What travel restrictions is the EU imposing on Russians?
The bloc has made it harder and costlier for Russian nationals to enter, but members are divided on an outright travel ban.
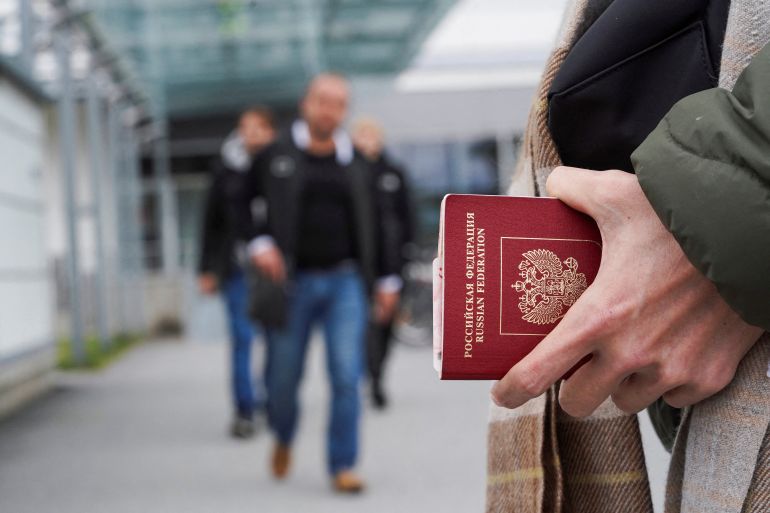

Before the Ukraine war began, the European Union was a popular port of call for Russians.
Under the terms of a 2007 visa agreement brokered when ties were significantly warmer, they enjoyed preferential access to the bloc and could visit easily for tourism or business.

Keep reading
Should europe shelter russians fleeing mobilisation, finland to bar russians after putin’s mobilisation order, latvia says it will not welcome russians fleeing mobilisation, is the war in ukraine entering a new phase.
But since February 24, when Russia launched its invasion, border controls tightened as the Kremlin’s relations with Western nations sank to post-Cold War lows.
Within days, the EU banned flights to and from Russia.
As the war dragged on, the bloc went further.
In early September, it suspended the 2007 visa deal.
The cost of an individual visa rose from 35 euros ($34) to 80 euros ($77), and Russians would now be made to provide additional documents and face longer processing times.
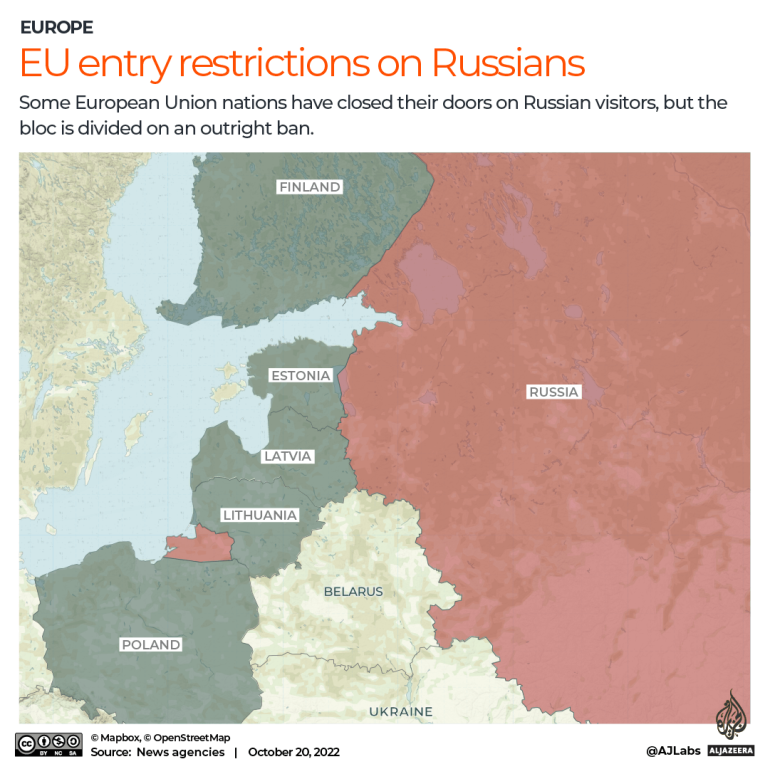
On September 19, the Baltic States and Poland closed their doors to Russian tourists, and condemned Finland for not joining them. Days earlier, their governments had released a statement citing security concerns.
“There are persons coming with the aim of undermining the security of our countries, insofar as three-fourths of Russian citizens support Russia’s war of aggression in Ukraine,” it said.
On September 21, Russian President Vladimir Putin announced a partial mobilisation, a move which sent thousands fearing the draft rushing to the borders to escape.
Most headed to Georgia and Kazakhstan, but some travelled towards Finland.
On September 30, Finland also banned Russian tourists, closing off the last direct route into the bloc.
The moves do not amount to an outright ban, but reflect the depth of deterioration in EU-Russia relations.
They also highlight divisions within the bloc – while those near Russia have taken action, others such as Germany and France say blanket restrictions feed into Moscow’s anti-Western narrative and risk estranging future generations of Russians.
Here is what you need to know:
What are the current EU-wide rules?
The EU imposed flight bans on February 27, meaning Russians would have to reach the bloc via third countries.
As the conflict intensified, discussions over further action became mired in disagreement.
More than six months later, EU leaders settled on suspending an historic visa facilitation agreement with Moscow, ending 15 years of privileged access for Russian nationals.
The 2007 visa deal had been agreed on when both sides expressed hope that smoother travel would contribute to a “steady development” of economic, humanitarian, cultural and scientific ties.
The visa application fee has risen and Russians must now produce additional documentation. The rules on issuing visas are tighter and processing times are longer.
However, Russian nationals can still technically access the EU via third countries and get 90-day short-stay visas, pending successful applications. They can also move freely within the majority of the Schengen Area once inside it.
Natia Seskuria, a Russia expert and associate fellow at the United Kingdom-based Royal United Services Institute for Defence and Security Studies (RUSI) think-tank, told Al Jazeera the suspension of the 2007 agreement had “not changed much in practicality”.
“So a lot of countries – especially the Baltic States [Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia] – have decided to act individually,” Seskuria said.
“This lack of consensus has driven European states into a bit of a chaotic situation because now there are … individual [national-level] bans against Russians, but there are also some countries that do business pretty much as usual, except that it has become harder for Russians to get visas,” she said.

What additional restrictions have some countries applied?
There are growing calls from Ukrainian leaders and those in the bloc’s east for an outright ban on Russian tourists.
Several member states have imposed additional travel restrictions themselves.
Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia and Finland announced in September that they would bar entry to Russians holding Schengen Area tourist visas, with exemptions for those requiring humanitarian assistance or visiting family.
Other countries, including Slovakia and the Czech Republic, announced they would not issue humanitarian visas for men attempting to escape Moscow’s military draft.
These moves were informally green-lighted by the EU at a summit in Prague weeks earlier, with the bloc’s foreign policy chief Josep Borrell acknowledging that “business as usual” could not continue for member states bordering Russia.
An outright travel ban “would be quite a radical decision, but … the times we are living in and what Ukrainians are experiencing now are very extreme,” Seskuria told Al Jazeera.
“There must be a sense of responsibility imposed upon the Russian citizens.
“And for the EU, if the borders are open [to Russians] they will get a lot of people [arriving] … who have voted for [President Vladimir] Putin and who will be happy if he wins the war in Ukraine but just don’t want to fight and risk their own lives.”
Which countries oppose stricter measures?
Two of the EU’s most powerful members, France and Germany, have opposed calls for a travel ban and continue to issue short-stay visas, in part to ensure Russian dissidents are provided an escape route.
Both have warned draconian measures could trigger “rally-around-the-flag” effects in Russia.
Even so, Russians are finding it harder to reach Europe after the EU declared on September 30 that members should not accept visa applications from those in a third country and as direct flights remain suspended.
Petr Tůma, a visiting fellow at the United States-based Atlantic Council think-tank’s Europe Center, told Al Jazeera a full tourist ban was a “long way away” given existing divisions.
But he predicted the likelihood of such a move would only increase the longer the conflict continues, and called on the EU to be ready to provide shelter to those who really need it.
“After more than half a year of war, even normal Russians have to assume some kind of responsibility … and may yet have to pay this very limited price,” Tuma said.
“But it is key that if the EU do ‘A’, the tourist visa ban, then they also have to do ‘B’ as well, and grant exceptions for people who need them, such as for the dissidents,” he added.
“We can’t close the door [completely] … this has to be done with some care.”

How many Russians have entered the EU since the war began?
It is not clear how many of those who have entered stayed in the EU, or where they remained if they did.
According to the bloc’s border agency Frontex, more than 1.4 million Russian citizens have entered the EU via its land borders since Moscow began its February 24 offensive. About the same number have also returned to Russia from the EU during the same period.
The similarity in the numbers suggests at least some of the trips may have been recreational – such as for tourism – rather than to resettle in the bloc.
Nearly 37 percent, more than 519,000, of the crossings from Russia were made into Finland, while about a quarter of those exiting the country for Europe, some 360,000, entered Estonia.
The number of overall crossings has dwindled in recent weeks after the EU tightened entry rules, member states bordering Russia imposed their own new restrictions, and as Russian authorities reportedly moved to block those attempting to flee the mobilisation drive.
According to the latest Frontex data, from October 10 – 16, 24,218 Russian citizens entered the EU. This is 1,400 fewer than the week before and less than half the overall figure recorded between September 26 – October 2. Most already had residence permits or visas, while others possessed dual citizenship.

Russia to resume flights with 52 'friendly' countries, PM says
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Reuters; editing by Raissa Kasolowsky and Grant McCool
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron
Ukraine peace summit pushes neutral swiss toward western embrace.
An upcoming Ukraine peace summit, ostensibly the most ambitious bid in years by neutral Switzerland to mediate a major conflict, is instead showing how Swiss economic and security interests increasingly align with Western Europe over Russia.

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
EU to tighten travel rules for Russians, but no visa ban
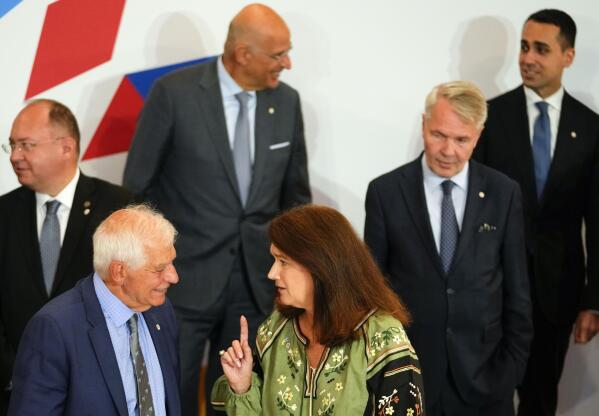

Sweden’s Foreign Minister Ann Linde, center, speaks with European Union foreign policy chief Josep Borrell, second left, during a group photo of EU foreign ministers at the Prague Congress Center in Prague, Czech Republic, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. Others from left, Romania’s Foreign Minister Bogdan Aurescu, Greek Foreign Minister Nikos Dendias, Finland’s Foreign Minister Pekka Haavisto and Italy’s Foreign Minister Luigi Di Maio. (AP Photo/Petr David Josek)
Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba speaks with the media as he arrives for a meeting of EU foreign ministers at the Prague Congress Center in Prague, Czech Republic, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. (AP Photo/Petr David Josek)
Estonia’s Foreign Minister Umas Reinsalu speaks with the media as he arrives for a meeting of EU foreign ministers at the Prague Congress Center in Prague, Czech Republic, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. (AP Photo/Petr David Josek)
Finland’s Foreign Minister Pekka Haavisto arrives for a meeting of EU foreign ministers at the Prague Congress Center in Prague, Czech Republic, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. (AP Photo/Petr David Josek)
Denmark’s Foreign Minister Jeppe Kofod arrives for a meeting of EU foreign ministers at the Prague Congress Center in Prague, Czech Republic, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. (AP Photo/Petr David Josek)
Belgium’s Foreign Minister Hadja Lahbib speaks with the media as she arrives for a meeting of EU foreign ministers at the Prague Congress Center in Prague, Czech Republic, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. (AP Photo/Petr David Josek)
German Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock arrives for a meeting of EU foreign and defense ministers at the Prague Congress Center in Prague, Czech Republic, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. (AP Photo/Petr David Josek)
German Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock speaks with the media as she arrives for a meeting of EU foreign and defense ministers at the Prague Congress Center in Prague, Czech Republic, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. (AP Photo/Petr David Josek)
European Union foreign policy chief Josep Borrell speaks with the media as he arrives for a meeting of EU foreign ministers at the Prague Congress Center in Prague, Czech Republic, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. (AP Photo/Petr David Josek)
- Copy Link copied
PRAGUE (AP) — European Union countries agreed Wednesday to make it harder for Russian citizens to enter the 27-nation bloc, but they failed to find a consensus on imposing an outright tourist ban in response to Russia’s war on Ukraine .
At talks in the Czech Republic, EU foreign ministers were desperate to put on a show of unity and further punish President Vladimir Putin for launching the war over six months ago. Still, they couldn’t bridge differences over whether Russian citizens, some of them possibly opposed to the invasion, should also pay a price.
The plan now is to make it more time-consuming and costly for Russian citizens to obtain short-term visas to enter Europe’s passport-free travel zone — a 26-country area made up of most of the EU members plus Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland known as the Schengen area.
The move will be done by freezing a 2007 agreement to ease travel between Russia and Europe. The EU already tightened visa restrictions on Russian officials and businesspeople under the accord in May.
Speaking after chairing the meeting in the Czech capital Prague, EU foreign policy chief Josep Borrell said that an increasing number of Russians have been arriving in Europe since mid-July, some “for leisure and shopping as if no war is raging in Ukraine.”
This, he said, “has become a security risk” for European countries bordering Russia.
Borrell said said he believed the additional delays will result in fewer visas being issued.
Students, journalists and those who fear for their safety in Russia would still be able to acquire visas. The move would have no immediate impact on the estimated 12 million visas already issued to Russian citizens, but EU officials will look into what could be done to freeze them.
Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba described the move as “a half measure.” He said that visas should only be issued to Russians on humanitarian grounds or to help those who clearly oppose Putin’s war.
“The age of peace in Europe is over, and so is the age of half measures. Half measures is exactly what led to the large-scale invasion,” he said after the meeting. “If I have to choose between half measure and no measure, I will prefer a no measure and continue a discussion until a strong solution is found.”
Calls have mounted from Poland and the Baltic countries — Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania — but also Denmark for a broader ban on Russian tourists. The foreign ministers of Estonia and Latvia said that they may push ahead with further visa restrictions, citing national security concerns.
“We need to immediately ramp up the price to Putin’s regime,” Estonian Foreign Minister Urmas Reinsalu told reporters. “The loss of time is paid by the blood of Ukrainians.”
Uniform rules are supposed to apply across the 26 countries that make up Europe’s passport free travel area, but Reinsalu said that “it’s our national competence, under the principle of national security, to decide the issues of entry to our soil.”
Over the years, several countries have reintroduced border controls for security reasons in the Schengen area, in which Europeans and visitors can travel freely without identification checks.
The foreign minister of Finland, which shares the EU’s longest border with Russia, underlined that his country would, as of Thursday, slash the number of visas being delivered to Russian citizens to 10% of normal. They’ll only be able to apply for the travel pass in four Russian cities.
“It’s important that we show that at the same time when Ukrainians are suffering, normal tourism shouldn’t continue business as usual,” Foreign Minister Pekka Haavisto said. “Finland has already made our decision to limit the amount of tourist visas. We hope that the whole European Union will do similar decisions.”
Before Wednesday’s talks, Danish Foreign Minister Jeppe Kofod had expressed hope that a common EU position could be found, pointing to the fact that most Ukrainian men don’t have the luxury to choose whether they can leave their war-torn country.
“It has to have consequences on all fronts,” Kofod said. “We want to limit visas for Russian tourists, send a clear signal to Putin, to Russia, (that) what he is doing in Ukraine is totally unacceptable.”
But European countries further from Russia and Ukraine’s borders are reluctant to go too far.
Belgium Foreign Minister Hadja Lahbib said it is important to avoid creating a patchwork system “where Russians could do a kind of visa shopping among the countries of the European Union.”
“It’s very important to target the right people. That is, those who support this unjust war against Ukraine and also those who try to evade the sanctions that we have imposed,” she said.
Follow the AP’s coverage of the war at https://apnews.com/hub/russia-ukraine
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Warnings and insurance
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
FCDO advises against all travel to Russia
Your travel insurance could be invalidated if you travel against FCDO advice. Consular support is also severely limited where FCDO advises against travel.
FCDO advises British nationals against all travel to Russia due to the risks and threats from its continuing invasion of Ukraine. The situation in Russia is unpredictable. This includes:
- security incidents, such as drone attacks, happening in some parts of the country
- lack of available flights to return to the UK
- limited ability for the UK government to provide consular assistance
There is also a high likelihood that terrorists will try to carry out attacks, including in major cities. See ‘Safety and Security’ section .
Security situation in Russia
The Russian invasion of Ukraine continues. There are reports of drone attacks and explosions in areas in western and southern Russia, particularly near the Russian border with Ukraine, Moscow and St Petersburg.
Political rallies and demonstrations can take place in Moscow, St Petersburg and across Russia. Check the local media for the latest information. Be vigilant and avoid any political demonstrations or gatherings.
The situation remains unpredictable and could escalate without warning.
Leaving Russia
FCDO advises British nationals to consider leaving Russia.
If you do not need to be in Russia, we strongly advise you to consider leaving.
You cannot fly directly from Russia to the UK or through EU countries. Commercial flight options are limited and can sell out quickly. Check with your airline or travel provider.
British nationals should exercise extreme caution at all times. Travel within or out of Russia is at your own risk.
You cannot fly direct from Russia to the UK or through EU countries. There are limited commercial airlines with indirect flights via the Middle East, Serbia and Turkey. Check the latest information with your airline or travel provider.
Land borders may be busy. Be prepared for a long wait to exit Russia. You may also be questioned at the border. During periods of unrest, check the local media for updates on the situation before travelling.
Road border crossings between Finland and Russia will be closed until at least 11 February 2024. Consult the Finnish border guard website for up-to-date information. Further changes may be announced at short notice.
Some European countries have restricted or banned the entry of vehicles registered in Russia, this includes:
If you plan to drive a vehicle registered in Russia into Europe check that you are eligible to do so.
Some bus companies have international routes. The situation may change quickly. From 18 November 2023, Finland will restrict entry at some road border crossings (See ‘Travelling from Russia to Finland’). Check these companies for availability of buses, timetables and tickets:
- Ecolines – buses to Riga (Latvia), Tallinn (Estonia), Vilnius (Lithuania) and other destinations in Europe
- Baltic Shuttle – buses from St Petersburg to Tallinn (Estonia)
- Lux Express – buses from St Petersburg to Riga (Latvia), Tallinn (Estonia)
Travelling from Russia to Latvia
Check the travel advice for Latvia .
See the Latvian government website for information on crossing the border.
Travelling from Russia to Finland
Check the travel advice for Finland .
Road border crossings between Finland and Russia will remain closed until further notice. Consult the Finnish border guard website for up-to-date information. Further changes may be announced at short notice.
The border crossing points for maritime traffic at Haapasaari, the port of Nuijamaa and Santio will be closed to leisure boating from 15 April until further notice.
The train service from Russia to Finland is no longer available.
Travelling from Russia to Estonia
Check the travel advice for Estonia .
See the Estonian police and border guard website for information on crossing the border.
From 1 February 2024, it is not possible to cross the border by vehicle via the Narva-Ivangorod crossing point, whilst construction works take place on the Russian side. The crossing is open to pedestrians.
Travelling from Russia to Lithuania
Check the travel advice for Lithuania .
If you’re planning to cross into Lithuania by road from Kaliningrad oblast at the Kybartai border crossing point, see the Lithuanian state border crossing website .
Travelling from Russia to Norway
Check the travel advice for Norway .
Staying in Russia
If you decide to stay in Russia, you should:
- keep your departure plans under constant review
- ensure your travel documents are up to date
- follow local media
- stay alert to security warnings and follow the advice of local authorities
- take cover in buildings or underground and avoid windows in the event of drone attack
- sign up to email alerts for Russia travel advice
Read FCDO advice on what to do if you’re affected by a crisis abroad and how to prepare.
Support for British nationals in Russia
The British Embassy in Moscow and British Consulate Ekaterinburg are open, but the situation could change at short notice.
In person consular support in Russia is limited. It is very limited in parts of Russia because of the security situation and the size of the country, particularly in the North Caucasus.
If you need consular assistance, call our 24-hour helpline +7 495 956 7200 and select the option for consular services for British nationals.
Contact the Russian emergency services on 112.
Dual nationals
Dual British-Russian nationals are treated as Russian nationals by local authorities. The consular support FCDO can provide is severely limited. If you are arrested or detained, Russian authorities are unlikely to allow us consular access.
In 2022, Russia declared a partial mobilisation of Russian citizens to join the military forces. Military recruitment continues. Anyone with a Russian passport could be conscripted.
In August, Russian law was amended to stop Russian nationals eligible for military conscription from leaving Russia from the day their draft notice appears on the federal electronic conscription register.
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide as well as support for British nationals abroad which includes:
- advice on preparing for travel abroad and reducing risks
- information for women, LGBT+ and disabled travellers
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
Related content
Invasion of ukraine.
- UK visa support for Ukrainian nationals
- Move to the UK if you're coming from Ukraine
- Homes for Ukraine: record your interest
- Find out about the UK’s response
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory September 5, 2023
Russia - level 4: do not travel.
Updated to remove COVID-specific information and the kidnapping risk indicator as well as updates to security risks.
Do not travel to Russia due to the unpredictable consequences of the unprovoked full-scale invasion of Ukraine by Russian military forces , the potential for harassment and the singling out of U.S. citizens for detention by Russian government security officials , the arbitrary enforcement of local law , limited flights into and out of Russia , the Embassy’s limited ability to assist U.S. citizens in Russia , and the possibility of terrorism . U.S. citizens residing or travelling in Russia should depart immediately. Exercise increased caution due to the risk of wrongful detentions.
The U.S. government’s ability to provide routine or emergency services to U.S. citizens in Russia is severely limited, particularly in areas far from the U.S. Embassy in Moscow, due to Russian government limitations on travel for embassy personnel and staffing, and the ongoing suspension of operations, including consular services, at U.S. consulates.
There have been numerous reports of drone attacks, explosions, and fires in areas in Western and Southern Russia, particularly near the Russian border with Ukraine, as well as in Moscow and St. Petersburg. In the event of an emergency, U.S. citizens should follow instructions from local authorities and seek shelter immediately.
In September 2022, the Russian government mobilized citizens to the armed forces in support of its invasion of Ukraine. Russia may refuse to acknowledge dual nationals’ U.S. citizenship, deny their access to U.S. consular assistance, subject them to mobilization, prevent their departure from Russia, and/or conscript them.
U.S. citizens should note that U.S. credit and debit cards no longer work in Russia, and options to electronically transfer funds from the United States are extremely limited due to sanctions imposed on Russian banks. There are reports of cash shortages within Russia.
Commercial flight options are extremely limited and are often unavailable on short notice. If you wish to depart Russia, you should make independent arrangements as soon as possible. The U.S. Embassy has severe limitations on its ability to assist U.S. citizens to depart the country and transportation options may suddenly become even more limited. Click here for Information for U.S. Citizens Seeking to Depart Russia.
U.S. Embassy personnel are generally not permitted to travel on Russian air carriers due to safety concerns. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) downgraded the air safety rating for Russia from Category 1 to Category 2 on April 21, 2022, due to Russia’s Federal Agency for Air Transport noncompliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) safety standards. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has issued a Notice to Air Missions (NOTAM) prohibiting U.S. aviation operations into, out of, within, or over those areas of the Moscow Flight Information Region (FIR), the Samara FIR (UWWW) and the Rostov-na-Donu (URRV) FIR within 160NM of the boundaries of the Dnipro (UKDV) Flight Information Regions. For more information, U.S. citizens should consult the Federal Aviation Administration’s Prohibitions, Restrictions, and Notices .
The right of peaceful assembly and freedom of expression are not consistently protected in Russia. U.S. citizens should avoid all political or social protests and not photograph security personnel at these events. Russian authorities have arrested U.S. citizens who have participated in demonstrations and there are numerous reports Russian nationals have been detained for social media activity.
Country Summary:
U.S. citizens, including former and current U.S. government and military personnel and private citizens engaged in business who are visiting or residing in Russia, have been interrogated without cause and threatened by Russian officials, and may become victims of harassment, mistreatment, and extortion.
Russian security services may fail to notify the U.S. Embassy of the detention of a U.S. citizen and unreasonably delay U.S. consular assistance. Russian security services are increasing the arbitrary enforcement of local laws to target foreign and international organizations they consider “undesirable.”
Russian security services have arrested U.S. citizens on spurious charges, singled out U.S. citizens in Russia for detention and harassment, denied them fair and transparent treatment, and convicted them in secret trials or without presenting credible evidence. Furthermore, Russian authorities arbitrarily enforce local laws against U.S. citizen religious workers and have opened questionable criminal investigations against U.S. citizens engaged in religious activity. U.S. citizens should avoid travel to Russia to perform work for or volunteer with non-governmental organizations or religious organizations.
There have been multiple security incidents in southwestern Russia related to Russia’s unprovoked and unjustified invasion of Ukraine. The Russian government declared martial law in Russia’s regions bordering Ukraine (Bryansk, Kursk, Belgorod, Voronezh, Rostov, Krasnodar) on October 20, 2022. The martial law regime allows the rapid introduction of restrictive measures such as curfew, seizure of private property, restriction of entry/exit and freedom of movement, internment of foreigners, forced relocation of local residents, and restrictions on public gatherings. U.S. citizens should avoid all travel to these areas.
Recent legislation has expanded the ability of Russian authorities to detain, question, and arrest individuals suspected of acting against Russia’s interests, including posts on personal social media accounts, engaging with foreign and international entities, discrediting the Russian state or military, as well as advocating for the rights of LGBTQI+ persons.
Terrorist groups, both transnational and local terrorist organizations, and individuals inspired by extremist ideology continue plotting possible attacks in Russia. Terrorists may attack with little or no warning, targeting tourist locations, transportation hubs and systems, markets/shopping malls, local government facilities, hotels, clubs, restaurants, places of worship, parks, major sporting and cultural events, educational institutions, airports, and other public areas. Travel to the North Caucasus (including Chechnya and Mt. Elbrus) is prohibited for U.S. government employees and strongly discouraged for U.S. citizens.
The international community, including the United States and Ukraine, does not recognize Russia’s purported annexation of Crimea as well as four other Ukrainian oblasts – Donetsk, Luhansk, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhya – that Russia has purported to annex more recently. There is extensive Russian Federation military presence in these areas. Russia staged its further invasion of Ukraine, in part, from occupied Crimea, and Russia is likely to take further military actions in Crimea, and the four other Ukrainian oblasts are the subject of intensive fighting. There are continuing abuses against foreigners and the local population by the occupation authorities in these regions, particularly against those who are seen as challenging Russia’s authority.
The U.S. Embassy in Kyiv continues to provide consular services to U.S. citizens in Crimea as well as four other Ukrainian oblasts partially occupied by Russia – Donetsk, Luhansk, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhya, although the ongoing conflict severely restricts the Embassy’s ability to provide services in these areas.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Russia.
If you decide to travel to Russia:
- Familiarize yourself with the information on what the U.S. government can and cannot do to assist you in a crisis overseas .
- Have a contingency plan in place that does not rely on U.S. government assistance. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Monitor local and international media for breaking events and adjust your contingency plans based on the new information.
- Ensure travel documents are valid and easily accessible.
- Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Russia.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
Important Information for U.S. Citizens Seeking to Depart Russia (Updated Monthly).
Click Here for Important Information for U.S. Citizens Seeking to Depart Russia (Updated Monthly) .
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Required six months beyond intended stay
2 pages per stamp
$10,000 or more must be declared
You may export up to $3,000 (or equivalent) without declaring it
Embassies and Consulates
U.S. Embassy Moscow Bolshoy Deviatinsky Pereulok No. 8 Moscow 121099 Russian Federation Telephone: +(7) (495) 728-5000 or +(7) (495) 728-5577 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(7) (495) 728-5000 Fax: +(7) (495) 728-5084 Email: [email protected]
U.S. Consulate General Vladivostok 32 Ulitsa Pushkinskaya Vladivostok 690001 Russian Federation
Consular services at U.S. Consulate General Vladivostok remain suspended. Contact Embassy Moscow for all consular services.
U.S. Consulate General Yekaterinburg Ulitsa Gogolya 15a, 4th floor, Yekaterinburg 620151 Russian Federation
Effective April 1, 2021, Consulate General Yekaterinburg suspended all consular services. Contact Embassy Moscow for all consular services.
U.S. Consulate General St. Petersburg
Due to the Russian government’s ordered closure of the U.S. Consulate General, as of March 31, 2018, U.S. citizen visitors and residents in St. Petersburg must contact the U.S. Embassy in Moscow for all consular services .
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Russian authorities strictly enforce all visa and immigration laws. The Embassy of the Russian Federation website provides the most up to date information regarding visa regulations and requirements. In accordance with Russia’s Entry-Exit Law, Russian authorities may deny entry or reentry into Russia for 5 years or more and cancel the visas of foreigners who have committed two administrative violations within the past three years. Activities that are not specifically covered by the traveler’s visa may result in an administrative violation and deportation.
Under a bilateral agreement signed in 2012, qualified U.S. applicants for humanitarian, private, tourist, and business visas may request and receive multiple-entry visas with a validity of three years or a single entry, three-month validity visa. ( Please note that other types of visas are not part of the agreement and those visa holders should pay close attention to the terms of their visas.) You cannot enter Russia prior to the date on your visa, and you must exit Russia before your visa expires . The maximum period of stay is shown on the visa.
- You must have a current U.S. passport with the appropriate visa . Russian visas in an expired or canceled passport are not valid.
- You must obtain a valid visa for your specific purpose of travel before arriving in Russia, unless you are arriving as a cruise ship passenger (see below information for passengers of cruise ships and ferries). Do not attempt to enter Russia before the date shown on your visa. If you are staying in Russia for more than 7 days, you must register your visa and migration card with the General Administration for Migration Issues of the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
- Cruise ship passengers in St. Petersburg should seek assistance from the U.S. Embassy in Moscow for all emergency and passport services.
- Cruise ship passengers should be aware that loss or theft of a passport and/or migration card could result in the inability to obtain lodging. Hotels and hostels may not allow guests to check in without a passport, a migration card, or Russian visa.
- We recommend U.S. citizens obtain a Russian visa before traveling to Russia, in case of an emergency while in the country, such as unexpected medical issues or if you are not able to return on the cruise ship for any reason.
- Students and English teachers should be certain that their activities are in strict keeping with their visa type. Students must not teach or coach English, whether compensated or not, while traveling on a student visa as it is considered a visa violation and may subject you to detention and deportation.
- With the exceptions noted below, travelers will are not required to have a transit visa if they are transiting through an international airport in Russia, do not leave the Customs zone, and depart from the same airport within 24 hours.
- Travelers must have a Russian transit visa if they plan to transit through Russia by land en route to a third country or if they transfer to another airport.
- Travelers must possess a Russian transit visa in addition to a Belarusian visa if their travel route either to or from Belarus goes through Russia.
Dual Nationals: Anyone entering Russia who has claim to Russian citizenship, regardless of any other citizenship held, is fully accountable to the Russian authorities for all obligations of a Russian citizen, including the required military service.
- U.S.-Russian dual nationals and Russian citizens who are Legal Permanent residents of the United States must register their dual nationality/foreign residency. Registration forms and further information (in Russian only) can be found on the website of the General Administration for Migration Issues of the Interior Ministry of Russia.
- U.S.-Russian dual nationals must both enter and exit on a Russian passport. You will not be permitted to depart on an expired passport. Applying for a passport can take several months.
- U.S.-Russian dual nationals who return to Russia on a “Repatriation Certificate” are only permitted to enter Russia and will not be permitted to depart Russia until they obtain a valid Russian passport.
- Minors who also have Russian citizenship and are traveling alone or in the company of adults who are not their parents, must carry a Russian passport as well as their parents’ notarized consent for the trip, which can be obtained at a Russian embassy or consulate, or a U.S. notary public. A consent obtained in the United States from a U.S. notary public must be apostilled, translated into Russian, and properly affixed. Authorities will prevent such minors from entering or leaving Russia if they cannot present this consent.
Crimea: Follow the guidance in the Travel Advisory for Ukraine and do not travel to the Crimean Peninsula.
Documentary Requirements for obtaining a Russian visa: Consult with the Embassy of the Russian Federation for detailed explanations of documentary requirements.
HIV/AIDS Entry Restrictions: Some HIV/AIDS entry restrictions exist for visitors to and foreign residents of Russia. Applicants for longer-term tourist and work visas or residence permits are required to undergo an HIV/AIDS test.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
Terrorism: Terrorist groups, transnational and local terrorist organizations, and lone actors inspired by extremist ideology and messaging continue plotting possible attacks in Russia. Terrorists may attack with little or no warning, targeting tourist locations, transportation hubs, markets/shopping malls, local government facilities, hotels, clubs, restaurants, places of worship, parks, major sporting and cultural events, educational institutions, airports, and other public areas
- Moscow and St. Petersburg have been the targets of terrorist attacks, and bomb threats against public venues are common. If you are at a location that receives a bomb threat, follow all instructions from the local police and security services.
North Caucasus Region: A risk of civil and political unrest continues throughout the North Caucasus region including Chechnya, North Ossetia, Ingushetia, Dagestan, Stavropol, Karachayevo-Cherkessiya, and Kabardino-Balkariya. Local criminal gangs have kidnapped foreigners, including U.S. citizens, for ransom. In the Republic of Chechnya, local authorities may harbor particular hostility towards U.S. travelers.
- Do not travel to Chechnya or any other areas in the North Caucasus region.
- If you reside in these areas, depart immediately.
- U.S. government travel to the region is prohibited, due to ongoing security concerns.
- The U.S. Government has no ability to assist U.S. citizens in the North Caucasus Region.
Mt. Elbrus:
- Do not attempt to climb Mt. Elbrus, as individuals must pass close to volatile and insecure areas of the North Caucasus region.
- Do not travel to this Russian occupied territory of Ukraine.
- The U.S. government is unable to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in Crimea. Contact the U.S. Embassy in Kyiv for questions regarding consular services.
- U.S. government officials are prohibited from traveling to Crimea. See the Departments Travel Advisory for Ukraine .
Harassment: Harassment of U.S.-based religious and student groups can take place in Russia, and you should be aware of the possibility of anti-U.S. sentiment or harassment. U.S. citizens, including current and former U.S. government and military personnel, maybe subject to additional scrutiny by Russian security services. Remain alert, avoid any protests or demonstrations, and use discretion when commenting publicly on political developments. You can find safety and security Alerts on the Embassy’s website .
- Police do not need to show probable cause in order to stop, question, or detain individuals. Please comply with the requests of local law enforcement officials.
- Report harassment or crimes to the U.S. Embassy in Moscow or the nearest U.S. Consulate General.
Demonstrations:
- Avoid public demonstrations. U.S. citizens who have participated in demonstrations have been arrested by the Russian authorities.
Crime: Crimes against tourists do occur at popular tourist sites and on public transportation. U.S. citizens have been victims of serious crimes when visiting Russia. Russian authorities are not always willing to impartially and thoroughly investigate crimes.
- Be cautious and aware of your surroundings.
- Exercise caution in the vicinity of large crowds.
- Do not leave bags unattended.
- Never leave your drink unattended in a bar or club. Alcohol was a significant factor in most criminal activity reported by foreign visitors.
- Report Credit card or ATM card theft to the credit card company or issuing bank immediately.
- Avoid carrying large sums of cash .
Cybercrime: Cybercrime is a significant problem across Russia. Russian hackers and traditional organized crime structures continue to work together, raising threats to the financial sector. The risk of infection, compromise, and theft via malware, spam e-mail, sophisticated spear phishing, and social engineering attacks is significant. U.S. citizens and companies should remain vigilant against cyber threats and actively use cyber security measures to mitigate risks.
U.S. citizens have no reasonable expectation of privacy in Russia. Telephone and electronic communications are subject to surveillance at any time and without advisory, which may compromise sensitive information. The Russian System for Operational-Investigative Activities (SORM) legally permits authorities to monitor and record all data that traverses Russia’s networks.
See the Department of State and the FBI pages for additional information on scams.
Victims of Crime : U.S. citizen victims of sexual assault are encouraged to contact the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate for assistance. Report crimes to the local police at 02 or 102, or 112 if using a mobile phone, and the U.S. Embassy at +7 495 728-5000..
Remember that local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting the crime. United States law enforcement agencies do not have jurisdiction to investigate crimes against U.S. citizens that occur on Russian territory.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Help you find appropriate medical care
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent
- Provide general information regarding the victim’s role during the local investigation and following its conclusion
- Provide a list of local attorneys
- Provide our information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical
- Support in cases of destitution
- Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home
- Replace a stolen or lost passport.
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence are encouraged to contact the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate General for assistance.
Tourism: The tourism industry is unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities do not commonly occur. Hazardous areas/activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is typically available only in/near major cities. First responders are generally unable to access areas outside of major cities and to provide urgent medical treatment. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Arrest Notification: Russia routinely fails to meet its obligation to inform the U.S. Embassy of arrests of U.S. citizens. If you are detained, ask the police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy or Consulate immediately. Your U.S. passport does not protect you from arrest or prosecution. See our webpage for further information.
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to all Russian laws. If you violate these laws, even unknowingly, you may be arrested, fined, imprisoned, or expelled and may be banned from re-entering Russia.
Some crimes committed outside the United States are prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
- You can be arrested, detained, fined, deported and banned for 5 years or more if you are found to have violated Russian immigration law.
- Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Russia are severe. Convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
- You can be detained for not carrying your passport with you.
- You can be jailed immediately for driving under the influence of alcohol.
- It is illegal to pay for goods and services in U.S. dollars, except at authorized retail establishments.
- You can be arrested for attempting to leave the country with antiques, even if they were legally purchased from licensed vendors. Cultural value items like artwork, icons, samovars, rugs, military medals and antiques, must have certificates indicating they do not have historical or cultural value. You may obtain certificates from the Russian Ministry of Culture .
- Retain all receipts for high-value items, including caviar.
- You must have advance approval to bring in satellite telephones.
- Global Positioning System (GPS) and other radio electronic devices, and their use, are subject to special rules and regulations in Russia. Contact the Russian Customs Service for required permissions.
Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: Although counterfeit and pirated goods are prevalent in many countries, they may still be illegal according to local laws. You may also pay fines or have to give them up if you bring them back to the United States. See the U.S. Department of Justice website for more information.
Faith-Based Travelers: Russian authorities have detained, fined, and in some cases deported travelers for engaging in religious activities. Russian officials have stated that Russia recognizes four historic religions: Orthodox Christianity, Judaism, Islam, and Buddhism. The Russian government places restrictions on missionary activity and defines it broadly – travelers engaging in certain types of religious work may risk harassment, detention, fines, or deportation for administrative violations if they do not have proper authorization from a registered religious group. Russian law criminalizes proselytizing outside of a registered house of worship. The Russian government has detained U.S. citizens for religious activities that they contend are not permitted under a tourist or humanitarian visa. See the Department of State’s International Religious Freedom Report .
LGBTI Travelers: Russian law bans providing "the propaganda of nontraditional sexual relations" to minors. Foreign citizens face fines, up to 15 days in jail, and deportation. The law is vague as to what Russia considers propaganda of nontraditional sexual relations.
- Discrimination based on sexual orientation is widespread in Russia. Acts of violence and harassment targeting LGBTI individuals occur.
- Government officials have made derogatory comments about LGBTI persons and violence against the LGBTI community has increased.
- There have been credible reports of arrest, torture, and extrajudicial killing of LGBTI persons in Chechnya allegedly conducted by Chechen regional authorities.
See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers Who Require Accessibility Assistance: Getting around in Russia is often difficult for persons with mobility issues. In general, public transportation is not accommodating to people with disabilities. The Moscow Metro, though extremely safe and efficient in other areas, is generally not accessible to persons with disabilities.
- Sidewalks are narrow and uneven.
- Mobility is usually easier in major cities such as Moscow and St. Petersburg.
- Crossing streets in large cities can be difficult, since it usually requires the use of a pedestrian underpass, which includes stairs, steep ramps, and no elevators.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
Private medical care in major metropolitan cities and tourism centers in Russia is often equal to Western standards. However, medical care is generally below Western standards in non-metropolitan areas.
- Private medical facilities require payment by cash or credit card before providing services (unless they are life threatening), and are unlikely to accept proof of U.S. insurance as guarantee of future payment. Payment is expected at the time of service .
- The Embassy does not pay the medical bills of private U.S. citizens.
- U.S. Medicare does not provide coverage outside the United States without the purchase of supplemental coverage.
- Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance coverage.
- Elderly travelers and those with existing health problems are particularly at risk.
Prescription Medication:
- Certain classes of over-the-counter cold medicines, such as those containing pseudoephedrine, are illegal in Russia. We recommend against bringing cold medication with you to Russia.
- Carry a copy of valid U.S. prescriptions, including a notarized translation into Russian of each prescription, when entering Russia with prescription medications.
- Prescription medication should be in its original packaging.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Road conditions and driver safety customs differ significantly from those in the United States. In some more remote areas of Russia, roads are practically nonexistent or have poor or nonexistent shoulders.
- Drivers are required by law to yield to pedestrians in crosswalks, and this is generally observed. It is dangerous to cross where there is not a crosswalk present.
- Do not drive outside the major cities at night.
- Construction sites and road hazards are often unmarked.
Traffic Laws : Russian authorities have been known to consider traffic or parking infractions as “administrative violations” that provide a sufficient basis for deportation and/or denial of entry back to Russia at a later date.
- Drivers must carry third-party liability insurance under a policy valid in Russia.
- You may drive for 60 days using your U.S. driver’s license, with a notarized Russian translation.
- Tourists may also use International Driving Permits issued by the American Automobile Association or the American Automobile Touring Alliance to drive in Russia.
- Russian law requires foreigners on business or employment visas or with permanent residence status to have a Russian driver's license.
- Driving regulations are strictly enforced and violators are subject to severe legal penalties.
- Russia practices a zero-tolerance policy for driving under the influence of alcohol. Authorities can detain an intoxicated driver and your driver’s license can be suspended up to two years.
- If you are involved in an accident, do not move your vehicle from the accident site. You may be held liable if you move your car even if you are not at fault.
- Roadside police checkpoints are commonplace. Be prepared to stop and show identity documents and proof of registration and insurance.
Public Transportation:
- Moscow and St. Petersburg have extensive, efficient public transit systems, as do many other urban areas in Russia.
- In metropolitan areas, well-marked taxis are generally safe and reliable Do not use unmarked taxis. Passengers have been the victims of robbery, kidnapping, extortion and theft.
See our Road Safety page for more information.
AVIATION SAFETY OVERSIGHT: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed that the Government of Russia's Civil Aviation Authority is not in compliance with the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Russia's air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA's safety assessment page.
Maritime Travel: Mariners should check the U.S. Department of Transportation’s Maritime Administration site for U.S. maritime advisories and alert s, the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and NGA broadcast warnings .
The Commandant of the Coast Guard is unable to determine if effective anti-terrorism measures are in place in Russia ports as required by 46 U.S. Code § 70108.
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Russia . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, russian federation map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
- #Luxury travel
- #Unusual Moscow
- #Jewish Heritage
- #Russian traditions

Coronavirus (COVID19) travel Information
- #Travel tips
When planning your trip, it is essential to inform the ongoing coronavirus (COVID-19) situation. Below is the latest information regarding the current situation.
- Border closing
Russia closed its borders for foreign visitors from 18.03.2020 till further notice. Here are the few exceptions: foreigners studying in Russia; diplomatic workers and members of their families; relatives of a deceased person, provided that they have documents confirming their relations; transit passengers; foreigners seeking medical treatment; international ship, cargo, train, sea crew members performing their work duties; specialists who carry out adjustment and maintenance of imported equipment; holders of special visas, issued to visit the funeral of a person, permanently residing in Russia; Russian citizens and permanent residents.
- Border opening
Russia's borders are open for the citizens of certain countries with which Russia has resumed regular air travel.
The international flight connection reopened between Russia and several counties from the particular list approved by the government. Today the list of such countries includes 50 countries:
- Turkey
- Switzerland
- South Korea
- Tanzania (temporarily no air connection)
- Azerbaidzhan
- Tadzhikistan
- Saudi Arabia
- North Macedonia
Citizens of the foreign states, according to the list, can visit Russia if they enter the Russian Federation from the country of their citizenship through air checkpoints across the state border of the Russian Federation.
- Special requirements
On the departure to Russia, travelers must show a negative result for a COVID test conducted within 72 hours before arrival English or Russian). Russian citizens arriving without a test result must submit to this test within 72 hours of arrival. Foreign citizens will not be accepted onboard without this test.
There is no quarantine upon arrival.
- Boutique Hotels in St. Petersburg read
- Travel tips read
- Quick facts about Russia read

We use cookies to improve your experience on our Website, tailor content, and measure advertising. By continuing to use our Website, you accept our Privacy Policy .
Your request has been sent successfully! Our travel expert will contact you shortly.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
We continue to advise:
Do not travel to Russia due to the security situation and the impacts of the military conflict with Ukraine.
Russia (PDF 2.04 MB)
Europe (PDF 2.62 MB)
Local emergency contacts
All emergency services, fire and rescue services, medical emergencies, advice levels.
Do not travel to Russia.
Do not travel to Russia due to the dangerous security situation and the impacts of the military conflict with Ukraine.
Do not travel to North Caucasus.
Do not travel to North Caucasus due to the high threat of terrorism and political unrest.
See Safety .
- There's an ongoing threat of terrorism. Terrorist groups, including al-Qaeda and Daesh-aligned groups, continue to call for attacks in Russia. Attacks can be indiscriminate and may occur on or around seasonal, festive, or religious events in public places and could include popular tourist sites. Attacks may occur with little or no warning. Always be alert to possible threats and have a clear exit plan. On 23 March, there was a terrorist attack at Crocus City Hall in Moscow, resulting in significant loss of life.
- Security incidents, such as drone attacks and explosions, often occur in southern and western areas of Russia, including regions bordering Ukraine, Moscow, and St Petersburg. This can cause significant flight delays and travel disruption. You shouldn't attempt to travel to the Russia-Ukraine border or cross into Ukraine from Russia.
- The security situation could deteriorate further with little warning. If you're in Russia, leave immediately using the limited commercial options available or private means if it's safe to do so. Departure routes from Russia may become disrupted at short notice, so have an alternate exit plan.
- If you decide to stay in Russia, review your personal security plans. You're responsible for your own safety and that of your family. Our ability to provide consular assistance in Russia is limited. The Australian Government will not be able to evacuate you from Russia.
- There are limited transportation options, restrictions on financial transactions and possible shortages of essential products and services.
- The Russian Government has introduced a 'medium response level' in several regions of Russia, including Krasnodar, Belgorod, Bryansk, Voronezh, Kursk, and Rostov and a 'heightened preparedness level' in the remainder of the Central and Southern Federal districts. A basic readiness level covers the rest of Russia. There may be an increase in security personnel and installations. Security measures or restrictions may be introduced with little to no notice. Monitor the media for developments.
- Russian authorities have made strong, negative comments in relation to Western countries. Local authorities may adopt a more negative attitude towards foreigners in Russia in reaction to perceived support for Ukraine and sanctions on Russia. Non-participating bystanders can draw scrutiny from security forces and have been detained. Remain vigilant, avoid protests or demonstrations and avoid commenting publicly on political developments.
- Continue to follow the advice on Smartraveller. If you have significant concerns for your welfare or that of another Australian, contact the Consular Emergency Centre on 1300 555 135 in Australia or +61 2 6261 3305 outside Australia.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Laws about the import and use of medicines are strict. You need a doctor's letter and a notarised translation confirming your need for each medication that contains restricted substances. Contact the Embassy of Russia for details.
- Rabies and tick-borne encephalitis are on the rise. Ticks are common from April to October. Take care when travelling through forests.
- Infectious diseases such as typhoid, hepatitis, diphtheria, measles and tuberculosis are a risk. Boil drinking water or drink bottled water.
- Public medical facilities in Russian cities are below Australian standards and basic in rural areas.
Full travel advice: Health
- Russia may subject males it regards as Russian to mobilisation, regardless of any other citizenship held. Laws introducing heavy penalties for 'crimes against military service' have been passed. The Australian Government won't be able to intervene if you're subjected to mobilisation.
- Conscription occurs regularly in Russia. The Government may subject males it regards as Russian to mandatory conscription, regardless of any other citizenship held. From 1 January 2024, the maximum age of conscription will change from 27 to 30 years old. Russian authorities have also passed laws allowing for the draft notice to be serviced to the conscripts online, preventing conscripts from leaving the country once the notice is registered and sent.
- Russia has passed laws that severely inhibit free speech related to the current situation, imposing severe restrictions on the publishing and distribution of information related to the Russian armed forces and any military operations. Foreign journalists and other media workers in Russia may face considerable risks, including arrest and imprisonment. Don't share or publish information related to the current events in Ukraine and Russia.
- Russian authorities may enforce local laws in an arbitrary manner. You may be interrogated without cause by Russian officials and may become a victim of harassment, mistreatment, and extortion.
- Don't use or carry any illegal drugs. Penalties are severe. Carry your passport, visa and migration card at all times. Authorities won't accept copies.
- Don't take photos of military places or sensitive areas, such as passport control. It's also illegal to use commercial film, television, camera equipment or drones in public without permission. Hand-held video cameras are legal.
- Russia doesn't recognise dual nationals. We can only provide limited consular assistance to dual nationals who are arrested or detained. You'll need a valid Russian passport to leave.
- Same-sex relationships are technically legal but are not widely accepted. Violence against members of the LGBTI community occurs. Russia's parliament passed a law banning "LGBT propaganda", criminalising any act regarded as an attempt to promote what Russia calls "non-traditional sexual relations". The promotion of LGBTI issues may be considered illegal by local authorities, and activists may face consequences under Russian law. In July 2023, the Russian President signed a decree banning gender changes without medical requirements. The law also annuls marriages in which one person "changed gender" and prevents transgender couples from adopting children.
- Law enforcement agencies in Russia cooperate closely with agencies in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries. If you commit an offence in one of these countries, you may be detained in another (including at the border) and extradited for prosecution.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- If you're in Russia, leave immediately using the limited commercial options available or private means if it's safe to do so. The security situation could deteriorate further with little warning. If you decide to stay in Russia, review your personal security plans. You're responsible for your own safety and that of your family. Have an alternate exit plan.
- Confirm with your transport operator that services are still operating if you plan to depart Russia. Commercial travel routes between Russia and Europe are often disrupted due to measures taken in response to military action in Ukraine. Several Russian airports are now closed to the public, disrupting internal flights to and from Moscow and other cities. The train and bus service between St Petersburg and Helsinki is suspended.
- If you're travelling through an overland border crossing into Estonia or Latvia , confirm the entry requirements for your destination before arrival. Finland has closed border crossings with Russia indefinitely and maritime borders will close on 15 April. Latvia introduced an entry ban on vehicles registered in Russia in September 2023. There's a ban on vehicles crossing into/from Estonia at the Ivangorod- Narva crossing. Train service is also suspended. Entry and exit on foot will still be allowed. Additional restrictions or entry requirements could be imposed or changed suddenly. Be aware that some borders may close without notice. Australia and other countries have placed sanctions on Russia. Russia's response to these sanctions may disrupt travel and affect travellers.
- Russian airlines and railways may be affected by shortages of parts and essential technical components for their fleets, affecting maintenance and safety standards. Research your railway and aviation provider before choosing their services. The International Civil Aviation Organisation has issued a Significant Safety Concern (or 'red flag') notice regarding the capacity of Russian airlines to oversee safety.
- If, despite our advice, you decide to enter Russia, expect thorough security checks at the border, including questioning and inspections of electronic devices. Entry requirements can change at short notice. Contact your airline or the nearest embassy or consulate of Russia to confirm entry requirements.
- Bank cards issued outside of Russia don't work in Russia. You won't be able to access funds from these cards once you enter Russia. You may not be able to exchange Australian dollars as well as old, worn, or damaged US dollar and euro banknotes into Russian rubles in Russia. Ensure you have enough money to cover your stay.
- Dual nationals can't leave Russia without a valid Russian passport. If your Russian passport expires while you're in Russia or if you enter Russia using a repatriation certificate, you'll need to get a new Russian passport before you leave. This can take up to 3 months. The Australian Government won't be able to intervene or fast-track this process.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what we can and can't do to help you overseas.
- For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy in Moscow. Our ability to provide consular assistance in Russia is limited due to the evolving security situation. The Australian Government will not be able to evacuate you from Russia.
- The Australian Consulate in St Petersburg can provide limited help.
- If you have significant concerns for your welfare or that of another Australian, contact the Consular Emergency Centre on 1300 555 135 in Australia or +61 2 6261 3305 outside Australia.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Terrorists are very likely to try to carry out attacks in Russia. Terrorist groups, including al-Qaeda and Daesh-aligned groups, continue to call for attacks in Russia. Attacks can be indiscriminate and may occur on or around seasonal, festive, or religious events in public places and could include popular tourist sites. Attacks may occur with little or no warning. Always be alert to possible threats and have a clear exit plan. Russia has seen a number of terrorist attacks which have caused large casualty numbers. On 23 March, there was a terrorist attack at Crocus City Hall in Moscow, resulting in significant loss of life. Russia's aviation has also been targeted.
Russian authorities continue to announce arrests and the disruption of planned attacks.
Terrorists have attacked other European cities. Targets have included:
- places of worship
- government buildings
- shopping areas
- tourist sites
- restaurants
- entertainment venues
- transportation hubs
- major events which attract large crowds
To protect yourself from terrorism:
- be alert to possible threats, especially in public places
- be extra cautious around possible terrorist targets
- always have a clear exit plan
- report anything suspicious to the police
- monitor the media for any new threats
- take official warnings seriously and follow the instructions of local authorities
If there's an attack, leave the area as soon as it's safe. Avoid the affected area in case of secondary attacks.
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
More information:
North Caucasus
There's a high threat of terrorism in parts of the North Caucasus, including:
- North Ossetia
- the south-eastern part of Stavropol bordering Chechnya
- Karbardino-Balkaria
- Karachay-Cherkessia
Terrorist attacks continue to occur in Chechnya. Several people have been killed and injured.
Our ability to provide consular assistance to Australians in those parts of the North Caucasus is limited.
If, despite our advice, you travel to these parts of the North Caucasus:
- monitor local conditions via media and travel operators
- arrange personal security measures
Georgia-Russia border
The Georgia-Russia border area is volatile because of tensions in Georgia.
If, despite our advice, you travel in the border region, read our Georgia travel advice .
Security situation
Security incidents, such as drone attacks and explosions, often occur in southern and western areas of Russia, including regions bordering Ukraine, Moscow, and St Petersburg. This can cause significant flight delays and flight cancellations. You shouldn't attempt to travel to the Russia-Ukraine border or cross into Ukraine from Russia.
The security situation could deteriorate further with little warning. If you're in Russia, leave immediately using the limited commercial options available or private means if it's safe to do so. Departure routes from Russia may become disrupted at short notice. If you decide to stay in Russia, review your personal security plans. You're responsible for your own safety and that of your family.
The Russian Government has introduced a 'medium response level' in several regions of Russia, including Krasnodar, Belgorod, Bryansk, Voronezh, Kursk, and Rostov and a 'heightened preparedness level' in the remainder of the Central and Southern Federal districts. A basic readiness level has been introduced in the rest of Russia. There may be an increase in security personnel and installations. Security measures or restrictions may be introduced with little to no notice. Monitor the media for developments.
Ukraine border areas and Crimea
The Russia-Ukraine border is volatile due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Security incidents regularly occur in Belgorod, Bryansk, Kursk and other regions of Russia bordering Ukraine, including explosions and large fires. The security situation in the region could deteriorate at short notice. You shouldn't travel to the Russia-Ukraine border or cross into Ukraine from Russia.
We currently advise you do not travel to Ukraine due to the volatile security environment and military conflict. Read the Ukraine travel advice for more information.
The Australian Government doesn't recognise Russia's claimed annexation of the Ukrainian region of Crimea or its other territorial claims in occupied Ukraine.
Leaving Russia
Where it's safe to do so, you should leave Russia immediately. Use your judgment to decide the best time and safest means of exit.
Transport routes may be disrupted. Plan for delays at land border crossings. Expect disruption to travel and changes at short notice. Make sure you have an adequate supply of food, water, medication and fuel. Make sure you have payment options that will work during your journey and at your destination.
Read your destination's travel advice to ensure you meet the entry requirements. These may differ when entering by road, rail or air. Be aware that some borders may close without notice. Commercial travel routes between Russia and Europe have been impacted by measures taken in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Check with your airline or travel agent for current flight availability. Any travel options you pursue are at your own risk. See ' Travel '
For more information on entry requirements for countries bordering Russia, read the travel advice:
The European Union also has a website with information on travel restrictions for people seeking to enter member states .
If you decide to stay in Russia:
- follow the instructions of authorities
- ensure your travel documents are up-to-date, and keep your passport and other travel documentation safe
- contact your family and friends in Australia so they're aware of your location and situation
- keep up to date with developments on the security situation, monitor reputable media, and regularly check our travel advice and social media
- review your personal security plans and make contingency plans to leave as soon as you judge it safe to do so
- always be alert and aware of your surroundings
- avoid large gatherings and areas with groups of fighters and military equipment.
Civil unrest and political tension
Russia's parliament has passed laws that severely restrict free speech related to the current situation. Foreign journalists and other media workers in Russia may face considerable risks, including arrest and imprisonment.
While the effects of this law are still unclear, you may be detained or fined for:
- sharing or publishing information that local authorities deem false
- sharing or publishing information that may be detrimental to the armed forces
- calling for, sharing or publishing speech in support of sanctions against Russia
You should not:
- share or publish information related to the current events in Ukraine and Russia
- participate in demonstrations and large gatherings
Russian authorities may adopt a more negative attitude towards foreigners in Russia due to perceived support for Ukraine and sanctions on Russia. Russian authorities may enforce local laws in an arbitrary manner. You may be interrogated without cause by Russian officials and may become a victim of harassment, mistreatment, and extortion.
Avoid commenting publicly on political developments.
Anti-war and anti-mobilisation protests have taken place in cities across Russia over the invasion of Ukraine. Many protesters have been arrested.
Unsanctioned protests are illegal, and you can be arrested if you participate. Remain vigilant and avoid rallies, protests, demonstrations and other large public gatherings, as they can turn violent, and you may be arrested.
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Theft and assault
Petty crime, pickpocketing and mugging is common. Groups of children sometimes commit crimes, too.
Hot spots for crime include:
- the Izmailovsky Market
- other tourist attractions
- the Moscow and St Petersburg metros
Thieves often steal passports. They target travellers in robberies and assaults , particularly in large cities.
To protect yourself from theft and assault:
- keep your personal belongings close, particularly in tourist areas
- be aware of your security in public places, particularly at night
- monitor local media on crime
- racially or religiously motivated assaults may occur throughout Russia.
Drink spiking
Criminals may drug and rob travellers at nightclubs and bars. Sometimes this happens after people accept offers of food, drink or transportation from strangers.
To protect yourself from spiking-related crime:
- never accept food or drinks from strangers
- don't leave drinks unattended
- leave your drink if you're not sure it's safe
- stick with people you trust in bars, nightclubs and taxis
- don't accept offers of transport from strangers
- Partying safely
Using taxis
People have reported extortion and robbery while taking unauthorised taxis.
To protect yourself from robbery while travelling in taxis:
- only use official taxi companies
- always book your taxi in advance
- don't flag down taxis on the street
- don't share taxis with strangers
- always negotiate and confirm the fare before you get in a taxi
Credit card and ATM fraud
Credit card and ATM fraud is common.
To protect yourself from fraud:
- only exchange currency at banks
- keep your credit card in sight during transactions
- only use ATMs inside banks and during business hours
- always hide your PIN
Other scams
Criminals may try to cheat you by changing money in the street or a bank queue.
Some Australians have been victims of fraud by bogus internet friendship, dating and marriage schemes operating from Russia.
These are large-scale, well-organised scams .
Criminals arrange to meet people through internet dating schemes or chat rooms. After getting to know each other, the criminal asks the Australian to send money so they can travel to Australia. However, the relationship ends after the money has been received, and the funds can't be recovered.
Be wary of people you meet through internet dating schemes or chat rooms.
People have also reported harassment, mistreatment and extortion by police and other local officials.
If you suspect you're being extorted by a police officer or other local official, offer to walk with them to the nearest police station. Once there, you can check their identity and their demands.
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
More information:
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Kidnapping is common in parts of the Northern Caucasus.
It can be for:
- political purposes
- retribution
Foreigners have been targeted in the past.
If, despite the risks, you travel to an area where there is a particular threat of kidnapping:
- get professional security advice
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
Climate and natural disasters
Severe weather during winter can disrupt travel in Russia.
To protect yourself from accidents caused by severe weather:
- take care when walking in snowy, icy or windy conditions
- take care when driving
- use appropriate driving equipment, such as winter tyres or chains
- monitor the media and other sources for updates
If you're delayed, contact local authorities about a visa extension if required.
In April, severe flooding affected multiple settlements across Russia in the South Urals region east of Moscow, in Western Siberia and near the Volga River.
Snow and ice
People are injured or killed yearly in wind, snow and ice-related accidents. These include:
- traffic accidents
- collapsed roofs and snow falling from roofs
- falling debris
- prolonged exposure to extreme cold
Slipping on ice can result in serious injuries, such as broken bones, back injuries or paralysis.
During summer, forest and peat fires can occur in Russia, including in the Moscow region.
Earthquakes and tsunamis
The North Caucasus and the far eastern region of Russia can experience earthquakes .
Tsunamis are common in all oceanic regions of the world.
To protect yourself from natural disasters, take official warnings seriously.
If a natural disaster occurs, follow the advice of local authorities.
Get updates on major disasters from the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System .
Travel insurance
Most Australian travel insurance policies won't cover you for travel to Russia. Do not travel to Russia. See ' Safety '
If you're not insured, you may have to pay thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.

Physical and mental health
Do not travel to Russia. If, despite our advice, you travel to Russia, consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least eight weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice (World Health Organization)
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Medications
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
Russia has imposed temporary restrictions on exporting certain categories of goods, including foreign-made medical products.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in Russia. Take enough legal medication for your trip.
Russia has strict laws about the import and use of medications. This includes medications that are available over the counter in Australia, such as cold and flu tablets.
When you arrive in Russia, you must present a doctor's letter to authorities confirming your need for each medication. This is the case if your medications contain the following:
- barbiturate
- sibutramine
- anabolic steroids
- androgens and other sex hormones
- analgesic, such as tramadol
- psychostimulants
- other restricted substances
The letter must:
- contain a description of the medication, including the chemical composition
- describe the required dosage
- explain the underlying medical condition
- confirm the medicine is for personal use only
- be signed by your treating doctor
You must also have a notarised translation of the letter into Russian.
Before you leave Australia, contact the Embassy of Russia for the latest rules for bringing medicines into Russia.
- Russian Government website
Health risks
Tick-borne diseases.
Tick-borne encephalitis (World Health Organization) and other tick-borne diseases are a risk, especially if you travel through forested areas.
Ticks are common in rural areas from spring to autumn: April to October.
People have reported increased incidents of tick-borne encephalitis.
Measles cases can routinely occur in Russia, with the country currently experiencing increased measles activity. Make sure your vaccinations are up-to-date before you travel.
- Measles immunisation service (Department of Health and Aged Care)
Bird flu (avian influenza)
Avian influenza is a risk in Russia.
HIV/AIDS is a risk.
Take steps to reduce your risk of exposure to the virus.
There has been a reported increase in rabies across Russia.
Rabies is deadly. Humans can get rabies from mammals, such as:
- other animals
If you're bitten or scratched by a dog, monkey or other animal, get treatment as soon as possible.
Other health risks
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases are common, including these listed by the World Health Organization:
- tuberculosis
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid uncooked and undercooked food, such as salads
- avoid unpasteurised dairy products
Get urgent medical attention if you have a fever or diarrhoea or suspect food poisoning.
Medical facilities
Public medical facilities in Russian cities are below Australian standards.
Standards are extremely basic in rural areas.
There are a few international-standard private facilities in major cities – these clinics can be very expensive to access.
Before you're treated, private facilities need either:
- up-front payment
- evidence of adequate insurance
- a written guarantee of payment
If you become seriously ill or injured, you'll need to be evacuated to get proper care. Medical evacuation can be very expensive.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
In July, the Russian President signed a decree banning gender changes, including gender transition surgery, hormone therapy and changing gender on official documents without medical requirements. The law also annuls marriages in which one person "changed gender" and prevents transgender couples from adopting children.
In November 2022, Russia's parliament passed a law banning "LGBT propaganda", criminalising any act regarded as an attempt to promote what Russia calls "non-traditional sexual relations". Sharing information or public display of any material promoting "non-traditional relationships" is now a serious criminal offence.
In November 2022, Russia announced that the partial mobilisation of military reservists for the conflict in Ukraine was complete. However, a decree formalising the completion has not been issued. The Russian Government may subject males it regards as Russian to mobilisation, regardless of any other citizenship held. Laws introducing heavy penalties for 'crimes against military service' have been passed. The Australian Government will not be able to intervene if you are subjected to mobilisation.
The US Government issued travel advice in March 2022 advising that Russian security services have arrested US citizens on spurious charges, singled out US citizens in Russia for detention and/or harassment, denied them fair and transparent treatment, and have convicted them in secret trials and/or without presenting credible evidence. The US Government warns that Russian officials may unreasonably delay consular assistance to detained US citizens.
Russian authorities have introduced criminal liability for publishing and distributing 'deliberately misleading' information about the Russian armed forces and any military operations. These laws have been interpreted and applied very broadly to many forms of dissent.
Law enforcement agencies in Russia cooperate closely with agencies in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries. If you commit an offence in one of these countries, you may be detained in another (including at the border) and extradited for prosecution.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Russian authorities imposed restrictions on real estate and foreign currency transactions for foreign residents. These restrictions can be revised at short notice. Seek advice from local authorities.
Possessing, selling, consuming, or carrying any illegal drugs is illegal.
Penalties are severe and include long prison terms.
Russia has strict rules around medication carried into the country for personal use, including some medications that you can get over the counter in Australia.
If you don't declare restricted medications, authorities could detain you. See Health .
- Carrying or using drugs
Routine police checks are common in public places.
Carry your passport, visa and migration card with you at all times. Authorities won't accept copies.
If you can't provide travel documentation on request, authorities can detain and fine you.
In Russia, it's illegal to:
- take photos of military places, strategic sites and other sensitive areas, such as passport control and guarded railway sites
- use commercial film, television or camera equipment in public areas without permission, but hand-held home video cameras are allowed
- use drones without permission from the Russian aviation authority.
Penalties for breaching the law include fines, jail and deportation.
Russia regulates religious activity. Authorities restrict activities such as preaching and distributing religious materials.
If you plan to engage in religious activity, ensure you're not breaking local laws.
Contact the Embassy or Consulate of Russia for more information.
Cybersecurity laws
Russia has blocked or restricted some social media platforms and websites, including Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn and Twitter.
Russia has banned certain Virtual Private Networks (VPN) and has indicated it will implement a nationwide ban on VPNs in March 2025.
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
- Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technology and Mass Media (Roskomnadzor)
Official documents
Some Australian documents, such as birth or marriage certificates, need to be legalised before Russian authorities will accept them.
If you have an Australian document that you need to use while in Russia, contact the Embassy or Consulate of Russia for information.
Apostilles and some legal certificates can be issued by:
- DFAT in Australia
- Australian embassies and high commissions overseas
Surrogacy laws
Russia has laws governing child surrogacy and has passed legislation banning surrogacy for all foreigners except those married to Russian citizens. Recent court cases have resulted in long custodial sentences for some providers of surrogacy services. All children born through surrogacy in Russia are granted Russian citizenship, regardless of their parent's citizenship.
Get independent legal advice before making surrogacy arrangements in Russia or with residents of Russia.
- Going overseas for international surrogacy
- Going overseas to adopt a child
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law and respecting customs
Dual nationality
Russia doesn't recognise dual nationality.
In November 2022, Russia announced that the partial mobilisation of military reservists for the conflict in Ukraine was complete. However, a decree formalising the completion hasn't been issued. Russia may subject males it regards as Russian to mobilisation, regardless of any other citizenship held. Laws introducing heavy penalties for 'crimes against military service' have been passed. The Australian Government won't be able to intervene if you are subjected to mobilisation.
Conscription occurs regularly, and Russia may subject males it regards as Russian to mandatory conscription, regardless of any other citizenship held. Conscription in Russia occurs semi-annually, and conscripts typically serve one year. From 1 January 2024, the maximum conscription age will change from 27 to 30 years old. Russian authorities have also passed laws allowing for the draft notice to be serviced to the conscripts online and preventing conscripts from leaving the country once the notice is registered and sent.
Russian authorities won't recognise your Australian nationality if you're a dual national. They will treat you like any other national of Russia.
If you're a dual national:
- you must enter and leave Russia on a Russian passport
- you can enter Russia using a repatriation certificate (svidetelstvo na vozvrashcheniye) if you don't have a Russian passport, but you must still leave Russia on a Russian passport
- you must declare any other nationalities or foreign residency permits to the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs
- you could be conscripted into the Russian military if you're a male between the ages of 18 and 30
If you're a dual national, this limits the consular services we can give if you're arrested or detained.
Contact the Embassy or Consulate of Russia well before any planned travel to Russia.
Dual nationals can't leave Russia without a valid Russian passport.
You'll need to get a new Russian passport before you leave if:
- your Russian passport expires while you're in Russia
- you enter Russia using a repatriation certificate
Getting a new Russian passport for non-residents is complex and can take up to 3 months. The Australian Government is unable to intervene or fast-track this process.
Children born outside Russia and added to their parents' Russian passports need their own passport to leave Russia.
If you're travelling alone with a child, Russian border authorities may require the following:
- documentary evidence of your relationship to the child
- written permission for the child to travel from the non-travelling parent
- Dual nationals
Local customs
Same-sex relationships are legal in Russia but not widely accepted.
Intolerance towards the LGBTI community is common, particularly outside Moscow and St Petersburg.
People have reported violence against members of the LGBTI community, including by local security forces.
In April 2017, there were reports of arrests and violence against LGBTI people in Chechnya.
In November 2022, Russia passed a law banning "LGBT propaganda", criminalising any act regarded as an attempt to promote what Russia calls "non-traditional sexual relations". Sharing or displaying material promoting "non-traditional relationships" is now a serious criminal offence. The bill broadens the existing law banning the promotion of 'non-traditional sexual relationships' to minors.
- Advice for LGBTI travellers
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Australia and other countries have placed sanctions on Russia. Russia's response to these sanctions may disrupt travel and affect travellers.
You need a visa to enter Russia unless you're travelling on certain commercial cruise ships.
You can't get a visa on arrival.
If you arrive in Russia without a valid visa, authorities will fine, detain and deport you at your own expense. They may bar you from re-entering.
Make sure you apply for the correct visa type, such as 'tourist' and 'visitor' visas.
If your visa type doesn't match the purpose of your visit, authorities may:
- not let you enter
You may need to provide biometric fingerprints for the visa application process.
After you get your Russian visa, check your passport details are correct, including the following:
- passport number
- date of birth
- intention of stay
- validity dates
If there are errors, return your passport to the Russian Embassy or Consulate for correction.
It's impossible to amend visa details once you're in Russia.
Discuss your travel plans with your cruise operator before you travel to check if you need a visa.
Check transit visa requirements if you transit through Russia to a third country.
- Russian Embassy
- Going on a cruise
Border measures
If, despite our advice, you decide to enter Russia, expect thorough security checks at the border, including questioning and inspections of electronic devices.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest embassy or consulate for details about visas, currency, customs and quarantine rules.
Australians sanctioned by Russia
The Russian Foreign Ministry issued statements on its website advising that, in response to Australian sanctions, the Russian Government had added several Australians to a 'stop list', denying them entry into Russia on an indefinite basis.
These statements can be viewed here (copy and paste the URL into a new browser if you can't open the link):
- 17 April 2024 statement – https://www.mid.ru/ru/foreign_policy/news/1944697/ (in Russian)
- 21 June 2023 statement - https://mid.ru/en/foreign_policy/news/1890258/
- 16 September 2022 statement - https://mid.ru/ru/foreign_policy/news/1830085/ (in Russian)
- 21 July 2022 statement - https://www.mid.ru/en/foreign_policy/news/1823204/
- 16 June 2022 statement - https://www.mid.ru/en/foreign_policy/news/1818118/
- 7 April 2022 statement - https://www.mid.ru/en/foreign_policy/news/1808465/
DFAT can't provide advice on the implications of another country's sanctions. If you're listed, you should obtain legal advice if you have concerns about the potential impacts of the Russian sanctions. Do not travel to Russia if you're on Russia's 'stop list'.
Other formalities
Migration card.
All foreign visitors receive a migration card on arrival in Russia.
If you receive a paper migration card, keep the stamped exit portion of the card with your passport.
The migration card covers both Russia and Belarus. You must show the stamped card to passport control when leaving either country.
If you lose your migration card:
- your departure could be delayed
- you could be stopped from staying at a hotel in Russia
You can get a replacement from the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs, which is complex and could delay your departure.
Biometric fingerprinting
Foreign citizens entering Russia for work or intending to stay over 90 calendar days may be subject to biometric fingerprinting and regular medical check-ups. The procedure of biometric fingerprinting will need to be done only once. Medical check-ups will need to be re-taken upon the certificate's expiry (valid for 1 year).
Travel with children
If you're travelling with a child , you may need to show evidence of parental, custodial or permission rights. This is particularly the case for dual nationals. See Local laws
- Advice for people travelling with children
Electronics
The government strictly controls the import of electrical and some high-technology equipment.
The rules are complex.
You may import terminal global positioning systems (GPS) devices if you declare them on arrival. However, you'll need a special permit to import a GPS device connected to a computer or an antenna.
Authorities can detain you if you don't have a permit.
You must show proof of advanced approval to import a satellite phone. Request approval from the Federal Service for the Supervision of Communications .
Russian border officials can demand to inspect any electronic device, including installed software when you leave.
Travel between Russia and Belarus
Do not travel to Russia and Belarus due to the security environment and impacts of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. If you’re in Russia or Belarus, leave immediately using the limited commercial options available or private means if it's safe to do so.
If, despite our advice, you decide to enter Belarus from Russia, note that the government doesn't allow foreigners to cross the land border between Russia and Belarus.
If you travel between Russia and Belarus, it must be by air.
If you're travelling between Russia and Belarus, you must have visas for both countries.
Visa-free entry into Belarus doesn't apply to travellers arriving from or travelling to Russia.
Contact the Embassy of Russia and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Belarus for details.
Registering your stay in Russia
If you stay more than 7 working days, including your arrival and departure day, you must register with the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs.
You have to pay a registration fee.
Most hotels do this for their guests, but you're legally responsible. Confirm with check-in staff on arrival that they've registered you.
The registration process can be complex if you're not staying at a hotel.
Register at the nearest post office if you're travelling on a visitor visa.
Register through your employer if you're travelling on a visa that lets you work. Confirm with your employer that they've registered you.
If you don't register, authorities can fine you or delay your departure.
- The Russian Embassy
Visa overstays
Make sure you leave Russia before your visa expires. Some visas, including tourist visas, can't be extended.
If you overstay your visa, you won't be allowed to leave Russia until the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs determines your legal status or deports you.
Authorities can detain you until they've processed your case.
Penalties for overstaying include fines and deportation.
You may be banned from re-entering.
Exporting goods
Russia has imposed temporary restrictions on exporting certain categories of goods, including foreign-made medical products. Seek advice from local authorities.
Russia has strict regulations on the export of antiques, artworks and items of historical significance. This is for items purchased in Russia or imported to Russia from overseas. It includes modern art and posters if they are particularly rare or valuable.
Authorities may not allow the export of items more than 100 years old.
If you want to export any antiques, artworks or items of historical significance:
- keep receipts of your purchases
- obtain an export permit from the Ministry of Culture in advance of travel — export permits aren't issued at the airport
- declare each item to border authorities when you leave Russia
- be ready to show each item to border authorities
- be ready to show receipts for each item to border authorities
Don't try to export items requiring permits without the relevant paperwork. This is a serious offence.
Legislation about the export of artwork and antiques from Russia may change without warning.
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for six months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than six months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
If your passport is lost or stolen while ashore, you will need to obtain an emergency passport and an exit visa to leave Russia within the 72-hour visa-free period. If it’s not done within 72 hours, you will face a court hearing and possible fine, deportation and entry ban.
To arrange a new visa:
- obtain an official police report
- apply for a replacement passport through the Australian Embassy in Moscow
- apply to Russian authorities for an exit visa
- include the police report with your application
If you replace your passport while in Russia, make sure authorities transfer your visa to the new passport.
Passport with 'X' gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can't guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
More information:
- LGBTI travellers
The currency of Russia is the Rouble (RUB).
Russian authorities have imposed temporary restrictions on the export of foreign currency in cash out of Russia. Travellers exiting Russia can't take more than the equivalent of $US10,000 in cash.
Make sure a customs official stamps your declaration. Only stamped declarations are valid.
You must carry proof that your funds were imported and declared or legally obtained in Russia.
Due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine, Mastercard, Visa, and American Express have suspended operations in Russia. Cards issued outside of Russia will not work at Russian merchants or ATMs. Cards issued inside Russia may continue to work, but they won't work outside Russia. It may not be possible for you to access your funds through Russian banks or to make payments to Russian businesses with non-Russian credit/debit cards. Be prepared with alternate means of payment should your cards be declined.
You may not be able to exchange Australian dollars as well as old, worn or damaged US dollar and euro banknotes into Russian rubles in Russia. Ensure you have enough money to cover your stay in Russia.
Traveller's cheques aren't widely accepted, even in Moscow and St Petersburg.
Local travel
Postal services between Russia and Australia are temporarily suspended.
More information
- Australia Post website
Confirm with your transport operator that services are still operating if you plan to depart Russia. Commercial travel routes between Russia and Europe are disrupted. Expect thorough security checks at the border, including questioning and inspections of electronic devices.
Flights between Russia and Europe have been affected by measures taken in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Several Russian airports are now closed to the public, disrupting internal flights to and from Moscow and other cities. The train and bus service between St Petersburg and Helsinki is suspended.
Finland has closed border crossings with Russia indefinitely and maritime borders will close on 15 April.
Latvia introduced an entry ban on vehicles registered in Russia in September 2023. More information can be found on the State Revenue Service website . There's a ban on vehicles crossing into/from Estonia at the Ivangorod-Narva crossing. Train service is also suspended. Entry and exit on foot will still be allowed. Additional restrictions or entry requirements could be imposed or changed suddenly. Be aware that some borders may close without notice.
If you're travelling through an overland border crossing into Estonia or Latvia , confirm the entry requirements for your destination before arrival.
Australia and other countries have placed sanctions on Russia. Russia's response to these sanctions may disrupt travel and affect travellers. Confirm entry requirements for your destination before arrival, as additional restrictions or entry requirements could be imposed or changed suddenly.
If, despite our advice, you decide to go to Chechnya or the North Caucasus, you must first get permission from the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs.
Several other areas of Russia, especially in Siberia and the Russian Far East, are also 'closed' areas.
Foreigners need government permission to enter 'closed' areas.
If you need government permission or are unsure if you need it, contact the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs.
Driving permit
You should carry an International Driving Permit (IDP).
You may drive with an Australian driver's license if you carry it with a notarised Russian translation.
Road travel
Driving in Russia can be hazardous due to:
- poor driving standards
- ice and snow in winter
- poor road conditions in rural areas
The blood alcohol limit for drivers is 0%.
- Driving or riding
- the Russian Embassy
Some taxis appear official but aren't licensed by local authorities.
People have reported extortion and robbery while taking unauthorised taxis. See Safety
Book an official taxi by phone, at major hotels and from inside airports.
Flights from Russia to other countries are limited. These may change or be suspended at short notice. You should contact airlines or travel agents directly for the most current information.
The EU announced that 21 Russian-owned airlines were banned from flying in EU airspace due to safety concerns.
Russian airlines and railways may be affected by shortages of parts and essential technical components for their fleets, affecting maintenance and safety standards. If you're flying domestically or internationally, research your aviation provider before choosing their services.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Russia's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy in Moscow. Our ability to provide consular assistance in Russia is limited. The Australian Government will not be able to evacuate you from Russia.
Australian Embassy, Moscow
13 Kropotkinsky Pereulok Moscow 119034 Russia Phone: (+7 495) 956-6070 Fax: (+7 495) 956-6170 Website: russia.embassy.gov.au Twitter: @PosolAustralia
If you're in St Petersburg, you can also contact the Australian Consulate for limited consular help.
Australian Consulate, St Petersburg
Moika 11 St Petersburg 191186 Russia Tel: (+7 964) 333 7572 (NOT for visas) Email: [email protected] (NOT for visas)
Check the Embassy website for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
Australians in need of consular assistance should contact the Australian Government 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Russia?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Slovenščina
- Science & Tech
- Russian Kitchen
FAQ: How to travel to and from Russia right now
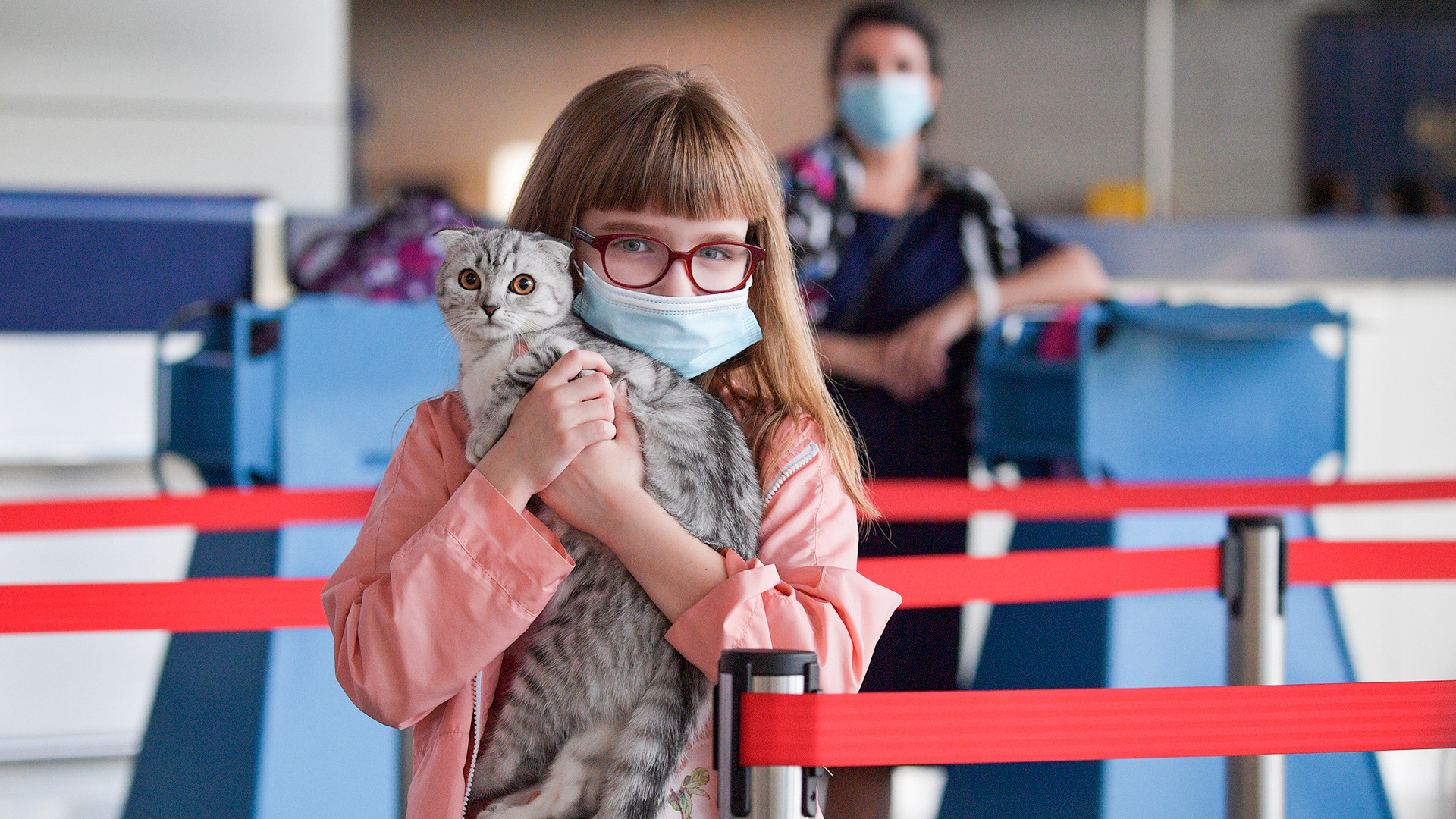

A girl holds a kitten in her arms in one of the terminals at Vnukovo international airport
Who can enter Russia
At the time of writing, Russia has opened its borders for citizens of the following countries:
- Great Britain
Citizens of these countries can freely enter and leave Russia subject to visa regulations. That is, citizens of the UK, Tanzania and Turkey need to obtain a visa prior to arrival in Russia. As for Abkhazia and Belarus, Russia has a visa-free regime with these countries.
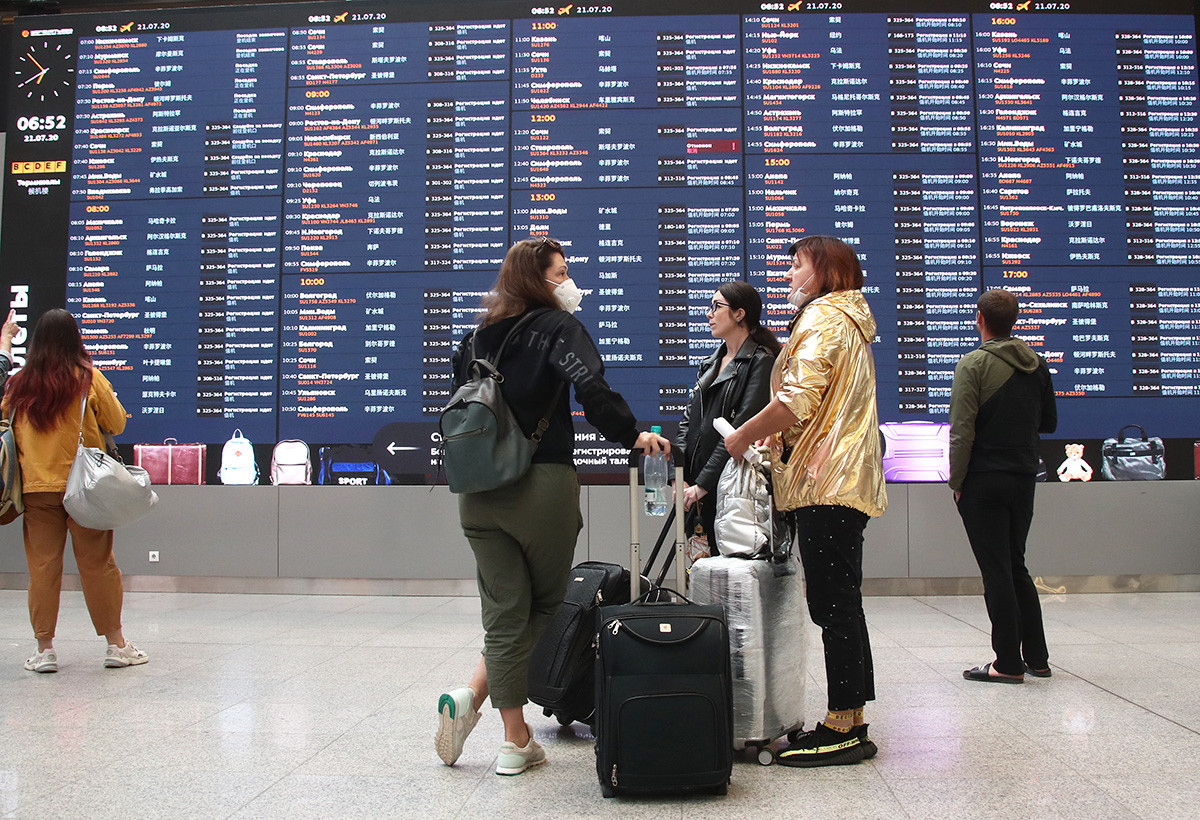

People near an information board at Terminal B at the Sheremetyevo International Airport near Moscow during the pandemic of the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19), july 21,2020
Additionally, on August 2, 2020 Russia opened its borders for Swiss nationals, but international flights to and from Switzerland will only resume on August 15. Flights will be operated once a week on the Moscow-Geneva-Moscow route.
Nationals of other states can also enter Russia if they:
- are family members of Russian citizens (family members include spouses, parents, children, carers and guardians). Grandparents and siblings are not included on the list. When applying for a visa, you will need to provide documents showing proof of kinship;
- have permanent residency in the Russian Federation. A temporary Russian residence permit is not accepted;
- are travelling to attend the funeral of a close relative. To enter the country, they will need to provide the death certificate and documents showing proof of kinship;
- are travelling to look after close relatives. To enter the country, they will need medical certificates and documents showing proof of kinship;
- are travelling to Russia for medical treatment. To enter the country, they will need to provide a certificate issued by a Russian state-run or private clinic. The document must state the date of the medical appointment, the patient’s full name, the name of the procedure and also the particulars and stamp of the medical organization.
There are several categories of foreign nationals to whom Russia has not prohibited entry. They include:
- Employees of consular establishments in the Russian Federation;
- Truck drivers delivering goods to Russia;
- Members of official delegations and persons who hold official visas;
- Aircraft crews, sea and river vessel crews and train and locomotive crews of international railway services.
In all other cases, crossing the border of the Russian Federation will be regarded as illegal. People violating this law can be fined up to 200,000 rubles (approx. $2,668) or face compulsory labor or imprisonment for up to two years.
No travel without a certificate

Passengers queue for rapid COVID-19 testing launched at Vnukovo International Airport with the use of testing kits developed by the Russian-Japanese joint venture Evotech-Mirai Genomics. The results are issued in 60min in Russian and English, August 7,2020
On July 27, 2020, Anna Popova, the head of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare (Rospotrebnadzor), signed an instruction under which all foreigners coming to Russia must, on boarding their flight, have a certificate confirming they have tested negative for Covid-19.
The certificate must be issued no more than three days prior to arrival in Russia and the document can be printed in either Russian or English.
There is no longer a mandatory two-week period of self-isolation on arrival in Russia - Popova lifted that requirement from July 15, 2020.
Traveling out of Russia

People who have arrived from New York City on an Aeroflot - Russian Airlines flight, carry their luggage at the arrivals area of Sheremetyevo International Airport. June 17.2020
The following categories of citizens can also travel out of the country:
- Persons with dual nationality;
- Persons with permanent residency in another country;
- Citizens in possession of a work visa or a visa issued for medical treatment in another country.
Resumption of air travel and flight cancellations
Despite the lifting of restrictions on travel to and from Russia, Russian passenger airlines have started to experience problems with international flights.
From early June, the Russian flagship carrier Aeroflot was selling tickets for flights from Moscow to dozens of cities, including Frankfurt am Main, Paris, London, New York, Rome, Seoul and Tel Aviv.
Another large airline, S7, is also operating flights from Moscow to Alicante and Nice, and promised to resume flights to Turkey from August 10.
Aeroflot was suspected of illegally selling tickets to countries with which air links remain restricted. This was pointed out by the Federal Antimonopoly Service.
As a result, on August 6, 2020, Aeroflot announced the cancellation of practically all of its international flights. A full list of cities to which the airline will not be operating flights up untilAugust 31 has been published on the air carrier’s website.

A stewardess wait outside the Sheremetyevo A.S. Pushkin international airport following the easing of the coronavirus restrictions, outside Moscow, Russia
According to the Russian Federal Air Transport Agency’s (Rosaviatsiya) website, the majority of Russian airlines are primarily planning to resume flights to Turkey, which is a popular summer vacation destination among Russians.
“The number of regular and charter flights to Turkey is to be significantly increased from August 10. Russian carriers Sibir, Ural Airlines, Royal Flight, Nordwind Airlines, Azur Air, Rossiya Airlines and iFly are all planning to commence flights,” the air regulator’s website says. Flights to Moscow by international air carriers Turkish Airlines and British Airways are also expected to resume.
If using any of Russia Beyond's content, partly or in full, always provide an active hyperlink to the original material.
to our newsletter!
Get the week's best stories straight to your inbox
- Coronavirus has closed Russia’s borders. What next for foreigners stuck in Russia?
- 5 most controversial monuments in Moscow
- E-visas covering all of Russia to be introduced in 2021
This website uses cookies. Click here to find out more.
Advertisement
Supported by
Changed Itineraries, Higher Fares: How the War in Ukraine Is Affecting Travel
How travelers feel the effects of Russia’s assault on Ukraine depends largely on where they’re going, though the price of oil will weigh on all airfares, even domestic.
- Share full article

By Elaine Glusac
Just as the travel industry was seeking to climb out of a two-year depression, Russia’s assault on Ukraine has scrambled schedules and given Americans pause as they consider international vacations.
The extent to which travelers will feel the effects of the war depends on where they’re going, though experts say the rising price of oil will likely affect all airline ticket prices, even on domestic routes.
For Americans with international plans, the world map, which recently seemed to be expanding with the relaxation of Covid restrictions in many countries, has shrunk anew. Operators have largely scrapped travel in Russia for the rest of the year, which greatly affects Baltic cruise itineraries where the marquee port of call was St. Petersburg.
All of this comes at the time of year when many Americans plan their summer vacations. Some are hesitating. In a recent survey of about 350 American travelers on the impact of the war, the market research firm MMGY Global found that 47 percent are waiting to see how things pan out in Ukraine before making Europe plans. The conflict leapfrogged Covid-19 as a factor influencing decision-making, with twice as many respondents citing concern about the war spreading beyond Ukraine as those who fear the pandemic.
So far, travel companies are not seeing mass cancellations as travelers, who may have been conditioned to remain flexible by the pandemic, are sticking to their resolve. Nearly 65 percent of American adults surveyed by TheVacationer.com , a travel strategy website, said they would accept higher prices, longer transit times or another deterrent in order to travel in 2022.
“We’re not seeing a change in behavior for now from our American travelers,” said Sarah Casewit, a senior travel curator with Origin , a membership-based travel-planning service, which has seen a rise in Europe bookings in recent weeks.
Whatever inconveniences travelers experience is, of course, nothing compared to the suffering inflicted on Ukrainians. Many travelers want to support Europeans who have been hoping for a robust summer season, but do not want to complicate humanitarian efforts to help war refugees.
Given the unpredictability of the war, travelers will need to remain flexible as flight operations, cruises and tours adjust to the conflict.
Turbulence in the air
No commercial carriers from the United States fly to Russia, and those with code-share and interline agreements with Russian carriers, including Delta and American, have cut them.
But the Federal Aviation Administration’s prohibition on flying over Ukraine, Belarus and much of Russia requires some routes to make costly diversions. For commercial flights departing from the United States, these routes are largely limited to India, which only reopened to tourists in mid-November. United Airlines has temporarily suspended service between San Francisco and Delhi and between Newark and Mumbai, though it is continuing service to Delhi from Chicago and Newark.
Rerouting to avoid Russian airspace on Asia flights by flying lower latitude routes over Alaska adds to the cost of operating those flights, said Robert Mann, an airline consultant, who estimated an extra hour of flight time can add up to $12,000.
Those aren’t the only additional expenses that will be passed on through higher ticket prices. The rising cost of oil, expected to rise even more after the Biden administration banned Russian oil imports, is contributing to higher airfares.
But for now, interest in Europe remains high among fliers. The airfare app Hopper found prices on Europe-bound flights from the U.S. have risen 16 percent since mid-February, from $660 to $763 round trip, which it attributes to post-Omicron travel enthusiasm and the usual seasonal cycle of rising prices.
Chelsea Randall and Jacob Meziani became digital nomads during the pandemic — they both work in information technology — living in 16 cities in North America in the past year. In April, the engaged couple plan to move to Europe for several months, first traveling to Portugal and then Poland where they plan to visit Mr. Meziani’s family in Lublin, about four hours from the Russian border.
“We are going to stall a little bit, maybe a week or two, to see how it looks for surrounding countries to Ukraine since we don’t know what will happen with refugees,” he said. “If it stays the same as it is, we will book and get trip insurance or an Airbnb with a later cancellation date that can be more flexible.”
Cruises changing course
Cruise lines were counting on 2022 as their comeback year. But those that operate in and around Russia are quickly changing their routes.
From boutique lines like Silversea to big-ship specialists like Carnival , cruise lines have canceled Russian port visits. Princess Cruise Lines is modifying 24 itineraries initially scheduled to visit St. Petersburg.
“Some spend three full days there, longer than any other city in Europe,” said Samuel Spencer, the general manager of Ocean & River Cruises Travel , an agency based in Calgary, who describes the city’s attractions, such as the State Hermitage Museum and Peterhof Palace, as unmatched. “It’s a major blow.”
Nonetheless, lines are working to secure substitute ports. Oceania Cruises , which is also canceling Russian stops in Murmansk, Archangel, Vladivostok and the Solovetsky Islands, plans to add additional overnights in Copenhagen and Stockholm in place of St. Petersburg.
Outside of Russia and Ukraine, where Viking canceled its river sailings, river cruise companies largely remain committed to their European schedules.
“As we have yet to set sail for the 2022 cruise season, we have no current plans to cancel or adjust Eastern European cruises at this time,” said Pam Hoffee, the managing director of Avalon Waterways , which does not operate in Russia, in a statement.
As with pandemic-inspired travel cancellations, domestic destinations may benefit. Bookings at American Queen Voyages , which offers cruises on American rivers and lakes, shot up 30 percent in the past two weeks, which it attributed to travelers choosing domestic over European travel.
“The biggest impact I have seen are those that have a cruise booked who do not want their money to go to Russia,” said Victoria Hardison-Sterry, a Florida-based travel adviser with Lakeshore Travel who had one client switch from a Baltic cruise in 2023 to an Alaska cruise. “My clients have been outspoken about not adding to the Russian economy.”
Others are worried about traveling in neighboring regions that may be flooded by war refugees, and where the presence of tourists would be a hindrance.
In about six weeks, Mr. Spencer is slated to take a group on an AmaWaterways cruise through southeastern Europe, including traveling through Romania and ending in Budapest. “Clients were initially reassured that the route was 1,200 to 1,500 kilometers away from the Russia-Ukraine border, but that situation has changed as cities far inland have been targeted by Russia,” he said, noting Budapest is only a few hours from Ukraine. For now, the trip is on, though Mr. Spencer is following the news closely. “We travel to support local economies and interact with the cultures, but if they’re dealing with an exodus from Ukraine, we don’t want to be a burden.”
Ensemble Travel Group , a travel adviser consortium, is taking about 150 of its agents on a river cruise in Europe in April. The travelers plan to pack blankets and hygiene kits to donate to a nonprofit helping refugees while they are in Budapest with the goal of doing “something meaningful to help those impacted by this horrible situation,” said Todd Hutzulak, Ensemble’s executive director of marketing, whose grandfather is from Kyiv.
Redirecting tours
Perhaps no sector of the travel industry has been more affected than tour operators that had trips scheduled in Russia and, to a lesser extent, its neighbors.
Companies including smarTours , Kensington Tours and G Adventures have canceled upcoming trips there. Smithsonian Journeys canceled or rerouted all 2022 trips that visited Russia and said cancellations in Europe have been less than one percent since the war began. Ride and Seek, a bike tour company, plans to continue to operate its Paris-to-St.-Petersburg tour , adjusted to ride to the Russian border, then retreat to Tallinn, Estonia, for the final evening.
“Traditionally, Russia is an emerging market for us that’s growing,” said Bruce Poon Tip, the founder of G Adventures, which canceled a dozen tours in the country including its popular trans-Siberian train trips.
The company’s trips in border countries like Mongolia, the former Soviet republics of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan, and Turkey remain on the books. The conflict so far has not triggered mass cancellations.
“In regular times, clients would have said, ‘I’m not going to travel,’ but people have gone two years not traveling,” he said. “There’s a push and pull thing going on.”
Many travelers, newly unbound by Covid-19 restrictions, are sticking to their bucket-list plans. The tour company Atlas Obscura said Romania, which borders Ukraine, was among the top-selling trips in the past week.
“After two years spent close to home, our travelers are planning ambitious, far-flung trips,” wrote Mike Parker, the general manager of the company’s travel division, in an email.
Mir Corporation , a Seattle-based tour company that specializes in travel to Russia and the region — and whose name translates from Russian as “peace” and “world” — has had to cancel a “significant” number of its trips, according to Annie Lucas, the vice president. Meanwhile, trips to the southern Caucasus region, Central Asia and the Middle East are on.
“People are hesitant, of course,” she said in a call from Tbilisi, Georgia, where she travels frequently. “We are hoping the strengthening of U.S. and European efforts will lead to cease-fire negotiations to end this senseless suffering.”
Elaine Glusac writes the Frugal Traveler column. Follow her on Instagram at @eglusac .
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places list for 2022 .
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
EU plans to impose restrictions on 11 Russian ships in new sanction package
The European Commission has proposed restrictions on 11 vessels that contribute to Russia's ability to wage its full-scale war against Ukraine.
Source: Bloomberg , as reported by European Pravda
Details: If member states agree to the proposed regulations, the ships would not be allowed to enter EU ports or anchorage zones, and their logistics operations would become more challenging as they would not be able to use European companies for a variety of services.
Four fuel tankers, two oil tankers, two gas storage facilities utilised in the Novatek project for the transshipment of liquefied gas on the Kamchatka Peninsula, and a cargo ship are among the vessels that will be subject to sanctions.
Among the ships is the tanker Andromeda Star, which was discovered to have invalid European insurance after it crashed in the Baltic Sea.
These proposals are part of the EU's efforts to curb Russia's ability to circumvent price caps on Russian oil through the use of a shadow fleet.
The draft, which has been studied by Bloomberg, states that insurance and technical support will be prohibited. Additionally, European providers will not be permitted to unload cargo between ships.
The European Commission suggested targeting multiple LNG projects and outlawing the transshipment of Russian LNG from the EU to third nations as part of the same set of penalties, which will be the EU's 14th package of sanctions.
The proposal for EU sanctions may be amended before it is ultimately adopted. It has to be approved by all 27 member states.
The media previously reported that the European Commission sent EU countries a draft proposal for a 14th package of sanctions against Russia. The proposal includes, among other things, restrictions on imports of liquefied natural gas (LNG) from Russia, although there are no plans for a full embargo.
Support UP or become our patron !
Recommended Stories
Former house speaker paul ryan says he’s not voting for trump : 'character is too important'.
Ryan says he would be writing in a Republican candidate instead of voting for Donald Trump.
Biden is sending $61 billion to Ukraine. Much of it will pass through the US economy first.
Washington is spending another $61 billion to help Ukraine. But most of the money will flow through the US economy first.
Fed’s Kashkari: Rates will stay high for 'extended period' and can't rule out a hike
Minneapolis Fed president Neel Kashkari said interest rates will likely stay at current levels for an "extended period" and didn't rule out a hike if inflation stalls near 3%.
Trump trial live updates: Judge finds Trump violated gag order again and threatens jail time, while jury sees paper trail in hush money case
The former president’s criminal hush money trial resumes Monday in Manhattan, where the prosecution will continue presenting its case.
Trump wants to levy his new tariff regime 'quickly.' Here's how long it might take.
Donald Trump and his allies have made new tariffs a centerpiece of his potential second-term economic agenda. They are openly exploring legally untested options for making them a reality.
Texas Gov. Greg Abbott vows student Gaza protester demands will 'NEVER' be met. Here's how we got here.
Texas Gov. Greg Abbott said in a social media post Sunday that the University of Texas would not meet the demands of student protesters.
Iran launched 200 drones and missiles in a retaliatory attack on Israel. How we got here, and what happens next.
Here's what to know about the latest in the conflict between Israel and Iran.
Trump trial updates: Stormy Daniels describes alleged sexual encounter with Trump — and faces testy cross-examination
Adult film actress Stormy Daniels recounted the details of her alleged extramarital affair with former President Donald Trump during Tuesday’s testimony in the hush money trial.
Trump trial updates: Trump fined again for gag order violations, jury hears testimony about Cohen reimbursement payments
After Judge Juan Merchan fined former President Donald Trump an additional $1,000 for gag order violations, the jury heard testimony Monday from two Trump Organization employees about payments Trump made to his lawyer Michael Cohen.
New inflation reading reinforces Fed's higher-for-longer stance
Another hot inflation reading released Friday reinforces that any near-term interest rate cuts are less likely, as the Federal Reserve shifts to a higher-for-longer stance.
Trump trial live updates: Prosecution calls more witnesses to establish Trump ties with Stormy Daniels, Karen McDougal
The former president’s criminal hush money is set to resume in Manhattan Friday when former National Enquirer publisher David Pecker returns to the witness stand to face cross-examination by the defense.
Pro-Palestinian protests spread as hundreds arrested at Emory University, Emerson College and elsewhere across the U.S. Here's what's happening.
Pro-Palestinian protests and encampments are springing up at numerous colleges, leading to arrests and heightened security concerns. Here’s what's happening.
Kristi Noem says she shot and killed her dog. What to know about the South Dakota governor's recent controversy.
The controversial politician revealed in her new book that she killed her dog.
FCC officially votes to reinstate net neutrality
The Federal Communications Commission made its official vote Thursday to reinstate net neutrality, which bars broadband providers from slowing or even blocking internet traffic to some sites while improving access to others that pay extra fees. With some changes and protections, passing the order titled Safeguarding and Securing the Open Internet restores rules passed back during the Obama administration in 2015 and rolled back in 2017, after Donald Trump was elected president. Since the FCC announced in September that it would be pursuing this as a policy goal, it was more or less a fait accompli; there was no real reason why the Commission, split 3-2 in favor of the Democrats, would vote against it.
What does Trump need most from his running mate?
The typical rules would suggest the former president should choose someone unlike himself to round out his ticket, but typical rules rarely apply to Trump.
India's election overshadowed by the rise of online misinformation
As India kicks off the world's biggest election, which starts on April 19 and runs through June 1, the electoral landscape is overshadowed by misinformation. The country -- which has more than 830 million internet users and is home to the largest user base for social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram -- is already at the highest risk of misinformation and disinformation, according to the World Economic Forum. Misinformation is not just a problem for election fairness -- it can have deadly effects, including violence on the ground and increase hatred for minorities.
Timeline: Key legal and electoral dates for Donald Trump
In order to make sense of Trump's often-overlapping election and court dates, we’ve put together a comprehensive timeline that is constantly being updated.
Biden wants dishwashers to be more efficient. Republicans see a 'war on appliances.'
The government has been setting standards for how much energy and water household appliances use for decades, but the president’s critics say his latest rules go too far.
India urges political parties to avoid using deepfakes in election campaigns
India's Election Commission has issued an advisory to all political parties, urging them to refrain from using deepfakes and other forms of misinformation in their social media posts during the country's ongoing general elections. The move comes after the constitutional body faced criticism for not doing enough to combat such campaigns in the world's most populous nation. The advisory, released on Monday (PDF), requires political parties to remove any deepfake audio or video within three hours of becoming aware of its existence.
Ukrainian former Olympic weightlifter Oleksandr Pielieshenko killed defending his country
Oleksandr Pielieshenko joined his country's military soon after Russia's invasion, the National Olympic Committee of Ukraine said Monday.
Ukraine-Russia war: Latest updates
Ask our military analysts or international correspondents a question on the Ukraine war in the box below.
Thursday 9 May 2024 09:18, UK
- Putin: We want to avoid global confrontation, but nuclear forces ready if needed
- Home Office expels Russian diplomat who was 'undeclared military intelligence officer'
- Dominic Waghorn: Russia may have crossed the line - but UK move to expel attache increases risk of dangerous escalation
- Ed Conway : Russian oil still seeping into UK - the reasons why sanctions are not working
Ask a question or make a comment
Vladimir Putin used his Victory Day speech this morning to warn that Russia's combat forces were "always ready".
But he admitted the country was going through a "difficult period".
You can watch a segment from his speech here:
We aren't bringing you live updates today, but here is the main story this morning.
Vladimir Putin has just finished speaking at Russia's annual Second World War victory parade.
The president, now in his fifth term, said that Russia will do all it could to avoid a global confrontation, amid rising rhetoric about a face-off with NATO.
Mr Putin, however, said it would not allow any nation or alliance to threaten Russia.
As he's said multiple times since he invaded Ukraine, the Russian leader warned the West that his nuclear forces were always at a state of combat readiness.
He was addressing scores of troops in Moscow's Red Square - here are the best images from the Russian capital...
Thanks for following our live coverage, we'll be back soon with more live updates.
Kosovo's foreign minister has said her country is convinced Russia must lose the war in Ukraine for conflict not to spread further in Europe.
Donika Gervalla-Schwarz said her young nation's support for Ukraine was unconditional - despite Kyiv not having recognised Kosovo's independence.
Ms Gervalla-Schwarzd her small Balkan nation, which declared its independence from Serbia in 2008, is repeatedly reminded of the aggressive intentions of both Serbia and its ally Russia.
"Ukraine hasn't recognised the Republic of Kosovo as a state, but we really believe that we know exactly what Ukraine is going through," she told The Associated Press in an interview.
"And we know that there is only one solution, not only for Ukraine, but for Europe," she said.
"It can only be Russia to lose the war and Ukraine to win this war. Otherwise, Europe should prepare for other conflicts in our continent."
The people of Kosovo were the targets of war crimes and other atrocities by Serbia's security forces in the 1990s, an experience that led Kosovo to seek independence.
"While Kosovo is a small state with very modest possibilities to help, we have tried to be very helpful with Ukraine and have not hesitated to show our unconditional support and sympathy to the people and to the state of Ukraine," Ms Gervalla-Schwarz said.
Lord Cameron has called the UK's measures on a Russian defence attache "an unequivocal message" to Moscow.
The foreign secretary was replying to James Cleverly's post on X in which he said the Home Office expelled a Russian defence attache as part of a series of measures against the country.
Other measures in the package include removing the diplomatic premises status from several Russian owned properties in the UK and capping the amount of time Russian diplomats can spend in the UK.
Budapest is once again raising eyebrows across the world's biggest military alliance as it pledges to defy a NATO initiative.
The alliance's long-term plan to support Ukraine militarily was agreed in April, but was dubbed a "crazy mission" by Hungary's foreign minister today.
Under the plans, NATO would take over some coordination work from a US-led coalition known as the Ramstein group.
Discussing the plans today, Peter Szijjarto said: "Hungary will stay out of NATO's crazy mission despite all the pressure."
Relations between Budapest and NATO have soured because of Hungary's foot-dragging over the ratification of Sweden's NATO accession - finally passed by Budapest in March - and also over nationalist Prime Minister Viktor Orban's close ties with Moscow.
The Russian embassy in London has said there will be "an appropriate response" after Britain expelled a Russian defence attache.
The embassy said the restrictions that had been imposed were done under a "groundless and ridiculous pretext", according to Russian state news agency TASS.
It comes after Russian foreign ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova was reported as telling journalists that the Kremlin will respond appropriately following the expulsion.
Dominic Waghorn, international affairs editor
It's always assumed defence attaches play some kind of role gatherling intelligence and that is generally tolerated by their host countries.
They could be gathering data about weapons production for instance or ship building but there is a line they are expected not to cross.
The assumption here is that the Russians have broken the rules of the game.
But the British government will have thought long and hard before expelling the Russian. It doesn't come without cost.
In their day jobs defence attaches play a crucial role in liaising with their hosts. That can be very important in terms of avoiding misunderstandings that could lead to unnecessary and dangerous escalation.
Losing Russia’s defence attache in London deprives the UK of one more line of liaison at a time when clear understanding and clarification could be essential to avoiding deepening conflict.
That is not ideal at a time of war.
What is not clear is how much these moves are connected specifically to the conduct of the Russians involved or should they actually be seen more as another chapter in the diplomatic war underway between Russia and the UK.
The UK has undoubtedly weakened Russia's ability to spy in the UK and gather intelligence but these measures will also affect Britain's ability to predict and avoid potential escalation.
That will be made even worse if Russia, as may be expected, responds with like-for-like retaliation
Seven people have been injured by Russian shelling in eastern Kharkiv, according to the region's governor.
Oleg Synegubov said among those wounded was an eight-year-old girl and three boys, two aged 14 and the other 15.
"Two [of the] boys are in serious condition, [the other] boy and [the] girl are in average condition," he said.
One 55-year-old civilian of unspecified gender was also hospitalised.
Two women had minor injuries.
Defence Secretary Grant Shapps has offered his thoughts on the expulsion of a Russian defence attache the government has accused of being an undeclared military intelligence officer.
"Today we've expelled Russia's defence attache who has been working as an intelligence officer for Putin in the UK," he said on X.
"We will not tolerate Putin’s efforts to undermine our nation and democracy and will continue to stand up for freedom here and in Ukraine."
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Within days, the EU banned flights to and from Russia. As the war dragged on, the bloc went further. In early September, it suspended the 2007 visa deal. The cost of an individual visa rose from ...
Russia imposed broad travel restrictions at the start of the coronavirus pandemic in March 2020, many of which remain in force, but has gradually expanded the list of countries deemed safe for air ...
Schengen visas in the bullseye. The 26 countries making up the Schengen free movement area -- 22 EU states, Norway, Iceland, Sweden and Liechtenstein -- received 3 million visa applications in ...
Travel Advisory. September 5, 2023. Russia - Level 4: Do Not Travel. O D U T. Updated to remove COVID-specific information and the kidnapping risk indicator as well as updates to security risks. Do not travel to Russia due to the unpredictable consequences of the unprovoked full-scale invasion of Ukraine by Russian military forces, the ...
The move will be done by freezing a 2007 agreement to ease travel between Russia and Europe. The EU already tightened visa restrictions on Russian officials and businesspeople under the accord in May. Speaking after chairing the meeting in the Czech capital Prague, EU foreign policy chief Josep Borrell said that an increasing number of Russians ...
In August 2022, amid Russia's continued aggression against Ukraine, several Member States1 called for drastically restricting Russian nationals' access to Schengen visas. A third-country national in possession of a Schengen visa can enter the Schengen area2 and stay in it for a maximum of 90 days in any 180-day period.
Travel to Russia is not advised due to the lack of available flight options to return to Europe, and the increased volatility in the Russian economy. On 24 February 2022 Russia launched a large ...
Study and training opportunities for Russian citizens in the EU. Erasmus+ is the EU's programme for education, training, youth and sport for the period 2021-2027, offering EU-funded opportunities for higher education students, staff and institutions. The key aim of Erasmus+ is the learning mobility of individuals, which includes the following ...
The European Union has agreed to reduce the number of new visas available to Russian citizens, but stopped short of an outright ban on travel to the bloc.. EU foreign ministers decided Wednesday ...
The EU imposed a number of visa restrictions after Russia's invasion began on Feb. 24, including partial suspension of visa-facilitation agreements for Russian officials. In practice, most EU ...
Sanctions on individuals consist of travel bans and asset freezes. ... As part of the economic sanctions, the EU has imposed a number of import and export restrictions on Russia. This means that European entities cannot sell certain products to Russia (due to export restrictions) and that Russian entities are not allowed to sell certain ...
Crimea - Level 4: Do Not Travel. The international community, including the United States and Ukraine, does not recognize Russia's purported annexation of Crimea. There is extensive Russian Federation military presence in Crimea. Russia staged its further invasion of Ukraine, in part, from occupied Crimea, and Russia is likely to take ...
The European Union deplores the decision by Russian authorities, announced on Friday, to ban an unknown number of representatives of EU Member States and institutions from entry into Russia. This decision lacks any legal justification and transparency and will meet an appropriate response.
Level 4 Travel Advisory. The U.S. State Department currently assigns a Level 4 travel advisory (Do Not Travel) to Ukraine and Russia. This is the highest warning level and will remain until the ...
It is very limited in parts of Russia because of the security situation and the size of the country, particularly in the North Caucasus. If you need consular assistance, call our 24-hour helpline ...
Russian authorities strictly enforce all visa and immigration laws. The Embassy of the Russian Federation website provides the most up to date information regarding visa regulations and requirements. In accordance with Russia's Entry-Exit Law, Russian authorities may deny entry or reentry into Russia for 5 years or more and cancel the visas of foreigners who have committed two administrative ...
Border closing. Russia closed its borders for foreign visitors from 18.03.2020 till further notice. Here are the few exceptions: foreigners studying in Russia; diplomatic workers and members of their families; relatives of a deceased person, provided that they have documents confirming their relations; transit passengers; foreigners seeking medical treatment; international ship, cargo, train ...
Commercial travel routes between Russia and Europe have been impacted by measures taken in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Check with your airline or travel agent for current flight availability. ... Russia has imposed temporary restrictions on exporting certain categories of goods, including foreign-made medical products. ...
Russia has significantly eased the restrictions for travel to and from the country in August 2020, but the situation regarding international flights is still causing problems owing to quarantine ...
Ensemble Travel Group, a travel adviser consortium, is taking about 150 of its agents on a river cruise in Europe in April. The travelers plan to pack blankets and hygiene kits to donate to a ...
All foreign travelers arriving in Russia are required to present a certificate for a negative PCR test result taken within 48 hours of the time of their arrival. The certificate needs to be in English or Russian. Children of all ages need to obtain and present a negative COVID-19 (PCR) test result, dated within 48 hours before arrival in Russia.
The European Commission has proposed restrictions on 11 vessels that contribute to Russia's ability to wage its full-scale war against Ukraine. Source: Bloomberg, as reported by European Pravda ...
Kosovo's foreign minister has said her country is convinced Russia must lose the war in Ukraine for conflict not to spread further in Europe. Donika Gervalla-Schwarz said her young nation's ...