table 3 illustrates that the estimated value of F-statistics, which is higher than the lower and upper limit of the bound value, when InEG is used as a dependent variable. Hence, we reject the null hypothesis of no cointegration \(H_{0 } : \emptyset_{1} = \emptyset_{2} = \emptyset_{3} = 0\) of Eq. ( 1 ). Therefore, the result asserts that international tourism, financial development and economic growth are significantly cointegrated over the period (1995–2015).
Subsequently, the study investigates the long-run and short-run impact of international tourism and financial development on economic growth. Lag length is selected on the principle of minimum Bayesian information criterion (SBC) value, which is 2 in our case. The long-run coefficients of financial development and tourism receipts with respect to economic growth in Table 4 indicate that tourism growth and financial development exerts positive influence on economic growth in the long run. In other words, an increase in volume of tourism receipts per capita and financial depth spurs economic growth and both the coefficients are statistically significant in case of BRICS nations in the long run. The results are interpreted in detail as below:
The elasticity coefficient of economic growth with respect to tourism shows that 1% rise in international tourism receipts per capita would imply an estimated increase of almost 0.31% domestic real income in the long run, all else remaining the same. Thus, the earnings in the form of foreign exchange from international tourism affect growth performance of BRICS nations positively. This finding of our study is in consonance with the empirical results of Kreishan for Jordan [ 30 ], Balaguer and Cantavella-Jordá [ 3 ] for Spain and Ohlan [ 43 ] for India.
Further our finding lend support to the wide applicability of the new growth theory proposed by Balassa which states that export expansion promote growth performance of nations. Thus, validates TLGH coined by Balaguer and Cantavell-Jorda [ 3 ] which states that inbound tourism acts a long-run economic growth factor. The so called tourism-led growth hypothesis suggests that the development of a country’s tourism industry will eventually lead to higher economic growth and, by extension, further economic development via spillovers and other multiplier effects.
Likewise, financial development as expected is found to be positively associated with economic growth. The coefficient of financial development states that 1% improvement in financial development will push up economic growth by 0.22% in the long run, keeping all other variables constant. The empirical results are consistent with the finding of Hassan et al. [ 19 ] for a panel of South Asian countries. Well-regulated and properly functioning financial development enhances domestic production through savings, borrowings & investment activities and boosts economic growth. Further, it promotes economic growth by increasing efficiency [ 7 ]. Levine [ 33 ] believes that financial intermediaries enhance economic efficiency, and ultimately growth, by helping allocation of capital to its best use. Modern growth theory identifies two specific channels through which the financial sector might affect long-run growth; through its impact on capital accumulation and through its impact on the rate of technological progress. The sub-prime crisis which depressed the economic growth worldwide in 2007 further substantiates the growth-financial development nexus.
In the third and final step of the bounds testing procedure, we estimate short-run dynamics of variables by estimating an error correction model associated with long-run estimates. The empirical finding indicates that the coefficient of error correction term (ECT) with one period lag is negative as well as statistically significant. This finding further substantiates the earlier cointegration results between tourism, financial development and economic growth, and indicates the speed of adjustment from the short-run toward long-run equilibrium path. The coefficient of ECT reveals that the short-run divergences in economic growth from long-run equilibrium are adjusted by 43% every year following a short-run shock.
The short-run parameters in Table 5 demonstrates that tourism and financial development acts as an engine of economic growth in the short run as well. The coefficient of both tourism receipts per capita and financial development with one period lag is also found to be progressive and significant in the short run. These results highlight the role of earnings from international tourism and financial stability as an important driving force of economic growth in BRICS nations in the short run as well.
Further, a comparison between short-run and long-run elasticity coefficients evince that long-run responsiveness of economic growth with respect to tourism and financial development is higher than that of short run. It exemplifies that over time higher international tourism receipts and well-regulated financial system in BRICS nations give more boost to economic growth.
Analysis of causality
At this stage, we investigate the causality between tourism, financial development and economic growth presented in Table 6 . The result shows bi-directional causal relationship between tourism and economic growth, thereby validates ‘feedback hypothesis’ and consequently supported both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) and its reciprocal, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis (EDTH). The bi-directional causality between inbound tourism and GDP, which directs the level of economic activity and tourism growth, mutually influences each other in that a high volume of tourism growth leads to a high level of economic development and reverse also holds true. These results replicate the findings of Banday and Ismail [ 5 ] in the context of BRICS countries, Yazdi et al. [ 27 ] for Iran and Kim et al. [ 28 ] for Taiwan. One of the channels through which tourism spurs economic growth is through the use of receipts earned in the form of foreign currency. Thus, growth in foreign earnings may allow the import of technologically advances goods that will favor economic growth and vice versa. Thus, results demonstrate that international tourism promotes growth and in turn economic expansion is necessary for tourism development in case of BRICS countries. With respect to policy context, this finding suggests that the BRICS nations should focus on economic policies to promote tourism as a potential source of economic growth which in turn will further promote tourism growth.
Similarly, in case of economic growth and financial development, the findings demonstrate the presence of bi-directional causality between two constructs. The findings validate thus both ‘demand following’ and supply leading’ hypothesis. The findings suggests that indeed financial development plays a crucial role in promoting economic activity and thus generating economic growth for these countries and reverse also holds. Our findings are in line with Pradhan [ 48 ] in case of BRICS countries and Hassan et al. [ 19 ] for low and middle-income countries. This suggests that finance development can be used as a policy variable to foster economic growth in the five BRICS countries and vice versa. The study emphasizes that the current economic policies should recognize the finance-growth nexus in BRICS in order to maintain sustainable economic development in the economy. The empirical results in this paper are in line with expectations, confirming that the emerging economies of the BRICS are benefiting from their finance sectors.
Finally, two-sided causal relationship is found between tourism receipts and financial development. That is, tourism might contribute to financial development and, in return, financial development may positively contribute to tourism. This means that financial depth and tourism in BRICS have a reinforcing interaction. The positive impact of tourism on financial development can be attributed to the fact that inflows of foreign exchange via international tourism not only increases income levels but also leads to rise in official reserves of central banks. This in turn enables central banks to adapt expansionary monetary policy. The positive contribution of financial sector to tourism is further characterized by supply leading hypothesis. Further, better financial and market conditions will attract tourism entrepreneurship, because firms will be able to use more capital instead of being forced to use leveraging [ 13 ]. Hence, any shocks in money supply could adversely affect tourism industry in these countries. Song and Lin [ 56 ] found that global financial crisis had a negative impact on both inbound and outbound tourism in Asia. This result is in consistent with Başarir and Çakir [ 6 ] for Turkey and four European countries.
Stability tests
In addition, to test the stability of parameters estimated and any structural break in the model CUSUM and CUSUMSQ tests are employed. Figs. 1 and 2 show blue line does not transcend red lines in both the tests, thus provides strong evidence that our estimated model is fit and valid policy implications can be drawn from the results.
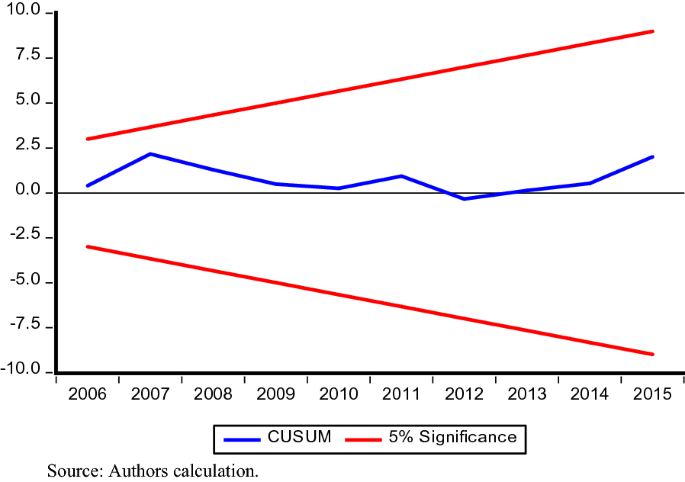
Plot of CUSUM
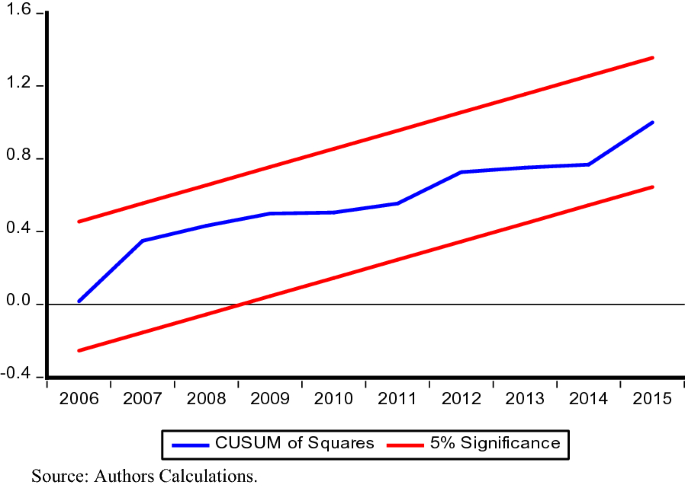
Plot of CUSUMQ
Summary and concluding remarks
A rigorous study of the relationship between tourism and economic growth, through the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) perspective has remained a debatable issue in the economic growth literature. This study aims to empirically investigate the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth in BRICS countries by utilizing the panel data over the period 1995–2015. The study employs the panel ARDL approach to cointegration and Dumitrescu-Hurlin panel Granger causality test to detect the direction of causation.
To the best of authors’ knowledge, this is the first study which explored the relationship between economic growth and tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. The empirical results of ARDL model posits that in BRICS countries inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth are significantly cointegrated, i.e., variables have stable long-run relationship. This methodology has allowed obtaining elasticities of economic growth with respect to tourism and financial development both in the long run and short run. The result reveals that international tourism growth and financial development positively affects economic growth both in the long run and short run. The coefficient of tourism indicates that with a 1% rise in tourism receipts per capita, GDP per capita of BRICS economies will go up by 0.31% in the long run. This finding lends support to TLGH coined by Balaguer and Cantavell-Jorda [ 3 ] which states that inbound tourism acts a long-run economic growth factor. The so called tourism-led growth hypothesis suggests that the development of a country’s tourism industry will eventually lead to higher economic growth and, by extension, further economic development via spillovers and other multiplier effects.
Likewise, 1% improvement in financial development, on average, will increase economic growth in BRICS countries by 0.22% in the long run. The result seems logical as modern growth theory identifies two channels through which the financial sector might affect long-run growth: first, through its impact on capital accumulation and secondly, through its impact on the rate of technological progress. The sub-prime crisis which hit the economic growth Worldwide in 2007 further substantiates the growth-financial development nexus.
The negative and statistically significant coefficient of lagged error correction term (ECT) further substantiates the long-run equilibrium relationship among variables. The negative coefficient of ECT also shows the speed of adjustment toward long-run equilibrium is 43% per annum if there is any short-run deviation. The estimates of parameters are found to be stable by applying CUSUM and CUSUMQ for the time period under consideration. Therefore, inbound tourism earnings and financial institutions can be used as a channel to increase economic growth in BRICS economies.
Further, Granger causality test result indicates the bi-directional causation in all cases. Hence, the causal relationship between international tourism and economic growth is bi-directional. And, consequently this empirical finding lends support to both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) and its reciprocal, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis (EDTH). This means that tourism is not only an engine for economic growth, but the economic outcome on itself can play an important role in providing growth potential to tourism sector.
The Granger causality findings provide useful information to governments to examine their economic policy, to adjust priorities regarding economic investment, and boost their economic growth with the given limited resources. Thus, it is suggested that more resources should be allocated to tourism industry and tourism-related industries if the tourism-led growth hypothesis holds true. On the other side, if economic-driven tourism growth is supported then more resources should be diverted to leading industries rather than the travel and tourism sector, and the tourism industry will in turn benefit from the resulting overall economic growth. And, when bi-directional causality is detected, a balanced allocation of economic resources for the travel and tourism sector and other industries is important and necessary. The policy implication is that resource allocation supporting both the tourism and tourism-related industries could benefit both tourism development and economic growth.
To sum up, the major finding of this study lends support to wide applicability of the tourism-led growth hypothesis in case of BRICS countries. Thus, in the Policy context, significant impact of tourism on BRICS economy rationalizes the need of encouraging tourism. Tourism can spur economic prosperity in these countries and for this reason; policymakers should give serious consideration toward encouraging tourism industry or inbound tourism. BRICS countries should focus more on tourism infrastructure, such as, convenient transportation, alluring destinations, suitable tax incentives, viable hostels and proper security arrangements to attract the potential tourists. Most of these countries are devoid of rich facilities and popular tourist incentives, to get promoted as important destination and in the long-run promotes economic growth. Further, they need a staunch support from all sections of authorities, non-government organizations (NGOs), and private and allied industries, in the endeavor to attain sustainable growth in tourism. Both state and non-state actors must recognize this growing industry and its positive implication on economy.
For future research, we suggest that researchers should consider the nonlinear factor in the dynamic relationship of tourism and economic growth in case of BRICS countries. Further one can go for comparative study to examine the TLGH in BRICS countries.
Availability of data and materials
Data used in the study can be provided by the corresponding author on request.
There are no fixed definitions of short, medium and long run and generally in macroeconomics, short run can be viewed as 1 to 2 or 3 years, medium up to 5 years and long run from 5 years to 20 or 25 years.
Abbreviations
autoregressive distributed lag model
Brazil, Russia, India, China and South-Africa
United Nations World Tourism Organization
World Travel & Tourism Council
gross domestic product
world development indicators
tourism-led growth hypothesis
export-led growth hypothesis
economic-driven tourism hypothesis
augmented Dickey–Fuller test
error correction model
error correction term
Andriotis K (2002) Scale of hospitality firms and local economic development—evidence from Crete. Tourism Manag 23(4):333–341
Google Scholar
Antonakakis N, Dragouni M, Filis G (2015) How strong is the linkage between tourism and economic growth in Europe? Econ Modell 44:142–155
Balaguer J, Cantavella-Jorda M (2002) Tourism as a long-run economic growth factor: the Spanish case. Appl Econ 34(7):877–884
Balassa B (1978) Exports and economic growth: further evidence. J Dev Econ 5(2):181–189
Banday UJ, Ismail S (2017) Does tourism development lead positive or negative impact on economic growth and environment in BRICS countries? A panel data analysis. Econ Bull 37(1):553–567
Basarir C, Çakir YN (2015) Causal interactions between CO 2 emissions, financial development, energy and tourism. Asian Econ Financ Rev 5(11):1227
Bell C, Rousseau PL (2001) Post-independence India: a case of finance-led industrialization? J Dev Econ 65(1):153–175
Belloumi M (2010) The relationship between tourism receipts, real effective exchange rate and economic growth in Tunisia. Int J Tour Res 12(5):550–560
Blake A, Sinclair MT, Soria JAC (2006) Tourism productivity: evidence from the United Kingdom. Ann Tourism Res 33(4):1099–1120
Brida JG, Pulina M (2010) A literature review on the tourism-led-growth hypothesis. Working paper CRENoS201017. Centre for North South Economic Research, Sardinia
Brida JG, Cortes-Jimenez I, Pulina M (2016) Has the tourism-led growth hypothesis been validated? A literature review. Curr Issues Tourism 19(5):394–430
Chatziantoniou I, Filis G, Eeckels B, Apostolakis A (2013) Oil prices, tourism income and economic growth: a structural VAR approach for European Mediterranean countries. Tourism Manag 36:331–341
Chen M-H (2010) The economy, tourism growth and corporate performance in the Taiwanese hotel industry. Tourism Manag 31:665–675
Croes R (2006) A paradigm shift to a new strategy for small island economies: embracing demand side economics for value enhancement and long term economic stability. Tourism Manag 27:453–465
Dhungel KR (2015) An econometric analysis on the relationship between tourism and economic growth: empirical evidence from Nepal. Int J Econ Financ Manag 3(2):84–90
Dumitrescu EI, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Modell 29(4):1450–1460
Daniel Mminele (2016) The role of BRICS in the global economy. Speech at the Bundesbank Regional Office in North Rhine-Westphalia, Düsseldorf, Germany. https://www.bis.org/review/r160720c.pdf
Goldsmith RW (1969) Financial structure and development (No. HG174 G57)
Hassan MK, Sanchez B, Yu JS (2011) Financial development and economic growth: new evidence from panel data. Quart Rev Econ Financ 51(1):88–104
Haug AA (2002) Temporal aggregation and the power of cointegration tests: A Monte Carlo study. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 64:399–412
Henry EW, Deane B (1997) The contribution of tourism to the economy of Ireland in 1990 and 1995. Tourism Manag 18(8):535–553
Hur J, Raj M, Riyanto YE (2006) Finance and trade: a cross-country empirical analysis on the impact of financial development and asset tangibility on international trade. World Dev 34(10):1728–1741
Im KS, Pesaran MH, Shin Y (2003) Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J Econ 115(1):53–74
Kadir N, Karim MZA (2012) Tourism and economic growth in Malaysia: evidence from tourist arrivals from Asean-S countries. Econ Res Ekonomska istraživanja 25(4):1089–1100
Katircioglu S (2009) Testing the tourism-led growth hypothesis: the case of Malta. Acta Oeconomica 59(3):331–343
Khan M, Senhadji A (2003) Financial development and economic growth: a review and new evidence. J Afr Econ 12:89–110
Khoshnevis Yazdi S, Homa Salehi K, Soheilzad M (2017) The relationship between tourism, foreign direct investment and economic growth: evidence from Iran. Curr Issues Tourism 20(1):15–26
Kim HJ, Chen MH (2006) Tourism expansion and economic development: the case of Taiwan. Tourism Manag 27(5):925–933
King R, Levine R (1993) Finance, entrepreneurship, and growth: theory and evidence. J Monet Econ 32:513–542
Kreishan FM (2010) Tourism and economic growth: the case of Jordan. Eur J Soc Sci 15:229–234
Krueger A (1980) Trade policy as an input to development. Am Econ Rev 70:188–292
Kumar RR (2014) Exploring the role of technology, tourism and financial development: an empirical study of Vietnam. Qual Quant 48(5):2881–2898
Levine R (1997) Financial development and economic growth: views and agenda. J Econ Lit 35(2):688–726
Lee CC, Chang CP (2008) Tourism development and economic growth: a closer look at panels. Tourism Manag 29(1):180–192
Levin A, Lin CF, Chu CSJ (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Econ 108(1):1–24
Mallick L, Mallesh U, Behera J (2016) Does tourism affect economic growth in Indian states? Evidence from panel ARDL model. Theor Appl Econ 23(1):183–194
Mastny L (2001) Treading lightly: new paths for international tourism. In: Peterson JA (ed) World Watch Paper 159. World Watch Institute
McKinnon RI (1964) Foreign exchange constraints in economic development and efficient aid allocation. Econ J 74(294):388–409
McKinnon RI (1973) Money and capital in economic development. The Brookings Institution, Washington
Narayan PK (2004) Economic impact of tourism on Fiji’s economy: empirical evidence from the computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Econ 10(4):419–433
Oh CO (2005) The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tourism Manag 26(1):39–44
Ohlan R (2015) The impact of population density, energy consumption, economic growth and trade openness on CO 2 emissions in India. Nat Hazards 79(2):1409–1428
Ohlan R (2017) The relationship between tourism, financial development and economic growth in India. Future Bus J 3(1):9–22
Parrilla JC, Font AR, Nadal JR (2007) Tourism and long-term growth a Spanish perspective. Ann Tourism Res 34(3):709–726
Payne JE, Mervar A (2010) Research note: the tourism-growth nexus in Croatia. Tourism Econ 16(4):1089–1094
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Po WC, Huang BN (2008) Tourism development and economic growth—a nonlinear approach. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 387(22):5535–5542
Pradhan RP, Dasgupta P, Bele S (2013) Finance, development and economic growth in BRICS: a panel data analysis. J Quant Econ 11(1–2):308–322
Ridderstaat J, Oduber M, Croes R, Nijkamp P, Martens P (2014) Impacts of seasonal patterns of climate on recurrent fluctuations in tourism demand: evidence from Aruba. Tourism Manag 41:245–256
Schumpeter JA (1911) The theory of economic development: an inquiry into profits, capital, credit, interest, and the business cycle. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, p 1934
Shaw ES (1973) Financial deepening in economic development. Oxford University Press, London
Sugiyarto G, Blake A, Sinclair MT (2003) Tourism and globalization: economic impact in Indonesia. Ann Tourism Res 30(3):683–701
Szivas E, Riley M (1999) Tourism employment during economic transition. Ann Tourism Res 26(4):747–771
Savaş B, Beşkaya A, Şamiloğlu F (2010) Analyzing the impact of international tourism on economic growth in Turkey. Uluslararası Yönetim İktisat ve İşletme Dergisi 6(12):121–136
Schubert SF, Brida JG, Risso WA (2011) The impacts of international tourism demand on economic growth of small economies dependent on tourism. Tourism Manag 32(2):377–385
Song H, Lin S (2010) Impacts of the financial and economic crisis on tourism in Asia. J Travel Res 49(1):16–30
Tang CF (2013) Temporal Granger causality and the dynamics relationship between real tourism receipts, real income and real exchange rates in Malaysia. Int J Tourism Res 15(3):272–284
Tang CF, Tiwari AK, Shahbaz M (2016) Dynamic inter-relationships among tourism, economic growth and energy consumption in India. Geosyst Eng 19(4):158–169
United Nations World Tourism Report (2014) Annual report 2014
World Travel & Tourism Council (2012) Travel & Tourism Economic Impact. World, London: World Travel & Tourism Council.
World Travel and Tourism Council (2016) Global travel and tourism economic impact update August 2016
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research has received no specific funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economics, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India
Haroon Rasool & Md. Tarique
Department of Commerce, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India
Shafat Maqbool
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
HR has written introduction, research methodology and results and discussion part. Review of literature and data analysis was done by SM. Conclusion was written jointly by HR and SM. MT has provided useful inputs and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Haroon Rasool .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
Authors declare that there are no competing interests.

Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Rasool, H., Maqbool, S. & Tarique, M. The relationship between tourism and economic growth among BRICS countries: a panel cointegration analysis. Futur Bus J 7 , 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-020-00048-3
Download citation
Received : 02 August 2019
Accepted : 30 November 2020
Published : 05 January 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-020-00048-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Economic growth
- Inbound tourism
- Financial development
- Cointegration
- Panel granger causality
International tourism revenue, percent of GDP - Country rankings
International tourism revenue, percent of gdp, 2020:.
Rwanda Economic Update: Nature-based Tourism Holds Tremendous Economic Potential
KIGALI, February 21, 2023— The Rwandan economy continued to achieve strong growth in 2022 despite global headwinds and an unprecedented increase in food prices, according to the 20 th edition of the Rwanda Economic Update report released today.
Rwanda’s GDP grew by 8.4 percent in the first three quarters of 2022, after reaching 11 percent in 2021. Growth was spurred by the services sector, especially the revival of tourism, leading to the improvement of employment indicators to levels similar to those at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020.
However, rising food prices may have exacerbated poverty and food insecurity, according to the Rwanda Economic Update. The increase in international commodity prices, related to the war in Ukraine combined with the poor harvest in Rwanda, have led to substantial increases in energy, transport, and food prices, with urban inflation rising to 21.7 percent in November 2022. Rising food prices particularly affected the poor, who devote a large share of their spending to food and appear to have faced higher food inflation than richer households did. Measures adopted by the government to mitigate the effects of inflation over the past year include an increase in subsidies (primarily on fuels, fertilizers, seeds, and public transit), increased spending on social protection, and increases in teachers’ salaries, as well as government contributions to school feeding programs.
“While the authorities have taken several measures to mitigate the impact of inflation on households, further steps are required to protect the poor and vulnerable from the impact of rising food prices as well as to strengthen policies to address food insecurity and prevent child stunting,” according to Peace Aimee Niyibizi, World Bank Economist.
Going forward, Rwanda’s economy is projected to expand at a slower pace in 2023-2025. While tourism is likely to continue to recover, external demand is likely to weaken as a result of a major increase in interest rates by the central bank to reduce inflation.
In its special focus on “Making the Most of Nature-Based Tourism in Rwanda”, the report provides a thorough analysis of challenges and opportunities in the nature-based tourism sector in Rwanda.
Nature-based tourism holds tremendous potential for creating employment and spurring economic growth in Rwanda. But to fully use that opportunity, innovative actions would be needed to mobilize more resources, beyond government budget, and enhance private sector participation to protect natural assets and develop appropriate infrastructure said Rolande Pryce, World Bank Country Manager for Rwanda.
Tourism is a major source of Rwanda’s foreign exchange earnings and tends to generate a higher proportion of formal sector jobs than other sectors. Within the tourism sector, nature-based tourism, which accounts for 80 percent of leisure and business visitors in Rwanda, not only helps protect biodiversity and advance Rwanda’s efforts to adapt to climate change, but also plays an important role in job creation: for every $1 million (about Rwf 1,050 million) that nature-based tourism activities inject into the economy, it is estimated that an additional 1,328 new jobs could be created.
The report notes that nature-based tourism in Rwanda faces significant challenges, including potential limits on the expansion of revenues for one of the primary international attractions (gorilla trekking), degradation of the natural assets, risks presented by infectious diseases, land degradation, and overexploitation of natural resources, and the impact of climate change.
Investment requirements to address challenges hampering the development of nature-based tourism in Rwanda are estimated at $97.5-107.7 million for the period from 2019 through 2030. The Update recommends accelerating efforts to secure private sector participation in financing and operating nature-based tourism facilities by introducing innovative financing methods, as well as strengthening capacity and the management of tourism facilities and services.
Efforts are required to enhance revenue sharing mechanisms and increase incentives for local communities to conserve natural assets and unlock new opportunities for community-led enterprises that generate revenue from tourism and sustainable management of natural resources, including forests. This is essential to address poverty, to mitigate poaching threats and other illegal activities, and to reduce the unsustainable exploitation of the natural assets that are vital for successful nature-based tourism, according to the Update.
DOWNLOAD REPORT Rwanda Economic Update: Making the Most of Nature Based Tourism in Rwanda (English)
EVENT | FEBRUARY 21, 2023 Launch of the 20th edition of the World Bank Rwanda Economic Update
World Bank in Rwanda
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .
- Tourism Data Leadership Group
- The Tourism Information and Data Hui
- 2018 Tourism Data Domain Plan
- Tourism data sources diagram
- Data release calendar
- Quarterly Tourism Report
- Tourism Evidence and Insights Centre
- Monthly unique regional population estimates (MURPEs)
- Tourism Electronic Card Transactions (TECTs)
- Accommodation Data Programme (ADP)
- International Visitor Survey (IVS)
Tourism and the economy
- International travel
- Tourism employment earnings and filled jobs
- Cruise data
- Monthly Regional Tourism Estimates (MRTEs, 2016-2020)
- Business Events Research Programme (2009-2019)
- Domestic Travel Survey 1999–2012
- Tourism Insight Series
- Tourism sector report
- Kaikōura report
- Tourism Flows Model
- Understanding variation in tourism spend
- 2019-2025 international tourism forecasts
- Market forecast summaries
- About the tourism forecasts
- International forecast microdata
- Previous international tourism forecasts
- Subscribe to tourism data alerts
The Tourism Satellite Account (TSA) report presents information on tourism's contribution to the New Zealand economy in terms of expenditure and employment.
On this page
Latest tourism satellite account — december 2023 update.
Stats NZ develops and publishes the Tourism Satellite Account (TSA) with funding we provide.
The 2023 TSA report provides a picture of the role tourism plays in New Zealand, with information on the changing levels and impact of tourism activity. Results cover provisional figures for the year ended March 2023, and detailed results for 2022.
Note : Tables 19-26 contain detailed tables for the year ended March 2022.
2023 Key Provisional Estimates
Note: The 2023 annual estimates featured capture the impact of COVID-19 in New Zealand through to March 2023 and are expressed in nominal terms.
Key provisional estimates for the year ended March 2023:
- total tourism expenditure was $37.7 billion, an increase of 39.6% ($10.7 billion) from the previous year
- international student expenditure (studying less than 12 months) was $2.1 billion, an increase of 1068.2% ($2.0 billion)
- international tourism’s overall contribution to New Zealand’s total exports of goods and services was 11.4%, an increase of 9.0 percentage points
- GST generated from international tourists totalled $209 million, an increase of $72 million
- overseas visitor arrivals to New Zealand increased 858.7% to 2,199,073
- household tourism expenditure decreased 2.8% ($576 million)
- business and government increased 26.5% ($1.2 billion)
- tourism generated a direct contribution to GDP of $13.3 billion, or 3.7% of GDP, an increase of 30.9% ($3.1 billion)
- the indirect value added of industries supporting tourism generated an additional $8.8 billion, or 2.5% of GDP
- the number of tourism employees was 164,619 – an increase of 49.7% (54,663)
- the number of tourism working proprietors was 24,813 – a decrease of 37.6% (6,786)
- as a share of the total number of people employed in New Zealand, direct tourism employment was 6.7% .
Interpretation of data
- The data sources used in deriving the numbers for the March 2022 and 2023 years at an industry, commodity, and resultant aggregate level will be subject to future updates. These updates reflect COVID-19 related methodological challenges and further assessment and interpretation of the expenditure compositional change as part of the 2023 cycle of annual analysis and updated input datasets. Data presented in this TSA for these years should serve to provide initial guidance but may be subject to larger than usual updates.
- Accommodation expenditure in the March 2023 year continued to be impacted by both Managed Isolation and Quarantine (MIQ), and the use of traditional accommodation providers for emergency housing, including in response to the Auckland Anniversary floods and Cyclone Gabrielle. In line with the definition of a tourist, the vast majority of MIQ expenditure would not fully constitute tourism activity, particularly so for returning New Zealand residents, and emergency housing is not considered tourism activity. While this expenditure would be captured on the supply side, an allowance has been made to exclude this from the tourism demand side. This has consequently led to lower accommodation product and industry ratios which flow through to tourism employment derivations. These derived numbers therefore better reflect ‘employees’ engaged in tourism as opposed to those in accommodation industry entities servicing MIQ and emergency housing.
- The derivation of tourism employment is reliant on the relationship between tourism expenditure as a proportion of an industry’s output multiplied by that industry’s employment counts. The substantial loss of international tourism expenditure, and some domestic tourism expenditure, together with COVID-19’s wider impact on industries’ output, and the tourism recovery to date has seen these historically relatively consistent industry ratios change significantly. Furthermore, employment counts in industries have also been affected, noting that during COVID-19 this included a number of people being determined as being employed who have been supported by wage subsidy payments.
The Sustainable Tourism Explorer (STE) has been updated with the new TSA data
TSA data are now available in the STE in the form of interactive graphs. As well as visualising the data, you can also customise the graphs and download them or the related data.
Tourism GDP as a proportion of total GDP (external link) — Tourism Evidence and Insights Centre (TEIC)
Direct tourism value added by industry (external link) — TEIC (not available for the provisional year-ended March 2023)
Direct and indirect employment from tourism (external link) — TEIC
2023 Revisions
Tourism satellite account: Year ended March 2023 includes updates made to both the domestic and international tourism expenditure series. These updates cause changes to the value of tourism expenditure in the New Zealand economy, and affect the official tourism satellite account (TSA) time series.
Updates to the expenditure series included the following.
- Historic changes to export education source data used to derive international student expenditure.
- Updated source data used in the derivation of imputed rental on holiday homes.
- integrating updated Annual Enterprise Survey (AES) data (2019 and 2020) and AES 2021 data with household tourism expenditure estimates (HTEE)
- continued modelling of the HTEE across the full year ended March 2023 due to changes in data supply arrangements (covered in detail in 'Appendix 2: Methodology' in download document)
- updated HTEE supplementary data sources
- national accounts data, including updated nominal GDP statistics from 2015 to 2021 (see 2023 preview of national accounts improvements).
- Updates were also made to annual Linked Employer-Employee Data and Household Labour Force Survey sources used in determining tourism employment.
Tourism satellite account: Year ended March 2022 Appendix 2: Methodology (external link) — Stats NZ
2022 national accounts improvements preview (external link) — Stats NZ
Tourism industry ratios are impacted because of these updates. These ratios are the proportion of an industry’s output that is consumed by tourists and are used to calculate value-added and tourism employment estimates. As a result of the ratio changes, StatsNZ updated the historical value added-time series. Together with the ratio changes, StatsNZ also updated the tourism employment time series.
More detailed Tourism Satellite Account data and technical information is available on Stats NZ's website.
Tourism statistics (external link) — Stats NZ
Previous Tourism Satellite Account tables
2022 tourism satellite account tables.
Tourism Satellite Account 2022: Excel Tables 1-18 [XLSX, 149 KB]
Tourism Satellite Account 2022: Excel Tables 19-26 [XLSX, 49 KB]
2021 Tourism Satellite Account Tables
Tourism Satellite Account 2021: Excel Tables 1-18 [XLSX, 191 KB]
Tourism Satellite Account 2021: Excel Tables 19-26 [XLSX, 77 KB]
2020 Tourism Satellite Account Tables
Tourism Satellite Account 2020: Excel Tables 1-18 [XLSX, 192 KB]
Tourism Satellite Account 2020: Excel Tables 19-26 [XLSX, 77 KB]
2019 Tourism Satellite Account Tables
Tourism Satellite Account 2019: Excel Tables 1-18 [XLSX, 190 KB]
Tourism Satellite Account 2019: Excel Tables 19-26 [XLSX, 79 KB]
Note: Tables 19-26 contain detailed tables for the year ended March 2018.
2018 Tourism Satellite Account Tables
Tourism Satellite Account 2018: Excel Tables 1-18 [XLSX, 193 KB]
Tourism Satellite Account 2018: Excel Tables 19-26 [XLSX, 82 KB]
Note : Tables 19-26 contain detailed tables for the year ended March 2017.
2017 Tourism Satellite Account Tables
Tourism Satellite Account 2017: Excel Tables 1-18 [XLSX, 189 KB]
Tourism Satellite Account 2017: Excel Tables 19-26 [XLSX, 78 KB]
Note: Tables 19-26 contain detailed tables for the year ended March 2016.
2016 Tourism Satellite Account Tables
Tourism Satellite Account 2016: Excel Tables 1-16 [XLSX, 154 KB]
Tourism Satellite Account 2016: Excel Tables 19-26 [XLSX, 60 KB]
Note: Tables 19-26 contain detailed tables for the year ended March 2013.
2015 Tourism Satellite Account Tables
Tourism Satellite Account 2015: Excel Tables 1-14 [XLSX, 185 KB]
Tourism Satellite Account 2015: Excel Tables 17-24 [XLSX, 57 KB]
Note: Tables 17-24 contain detailed tables for the year ended March 2012.
2014 Tourism Satellite Account Tables
Tourism Satellite Account 2014: Excel Tables 1-14 [XLSX, 193 KB]
Tourism Satellite Account 2014: Excel Tables 17-24 [XLSX, 69 KB]
Note: Tables 17-24 contain detailed tables for the year ended March 2011.
© Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment
https://www.mbie.govt.nz/immigration-and-tourism/tourism-research-and-data/tourism-data-releases/tourism-and-the-economy/ Please note: This content will change over time and can go out of date.

Philippines eyes a million American tourist arrivals in 2024 -DOT
N EW YORK CITY - The Philippines is looking to increase the number of American visitors to the country this year to about a million visitors amid renewed ties between the two allied nations.
In a dialogue with Filipino journalists participating in the Friends, Allies, Partners Program at the Philippine Consulate in New York, Tourism Attaché Francisco Lardizabal said that while American tourists ranked second only to South Koreans in terms of visitor numbers, “the US contribution was bigger… in terms of receipts.”
Data from the Department of Tourism showed South Koreans accounted for 26.62% or 1.45 million visitors to the Philippines out of the total 5.45 million foreign tourists in 2023.
The United States came in second, accounting for 16.57% or 903,299 visitors.
However, in terms of visitor receipts, tourism revenues from Americans were the highest at P35.46 billion, followed by Australians at P17.74 billion and South Koreans at P16.41 billion.
“This is the importance of the American market. While the arrivals are fewer, the contribution to the tourism receipts is bigger,” Lardizabal said.
“Because Americans spend higher and stay longer,” he added.
For this year, the tourism attaché said the DOT expected about “one million” visitors from the US, growing the number by “something like 15% more or less.”
Lardizabal said the majority of American travelers - 55.71% - were former Filipinos, while the remaining 44% were mainstream Americans.
“Those who are former Filipinos, of course, they are being motivated by… they have friends and relatives [in the Philippines]," he said.
"What they are looking for is, what did the Philippines change when I left? Because that is what they want to see here in the Philippines… and then they venture around.”
He added that Filipinos in the US would go around the Philippines.
Meanwhile, mainstream American visitors looked for a “more immersive dining experience.”
“They want to know the story about the food, how it’s prepared… or even having culinary experience by learning how to cook it,” Lardizabal said.
Among the top destinations for American visitors were Boracay, Palawan, and Siargao, according to the Tourism official. — DVM, GMA Integrated News
This article Philippines eyes a million American tourist arrivals in 2024 -DOT was originally published in GMA News Online .

Saudi Arabia wants big spenders for the first part of its Neom megaproject
- Saudi Arabia plans to open the first part of its Neom megaproject this year.
- Sindalah, an island resort, is aimed at a luxury clientele and the global yachting community.
- Saudi Arabia is pushing to distinguish itself in the high-end luxury market to compete with Dubai.

Saudi Arabia plans to open the first region of its Neom megacity by the end of the year.
The island of Sindalah will provide the first physical glimpse into the ambitious desert project, which has reportedly been scaled back from its initial plans due to financial struggles .
Developers say they want the island to be an "exclusive gateway to the stunning Red Sea," adding that they planned to cater to luxury clientele and the global yachting community.
Neom recently ended investor roadshows in China by confirming the luxury island resort would open this year, Arab News reported . It's set to have three luxury hotels, a golf course and sports club, beach club, marina, and dozens of restaurants and shops.
In January Marriott International said it had signed an agreement to bring Apartments by Marriott Bonvoy to Sindalah. Chadi Hauch of the hotel operator said the concept was a "great fit" for the island and reflected a "growing desire for premium and luxury apartment-style accommodation" from travelers.
The following month Saudi music entertainment company, MDLBEAST, announced it would operate the Sindalah Beach Club on the island.
Vives, Neom's chief urban planning and islands officer, said in a press release that Sindalah will be a "new model for luxury travel and living."
Capturing the luxury tourism market
The Saudi government's focus on the luxury market is an attempt to distinguish itself from nearby Dubai, part of the United Arab Emirates.
Related stories
"Dubai goes for the mass market of people wanting to go and have fun in the winter," Kristian Coates Ulrichsen, a fellow for the Middle East at Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy, told Business Insider.
"The Saudis are increasingly pushing themselves toward a high-end luxury market, which is what Sindalah and, to some extent, some of the other Red Sea projects are going to cater for," he said.
Saudi Arabia hasn't been shy about its tourism aspirations, claiming it aims to attract between 100 million and 150 million visitors by 2030 .
However, Dubai is a formidable competitor. It already has a 20-year head start in the tourism race, both in terms of infrastructure and aspirational appeal. It also has Emirates, the popular long-haul airline that brings tens of millions of people through Dubai annually.
If Neom's ambitious plans become a reality, the Saudis are betting that their megaprojects can attract some high-end travelers from the glitz and glamor of its neighbor.
Managing ambition
Developing luxury resorts like Sindalah may also help Saudi Arabia encourage tourism sooner by starting smaller.
Sindalah is one of the more realistic elements of Neom's futuristic plans . It pales in comparison to structures like the mirrored "horizontal skyscraper" known as The Line.
"It's less ambitious in scope and scale," Ulrichsen said. "That might mean that it's more realistic to open first."
Recent reports have indicated the Saudis may be facing a harsh reality when it comes to f inancing some of the megaprojects included in Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman's Vision 2030 project .
Previous deadlines have already been pushed back for some of Neom's more ambitious projects.
Earlier this month, Bloomberg reported that the Gulf Kingdom had reduced estimates for the number of people expected to live in The Line .
The report said the realities of some of the trillion-dollar investments included in the Vision 2030 project were starting to cause alarm at the highest level of the country's government.
Neom did not immediately respond to a request for comment from Business Insider.
Watch: Marriott International's Tina Edmundson tells Insider that the travel mindset has changed since the pandemic
- Main content
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Secretary-general’s policy brief on tourism and covid-19, share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Tourism and COVID-19 – unprecedented economic impacts
The Policy Brief provides an overview of the socio-economic impacts from the pandemic on tourism, including on the millions of livelihoods it sustains. It highlights the role tourism plays in advancing the Sustainable Development Goals, including its relationship with environmental goals and culture. The Brief calls on the urgency of mitigating the impacts on livelihoods, especially for women, youth and informal workers.
The crisis is an opportunity to rethink how tourism interacts with our societies, other economic sectors and our natural resources and ecosystems; to measure and manage it better; to ensure a fair distribution of its benefits and to advance the transition towards a carbon neutral and resilient tourism economy.
The brief provides recommendations in five priority areas to cushion the massive impacts on lives and economies and to rebuild a tourism with people at the center. It features examples of governments support to the sector, calls for a reopening that gives priority to the health and safety of the workers, travelers and host communities and provides a roadmap to transform tourism.
- Tourism is one of the world’s major economic sectors. It is the third-largest export category (after fuels and chemicals) and in 2019 accounted for 7% of global trade .
- For some countries, it can represent over 20% of their GDP and, overall, it is the third largest export sector of the global economy.
- Tourism is one of the sectors most affected by the Covid-19 pandemic, impacting economies, livelihoods, public services and opportunities on all continents. All parts of its vast value-chain have been affected.
- Export revenues from tourism could fall by $910 billion to $1.2 trillion in 2020. This will have a wider impact and could reduce global GDP by 1.5% to 2.8% .
- Tourism supports one in 10 jobs and provides livelihoods for many millions more in both developing and developed economies.
- In some Small Island Developing States (SIDS), tourism has accounted for as much as 80% of exports, while it also represents important shares of national economies in both developed and developing countries.

100 to 120 MILLON
direct tourism jobs at risk
Massive Impact on Livelihoods
- As many as 100 million direct tourism jobs are at risk , in addition to sectors associated with tourism such as labour-intensive accommodation and food services industries that provide employment for 144 million workers worldwide. Small businesses (which shoulder 80% of global tourism) are particularly vulnerable.
- Women, who make up 54% of the tourism workforce, youth and workers in the informal economy are among the most at-risk categories.
- No nation will be unaffected. Destinations most reliant on tourism for jobs and economic growth are likely to be hit hardest: SIDS, Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and African countries. In Africa, the sector represented 10% of all exports in 2019.

US$ 910 Billon to US$ 1.2 Trillon
in export from tourism - international visitors' spending
Preserving the Planet -- Mitigating Impacts on Nature and Culture
- The sudden fall in tourism cuts off funding for biodiversity conservation . Some 7% of world tourism relates to wildlife , a segment growing by 3% annually.
- This places jobs at risk and has already led to a rise in poaching, looting and in consumption of bushmeat , partly due to the decreased presence of tourists and staff.
- The impact on biodiversity and ecosystems is particularly critical in SIDS and LDCs. In many African destinations, wildlife accounts for up to 80% of visits, and in many SIDS, tourism revenues enable marine conservation efforts.
- Several examples of community involvement in nature tourism show how communities, including indigenous peoples, have been able to protect their cultural and natural heritage while creating wealth and improve their wellbeing. The impact of COVID-19 on tourism places further pressure on heritage conservation as well as on the cultural and social fabric of communities , particularly for indigenous people and ethnic groups.
- For instance, many intangible cultural heritage practices such as traditional festivals and gatherings have been halted or postponed , and with the closure of markets for handicrafts, products and other goods , indigenous women’s revenues have been particularly impacted.
- 90% of countries have closed World Heritage Sites, with immense socio-economic consequences for communities reliant on tourism. Further, 90% of museums closed and 13% may never reopen.

1.5% to 2.8 of global GDP
Five priorities for tourism’s restart.
The COVID-19 crisis is a watershed moment to align the effort of sustaining livelihoods dependent on tourism to the SDGs and ensuring a more resilient, inclusive, carbon neutral, and resource efficient future.
A roadmap to transform tourism needs to address five priority areas:
- Mitigate socio-economic impacts on livelihoods , particularly women’s employment and economic security.
- Boost competitiveness and build resilience , including through economic diversification, with promotion of domestic and regional tourism where possible, and facilitation of conducive business environment for micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs).
- Advance innovation and digital transformation of tourism , including promotion of innovation and investment in digital skills, particularly for workers temporarily without jobs and for job seekers.
- Foster sustainability and green growth to shift towards a resilient, competitive, resource efficient and carbon-neutral tourism sector. Green investments for recovery could target protected areas, renewable energy, smart buildings and the circular economy, among other opportunities.
- Coordination and partnerships to restart and transform sector towards achieving SDGs , ensuring tourism’s restart and recovery puts people first and work together to ease and lift travel restrictions in a responsible and coordinated manner.

a lifelive for
SIDS, LDCs and many AFRICAN COUNTRIES
tourism represents over 30% of exports for the majority of SIDS and 80% for some
Moving Ahead Together
- As countries gradually lift travel restrictions and tourism slowly restarts in many parts of the world, health must continue to be a priority and coordinated heath protocols that protect workers, communities and travellers, while supporting companies and workers, must be firmly in place.
- Only through collective action and international cooperation will we be able to transform tourism, advance its contribution to the 2030 Agenda and its shift towards an inclusive and carbon neutral sector that harnesses innovation and digitalization, embraces local values and communities and creates decent job opportunities for all, leaving no one behind. We are stronger together.

RESOURCES FOR CONSEVATION
of natural and cultural heritage
Related links
- Policy Brief: Tourism and COVID-19
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Tourism
- António Guterres - Video
- Updated Terms of Use
- New Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Closed Captioning Policy
Quotes displayed in real-time or delayed by at least 15 minutes. Market data provided by Factset . Powered and implemented by FactSet Digital Solutions . Legal Statement .
This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed. ©2024 FOX News Network, LLC. All rights reserved. FAQ - New Privacy Policy
Vacationing at these destinations? You will pay tourist taxes, fees
There are a slew of places with tourist taxes or fees.

FOX Business Flash top headlines for April 24
Check out what's clicking on FoxBusiness.com
Travelers may encounter a tourist tax or fee depending on their destination.
That additional travel cost could come up if a person visits one of the slew of places around the world that have such charges. Factors that spurred the taxes can vary, ranging from climate change to overtourism, according to reports.
CLICK HERE TO READ MORE ON FOX BUSINESS
Five locales with tourist taxes or fees include:
Venice, Italy

Piazza San Marco square view from the Giudecca Canal, Venice, Veneto, Italy. (Photo by: Mauro Flamini/REDA&CO/Universal Images Group via Getty Images) (Mauro Flamini/REDA&CO/Universal Images Group via Getty Images / Getty Images)
The roughly $5.35 daily tourist access fee for Venice, home to the Rialto Bridge, Doge’s Palace and St. Mark’s Basilica, launched as a pilot on Thursday after it received the go-ahead from city officials in mid-September. It targets day-trippers coming into the city between 8:30 a.m. to 4 p.m. and is required on specific dates in April, May, June and July during the test period.

Mount Fuji and the Shinjuku skyline seen from an observation deck in Tokyo, Japan, on Tuesday, Dec. 26, 2023. Japan's industrial output in November is scheduled to be released by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry on Dec. 28. Photographer: A (Akio Kon/Bloomberg via Getty Images / Getty Images)
International tourists can face an "International Tourist Tax" while exiting Japan, per the Japanese National Tax Agency . It amounts to about $6.30 per departure and must be paid by those taking planes or boats to do so.
Barcelona, Spain

BARCELONA, SPAIN - 2023/12/11: View of the Sagrada Familia, the largest unfinished Catholic church in the world which has been under construction for 144 years, and part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Its completion is estimated to be in 2026. (Pho (Xavi Lopez/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images / Getty Images)
While the city’s nightly tax for travelers staying at tourist accommodations has existed for quite some time, it went up at the beginning of the month, becoming about $3.47. It is capped at seven nights. Catalonia, the region where Barcelona is located, also has a graduated tourist tax that’s size is determined by one’s accommodation, according to The Points Guy.
GET FOX BUSINESS ON THE GO BY CLICKING HERE

This photograph taken on January 10, 2024, shows a a residential area (L) on the banks of the Wang Chuu River also known as Raidak River flowing through Bhutan's capital Thimphu. (Photo by Money SHARMA / AFP) (Photo by MONEY SHARMA/AFP via Getty Imag (MONEY SHARMA/AFP via Getty Images / Getty Images)
Bhutan, nestled in the Himalayas in Asia, asks most tourists to hand over nightly Sustainable Development Fees of $100 for adults and $50 for ages 6-12. It charges a differently-priced fee from those coming from India. The money goes toward "various projects that create long-term, sustainable opportunities for the Bhutanese people," the country’s department of tourism website said.
New Zealand

Buildings in Auckland, New Zealand, on Tuesday, Sept. 13, 2022. New Zealand is scheduled gross domestic product (GDP) figures on Sept. 15. Photographer: Fiona Goodall/Bloomberg via Getty Images (Fiona Goodall/Bloomberg via Getty Images / Getty Images)
New Zealand’s tourist tax, called the International Visitor Conservation and Tourism Levy, costs $35. Tourists encounter it during the visa application process. The country requires it for "most people entering New Zealand on a temporary basis" such as vacation and certain student and short-term work visas, according to the government.
Tourism a boon for economy
Travel and tourism provides major benefits to local economies and the global economy alike.
Countries around the world will see travel and tourism produce $11.1 trillion in 2024, according to a report recently released by the World Travel & Tourism Council.
TRAVEL AND TOURISM TO BREAK RECORDS, BRING OVER $11 TRILLION IN 2024: REPORT
Part of that will include spending by international travelers. They will reportedly contribute $1.89 trillion, according to the WTTC.
Travel, Tourism & Hospitality
Tourism contribution to GDP in the U.S. 2019-2022
Total contribution of travel and tourism to the gross domestic product (gdp) in the united states in 2019 and 2022 (in trillion u.s. dollars).
Additional Information
Show sources information Show publisher information Use Ask Statista Research Service
United States
2019 and 2022
Figures have been rounded.
Other statistics on the topic Travel and tourism in the U.S.
Accommodation
ADR of hotels in the U.S. 2001-2022
Parks & Outdoors
Most visited amusement and theme parks worldwide 2019-2022
Occupancy rate of the U.S. hotel industry 2001-2022
Most visited states in the U.S. 2022
- Immediate access to statistics, forecasts & reports
- Usage and publication rights
- Download in various formats
You only have access to basic statistics.
- Instant access to 1m statistics
- Download in XLS, PDF & PNG format
- Detailed references
Business Solutions including all features.
Other statistics that may interest you
- Tourism GDP in the Balearics 2016-2021
- Tourism share of GDP in the Canary Islands 2010-2021
- Total tourism contribution to GDP in Iceland 2019-2021
- Travel and tourism: share of global GDP 2019-2033
- Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Europe 2019-2022
- Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Ireland 2019-2022
- Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Greece 2019-2022
- Distribution of travel and tourism expenditure in Greece 2019-2022, by tourist type
- Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in the UK 2019-2022
- Leading global travel markets by travel and tourism contribution to GDP 2019-2022
- Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in the U.S. 2013-2017, by type
- Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in the U.S. 2013-2017, by travel type
- Share of travel and tourism spending in the U.S. 2019-2022, by spending type
- Forecast travel expenditures in the U.S. 2023-2026
- Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in the U.S. 2013-2017, by visitor origin
- Daily national park visitor spending in the U.S. 2010-2022, by category
- Visitor travel spending in the U.S. in 2021, by country of origin
- International overnight visitors to New York 2010-2018
- Contribution of travel and tourism to employment in the U.S. 2013-2017, by type
- Market share of outbound visits to the US from the GCC 2011-2021
- Revenue share from tourism in India 2013-2022, by segment
- Countries with the highest outbound tourism expenditure worldwide 2019-2022
- Leading countries in the MEA in the Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Index 2018
- Countries with the highest number of inbound tourist arrivals worldwide 2019-2022
- Change in number of visitors from Mexico to the U.S. 2018-2024
- International tourist arrivals in Europe 2006-2023
- Annual revenue of China Tourism Group Duty Free 2013-2023
- Foreign exchange earnings from tourism in India 2000-2022
- Number of international tourist arrivals in India 2010-2021
- Distribution of travel and tourism spending in Ireland 2019-2022, by tourist type
- Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Germany 2019-2022
- Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Turkey 2019-2023
- Tourism GDP in the Canary Islands 2015-2021
- Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP Egypt 2017, by type
- Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Italy 2019-2022
- International transactions in Canada related to educational travel 2007-2022
- Travel & tourism to GDP impact in South Korea 2017, by type
- Distribution of travel and tourism expenditure in Malta 2019-2022, by tourist type
- Distribution of travel and tourism expenditure in Europe 2019-2022, by tourist type
- International transactions in Canada related to personal travel 2008-2022
- Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in Canada 2019-2022
- Domestic tourism expenditure in Canada 2000-2020
- International transactions in Canada related to travel 2002-2022
- Total tourism spend on travel agency services in Canada 2000-2019
- Tourism expenditure in Canada 2000-2019, by commodity
- Domestic tourism expenditure in Canada 2000-2019, by commodity
- Tourism expenditure in Canada 2000-2019
- Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in Canada 2016-2017, by type
- Contribution of travel and tourism to employment in Canada 2019-2022
Other statistics that may interest you Statistics on
About the industry
- Premium Statistic Tourism GDP in the Balearics 2016-2021
- Premium Statistic Tourism share of GDP in the Canary Islands 2010-2021
- Basic Statistic Total tourism contribution to GDP in Iceland 2019-2021
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism: share of global GDP 2019-2033
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Europe 2019-2022
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Ireland 2019-2022
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Greece 2019-2022
- Basic Statistic Distribution of travel and tourism expenditure in Greece 2019-2022, by tourist type
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in the UK 2019-2022
- Basic Statistic Leading global travel markets by travel and tourism contribution to GDP 2019-2022
About the region
- Basic Statistic Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in the U.S. 2013-2017, by type
- Basic Statistic Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in the U.S. 2013-2017, by travel type
- Basic Statistic Share of travel and tourism spending in the U.S. 2019-2022, by spending type
- Premium Statistic Forecast travel expenditures in the U.S. 2023-2026
- Basic Statistic Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in the U.S. 2013-2017, by visitor origin
- Premium Statistic Daily national park visitor spending in the U.S. 2010-2022, by category
- Premium Statistic Visitor travel spending in the U.S. in 2021, by country of origin
- Premium Statistic International overnight visitors to New York 2010-2018
- Basic Statistic Contribution of travel and tourism to employment in the U.S. 2013-2017, by type
- Premium Statistic Market share of outbound visits to the US from the GCC 2011-2021
Selected statistics
- Basic Statistic Revenue share from tourism in India 2013-2022, by segment
- Premium Statistic Countries with the highest outbound tourism expenditure worldwide 2019-2022
- Premium Statistic Leading countries in the MEA in the Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Index 2018
- Premium Statistic Countries with the highest number of inbound tourist arrivals worldwide 2019-2022
- Premium Statistic Change in number of visitors from Mexico to the U.S. 2018-2024
- Premium Statistic International tourist arrivals in Europe 2006-2023
- Premium Statistic Annual revenue of China Tourism Group Duty Free 2013-2023
- Basic Statistic Foreign exchange earnings from tourism in India 2000-2022
- Basic Statistic Number of international tourist arrivals in India 2010-2021
Other regions
- Basic Statistic Distribution of travel and tourism spending in Ireland 2019-2022, by tourist type
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Germany 2019-2022
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Turkey 2019-2023
- Premium Statistic Tourism GDP in the Canary Islands 2015-2021
- Basic Statistic Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP Egypt 2017, by type
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP in Italy 2019-2022
- Premium Statistic International transactions in Canada related to educational travel 2007-2022
- Basic Statistic Travel & tourism to GDP impact in South Korea 2017, by type
- Basic Statistic Distribution of travel and tourism expenditure in Malta 2019-2022, by tourist type
- Basic Statistic Distribution of travel and tourism expenditure in Europe 2019-2022, by tourist type
Related statistics
- Premium Statistic International transactions in Canada related to personal travel 2008-2022
- Basic Statistic Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in Canada 2019-2022
- Premium Statistic Domestic tourism expenditure in Canada 2000-2020
- Premium Statistic International transactions in Canada related to travel 2002-2022
- Premium Statistic Total tourism spend on travel agency services in Canada 2000-2019
- Premium Statistic Tourism expenditure in Canada 2000-2019, by commodity
- Premium Statistic Domestic tourism expenditure in Canada 2000-2019, by commodity
- Premium Statistic Tourism expenditure in Canada 2000-2019
- Basic Statistic Contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in Canada 2016-2017, by type
- Basic Statistic Contribution of travel and tourism to employment in Canada 2019-2022
Further related statistics
- Basic Statistic Contribution of China's travel and tourism industry to GDP 2014-2023
- Premium Statistic National park visitor spending in the U.S. 2012-2022, by trip type
- Premium Statistic Music tourist spending at concerts and festivals in the United Kingdom (UK) 2012-2016
- Basic Statistic Growth of inbound spending in the U.S. using foreign visa credit cards
- Premium Statistic Economic contribution of national park visitor spending in the U.S. 2012-2022
- Premium Statistic Number of international tourist arrivals APAC 2019, by country or region
- Premium Statistic Middle Eastern countries with the largest international tourism receipts 2018
- Premium Statistic Camping expenditures for food, beverages and entertainment in North America 2014
- Premium Statistic Passenger traffic at Dubai Airports from 2010 to 2020*
- Basic Statistic Importance of BRICS countries to UK tourism businesses 2011
Further Content: You might find this interesting as well
- Contribution of China's travel and tourism industry to GDP 2014-2023
- National park visitor spending in the U.S. 2012-2022, by trip type
- Music tourist spending at concerts and festivals in the United Kingdom (UK) 2012-2016
- Growth of inbound spending in the U.S. using foreign visa credit cards
- Economic contribution of national park visitor spending in the U.S. 2012-2022
- Number of international tourist arrivals APAC 2019, by country or region
- Middle Eastern countries with the largest international tourism receipts 2018
- Camping expenditures for food, beverages and entertainment in North America 2014
- Passenger traffic at Dubai Airports from 2010 to 2020*
- Importance of BRICS countries to UK tourism businesses 2011

Shapiro Administration Opens Application Period for Sports Marketing and Tourism Program Grants
- April 22, 2024
Pennsylvania is a world-class destination, with the most passionate and dedicated fanbase in the world – and Governor Josh Shapiro’s Administration is working hard to attract more marquee sporting events to the Commonwealth to drive tourism and economic growth.
SMAT has helped bring nationally known sporting events to Pennsylvania – including the 2026 World Cup, the 2025 United States Men’s Open, the 2024 United States Women’s Open, and more.
Harrisburg, PA – Today, Department of Community and Economic Development (DCED) Secretary Rick Siger announced that the application period for grants through DCED’s Sports Marketing and Tourism Program (SMAT) opened this morning, April 22 at 9:00AM EST. The application period will close on June 30 at 4:00PM EST.
The Sports Marketing and Tourism Program was created to attract high-quality, amateur, and professional sporting and e-sports events to Pennsylvania. The goal of the investment in the program is to capitalize on the influx of tourism that comes with hosting a major national or international event, which can increase sales to both large and small businesses in the surrounding area and in turn boost the regional economy, as well as improve the quality of life for residents.
“This is an exciting time for Pennsylvania as we prepare to host a number of incredibly exciting events in the coming years, including the 2026 World Cup, the 2024 USGA Women’s Open, and the 2025 USGA Men’s Open,” said Secretary Siger. “SMAT is helping to bring major events like these to the Commonwealth, providing a huge boost to our economy. With the new application period opening up, we look forward to supporting even more major sporting events here in the coming years.”
Eligible program applicants include a municipality, a local authority, a nonprofit organization, or a legal entity that meets all of the following criteria:
- The applicant participates or plans to participate in a competitive selection process;
- The site selection process is conducted by a Site Selection Organization not located in Pennsylvania; and
- The applicant is seeking to secure a single year or multiyear commitment from a site selection organization to conduct high quality, amateur and professional sporting or esports events at one or more locations in Pennsylvania.
Last September, DCED announced the previous round of SMAT grant approvals , with $5 million in grant funding awarded. Recipients included Philadelphia Soccer for the 2026 World Cup in Philadelphia, the United States Golf Association (USGA) for the 2025 United States Men’s Open in Oakmont, and the 2024 United States Women’s Open in Lancaster.
Applicants can use DCED’s Electronic Single Application (ESA) to apply. For full program guidelines, visit the Sports Marketing and Tourism website .
For more information about the Department of Community and Economic Development, visit DCED website , and be sure to stay up-to-date with all of our agency news on Facebook , X , and LinkedIn .
MEDIA CONTACT: Penny Ickes, [email protected]
- DCED Funding tourism
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Employment in tourism-related industries per 1,000 people. Fatal airliner accidents and hijacking incidents. Fatal airliner accidents per million commercial flights. Fatalities from airliner accidents and hijackings. Foreign guests in hotels and similar establishments. Global aviation fatalities per million passengers. International one-day trips.
WTTC's latest annual research shows: In 2023, the Travel & Tourism sector contributed 9.1% to the global GDP; an increase of 23.2% from 2022 and only 4.1% below the 2019 level. In 2023, there were 27 million new jobs, representing a 9.1% increase compared to 2022, and only 1.4% below the 2019 level.
10 Nov 2023. Tourism has again been identified as a key driver of economic recovery and growth in a new report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). With UNWTO data pointing to a return to 95% of pre-pandemic tourist numbers by the end of the year in the best case scenario, the IMF report outlines the positive impact the sector's rapid ...
In 2022, the share of travel and tourism's total contribution to global gross domestic product (GDP) experienced a decline of 2.8 percentage points compared to 2019, the year prior to the onset of ...
In 2022, the total contribution of travel and tourism to the global gross domestic product (GDP) was 23 percent lower than in 2019, the year prior to the onset of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic.
Economic Contribution and SDG. As UN custodian, the UNWTO Department of Statistics compiles data on the Sustainable Development Goals indicators 8.9.1 and 12.b.1, included in the Global Indicator Framework . Data collection started in 2019 and provides data from 2008 onwards, the latest update took place on 29 August 2023.
The UN Tourism Data Dashboard - provides statistics and insights on key indicators for inbound and outbound tourism at the global, regional and national levels. Data covers tourist arrivals, tourism share of exports and contribution to GDP, source markets, seasonality and accommodation (data on number of rooms, guest and nights)
Tourism has massively increased in recent decades. Aviation has opened up travel from domestic to international. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of international visits had more than doubled since 2000. Tourism can be important for both the travelers and the people in the countries they visit. For visitors, traveling can increase their ...
Tourism made up 10 percent of global GDP in 2019 and was worth almost $9 trillion, 1 See "Economic impact reports," World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), wttc.org. making the sector nearly three times larger than agriculture. However, the tourism value chain of suppliers and intermediaries has always been fragmented, with limited coordination among the small and medium-size enterprises ...
Globally, travel and tourism's direct contribution to gross domectic product (GDP) was approximately 7.7 trillion U.S. dollars in 2022. This was a, not insignificant, 7.6 percent share of the ...
Travel and Tourism Satellite Account for 2017-2021 The travel and tourism industry—as measured by the real output of goods and services sold directly to visitors—increased 64.4 percent in 2021 after decreasing 50.7 percent in 2020, according to the most recent statistics from BEA's Travel and Tourism Sate.
Tourism GDP. Tourism direct GDP corresponds to the part of GDP generated by all industries directly in contact with visitors. This indicator is measured as a percentage of total GDP or a percentage of GVA.
Tourism Statistics. Get the latest and most up-to-date tourism statistics for all the countries and regions around the world. Data on inbound, domestic and outbound tourism is available, as well as on tourism industries, employment and complementary indicators. All statistical tables available are displayed and can be accessed individually ...
5. AGENCIES INVOLVED WITH THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE INDICATOR. (a) Lead Agency: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), located in Madrid, Spain. Contact: Statistics and Economic ...
Tourism-dependent economies are among those harmed the most by the pandemic Before COVID-19, travel and tourism had become one of the most important sectors in the world economy, accounting for 10 percent of global GDP and more than 320 million jobs worldwide. In 1950, at the dawn of the jet age, just 25 million people took foreign trips.
Tourism has become the world's third-largest export industry after fuels and chemicals, and ahead of food and automotive products. From last few years, there has been a great surge in international tourism, culminates to 7% share of World's total exports in 2016. To this end, the study attempts to examine the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth ...
International tourism revenue, percent of GDP, 2020: The average for 2020 based on 125 countries was 3.37 percent. The highest value was in Aruba: 42.09 percent and the lowest value was in Guinea: 0.01 percent. The indicator is available from 1995 to 2020. Below is a chart for all countries where data are available.
13 Jan 2022. The important role that tourism will play in the recovery of national economies and global trade has been highlighted in the 2022 edition of the World Economic Situation and Prospects (WESP) report by the United Nations. Drawing on data from the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), WESP underlines the sector's importance for the ...
The tourism sector in Namibia is a significant industry that directly contributes 6.9% to the country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which amounts to N$14.3 billion in monetary value According to the 2022 Namibia Tourist Satellite Account Report, tourism-related industries employ a total of 57 277 individuals, accounting for 7.9% of the ...
KIGALI, February 21, 2023— The Rwandan economy continued to achieve strong growth in 2022 despite global headwinds and an unprecedented increase in food prices, according to the 20 th edition of the Rwanda Economic Update report released today. Rwanda's GDP grew by 8.4 percent in the first three quarters of 2022, after reaching 11 percent in 2021. Growth was spurred by the services sector ...
Total contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in leading travel markets worldwide in 2019 and 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars) Records: Characteristic. 2019. 2022. United States. 2,172.4. 2,018.3 ...
the indirect value added of industries supporting tourism generated an additional $8.8 billion, or 2.5% of GDP. the number of people attributed to being directly employed in tourism was 189,432 - an increase of 48.0% (61,452 people) the number of tourism employees was 164,619 - an increase of 49.7% (54,663)
Meanwhile, according to The Whiskey Wash, Tourism Economics, a subdivision of Oxford Economics, crunched the numbers to reveal a direct economic impact of $831.7 million statewide, along with the ...
Data from the Department of Tourism showed South Koreans accounted for 26.62% or 1.45 million visitors to the Philippines out of the total 5.45 million foreign tourists in 2023.
Saudi Arabia hasn't been shy about its tourism aspirations, claiming it aims to attract between 100 million and 150 million visitors by 2030. However, Dubai is a formidable competitor.
Tourism is one of the world's major economic sectors. It is the third-largest export category (after fuels and chemicals) and in 2019 accounted for 7% of global trade . For some countries, it can represent over 20% of their GDP and, overall, it is the third largest export sector of the global economy.
Tourism a boon for economy. Travel and tourism provides major benefits to local economies and the global economy alike. Countries around the world will see travel and tourism produce $11.1 ...
In 2022, the gross domestic product (GDP) of the travel and tourism sector in the United States amounted to approximately 2.02 trillion U.S. dollars. This figure remained below the pre-pandemic ...
Pennsylvania is a world-class destination, with the most passionate and dedicated fanbase in the world - and Governor Josh Shapiro's Administration is working hard to attract more marquee sporting events to the Commonwealth to drive tourism and economic growth. SMAT has helped bring nationally known sporting events to Pennsylvania - including the 2026 World Cup, […]
Germany's economic prospects are looking up after two grueling years of near-zero growth. The consumer-led revival, though, papers over enduring industrial weakness for which there's no quick fix.