- Shop Early Amazon Prime Day Deals
- I Tried Both: Ring vs Nest Doorbell

What Is Safari?
What you need to know about Apple's web browser
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/DanNations-b3e3901c63b544bf8588ac2fc6231f60.jpg)
- University of Texas at Arlington
In This Article
Jump to a Section
- Benefits of Safari
- Drawbacks With Safari
Safari Alternatives
Safari web browser is the default for the iPhone , iPad, and macOS , first released by Apple in 2003 and briefly offered on Windows from 2007 to 2012. The popularity of the Safari browser exploded with the iPhone and the iPad, and currently has about a 54% market share of mobile browser usage in the United States.
In most ways, Safari is like any other popular browser. Users can browse websites, bookmark favorites, and open multiple sites in tabs. Built using the WebKit engine, Safari was one of the first web browsers to support the new HTML 5 standard. It was also one of the first browsers to have support for Adobe Flash turned off by default, with the mobile versions of Safari having never supported Flash .
Safari on Mac OS is currently on version 11.1, which includes an upgrade to Intelligent Tracking Prevention. This feature helps prevent a specific website from tracking pages browsed on other websites, a process called 'cross-site tracking. Safari on iOS shares its version with the iOS version, which is currently on 12.1.
What Makes Safari Stand out From Other Web Browsers?
While you might have trouble spotting the differences between Google Chrome, Apple's Safari, or Microsoft Edge at first glance, the Safari browser has some key features that help separate it from the pack, including the ability to format articles for easier reading.
- iCloud Tab Browsing . This feature automatically syncs open tabs across devices with the same iCloud account. You can view a list of all tabs open on your MacBook while using Safari on the iPhone or iPad. It's similar to Chrome's bookmark sharing but doesn't require logging in.
- Sharing . The Safari app has a built-in share button that enables users to quickly share a website through messaging, email, or social media. The coolest feature is the ability to share a site directly with another nearby iPhone, iPad, or Mac using AirDrop.
- Reader View . Safari can detect articles and present them in a format that strips out navigation and advertisement in favor of a more readable view. This view is especially great for websites that load new windows as you scroll or become unreadable on an iPhone or iPad because of navigation.
- Energy Efficient . While iMacs are great desktop computers, Apple is primarily a laptop and mobile device provider. Safari proves this by being extremely energy efficient, buying you precious minutes, and sometimes even hours of extra use compared to Chrome, Firefox, and other popular browsers.
What Are Safari's Deficits?
The Safari web browser has a lot going for it, especially for those who are rooted in the Apple ecosystem and own a Mac along with an iPhone or iPad. However, it's not all roses and butterflies:
- Limited Plugin Support. Safari supports Extension, but the plugins available for Safari lag behind those available for Chrome.
- Exclusive to Apple . While it's possible to run Safari on Linux and it was briefly supported on Windows, Safari is primarily a web browser made to run on Apple hardware. You can't run it on Android smartphones or tablets, and you should avoid the Windows version because Apple no longer supports it with critical security updates.
- No Tab Icons . Favicons are essentially icons for websites. And while browsers like Google Chrome use these icons in tabs to help differentiate browser tabs and help the user pick out the one they want, Safari doesn't include them on tabs.
While Safari is the default browser for iOS and Mac, users can download a wide range of browsers on either platform. The Mac supports Chrome, Firefox, Opera, Vivaldi, and many other web browsers, while iPhone and iPad users can download Chrome, Firefox, Opera, and even Microsoft Edge.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- How to Close All Tabs in Safari on the iPhone or iPad
- 10 Hidden Features in macOS Sonoma
- The Top 10 Internet Browsers for 2024
- Can You Install the Safari Browser on Android?
- What's the Current macOS? The Complete macOS Versions Guide
- Managing History and Other Private Data in Safari for macOS
- What is Dolphin Browser and How Does It Work?
- How to Clear Cache and Cookies in Every Major Browser
- How to Use the Safari Web Browser on iPhone
- How to Check the Version Number of Apple Safari Browser
- How to Manage Your Browsing History in Safari
- Apple Safari vs. Mozilla Firefox
- How to Increase Web Browser Security
- How to Delete Cookies in Every Major Browser
- Mac and PC Differences: What Are They Really?
- How to Turn on Incognito Mode in Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari and Opera
Web Browser
- Google Chrome Browser
- Mozilla Firefox Browser
- Microsoft Edge Browser
- Apple Safari Browser
- Tor Browser
- Opera Browser
- DuckDuckGo Browser
- Brave Browser
- CBSE Class 12 Informatics Practices Syllabus 2023-24
- CBSE Class 12 Informatics Practices 2023-24 Distribution of Marks
- CBSE Class 12 Informatics Practices Unit-wise Syllabus
- Unit 1 Data Handling using Pandas I
- Introduction to Python Libraries Series
- Importing and Exporting Data between CSV
- Files and DataFrames
- Pandas Series Vs NumPy ndarray
- Data Handling using Pandas II
- Introduction
- Descriptive Statistics
- Data Aggregations
- Sorting a DataFrame
- Group by Functions
- Handling Missing Values
- Plotting using Matplotlib
- Linewidth and Line Style
- The Pandas Plot Function Pandas Visualisation
- Plotting a Line chart
- Plotting Bar Chart
- Plotting Histogram
- Plotting Scatter Chart
- Plotting Quartiles and Box plot
- Plotting Pie Chart
- Unit 4 Societal Impacts
- Digital Footprints
- Net Etiquettes
- Intellectual Property Right
- Violation of IPR
- Public Access and Open Source Software
- Cyber Crime
- Phishing and Fraud Emails
- Indian Information Technology Act
- E waste Hazards and Management
When we need any kind of information most of the time we get help from the Internet, and we get information. The Internet provides us with useful information easily. We use mobile phones, computers, and tablets. We search for a lot of things in our daily lives, so we get information about all over the world, but we can not get information by just only getting connected to the Internet. We need a platform where we can search for our questions. The platform that provides such kinds of services is called a web browser, without a web browser internet will not be able to provide information.
What is a Web Browser?
The web browser is an application software to explore www ( World Wide Web) . It provides an interface between the server and the client and it requests to the server for web documents and services. It works as a compiler to render HTML which is used to design a webpage. Whenever we search for anything on the internet, the browser loads a web page written in HTML, including text, links, images, and other items such as style sheets and JavaScript functions. Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, and Safari are examples of web browsers.
History of the Web Browsers
The first web browser World Wide Web was invented in the year of 1990 by Tim Berners-Lee. Later, it becomes Nexus. In the year of 1993, a new browser Mosaic was invented by Mark Andreessen and their team. It was the first browser to display text and images at a time on the device screen. He also invents another browser Netscape in 1994. Next year Microsoft launched a web browser Internet Explorer which was already installed in the Windows operating system. After this many browsers were invented with various features like Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Safari, Opera, etc. For more detail refer this article: History of Web Browsers
The choice of a web browser depends on the user’s preference and requirements. To know more about individual browsers please go through our Web Browser – A Complete Overview
How does a Web Browser Work?
A web browser helps us find information anywhere on the internet. It is installed on the client computer and requests information from the web server such a type of working model is called a client-server model.
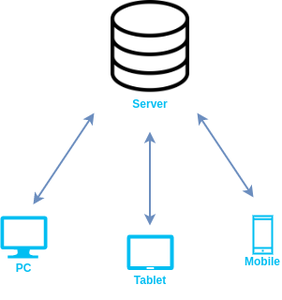
Client-server model
The browser receives information through HTTP protocol. In which transmission of data is defined. When the browser received data from the server, it is rendered in HTML to user-readable form and, information is displayed on the device screen.
Website Cookies
When we visited any website over the internet our web browser stores information about us in small files called cookies. Cookies are designed to remember stateful information about our browsing history. Some more cookies are used to remember about us like our interests, our browsing patterns, etc. Websites show us ads based on our interests using cookies.
Some Popular Web Browsers
Here is a list of 7 popular web browsers:
1. Google Chrome:
Developed by Google, Chrome is one of the most widely-used web browsers in the world, known for its speed and simplicity.
2. Mozilla Firefox:
Developed by the Mozilla Foundation, Firefox is an open-source browser that is known for its privacy features and customization options.
3. Apple Safari:
Developed by Apple, Safari is the default browser on Mac and iOS devices and is known for its speed and integration with other Apple products.
4. Microsoft Edge:
Developed by Microsoft, Edge is the default browser on Windows 10 and is known for its integration with other Microsoft products and services.
5. Tor Browser:
Developed by The Tor Project, Tor Browser is a web browser that is designed for anonymous web browsing and is based on Mozilla Firefox.
Developed by Opera Software, Opera is a web browser that is known for its speed and built-in VPN feature.
Developed by Brave Software, Brave is a web browser that is focused on privacy and security and blocks third-party ads and trackers by default.
These are some of the most popular web browsers, there are other browsers available such as Vivaldi, Waterfox, and so on. The choice of a web browser depends on the user’s preference and requirements.

Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Learning
- School Programming
- Web Browsers
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

What is Safari

Safari is a web browser developed by the North American company Apple for its macOS (used by MAC computers) and iOS (used by iPhone, iPod and iPad) operating systems. The name Safari refers to the spirit of exploration that the company wanted to give to the browser.
Safari Origin
The project to launch its own web browser by Apple emerged in 2003, when at that time its computers still included as default the browser of the Microsoft company, Internet Explorer. In this way, in June of this same year the first beta of the browser was launched, which every two years was launching a new version. With the growth of the company, especially following the launch of the iPhone smartphone in 2007, the browser was becoming popular and is currently the fourth most used web browser in the world with a share of 4.74% only behind Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox and Google Chrome.
Related Terms
- Microsoft Edge

Digital Marketing, Analytics and Marketplaces Agency
- Digital Marketing
- Marketplaces
MADRID OFFICES
- Ferrocarril, 18. 28045 Madrid
- +34 91 060 64 28
- [email protected]
- Arimetrics © 2022
- Legal Notice
Privacy Overview
Home / SEO SEM glossary / Safari
What is Safari? – Definition
Safari is a web browser developed by Apple for devices running the OS X operating system. Safari is the default browser installed on iOS-based devices, such as iPhone, iPod or iPad, and Mac. It is based on the open source WebKit engine. For the first time, Safari was introduced in 2003 on desktop devices. Currently, there is no Windows version available – a version tailored for this operating software only ran from 2007 to 2012.
Features of Safari
This browser has been developed for many years, so currently it offers a wide range of great features. Its users especially appreciate the ability to synchronize with the cloud, launch the Private Browsing mode, and use the Download Manager. There is also a possibility to customize Safari and add more features by installing free extensions.
Popularity of Safari
The number of users of this browser worldwide is increasing year by year. According to Statcounter, in December 2020, Safari was the second most popular web browser in the world, covering 19.25% of the market share. Interestingly, in December 2020, OS X was the 4th most popular operating system (7.08% of market share worldwide)
Related definitions

Read related posts

How to Measure Your Website Loading Time? 7 Helpful Tools

Foreign Search Engines – Not So Popular Alternatives to Google

Mobile SEO. A Complete Guide for Mobile Devices SEO
Get a free quote.
- Copywriting
- Linkbuilding
Check our Privacy Policy
- By providing your e-mail and clicking "Start here!", you give your voluntary consent to receive periodic commercial and marketing information from Delante. Read Privacy Policy to learn how we process personal data and what rights you have.
SEO SEM Agency based in Europe
Aby zapewnić najlepsze doświadczenia, używamy technologii takich jak pliki cookie do przechowywania i/lub uzyskiwania dostępu do informacji o urządzeniu. Wyrażenie zgody na te technologie umożliwi nam przetwarzanie danych, takich jak zachowanie podczas przeglądania lub unikalne identyfikatory na tej stronie. Brak wyrażenia zgody lub jej wycofanie może niekorzystnie wpłynąć na niektóre cechy i funkcje.
To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
- Polski ( Polish )

What is a Web Browser? Types and Examples You Need to Know
By Tibor Moes / Updated: July 2023

What is a Web Browser?
It’s impossible to use the internet in the modern world without a web browser. This powerful tool takes you across the web and shows you images, text, videos, and any other content type.
Maybe you don’t know it yet, but you’re using a web browser right now to read this article! There are plenty of browsers out there and they all work using (more or less) the same technology that we will explain below.
- A web browser is a software application, acting as a user interface, that allows users to access, navigate, and interact with internet content through HTTP, often in the form of web pages.
- Core components of a web browser include the rendering engine to interpret and display HTML documents, JavaScript engine for dynamic content, and network components for data communication, providing an integral user experience.
- Browsers also provide critical features like bookmarking, privacy modes, extensions for added functionalities, and security measures like phishing and malware detection to ensure safe and efficient web browsing.
Don’t become a victim of cybercrime. Protect your devices with the best antivirus software and your privacy with the best VPN service .
A web browser can be defined as a computer program that the user relies on to access information or sites on the World Wide Web or similar networks.
So how does a web browser work?
Not all web browsers work the same way. Some of them may interpret different formats in different ways. This is bad news for the user, given that a website may look different to them depending on the browser they use. That’s why it’s important to create consistency between different browser applications. For this reason, there are certain web standards that are used.
Web browsers work by talking to a server and asking for particular pages users want to visit. The browser program will retrieve or fetch the code that’s often written in HyperText Markup Language (HTML) or similar languages.
Once it does that, the browser will interpret the code behind the script or language and show it as a web page the user wants to see.
Most of the time, this action requires user interaction in order for the browser to know which website or page to show. This means that you as a user have to use the address bar of the browser and enter the URL of the website you want to visit.
But what exactly is a URL and why is it important? Learn more below.
The Story of URLs
A web address of a website is provided in its URL form. The acronym “URL” stands for “Uniform Resource Locator,” and it’s the type of information that lets the browser know which site you want to visit.
For example, when you enter the following URL into the address bar of a browser: http://www.google.com , a browser will take you to the Google search engine.
What the browser did was study the URL in two ways.
First, it studied the “http://” section that refers to HyperText Transfer Protocol. This is the protocol used for requesting and transmitting files on the internet, and it can be found on most web pages. It defines how images, text, and other content are transmitted on the internet.
It’s important for this type of information to be transmitted consistently so anyone using a browser can access the information. A browser will know how to interpret the data located on the right of the forward slashes because it knows the HTTP protocol.
Next, the browser will examine the domain name, which is www.google.com in this example. The domain name lets the browser know the location of the server from which it will have to retrieve a page.
If you were to use a web browser ten or more years ago, you would have to type in the whole domain name http://www.google.com . But web browsers are smarter today and no longer require you to specify the protocol. You can now simply type google.com and be taken to the desired page.
You can often find additional information or parameters at the end of a page. For example, if you were to visit the Nike website, you can find parameters such as http://www.nike.com/women that share more information about a particular web page on one website. For example, the “women” parameter lets the browser know you’re asking to see a women’s section on Nike’s website.
Browsers let users open multiple links or URLs at the same time. This is possible thanks to tabs. A tab creates a dedicated space for a website inside the same browser window. This prevents the program from cluttering your screen with different windows. It’s meant to emulate an old-fashioned cabinet of file folders.
Bookmarks and History
Web browsers have a great functionality that lets users access websites they want to visit at a later date. Users can do so with the help of bookmarks that allow saving pages inside a browser.
There’s also an easy way to access a list of all your previously visited pages that can be found in the “History” section.
Introducing Cookies
If you ever visited a website on the web, you must have seen a cookie notice at the bottom of the page. Unfortunately, this isn’t a notice about the yummy cookies hidden on your kitchen shelf.
In the world of web browsers, cookies relate to information that websites save about their users. These files are saved locally on your computer so when you visit the site again, your browser can open the page faster. Also, the website will recognize that it’s you who wants to visit and may remember your login credentials.
There are also more advanced cookies that are made to remember detailed information about users . This can be the browsing pattern, personal interests, and more. This behavior is performed to provide a more customized experience, and it’s mostly used by businesses that promote their services.
You can also encounter third-party cookies that come from different websites you aren’t using. They can track your activity on another site and sell the information they get to companies. You can block this kind of behavior, but not all browsers will let you do that.
Now that we have covered the basics of what a browser is and its main features, let’s introduce some of the most popular browsers available today.
Web Browser Examples
There are dozens of web browsers to choose from today. Each example has its own nuance that makes some users prefer it over another.
The best programs out there are completely free. The options regarding interface, security, shortcuts, and other elements are different, so you can choose the one that works best for you.
Here’s an overview of the most popular browsers.
Google Chrome
Google Chrome is arguably the most popular browser today. It’s developed by Google, and it has the biggest web browser market share, with a whopping 65.87% as of June 2023. If you were to look for the best browsers on the internet, you’d find Chrome to be the winner in the Best Overall category.
This browser works with all operating systems , it’s fast and expandable, and allows cross-syncing between devices. This cross-platform browser is easy to use and has a dedicated feature for using less data. You can browse without saving the browsing history and use the incognito mode.
Some other notable features include an offline download manager, security alerts, and personalized recommendations.
Safari , or Apple Safari, has the second-biggest market share among web browsers with 18.61%, and it’s the default browser for Apple devices.
If you’re an Apple user, you’ll find the Safari browser to be powerful, efficient, and secure.
Safari is the first browser to introduce a reading mode to its users. This option will clear unnecessary elements from the page so you can focus on reading or watching a video without distractions.
The browser was also the first to introduce fingerprinting protection . This feature prevents web trackers from identifying you according to your system specifications, which is a very common issue found in most other browsers.
New versions of Safari also allow for added customization options and provide a very modern browsing experience. You can use the company’s Handoff feature and continue your browsing sessions between devices.
This browser only operates on Apple devices , which is its main downside for non-Apple users.
The Opera browser is great for collecting content. It works on all operating systems , and it’s completely free. Some of the best reasons to use Opera include its built-in proxy, excellent security, and great interface.
There’s a built-in ad blocker, as well as a VPN , so you can use the browser for a safer internet experience. This is especially important if you enter sensitive information on the web such as your phone number, address, crypto wallet information, and other personal or financial data.
Gamers will love the special browser version designed solely for gamers – Opera GX . The browser includes Twitch integration, Razer Chroma support, and other features most gamers appreciate.
Chrome and Opera use the same Chromium-based technology, so you can use the Chrome store to add different integrations and add-ons to Opera.
The Mozilla browser is one of the best applications for private browsing, as well as for power users . It’s one of the most flexible browsers out there and comes with cross-platform syncing. This means you can use the browser on your computer, mobile device, and tablet, and save your log-in information, passwords, or browsing history across devices.
This browser also has excellent privacy protection, and it’s endlessly customizable in terms of plug-ins, extensions, and theme support.
Some downsides include the app being a bit slower compared to the competitors. The program also uses more system memory than other browsers.
Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Edge is the cousin of a once extremely popular browser called Internet Explorer designed by Microsoft. Edge is now the default browser for Windows devices. The browser uses the same code for rendering pages as Chrome, called Chromium, which means you can download add-ons, extensions, and integrations using the Chrome Store.
Edge runs just as well on macOS devices, so you can try it out if you’re a Mac user. This browser performs great when it comes to thrifty memory, disk usage, and overall performance. The developers use a new Startup Boost technology to reduce the time for opening a browser and its sleeping tabs.
Smaller Players Worth Noting
In the overview above, we listed some of the biggest players in the web browser world. There are many smaller names that offer quality services.
Vivaldi is the best alternative browser when it comes to customization options . It works on Chromium, so it’s closely related to Google Chrome. The best part about the experience is that it lets users change even the smallest details about the program. The interface is similar to Opera, so the tab previews, start page, buttons, and other tools look very familiar.
Some of the browser’s unique features include an Image Properties view with histogram, clutter-free printing, screenshot options, and more.
Brave is a popular alternative web browser that strives to reshape the web economy from the ground up. The browser blocks web ads by default, and it introduces an innovative way for websites to monetize users’ attention. It rewards users for browsing by offering them their own company-made cryptocurrency. This makes Brave a popular option for users interested in the crypto world and tokens.
Like many other browsers on the list, this one is also based on Chromium, so you can find similarities with Google Chrome, Opera, and other browsers from the same family.
Tor Browser
Tor is a great browser for users concerned about privacy who are not interested in the world of ads. The software offers access to the dark web , which is the ad- and tracking-free world of the internet. Any traffic users make on Tor is encrypted in a company-specific way that makes it impossible to track.
The browser is based on Firefox, and it opens most websites just fine despite some privacy extensions and settings being locked.
A major downside of this browser is that the heavy encryption significantly slows down the speed of internet browsing.
Web Browsers Explained
Web browsers are powerful tools all internet users rely on for easy access to websites, web pages, images, text, and any other content. It’s important to understand how web browsers work to be able to get the most out of them, and this is exactly what this article aims to explain.
Now that you understand how browsers work, you can choose the best browser for your particular needs to make your daily internet experience better and more customized.
How to stay safe online:
- Practice Strong Password Hygiene : Use a unique and complex password for each account. A password manager can help generate and store them. In addition, enable two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever available.
- Invest in Your Safety : Buying the best antivirus for Windows 11 is key for your online security. A high-quality antivirus like Norton , McAfee , or Bitdefender will safeguard your PC from various online threats, including malware, ransomware, and spyware.
- Be Wary of Phishing Attempts : Be cautious when receiving suspicious communications that ask for personal information. Legitimate businesses will never ask for sensitive details via email or text. Before clicking on any links, ensure the sender's authenticity.
- Stay Informed. We cover a wide range of cybersecurity topics on our blog. And there are several credible sources offering threat reports and recommendations, such as NIST , CISA , FBI , ENISA , Symantec , Verizon , Cisco , Crowdstrike , and many more.
Happy surfing!
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are the most frequently asked questions.
Is Google a web browser or not?
Google is an example of a search engine, not a web browser. You can use Google on different web browsers to perform your internet search. Google Chrome, however, is a web browser of the same company.
How do I open a web browser?
Web browsers can be downloaded to your local computer or mobile device space and used from there. All you have to do is install the program and launch it whenever you need to use it.
What are the most popular web browsers?
The most popular web browsers include Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari and Microsoft Edge.

Author: Tibor Moes
Founder & Chief Editor at SoftwareLab
Tibor has tested 39 antivirus programs and 30 VPN services , and holds a Cybersecurity Graduate Certificate from Stanford University.
He uses Norton to protect his devices, CyberGhost for his privacy, and Dashlane for his passwords.
You can find him on LinkedIn or contact him here .
Antivirus Comparisons
Best Antivirus for Windows 11 Best Antivirus for Mac Best Antivirus for Android Best Antivirus for iOS
Antivirus Reviews
Norton 360 Deluxe Bitdefender Total Security TotalAV Antivirus McAfee Total Protection
Internet Browsers: A Simple Guide to How Browsers Work
What's an Internet Browser? Here's an Easy Overview
- Tips and Tricks
- Dream Vacations
- Win Electronics
- Home and Garden
- Win Vehicles
- Jewelry and Clothing
- Types of Contests
- Creative Contests
- Frugal Living
- Fine Arts & Crafts
- Card Games & Gambling
- Cars & Motorcycles
- Playing Music
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/LAbio-SandraG-71d952ecca9342619f0f66c0f4eff19c.jpeg)
- University of Maryland
An internet browser, also known as a web browser or simply a browser, is a software program that lets you view web pages on your computer. You can think of your browser as your gateway to the internet. If you want to enter online sweepstakes , for example, you must first open a giveaway's website in your internet browser.
The main purpose of an internet browser is to translate the code that computers use to create websites into the text, graphics, and other features of the web pages that we're used to seeing today.
Web browsers were first introduced in 1990, but they've evolved significantly since then.
The First Web Browser
The first web browser was called WorldWideWeb; later, it changed its name to Nexus. Created by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, it gave people a basic way to view web pages. However, it was a long way from the immersive online experience we have today.
Without graphical browsers, the internet as we know it today would not be possible. In the 90s, the internet was text-based, bland, and couldn't be used without some fairly significant technical knowledge. This limited the number of people who had the interest and the ability to use the internet.
In the early 90s, the audience was so small and so niche that most companies didn't have an online presence. Shopping giants like eBay and Amazon would never have had a chance of drawing a decent crowd.
That started to change with the introduction of Mosaic in 1992.
The Mosaic browser helped make the internet ubiquitous. The graphical interface made navigating the web easy to understand and the ability to display graphics on websites made web pages more interesting. Best of all, people no longer needed to be programmers to enjoy themselves online.
With more people spending more time on the internet, companies were quick to follow. E-commerce, online sweepstakes, social media, and many other things we take for granted today followed closely on the heels of the first graphical browsers.
Modern Internet Browsers
Internet browsers have developed into powerful tools that let you safely and quickly access your favorite websites.
Modern internet browsers have many helpful features. Tabbed browsing, for example, lets you open up many web pages in individual tabs, instead of needing a resource-intensive separate window for each page. This is very helpful if you want to enter sweepstakes faster .
Modern browsers offer security features, embedded video, nigh-instant loading times, and many other things that make the net such a fun place to spend time.
Which Internet Browsers Are Available Today?
Most browsers are available for free download. The six most popular internet browsers today include:
- Mozilla Firefox ( Download Firefox )
- Google Chrome ( Download Chrome )
- Microsoft Edge (formerly Internet Explorer)
- Apple Safari (Download Safari)
- Opera ( Download Opera )
Each of these internet browsers has advantages and disadvantages. Read their websites, then try out the ones that appeal to you the most.
Due to the way they are coded, some websites display better in one internet browser or another. For this reason, it's a good idea to have at least two browsers available on your computer, especially if you want to enter sweepstakes. If an entry form doesn't display properly in your primary browser, it might work flawlessly on your secondary internet browser.
Many internet browsers support plug-ins, which are helper programs that you can download to customize your browsing experience. Plug-ins can help you fill out forms automatically , check your grammar and spelling, mute unwanted sounds in your browser , send you reminders, and much more.
Plug-ins can help you work or play online, but not every browser allows them. Firefox and Chrome each allow plug-ins, for example, but even then, some plug-ins are only available for specific systems.
The best way to find out which browser is right for you is to download a couple and play around with them. Which extra features are important to you? Do websites load quickly and reliably? Is your browser using too many resources and slowing down other programs you're using?
How Internet Browsers Work:
Here's a very quick overview of how browsers work:
- You type a website's URL into your browser's address bar; "http://www.dotdash.com" is an example of a URL.
- The browser locates and requests that page's information from a web server.
- The browser receives a file written in computer code, like HTML or Javascript, which includes instructions about how to display the information on that page.
- The browser interprets that file and displays the page for you to read and interact with. And it does all of this in just a few seconds, usually.
If you want a more detailed technical breakdown of how browsers work, check out Behind the Scenes of Modern Web Browsers by Tali Garsiel and Paul Irish on HTML5Rocks.com.
The important thing to know is that different browsers have slightly different ways of working so that if you are having trouble getting pages to display or sweepstakes to load on one browser, it makes sense to try another. Install two or three of your favorite browsers and switch between them if you're having trouble seeing a website properly.
- A Simple Guide to Understanding and Using URLs
- How to Mute Sound in Your Internet Browser
- What Is a Search Engine?
- Enter Online Sweepstakes Like a Pro: How to Get Started
- Request a Free Delia's Catalog
- 6 Places to Find Free Printable Graph Paper
- How to Request a Free Baker Creek Heirloom Seeds Catalog
- How to Request a Free Collections Etc. Catalog
- Problems Printing Online Coupons?
- 9 Top Places to Find Free Wedding Invitation Templates
- How to Delete & Clear Autofill Suggestions in Your Browser
- The Mac-Centric Tools More and More eBay Sellers Use
- The Best Form-Filling Programs for Entering Sweepstakes
- Online-Sweepstakes.com: What It Was, and What Happened to It
- Faster Sweepstakes Entry: Enter Sweepstakes in Half the Time
- Places to Learn JavaScript Online
- Best SEO Tools
- Social Media Scheduling Tools
- Social Listening Tools
- Website Analytics Tools
- Rank Tracking Software
- Hashtag Generator Tools
- Paraphrasing Tools
- Reputation Management Software
- Email Marketing Software
- Free Email Marketing Services
- Email Tracking Software
- Email Newsletter Software
- Mass Email Services
- Email Verifier Tools
- Email Signature Generators
- Email Marketing Services
- Mailchimp Pricing
- ActiveCampaign Pricing
- Sendinblue Pricing
- GetResponse Pricing
- ConvertKit Pricing
- Constant Contact Pricing
- MailerLite Pricing
- Klaviyo Pricing
- What is Advertising?
- What is Affiliate Marketing?
- What is Omnichannel Marketing?
- What is Marketing Mix?
- What is Service Marketing?
- Important Marketing KPIs
- What is Integrated Marketing?
- Types of Market Segmentation
- Beginner’s Guide to SEO
- How to Increase Domain Authority
- Beginner’s Guide to Email Marketing
- Guide to Facebook Marketing
- Pricing Strategies Guide
- How to Define Target Audience
- How to Do Market Research
8 Different Types of Web Browsers (and Their Purposes)
Web browsers allow you to open websites to get information, order food and check your messages. In a nutshell, web browsing has become an integral part of our daily life, and web browsers make it possible.
In this article, we are going to discuss the most popular web browsers and the purpose they serve, so you can choose one that suits you best.
But before we dive into the features and functions of web browsers, let’s understand what web browsers are, and how they work.
What is a Web Browser?
Back in History: The first web browser, developed in 1990, was named WorldWideWeb, and it had very basic features for web surfing compared to modern browsers.
A web browser is a software application that fetches and interprets the code written in HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), CSS, and Javascript to display a webpage that you request. Some web browser examples are Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Safari.
Web browsers let users locate, view, and use websites. Not to be confused with search engines that rank websites and are accessible via web browsers.
For example, Google is a search engine that has a database of websites that it maintains and ranks. In contrast, Google Chrome is a web browser that uses search engines such as Google to find information, which it displays to the user after interpreting the code.
How Do Web Browsers Work?
When a user types a URL into the address bar and clicks on the link to access a particular website, the browser sends a request to the web servers of the website web host.
The web server responds to the request by sending the requested data back to the web browser. The requested data is sent in computer code . The code contains HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and any other files required to display the requested web page.
The web browser renders the page by applying CSS and Javascript rules to display the web page to the user. It renders the entire web page, including text, images, animations, and other media files embedded in HTML.
A web browser is one of the most important applications on your computer, tablet, or phone. It displays websites and web pages on your device. But displaying a website is not the only function of a web browser.
Other than displaying web pages, web browsers can also execute scripts, run plug-ins, and interact with other web technologies, such as cookies and cache for web storage. Most web browsers offer features like bookmarks, history, and tabbed browsing. Different types of web browsers allow users to manage their browsing experience and access website pages later quickly (pocket).
Different Types of Web Browsers
Here is a breakdown of the different types of web browsers that you can choose from:
1. Google Chrome
Google Chrome, launched in 2008, has become the most popular browser mainly because of its fast speed. It can load several pages instantaneously with just a single click. The web browser is also constantly updated with the latest security features to ensure safe web browsing. It is the default web browser for all google devices.
It is also compatible with other devices, operating systems, and web technologies. Google’s streamlined design focuses on a minimalistic user interface that is clutter-free. You can also customize your browsing experience with extensions. Its incognito mode will not save the browsing history and site cookies.
Key Features
Google Chrome is the only browser well-known for its fast-loading speed and stability. Even with multiple tabs running and extensions enabled, Chrome is designed to prevent crashes.
Google pays millions of dollars to hackers every year to find vulnerabilities in its system and fix them, making Chrome the most secure browser on the internet. It protects users from websites that steal passwords and infect computers with malware.
Clean User Interface
Google Chrome has an easy-to-use and intuitive interface that allows people of all ages to find what they need on Chrome without much effort. Its Omnibox combines a search bar and web address bar and works like a search engine. The users can type in math equations and unit conversion queries to find answers with just one click.
Google Chrome has the biggest library of extensions, which makes the web browser highly customizable.
Google Services Integration
A list of Google services can be accessed from the Chrome browser, such as Google Meet, Google Classroom, and Google Translate, that make working and studying on Chrome seamless.
Google Chrome can be synced on all your devices so you can access its browsing data and preferences everywhere, such as a bookmark that can be checked on your phone.
Developer Tools
Google Chrome also includes a suite of developer tools that developers can use to optimize or debug their websites.
Pros and Cons
Final verdict.
Google Chrome is the right browser for you if you want to switch to fast web browsing and better security. If you want to always have your information synchronized on your phone, tablet, laptop, or any other device, all you have to do is simply turn on the sync feature on Google Chrome.
Apple Safari, or simply Safari, is a popular browser invented by Apple and is therefore preinstalled and set as the default web browser on all Apple iOS devices.
Safari has cross-site tracking prevention, which protects you from third-party web trackers when you surf the web. It is a free browser for all iOS devices, and you can sync and access your browsing history on any of your Apple devices.

Intelligent Tracking Prevention
This Safari feature blocks third-party trackers from following you across the web for private browsing.
Reader View
To make reading easier and uninterrupted, the web browser has a reader view that blocks ads and popups. This makes Safari one of the most popular browsers for reading.
iCloud Keychain
Safari's iCloud Keychain feature lets users store passwords and payment information across all Mac OS and iOS devices. This makes online payments and ordering quick and convenient.
Picture-in-Picture
With the Picture-in-Picture feature, you can watch videos in a floating window and browse the web simultaneously.
With the AirPlay feature, Apple users can stream videos and audio from their Safari browser opened on any of their devices to an Apple TV or AirPlay-compatible speaker.
Safari browser also has its own developer tools to debug websites.
Energy Efficient
It does not drain your battery like most popular browsers.
Overall, Apple Safari offers a few features that make it a great browser for users. But it lacks openness and is suitable for Apple Users.
It is known for being one of the most popular browsers for security, as it protects your privacy and supports a wide range of extensions that make web browsing manageable.
3. Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Edge is an open-source web browser built by software giant Microsoft in 2015. It comes as a default browser on Windows 10. It is also available on macOS, iOS, and Android. Microsoft Edge has replaced Internet Explorer, its older and slower ancestor.
This web browser is designed to be compatible with all web standards and is capable of rendering modern websites and applications. Unlike its predecessor, Internet Explorer, it is faster and more secure.
Cortana Integration
Microsoft's virtual assistant, Cortana, is integrated into Edge and can provide users with quick access to information and assistance.
Users can annotate web pages within the browser window with digital inks, highlights, and text notes using Edge's Web Note feature.
Collections
Edge's Collections feature allows users to organize and save web content into easily shareable collections.
Built-in PDF Reader
It can directly open PDFs from the web and your PC in a new tab.
Reading View
Edge has a reading mode that strips away ads and other distractions, making articles and other content easier to read.
Microsoft Edge has built-in security features that protect you from online phishing and malware.
Microsoft Edge is the right browser for you if you like to read web pages without distractions, view PDFs, and doodle on web pages. It is the new and improved version of Internet Explorer that offers immaculate security and is relatively faster than other browsers.
4. Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, launched in 2004 by Mozilla Foundation, is a web browser well-known for its security and performance. Its cross-platform compatibility and support for web standards make it a popular choice among users and web developers alike.
Its Gecko layout engine seamlessly renders websites and implements the most modern and current web standards. Mozilla Firefox is available on Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS.
It is designed to be fast and efficient, with a streamlined interface and optimized performance.
Mozilla Firefox allows you to use multiple applications on your PC without draining much of your device’s battery.
Web Standards Support
Firefox is known for its support of web standards, making it a reliable browser for accessing modern websites and applications.
Smart Search Suggestion
Mozilla Firefox provides users with search suggestions based on their browsing history and search queries, making it easier to find what they are looking for.
Its readers view blocks ads so you can read without any distractions.
Mozilla Firefox is a good web browser for users and developers who are looking for a web browser that is not resource hungry. Also, Mozilla Firefox has better performance than Chrome as it uses less RAM.
Opera is a web browser developed by Opera Software and is one of the best battery-saving browsers. It has a customizable interface that allows you to personalize your browsing experience.
Opera browser is on the list of popular web browsers because of its exceptional features, such as integration for messaging apps such as Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, and Telegram. And its speed dial allows you to quickly open your favorite or most-visited websites.
Built-in Ad Blocker
Opera comes with an ad blocker, so users can load websites quickly and without ads.
Personalized News Feed
Opera has a personalized news feed feature that displays news stories based on your interests.
Battery Saver
Opera has a battery saver feature that can extend your laptop or mobile device's battery life by reducing the amount of power used by the browser.
You can turn on the turbo mode for faster browsing even on a poor internet connection.
Opera’s ad blocker and messaging app integrations make it a great choice for users who like to socialize. Its built-in news feed lets you know what is happening in the world.
If you often face network problems, you should switch to Opera browser to benefit from its Turbo mode.
6. Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer, also known as Microsoft Internet Explorer, was a web browser developed by Microsoft and launched on the World Wide Web in 1995. Since then, Microsoft has rolled out 11 versions of Internet Explorer.
Support for Internet Explorer 11 ended on June 15, 2022. It has now been replaced with Microsoft Edge.
Some problems that led to the demise of Internet Explorer include:
- Slow browsing
- Lack of active updates
- Limited Customization
- Lack of essential browser features
Brave is a relatively new web browser that is open-source. The Chromium-based web browser was launched by Brave Software, Inc. in 2016. Brave offers an exceptionally secure and efficient web browsing experience. It is light on the system resources, and even with multiple pages open, it consumes little RAM, which ultimately offers fast and smooth browsing.
Brave blocks trackers and ads by default, which helps protect your privacy and security while browsing the web.
Brave is known to be one of the fastest web browsers available on the World Wide Web, thanks to its lightweight design and efficient use of resources.
Brave is designed to protect your privacy with features like private browsing, fingerprint protection, and script & tracker blocking.
Rewards Program
Brave web browser has a rewards program that allows users to earn cryptocurrency in exchange for viewing ads.
The Brave browser works for you if you are tired of malicious websites infecting your PC. Brave provides an incredibly secure and efficient browsing experience. It is also very fast and efficient, just like other more popular web browsers.
Launched in 2008 by the Tor Project, the Tor browser lets users access restricted websites and the dark web.
It defends you against traffic analysis through multi-layered encryption so that you can browse freely. Tor makes it very hard for websites to trace back your data and location.
The primary advantage of the Tor Browser is that it provides anonymity to users. It uses a complex system of encryption and routing to conceal users' IP addresses and make their online activities untraceable.
Privacy & Security
The Tor Browser also provides security to users by encrypting their data and protecting them from hackers and surveillance. It is especially useful for people who use public Wi-Fi networks or access the internet from countries with poor internet privacy laws.
Access Blocked Content
Tor allows users to access different websites that may be blocked or restricted in their country. This can be useful for people living in countries with censorship or those who want to access content that may be restricted in their region.
Tor Browser is one of the best browsers for users who want anonymity and security, but it can be slow and may not be able to handle all types of websites.
Which Browser is Right For Me?
You can choose your browser based on features that will make web browsing manageable for you.
Explore Further
- Best Free Auto Clicker Tools for PC
- Types of Malware Attacks
- 11 Best VPN Services
- 7 Best VPN Services with Free Trial
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
Web Browser
A web browser, or simply "browser," is an application used to access and view websites . Common web browsers include Microsoft Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Apple Safari.
The primary function of a web browser is to render HTML , the code used to design or "mark up" webpages . Each time a browser loads a web page, it processes the HTML, which may include text, links , and references to images and other items, such as cascading style sheets and JavaScript functions. The browser processes these items, then renders them in the browser window.
Early web browsers, such as Mosaic and Netscape Navigator, were simple applications that rendered HTML, processed form input, and supported bookmarks . As websites have evolved, so have web browser requirements. Today's browsers are far more advanced, supporting multiple types of HTML (such as XHTML and HTML 5), dynamic JavaScript, and encryption used by secure websites.
The capabilities of modern web browsers allow web developers to create highly interactive websites. For example, Ajax enables a browser to dynamically update information on a webpage without the need to reload the page. Advances in CSS allow browsers to display responsive website layouts and a wide array of visual effects. Cookies allow browsers to remember your settings for specific websites.
While web browser technology has come a long way since Netscape, browser compatibility issues remain a problem. Since browsers use different rendering engines, websites may not appear the same across multiple browsers. In some cases, a website may work fine in one browser, but not function properly in another. Therefore, it is smart to install multiple browsers on your computer so you can use an alternate browser if necessary.
Test Your Knowledge
Which of the following is used to verify the integrity of a file or disk image?
Tech Factor
Related terms.
- Application
The Tech Terms Computer Dictionary
The definition of Web Browser on this page is an original definition written by the TechTerms.com team . If you would like to reference this page or cite this definition, please use the green citation links above.
The goal of TechTerms.com is to explain computer terminology in a way that is easy to understand. We strive for simplicity and accuracy with every definition we publish. If you have feedback about this definition or would like to suggest a new technical term, please contact us .
Sign up for the free TechTerms Newsletter
You can unsubscribe or change your frequency setting at any time using the links available in each email. Questions? Please contact us .
We just sent you an email to confirm your email address. Once you confirm your address, you will begin to receive the newsletter.
If you have any questions, please contact us .
Web Browser - What is a Web/Internet Browser?

Choose your web browser:
- Google Chrome
Mozilla Firefox
Microsoft edge.
- Internet Explorer
Google Chrome

Safari is the best way to experience the Internet on all your Apple devices. It brings robust customisation options, powerful privacy protections and optimises battery life — so you can browse how you like, when you like. And when it comes to speed, it’s the world’s fastest browser. 1
Performance
More with the battery. less with the loading..
With a blazing-fast JavaScript engine, Safari is the world’s fastest browser. 1 It’s developed to run specifically on Apple devices, so it’s geared to make the most out of your battery life and deliver long-lasting power.
Increased performance
We’re always working to make the fastest desktop browser on the planet even faster.
Improved power efficiency
Safari lets you do more online on a single charge.
Up to 4 hours more streaming videos compared with Chrome 3
Up to 17 hours of video streaming 3
Best-in-class browsing
Safari outperforms both Mac and PC browsers in benchmark after benchmark on the same Mac. 4
- JetStream /
- MotionMark /
- Speedometer /
JavaScript performance on advanced web applications. 4
Safari vs. other Mac browsers
Safari on macOS
Chrome on macOS
Edge on macOS
Firefox on macOS
Safari vs. Windows 11 browsers
Chrome on Windows 11
Edge on Windows 11
Firefox on Windows 11
Rendering performance of animated content. 4
Web application responsiveness. 4
4K video streaming
See your favourite shows and films in their best light. Safari supports in-browser 4K HDR video playback for YouTube, Netflix and Apple TV+. 5 And it runs efficiently for longer-lasting battery life.
Privacy is built in.
Online privacy isn’t just something you should hope for — it’s something you should expect. That’s why Safari comes with industry-leading privacy protection technology built in, including Intelligent Tracking Prevention that identifies trackers and helps prevent them from profiling or following you across the web. Upgrading to iCloud+ gives you even more privacy protections, including the ability to sign up for websites and services without having to share your personal email address.
Intelligent Tracking Prevention
Safari stops trackers in their tracks.
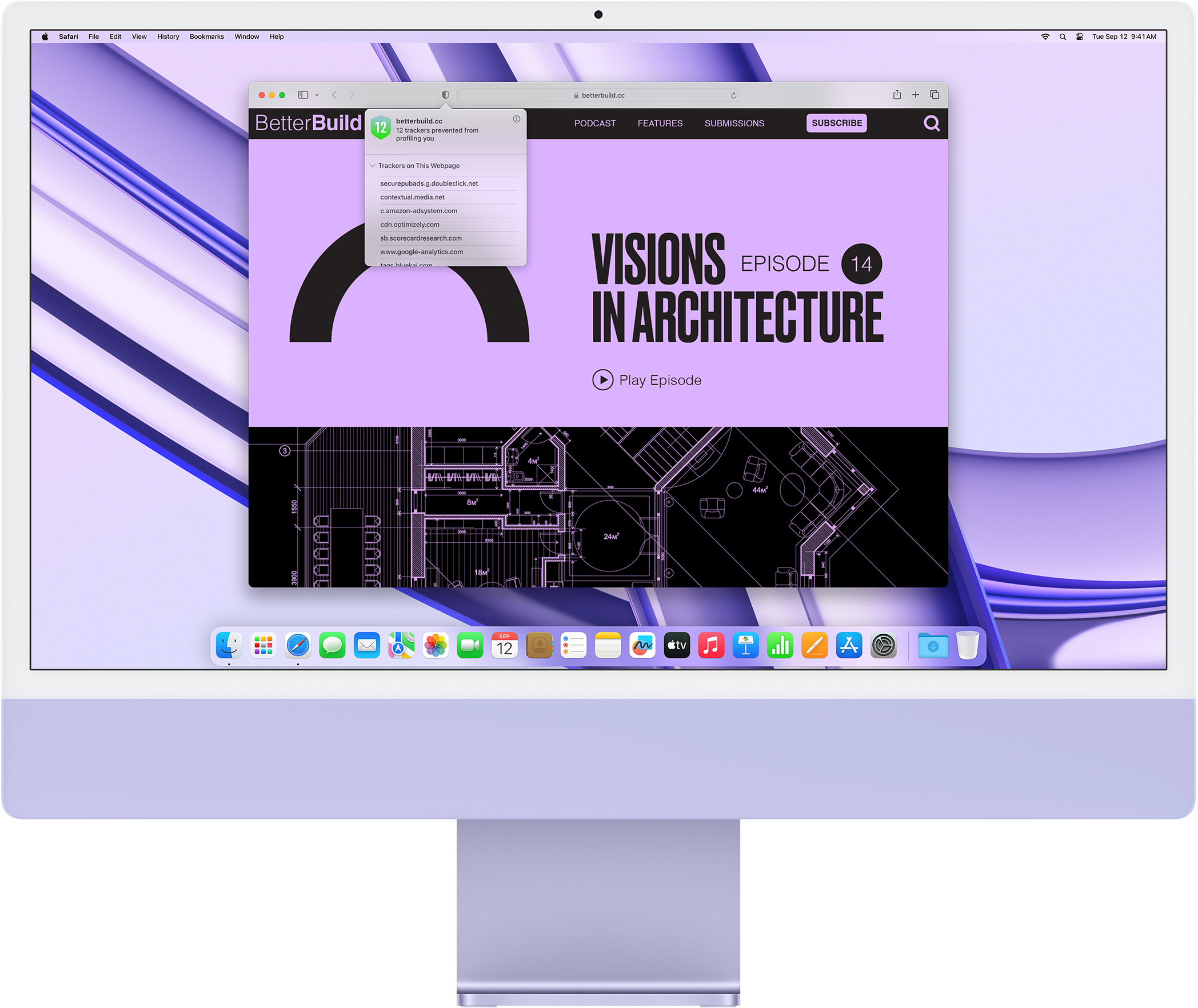
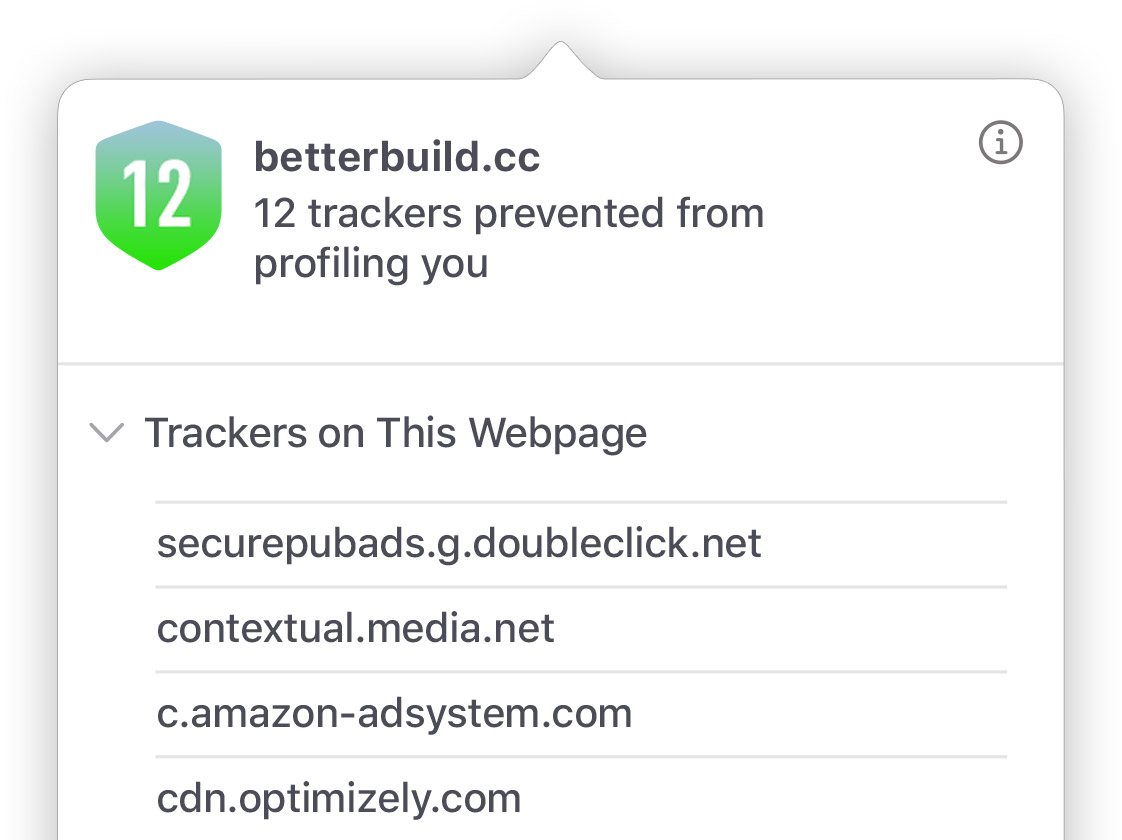
What you browse is no one’s business but your own. Safari has built‑in protections to help stop websites and data-collection companies from watching and profiling you based on your browsing activity. Intelligent Tracking Prevention uses on-device intelligence to help prevent cross-site tracking and stops known trackers from using your IP address — making it incredibly difficult to learn who you are and what you’re interested in.
Privacy Report
Safari makes it simple to see how your privacy is protected on all the websites you visit. Click Privacy Report in the Safari menu for a snapshot of cross-site trackers currently prevented from profiling you on the website you’re visiting. Or view a weekly Privacy Report to see how Safari protects you as you browse over time.
Customisation
Putting the you in url..
Safari is more customisable than ever. Organise your tabs into Tab Groups so it’s easy to go from one interest to the next. Set a custom background image and fine-tune your browser window with your favourite features — like Reading List, Favourites, iCloud Tabs and Siri Suggestions. And third-party extensions for iPhone, iPad and Mac let you do even more with Safari, so you can browse the way you want across all your devices.
Safari Profiles allow you to separate your history, extensions, Tab Groups, favourites, cookies and more. Quickly switch between profiles for topics you create, like Personal and Work.
Web apps let you save your favourite websites to the Dock on Mac and to the Home Screen on iPhone and iPad. A simplified toolbar and separate settings give you an app-like experience.
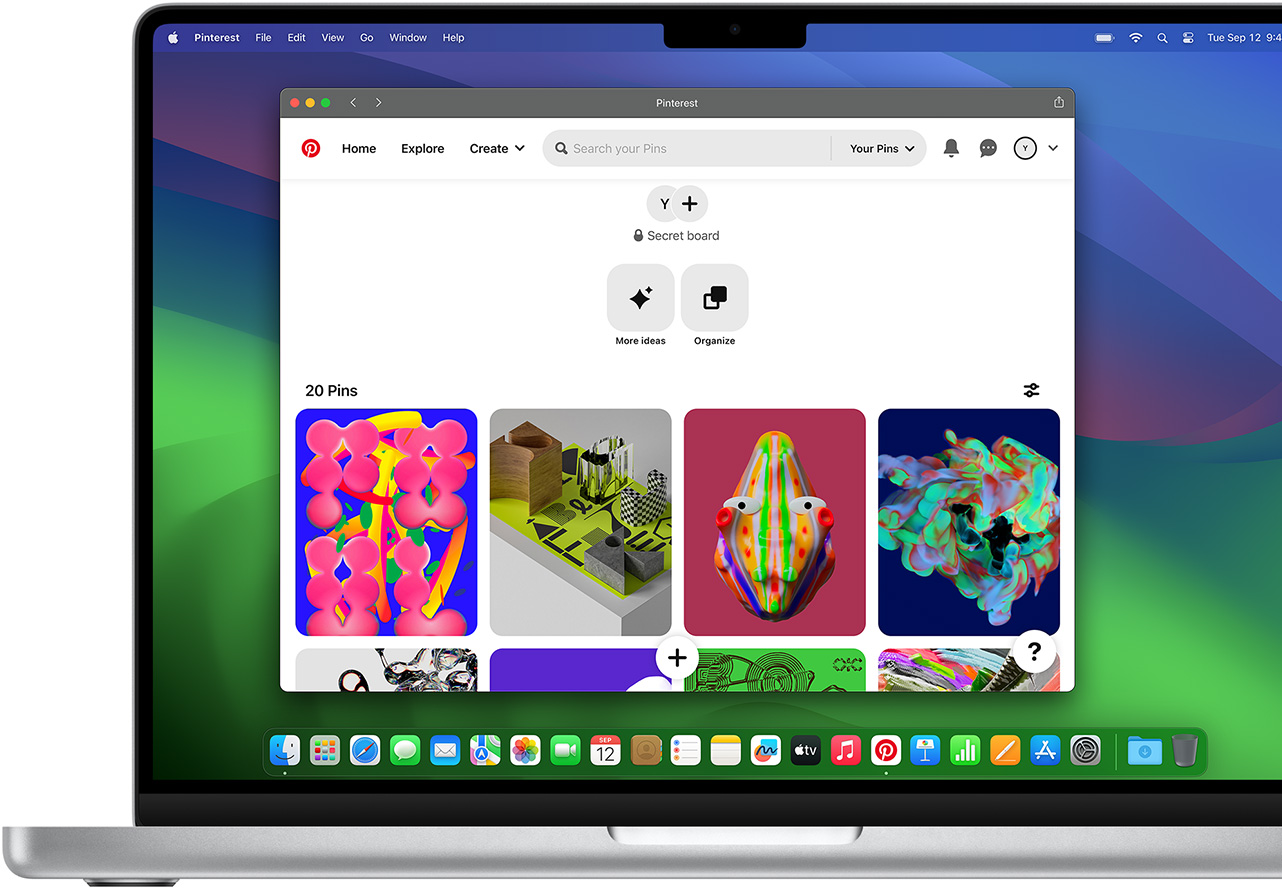
Safari Extensions add functionality to your browser to help you explore the web the way you want. Find and add your favourite extensions in the dedicated Safari category on the App Store.
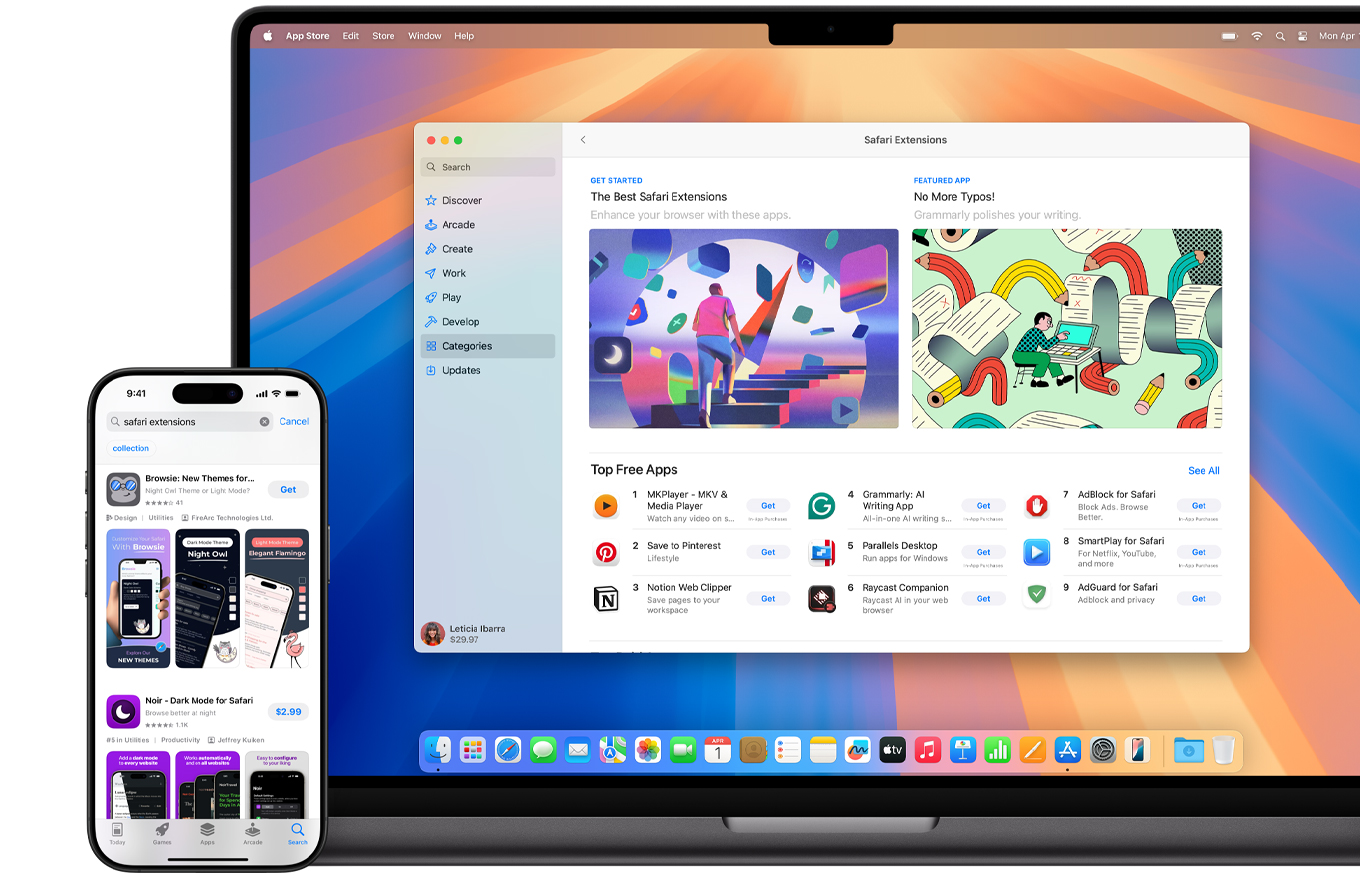
Save and organise your tabs in the way that works best for you. Name your Tab Groups, edit them and switch among them across devices. You can also share Tab Groups — making planning your next family trip or group project easier and more collaborative.
Smart Tools
Designed to help your work flow..
Built-in tools create a browsing experience that’s far more immersive, intuitive and immediate. Get detailed information about a subject in a photo with just a click, select text within any image, instantly translate an entire web page and quickly take notes wherever you are on a site — without having to switch apps.
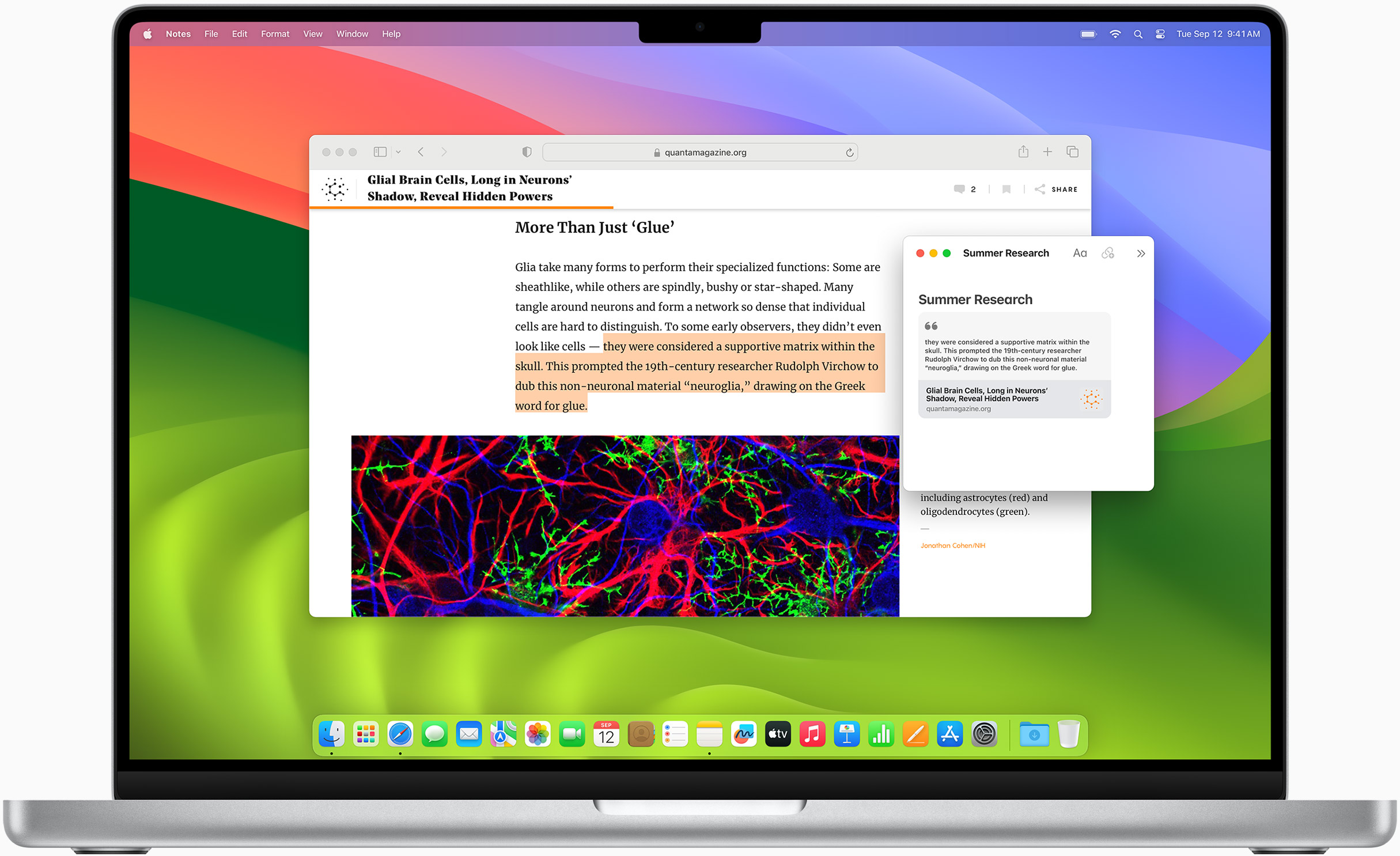
Notes is your go-to app to capture any thought. And with the Quick Note feature, you can instantly jot down ideas as you browse websites without having to leave Safari.
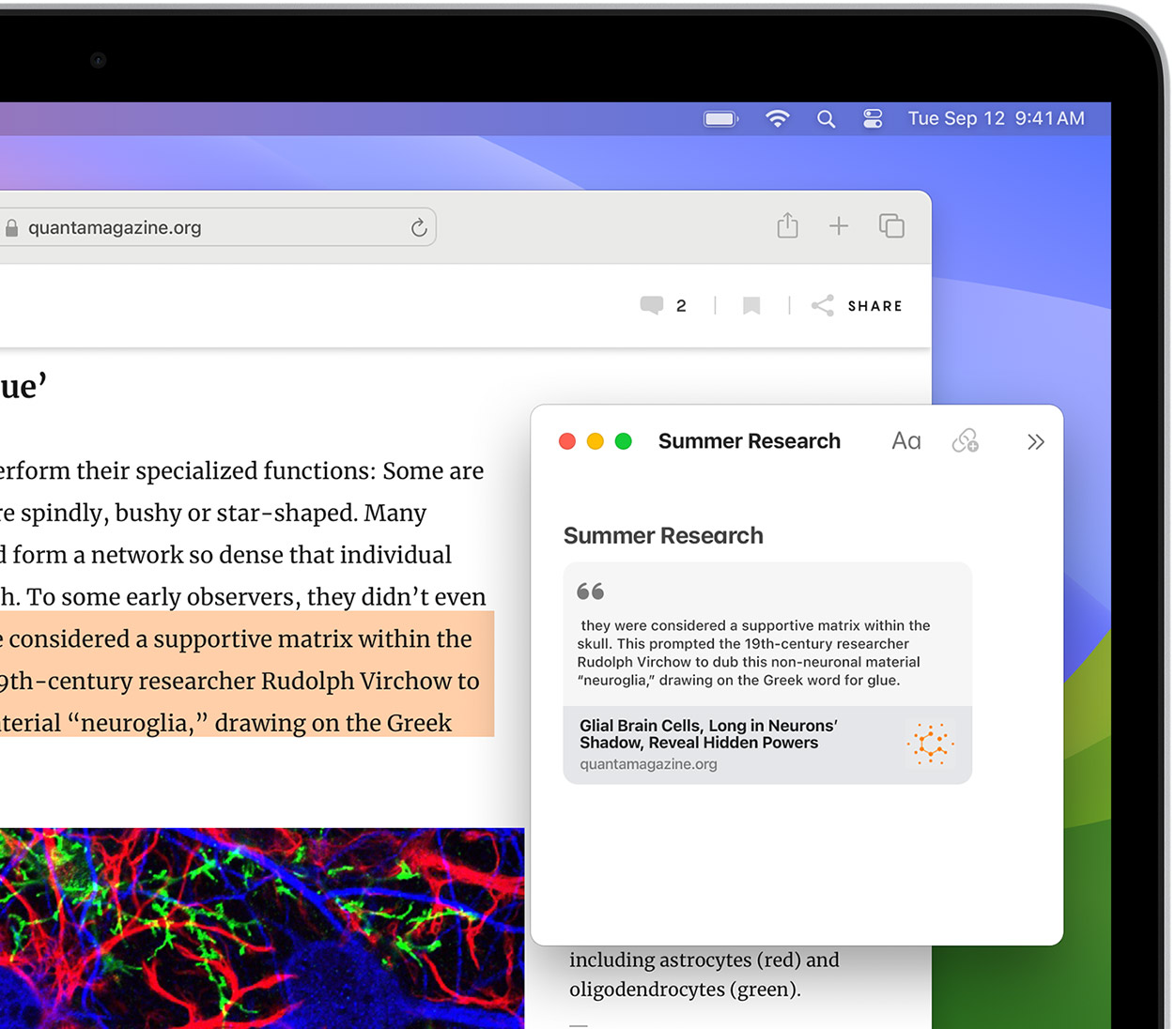
Translation
Translate entire web pages with a single click. You can also get translations for text in images and paused video without leaving Safari.
Interact with text in any image or paused video on the web using functions like copy and paste, translate and lookup. 6
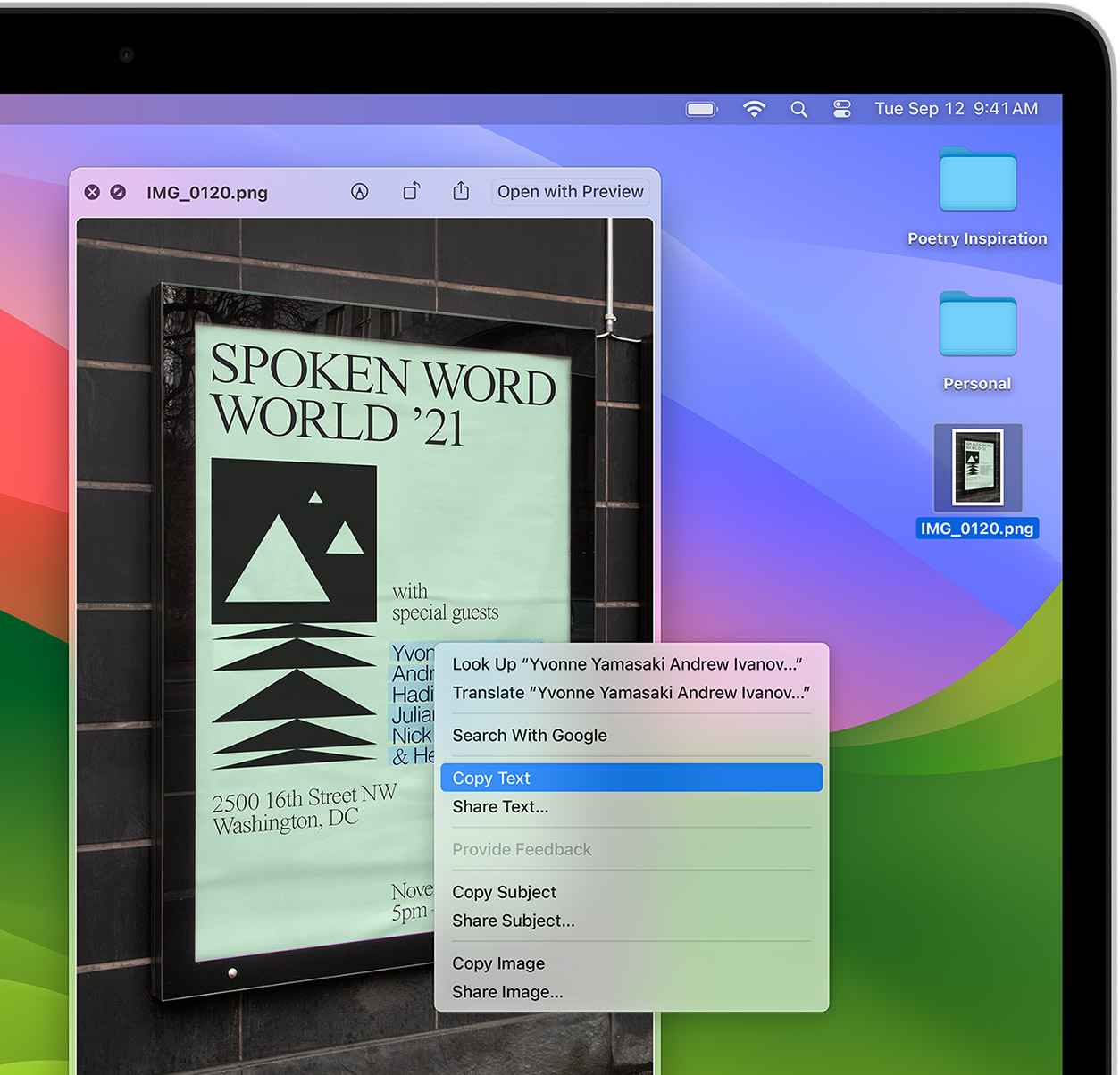
Visual Look Up
Quickly learn more about landmarks, works of art, breeds of dogs and more with only a photo or an image you find online. And easily lift the subject of an image from Safari, remove its background and paste it into Messages, Notes or other apps.

Surf safe and sound.
Strong security protections in Safari help keep you safe. Passkeys introduce a safer way to sign in. iCloud Keychain securely stores and autofills passkeys and passwords across all your devices. Safari also notifies you when it encounters suspicious websites and prevents them from loading. Because it loads each web page in a separate process, any harmful code is always confined to a single browser tab so it won’t crash the entire application or access your data. And Safari automatically upgrades sites from HTTP to the more secure HTTPS when available.
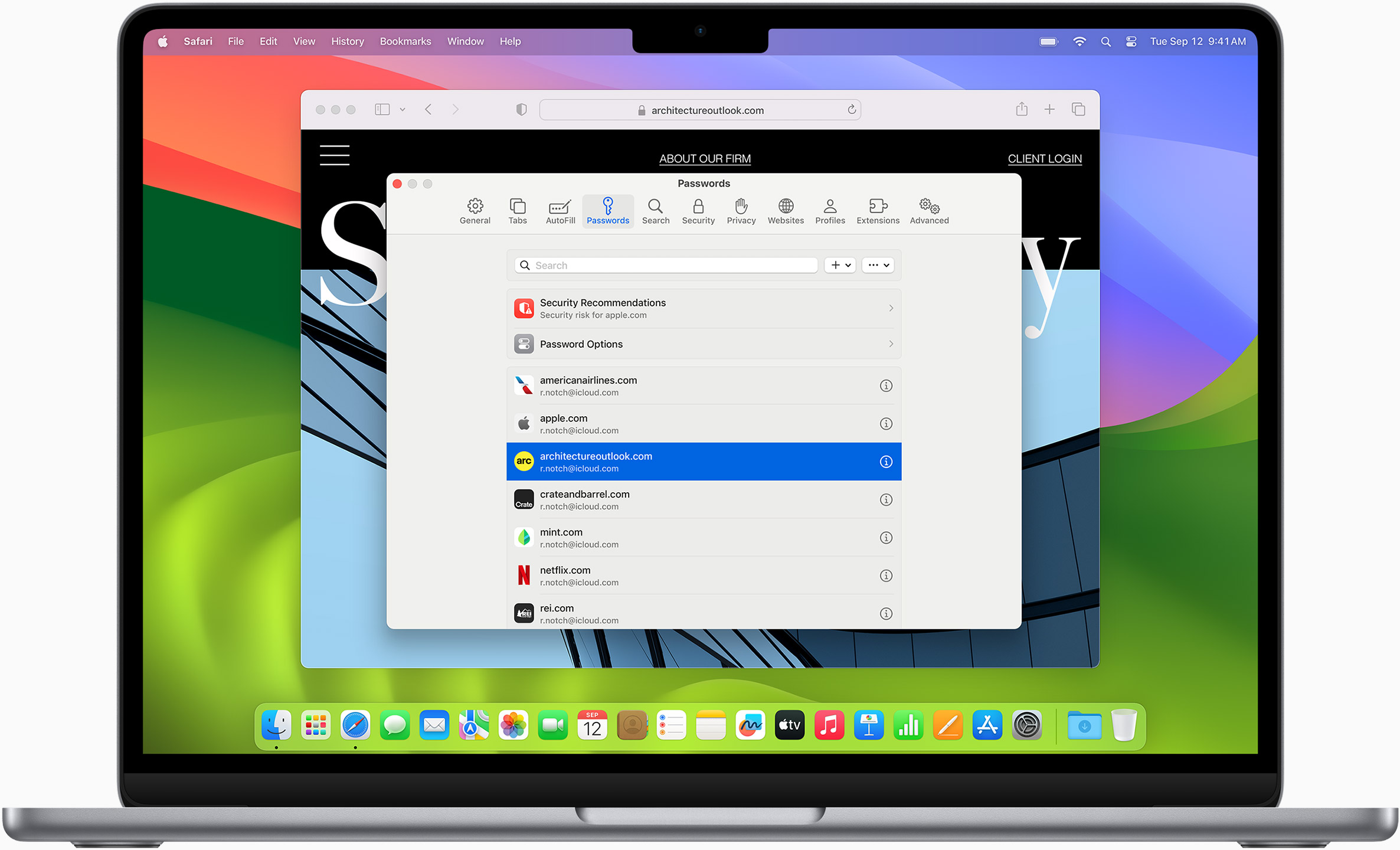
Passkeys introduce a more secure and easier way to sign in. No passwords required.
Passkeys are end-to-end encrypted and safe from phishing and data leaks, and they are stronger than all common two-factor authentication types. Thanks to iCloud Keychain, they work across all your Apple devices, and they even work on non-Apple devices.
Learn more about passkeys
Same Safari. Different device.
Safari works seamlessly and syncs your passwords, bookmarks, history, tabs and more across Mac, iPad, iPhone and Apple Watch. And when your Mac, iOS or iPadOS devices are near each other, they can automatically pass what you’re doing in Safari from one device to another using Handoff. You can even copy images, video or text from Safari on your iPhone or iPad, then paste into another app on your nearby Mac — or vice versa.
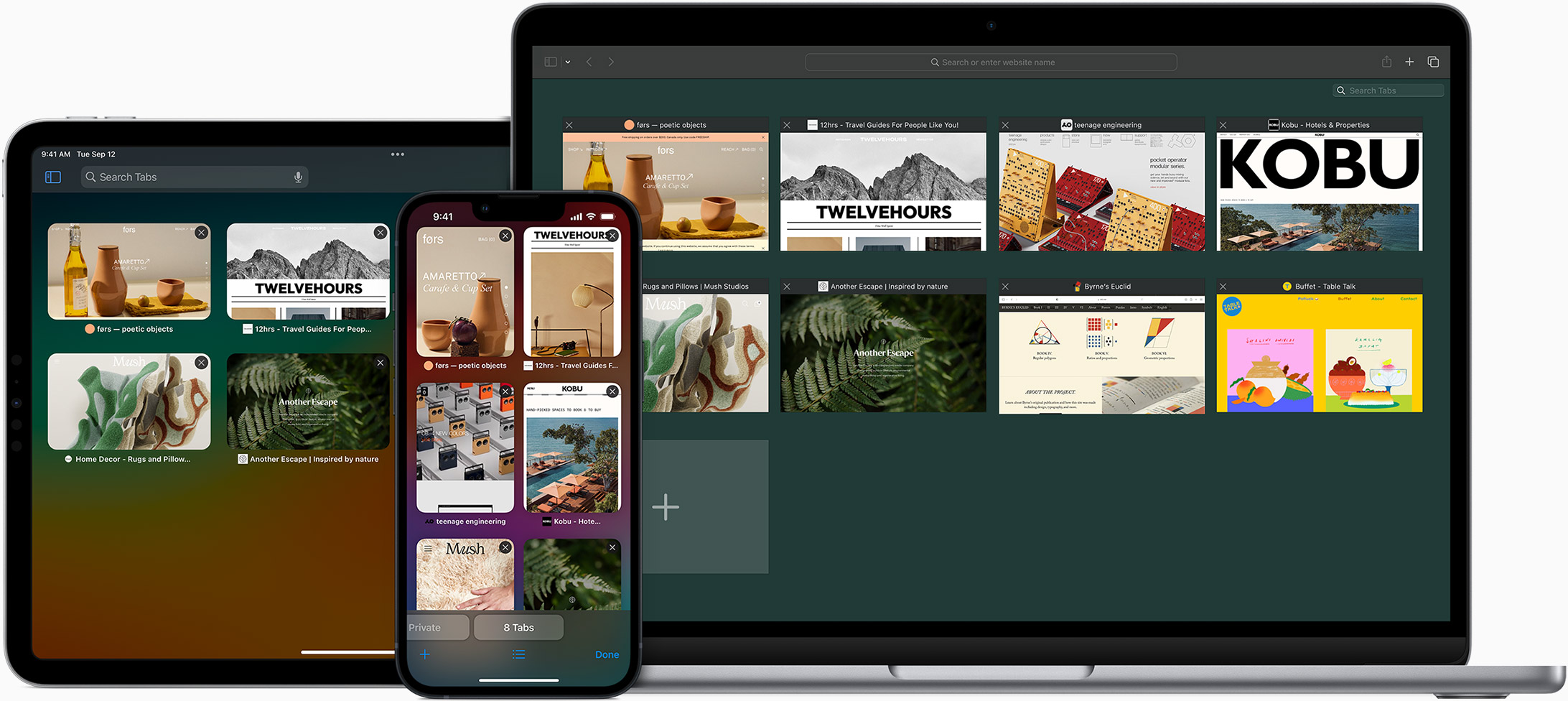
When you use Safari on multiple devices, your tabs carry over from one Apple device to another. So you can search, shop, work or browse on your iPhone, then switch to your iPad or Mac and pick up right where you left off.
Save web pages you want to read later by adding them to your Reading List. Then view them on any of your iCloud-connected devices — even if you’re not connected to the Internet.
iCloud Keychain securely stores your user names, passwords and credit card numbers, and keeps them up to date on your trusted devices. So you can easily sign in to your favourite websites — as well as apps on iOS and iPadOS — and quickly make online purchases.
Designed for developers.
Deep WebKit integration between Mac hardware and macOS allows Safari to deliver the fastest performance and the longest battery life of any browser on the platform, while supporting modern web standards for rich experiences in the browser. WebKit in macOS Sonoma includes optimisations that enable even richer browsing experiences, and give developers more control over styling and layout — allowing for more engaging content.
Make Safari your default browser
Customise your start page, view your browsing privacy report, monitor your saved passwords, view your tabs across all your devices, read the safari user guide, get safari support.
Firefox is no longer supported on Windows 8.1 and below.
Please download Firefox ESR (Extended Support Release) to use Firefox.
Download Firefox ESR 64-bit
Download Firefox ESR 32-bit
Firefox is no longer supported on macOS 10.14 and below.
What is a web browser?
A web browser takes you anywhere on the internet, letting you see text, images and video from anywhere in the world.
The web is a vast and powerful tool. Over the course of a few decades, the internet has changed the way we work, the way we play and the way we interact with one another. Depending on how it’s used, it bridges nations, drives commerce, nurtures relationships, drives the innovation engine of the future and is responsible for more memes than we know what to do with.
It’s important that everyone has access to the web, but it’s also vital that we all understand the tools we use to access it. We use web browsers like Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge and Apple Safari every day, but do we understand what they are and how they work? In a short period of time we’ve gone from being amazed by the ability to send an email to someone around the world, to a change in how we think of information. It’s not a question of how much you know anymore, but simply a question of what browser or app can get you to that information fastest.
In a short period of time, we’ve gone from being amazed by the ability to send an email to someone around the world, to a change in how we think about information.
How does a web browser work?
A web browser takes you anywhere on the internet. It retrieves information from other parts of the web and displays it on your desktop or mobile device. The information is transferred using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, which defines how text, images and video are transmitted on the web. This information needs to be shared and displayed in a consistent format so that people using any browser, anywhere in the world can see the information.
Sadly, not all browser makers choose to interpret the format in the same way. For users, this means that a website can look and function differently. Creating consistency between browsers, so that any user can enjoy the internet, regardless of the browser they choose, is called web standards .
When the web browser fetches data from an internet connected server, it uses a piece of software called a rendering engine to translate that data into text and images. This data is written in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) and web browsers read this code to create what we see, hear and experience on the internet.
Hyperlinks allow users to follow a path to other pages or sites on the web. Every webpage, image and video has its own unique Uniform Resource Locator (URL), which is also known as a web address. When a browser visits a server for data, the web address tells the browser where to look for each item that is described in the html, which then tells the browser where it goes on the web page.
Cookies (not the yummy kind)
Websites save information about you in files called cookies . They are saved on your computer for the next time you visit that site. Upon your return, the website code will read that file to see that it’s you. For example, when you go to a website, the page remembers your username and password – that’s made possible by a cookie.
There are also cookies that remember more detailed information about you. Perhaps your interests, your web browsing patterns, etc. This means that a site can provide you more targeted content – often in the form of ads. There are types of cookies, called third-party cookies, that come from sites you’re not even visiting at the time and can track you from site to site to gather information about you, which is sometimes sold to other companies. Sometimes you can block these kinds of cookies, though not all browsers allow you to.
When you go to a website and the page remembers your username and password – that’s made possible by a cookie.
Understanding privacy
Nearly all major browsers have a private browsing setting. These exist to hide the browsing history from other users on the same computer. Many people think that private browsing or incognito mode will hide both their identity and browsing history from internet service providers, governments and advertisers. They don’t. These settings just clear the history on your system, which is helpful if you’re dealing with sensitive personal information on a shared or public computer. Firefox goes beyond that.
Firefox helps you be more private online by letting you block trackers from following you around the web.
Making your web browser work for you
Most major web browsers let users modify their experience through extensions or add-ons. Extensions are bits of software that you can add to your browser to customize it or add functionality. Extensions can do all kinds of fun and practical things like enabling new features, foreign language dictionaries, or visual appearances and themes.
All browser makers develop their products to display images and video as quickly and smoothly as possible, making it easy for you to make the most of the web. They all work hard to make sure users have a browser that is fast, powerful and easy to use. Where they differ is why. It’s important to choose the right browser for you. Mozilla builds Firefox to ensure that users have control over their online lives and to ensure that the internet is a global, public resource, accessible to all.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to select language
- Sign up for free
- Português (do Brasil)
Web Components
Baseline widely available.
This feature is well established and works across many devices and browser versions. It’s been available across browsers since January 2020 .
- See full compatibility
- Report feedback
Web Components is a suite of different technologies allowing you to create reusable custom elements — with their functionality encapsulated away from the rest of your code — and utilize them in your web apps.
Concepts and usage
As developers, we all know that reusing code as much as possible is a good idea. This has traditionally not been so easy for custom markup structures — think of the complex HTML (and associated style and script) you've sometimes had to write to render custom UI controls, and how using them multiple times can turn your page into a mess if you are not careful.
Web Components aims to solve such problems — it consists of three main technologies, which can be used together to create versatile custom elements with encapsulated functionality that can be reused wherever you like without fear of code collisions.
A set of JavaScript APIs that allow you to define custom elements and their behavior, which can then be used as desired in your user interface.
A set of JavaScript APIs for attaching an encapsulated "shadow" DOM tree to an element — which is rendered separately from the main document DOM — and controlling associated functionality. In this way, you can keep an element's features private, so they can be scripted and styled without the fear of collision with other parts of the document.
The <template> and <slot> elements enable you to write markup templates that are not displayed in the rendered page. These can then be reused multiple times as the basis of a custom element's structure.
The basic approach for implementing a web component generally looks something like this:
- Create a class in which you specify your web component functionality, using the class syntax.
- Register your new custom element using the CustomElementRegistry.define() method, passing it the element name to be defined, the class or function in which its functionality is specified, and optionally, what element it inherits from.
- If required, attach a shadow DOM to the custom element using Element.attachShadow() method. Add child elements, event listeners, etc., to the shadow DOM using regular DOM methods.
- If required, define an HTML template using <template> and <slot> . Again use regular DOM methods to clone the template and attach it to your shadow DOM.
- Use your custom element wherever you like on your page, just like you would any regular HTML element.
A guide showing how to use the features of custom elements to create simple web components, as well as looking into lifecycle callbacks and some other more advanced features.
A guide that looks at shadow DOM fundamentals, showing how to attach a shadow DOM to an element, add to the shadow DOM tree, style it, and more.
A guide showing how to define a reusable HTML structure using <template> and <slot> elements, and then use that structure inside your web components.
Custom elements
Contains functionality related to custom elements, most notably the CustomElementRegistry.define() method used to register new custom elements so they can then be used in your document.
Returns a reference to the CustomElementRegistry object.
Special callback functions defined inside the custom element's class definition, which affect its behavior:
Invoked when the custom element is first connected to the document's DOM.
Invoked when the custom element is disconnected from the document's DOM.
Invoked when the custom element is moved to a new document.
Invoked when one of the custom element's attributes is added, removed, or changed.
The following extensions are defined:
Allows you to specify that a standard HTML element should behave like a registered custom built-in element.
Allows you to create an instance of a standard HTML element that behaves like a given registered custom built-in element.
Pseudo-classes relating specifically to custom elements:
Matches any element that is defined, including built in elements and custom elements defined with CustomElementRegistry.define() .
Selects the shadow host of the shadow DOM containing the CSS it is used inside.
Selects the shadow host of the shadow DOM containing the CSS it is used inside (so you can select a custom element from inside its shadow DOM) — but only if the selector given as the function's parameter matches the shadow host.
Selects the shadow host of the shadow DOM containing the CSS it is used inside (so you can select a custom element from inside its shadow DOM) — but only if the selector given as the function's parameter matches the shadow host's ancestor(s) in the place it sits inside the DOM hierarchy.
Matches custom elements that are in a specified custom state. More precisely, it matches anonymous custom elements where the specified state is present in the element's CustomStateSet .
Pseudo-elements relating specifically to custom elements:
Represents any element within a shadow tree that has a matching part attribute.
Represents the root node of a shadow DOM subtree.
Extensions to the Element interface related to shadow DOM:
- The Element.attachShadow() method attaches a shadow DOM tree to the specified element.
- The Element.shadowRoot property returns the shadow root attached to the specified element, or null if there is no shadow root attached.
Additions to the Node interface relevant to shadow DOM:
- The Node.getRootNode() method returns the context object's root, which optionally includes the shadow root if it is available.
- The Node.isConnected property returns a boolean indicating whether or not the Node is connected (directly or indirectly) to the context object, e.g. the Document object in the case of the normal DOM, or the ShadowRoot in the case of a shadow DOM.
Extensions to the Event interface related to shadow DOM:
Returns true if the event will propagate across the shadow DOM boundary into the standard DOM, otherwise false .
Returns the event's path (objects on which listeners will be invoked). This does not include nodes in shadow trees if the shadow root was created with ShadowRoot.mode closed.
HTML templates
Contains an HTML fragment that is not rendered when a containing document is initially loaded, but can be displayed at runtime using JavaScript, mainly used as the basis of custom element structures. The associated DOM interface is HTMLTemplateElement .
A placeholder inside a web component that you can fill with your own markup, which lets you create separate DOM trees and present them together. The associated DOM interface is HTMLSlotElement .
Assigns a slot in a shadow DOM shadow tree to an element.
A read-only attribute which returns a reference to the <slot> in which this element is inserted.
A read-only attribute which returns a reference to the <slot> in which this text node is inserted.
Extensions to the Element interface related to slots:
Returns the name of the shadow DOM slot attached to the element.
Pseudo-elements relating specifically to slots:
Matches any content that is inserted into a slot.
Fired on an HTMLSlotElement instance ( <slot> element) when the node(s) contained in that slot change.
We are building up a number of examples in our web-components-examples GitHub repo. More will be added as time goes on.
Specifications
Browser compatibility, html.elements.template.
BCD tables only load in the browser with JavaScript enabled. Enable JavaScript to view data.
api.ShadowRoot

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Safari is a web browser developed by Apple. It is built into Apple's operating systems, including macOS, iOS, iPadOS and visionOS, and uses Apple's open-source browser engine WebKit, which was derived from KHTML. Safari was introduced in Mac OS X Panther in January 2003. It has been included with the iPhone since the first generation iPhone in ...
Safari is the best way to experience the internet on all your Apple devices. It brings robust customization options, powerful privacy protections, and optimizes battery life — so you can browse how you like, when you like. And when it comes to speed, it's the world's fastest browser. 1. Learn how to make Safari your default browser.
Safari web browser is the default for the iPhone, iPad, and macOS, first released by Apple in 2003 and briefly offered on Windows from 2007 to 2012. The popularity of the Safari browser exploded with the iPhone and the iPad, and currently has about a 54% market share of mobile browser usage in the United States. In most ways, Safari is like any ...
Apple Safari Browser is a fast, secure, and privacy-focused web browser that is available on all Apple devices, including Mac, iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch. Safari implements high security using Intelligent Tracking Prevention and has a Private Browsing mode. It offers a variety of features and functions that make it a great choice for users ...
Apple Safari is a Web browser available for the Macintosh and Windows operating systems as well as the iPhone, iPod Touch and iPad. Safari has been designed based on the premise that the most useful browser is one that "gets out of your way and lets you simply enjoy the Web.". At the heart of Apple's Safari browser is the WebKit engine ...
Chrome maintains its longtime lead on this test with a score of 528. Edge, Opera, and other Chromium-based browsers hew closely to Chrome. Firefox and Safari bring up the rear, at 515 and 468 ...
Safari is a web browser developed by Apple and is built into Apple's operating systems, including macOS (for Mac computers), iPadOS (for iPad tablets), iOS (for iPhones), and visionOS (for augmented reality devices like the Apple Vision Pro).
Safari is a Web browser developed by Apple, Inc., and is the default browser of the operating systems used in its product lines such as OS X for the Mac and MacBook computers and iOS for the iPhone and iPad mobile devices. Safari was originally developed for OS X and was released as a public beta on January 7, 2003, with a major update in ...
Safari is a web browser developed by Apple Inc. which can be downloaded free of charge. It also comes with a Mac computer. It is based on the WebKit engine, which is a fork of KDE's KHTML engine. History. Apple Inc. replaced the previous default web browser, Internet Explorer, with their Safari many years ago.
A web browser helps us find information anywhere on the internet. It is installed on the client computer and requests information from the web server such a type of working model is called a client-server model. The browser receives information through HTTP protocol. In which transmission of data is defined.
Definition:. Safari is a web browser developed by the North American company Apple for its macOS(used by MAC computers) and iOS (used by iPhone, iPod and iPad) operating systems.The name Safari refers to the spirit of exploration that the company wanted to give to the browser. Safari Origin. The project to launch its own web browser by Apple emerged in 2003, when at that time its computers ...
What is Safari? - Definition. Safari is a web browser developed by Apple for devices running the OS X operating system. Safari is the default browser installed on iOS-based devices, such as iPhone, iPod or iPad, and Mac. It is based on the open source WebKit engine. For the first time, Safari was introduced in 2003 on desktop devices.
World Wide Web. Apple's Safari was released in 2003 as the default browser on Macintosh personal computers and later on iPhones (2007) and iPads (2010). Safari 2.0 (2005) was the first browser with a privacy mode, Private Browsing, in which the application would not save websites in its history,…. Other articles where Safari is discussed ...
Brave. Brave is a popular alternative web browser that strives to reshape the web economy from the ground up. The browser blocks web ads by default, and it introduces an innovative way for websites to monetize users' attention. It rewards users for browsing by offering them their own company-made cryptocurrency.
Safari's Tab Groups feature allows users to create separate windows for different tasks, making it easier to organize and access tabs across devices. Safari's deep integration with other Apple ...
The First Web Browser . The first web browser was called WorldWideWeb; later, it changed its name to Nexus. Created by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, it gave people a basic way to view web pages. However, it was a long way from the immersive online experience we have today.
A web browser is a software application that fetches and interprets the code written in HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), CSS, and Javascript to display a webpage that you request. Some web browser examples are Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Safari. Web browsers let users locate, view, and use websites.
Web Browser: A web browser, or simply "browser," is an application used to access and view websites . Common web browsers include Microsoft Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Apple Safari.
A web browser, or browser for short, is a computer software application that enables a person to locate, retrieve, and display content such as webpages, images, video, and other files on the World Wide Web. Browsers work because every web page, image, and video on the web has its own unique Uniform Resource Locator (URL), allowing the browser ...
A web browser displaying a web pageA web browser is an application for accessing websites.When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones.In 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people have used a ...
A web browser is a software that enables users to access and view content on the World Wide Web. Its primary function is to locate and retrieve web pages, images, videos, documents, and other files from servers and display them on the user's device. For instance, imagine you want to visit a website.
Definition of a "web browser" and links to support websites for further information and help. "A web browser, or simply 'browser,' is an application used to access and view websites. Common web browsers include Microsoft Edge, Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Apple Safari. The primary function of a web browser is to render ...
Safari is the best way to experience the Internet on all your Apple devices. It brings robust customisation options, powerful privacy protections and optimises battery life — so you can browse how you like, when you like. And when it comes to speed, it's the world's fastest browser. 1. Learn how to make Safari your default browser.
A web browser takes you anywhere on the internet. It retrieves information from other parts of the web and displays it on your desktop or mobile device. The information is transferred using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, which defines how text, images and video are transmitted on the web. This information needs to be shared and displayed in a ...
Web Components is a suite of different technologies allowing you to create reusable custom elements — with their functionality encapsulated away from the rest of your code — and utilize them in your web apps. ... Developing extensions for web browsers. Web Technology. Web technology reference for developers ... A set of JavaScript APIs that ...