Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice

Saudi Arabia
Entry requirements.
This advice reflects the UK government’s understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Saudi Arabia set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Saudi Embassy in the UK .
COVID-19 rules
There are no COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements for travellers entering Saudi Arabia.
Passport validity requirements
Your passport must have an ‘expiry date’ at least 6 months after the date you arrive.
Check with your travel provider that your passport and other travel documents meet requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.
You will be denied entry if you do not have a valid travel document or try to use a passport that has been reported lost or stolen.
Previous travel to Israel
You may not be allowed to enter Saudi Arabia if your passport shows that you have travelled to, or were born, in Israel.
Visa requirements
You must get an e-visa or an electronic visa waiver (EVW) either before you travel or on arrival at any of Saudi Arabia’s international airports. The type of e-visa or EVW you choose depends on your reason for travelling and how long you want to stay.
If you overstay your visa, you could face large fines, detention and deportation. You could be banned from returning to Saudi Arabia.
Applying for an e-visa
You can apply for an e-visa if you are a tourist. You must get an e-visa to perform Umrah.
E-visas are:
- valid for 365 days from the date of issue
- for visits of up to 90 days
- for multiple entries
Apply online or on arrival at any of Saudi Arabia’s international airports.
You will need a separate visa for Hajj. See Pilgrimage .
Applying for an electronic visa waiver (EVW)
You can apply for an electronic visa waiver (EVW) if you’re travelling for:
- medical treatment
- Umrah (outside of Hajj Season)
An EVW allows you to enter Saudi Arabia once and stay for up to 6 months.
Apply online for an EVW at least 48 hours before your flights, or up to 90 days in advance. You will need to give your flight details.
Travelling overland
Your visa may only allow you to enter Saudi Arabia by air. If you plan to travel to Saudi Arabia by the Bahrain causeway, check your visa before travelling. Ask your travel agent or the Saudi Embassy if you need help.
Travelling through Saudi Arabia
If you’re transferring through Saudi Arabia, you may need a transit visa if:
- you will pass through immigration control
- you will leave Saudi Arabia on a separate ticket to the one you arrive on
- the connecting time between your flights is more than 12 hours
Check with your airline or travel agency if you require a transit visa.
Exit, re-entry and final exit permits
If you live in Saudi Arabia, you must get an exit or re-entry permit from your sponsor to leave and re-enter the country. If you leave Saudi Arabia on a final exit permit, you must apply for a new visa to return to the country.
Wives and children of Saudi nationals
If you’re a woman married to a Saudi national, you must get a re-entry or final exit permit from your husband to leave Saudi Arabia. This also applies to children of Saudi nationals.
Flight restrictions around Hajj
If you plan to travel around the time of the Hajj pilgrimage, check with your airline for any flight restrictions.
The Saudi authorities have stopped visitors who are not performing Hajj from flying to Jeddah, Madinah and Taif. You may need a Hajj visa to board flights to these places during Hajj.
You will still be able to enter Saudi Arabia through other airports.
Vaccination requirements
At least 8 weeks before your trip, check the vaccinations and certificates you need in TravelHealthPro’s Saudi Arabia guide .
Depending on your circumstances, these may include:
- a yellow fever vaccination certificate
- meningococcal quadrivalent vaccine
Customs rules
There are strict rules about goods you can take into or out of Saudi Arabia. You must declare anything that may be prohibited or subject to tax or duty.
It is illegal to import:
- pork and pork products
- pornographic material
- distillery equipment
- re-treaded or used tyres
- used clothing except for personal use
certain sculptures such as religious symbols Other items may be examined, including:
- personal videos
- electronic devices
You may need to special approval to bring:
- agricultural seeds
- live animals
- religious books (except for personal use)
- chemicals and harmful materials
- some pharmaceutical products
- wireless equipment
- radio-controlled model airplanes
- archaeological artefacts
Using technical equipment
You may need a licence for:
- satellite phones
- listening or recording devices
- radio transmitters
- powerful cameras or binoculars
If you need information on customs rules, contact the Saudi Embassy .
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
Saudi Arabia Travel Restrictions
Traveller's COVID-19 vaccination status
Travelling from the United Kingdom to Saudi Arabia
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Not required in enclosed environments.
Ready to travel?
Find flights to saudi arabia, find stays in saudi arabia, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, netherlands, new zealand, philippines, switzerland, united arab emirates, united states, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Saudi Arabia from the United Kingdom?
Most visitors from the United Kingdom, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saudi Arabia.
Can I travel to Saudi Arabia if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United Kingdom can enter Saudi Arabia without restrictions.
Can I travel to Saudi Arabia without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from the United Kingdom can enter Saudi Arabia without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Saudi Arabia?
Visitors from the United Kingdom are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Saudi Arabia.
Can I travel to Saudi Arabia without quarantine?
Travellers from the United Kingdom are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Saudi Arabia?
Mask usage in Saudi Arabia is not required in enclosed environments.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Saudi Arabia?
Restaurants in Saudi Arabia are open. Bars in Saudi Arabia are .
- Environment
- Road to Net Zero
- Art & Design
- Film & TV
- Music & On-stage
- Pop Culture
- Fashion & Beauty
- Home & Garden
- Things to do
- Combat Sports
- Horse Racing
- Beyond the Headlines
- Trending Middle East
- Business Extra
- Culture Bites
- Year of Elections
- Pocketful of Dirhams
- Books of My Life
- Iraq: 20 Years On
Saudi Arabia Covid-19 travel guide: what are the latest rules for visiting the kingdom?
Vaccinated travellers no longer need pre-departure pcr tests and face masks are only required indoors.
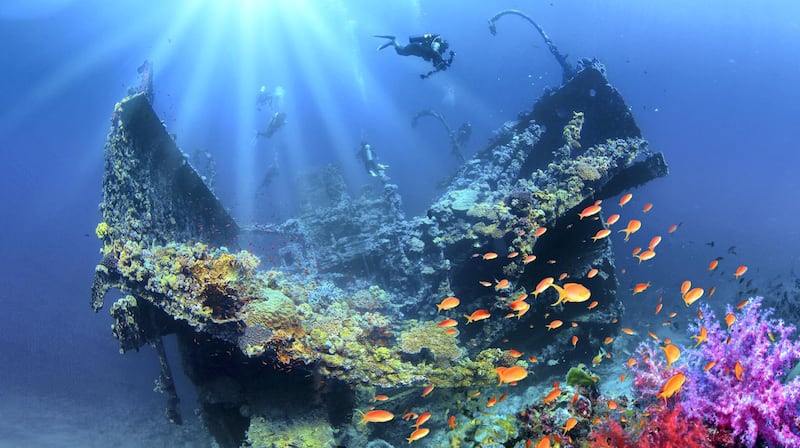

Abundant marine life in the Red Sea. Photos: Saudi Tourism Authority

Saudi Arabia has further eased Covid-19 travel restrictions for vaccinated visitors.
Travellers flying to the kingdom no longer need to take a pre-departure PCR or antigen test on arrival.
The new rules also mean that face masks are not required in outdoor places, and social-distancing measures have been relaxed.
Suspensions on 17 countries have also been lifted, with flights once again able to land in the kingdom from a host of African and Asian countries where travel was previously restricted.
The news comes after the number of coronavirus infections in Saudi Arabia dropped by nearly 50 per cent in a week. It is likely to provide a boost to the kingdom ahead of Hajj , one of Saudi Arabia's busiest times for travel, which is due to start in early July.
If you're considering taking a trip to the kingdom, here’s everything you need to know about travelling there, from which vaccines are accepted to what you need to do before setting off, the rules in place when you get there and what to add to your tourism itinerary.
Is Saudi Arabia open to tourists?

Yes, Saudi citizens and residents, GCC nationals, diplomats, health practitioners and fully vaccinated tourists can fly to Saudi Arabia .
What do I need to do before I fly to the kingdom?

Most visitors to Saudi Arabia need a tourist visa to enter. The multiple-entry e-visa is valid for a year, with tourists allowed to stay in the country for up to 90 days.
It is available online , and travellers can check if they are eligible by identifying their nationality on the dropdown list on the same website.
GCC citizens do not require a tourist visa to visit Saudi Arabia. However, GCC ID cards are not accepted for travel, and all visitors must have their passports with them to ensure entry.
Before flying, travellers must register their details, including comprehensive vaccination information, with Saudi health authorities via this online form . All tourists with a visit visa must also have insurance to cover the cost of any Covid-19 medical treatment during their trip.
Do I need a PCR test to fly?
No, vaccinated travellers no longer need a PCR test to fly to Saudi Arabia. Previous requirements for a negative PCR test result taken no more than 72 hours before departing no longer apply.
Children under aged 18 can travel without being vaccinated or having a negative PCR test result.
Which vaccinations are recognised?
Saudi Arabia has approved four Covid-19 vaccines for entry: AstraZeneca, Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna and Johnson & Johnson. Anyone vaccinated with Sinovac or Sinopharm can travel to the kingdom once a booster shot from one of the four recognised vaccines has also been administered.
Travellers must have received both doses of the vaccine, except for those inoculated with Johnson & Johnson, which is a single-dose shot. To be considered fully vaccinated, the final dose must have been taken at least 14 days and at most eight months before departure. If more than eight months have passed, travellers will need to have a booster shot.
All tourists must also register on the Quddum platform no less than 72 hours before flying to the kingdom.
Do I need to quarantine?

There’s no need to quarantine in Saudi Arabia as long as you’re fully vaccinated.
Upon return to the UAE, there's no quarantine necessary for travellers arriving in any emirate after the country relaxed its Covid-19 travel requirements , including dropping its green list for travel.
Unvaccinated travellers can fly to Saudi Arabia, but must undertake a five-day period of institutional quarantine at their own expense. This can be booked via the airline they are flying with at least 72 hours before departure.
Passengers who have had a single dose of a vaccine administered in the kingdom, or have been immunised with a vaccine approved by the World Health Organisation but not approved in the kingdom, should undergo a three-day quarantine period.
Will Al Hosn app work in Saudi Arabia?

The UAE’s Al Hosn app is not in use in Saudi Arabia. Instead, the kingdom uses Tawakkalna as a track-and-trace app. Visitors must download it and register their passport details.
Similar to Al Hosn, proof of vaccination on the Tawwakalna app is required for entry to many public places in the kingdom, including shopping malls, cinemas, restaurants and entertainment venues.
Which airlines are flying to the kingdom?

Several are flying between the UAE and Saudi Arabia, including Etihad Airways, Emirates, Saudia, flynas, flydubai and more.
Travellers can fly to Riyadh, Dammam, Jeddah , Madinah and AlUla direct from the UAE.
Dubai to Riyadh and Jeddah were two of the busiest routes in the world in February 2022, according to aviation data firm OAG.
What can I see and do once there?

Often called the final frontier of travel, the kingdom is huge, with plenty of things to see and do. From the bustling cities of Riyadh and Jeddah to endless sand dunes, mountain peaks and desert oases, and not to mention its thriving Red Sea coastline , the sprawling destination is unlike anywhere in the world.
“Saudi [Arabia] is the authentic home of Arabia, a destination redolent of the mystique and romance of ancient civilisations, rich in iconic locations and unexpected stories delivered with the unparalleled hospitality for which Saudi people are renowned," said Fahd Hamidaddin, chief executive of Saudi Tourism Authority.
The kingdom is massive – spanning more than 2.15 million square kilometres, it is the 13th-largest country in the world – so there's a wealth of things to do and see.
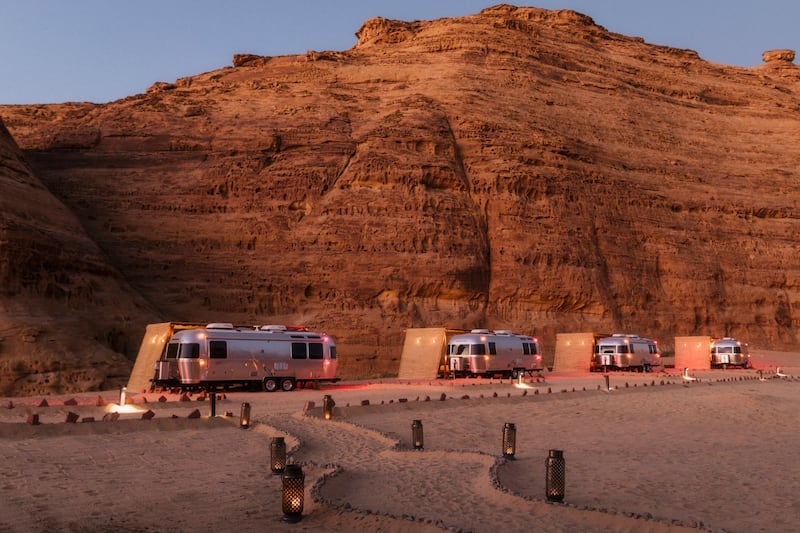

Caravan by Habitas glamping site opens in AlUla, Saudi Arabia in March. All photos: Habitas
City breaks await in the capital, Riyadh , where centuries-old history sits alongside a modern metropolis, or in port-side Jeddah, with its coveted waterfront and al fresco dining or the ancient maze-like streets of Al Balad . The port city of Jazan is a good jumping-off point for the unspoilt Farasan Islands.
Al Ahsa’s cool desert springs are a good place to escape the midday sun and children will enjoy exploring one of the biggest oases in the world . Ocean lovers can go into the blue as Saudi Arabia’s coastal waters are rich in marine life and home to some of the most untouched dive sites in the world.
If it's deserts you seek, the country has dunes in droves. Pay a visit to the Rub Al Khali or Empty Quarter , a favourite with adventure-seekers, or the Great Nafud Desert, where dunes tower about 1,000 metres in height.
In Taif, mountain peaks, flower fields and ancient souqs await, or visit AlUla , one of the kingdom’s mega-projects where visitors can explore several ancient heritage sites and see the world’s largest mirrored building. You can even take in the historic region from the sky, with a newly launched helicopter tour flying travellers over the kingdom’s first Unesco-listed site.
What Covid-19 restrictions are in place?
Mosques and sporting venues return to full capacity in saudi arabia.
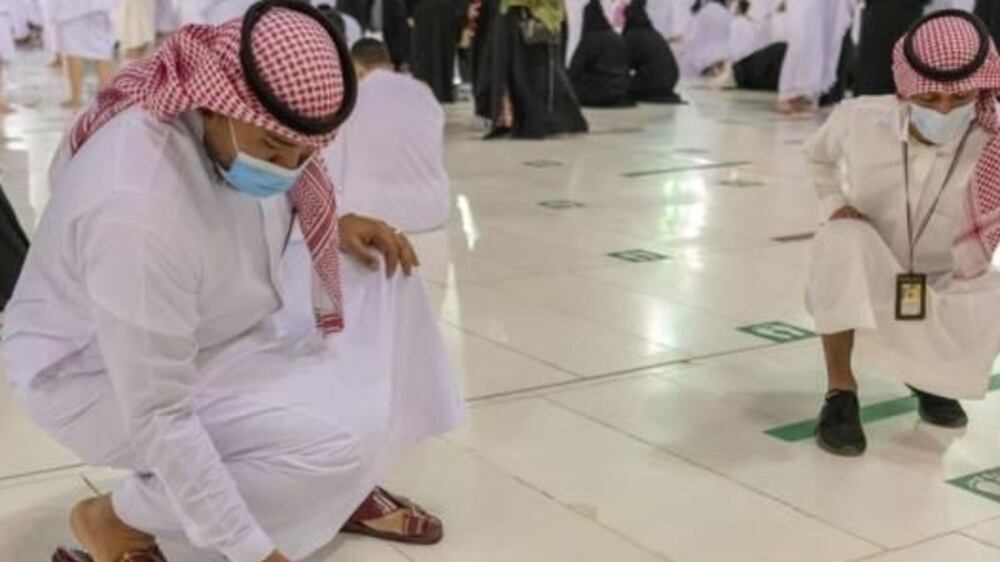

People are no longer obliged to wear face masks in open spaces, except at sites such as the Grand Mosque in Makkah and the Prophet’s Mosque in Madinah. Face masks must still be worn in closed areas.
Social-distancing measures have been dropped in most public places.
Travellers and residents must continue to show their health status on the Tawakkalna app before being allowed into places such as cafes, hotels, restaurants, shopping malls and cinemas.

This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn more

Information on how to stay safe and healthy abroad. About us.
- Destinations
- Middle East
- Asia (Central)
- Asia (East)
- Australasia & Pacific
- Central America
- Europe & Russia
- North America
- South America & Antarctica
Saudi Arabia (Middle East)
Advice for all destinations.
Read the information on the COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel page for advice on travelling during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Vaccinations and malaria risk
Review both the Vaccination and Malaria sections on this page to find out if you may need vaccines and/or a malaria risk assessment before you travel to this country.
If you think you require vaccines and/or malaria risk assessment, you should make an appointment with a travel health professional:
- How to make an appointment with a travel health professional
A travel health risk assessment is also advisable for some people, even when vaccines or malaria tablets are not required.
- Do I need a travel health risk assessment?
Risk prevention advice
Many of the health risks experienced by travellers cannot be prevented by vaccines and other measures need to be taken.
Always make sure you understand the wider risks at your destination and take precautions, including:
- food and water safety
- accident prevention
- avoiding insect bites
- preventing and treating animal bites
- respiratory hygiene
- hand hygiene
Our advice section gives detailed information on minimising specific health risks abroad:
- Travel Health Advice A-Z
Other health considerations
Make sure you have travel insurance before travel to cover healthcare abroad.
Find out if there are any restrictions you need to consider if you are travelling with medicines .
Know how to access healthcare at your destination: see the GOV.UK English speaking doctors and medical facilities: worldwide list
If you feel unwell on your return home from travelling abroad, always seek advice from a healthcare professional and let them know your travel history.
Vaccinations
- Confirm primary courses and boosters are up to date as recommended for life in Britain - including for example, seasonal flu vaccine (if indicated), MMR , vaccines required for occupational risk of exposure, lifestyle risks and underlying medical conditions.
- Courses or boosters usually advised: Tetanus.
- Other vaccines to consider: Diphtheria; Influenza; Hepatitis A; Hepatitis B; Meningococcal Meningitis; Rabies.
- Selectively advised vaccines - only for those individuals at highest risk: none.
Yellow fever vaccination certificate required for travellers aged 9 months or over arriving from countries with risk of yellow fever transmission and for travellers having transited for more than 12 hours through an airport of a country with risk of yellow fever transmission.
Notes on the diseases mentioned above
- Diphtheria : spread person to person through respiratory droplets. Risk is higher if mixing with locals in poor, overcrowded living conditions.
- Flu (Influenza) : spread mainly through airborne droplets (when an infected person coughs or sneezes) among crowds and in enclosed spaces. Travellers in the UK 'flu' risk groups should ensure that they have received their seasonal influenza vaccine before travel. The Saudi Ministry of Health recommends seasonal influenza vaccine for Hajj and Umrah attendees.
Risk is higher where personal hygiene and sanitation is poor.
Risk is higher for long stays, frequent travel and for children (exposed through cuts and scratches), those who may require medical treatment during travel.
- Meningococcal Meningitis : spread by droplet infection through close person to person contact. Meningococcal disease is found worldwide but epidemics may occur within this country, particularly during the dry season. Risk is higher for those mixing with locals for extended periods. The Saudi Ministry of Health recommends seasonal meningococcal meningitis vaccine for Hajj and Umrah attendees.
- Tetanus : spread through contamination of cuts, burns and wounds with tetanus spores. Spores are found in soil worldwide. A total of 5 doses of tetanus vaccine are recommended for life in the UK. Boosters are usually recommended in a country or situation where the correct treatment of an injury may not be readily available.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease transmitted by mosquitoes.You cannot be vaccinated against malaria.
Malaria precautions
- Malaria risk is present throughout the year in the provinces of Jizan, 'Asir, Najran and all other areas. Hajj pilgrims , may travel between Makkah (Mecca) and Medina. The risk of malaria is low in both cities and antimalarial prophylaxis is not advised. However, pilgrims who are outdoors or walking at night should take strict mosquito bite precautions.
- Malaria precautions are essential. Avoid mosquito bites by covering up with clothing such as long sleeves and long trousers especially after sunset, using insect repellents on exposed skin and, when necessary, sleeping under a mosquito net.
- See malaria map – additional information can be found by clicking on the Regional Information icon below the map.
- Low to no risk areas: antimalarials are not usually advised.
- If you have been travelling in a malarious area and develop a fever seek medical attention promptly. Remember malaria can develop even up to one year after exposure.
Other Health Risks
Hajj and umrah pilgrimage, schistosomiasis.
There is a risk of exposure to coronavirus (COVID-19) in this country.
Please be aware that the risk of COVID-19 in this country may change at short notice and also consider your risk of exposure in any transit countries and from travelling itself.
- The 'News' section on this page will advise if significant case increases or outbreaks have occurred in this country.
Prior to travel, you should:
- Check the latest government guidance on the FCDO Foreign travel advice and country specific pages for travel to this country and the rules for entering the UK on return.
- Ensure you are up to date with UK recommendations on COVID-19 vaccination.
- You can check this in the FAQ's.
- If you are at increased risk of severe COVID-19 you should carefully consider your travel plans and consider seeking medical advice prior to making any decisions.
For further information, see Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel pages.
- 09 May 2024 - Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) in Saudi Arabia
- 02 May 2024 - Hajj and Umrah 1445H/2024 (Update 1)
- 08 Apr 2024 - Hajj and Umrah 1445H/2024
- 97 additional items in the news archive for this country
back to top
- COUNTRY INFORMATION
- LATEST NEWS
- OUTBREAK SURVEILLANCE
- TOPICS IN BRIEF
- FACTSHEETS & RESOURCES
- WORLD OVERVIEW

Saudi Arabia
Capital City: Riyadh
Official Languages: Arabic
Monetary Unit: Saudi riyal (SR)
- General Information
- Vaccine Recommendations
- Other Risks
TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS ARE IN PLACE FOR THIS COUNTRY
There are entry requirements for anyone who plans to travel to England from this country. Please check here for further information. Advice may vary in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland.
The information on these pages should be used to research health risks and to inform the pre-travel consultation.
Due to COVID-19, travel advice is subject to rapid change. Countries may change entry requirements and close their borders at very short notice. Travellers must ensure they check current Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) travel advice in addition to the FCDO specific country page (where available) which provides additional information on travel restrictions and entry requirements in addition to safety and security advice.
Travellers should ideally arrange an appointment with their health professional at least four to six weeks before travel. However, even if time is short, an appointment is still worthwhile. This appointment provides an opportunity to assess health risks taking into account a number of factors including destination, medical history, and planned activities. For those with pre-existing health problems, an earlier appointment is recommended.
All travellers should ensure they have adequate travel health insurance .
A list of useful resources including advice on how to reduce the risk of certain health problems is available below.
- Food and water hygiene
- Insect and tick bite avoidance
- Personal safety
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Sun protection
Details of vaccination recommendations and requirements are provided below.
All travellers
Travellers should be up to date with routine vaccination courses and boosters as recommended in the UK . These vaccinations include for example measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine and diphtheria-tetanus-polio vaccine.
Country-specific diphtheria recommendations are not provided here. Diphtheria tetanus and polio are combined in a single vaccine in the UK. Therefore, when a tetanus booster is recommended for travellers, diphtheria vaccine is also given. Should there be an outbreak of diphtheria in a country, diphtheria vaccination guidance will be provided.
Those who may be at increased risk of an infectious disease due to their work, lifestyle choice, or certain underlying health problems should be up to date with additional recommended vaccines. See the individual chapters of the 'Green Book' Immunisation against infectious disease for further details.
Certificate requirements
Please read the information below carefully, as certificate requirements may be relevant to certain travellers only. For travellers further details, if required, should be sought from their healthcare professional.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country, however, there is a certificate requirement.
- Under International Health Regulations, proof of vaccination against yellow fever is required from travellers aged 9 months or over, arriving from countries with risk of yellow fever transmission, and for travellers having transited for more than 12 hours through an airport of a country with risk of yellow fever transmission.
- According to World Health Organization (WHO), from 11 July 2016 (for all countries), the yellow fever certificate will be valid for the duration of the life of the person vaccinated. As a consequence, a valid certificate, presented by arriving travellers, cannot be rejected on the grounds that more than ten years have passed since the date vaccination became effective as stated on the certificate; and that boosters or revaccination cannot be required.
- View the WHO list of countries with risk of yellow fever transmission.
- Proof of vaccination with the meningococcal quadrivalent vaccine (A, C, W, Y) is a visa requirement for Hajj and Umrah pilgrims and seasonal workers (see 'Some Travellers’ section below).
- Saudi Arabia have also listed other requirements for travellers visiting for Hajj and Umrah. Details are available from the Ministry of Health, in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Health Requirements and Recommendations for Travelers to Saudi Arabia for Hajj – 1445H (2024) and Health Requirements and Recommenations for Travellers to Saudi Arabia for Umrah – 1445H (2024) .
Most travellers
The vaccines in this section are recommended for most travellers visiting this country. Information on these vaccines can be found by clicking on the blue arrow. Vaccines are listed alphabetically.
Tetanus is caused by a toxin released from Clostridium tetani bacteria and occurs worldwide. Tetanus bacteria are present in soil and manure and may be introduced through open wounds such as a puncture wound, burn or scratch.
Travellers should thoroughly clean all wounds and seek medical attention for injuries such as animal bites/scratches, burns or wounds contaminated with soil.
Tetanus vaccination
- Travellers should have completed a tetanus vaccination course according to the UK schedule.
- If travelling to a country or area where medical facilities may be limited, a booster dose of a tetanus-containing vaccine is recommended if the last dose was more than ten years ago even if five doses of vaccine have been given previously.
Country-specific information on medical facilities may be found in the 'health' section of the FCDO foreign travel advice pages.
Tetanus in brief
Some travellers.
The vaccines in this section are recommended for some travellers visiting this country. Information on when these vaccines should be considered can be found by clicking on the arrow. Vaccines are listed alphabetically.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a viral infection transmitted through contaminated food and water or by direct contact with an infectious person. Symptoms are often mild or absent in young children, but the disease can be more serious with advancing age. Recovery can vary from weeks to months. Following hepatitis A infection immunity is lifelong.
All travellers should take care with personal, food and water hygiene.
Hepatitis A vaccination
Vaccination is recommended for those whose activities put them at increased risk. This includes:
- those who are staying with or visiting the local population.
- frequent and/or long-stay travellers to areas where sanitation and food hygiene are likely to be poor.
- adventure travellers visiting rural areas and staying in basic accommodation such as backpackers.
- those with existing medical conditions such as liver disease or haemophilia.
- men who have sex with men.
- people who inject drugs.
- those who may be exposed to the virus through their work.
- those going to areas of hepatitis A outbreaks who have limited access to safe water and medical care.
Hepatitis A in brief
Hepatitis b.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection; it is transmitted by exposure to infected blood or body fluids. This mostly occurs during sexual contact or as a result of blood-to-blood contact (for example from contaminated equipment during medical and dental procedures, tattooing or body piercing procedures, and sharing of intravenous needles). Mothers with the virus can also transmit the infection to their baby during childbirth.
Hepatitis B in Saudi Arabia
2% or more of the population are known or thought to be persistently infected with the hepatitis B virus (intermediate/high prevalence).
Travellers should avoid contact with blood or body fluids. This includes:
- avoiding unprotected sexual intercourse.
- avoiding tattooing, piercing, public shaving, and acupuncture (unless sterile equipment is used).
- not sharing needles or other injection equipment.
- following universal precautions if working in a medical/dental/high risk setting.
A sterile medical equipment kit may be helpful when travelling to resource poor areas.
Hepatitis B vaccination
Vaccination could be considered for all travellers, and is recommended for those whose activities or medical history put them at increased risk including:
- those who may have unprotected sex.
- those who may be exposed to contaminated needles through injecting drug use.
- those who may be exposed to blood or body fluids through their work (e.g. health workers).
- those who may be exposed to contaminated needles as a result of having medical or dental care e.g. those with pre-existing medical conditions and those travelling for medical care abroad including those intending to receive renal dialysis overseas.
- long-stay travellers.
- those who are participating in contact sports.
- families adopting children from this country.
Hepatitis B in brief
Meningococcal disease.
For Hajj and Umrah pilgrims and seasonal workers to this area, proof of vaccination with a meningococcal ACWY vaccine is a visa requirement for entry.
Meningococcal disease is a bacterial infection transmitted by inhaling respiratory droplets or direct contact with respiratory secretions from an infected person. This is usually following prolonged or frequent close contact. The most common forms of meningococcal disease are meningococcal meningitis (infection of the protective lining around the brain) and septicaemia (blood poisoning).
Hajj and Umrah pilgrims and seasonal workers at the pilgrimages are at increased risk due to the crowded conditions and possible close contact with people from countries with higher rates of meningococcal disease.
Meningococcal disease in Saudi Arabia
Outbreaks of meningococcal meningitis were reported in 1987, 2000 and 2001 during the Hajj.
Travellers may reduce their risk by avoiding overcrowded situations where possible.
Meningococcal disease vaccination
For pilgrims and seasonal workers proof of vaccination with a meningococcal ACWY vaccine is a visa requirement for entry. When the meningococcal ACWY conjugate vaccine is used, this should be given at least 10 days before, and within the last 5 years of planned travel. Details of the vaccine name and type (i.e. conjugate vaccine) should be recorded in a patient held vaccine record showing the traveller’s full name. It is advisable that this vaccination record is issued by the traveller's doctor, nurse or pharmacist and should reflect accurately details of the vaccine administered and be authenticated with the healthcare providers official stamp.
Pilgrims and seasonal workers must carry vaccination certificates with them for inspection by the Saudi Authority at port of entry.
The meningococcal ACWY conjugate vaccine is recommended. If a polysaccharide ACWY vaccine has been administered previously (no longer available in UK) it should have been administered within the last 3 years of planned travel.
Meningococcal disease in brief
Rabies is a viral infection which is usually transmitted following contact with the saliva of an infected animal most often via a bite, scratch or lick to an open wound or mucous membrane (such as on the eye, nose or mouth). Although many different animals can transmit the virus, most cases follow a bite or scratch from an infected dog. In some parts of the world, bats are an important source of infection.
Rabies symptoms can take some time to develop, but when they do, the condition is almost always fatal.
The risk of exposure is increased by certain activities and length of stay (see below). Children are at increased risk as they are less likely to avoid contact with animals and to report a bite, scratch or lick.
Rabies in Saudi Arabia
Rabies is considered a risk and has been reported in domestic animals in this country. Bats may also carry rabies-like viruses.
- Travellers should avoid contact with all animals. Rabies is preventable with prompt post-exposure treatment.
- Following a possible exposure, wounds should be thoroughly cleansed and an urgent local medical assessment sought, even if the wound appears trivial.
- Post-exposure treatment and advice should be in accordance with national guidelines.
Rabies vaccination
A full course of pre-exposure vaccines simplifies and shortens the course of post-exposure treatment and removes the need for rabies immunoglobulin which is in short supply world-wide.
Pre-exposure vaccinations are recommended for travellers whose activities put them at increased risk including:
- those at risk due to their work (e.g. laboratory staff working with the virus, those working with animals or health workers who may be caring for infected patients).
- those travelling to areas where access to post-exposure treatment and medical care is limited.
- those planning higher risk activities such as running or cycling.
- long-stay travellers (more than one month).
Rabies in brief
Malaria is a serious illness caused by infection of red blood cells with a parasite called Plasmodium. The disease is transmitted by mosquitoes which predominantly feed between dusk and dawn.
Symptoms usually begin with a fever (high temperature) of 38°C (100°F) or more. Other symptoms may include feeling cold and shivery, headache, nausea, vomiting and aching muscles. Symptoms may appear between eight days and one year after the infected mosquito bite.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment is required as people with malaria can deteriorate quickly. Those at higher risk of malaria, or of severe complications from malaria, include pregnant women, infants and young children, the elderly, travellers who do not have a functioning spleen and those visiting friends and relatives.
Travellers should follow an ABCD guide to preventing malaria:
A wareness of the risk – Risk depends on the specific location, season of travel, length of stay, activities and type of accommodation. B ite prevention – Travellers should take mosquito bite avoidance measures. C hemoprophylaxis – Travellers should take antimalarials (malaria prevention tablets) if appropriate for the area (see below). No antimalarials are 100% effective but taking them in combination with mosquito bite avoidance measures will give substantial protection against malaria. D iagnosis – Travellers who develop a fever of 38°C [100°F] or higher more than one week after being in a malaria risk area, or who develop any symptoms suggestive of malaria within a year of return should seek immediate medical care. Emergency standby treatment may be considered for those going to remote areas with limited access to medical attention.
- There is a low risk of malaria in the south western provinces of Saudi Arabia, along the border with Yemen including Asir province below 2,000m: awareness of risk and bite avoidance recommended.
- There is no risk in the cities of Jeddah, Makkah (Mecca), Medina, Riyadh, and Ta’if, or in Asir province above 2,000m: bite avoidance only recommended.
Special risk groups
In low risk areas, antimalarials may be considered in exceptional circumstances for travellers who are at higher risk of malaria (such as long term travellers visiting friends and relatives), or of severe complications from malaria (such as the elderly [over 70 years], the immunosuppressed,those with complex co-morbidities, pregnant women, infants and young children). The final decision whether or not to advise antimalarials rests with the travel health advisor and the traveller after individual risk assessment.
Travellers with an absent or poorly functioning spleen should be dissuaded from travel to any area with risk of malaria. Where travel is essential, awareness, rigorous bite avoidance and antimalarials should be advised, even for the low risk areas.
For special risk groups, you may wish to seek specialist advice. For the low risk areas in this country/area, atovaquone/proguanil OR doxycycline OR mefloquine would be suitable options.
Antimalarial recommendations map

- Click on map to open in a new window
- Malaria in brief
- Malaria factsheet
- Children's antimalarial dose table
- Malaria prevention guidelines for travellers from the UK
There are some risks that are relevant to all travellers regardless of destination. These may for example include road traffic and other accidents, diseases transmitted by contaminated food and water, sexually transmitted infections, or health issues related to the heat or cold.
Some additional risks (which may be present in all or part of this country) are mentioned below and are presented alphabetically. Select risk to expand information.
There is a risk of altitude illness when travelling to destinations of 2,500 metres (8,200 feet) or higher. Important risk factors are the altitude gained, rate of ascent and sleeping altitude. Rapid ascent without a period of acclimatisation puts a traveller at higher risk.
There are three syndromes; acute mountain sickness (AMS), high-altitude cerebral oedema (HACE) and high-altitude pulmonary oedema (HAPE). HACE and HAPE require immediate descent and medical treatment.
Altitude illness in Saudi Arabia
There is a point of elevation in this country higher than 2,500 metres.
- Travellers should spend a few days at an altitude below 3,000m.
- Where possible travellers should avoid travel from altitudes less than 1,200m to altitudes greater than 3,500m in a single day.
- Ascent above 3,000m should be gradual. Travellers should avoid increasing sleeping elevation by more than 500m per day and ensure a rest day (at the same altitude) every three or four days.
- Acetazolamide can be used to assist with acclimatisation, but should not replace gradual ascent.
- Travellers who develop symptoms of AMS (headache, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea and sleep disturbance) should avoid further ascent. In the absence of improvement or with progression of symptoms the first response should be to descend.
- Development of HACE or HAPE symptoms requires immediate descent and emergency medical treatment.
Altitude illness in brief
Biting insects or ticks.
Insect or tick bites can cause irritation and infections of the skin at the site of a bite. They can also spread certain diseases.

Diseases in Western Asia
There is a risk of insect or tick-borne diseases in some areas of Western Asia. This includes diseases such as chikungunya , Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever , leishmaniasis , Rift Valley fever and West Nile virus .
- All travellers should avoid insect and tick bites day and night.
- There are no vaccinations (or medications) to prevent these diseases.
Further information about specific insect or tick-borne diseases for this country can be found, if appropriate on this page, in other sections of the country information pages and the insect and tick bite avoidance factsheet .
Dengue is a viral infection spread by mosquitoes which mainly feed during daytime hours. It causes a flu-like illness, which can occasionally develop into a more serious life-threatening illness. Severe dengue is rare in travellers.
The mosquitoes that spread dengue are more common in towns, cities and surrounding areas.
There is a risk of dengue in the provinces of Al Madinah, Jizan and Makkah (including the cities of Mecca and Jeddah).
Dengue in Saudi Arabia
- Travellers should avoid mosquito bites particularly during daytime hours.
- A dengue vaccine is licensed in the UK for the prevention of dengue disease in individuals from 4 years of age. The Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI) and World Health Organization are in the process of reviewing the product information. Recommendations on the use of this vaccine will be published in due course.
Dengue in brief
Seasonal influenza is a viral infection of the respiratory tract and spreads easily from person to person via respiratory droplets when coughing and sneezing. Symptoms appear rapidly and include fever, muscle aches, headache, malaise (feeling unwell), cough, sore throat and a runny nose. In healthy individuals, symptoms improve without treatment within two to seven days. Severe illness is more common in those aged 65 years or over, those under 2 years of age, or those who have underlying medical conditions that increase their risk for complications of influenza.
Seasonal influenza in Saudi Arabia
Seasonal influenza occurs throughout the world. In the northern hemisphere (including the UK), most influenza occurs from as early as October through to March. In the southern hemisphere, influenza mostly occurs between April and September. In the tropics, influenza can occur throughout the year.
All travellers should:
- Avoid close contact with symptomatic individuals
- Avoid crowded conditions where possible
- Wash their hands frequently
- Practise ‘cough hygiene’: sneezing or coughing into a tissue and promptly discarding it safely, and washing their hands
- Avoid travel if unwell with influenza-like symptoms
- A vaccine is available in certain circumstances (see below)*
*In the UK, seasonal influenza vaccine is offered routinely each year to those at higher risk of developing of severe disease following influenza infection, and certain additional groups such as healthcare workers and children as part of the UK national schedule (see information on vaccination ). For those who do not fall into these groups, vaccination may be available privately.
If individuals at higher risk of severe disease following influenza infection are travelling to a country when influenza is likely to be circulating they should ensure they received a flu vaccination in the previous 12 months.
The vaccine used in the UK protects against the strains predicted to occur during the winter months of the northern hemisphere. It is not possible to obtain vaccine for the southern hemisphere in the UK, but the vaccine used during the UK influenza season should still provide important protection against strains likely to occur during the southern hemisphere influenza season, and in the tropics.
Avian influenza
Avian influenza viruses can rarely infect and cause disease in humans. Such cases are usually associated with close exposure to infected bird or animal populations. Where appropriate, information on these will be available in the outbreaks and news sections of the relevant country pages. Seasonal influenza vaccines will not provide protection against avian influenza.
Avian influenza in brief
Middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus.
MERS-CoV is a viral infection transmitted following direct or indirect contact with infected camels or camel-related products. Limited person to person transmission through coughing and sneezing from infected persons, typically in healthcare settings, has also been reported.
Symptoms include fever and cough that can progress to severe shortness of breath and breathing difficulties. Deaths have been reported, with the risk increasing with advancing age or underlying medical conditions.
MERS-CoV in Saudi Arabia
MERS-CoV has been reported to occur in this country.
All travellers, particularly those with chronic medical conditions, should practise good general health measures, such as regular hand washing with soap and water at all times, but especially after visiting farms, barns or market areas. They should:
- Avoid contact with camels
- Avoid raw camel milk and/or camel products
- Avoid consumption of any type of raw milk, raw milk products and any food that may be contaminated with animal secretions, unless peeled and cleaned and/or thoroughly cooked.
There is currently no vaccine to prevent MERS-CoV. More information about Hajj and Umrah is available from the Hajj and Umrah factsheet .
MERS-CoV in brief
Outdoor air quality.
Poor air quality is a significant public health problem in many parts of the world. Exposure to high levels of air pollution over short time periods (e.g. minutes/hours/days) and longer time periods (e.g. years) is linked to many different acute and chronic health problems. These effects are mainly on the respiratory (lungs and airways) and cardiovascular (heart function and blood circulation) systems.
Current information on world air quality is available from the world air quality index project .
Travellers with health problems that might make them more vulnerable to the effects of air pollution who are travelling to areas of high pollution should:
- discuss their travel plans with their doctor, and carry adequate supplies of their regular medication.
- take sensible precautions to minimise their exposure to high levels of air pollution.
- check local air quality data and amend their activities accordingly.
- take notice of any health advisories published by the local Ministry of Health and Department for Environment, and follow the guidance provided.
It is unclear if face masks are beneficial at reducing exposure and may make breathing more difficult for those with pre-existing lung conditions. Those who choose to use one should make sure that the mask fits well and know how to wear it properly.
Outdoor air quality in brief
Schistosomiasis.
Schistosomiasis is a parasitic infection. Schistosoma larvae are released from infected freshwater snails and can penetrate intact human skin following contact with contaminated freshwater. Travellers may be exposed during activities such as wading, swimming, bathing or washing clothes in freshwater streams, rivers or lakes.
Schistosomiasis infection may cause no symptoms, but early symptoms can include a rash and itchy skin ('swimmer's itch'), fever, chills, cough, or muscle aches. If not treated, it can cause serious long term health problems such as intestinal or bladder disease.
Schistosomiasis in Saudi Arabia
Cases of schistosomiasis have previously been reported from this country. There is a very low risk of schistosomiasis in this country.
- There is no vaccine or tablets to prevent schistosomiasis.
- All travellers should avoid wading, swimming, or bathing in fresh water. Swimming in adequately chlorinated water or sea water is not a risk for schistosomiasis.
- Drink water that is boiled, filtered or bottled.
- Application of insect repellent before exposure to fresh water, or towel drying after possible exposure to schistosomiasis are not reliable in preventing infection.
- If you have concerns about your risk discuss with your health care provider.
Schistosomiasis in brief
COVID-19 disease is caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV2. The main symptoms of COVID-19 are a new continuous cough, a high temperature, and a loss of, or change in, normal sense of taste or smell. Symptoms range from mild to life-threatening. Older people and those with underlying health problems are more likely to develop severe disease.
COVID-19 is spread through close contact with people who have the virus. It is mainly transmitted from person to person by breathing in droplets produced when someone infected with the virus breathes, speaks, coughs or sneezes. It is also spread by touching the infected droplets on surfaces, then touching the eyes, nose or mouth.
COVID-19 vaccines provide high levels of protection against severe illness, hospitalisation, or dying from the virus. Vaccination against COVID-19 reduces, but does not eliminate the risk of infection, so social distancing and personal and respiratory hygiene remain important interventions, particularly during overseas travel.
Travellers should always check the UK Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) travel advice and their country-specific pages for the latest COVID-19 travel advisories which may include information on travel restrictions, quarantine, COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements. This includes considering the recommendations and requirements for any transit countries.
Travellers should be aware that COVID-19 case numbers in individual countries/areas can increase rapidly, and healthcare capacity and country requirements can change at short notice.
COVID-19 in Saudi Arabia
Most countries worldwide present a risk of exposure to COVID-19. The risk of COVID-19, public health policy, and travel advice or restrictions may change quickly, therefore travellers should ensure they have access to up to date information on COVID-19 and be prepared for rapid changes in guidance both before and during travel.
All travellers should check the FCDO travel advice and carefully consider their personal situation and risks of COVID-19 before travel to this country. This is particularly important in those at higher risk from COVID-19 who may wish to seek medical advice before travel.
Individuals entering or returning to the UK may be required to follow additional UK border measures .
If travelling to this country, travellers should:
- Consider the risk at all destinations including any transit countries, and the risk during travel itself.
- Check with the airline/tour operator about preventive measures in place to reduce risk during travel.
- Follow the latest guidance on social distancing and face coverings, including any local requirements and maintain good hand, respiratory, and personal hygiene at all times. This may be particularly important if staying with friends and family.
- Ensure they are up to date with their COVID-19 vaccination courses and boosters as recommended in the UK vaccination programme.
See guidance on factors to consider when assessing the risk of COVID-19 for travellers .
If travellers develop COVID-19 symptoms while abroad, they should:
- Follow local guidelines on self-isolation, testing and avoiding travel.
- Contact their travel insurance provider.
- Seek medical advice if needed.
COVID-19 in brief

Hajj 1445H and Umrah update: 2024
Information for pilgrims planning to perform Hajj or Umrah in 2024

Travelling for Ramadan
Travelling abroad during Ramadan? Careful preparation helps you have a safe and healthy trip

Malaria: a reminder for travellers over the winter holiday season
Advice for travellers and health professionals about malaria
Using information collated from a variety of sources, we regularly review and update information on overseas disease outbreaks and other health issues that may affect the UK traveller.
Please note that not all cases of disease or outbreaks are reported ; some diseases may only be reported if they occur outside of the usual recognised risk area or season, or they have been reported in greater than usual numbers.
Further information on the Outbreak Surveillance section.

Foreign travel advice

FEEDBACK SURVEY
Personal information:, successfully submitted .
UK Health Security Agency
Hospital for Tropical Diseases
Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine
London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Saudi Arabia Traveler View
The Hajj , or pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, is one of the world’s largest mass gatherings . In 2024, Hajj will take place between June 14-19th. Mass gatherings are associated with unique health risks. Before you travel, visit a travel health specialist for specific advice related to your destination and this event. Make sure you are up to date on all routine and travel-related vaccines. Check information from the government of Saudi Arabia for their most current vaccine requirements and recommendations , especially regarding meningococcal vaccination. Monitor travel warnings and alerts from the U.S. Department of State and consider signing up for the Smart Travelers Enrollment Program .
Travel Health Notices
Vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
There are no notices currently in effect for Saudi Arabia.
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Saudi Arabia.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Saudi Arabia. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Saudi Arabia.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Saudi Arabia take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Saudi Arabia.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Meningitis (Meningococcal disease)
Required for all travelers going to Saudi Arabia to take part in the Hajj or Umrah. See the Saudi Arabia: Hajj/Umrah Pilgrimage Yellow Book section for more information.
Meningococcal disease - CDC Yellow Book
Rabid dogs are commonly found in Saudi Arabia. However, if you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in Saudi Arabia, rabies treatment is often available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Saudi Arabia.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
Required for travelers ≥9 months old arriving from countries with risk for YF virus transmission; this includes >12-hour airport transits or layovers in countries with risk for YF virus transmission. 1
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic fever
- Tick bite
- Touching the body fluids of a person or animal infected with CCHF
- Avoid Bug Bites
- Mosquito bite
Leishmaniasis
- Sand fly bite
- Avoid animals
Rift Valley Fever
- Touching blood, body fluids, or tissue of infected livestock
Rift Valley fever
Airborne & droplet
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)
- Scientists do not fully understand how the MERS virus spreads
- May spread from to others when an infected person coughs or sneezes
- May spread to people from camels.
Middle East Respiratory virus syndrome (MERS)
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Saudi Arabia, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Saudi Arabia. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Saudi Arabia include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Saudi Arabia. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Saudi Arabia’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Saudi Arabia. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Saudi Arabia may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Saudi Arabia, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Saudi Arabia for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
- Company History
- Mission Statement
- Philippines
- South Africa
- Afghanistan
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- British Virgin Islands
- Burkina Faso
- Canary Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Cote d'Ivoire
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Dominican Republic
- Easter Island
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- Guinea-Bissau
- Liechtenstein
- Madeira Islands
- Marshall Islands
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- North Korea
- North Macedonia
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Palestinian Territories
- Papua New Guinea
- Pitcairn Islands
- Puerto Rico
- Republic of the Congo
- Saint Barthelemy
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre-et-Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Sierra Leone
- Sint Eustatius
- Solomon Islands
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- South Korea
- South Sudan
- Switzerland
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- U.S. Virgin Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Wake Island
- Western Sahara
- Travel Vaccines
- Travel Health Consultations
- Travellers’ Diarrhea Kits
- Dengue Fever Prevention
- Malaria Prevention
- Chikungunya Prevention
- Zika Prevention
- Ebola Virus
- Yellow Fever
- Hepatitis A
- Japanese Encephalitis
- Hepatitis B
- Tickborne Encephalitis (TBE)
- Tetanus-Diphtheria-Pertussis
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella
- Influenza (Flu)
- Blood Tests
- Vitamin Injections
- Physician Referral Program
- London – Euston Travel Clinic

Travel Vaccines and Advice for Saudi Arabia

Among Saudi Arabia’s greatest sites are the holy cities of Mecca and Medina. These are both part of the Hajj, which brings thousands to The Kingdom every year.
Public entertainment is limited in Saudi Arabia. But, the nation possesses incredible natural wonders. Among available activities are day trips into the desert and deep sea diving off the coast.
When visiting Saudi Arabia, be aware of the limitations of the nightlife scene in any urban areas. Consumption of alcohol, public playing of music, and even mingling with the opposite sex are all forbidden. Saudi culture is very strict and should be researched before travelling.
Do I Need Vaccines for Saudi Arabia?
Yes, some vaccines are recommended or required for Saudi Arabia. The National Travel Health Network and Centre and WHO recommend the following vaccinations for Saudi Arabia: COVID-19 , hepatitis A , hepatitis B , yellow fever , rabies , meningitis , polio and tetanus .
See the bullets below to learn more about some of these key immunisations:
- COVID-19 – Airborne – Recommended for all travellers
- Hepatitis A – Food & Water – Recommended for most travellers to the region, especially if unvaccinated.
- Hepatitis B – Blood & Body Fluids – Accelerated schedule available
- Tetanus – Wounds or Breaks in Skin – Recommended for travelers to most regions, especially if not previously vaccinated.
- Yellow Fever – Mosquito – Required if travelling from a country with risk of yellow fever transmission.
- Rabies – Saliva of Infected Animals – High risk country. Vaccine recommended for long-stay travellers and those who may come in contact with animals.
- Meningitis – Airborne & Direct Contact – Required for Hajj travellers. Given to anyone unvaccinated or at an increased risk, especially students.
- Polio – Food & Water – May required for entry at certain times of year like Hajj. Single adult booster recommended.
See the tables below for more information:
Malaria and dengue are present in some areas of Saudi Arabia. Consult with a travel health specialist to learn if these diseases could affect your travel itinerary.
Visit our vaccinations page to learn more. Travel safely with Passport Health and schedule your appointment today by calling or book online now .
What Vaccines Do I Need for Hajj?
The following vaccines are recommended for Hajj – typhoid , polio , meningitis , hepatitis A , MMR and influenza . Some other vaccines may be recommended based on your private health history. Proof of meningitis vaccination is required for entry during Hajj.
Hajj is an annual Islamic pilgrimage that takes place in Saudi Arabia. The event brings thousands of Muslims and interested individuals to the country every year.
To avoid disease outbreaks and protect the health of citizens and travellers, Saudi Arabia has issues dome vaccine recommendations for during Hajj.
Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Saudi Arabia?
A visa is required for all travel to Saudi Arabia. Passports must have at least six months validity. Proof of meningitis vaccination is required for trips during Hajj (usually in September).
Sources: Embassy of Saudi Arabia and GOV.UK
What is the Climate Like in Saudi Arabia?
Saudi Arabia is has a desert climate. During the summer, temperatures can reach anywhere from 40 to 50 degrees.
- Riyadh – The capital suffers the worst heat in the country. It is not unusual for summer temperatures to reach 50 degrees. Winters can go below -1 degrees. Summer evenings are easier to withstand, as cooling winds blow after sunset.
- Jeddah – Unlike Riyadh, Jeddah maintains the warmth of summer throughout the winter. Temperatures can range from 55 to 25 in later months. The summer heat is oppressive, often surpassing 43 during the day. It often cools down to around 30 at night.
- Mecca – The holy city also maintains some of its summer climate during the winter months. In winter, temperatures are usually in the mid-20’s during the day, and drop down to around 15 degrees at night. In summer, Mecca suffers from blistering heat. Temperatures often exceed 45 degrees.
How Safe is Saudi Arabia?
For members of the LGBT community, it is strongly advised not to travel to Saudi Arabia. Homosexuality is punishable by death.
Be careful getting into taxis or taking rides with locals. One of the leading causes of death is due to automobile accidents.
Be mindful of where you leave your belongings, and how you carry them on your person when out in public. Pickpockets are common in urban areas.
Be sure to study local traditions before travelling to Saudi Arabia. Not abiding by Saudi customs can have severe consequences. It is best to learn the culture so as not to stand out when visiting.
Scuba Diving in Saudi Arabia
A great way to experience Saudi Arabia’s natural gifts is to take part in scuba diving. Diving is popular among foreigners travelling to the country.
Be careful when scuba diving. It can be dangerous and very few Saudi hospitals have the necessary equipment to deal with diving injuries. Do not touch anything underwater and to study the local marine life before taking the plunge. The Red Sea is known to be full of poisonous and aggressive fish. It is best to know the do’s and don’ts.
What Should I Take To Saudi Arabia?
Here are some essential items to consider for your trip to Saudi Arabia:
- Medical Supplies – These can be hard to come by in Saudi Arabia. Ensure to include a traveller’s diarrhoea kit, prescriptions and a small first-aid kit.
- Breathable Clothing – The climate of Saudi Arabia is one of extreme heat. Wear clothing that is not too thick, and that you wouldn’t mind sweating in.
- Conservative Clothing -Conservative dress styles are strongly encouraged due to cultural customs in Saudi Arabia. This is especially true for women.
Embassy of the United Kingdom in Saudi Arabia
If you are in Saudi Arabia and have an emergency (for example, been attacked, arrested or someone has died) contact the nearest consular services. Contact the embassy before arrival if you have additional questions on entry requirements, safety concerns or are in need of assistance.
British Embassy Riyadh PO Box 94351 11693 Riyadh Saudi Arabia Telephone: +966 (0) 11 4819 100 Emergency Phone: +966 (0) 11 4819 100 Fax: +966 (0) 11 481 9350 Contact Form: Click Here
If you have any questions about travelling to the Saudi Arabia or are wondering which jabs you may need for your trip, schedule an appointment with your local Passport Health travel medicine clinic. Ring us at or book online now and protect yourself today.
On This Page: Do I Need Vaccines for Saudi Arabia? What Vaccines Do I Need of Hajj? Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Saudi Arabia? What is the Climate Like in Saudi Arabia? How Safe is Saudi Arabia? Scuba Diving in Saudi Arabia What Should I Take To Saudi Arabia? Embassy of the United Kingdom in Saudi Arabia

- Privacy Policy
- Automatic Data Collection Statement
Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Saudi Arabia Travel Advisory
Travel advisory january 24, 2024, saudi arabia - level 3: reconsider travel.
Updated after periodic review to provide information on the risk of arrest due to social media use and the importation of prohibited items.
Reconsider travel to Saudi Arabia due to the threat of missile and drone attacks. Exercise increased caution in Saudi Arabia due to terrorism, the risk of arrest based on social media activity, and importation of prohibited items. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Do not travel to the following locations due to the threat of missile and drone attacks and terrorism :
- Within 50 miles of the Saudi-Yemen border, as well as the cities of Abha, Jizan, Najran, and Khamis Mushayt;
- Abha airport;
- Qatif in the Eastern Province and its suburbs, including Awamiyah.
Country Summary : U.S. government personnel under Chief of Mission responsibility must adhere to the above travel restrictions. As such, the U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in these locations.
Missile and drone attacks perpetrated by Iran and Iran-supported militant groups have occurred as recently as September 2023. The Islamic Republic of Iran has in the past supplied Yemen-based Houthis and regional proxy groups with weapons to conduct destructive and sometimes lethal attacks using drones, missiles, and rockets against a variety of Saudi sites, including critical infrastructure, civilian airports, military bases, and energy facilities throughout the country, as well as vessels in Red Sea shipping lanes. Past attacks were aimed at targets throughout Saudi Arabia including Riyadh, Jeddah, Dhahran, Jizan, Khamis Mushayt, the civilian airport in Abha, Al Kharj, military installations in the south, as well as oil and gas facilities.
Debris from intercepted drones and missiles has also represented a significant risk to civilian areas and populations in the recent past. Militant groups have threatened to conduct attacks against locations in Saudi Arabia. U.S. citizens living and working near military bases and critical civilian infrastructure, particularly near the border with Yemen, are at heightened risk if missile, drone, or rocket attacks reoccur.
Terrorism continues to be a concern in Saudi Arabia. Attacks can occur with little or no warning. Past attacks have targeted tourist locations, large gatherings, transportation hubs, markets/shopping malls, and local government facilities. Terrorists are also known to time attacks around major holidays and/or in response to military operations. Terrorists have targeted both Saudi and international interests, mosques and other religious sites (both Sunni and Shia), and places frequented by U.S. citizens.
Be advised that social media commentary – including past comments – which Saudi authorities may deem critical, offensive, or disruptive to public order, could lead to arrest . This may include posting, re-posting, or liking comments about Saudi institutions, policies, and public life. U.S. citizens have been convicted for social media activity under Saudi laws concerning cybercrime, terrorism, and disrupting public order. Punishment for social media activity has included prison sentences of up to 45 years in some cases. Saudi courts do not necessarily consider the timeframe of the posts or the location from which they were made to be material to these cases.
The importation of drugs (including marijuana), drug paraphernalia, alcohol, weapons, pork, or any materials that could be considered pornographic or suggestive, is prohibited. Penalties for drug possession, consumption, and trafficking are severe by U.S. standards. An extensive list of banned items is available on our Saudi Arabia country information page .
Due to risks to civil aviation operating within the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman region, including Saudi Arabia, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has issued an advisory Notice to Air Missions (NOTAM). For more information U.S. citizens should consult the Federal Aviation Administration’s Prohibitions, Restrictions and Notices .
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Saudi Arabia.
If you decide to travel to Saudi Arabia:
- Visit our website for information on travel to high-risk areas .
- Stay alert in large crowds and/or locations frequented by foreign nationals.
- Obtain comprehensive medical insurance that includes medical evacuation.
- Review local laws and conditions before traveling, including our Saudi Arabia country information on arrest notification and the Department of State’s general information on arrests of U.S. citizens abroad .
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Follow the U.S. Embassy in Saudi Arabia on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Saudi Arabia.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Yemen Border, Abha airport, and Qatif in the Eastern Province and its suburbs, including Awamiyah – Level 4: Do Not Travel
Militants in Yemen have attacked Saudi border towns and other sites in Saudi Arabia with armed drones, missiles, and rockets . Civilians that are near the border with Yemen are especially at risk. Terrorist groups continue plotting possible attacks in Saudi Arabia, including in Qatif.
The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens within 50 miles of the Saudi-Yemen border as U.S. government personnel and their families are restricted from travel to this area.
Visit our website for information on travel to high-risk areas
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, saudi arabia map, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
FCDO travel advice for Saudi Arabia. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
Are you planning to visit Saudi Arabia for tourism, business or cultural exchange? Find out the visa requirements for your specific traveling needs on the official website of Visit Saudi. Discover the ancient heritage, breathtaking landscapes and diverse activities that Saudi Arabia has to offer. Apply for a one-year, multiple entry visa online and have a seamless journey.
UK: 00 44 (+ Number) Saudi: 00966 (+ Number) ... Check with your airline or tour operator about the latest guidance on Saudi Arabia's entry requirements, immigration, visas and customs controls. ... under the Saudi judicial system. Emergency Travel Documents, (ETDs) Driving Licences and Passports ...
Saudi Arabia is opening its doors to the world through its new tourist visa. Through the fast and easy-to-use online portal, international visitors from 66 eligible countries can apply for an eVisa and discover the warm hospitality of Saudi people the rich heritage, vibrant culture, and diverse and breathtaking landscapes; from the mountains of Abha to the beaches of the Red Sea to the ...
Riyadh, June 12, 2023, SPA -- The Ministry of Tourism announced that the United Kingdom, United States, and Schengen tourism visa holders, as well as permanent residents from any European Union country, can now enjoy streamlined entry to the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia by applying for an instant eVisa via the Ministry of Foreign Affairs website. The preceding step is consistent with the Ministry ...
Find continuously updated travel restrictions for Saudi Arabia such as border, vaccination, COVID-19 testing, and quarantine requirements.
Saudi Arabia updates travel entry rules: All you need to know. Saudi Arabia's General Authority of Civil Aviation (GACA) on Monday issued updated rules for travelers entering the country, which ...
Photos: Saudi Tourism Authority. Saudi Arabia has further eased Covid-19 travel restrictions for vaccinated visitors. Travellers flying to the kingdom no longer need to take a pre-departure PCR or antigen test on arrival. The new rules also mean that face masks are not required in outdoor places, and social-distancing measures have been relaxed.
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
Travellers in the UK 'flu' risk groups should ensure that they have received their seasonal influenza vaccine before travel. The Saudi Ministry of Health recommends seasonal influenza vaccine for Hajj and Umrah attendees. Hepatitis A : spread through consuming contaminated food and water or person to person through the faecal-oral route.
Saudi Arabia have also listed other requirements for travellers visiting for Hajj and Umrah. Details are available from the Ministry of Health, in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Health Requirements and Recommendations for Travelers to Saudi Arabia for Hajj - 1445H (2024) and Health Requirements and Recommenations for Travellers to Saudi Arabia ...
SAUDIA uses necessary cookies to personalize content and ads, to provide social media features, and to analyze our traffic.We also share information about your use of our site with our social media, advertising and analytics partners who may combine it with other information that you've provided to them or that they've collected from your use of their services.
Short-term standard visitor visa. Residents from Saudi Arabia can apply for the Standard Visitor Visa to visit the UK as a Standard Visitor for tourism, business, study (courses up to 6 months) and other permitted activities, including: for tourism, for example on a holiday or vacation; to see your family or friends; to volunteer for up to 30 days with a registered charity
Saudi Arabia. The Hajj, or pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, is one of the world's largest mass gatherings. In 2024, Hajj will take place between June 14-19th. Mass gatherings are associated with unique health risks. Before you travel, visit a travel health specialist for specific advice related to your destination and this event.
If you are in Saudi Arabia and have an emergency (for example, been attacked, arrested or someone has died) contact the nearest consular services. Contact the embassy before arrival if you have additional questions on entry requirements, safety concerns or are in need of assistance. British Embassy Riyadh PO Box 94351 11693 Riyadh Saudi Arabia
This article is reviewed regularly by Wego's editorial team to ensure that the content is up to date & accurate. Updated February 2024 The United Kingdom attracts thousands of tourists every year from Saudi Arabia for its world-class museums and galleries, scenic countryside, and natural beauty, as well as its shopping and dining experiences. In this article, […]
Travel Advisory. January 24, 2024. Saudi Arabia - Level 3: Reconsider Travel. O T. Updated after periodic review to provide information on the risk of arrest due to social media use and the importation of prohibited items. Reconsider travel to Saudi Arabia due to the threat of missile and drone attacks. Exercise increased caution in Saudi ...
United Kingdom Visa. There are different requirements for entry to the UK and that based on nationality and country of residence, country of departure and the reason for the visit. Please be sure to provide all the necessary documents for travel, otherwise you the embassy will refuse to issue visa. For more information, visit the official ...