Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution, update may 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |

Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
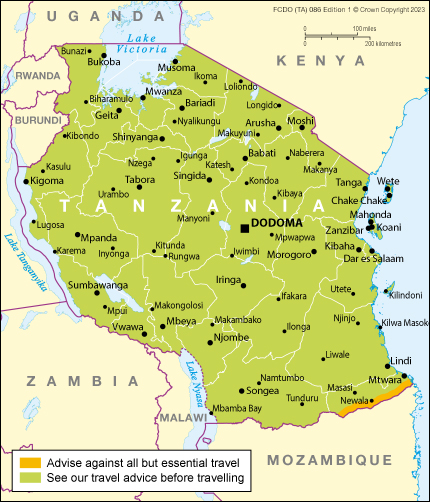
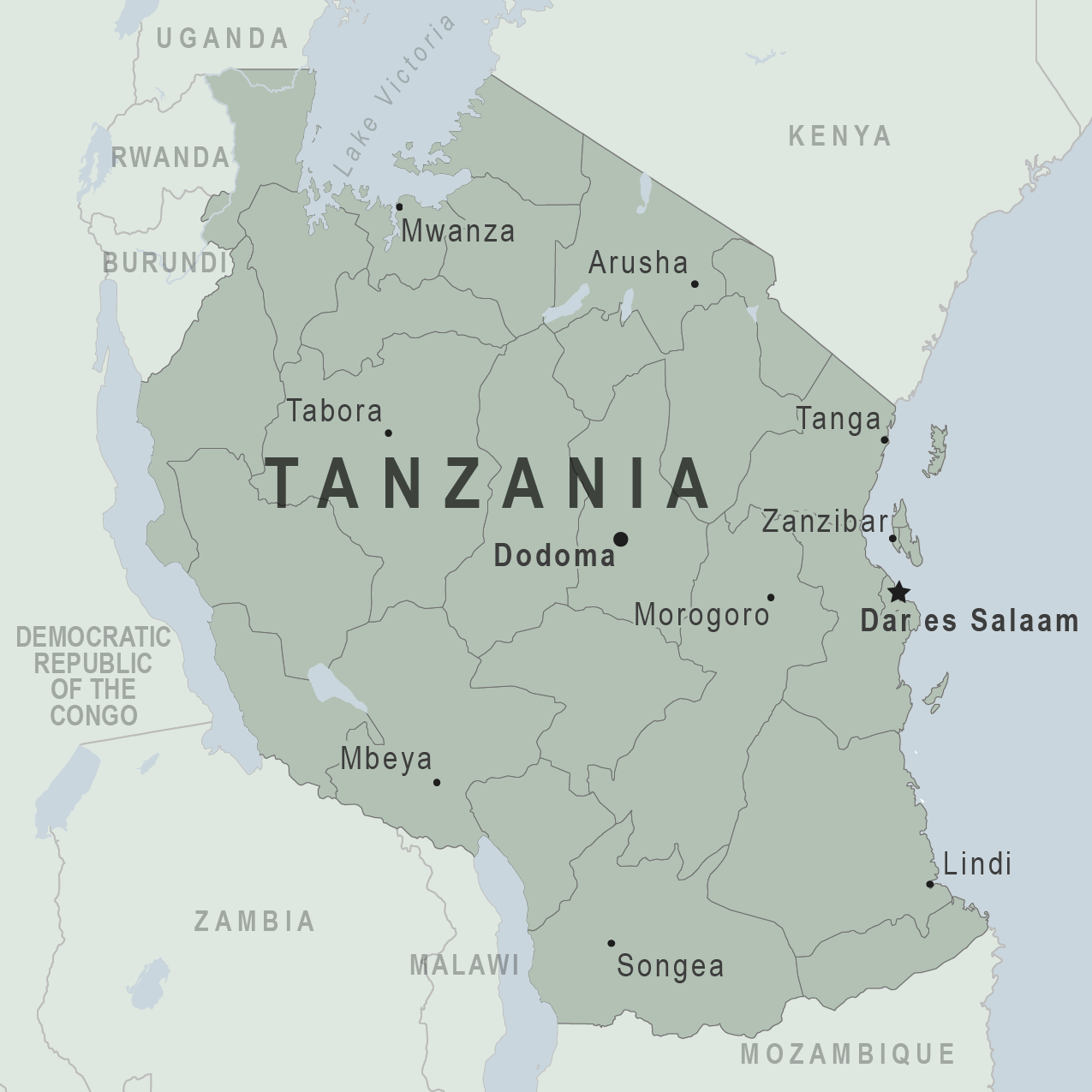
Tanzania Travel Advisory
Travel advisory july 31, 2023, tanzania - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Exercise increased caution in Tanzania due to crime, terrorism, and targeting of LGBTI persons . Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Reconsider Travel To:
- Mtwara Region in southern Tanzania due to the threat of terrorism.
Country Summary : Violent crime, such as assault, sexual assault, robberies, mugging, and carjacking, is common. Local police may lack the resources to respond effectively to serious crime.
Terrorist groups could attack in Tanzania with little or no warning, targeting embassies, police stations, mosques, and other places frequented by Westerners. Please see the additional information below regarding the increased threat of terrorism in Mtwara Region.
Members of the LGBTI community have been arrested, targeted, harassed, and/or charged with unrelated offenses. Individuals detained under suspicion of same-sex sexual conduct could be subject to forced anal examinations.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Tanzania.
If you decide to travel to Tanzania:
- Always carry a copy of your U.S. passport and visa and keep original documents in a secure location.
- Be aware of your surroundings.
- Do not leave your food or drink unattended.
- Stay alert in all locations, especially those frequented by Westerners.
- Avoid public displays of affection particularly between same-sex couples.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter.
- Review the Country Security Report for Tanzania.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
Mtwara Region in southern Tanzania – Level 3: Reconsider Travel There have been reports of violence in Mtwara Region in southern Tanzania. Increased activity by extremists along the southern border has led to attacks against both government and civilian targets.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, tanzania map, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:

ENTRY REQUIREMENTS
All travellers whether foreign nationals, Tanzanian citizens or Residents, MUST enter Tanzania through designated (formal) Entry Points. Upon arrival, the traveller will be responsible for:
- Appearing in person in front of an Immigration Officer with a completed and signed arrival declaration card, and
- Producing their passport or other acceptable document to an Immigration Officer; and
- In the case of foreign nationals; they may be required:
- To show their Visa or apply for Visa on arrival;
- To show Residence Permit/Pass If they are bonafide Residents in Tanzania;
- Return ticket or evidence of onward travel arrangement; and
- Evidence of funds for maintenance (upkeep budget
Download Visa Application Guidelines
Apart from the above immigration formalities, a traveller is supposed to observe health guidelines as provided by Ministry of Health in Tanzania from time to time. Currently there are special conditions imposed for yellow fever and Covid-19. Prospective visitors are advised to read respective guidelines from the Ministry of Health.
Visa nformation
- Visa Information
- FEES FOR VISA
- Entry Requirements
- Ordinary Visa
- Multiple Entry Visa
- Gratis Visa
- Transit Visa
- Business Visa
- Student Visa
- Referral Visa Cases
- Countries which their Nationals require Referral Visa.
- Countries Which are not Required to Apply for Visa
- Tips For Online Visa Service
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
Register to vote Register by 18 June to vote in the General Election on 4 July.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Warnings and insurance
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Areas where FCDO advises against all but essential travel
Your travel insurance could be invalidated if you travel against FCDO advice.
Mtwara Region along the Tanzania-Mozambique border
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to within 20km of the Tanzanian border with Cabo Delgado Province in Mozambique.
This is due to attacks by groups linked with Islamic extremism.
Find out more about why FCDO advises against travel .
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide and any specific travel advice that applies to you:
- women travellers
- disabled travellers
- LGBT+ travellers
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
- [email protected]
- +255 734 894 811 / +255 766 237 967

- DESTINATION EAST AFRICA
- Why Exhibit
- Who Exhibit
- KILIMANJARO-MKOMAZI FAM TRIP
- ZANZIBAR FAM TRIP
- TARANGIRE, NGORONGORO AND SERENGETI FAM TRIP
- RUAHA NATIONAL PARK and IRINGA ACTIVE SAFARI FAM TRIP
- LAKE ZONE, SERENGETI AND NGORONGORO FAM TRIP
- KILWA AND NYERERE FAM TRIP (NYRERERE N.P, KILWA RUINS, PUGU HILLS AND DAR CITY TOUR)
- INVESTMENT FORUMS
- Expo Layout
- Investment Forum
- Appointment
- Stand & Table Features
- New Registration
Tanzania Entry Requirements
- Accomodation
TANZANIA ENTRY REQUIREMENTS
Entry Requirement Documents to enter Tanzania
All foreign participants who wish to attend S!TE are advised to adhere to the following immigration requirements:
IMMIGRATION TIPS
IMPORTANT IMMIGRATION TIPS
Each EARTE PARTICIPANT is advised to read and observe immigration entry requirements;
VISA GUIDELINES
IMPORTANT NOTICE:
Applicants of Visa are strongly advised to read carefully the Visa Guideline before making an application;
Be part of S!TE 2024 for the truly business potential
Sign up for free newsletters and get more of S!TE 2024 event, delivered to your inbox.
Recent Post
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024, Tanzania Tourist Board. All Rights Reserved.
Tanzania Travel Restrictions
Traveler's COVID-19 vaccination status
Traveling from the United States to Tanzania
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Not required in public spaces.
Ready to travel?
Find flights to tanzania, find stays in tanzania, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Tanzania from the United States?
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tanzania.
Can I travel to Tanzania if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Tanzania without restrictions.
Can I travel to Tanzania without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Tanzania without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Tanzania?
Visitors from the United States are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Tanzania.
Can I travel to Tanzania without quarantine?
Travelers from the United States are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Tanzania?
Mask usage in Tanzania is not required in public spaces.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Tanzania?
Restaurants in Tanzania are open. Bars in Tanzania are .
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Tanzania, including Zanzibar Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
Be aware of current health issues in Tanzania. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 2 Practice Enhanced Precautions
- Global Polio May 23, 2024 Some international destinations have circulating poliovirus. Before any international travel, make sure you are up to date on your polio vaccines. Destination List: Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Guinea, Indonesia, Kenya, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Republic of the Congo, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, Sudan, Tanzania, including Zanzibar, Yemen, Zambia, Zimbabwe
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Active cholera transmission is widespread in Tanzania. Cholera is rare in travelers. Certain factors may increase the risk of getting cholera or having severe disease ( more information ). Avoiding unsafe food and water and washing your hands can also help prevent cholera.
Vaccination may be considered for children and adults who are traveling to areas of active cholera transmission.
Cholera - CDC Yellow Book
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Tanzania.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Tanzania. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Tanzania.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Tanzania take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Tanzania.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
In Tanzania poliovirus has been identified in the past year.
Travelers to Tanzania are at increased risk of exposure to poliovirus.
Vaccine recommendations : Adults traveling to Tanzania who received a complete polio vaccination series as children may receive a single lifetime booster dose of inactivated polio vaccine; travelers who are unvaccinated or not fully vaccinated should receive a complete polio vaccination series before travel. Children who are not fully vaccinated will be considered for an accelerated vaccination schedule .
Polio - CDC Yellow Book
Polio: For Travelers
Dogs infected with rabies are commonly found in Tanzania.
Rabies is also present in some terrestrial wildlife species.
If rabies exposures occur while in Tanzania, rabies vaccines may only be available in larger suburban/urban medical facilities.
Rabies pre-exposure vaccination considerations include whether travelers 1) will be performing occupational or recreational activities that increase risk for exposure to potentially rabid animals and 2) might have difficulty getting prompt access to safe post-exposure prophylaxis.
Please consult with a healthcare provider to determine whether you should receive pre-exposure vaccination before travel.
For more information, see country rabies status assessments .
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
Required for travelers ≥1 year old arriving from countries with risk for YF virus transmission; this includes >12-hour airport transits or layovers in countries with risk for YF virus transmission. 1
Generally not recommended for travel to Tanzania.
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
- Avoid floodwater
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
African sleeping sickness (african trypanosomiasis).
- Tsetse fly bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
African Trypanosomiasis
African Tick-Bite Fever
African Tick-bite fever
Chikungunya
- Mosquito bite
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic fever
- Tick bite
- Touching the body fluids of a person or animal infected with CCHF
- Mosquito bite
- Avoid animals
Rift Valley Fever
- Touching blood, body fluids, or tissue of infected livestock
Rift Valley fever
Airborne & droplet
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Tanzania, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH)
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Tanzania. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Some diseases in Tanzania—such as dengue, leishmaniasis, and African sleeping sickness—are spread by bugs and cannot be prevented with a vaccine. Follow the insect avoidance measures described above to prevent these and other illnesses.
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Tanzania include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Climbing Kilimanjaro is one of the most popular outdoor activities for travelers visiting Tanzania. The high altitude may lead to altitude sickness. Talk to your doctor about ways to prevent and treat altitude sickness.
See Travel to High Altitudes .
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Tanzania. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Tanzania’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in Tanzania. Fill your malaria prescription before you leave and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Tanzania may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Tanzania, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
Traffic flows on the left side of the road in Tanzania.
- Always pay close attention to the flow of traffic, especially when crossing the street.
- LOOK RIGHT for approaching traffic.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Tanzania, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Tanzania .
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
To call for emergency services while in Tanzania, dial either 112 or 999. Write these numbers down to carry with you on your trip.
Learn as much as you can about Tanzania before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Tanzania from the US Department of State.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Tanzania for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Resources » News and Events
Tanzania travel advisory no. 11 of 8th september 2022 - covid 19.
- 08 Sep 2022
- News and Events , Speeches and Press Release , Publications and Reports

THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA
TRAVEL ADVISORY NO. 11 OF 08 TH SEPTEMBER 2022
The Government of the United Republic of Tanzania (URT) through the Ministry responsible for Health continues to enhance prevailing preventive measures against the spread of COVID-19 including those related to international travel. In view of the current trend of COVID 19 globally, the Government is updating Travel Advisory No. 10 of 16th March, 2022 of Tanzania Mainland to version No. 11, effective from 15th September, 2022 to accommodate measures as follows:
1.Travelers entering URT including Tanzanians, returning residents, truck drivers/crew and those in transit through land borders who are;
a. Fully vaccinated will be exempted from both RT PCR and Rapid Antigen Test requirements. Travelers will be required to present a valid vaccination certificate with QR code for verification upon arrival. The only accepted vaccines are those which have been approved by the URT and the World Health Organization. [Full vaccinated means complete administered dose(s) of the vaccines as prescribed by manufacturer and approved by the World Health Organization].
b. Not fully vaccinated, unvaccinated and those not eligible for vaccination due to their country policies will be required to present a negative COVID-19 RT- PCR or NAATs certificate with QR code obtained within 72 hours before departure.
c. Not fully vaccinated, unvaccinated and those not eligible for vaccination due to their country policies and have no negative COVID-19 RT- PCR certificate will be tested for COVID 19 upon arrival using a Rapid Antigen Test at their own cost of TZS 23,000 (10 USD) for Tanzania Mainland except children aged 12 years and below and aircraft crew. Positive cases will be further confirmed by RT- PCR at a cost of 50 USD. For ground crossings, positive cases will be handled according to Bilateral and Joint Border agreements.
2. Travelers in transit by air transport are exempted from both vaccination and COVID 19 testing requirements unless stated otherwise by the conveyance to be used or countries of their final destinations.
3. All departing travelers are advised to seek information prior to departure from their travel agents regarding COVID-19 requirements of their country of destination or conveyance to be used. In case of any medical emergency while in the URT, please call Toll Free Health Emergency Number: 199 for Tanzania Mainland.
NB: The Travel Advisory will be reviewed from time to time as need arises.
MINISTRY OF HEALTH
SEPTEMBER 2022
(和訳)タンザニア連合共和国 渡航情報 第11号(2022年9月8日発行)
タンザニア連合共和国では保健に関する事項を担当する省庁を通じ、国際的な人の往来に関する対策を含むCOVID19感染症対策を継続するものととします。つきましてはCOVID19の最近の流行傾向を鑑み、渡航情報第10号(2022年3月16日発行)を更新した第11号が2022年9月15日より以下の通り実施されます。
- ワクチン接種完了者は 入国の際、QRコード付きの有効なワクチン接種証明書を提出することで RT PCRおよび 迅速抗原検査の免除対象となります。対象ワクチンは、タンザニア連合共和国およびWHOによって認められているもののみです。[ワクチン接種完了者とはWHOに承認され、ワクチン製造業者が定める回数の接種を完了した方を指します。]
- ワクチン未完了者、ワクチン未接種者および自身の国においてワクチン接種対象外となっている旅行者は入国の際、出発の72時間以内に取得したQRコード付きのCOVID19 RT-PCRもしくは核酸増幅検査(NAAT)陰性証明書を提出する必要があります。
- ワクチン未完了者、ワクチン未接種者、自身の国においてワクチン接種対象外となっている旅行者でCOVID19 RT-PCR検査の陰性証明書を所持しない旅行者は、タンザニア本土入国の際、自費(10USドルもしくは23,000TZシリング)で迅速抗原検査を受けていただきます(12歳以下の子供および航空機乗務員を除く)。陽性の場合は50USドルでRT-PCR検査を受けていただきます。陸路から入国し陽性の場合は、二国間/共同協定に従って対応されます。
- 空路でトランジットの場合には、利用する航空会社および最終目的地によって特に明記されていない限り、ワクチン接種およびCOVID19検査の免除対象となります。
- タンザニアから出国する際は、最終目的地および利用する航空会社のCOVID19に関する要件について出発前に旅行会社にご確認ください。
タンザニア本土滞在中に緊急の医療処置が必要な場合は、緊急医療番号(無料通話)199番までご連絡ください。
注意:渡航情報は必要に応じ、適宜内容が見直されます。
タンザニア保健省 事務次官
- News and Events
- Speeches and Press Release
- Exhibitions and Fairs
- Publications and Reports
- Bilateral Relation
- Tenders and Vacancies
- Related Links
- Photo Gallery
- Multimedia Videos
Related News and Events
- TANZANIA - JAPAN BUSINESS FORUM, ON 4 JULY 2024, AT MWALIMU J.K. NYERERE FAIR GROUND (SABA SABA)
- A COURTESY VISIT BY THE STUDENTS AND TEACHERS FROM ADACHI GAKUEN
- KAMPENI YA KUTANGAZA NA KUHAMASISHA FURSA ZA UWEKEZAJI ZA TANZANIA NCHINI JAPAN (TANZANIA INVESTMENT PROMOTION MISSION IN JAPAN) YAHITIMISHWA KWA MAFANIKIO MAKUBWA
- TANZANIA - JAPAN INVESTMENT PROMOTION MISSION TO KICK OFF FROM 27 MAY 2024 TO 8 JUNE 2024 IN TOKYO, OSAKA, SHIZOUKA AND CHIBA PREFECTURES, JAPAN
- STATE MINISTER FOR FOREIGN AFFAIRS OF JAPAN, MR. KIYOTO TSUJI VISIT TO TANZANIA ON MAY 21 - 22, 2024
- TANZANIA INVESTMENT PROMOTION MISSION (ROAD SHOW) IN JAPAN
- TIMU YA MPIRA WA MIGUU YA DIASPORA WA TANZANIA NCHINI JAPAN, “THE KILIMANJARO FC”, IMEKABIDHI KOMBE LA USHINDI LA MICHUANO YA KIMATAIFA YA SAMURAI SOCCER
- TANGAZO KWA WATANZANIA WAISHIO AUSTRALIA NA NEW ZEALAND WALIOOMBA PASIPOTI MPYA
- “Swahili International Tourism Expo (S!TE) 2024”
- WFP Walk the World 2024 Yokohama
Subscribe to Email Updates
Get all latest updates from the Embassy in Your Inbox
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Tanzania travel advice
Latest updates: Editorial change
Last updated: June 5, 2024 06:24 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, tanzania - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Tanzania due to crime levels and the threat of terrorism.
Border with Mozambique in Mtwara Region - Avoid all travel
Avoid all travel to within 10 km of the border with Mozambique, in the Mtwara Region, due to the presence of armed groups, the threat of terrorism and the risk of kidnapping.
Portion of Mtwara Region south of the A19 highway - Avoid non-essential travel
Avoid non-essential travel to the area between the A19 highway and the border with Mozambique in the Mtwara Region, due to the presence of armed groups, the threat of terrorism and the risk of kidnapping. This advisory excludes the areas within 10 km from the border with Mozambique, where you should avoid all travel. This advisory also excludes Mtwara City where you should exercise a high degree of caution.
Border with Burundi and Democratic Republic of Congo (Kinshasa) - Avoid non-essential travel
Avoid non-essential travel to the area within 20 km of the border with Burundi and 20 km from the shoreline of Lake Tanganyika along the border with the Democratic Republic of Congo (Kinshasa), due to the presence of armed groups and traffickers, and the threat of kidnappings. This excludes the city of Kigoma and Gombe, Katavi and Mahale national parks.
Back to top
Border with Mozambique in the Mtwara region
Extremist groups are active in the northern districts of Cabo Delgado, Mozambique. Security incidents have occurred along the border, in the Mtwara Region. Tanzanian military and security forces conduct counterinsurgency operations in the area. Access to the area is controlled in several locations and movements in and out are monitored.
Southern Mtwara region
Armed groups have been active in the southern Mtwara region between highway 19 and 10 km from the border with Mozambique. There is a threat of terrorism and kidnappings in this region.
Border with Burundi and Democratic Republic of Congo (Kinshasa)
Travel near refugee camps in northwestern Tanzania, particularly in the region of Kigoma and to the west of Kagera bordering Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo and Rwanda, is dangerous due to banditry.
Demonstrations
Demonstrations can occur anywhere across the country and sometimes on short notice. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, occurs, particularly in public places and popular tourist areas in Dar es Salaam, Zanzibar and Arusha.
Exercise caution in and around:
- restaurants
- nightclubs and cinemas
- shopping centres
In Dar es Salaam, exercise increased caution in and around:
- transportation hubs
- markets, particularly Kariakoo Market
- Masaki/Oyster Bay Peninsula, particularly along Toure Drive
In Zanzibar, exercise increased caution in and around Stone Town.
To mitigate the threat from theft:
- ensure that your belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- seek local advice on the security situation prior to visiting beaches
- avoid deserted beaches
Bag snatching from passing vehicles is very common.
- When walking along the street, do not carry your bag with the strap across your body. You could be badly injured if a thief drives by and attempts to steal your bag
Violent crime
Tourists have been victims of assaults, including sexual assaults, in Dar es Salaam, Zanzibar and Arusha.
If you are the victim of an armed robbery, do not resist. Attackers could assault you for failing to comply or not complying quickly enough.
- Exercise a high degree of caution
- Avoid walking around at night
Crimes against children and people with albinism, including murder, have occurred. Be particularly cautious.
Organized crime
Organized crime associated with international drug trafficking occurs in Tanzania, as it is situated along a transit route used to transport drugs from Asia to Africa. Though tourists are rarely affected, exercise caution in large cities.
Kidnappings
Kidnapping-for-ransom does not pose significant risk in Tanzania, though armed groups from bordering countries are known to employ this tactic.
Exercise caution along border areas, namely:
- areas bordering Lake Tanganyika, which marks the border between the Democratic Republic of Congo
- the southeastern border with Mozambique
Express kidnappings
Tourists have been taken to ATMs and forced to withdraw funds from their account after accepting a ride from a stranger, a local taxi, ride share companies or a recent acquaintance. These incidents have most often occurred near hotels and transportation hubs such as ferry, bus and train terminals in Dar es Salaam. To minimize the risk, do not accept unsolicited offers of assistance or rides from new acquaintances or strangers. Always book transportation from a reputable company or through your hotel.
Home invasions
Armed home robberies occur and foreigners’ homes have been targeted by criminals. Always lock your doors and windows and use reinforced barriers wherever possible. Do not rent temporary accommodations from new acquaintances. Be sure to go through a reputable agency if looking for long-term accommodations in Tanzania.
Road travel
While better in larger centres, road conditions and road safety are poor throughout the country.
Road conditions
Road signs are often missing, and visibility is poor due to insufficient lighting. Poorly maintained cars, roaming wildlife, livestock, cyclists and pedestrians also increase the risk associated with driving. Outside major cities, four-wheel drive vehicles are highly recommended.
- Avoid driving unless you are familiar with local conditions
- Avoid travelling by road at night. Due to the potential for assault or robbery when stopped at a light at night, some drivers ignore traffic lights. This practice makes intersections dangerous at night
- In the event of an accident, drive to the nearest police station
Tourist facilities are adequate in major cities but limited in remote areas, with the exception of principal game lodges and beach resorts.
Monitor fuel levels to ensure that your fuel tank is never lower than half full.
Road safety
Drivers often drive at excessive speeds, and they can be aggressive or reckless. Accident causing fatalities are common.
Armed robberies, carjackings and attacks on moving vehicles have occurred in Arusha and Dar es Salaam, particularly on Toure Drive (Msasani Peninsula).
- Avoid travelling alone
- Keep windows rolled up and doors locked
- Avoid travelling after dark
- Remain on tourist routes and avoid remote areas
- If you find yourself on less-travelled roads and trails, avoid stopping because armed robberies and carjackings may occur
- When travelling between cities, you should do so in a convoy, whenever possible
Crowds tend to form around accidents and foreigners are extorted for money or assaulted (even when they are not at fault).
There is a threat of terrorism, particularly in Dar es Salaam, Zanzibar, Arusha and border areas. Terrorist attacks could occur at any time. Targets could include:
- government buildings, including schools
- places of worship
- airports and other transportation hubs and networks
- public areas such as tourist attractions, restaurants, bars, coffee shops, shopping centres, markets, hotels and other sites frequented by foreigners
Stay at hotels that have robust security measures.
Always be aware of your surroundings when in public places.
Credit card and ATM fraud occurs. Be cautious when using your credit or debit card at ATMs, and:
- pay careful attention when your cards are being handled by others
- use ATMs located in well-lit public areas or inside a bank or business
- avoid using card readers that have an irregular or unusual feature
- cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements
Foreigners have been victims of scams relating to volunteer work visas and safaris.
If you plan to engage in these activities, only deal with reputable companies and check their references
Overseas fraud
Spiked food and drinks
Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
2SLGBTQI+ travellers
2SLGBTQI+ persons have been subject to physical and verbal harassment by locals and authorities.
2SLGBTQI+ travellers should carefully consider the risks of travelling to Tanzania.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Some officials solicit bribes as you go through customs at airports. In a common scheme, an official will ask the visitor to produce a certificate of proof of inoculation against yellow fever, even in cases where you don't need one.
If this happens to you, ask to speak to a senior official.
Police officers may approach you requesting money for alleged offences.
Before proceeding to a police station, insist they produce proper identification.
If you think you are dealing with a corrupt official, you may inform them you will contact the High Commission for advice. This tends to dissuade them from soliciting bribes. Report all such incidents to the High Commission of Canada in Dar es Salaam.
National parks and nature reserves
Organized tours and independent travellers have been victims of armed robbery in parks and nature reserves.
Exercise caution in:
- the northern circuit in the vicinity of Serengeti National Park
- Arusha National Park and Ngorongoro Conservation Area
- regions surrounding Mount Kilimanjaro
Avoid camping or travelling alone and hire a reputable tour guide. Hotels can make recommendations for reputable tour companies.
While camps and lodges are generally guarded, potentially dangerous wild animals often venture within the boundaries of the camp.
- Follow the advice and warnings of local tour guides and camp employees
- Do not walk around at night
- Never leave children unattended
Mountaineering
If you are considering climbing Mount Kilimanjaro, carefully consider the inherent risks involved. People are seriously injured or killed on the mountain every year, and emergency assistance is severely limited. If you intend to climb:
- never do so alone and always hire an experienced guide from a reputable company
- buy travel insurance that includes helicopter rescue and medical evacuation
- ensure that your physical condition is good enough to meet the challenges of your activity
- ensure that you are properly equipped and well informed about weather and other conditions that may pose a hazard
- inform a family member or friend of your itinerary, including when you expect to be back to camp
- know the symptoms of acute altitude sickness, which can be fatal
- obtain detailed information on trekking routes or ski slopes before setting out and do not venture off marked trails
Power outages
Power outages occur regularly across the country. Local authorities may impose rationing measures for electricity.
Power outages could affect your ability to purchase basic necessities and impact essential services, such as:
- public transportation
- medical services
- water supply
- telecommunications
Not all buildings are equipped with generators.
- Plan accordingly
- Keep a supply of water, food and fuel on hand
- Make sure you always have an emergency kit on hand
Public transportation
You should avoid travelling by bus (dala dala), as public buses are often overcrowded, poorly maintained and driven in a reckless manner. Public buses are frequently involved in accidents which have resulted in fatalities. There have been reports of sexual assault on buses.
Intercity buses are typically more safe and meet higher maintenance standards.
Do not travel on overnight buses.
Rail service is limited and maintenance standards are low. There have been reports of theft on crowded trains, particularly overnight trains.
A licensed taxi is a white car with a white (never yellow) licence plate, a coloured stripe running laterally on the side panels of the vehicle, a number located inside a circle on the passenger doors and visible insurance and registration numbers located on the windshield.
- Don't use motorcycle taxis (pika-pika or boda-boda) or three wheel taxis (bajaj), as drivers are often reckless and do not provide adequate safety equipment for passengers (such as helmets)
- Use only licensed taxis selected by a reputable hotel or restaurant, or one located at an official taxi stand
- Avoid taking a taxi that has been hailed for you by a recent acquaintance
- Always ask for identification before accepting transportation and check that the driver’s ID matches the name of the car registration and taxi licence
There are regular ferries travelling between Dar es Salaam and Zanzibar. Tanzanian ports are often frequented by persuasive ticket scalpers.
Vessels travelling between the following ports are less reliable and often overcrowded:
- Zanzibar and Pemba
- Tanga and Pemba
- Mafia and mainland Tanzania
Ferry accidents occur due to the overloading and poor maintenance of some vessels.
- Only use reputable ferry companies
- Do not board vessels that appear overloaded or unseaworthy
Pirate attacks and armed robbery against ships occur in coastal waters, particularly in the Gulf of Aden and Indian Ocean. Mariners should take appropriate precautions.
Live piracy report - International Maritime Bureau
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Tanzanian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Tanzania.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: required Business visa: required Student visa: required Work/volunteer visa: required
At main ports of entry, you can get a visa on arrival for a maximum of 3 months. When you arrive, ensure that immigration officials validate your visa by stamping your passport or writing any required information in it. Some visas are valid for a period shorter than three months. If you are a frequent visitor or business traveller, apply for a multiple-entry visa before the start of your trip.
Verify that you abide by the terms and expiry date indicated on your visa. You could receive a substantial fine if you overstay the period allowed by your visitor visa or residence permit.
Entry visas - Ministry of Home Affairs, Tanzania
Other entry requirements
You must be able to show proof of return or onward ticket. You could be refused entry if you fail to show it upon request.
Working and volunteering in Tanzania
You cannot perform any type of work, including volunteer work, on a tourist visa. When planning to travel to Tanzania to do volunteer work, contact the High Commission for the United Republic of Tanzania for information on specific requirements.
Work permits must be verified by Tanzanian immigration officials within 30 days of issuance. You can get this done at any Tanzanian Immigration office or online the Immigration Department’s online verification system.
- Ministry of Home Affairs - Tanzania
- Foreign diplomatic missions and consulates in Canada
- Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
- Polio: Advice for travellers - 6 May, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is low potential for yellow fever exposure in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from or have transited through an airport of a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination may be recommended depending on your itinerary.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites .
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
This destination is in the African Meningitis Belt, an area which has the highest rates of meningococcal disease in the world. Meningococcal disease is a serious and sometimes fatal infection.
Travellers who are at higher risk should discuss vaccination with a health care provider. High-risk travellers include those living or working with the local population (e.g., health care workers) or those travelling to crowded areas or taking part in large gatherings.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Cholera is a risk in parts of this country. Most travellers are at very low risk.
To protect against cholera, all travellers should practise safe food and water precautions .
Travellers at higher risk of getting cholera include those:
- visiting, working or living in areas with limited access to safe food, water and proper sanitation
- visiting areas where outbreaks are occurring
Vaccination may be recommended for high-risk travellers, and should be discussed with a health care professional.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
There is a risk of schistosomiasis in this destination. Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by tiny worms (blood flukes) which can be found in freshwater (lakes, rivers, ponds, and wetlands). The worms can break the skin, and their eggs can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, flu-like symptoms, or urinary problems. Schistosomiasis mostly affects underdeveloped and r ural communities, particularly agricultural and fishing communities.
Most travellers are at low risk. Travellers should avoid contact with untreated freshwater such as lakes, rivers, and ponds (e.g., swimming, bathing, wading, ingesting). There is no vaccine or medication available to prevent infection.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
Onchocerciasis (river blindness) is an eye and skin disease caused by a parasite spread through the bite of an infected female blackfly. Onchocerciasis often leads to blindness if left untreated. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from blackfly bites, which are most common close to fast-flowing rivers and streams. There is no vaccine available for onchocerciasis although drug treatments exist.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Rift Valley fever is a viral disease that can cause severe flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can be fatal. It is spread to humans through contact with infected animal blood or tissues, from the bite of an infected mosquito, or eating or drinking unpasteurized dairy. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from insect bites and avoid animals, particularly livestock, and unpasteurized dairy. There is no vaccine available for Rift Valley fever.
African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a tsetse fly. Tsetse flies usually bite during the day and the bites are usually painful. If untreated, the disease is eventually fatal. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from bites especially in game parks and rural areas. Avoid wearing bright or dark-coloured clothing as these colours attract tsetse flies. There is no vaccine available for this disease.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks and impairs the immune system, resulting in a chronic, progressive illness known as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
High risk activities include anything which puts you in contact with blood or body fluids, such as unprotected sex and exposure to unsterilized needles for medications or other substances (for example, steroids and drugs), tattooing, body-piercing or acupuncture.
Medical services and facilities
Medical facilities are limited and medicines are often unavailable, even in Dar es Salaam.
Medical evacuation, which can be very expensive, may be necessary in the event of serious illness or injury.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect lengthy jail sentences.
Alcohol is not sold in some parts of Zanzibar. Avoid consuming alcohol in those areas.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Plastic bags
The use, manufacture or importation of plastic bags is illegal.
Convicted offenders, including tourists, can face very heavy fines, imprisonment for up to 7 days, or both.

Identification
You must carry photo identification, such as a passport, and be ready to present it to authorities upon request. Keep a photocopy of your passport in a safe place in case it’s lost or confiscated.
Photography
Photography of military installations is forbidden. Individuals have been detained and/or had their cameras and film confiscated for taking pictures of public structures and buildings, including:
- industrial sites
Always ask permission before photographing individuals.
Pornography
Possession of pornographic material is illegal.
Flora and fauna
Collecting and removing any flora or fauna from its natural habitat is illegal. This includes removing seashells from marine parks.
Tanzanian law strictly regulates the sale, possession or removal from the country of animal or animal parts, including jewellery and hunting trophies. Certain items are exempt; however, you need a special permit from the Ministry of Natural Resources and Tourism before attempting to leave the country with these items.
Trophy dealing licences – Ministry of Natural Resources and Tourism, Tanzania
Ramadan
In 2025, the lunar month of Ramadan is expected to begin on or around February 28.
In public, between sunrise and sunset, be discreet when:
Dress and Behaviour
In Zanzibar, Islamic practices and beliefs are particularly influential.
To avoid offending local sensitivities:
- dress conservatively
- behave discreetly
- respect religious and social traditions
Women should cover their shoulders and refrain from wearing shorts.
Tanzanian law prohibits sexual acts between individuals of the same sex. Those convicted face up to life imprisonment and possibly a fine.
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is not legally recognized in Tanzania .
If local authorities consider you a citizen of Tanzania , they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
Travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Tanzania.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Tanzania by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Tanzania to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children's Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country's judicial affairs.
- International Child Abductions: A guide for affected parents
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Request emergency assistance
You must carry an international driving permit alongside your Canadian driver’s licence.
Traffic drives on the left.
Police roadblocks are common.
- If you are stopped by police, always cooperate and give proof of documentation requested of you
- If you are asked to pay an on-the-spot fine for a traffic violation, ask to travel to the nearest police station to file a report and to contact the High Commission of Canada in Tanzania
- Always ask for an official receipt
International Driving Permit
The currency is the Tanzanian shilling (TZS).
Credit cards are generally accepted at larger hotels, European carriers and other businesses that cater to international clientele, but are rarely accepted elsewhere. Outside of Dar es Salaam and at smaller establishments, cash in either Tanzanian shillings or U.S. dollars are the preferred method of payment, particularly for hotel bills, domestic airline tickets and entry to national parks.
ATMs are available in main cities, and some can be used to access Canadian bank accounts; however, they are subject to breakdowns. You should carry a small supply of cash in U.S. dollars for use in airports and at borders.
Rainy season
On the mainland, the rainy season extends from March to May and then again from November to December. Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services, particularly in the summer months. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged.
- Keep informed of regional weather forecasts and plan accordingly
- Use a four-wheel drive vehicle during the rainy seasons
Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
Seismic activity
Tanzania is located in an active seismic zone.
Local services
Dial 112 for emergency assistance.
Consular assistance
Comoros, Seychelles, Zambia
For emergency consular assistance, call the High Commission of Canada in Tanzania, in Dar es Salaam, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise a high degree of caution in Tanzania overall due to the risk of violent crime.
Higher levels apply in some areas.
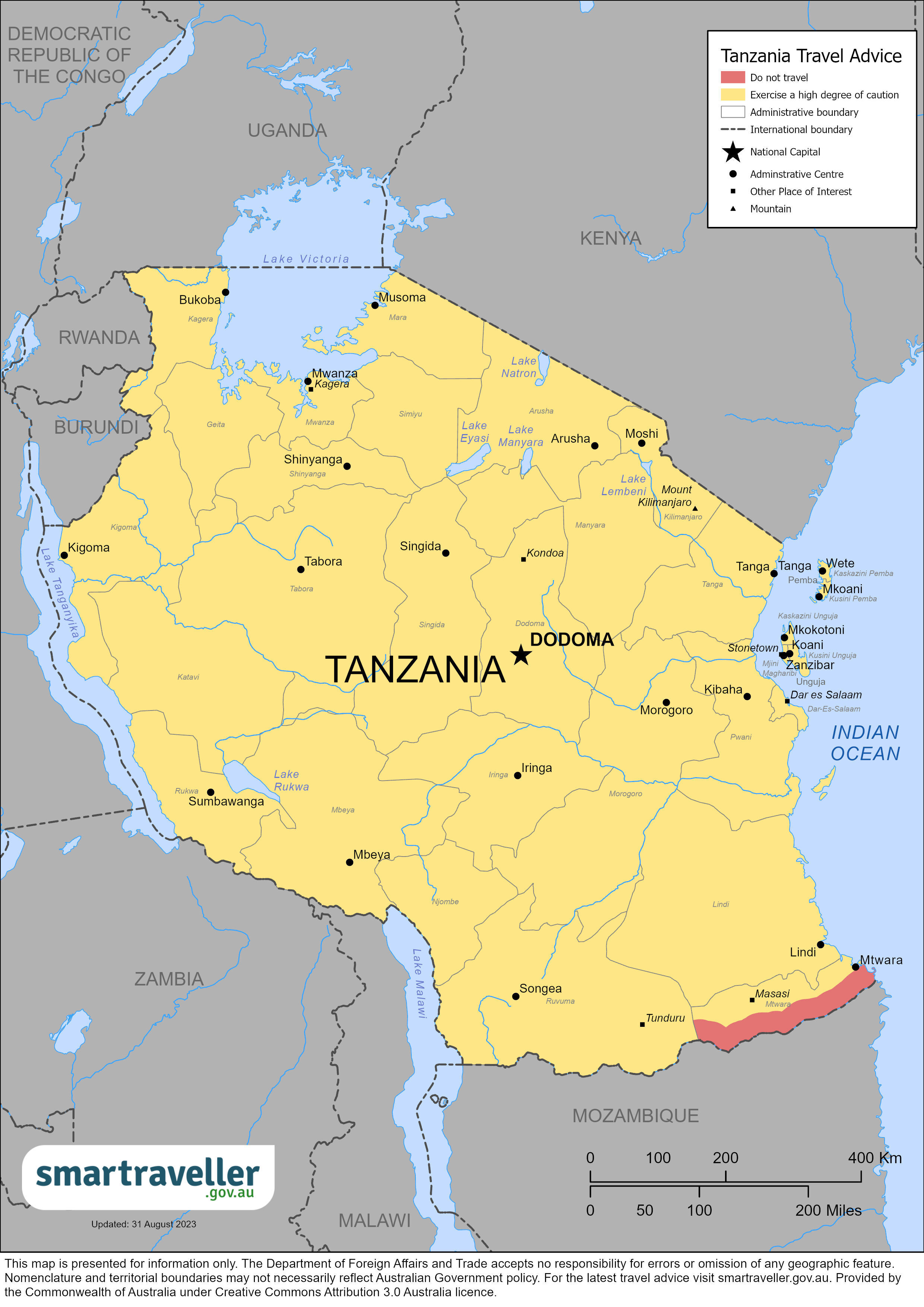
Tanzania (PDF 854.76 KB)
Africa (PDF 1.68 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 112 or go to the hospital.
Call 112 or contact the local police.
Advice levels
Exercise a high degree of caution in Tanzania overall.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Tanzania overall due to the risk of violent crime.
Do not travel to within 30km of the border with Mozambique, in the Mtwara region.
Do not travel to within 30km of the border with Mozambique, in the Mtwara region due to the threat of militant attacks, terrorism and kidnappings.
- During the rainy seasons (March to May and November to December), floods can block roads. Monsoons occur in coastal and island areas from July to October. Cyclones in coastal areas are also common. Follow the advice of local officials.
- Terrorists are likely to try to carry out attacks anywhere in Tanzania. Be alert to your surroundings and pay close attention to your personal security.
- Violent armed robbery, petty theft and threats of violence are common in Tanzania, especially in Dar es Salaam. Be extra careful in and around Arusha in northern Tanzania. Armed robberies, carjackings and home invasions have occurred. Bag snatching from moving vehicles is increasing. Victims can be injured or killed by being dragged behind vehicles. Don't resist bag-snatch attempts.
- Only use registered taxis. Travellers have been targeted by criminals while using unlicensed taxis.
- Security incidents continue along the Tanzania-Mozambique border. In October 2020, a violent attack occurred in Kitaya village, in Mtwara, close to the border with Mozambique. Do not travel within 30km of the border with Mozambique in the Mtwara region.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Malaria, including chloroquine-resistant strains, occurs year-round, except in areas above 1800 metres. Consider taking anti-malarial medication.
- Yellow fever can occur. Check with a health professional before travelling if you need to get vaccinated. Other insect-borne diseases include Zika virus, dengue, filariasis and East African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness). Ensure your accommodation is insect-proof and use insect repellent.
- HIV/AIDS is widespread. Take precautions if you're taking part in high-risk activities.
- Altitude sickness can affect anyone at heights over 2500 metres. If you plan to climb Mt Kilimanjaro (5895 metres), make sure you're physically fit and in good health. Talk to your doctor before you travel.
- Medical facilities are limited, and medicines are often not available. If you get injured or become ill, you may need to be evacuated to another country for treatment. This can be expensive. In the case of a medical emergency while in Tanzania, call the toll-free Health Emergency Number: 112.
Full travel advice: Health
- Don't use or carry illegal drugs. Penalties for drug offences are severe and include long prison sentences. It's also illegal to possess pornographic material.
- Plastic bags are banned in Tanzania.
- Same-sex relations are illegal and punishable by up to 30 years in jail. Authorities have targeted LGBTQIA+ rights activists.
- It's illegal to photograph military zones, weapons or personnel.
- Dress and behaviour standards are conservative in Tanzania, especially in Zanzibar. If you're female, don't wear shorts or sleeveless tops outside resorts.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- You need a visa to enter Tanzania. Tanzania has introduced an online visa application form that can be submitted and approved online before travel. Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. You should contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Tanzania for the latest details.
- Proof of yellow fever vaccination may be required for entry to Tanzania if arriving from or transiting through a yellow fever risk country.
- All ships, cruise liners and commercial vessels are targets for Somali pirates. Many attacks and kidnappings have happened off the Tanzanian coast. Be alert and exercise extreme caution in coastal waters. Don't leave sight of the coastline.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
- There's an Australian Consulate in Dar es Salaam. It can provide limited consular assistance.
- For full consular help, contact the Australian High Commission in Kenya .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the High Commission's social media accounts.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Terrorists are likely to try to carry out attacks anywhere in Tanzania. Terrorists could attack with little or no warning, targeting hotels, embassies, restaurants, malls and markets, police stations, places of worship, and other places frequented by Westerners.
Attacks have continued intermittently along the Tanzania-Mozambique border. In October 2020, a violent attack occurred in Kitaya village, in Mtwara, close to the border with Mozambique. Terrorists have targeted the Cabo Delgado province in northern Mozambique adjacent to the Tanzania border area. Avoid travelling to within 30km of the border with Mozambique, in the Mtwara region, due to the threat of militant attacks, terrorism and kidnappings.
Terrorists may target places associated with foreigners or Westerners, including:
- hotels, restaurants, bars and clubs
- embassies, high commissions and other diplomatic interests
- places of worship
- shopping malls, markets and outdoor events
- police stations
To avoid terrorism:
- be alert to your surroundings
- pay close attention to your personal security
- consider the level of security at places you visit
- stay alert in crowded places and locations frequented by foreigners
- keep a low profile
- monitor local media
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
More information:
Violent armed robbery , petty theft and threats of violence are common in Tanzania, especially in Dar es Salaam.
Travellers have been sexually assaulted . HIV/AIDS is widespread in Tanzania. If you're a victim of rape or violent crime, seek immediate medical attention.
Criminals in Dar es Salaam are becoming bolder and crime is more common. There are regular reports of crime along the Toure Drive on the Msasani Peninsula, especially bag snatching from moving vehicles.
Serious injury and death after resisting bag snatching is possible. Victims have been dragged behind vehicles. Don't resist or try to stop bag snatch attempts.
Take extra care in and around Arusha in northern Tanzania. Armed robberies, carjackings and home invasions have happened.
Don't accept food or drink from strangers — it may be spiked.
To protect yourself from violent crime:
- take care on public transport, in shared taxis and at bus stations
- take care at places frequented by travellers, including national parks and beaches
- avoid walking and travelling after dark
Thieves target travellers in isolated and coastal areas.
' Express kidnapping ' occurs. Kidnappers abduct people and force them to withdraw funds from ATMs before releasing them. This can happen after being befriended by strangers or while using unlicensed taxis. Only use registered taxis.
If you're stopped by police, ask to see their ID, especially before paying fines.
Border areas
There are bandits near the borders of Rwanda, Burundi and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Do not travel within 30km of the border with Mozambique in the Mtwara region. Terrorists are likely to target foreigners and foreign interests. The insurgency poses an extreme threat in neighbouring Cabo Delgado province in Mozambique, and attacks are highly likely to continue. Read the Mozambique travel advice for more information.
In August 2021, the South African Development Community (SADC) deployed military forces to Cabo Delgado, Mozambique. Terrorist organisations may increase operations in the Mtwara region as it may be outside the current reach of SADC operations.
The US Embassy and the United Nations recommend that you use police escorts on parts of the Rusomo to Kahama Road near the border with Rwanda. There's a threat of armed attacks.
Pay attention to your personal security when visiting national parks, game parks and reserves.
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
More information:
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Civil unrest and political tension
Be alert in public places. Avoid locations without an obvious security presence.
Avoid large gatherings or demonstrations. Public protests and events that draw large groups of people can turn violent.
Monitor the media and other sources for safety information.
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Tours and adventure activities
Transport and tour operators don't always follow safety and maintenance standards. This includes adventure activities, such as diving.
If you plan to do an adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
If proper safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Wildlife safety
Follow local wildlife laws. Keep a safe and legal distance when looking at animals. This includes marine animals and birds.
Only use trusted and professional guides or tour operators.
Follow park rules and the advice of wardens.
Don't swim in lakes and rivers. You could be attacked by wildlife. There's also a risk of catching waterborne diseases.
Climate and natural disasters
Tanzania experiences natural disasters and severe weather , such as:
- earthquakes
If a natural disaster happens, follow the advice of local authorities.
Register for updates from the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System .
The rainy seasons in Tanzania are from March to May and November to December. Unusual weather patterns may mean the rainy season is delayed or extended.
Floods may close roads.
Monsoons occur in coastal areas and on islands, between June and October.
Earthquakes
Tanzania lies on a fault line so earthquakes are possible.
All oceanic regions can experience tsunamis. In the Indian and Pacific Oceans, the risk is higher. There are many large earthquakes along major tectonic plate boundaries and ocean trenches in this region.
Cyclones can happen along coastal areas. The direction and strength of cyclones can change with little warning.
If there's a cyclone or severe storm:
- you may get stuck in the area
- ferries may stop running (to and from Zanzibar)
- flights could be delayed or suspended
- flights out may fill quickly
- adequate shelter may not be available
Severe weather may also affect:
- access to ports
- road travel and bridges
- essential services, such as water and electricity
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Medications
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in Tanzania. Take enough legal medication for your trip.
Carry a copy of your prescription or a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Medical care
Medical facilities.
There are limited medical facilities and medications are often not available, even in major cities.
If you have an accident or become ill, you may need to be evacuated by air to Kenya or another country. Medical evacuation can be very expensive.
Health risks
Insect-borne diseases.
Malaria is found throughout the year, except in areas above 1800 metres. Chloroquine-resistant strains of malaria have been reported.
Other insect-borne diseases occur. These include:
- yellow fever
- human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness)
The tsetse fly carries sleeping sickness. This is common to the northern safari area of Tanzania.
To protect yourself from disease:
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
- insect-proof your accommodation
- consider taking medication to prevent malaria
Get medical advice if you have a fever, muscle pain, rash or severe headache.
HIV/AIDS is widespread. Take steps to reduce your risk of exposure to the virus.
Marburg Virus
On 21 March 2023, the Tanzanian Government confirmed an outbreak of Marburg virus in the Bukoba District in Kagera Region. The disease is spread through contact with infected bodily fluid from people and animals. Take steps to reduce your potential risk of exposure to the virus, including practising good hygiene and avoiding high-risk activities.
Other health risks
Waterborne, foodborne and other infectious diseases are common. Serious outbreaks happen. These include:
- tuberculosis
- meningococcal disease
- Rift Valley virus
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- avoid ice cubes
- don't eat raw or undercooked food, such as salads
- don't touch domestic animals
- don't swim in fresh water
If you're bitten or scratched by an animal, get medical help straight away.
Get medical advice if you have a fever or diarrhoea.
Altitude sickness
If you plan to climb Mt Kilimanjaro (5895m) make sure you're physically fit and in good health. Be aware of altitude sickness.
If you rapidly climb to altitudes greater than 2500m, you can get altitude sickness. This can be life-threatening and affect anyone, even if you're physically fit.
People who are more at risk of altitude sickness are those who:
- have had altitude sickness before
- exercise or drink alcohol before adjusting to the change in altitude
- have health problems that affect breathing
If you're planning to visit high altitudes areas, check with your doctor before you go.
Make sure your insurance policy covers you.
While in Tanzania, you're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Pornography
It's illegal to possess or access pornographic material.
LGBTQIA+ laws
Same-sex activity is illegal. Authorities can jail you for up to 30 years. Authorities might subject you to an invasive examination.
In June 2017, the Tanzanian Government announced a crackdown on LGBTQIA+ rights advocates in Tanzania.
In September 2017, authorities arrested 20 people in Zanzibar while they were receiving training about HIV/AIDS prevention.
The Regional Commissioner of Dar es Salaam has formed a surveillance team to identify suspected LGBTQIA+ people.
Members of the LGBTQIA+ community and advocates can be targets for harassment. There are regular cases of harassment and arrests by authorities and intimidation by members of the public. LGBTQIA+ travellers should take precautions.
- Advice for LGBTQIA+ travellers
Penalties for drug offences are severe. They can include long jail terms.
- Carrying or using drugs
It's illegal to photograph military zones, weapons or personnel.
Serious crimes, such as treason and murder, carry the death penalty.
There's corporal punishment for some crimes. This includes rape or robbery with violence.
Be aware of how you use social media, and what you post online. You need to comply with cybercrime laws.
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law and respecting customs
Local customs
Dress and behaviour standards are conservative in Tanzania, especially in Zanzibar. Take care to be respectful and not offend.
Avoid public displays of affection.
If you're a woman, don't wear shorts or sleeveless tops outside tourist resorts.
- Advice for female travellers
Dual citizenship
Tanzania doesn't recognise dual nationality.
This limits the consular services we can give if you're a Tanzanian dual national and arrested or detained.
Always travel on your Australian passport .
- Dual nationals
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
You need a visa to enter Tanzania. Tanzania has introduced an online visa application form that can be submitted and approved online ahead of travel.
It is also possible to get some single-entry visas on arrival in Tanzania at the main points of entry if you meet all the requirements for entry. You may also be asked to provide proof of your return journey. For further information about visas, visit the Tanzanian immigration website .
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact an embassy or consulate of Tanzania for details about visas, currency, customs and quarantine rules and the online visa application form.
Yellow fever vaccination
Proof of yellow fever vaccination may be required for entry to Tanzania if arriving from or transiting through a yellow fever risk country. S ome airlines may want to see one when you leave.
Find out about returning to Australia after exposure to yellow fever and see the World Health Organization's advice on countries with a risk of yellow fever.
- Countries with a risk of yellow fever (PDF 152KB)
Border measures
If you intend to travel to Tanzania, confirm entry requirements with Tanzanian authorities prior to making any travel arrangements. Refer to the latest requirements on the Ministry of Health’s website .
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with 'X' gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can't guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
More information:
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
Other formalities
Single-use plastic bags are banned in Tanzania, including in travellers' luggage.
The Tanzanian currency is the Tanzanian Shiling (TZS).
Credit card fraud can occur in Tanzania. Always keep your credit card in sight during transactions.
Avoid using ATMs on the street. Use ATMs in banks, shops, hotels and shopping centres.
Local travel
Road travel.
Driving can be hazardous, especially at night.
Most roads and vehicles are in poor condition.
High speeds, poor driving and bad lighting are all road risks.
Accidents are common and deaths happen.
You're more likely to be killed in a car accident in Tanzania than in Australia.
- Driving or riding
Other transport
Use only well-maintained transport and taxis. This includes long-distance buses.
Ferries can be overloaded or unseaworthy. There have been 2 major incidents in recent years with many deaths.
Don't board any vessel that's overloaded or in bad condition.
- Transport and getting around safely
Piracy happens off the coast of Tanzania.
Somali pirates attack shipping vessels up to 1000 nautical miles (1852km) from the coast of Somalia.
All ships, cruise liners and commercial vessels are targets for Somali pirates. Many attacks and kidnappings have happened off the Tanzanian coast.
Be alert and exercise extreme caution anywhere in coastal waters. Don't leave sight of the coastline.
- International Maritime Bureau
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Tanzania's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
The Australian Consulate in Dar es Salaam provides limited consular help to Australians in Tanzania by appointment only. The consulate doesn't issue passports.
Full consular help is available from the Australian High Commission in Kenya.
Australian Consulate, Dar es Salaam
Level 3, Address Building Plot 1403/01, Bains Singh Avenue, Msasani Peninsula Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Phone: +255 (0)753 301 837 Email: [email protected]
Check the Australian High Commission in Kenya's website for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
Australian High Commission, Nairobi
Limuru Road, Rosslyn Nairobi, Kenya Phone: +254 20 4277 100 Fax: +254 20 4277 139 Website: kenya.highcommission.gov.au Facebook: Australian High Commission, Kenya Twitter: @AusHCKenya
Check the High Commission website for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Tanzania?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.

Introducing Tanzania
About tanzania.
- Images of Tanzania
- History, language & culture
- Weather & geography
- Doing business & staying in touch
Plan your trip
- Travel to Tanzania
- Where to stay
While you’re there
- Things to see & do
- Shopping & nightlife
- Food & drink
- Getting around
Before you go
- Passport & visa
- Public Holidays
- Money & duty free
Book your flights
- Dar es Salaam
- Dar es Salaam Julius Nyerere International Airport
Tanzania travel guide
If you close your eyes and conjure up the quintessential romantic image of Africa, what you’ll most likely imagine is Tanzania: the drama of the wildebeest migration along a seemingly-endless savannah; the incongruous snow and glaciers of Mt Kilimanjaro; the iconic and statuesque Maasai warriors; the exotic palm-fringed beaches on the spice islands of Zanzibar. It’s all here.
Tanzania boasts some of the most impressive national parks and game reserves in Africa. The Serengeti National Park is considered the continent’s premier spot to see wildlife roam unheeded across vast open plains.
Nearby, within the steep walls of the Ngorongoro Crater lies the most densely concentrated population of African mammals on earth. Not to be forgotten, the Selous Game Reserve is larger than Switzerland, and is wild, remote and still virtually untouched by humans.
Even further from the beaten path are parks in the extreme west of the country which offer the unique opportunity to track chimpanzees in their natural habitat on the fringes of Lake Tanganyika, one of Africa’s Great Lakes.
Beyond its safari stalwarts, Tanzania has no less than 804km (503 miles) of sublime coastline and pearly-white beaches with some magnificent islands offshore. Known as the Swahili Coast, this was a favoured stop on ancient trading routes between the Indian sub-continent and the Middle East. Spices, jewels and slaves once passed through, bringing with them a mélange of cultural riches that remain today.
Tanzania’s not short on mountains either. The striking and snow-capped Mt Kilimanjaro is Africa's tallest at 5,895m (19,341ft) and climbing it is an unforgettable experience. Its slightly smaller sister Mt Meru is arguably even prettier, and a quicker climb.
Tanzania is home to more than 120 different ethnic groups and cultures, but it has seen little of the ethnic or religious-based violence that has afflicted certain other nations in the region. In fact the country is an inherently peaceful place and embraces its multicultural heritage, which adds to its broad appeal.
945,087 sq km (364,900 sq miles).
55,155,473 (UN estimate 2016).
54 per sq km.
Federal republic.
President Samia Suluhu Hassan since 2021. Zanzibar is semi-autonomous and has its own parliament and president (President Hussein Mwinyi since 2020).
Kassim Majaliwa since 2015.
Travel Advice
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Areas where FCDO advises against all but essential travel
Your travel insurance could be invalidated if you travel against FCDO advice.
Mtwara Region along the Tanzania-Mozambique border
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to within 20km of the Tanzanian border with Cabo Delgado Province in Mozambique.
This is due to attacks by groups linked with Islamic extremism.
Find out more about why FCDO advises against travel .
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide and any specific travel advice that applies to you:
- women travellers
- disabled travellers
LGBT+ travellers
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
This advice reflects the UK government’s understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK, for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Tanzania set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Tanzania High Commission in the UK .
COVID-19 rules
There are no COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements for travellers entering Tanzania.
Passport validity requirements
To enter Tanzania, your passport must have an ‘expiry date’ at least 6 months after the date you arrive and at least one blank page.
Check with your travel provider that your passport and other travel documents meet requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.
You will be denied entry if you do not have a valid travel document or try to use a passport that has been reported lost or stolen.
Visa requirements
You must have a tourist or business visa to enter Tanzania.
If you are planning to work or volunteer, you will also need a work permit. Information on how to apply is available from the Tanzanian Prime Minister’s Office .
Your employer or volunteer organisation should help you arrange this before you travel.
If you overstay your visa or permit you can be arrested, detained and fined before being deported.
The Tanzanian Immigration Department has more information on visas .
Applying for a visa
Apply for an ‘e-visa’ before you travel. It is no longer possible to get a visa from the Tanzanian High Commission in London.
You can also get a tourist or business visa for a single entry on arrival at the main ports of entry to Tanzania , subject to meeting all immigration requirements. You may be asked to provide proof of your return journey. You will not be able to get a multiple entry visa on arrival.
Checks at border control
You must be ready to show your return or onward ticket at border control.
Vaccination requirements
To enter Tanzania, you must have a certificate to prove you’ve had a yellow fever vaccination if you’re coming from a country listed as a transmission risk .
For full details about medical entry requirements and recommended vaccinations, see TravelHealthPro’s Tanzania guide .
Customs rules
There are strict rules about goods you can take into or out of Tanzania. You must declare anything that may be prohibited or subject to tax or duty.
Taking wildlife products into and out of Tanzania
Do not bring animal skin accessories into Tanzania as you risk questioning or detention when leaving the country.
Border officials have arrested foreigners for trying to take wildlife items they’ve bought, including horns and seashells, out of the country. It’s illegal to do this without a certified export permit from the Ministry of Natural Resources and Tourism. If you’re caught you can be detained or fined.
This guide also has safety advice for regions of Tanzania .
There is a high threat of terrorist attack globally affecting UK interests and British nationals, including from groups and individuals who view the UK and British nationals as targets. Stay aware of your surroundings at all times.
UK Counter Terrorism Policing has information and advice on staying safe abroad and what to do in the event of a terrorist attack. Find out how to reduce your risk from terrorism while abroad .
Terrorism in Tanzania
Terrorists are very likely to try and carry out attacks in Tanzania.
Terrorist attacks could be indiscriminate, including in places frequented by foreign nationals, such as:
- places of worship
- transport hubs
- restaurants
- major gatherings like sporting or religious events
- crowded places
Stay aware of your surroundings, keep up to date with local media reports and follow the advice of local authorities.
Extremists linked to the Islamic terrorist group Al-Shabaab based in Somalia pose a threat across the East Africa region, and are thought to be active in Tanzania. Attacks by IS-Mozambique, who are based in the Cabo Delgado province of Mozambique, are possible near Tanzania’s border with this area of Mozambique. There is also thought to be some support for Daesh (formerly referred to as ISIL). The Tanzanian authorities have successfully made a number of arrests in connection to terrorism. However, many incidents in Tanzania are of unclear origin and may be conducted by criminal gangs.
In 2020, the village of Kitaya in the Mtwara region was attacked, close to the border with Mozambique, the attack was claimed by Islamic extremists operating from northern Mozambique. Most attacks target the local security forces, although attacks against western interests are also possible.
Political situation
On occasion demonstrations and political rallies across Tanzania have turned violent, resulting in fatalities. Police may use tear gas or live ammunition for crowd control. If you’re in and around areas where demonstrations are taking place, be aware of what is happening around you and move away if there are signs of disorder.
Violent crime
There is a risk of armed crime, including armed robbery, throughout Tanzania. Take particular care in places frequented by tourists and foreign residents. In Dar es Salaam, tourists and residents have been targeted:
- in the city centre
- in the Masaki and Oysterbay peninsula area, particularly at Coco Beach
- along Toure Drive
In Zanzibar incidents have taken place in Stone Town and at hotels and on popular tourist beaches throughout the island.
Bag snatching is a well-known tactic of criminals, who may operate from cars or motorbikes. If you are walking on the street:
- walk towards the traffic so you can see vehicles approaching
- walk as far away from the road as possible
- carry bags loosely by the handle or hanging off your shoulder and do not secure the strap across your chest
- avoid walking or cycling at night or alone
Do not carry large amounts of cash or display valuables such as expensive jewellery or watches. Leave your passport in a safe place and carry a copy for ID checks.
When in a vehicle, keep car doors locked, windows up and valuables out of sight. Be particularly careful at night when there is a higher incidence of crime. Do not stop if pedestrians or hitchhikers try to flag you down.
Express kidnap
In Dar es Salaam, tourists have been ‘express kidnapped’. This means they’ve been assaulted, robbed and forced with the threat of violence to withdraw cash from ATMs. Some have been forced to arrange cash transfers of up to £5,000 through Western Union after being befriended by strangers or getting into unlicensed taxis.
Protecting your property
Burglary is a risk. Make sure residential property is secure and lock all doors and windows, especially at night. If where you’re staying has a security guard, they should insist on official identification before allowing anyone to enter your property or compound. If in doubt, do not let strangers in and raise the alarm.
There have been cases where women travelling alone and in small groups have been verbally harassed.
Laws and cultural differences
There is a high proportion of Muslims in Tanzania, particularly in Zanzibar and Pemba. Respect local traditions, customs, laws and religions. Make sure your actions do not cause offence, especially during the holy month of Ramadan or if you intend to visit religious areas.
Personal ID
Always carry copies of your passport photo page and visa. Carry your work permit, if you have one. Immigration officials or police can request these documents at any time, so make sure you can get the originals quickly if you need them. If you’re a resident or longer term visitor, consider getting certified copies.
Ramadan is a holy month for Muslims. The dates vary by year and country. During this time, avoid eating or drinking in public, outside of hotels or restaurants. Get more advice when you arrive from your tour guide, hotel or business contacts.
Dress modestly throughout Tanzania. Women wearing shorts or sleeveless tops away from tourist resorts in Zanzibar and Pemba, particularly in Stone Town, may cause offence to the local population.
Zanzibari authorities can fine you 700 US dollars or more if you’re wearing what they consider inappropriate clothing in public. For guides or tour operators, the fine can be at least 1,000 US dollars.
Environmental laws
Plastic bags are banned for environmental reasons. If you arrive by air you’ll be asked to hand over all plastic bags on arrival. The ban does not include ‘ziplock’ bags for airline security procedures.
Illegal drugs and prison sentences
Tanzania has strict laws on drug use and if you are found in possession of even a small amount you will be fined. There are severe penalties, including prison sentences, for possessing an amount that indicates possible intent to supply (drug trafficking). Tanzanian prisons tend to be dirty and overcrowded.
Discrimination and harassment
Reports made to the British High Commission by Black, Asian and Minority Ethnic (BAME) British passport holders suggest that they are experiencing additional levels of harassment from immigration officials. If this happens, stay calm and ask that the British High Commission is immediately informed.
Same-sex sexual activity is illegal in Tanzania, including Zanzibar. Same-sex relationships are not tolerated in Tanzania’s conservative society. If you show affection in public, like holding hands or kissing in public places, you could be arrested or put in prison.
Read more advice for LGBT+ travellers .
US dollars are widely accepted in tourist areas. Travellers cheques are not widely accepted.
Most banks in major cities have ATMs that accept foreign debit cards and issue Tanzanian shillings. They sometimes break down or run out of money.
To minimise the risk of card cloning, use ATMs located within the bank. If you try to exchange non-Bank of England pound notes, you may get a reduced exchange rate.
Outdoor activities and adventure tourism
Trekking and climbing .
If you are trekking or climbing, only use a reputable travel company, stick to established routes and always walk in groups. Make sure you are well prepared and equipped to cope with the terrain and low temperatures.
Transport risks
Road travel.
If you’re planning to drive in Tanzania, see information on driving abroad .
The condition of cars rented out by some car hire companies is variable, so use a reputable firm. There are no roadside rescue or breakdown services. Road maps are hard to come by and not always up to date. Service stations are infrequent and may not have supplies of fuel. Consider using reputable taxis as an alternative.
You can drive in Tanzania with a UK driving licence for up to 6 months. For stays longer than this, an international driving permit ( IDP ) is required. Keep this with you in the car. To confirm the correct IDP to use, contact the Tanzanian High Commission in the UK .
To drive in Zanzibar, you’ll also need a local Zanzibar driving permit (which you can get through your hire car company). Carry several copies of your driving licence, permits and insurance documents.
Driving standards and road conditions
Road users often drive dangerously, ignoring the rules of the road. Accidents resulting in death and serious injury are common.
Watch out for:
- vehicles and motorbikes trying to undertake or overtake using any lane, including on the hard shoulder
- drivers making manoeuvres without signalling
- poor attention to rules at roundabouts
Many roads need repair, including in major towns and cities. During the rainy season, flooding can cause landslides and road surfaces can deteriorate.
Roads in Tanzania’s national parks, mainly dirt tracks, can become hazardous or impassable after heavy rain. It may be essential to have a 4-wheel drive vehicle.
Avoid driving outside major towns and cities at night.
Police checkpoints
There are frequent police checkpoints. If you’re stopped by the police, ask to see identification. If you are issued with a fine, the police should give you a government control number for payment. The police should not ask you to make any on the spot payments for traffic violations. If you’re involved in a road accident, co-operate with the local police.
If you see an unusual incident, or if somebody in plain clothes tries to flag you down, it is often safer not to stop.
Buses and taxis
Local buses (‘dala dalas’), motorbike taxis (‘boda bodas’), and tuk-tuks (known locally as ‘bijajis’) do not meet western safety standards. They are often poorly maintained and badly driven. They rarely have proper insurance cover. There are frequent accidents, some of which result in fatalities.
Do not accept lifts from strangers or anyone offering to find a taxi for you. It is safest to arrange a taxi through a hotel or travel operator. Always ask to see the driver’s ID and use reputable taxi services.
Pickpockets and bag-snatchers operate on overcrowded buses and at bus stations.
Rail travel
There have been several accidents on Tanzanian railways. Seek local advice for any long-distance train travel.
Lake and sea travel
In the last few years there have been several ferry disasters. Hundreds of people have died when travelling:
- between Dar es Salaam and Zanzibar
- between the islands of Zanzibar
- in the Lake Zone area
If you think a ferry is overloaded or not seaworthy, do not get on. If you do board, familiarise yourself with emergency procedures on board and make a note of where the life jackets and emergency exits are located.
You should also beware of aggressive ticket touts at Tanzanian ports.
Continual pirate attacks on vessels sailing off the coast of Somalia and in the Gulf of Aden show that the threat of piracy remains significant. The threat assessment of the combined international naval counter-piracy forces is that all sailing yachts under their own passage should avoid the designated high-risk area or accept the risk of being hijacked and held hostage for ransom. For more information and advice, see Piracy and armed robbery at sea .
Extreme weather and natural disasters
Rainy seasons.
The length of rainy seasons can vary, but they generally run from:
- the end of March to May
- October to mid-December
Heavy rainfall and strong winds can affect travel. Flooding and landslides can occur during heavy rain. If travelling to affected regions, you should take extra care and follow any advice given by the local authorities.
Monitor local and international weather reports and the TMA website for the latest updates. If travelling, plan your journeys carefully and make sure to follow local guidance.
Avoid walking, swimming, or driving through floodwater.
Find out what you can do to prepare for and respond to extreme weather and natural hazards .
Earthquakes
Earthquakes and tremors are a risk in Tanzania. The US Federal Emergency Management Agency website has advice about what to do before, during and after an earthquake .
The last significant earthquake (magnitude 6.0) happened on 12 August 2020, 66km north-east of Mafia Island.
This section has safety advice for regions of Tanzania. It only covers regions where The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) has specific advice.
You should also read FCDO ’s overall travel advice and safety and security advice .
Mtwara Province
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to the southern strip of Mtwara Province to within 20km of the border with Cabo Delgado Province in Mozambique.
The presence of groups linked to Islamic extremism in Cabo Delgado is creating cross-border tensions and instability. There is a risk of violent attacks. An attack on Kitaya village in October 2020 was claimed by groups linked to Islamic extremism operating from northern Mozambique.
Tanzania-Burundi border and Kigoma region
There have been armed robberies in the area bordering Burundi and in Kigoma region, including vehicle hijackings. Drive only in hours of daylight. There are few facilities for visitors.
National parks
Some parks are extremely remote, and emergency access and evacuation can be difficult. If you choose to camp, only use official sites. Make sure you are properly equipped and seek local advice when travelling to isolated areas.
There are risks associated with viewing wildlife, particularly on foot or at close range. Always follow park regulations and advice from wardens, and make sure you have the correct documentation or permit before entering a national park.
Before you travel check that:
- your destination can provide the healthcare you may need
- you have appropriate travel insurance for local treatment or unexpected medical evacuation
This is particularly important if you have a health condition or are pregnant.
Emergency medical number
Call 112 and ask for an ambulance.
Contact your insurance company quickly if you’re referred to a medical facility for treatment.
Vaccinations and health risks
At least 8 weeks before your trip check:
At least 8 weeks before your trip:
- check the latest vaccine recommendations for Tanzania
- see where to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS travel vaccinations page
See what health risks you’ll face in Tanzania , including:
Altitude sickness is a risk in parts of Tanzania. Read more about altitude sickness on TravelHealthPro .
The legal status and regulation of some medicines prescribed or bought in the UK can be different in other countries.
Read best practice when travelling with medicines on TravelHealthPro .
Healthcare facilities in Tanzania
Medical facilities are limited, especially outside Dar es Salaam.
FCDO has a list of English-speaking doctors in Tanzania .
There is also guidance on healthcare if you’re living in Tanzania .
Travel and mental health
Read FCDO guidance on travel and mental health . There is also mental health guidance on TravelHealthPro .
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) cannot provide tailored advice for individual trips. Read this travel advice and carry out your own research before deciding whether to travel.
Emergency services in Tanzania
Telephone: 112 (ambulance, fire, police)
Contact your travel provider and insurer
Contact your travel provider and your insurer if you are involved in a serious incident or emergency abroad. They will tell you if they can help and what you need to do.
Refunds and changes to travel
For refunds or changes to travel, contact your travel provider. You may also be able to make a claim through insurance. However, insurers usually require you to talk to your travel provider first.
Find out more about changing or cancelling travel plans , including:
- where to get advice if you are in a dispute with a provider
- how to access previous versions of travel advice to support a claim
Support from FCDO
FCDO has guidance on staying safe and what to do if you need help or support abroad, including:
- finding English-speaking lawyers , funeral directors and translators and interpreters in Tanzania
- dealing with a death in Tanzania
- being arrested or imprisoned in Tanzania
- getting help if you’re a victim of crime
- what to do if you’re in hospital
- if you’re affected by a crisis , such as a terrorist attack
Contacting FCDO
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this travel advice is updated.
You can also contact FCDO online .
Help abroad in an emergency
If you’re in Tanzania and you need emergency help from the UK government, contact the British High Commission in Dar es Salaam .
FCDO in London
You can call FCDO in London if you need urgent help because something has happened to a friend or relative abroad.
Telephone: 020 7008 5000 (24 hours)
Find out about call charges
Risk information for British companies
The Overseas Business Risk service offers information and advice for British companies operating overseas on how to manage political, economic, and business security-related risks.

Book a Hotel
© Columbus Travel Media Ltd. All rights reserved 2024
- Full Restrictions
Full Restrictions:
All travellers.
You do not need to show a COVID vaccination certificate or negative COVID test to enter Tanzania.
Health officials may screen you for COVID symptoms on arrival. They may also randomly select travellers for rapid antigen testing.
If you’re transiting through Tanzania
Your carrier or final destination country may have separate rules on vaccination and testing requirements. Check with your transport provider or travel agent for their COVID-19 requirements before you travel.
Check your passport and travel documents before you travel
Passport validity.
If you are visiting Tanzania, your passport should be valid for 6 months from the date you arrive.
If you are a resident in Tanzania, your passport must be valid for 6 months from the date you arrive.
Check with your travel provider to make sure your passport and other travel documents meet their requirements.
All British passport holders need a tourist or business visa to enter Tanzania. Tanzania has introduced an ‘e-visas’ system through which applications can be submitted and approved online in advance of travel. It is no longer possible to get a visa from the Tanzanian High Commission in London.
It is also possible to get a tourist or business visa for a single entry on arrival at main ports of entry to Tanzania, subject to the fulfilment of all immigration requirements. You may be asked to provide proof of your return journey. You will not be able to get a multiple entry visa on arrival. For further information about visas visit the Tanzanian immigration website .
If you are planning to work or volunteer, you will need a valid work permit which can also be applied for online via the Tanzanian immigration website . Your employer or volunteer organisation should arrange this before you travel.
If you overstay the validity of your visa or permit you can be arrested, detained and fined before being deported. Reports made to the British High Commission by Black, Asian and Minority Ethnic (BAME) British passport holders have indicated that they are experiencing additional levels of harassment from immigration officials. In these circumstances, you should stay calm and request that the Consular section of the British High Commission is immediately informed.
Yellow fever certificate requirements
Check whether you need a yellow fever certificate by visiting the National Travel Health Network and Centre’s TravelHealthPro website .
You are successfully subscribed!
Travel safe – Subscribe to Notifications to keep up-to-date about travel restrictions on your favorite destination country
No spam. You may cancel email subscription anytime

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tanzania Mainland by Air or Marine Vessels. For Zanzibar the cost for rapid test shall be 25 USD or equivalent TZS. 58,000. The updated list of countries for Rapid Antigen Test is available at https://www.moh.go.tz website or at Points of Entry. 5. Travelers to Mainland Tanzania are advised to pay for COVID-19 rapid test online to
Find out the latest travel advisory, visa requirements, health tips, and safety precautions for Tanzania. Learn about the passport validity, currency restrictions, and local laws for your trip.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA TRAVEL ADVISORY NO. 11 OF 08TH SEPTEMBER, 2022 The Government of the United Republic of Tanzania (URT) through the Ministry responsible for ... USD) for Tanzania Mainland except children aged 12 years and below and aircraft crew. Positive cases will be further confirmed by RT- PCR at a cost of 50 USD. For ground
Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory. Reconsider Travel To: Mtwara Region in southern Tanzania due to the threat of terrorism. Country Summary: Violent crime, such as assault, sexual assault, robberies, mugging, and carjacking, is common. Local police may lack the resources to respond effectively to serious crime.
Learn about the latest travel rules and requirements for entering Tanzania, including PCR and rapid tests, quarantine and fees. Find out how to stay safe and enjoy S!TE 2023 and 2024 events in Tanzania.
Find out the COVID-19, passport, visa, vaccination and customs rules for travelling to Tanzania from the UK. Check with the Tanzania High Commission or the Immigration Department for more details.
Learn about the latest travel requirements and health surveillance for entering Tanzania Mainland from 17th March, 2022. Find out if you need to fill in a form, present a vaccination certificate, or undergo a COVID-19 test before or upon arrival.
TRAVEL ADVISORY NO. 7 OF 4TH MAY, 2021. The Government of the United Republic of Tanzania has continued to implement measures towards controlling COVID-19 Pandemic. Based on the global epidemiological situation and emergence of new variants of viruses which cause COVID-19, there is an increased risk of their importation into our country.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA TRAVEL ADVISORY NO. 12 OF 12th JANUARY 2023 The Government of the United Republic of Tanzania (URT) through the Ministry responsible ... travel agents regarding COVID-19 requirements of their country of destination or conveyance to be used 5. For travelers departing from Tanzania whom conveyances and destination ...
Learn about the immigration formalities and health guidelines for travelling to Tanzania. Find out what documents you need, where to enter and what to do upon arrival.
FCDO travel advice for Tanzania. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences. ... Road users often drive dangerously, ignoring the rules of the road ...
Find out the latest entry and exit requirements, testing and quarantine procedures, and vaccine availability for U.S. citizens traveling to Tanzania. Learn how to book a COVID-19 test or vaccine in Tanzania and what to expect upon arrival.
Find out the latest information on travel to Tanzania from the UK government, including FCDO advice, entry requirements, safety and security, and regional risks. Check your travel insurance and get email alerts before you go.
tanzania entry requirements Entry Requirement Documents to enter Tanzania All foreign participants who wish to attend S!TE are advised to adhere to the following immigration requirements:
Find out if you can travel to Tanzania from the United States and what entry requirements you need. Learn about COVID-19 testing, quarantine, mask usage, and more for Tanzania.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA TRAVEL ADVISORY NO. 9 OF 24th DECEMBER, 2021 The Government of the United Republic of Tanzania (URT) through Ministries responsible ... The Travel Advisory will be reviewed from time to time as need arises. Dr. Fatma H. Mrisho Prof. Abel N. Makubi PRINCIPAL SECRETARY Ministry of Health, Social Welfare, ...
Make sure to have your credit card handy because this is the only method of payment accepted at the gate. 3. Play Nice With the Police. This Tanzania travel tip really applies to self-drivers, but the Tanzanian police are littered across the roads of the country just waiting to hand out "tickets.".
19 using RT PCR test at their own cost of 100 USD for Tanzania Mainland. Results will be sent to them while self-isolated. ii. In case of International regional and inland vessels will be tested by Rapid Antigen Test at their own cost of 10 USD while positive will be further confirmed by RT- PCR at a cost of 50 USD for Tanzania Mainland. iii.
Get travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, and tips to stay healthy and safe in Tanzania. Learn about COVID-19, malaria, cholera, polio, and other diseases and how to prevent them.
THE UNITED REPUBLIC OF TANZANIA. TRAVEL ADVISORY NO. 11 OF 08 TH SEPTEMBER 2022. The Government of the United Republic of Tanzania (URT) through the Ministry responsible for Health continues to enhance prevailing preventive measures against the spread of COVID-19 including those related to international travel.
Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country's entry rules. Regular Canadian passport. Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Tanzania. Passport for official travel. Different entry rules may apply. Official travel. Passport with "X" gender identifier
Cyclones in coastal areas are also common. Follow the advice of local officials. Terrorists are likely to try to carry out attacks anywhere in Tanzania. Be alert to your surroundings and pay close attention to your personal security. Violent armed robbery, petty theft and threats of violence are common in Tanzania, especially in Dar es Salaam.
This advice reflects the UK government's understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full 'British citizen' passport from the UK, for the most common types of travel. The authorities in Tanzania set and enforce entry rules. If you're not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Tanzania High Commission in the UK.
If you're transiting through Tanzania. Your carrier or final destination country may have separate rules on vaccination and testing requirements. Check with your transport provider or travel agent for their COVID-19 requirements before you travel. Check your passport and travel documents before you travel Passport validity