
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Fact Sheets

Fact Sheet: Guidance for Travelers to Enter the U.S. at Land Ports of Entry and Ferry Terminals
Updated Date: May 1, 2023
DHS Statement on the Lifting of Title 19 Requirements
Beginning May 12, 2023, DHS will no longer require non-U.S. travelers entering the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination upon request. DHS intends to rescind these Title 19 travel restrictions in alignment with the end of the Public Health Emergency and the termination of the Presidential Proclamation on air travel .
Updated Date: April 21, 2022
As of Thursday, April 21, 2022, DHS will extend COVID-19-related land border entry requirements. Non-U.S. travelers seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders are required to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 and provide proof of vaccination upon request.
These restrictions apply to non-U.S. travelers who are traveling for essential or non-essential reasons. They do not apply to U.S. citizens, Lawful Permanent Residents, or U.S. nationals.
This announcement does not affect requirements for entry into the United States by air.
What To Expect
As travel returns to pre-pandemic levels, wait times are expected to increase. The resources below are intended to prepare travelers to improve the cross-border travel experience. Travelers should plan for longer than normal wait times and longer lines at U.S. land border crossings when planning their trip and are reminded to exercise patience.
To help reduce wait times and long lines, travelers arriving or departing from air, sea or land ports of entry are encouraged to opt in to using Simplified Arrival or Mobile Passport Control , which can make the inspection process touchless and more expedient with the use of facial comparison technology . Documented non-citizens may also apply for and manage their I-94s through the CBP One TM mobile application, which serves as a single portal for individuals to access CBP mobile applications and services.
Arrival at Land Port of Entry or Ferry Terminal
Since January 22, 2022, DHS has allowed inbound non-U.S. travelers (non-U.S. citizens who are neither U.S. nationals nor lawful permanent residents) to seek to enter the United States via a land port of entry (POE) or ferry terminal if they are fully vaccinated and have appropriate documentation.
Non-U.S. individuals traveling to the United States via land ports of entry or ferry terminals, whether for essential or non-essential reasons, must:
- verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status;
- provide, upon request, proof of a CDC-approved COVID-19 vaccination, as outlined on the CDC website ;
- present a valid Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative (WHTI)-compliant document, such as a valid passport, Trusted Traveler Program Card, or Enhanced Tribal Card;
- be prepared to present any other relevant documents requested by a U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer during a border inspection; and
COVID-19 testing is not required for entry via a land or ferry port of entry.
Click here to see answers to frequently asked questions
In March 2020, to prevent the further spread of COVID-19, the U.S. government issued restrictions on travel into the United States. DHS implemented temporary restrictions, limiting entry at the U.S. northern and southern land borders to persons engaged in essential travel, including lawful trade, emergency response, and public health purposes. The White House also suspended entry to foreign nationals who had recently been in certain countries.
In October 2021, the White House announced that, starting November 8, 2021, the U.S. government would move away from the country-by-country restrictions previously applied during the COVID-19 pandemic and adopt travel policies that rely primarily on vaccination to advance the safe resumption of travel. Since January 22, 2022, DHS has imposed a vaccination requirement on non-U.S. individuals seeking to cross into the United States at land ports of entry or ferry terminals.
CDC Resources
- International Travel Landing Page
- Travel Requirements: Quiz
- International Travel : Information for U.S. Citizens, U.S. Nationals, Lawful Permanent Residents, and People Traveling to the U.S. on Immigrant Visas
- Non-U.S. Citizen Non-U.S. Immigrants: Air Travel to the United States
Additional Information
- Vaccines.gov
- DHS Response to Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Coronavirus.gov
- CDC.gov: Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- USA.gov: What the U.S. Government is Doing (link is no longer valid)
- Border Security
- Transportation Security
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Canada-U.S. border restrictions: The current rules with ArriveCan, COVID-19 tests, vaccine mandates
With the COVID-19 restrictions at the border to remain in place for at least another month , some Canadians may need a primer on what those rules are.
Public Health Agency of Canada announced that several pandemic restrictions will be extended at Canadian airports and land borders, including vaccine mandates, random COVID-19 tests and the mandatory use of the ArriveCan app, until at least June 30.
While few Canadians may still be anxious about travelling, some are ready to take a vacation after more than two years in a pandemic. CTVNews.ca breaks down what rules travellers need to be aware of as they plan their trips prior to jetting off.
- Newsletter sign-up: Get The COVID-19 Brief sent to your inbox
PRE-ENTRY TEST NO LONGER REQUIRED
As of April 1, fully vaccinated travellers no longer need to provide a negative pre-entry COVID-19 test result to enter Canada by air, land or water.
Passengers may still be subjected to mandatory, random PCR testing at the airport -- in part to monitor for new, emerging COVID-19 variants -- though they will not be required to isolate while awaiting their results.
As of April 25, children aged five to 11 who are travelling with a fully vaccinated parent or guardian will no longer be required to complete a COVID-19 test prior to entering Canada, regardless of whether the child is unvaccinated. Children under the age of five won’t be required to complete a pre-entry COVID-19 test either, and are exempt for vaccination requirements.
ARRIVECAN APP
All travellers coming to Canada, regardless of citizenship or vaccination status, still have to use the ArriveCAN app to submit their health information before arriving in Canada. Travellers must submit their information in ArriveCAN within 72 hours before arrival at a port of entry.
Travellers who arrive without completing their ArriveCAN submission may have to test on arrival and on the eighth day of their 14-day quarantine, regardless of their vaccination status. Foreign nationals may be denied entry as well if they have not completed their ArriveCAN submission.
Any travellers who fail to submit their information and proof of vaccination using ArriveCAN could be fined $5,000.
While travellers still have to use the ArriveCAN app, the federal government has dropped its requirement for those entering the country to monitor for and report any COVID-19 symptoms they experience. Those travelling from abroad also won’t be required to keep a list of close contacts and places visited for the first 14 days after their arrival in Canada.
PROOF OF VACCINATION STILL NEEDED
Despite the lifting of pre-entry test requirements, the requirement to be fully vaccinated with a government-approved COVID-19 vaccine in order to board federally-regulated air, rail, and marine transportation remains in effect.
Pre-entry testing requirements have not changed for partially vaccinated or unvaccinated travellers who are currently allowed to travel to Canada.
Unless otherwise exempt, all travellers age 12 or older who do not qualify as fully vaccinated – having received at least two doses of a COVID-19 vaccine accepted for travel or a mix of two vaccines – must continue to provide proof of a negative pre-entry COVID-19 test result.
Accepted pre-entry tests include a health professional-administered negative rapid antigen test taken no more than one day before arriving at a port of entry, or a negative molecular test taken no more than 72 hours before a scheduled flight or crossing at a land border.
Partially vaccinated or unvaccinated travellers may also provide a positive molecular test taken at least 10 days and no more than 180 days before their scheduled flight departure time or their arrival at the land border to enter Canada. Positive antigen test results are not accepted.
The government recommends completing a COVID-19 vaccine series, along with any additional recommended doses in Canada, at least 14 days before travelling internationally. For those who must travel, the government suggests delaying one's plans until they are fully vaccinated.
MASKING DURING TRAVEL AND AFTER ARRIVAL
Canadian adults and children aged five and older who are fully vaccinated are no longer expected to wear a mask in public spaces for 14 days following their arrival in Canada. However, children aged five to 11 who are either unvaccinated or partially vaccinated must continue to wear masks in public settings, such as school, for 14 days after entering Canada.
All travellers are also still required to wear a mask while travelling on federally-regulated modes of transportation, such as a plane or train, regardless of whether they are vaccinated.
BEFORE YOU GO
Prior to travelling, the government recommends checking the COVID-19 testing and vaccination requirements, as well as other entry requirements, at one's destination as they may be different from Canada's rules.
Travellers are also advised by the Canadian government to monitor the COVID-19 situation at their destination in the days before travelling should the status of COVID-19 infections and public health requirements there change.
CRUISE SHIPS
Cruise passengers aged five years or older are required to take an antigen or molecular COVID-19 test in order to board a ship no more than two days before their scheduled departure, but will not need to be tested before getting off the ship.
All other requirements for cruises, including providing proof of vaccination before boarding, remain in place.
The government continues to warn travellers that the virus can spread easily between people in close quarters, such as on cruise ships. The government says the chance of being infected with COVID-19 on cruise ships is still "very high," even for those who are fully vaccinated.
A previous version of this article misstated the timeline for passengers to submit an antigen or a molecular COVID-19 test before boarding a cruise ship.
CTVNews.ca Top Stories
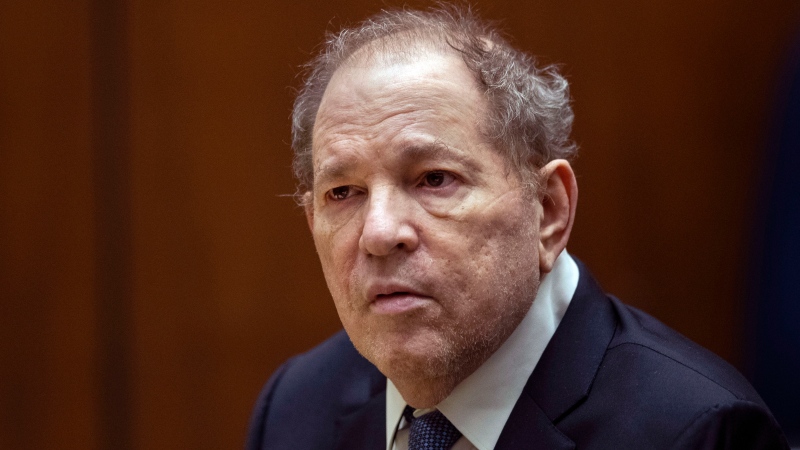

BREAKING | New York appeals court overturns Harvey Weinstein's 2020 rape conviction from landmark #MeToo trial
New York’s highest court on Thursday overturned Harvey Weinstein’s 2020 rape conviction, finding the judge at the landmark #MeToo trial prejudiced the ex-movie mogul with improper rulings, including a decision to let women testify about allegations that weren’t part of the case.
BREAKING | Monthly earnings rise, payroll employment falls: jobs report
The number of vacant jobs in Canada increased in February, while monthly payroll employment decreased in food services, manufacturing, and retail trade, among other sectors.
Doctors say capital gains tax changes will jeopardize their retirement. Is that true?
The Canadian Medical Association asserts the Liberals' proposed changes to capital gains taxation will put doctors' retirement savings in jeopardy, but some financial experts insist incorporated professionals are not as doomed as they say they are.
Remains from a mother-daughter cold case were found nearly 24 years later, after a deathbed confession from the suspect
A West Virginia father is getting some sense of closure after authorities found the remains of his young daughter and her mother following a deathbed confession from the man believed to have fatally shot them nearly two decades ago.
Something in the water? Canadian family latest to spot elusive 'Loch Ness Monster'
For centuries, people have wondered what, if anything, might be lurking beneath the surface of Loch Ness in Scotland. When Canadian couple Parry Malm and Shannon Wiseman visited the Scottish highlands earlier this month with their two children, they didn’t expect to become part of the mystery.
Metro Vancouver mayors call for serial killer Robert Pickton to be denied parole
A dozen mayors from around Metro Vancouver say federal Attorney General and Justice Minister Arif Virani should deny parole for notorious B.C. serial killer Robert Pickton, and reassess the parole and sentencing system for 'prolific offenders and mass murderers.'
What do weight loss drugs mean for a diet industry built on eating less and exercising more?
Recent injected drugs like Wegovy and its predecessor, the diabetes medication Ozempic, are reshaping the health and fitness industries.
2 military horses that broke free and ran loose across London are in serious condition
Two military horses that bolted and ran miles through the streets of London after being spooked by construction noise and tossing their riders were in a serious condition and required operations, a British government official said Thursday.
'It was instant karma': Viral video captures failed theft attempt in Nanaimo, B.C.
Mounties in Nanaimo, B.C., say two late-night revellers are lucky their allegedly drunken antics weren't reported to police after security cameras captured the men trying to steal a heavy sign from a downtown business.

Some Canadian cottage owners upset after Ottawa increases capital gains tax
The federal government says new capital gains tax changes will only affect the rich, but some realtors say they are hearing from 'middle-class' cottage owners who worry they may have to sell before the rules come into effect on June 25.
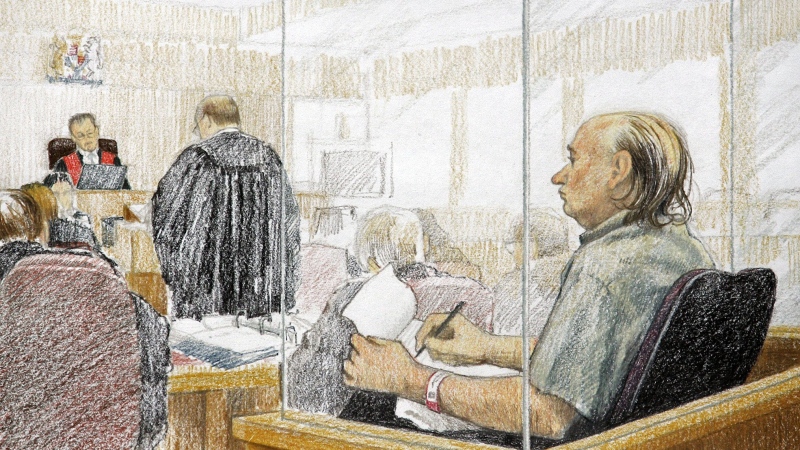

'Life was not fair to him': Daughter of N.B. man exonerated of murder remembers him as a kind soul
The daughter of a New Brunswick man recently exonerated from murder, is remembering her father as somebody who, despite a wrongful conviction, never became bitter or angry.
New Indigenous loan guarantee program a 'really big deal,' Freeland says at Toronto conference
Canada's Deputy Prime Minister Chrystia Freeland was among the 1,700 delegates attending the two-day First Nations Major Projects Coalition (FNMPC) conference that concluded Tuesday in Toronto.
Fair in Ontario, flurries in Labrador: Weather systems make for an erratic spring
It's no secret that spring can be a tumultuous time for Canadian weather, and as an unseasonably mild El Nino winter gives way to summer, there's bound to be a few swings in temperature that seem out of the ordinary. From Ontario to the Atlantic, though, this week is about to feel a little erratic.

Bishop stabbed during Sydney church service backs X's legal case to share video of the attack
A Sydney bishop who was stabbed repeatedly in an alleged extremist attack blamed on a teenager has backed X Corp. owner Elon Musk's legal bid to overturn an Australian ban on sharing graphic video of the attack on social media.
Ship comes under attack off coast of Yemen as Houthi rebel campaign appears to gain new speed
A ship travelling in the Gulf of Aden came under attack Thursday, officials said, the latest assault likely carried out by Yemen's Houthi rebels over Israel's ongoing war on Hamas in the Gaza Strip.
Iran's judiciary confirms rapper Toomaj Salehi death sentence
Iran's judiciary confirmed the death sentence of well-known Iranian rapper Toomaj Salehi but added that he is entitled to a sentence reduction, state media reported on Thursday.
Ukraine is putting pressure on fighting-age men outside the country as it tries to replenish forces
Ukraine worked Thursday to get much-needed new supplies of weapons and ammunition from a huge U.S. aid package to its eastern front line, where Russia was pressing forward with its efforts to take ground from outnumbered and outgunned troops.

'Anything to win': Trudeau says as Poilievre defends meeting protesters
Prime Minister Justin Trudeau is accusing Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre of welcoming 'the support of conspiracy theorists and extremists,' after the Conservative leader was photographed meeting with protesters, which his office has defended.
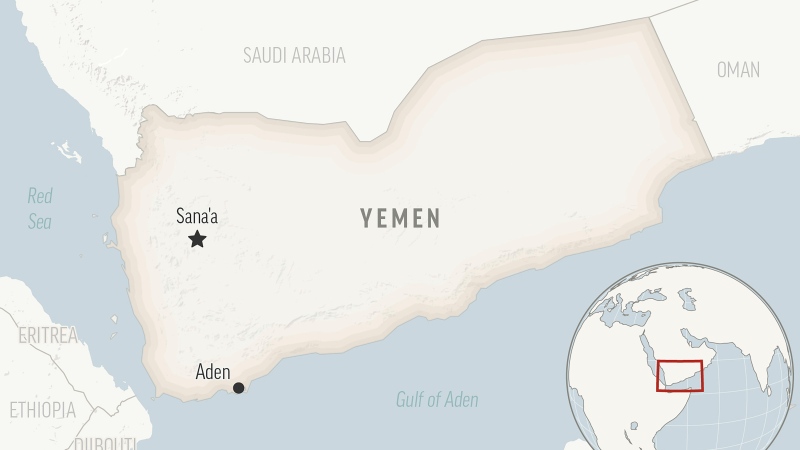
It could take years to catch up on child vaccinations in Ontario post-pandemic
Ontario is still playing catch up on routine vaccinations that many children missed during the pandemic and public health officials are warning that it could take years to solve the problem.
'Learn to walk again': Sask. doctor tells story of miracle recovery from deadly heart condition
It was a powerful morning at Regina's Conexus Arts Centre Wednesday, where the Lieutenant Governor hosted the annual Saskatchewan Prayer Breakfast and a provincial doctor told his story of survival from a deadly heart condition.

Biden just signed a bill that could ban TikTok. His campaign plans to stay on the app anyway
U.S. President Joe Biden signed legislation Wednesday that could ban TikTok in the U.S. while his campaign has embraced the platform and tried to work with influencers.
Giant prehistoric salmon had tusk-like spikes used for defence, building nests: study
A new paper says a giant salmon that lived five million years ago in the coastal waters of the Pacific Northwest used tusk-like spikes as defense mechanisms and for building nests to spawn.
Trudeau won't comment on future of TikTok in U.S., says Canadian safety a priority
Prime Minister Justin Trudeau says he's not going to comment on the future of TikTok in the United States, but his own government will continue to look out for Canadians' security.
Entertainment
'the last timbit': tim hortons musical coming to toronto.
In the last year, Tim Hortons has treated cottaging Canadians to a boat drivethru, revived its beloved Dutchie doughnut and launched flatbread pizzas. But perhaps its biggest surprise will come this summer.
Woman who killed Reena Virk calls new TV series disrespectful to victim
The B.C. woman convicted of killing Reena Virk described the TV series dramatizing the notorious 1997 murder as disrespectful to the victim and her family.

Boeing's financial woes continue, while families of crash victims urge U.S. to prosecute the company
Boeing said Wednesday that it lost US$355 million on falling revenue in the first quarter, another sign of the crisis gripping the aircraft manufacturer as it faces increasing scrutiny over the safety of its planes and accusations of shoddy work from a growing number of whistleblowers.
New condo sales in the Toronto area hit low not seen since financial crisis
New condo sales in the Toronto region dropped to the lowest quarterly total since the financial crisis in 2009 amid high interest rates and affordability issues, a new report has found.

Pilot proposes to flight attendant girlfriend in front of passengers
A Polish pilot proposed to his flight attendant girlfriend during a flight from Warsaw to Krakow, and she said yes.
Made-in-Newfoundland vodka claims top prize at worldwide competition
A Newfoundland-made vodka has been named one of the world’s best by judges at this year’s World Vodka Awards.

Maple Leafs fall to Bruins in Game 3, trail series 2-1
Brad Marchand scored twice, including the winner in the third period, and added an assist as the Boston Bruins downed the Toronto Maple Leafs 4-2 to take a 2-1 lead in their first-round playoff series Wednesday
He replaced Mickey Mantle. Now baseball's oldest living major leaguer is turning 100
The oldest living former major leaguer, Art Schallock turns 100 on Thursday and is being celebrated in the Bay Area and beyond as the milestone approaches.
Nashville Predators level playoff series with 4-1 victory over Canucks
The Nashville Predators downed the Vancouver Canucks 4-1 Tuesday night and levelled the series at 1-1.
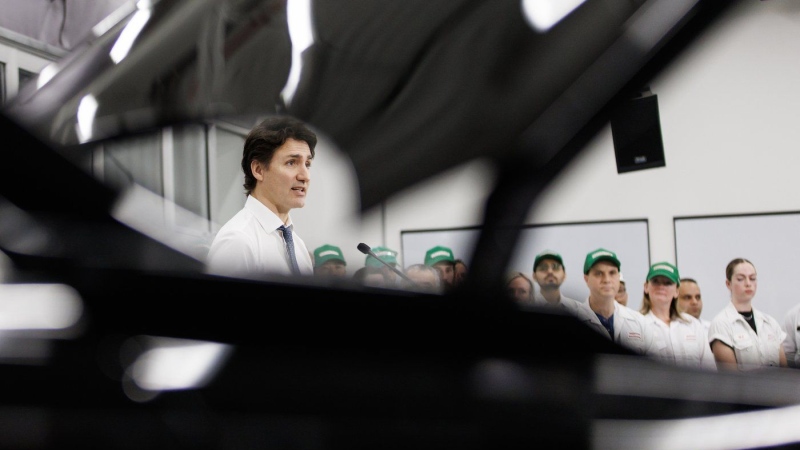

Honda expected to announce Ontario EV battery plant, part of a $15B investment
Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, Ontario Premier Doug Ford and Honda executives are expected to announce today that the Japanese automaker is building an electric vehicle battery plant in Alliston, Ont., part of a $15-billion investment.
How Volvo landed a cheap Chinese EV on North American shores in a trade war
A made-in-China electric vehicle will hit North American dealers this summer offering power and efficiency similar to the Tesla Model Y, the world's best-selling EV, but for about US$8,000 less.
Tesla's first-quarter net income tumbles as falling global sales and price cuts reduce profits
Tesla's first-quarter net income plummeted 55 per cent as falling global sales and price cuts sliced into the electric vehicle maker's revenue and profit margins.
Local Spotlight

Fergus, Ont. man feels nickel-and-dimed for $0.05 property tax bill
A property tax bill is perplexing a small townhouse community in Fergus, Ont.
Twins from Toronto were Canada's top two female finishers at this year's Boston Marathon
When identical twin sisters Kim and Michelle Krezonoski were invited to compete against some of the world’s most elite female runners at last week’s Boston Marathon, they were in disbelief.
Mystery surrounds giant custom Canucks jerseys worn by Lions Gate Bridge statues
The giant stone statues guarding the Lions Gate Bridge have been dressed in custom Vancouver Canucks jerseys as the NHL playoffs get underway.
'I'm committed': Oilers fan won't cut hair until Stanley Cup comes to Edmonton
A local Oilers fan is hoping to see his team cut through the postseason, so he can cut his hair.
'It's not my father's body!' Wrong man sent home after death on family vacation in Cuba
A family from Laval, Que. is looking for answers... and their father's body. He died on vacation in Cuba and authorities sent someone else's body back to Canada.
'Once is too many times': Education assistants facing rising violence in classrooms
A former educational assistant is calling attention to the rising violence in Alberta's classrooms.
What is capital gains tax? How is it going to affect the economy and the younger generations?
The federal government says its plan to increase taxes on capital gains is aimed at wealthy Canadians to achieve “tax fairness.”
UBC football star turning heads in lead up to NFL draft
At 6'8" and 350 pounds, there is nothing typical about UBC offensive lineman Giovanni Manu, who was born in Tonga and went to high school in Pitt Meadows.
Cat found at Pearson airport 3 days after going missing
Kevin the cat has been reunited with his family after enduring a harrowing three-day ordeal while lost at Toronto Pearson International Airport earlier this week.
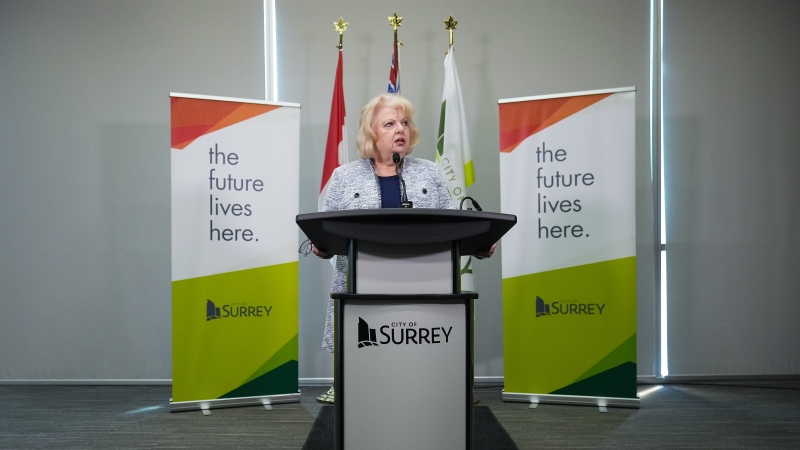

War of words heats up as Surrey's mayor calls 'hidden' document a 'bombshell'
The ongoing battle over policing in Surrey took another turn Wednesday, as Mayor Brenda Locke shared details of an independent report she said shows a municipal police force would cost $75 million a year more than the RCMP.
B.C. mom distributes air quality monitors after 9-year-old's asthma death during wildfires
Nine-year-old Carter Vigh was having a great day last July 11, visiting a waterpark, enjoying a picnic lunch and playing soccer with other kids at a day camp run by his mother, Amber Vigh.
Man dead after reported push from downtown balcony: Toronto police
Toronto police say the homicide unit is investigating after a man was reportedly pushed to his death from a balcony downtown late Wednesday night.
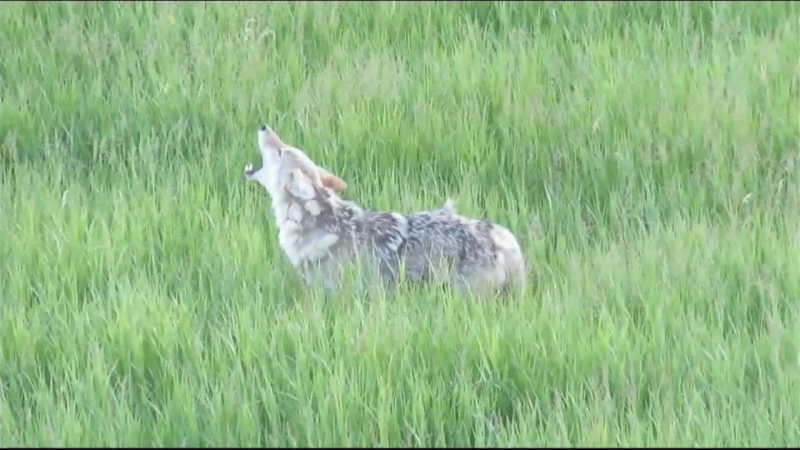

Coyote calls on the rise in Calgary; city wildlife team advises caution
The City of Calgary's wildlife team says they're fielding hundreds of calls about coyotes.
Ex-Calgary mayor Nenshi expected to be focus of first Alberta NDP leadership debate
Former Calgary mayor Naheed Nenshi is expected to be the centre of attention as the first debate in the Alberta NDP leadership race is held Thursday night.
Mounties respond to serious crash near Okotoks, Alta.
A serious vehicle collision near Okotoks, Alta., shut down roadways on Wednesday evening.

Off to a sunny day in Ottawa, here’s how it feels Thursday
The capital is set to have a sunny day with mild temperatures this Thursday.
Shots fired at wrong address in Champlain Township, police investigating
The Ontario Provincial Police (OPP) is investigating following a shooting that happened earlier this month at the wrong residence in the Champlain Township.
OCDSB program review aims to keep kids in schools closer to home, director says
The director of education for the Ottawa-Carleton District School Board says making sure elementary school students can attend classes close to home is an important part of making schooling in Ottawa more equitable.

'There's really no justice': Quebec mother, daughter speak out after man gets house arrest for years of abuse
A mother and daughter are speaking out after a Quebec man was sentenced to house arrest for years of domestic abuse. They were both physically assaulted by the mother's ex-partner and say the offender got off with another light sentence.
Ontario is increasing the speed limit to 110 km/h on some highways. Should Quebec?
Speaking to CTV News, some Montreal drivers said they were in favour of the new measure and said they'd like to see Quebec follow suit.
Police in Quebec arrest 40 alleged sex offenders
A major operation rallying 25 police forces across Quebec has led to the arrest of 40 alleged sex offenders considered at high risk of reoffending.

Nurse practitioners to make 80% as much as family doctors for publicly-funded primary care
The Alberta government says it will pay nurse practitioners 80 per cent of what family doctors are paid – if they want to practice comprehensive primary care.
Kopitar's OT winner lifts Kings to 5-4 win over Oilers, even series at 1-1
The Los Angeles Kings weren’t about to bow out quietly.
Measles case in Edmonton prompts exposure warning
Alberta Health Services issued a measles alert in Edmonton Wednesday after confirming a case.

A community in mourning: 16-year-old Halifax murder victim remembered
Community members gathered at a Bedford, N.S., mosque for Ahmad Al Marrach — a 16-year-old murder victim — for his funeral on Wednesday.
N.S. man wins $1.5M through Atlantic Lottery
A Cape Breton man won $1.5 million after buying $200-worth of Atlantic Lottery Scratch’N Win tickets.
Moncton-area woman charged with human trafficking, three people rescued
New Brunswick RCMP says officers rescued three people from alleged human trafficking in Moncton, arresting an 18-year-old woman in the process.

'We are not here for tree preservation': Development company appealing latest decision with Lemay Forest
A new fight is gearing up at city hall over Lemay Forest.
'I just wanted to stand out': Winnipeg Jets fan goes viral for wearing salmon shirt at Whiteout
A Winnipeg Jets fan found a unique way to stand out amid the Winnipeg Whiteout; he wore a salmon-coloured shirt.
'We feel good about ourselves:' Jets coach Bowness optimistic after Game 2 loss
We feel good about ourselves and we feel we can go in there and win a game," Bowness said.

Revitalization of Regina's Dewdney Avenue to begin next week
Beginning April 29, Dewdney Avenue between Albert Street and Broad Street will see a number of construction sites.
Throwing star, crossbow found during Sask. RCMP searches at George Gordon FN, Punnichy
A throwing star and crossbow were among the seizures by police as part of a drug trafficking investigation on George Gordon First Nation and in Punnichy, Sask. last week.

Air ambulance needed for serious crash on King Street in Kitchener
A Waterloo man needed to be taken away by air ambulance following a crash on King Street.
Ont. teacher says she's being forced to switch pharmacies to maintain medication coverage
A Waterloo, Ont. teacher says she’s frustrated after learning the arthritis medication she depends on is no longer covered under her benefits plan and she'll have to switch pharmacies to avoid paying out of pocket.
Late night transit route temporarily returning to Waterloo university district
Students will soon have another late night travel option in Waterloo's university district.
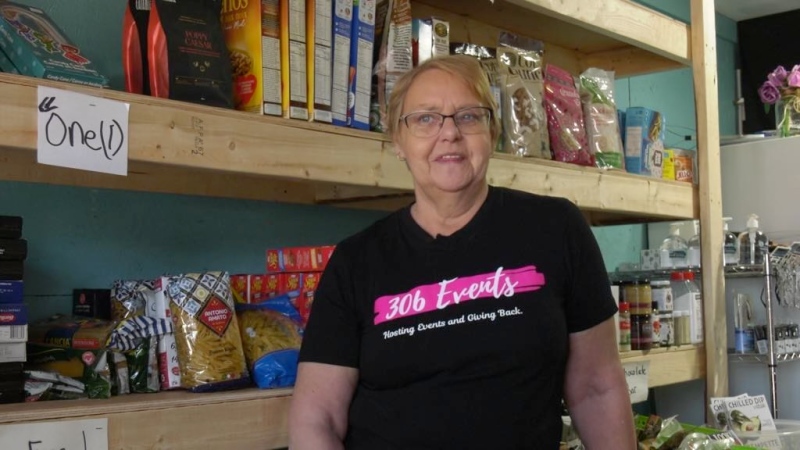

This Saskatchewan woman is helping fill bellies and hearts with a free grocery store
Darlene Hartshorn is a mother and grandmother from Warman who is making a difference by helping those who need a hand up.
Sask. woman fights to find out who had her apprehended for a psych. assessment
A Saskatchewan woman who was taken for an involuntary mental health assessment is entitled to find out who had her committed, a provincial court judge has ruled.
Boeing invests $17 million in Sask. aviation program
International aircraft giant Boeing has made a multi-million dollar commitment to the Saskatchewan Indian Institute of Technology (SIIT) to help address shortages in the aviation industry.
Northern Ontario

Secret $70M LOTTO MAX winners break their silence
During a special winner celebration near their hometown, Doug and Enid shared the story of how they discovered they were holding a LOTTO MAX ticket worth $70 million and how they kept this huge secret for so long.
DEVELOPING | Highway 101 crash closes in Timmins area near Kidd Creek Met site
A serious crash involving two vehicles has closed Highway 101 in the Timmins area since 1 a.m., police say.

Asylum claimants occupying 12% of London’s homeless shelter beds
In the midst of a homelessness crisis, an influx of asylum seekers is putting additional pressure on London, Ont.’s limited number of permanent shelter beds.
'You made me look for money while he bled on the floor': Man sentenced in manslaughter case nearly a decade after botched robbery
Nine years after a London, Ont. man was shot to death in a botched robbery at his home, the man responsible for the shooting was given a prison sentence on Wednesday.
Protest at shuttered auto parts maker over unpaid severance
Frustrated employees of Wescast’s shuttered auto parts manufacturer in Wingham, Ont. will be sending a message to their former ownership on Thursday.
Major Honda Canada announcement expected today in Alliston
Reports indicate Honda is retooling its assembly plant in Alliston to produce fully electric vehicles.
U.K. instructors train Barrie police in victim support services
Instructors from the United Kingdom College of Policing brought the victim support instructors to Barrie.

Arrests made after 911 hang-up call in Chatham
A 911 hang-up call has led to the arrest of two people in Chatham-Kent. Just after 6:30 a.m. on Wednesday, officers responded to an address on Bloomfield Road for the hang-up call.
Convicted killer can ask for parole now: Windsor, Ont. jury accepts 'faint hope' application
A Windsor man convicted in a violent murder 20 years ago was successful in his ‘faint hope’ bid for an early chance at freedom after a jury agreed he should be given the chance to apply for early parole eligibility.
Vancouver Island
'Enjoy the run' but don’t expect major economic boost from Canucks playoffs: expert
A Canadian sports economist is encouraging Canucks fans to enjoy the team’s playoff run, but cautioning against having big expectations around economic spinoffs.
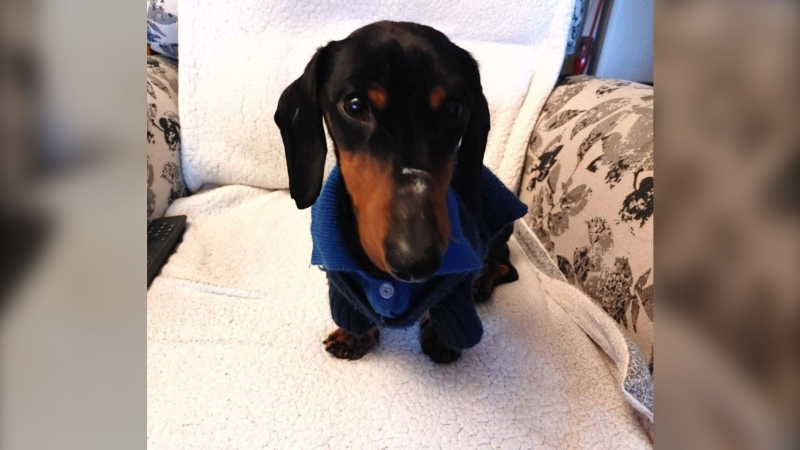

B.C. man rescues starving dachshund trapped in carrier: BC SPCA
An emaciated dachshund is now recovering thanks to a Good Samaritan who found the pup near a biking trail in Kelowna, according to the BC SPCA.
Search crews called in after missing Kelowna senior's truck found
Search and rescue crews have been called in after a vehicle belonging to a missing senior was located near a rural intersection outside of Kelowna Tuesday.
Homicide investigation underway after body found near Kelowna, B.C.
Major crime detectives in British Columbia are investigating a suspected homicide after a body was found in a remote area southeast Kelowna over the weekend.
Fire risk for southern Alberta high: Natural Resources Canada
It’s not even May 1 and the fire risk for southern Alberta is already alarming.
Lethbridge’s Whoop-Up Days accepting applications to be in 2024 parade
Whoop-Up Days is still four months away, but applications to be in this year’s parade are now open.
Lethbridge added 28 physicians over the past year, AHS continues search for more
Lethbridge has added 28 physicians over the past year, according to a quarterly report published by the College of Physicians and Surgeons of Alberta.
Sault Ste. Marie

Garden River chief meets with disgruntled band members over payout concerns
Some members of the Garden River First Nation are demanding answers regarding the disbursement of the Robinson-Huron Treaty settlement funds.
OPP and Treaty Three police lay murder charge in northwestern Ont.
The Ontario Provincial Police, in partnership with the Treaty Three Police Service, have charged a suspect with murder following a homicide in a remote northwestern Ontario community.
Youth charged in the Sault for firing cap gun at passersby
A 15-year-old in Sault Ste. Marie has been charged following an incident on Bay Street on Tuesday.

Rideshare platform Uber expands to Newfoundland and Labrador
Uber Technologies Inc. says it has brought its ridesharing platform to Newfoundland and Labrador.
Newfoundland director found creeping terror of 'The King Tide' in a tiny coastal town
Newfoundlander Christian Sparkes has shot several films around his home province, but with his new psychological thriller 'The King Tide' he saw an opportunity to wander into one unique town that had eluded him over the years.
Shopping Trends
The Shopping Trends team is independent of the journalists at CTV News. We may earn a commission when you use our links to shop. Read about us.
Editor's Picks
17 practical things for your backyard that you'll want to order immediately, 19 of the best mother's day gifts under $50, here are the best deals you'll find on amazon canada right now, our guide to the best fire pits in canada in 2024 (and where to get them), 16 game-changing products that'll make your old things look new again, 13 blackout curtains for anyone who needs complete darkness to fall asleep, 22 of the best mother's day gifts to give in 2024, 17 unique mother's day gifts your mom definitely wants, but probably won’t buy herself, if your mom needs a bit of rest and relaxation, here are 20 of the best self-care gifts for mother's day, 14 of the best tinted lip balms you can get online right now, 12 travel-sized skincare products that'll fit in your toiletry bag, 15 wrinkle-smoothing serums that’ll help reduce the appearance of fine lines, stay connected.

- What's My Car Worth?
- Buyer's Guide
Canada Opens Border to U.S. Travelers Once Again, and Cars Are Lining Up
If you're going, there are still COVID-19 vaccination and testing rules, and a stiff fine for those who submit false information.

- Since March 2020, Americans have not been able to travel to Canada for tourism or other nonessential reasons. That changed this week, but getting across the border is still a bit tricky.
- More than 112 million vehicles crossed from Canada to the U.S. in 2019, but the number dropped to 68.5 million in 2020. The drop was mostly due to lower numbers of personal vehicles and buses, as the number of trucks crossing remained relatively steady.
CORRECTION 8/14/21, 10:00 a.m.: We added a digit that was missing in the amount of a government fine Canada threatens to charge people who falsify documents about their COVID-19 status. That number truly is $600,000 U.S.
The U.S.-Canada border could see its traditional long lines again soon. The Canadian government lifted its ban on Americans making nonessential border crossings this week, but news reports from around the country, from Washington State to Vermont, suggest that massive amounts of Americans are in no great rush to head north. On-the-ground reporting from The New York Times suggests the long lines seen at some border crossings are due to people not using the necessary app correctly, or simply not having the required documents, and not caused by a massive number of people trying to cross.
The border-crossing prohibition has been in place since March 21, 2020. The U.S. government is keeping similar restrictions on Canadians coming to the U.S. until at least August 21. Canada said it will tentatively open its borders to other foreign nationals who are fully vaccinated on September 7. Anyone with COVID symptoms will, unsurprisingly, not be able to enter. Just because the border is open again doesn't mean you can drive across the way you could before COVID-19 was a thing. Before U.S. citizens and legal residents can enter Canada, they have to be fully vaccinated and show a negative COVID-19 test that was taken within the past three days. Children under 12 years old, who are not yet eligible for the vaccine, can travel with a fully vaccinated parent or guardian. The vaccination and test result documents need to be uploaded alongside a filled-out digital visitor application in the arriveCAN smartphone app or website to assist Canadian officials with determining if an individual is able to enter Canada. Submitting false information could result in a fine of up to $750,000 (Canadian), the equivalent of about $600,000 U.S., or a six-month prison term.
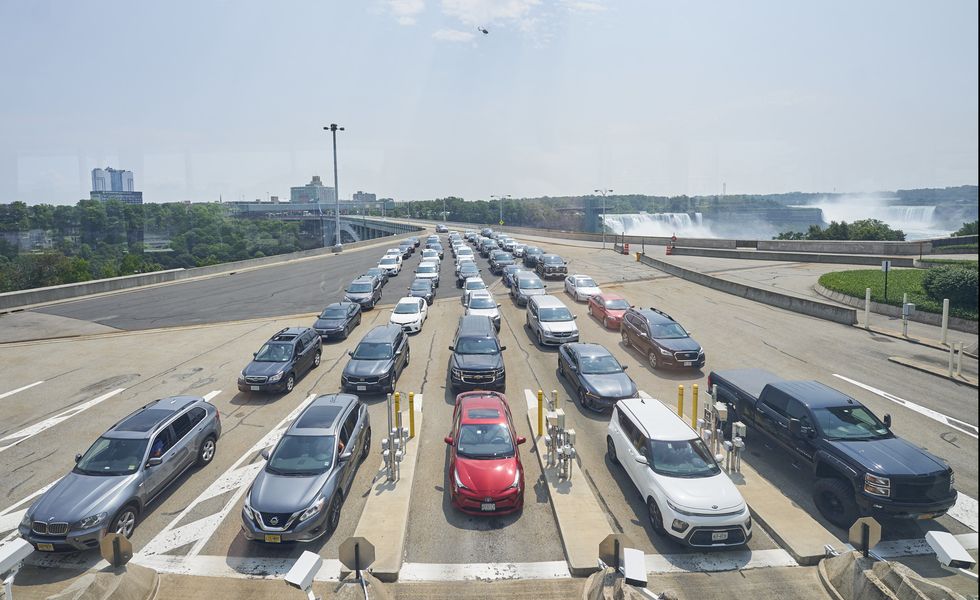

Statistics from the U.S. Department of Transportation show that there were over 112 million vehicle crossings into the U.S. from Canada in 2019, compared to 68.5 million in 2020. Most of that drop came from fewer bus and personal vehicle crossings, which were both down around 50 percent. Cross-border truck traffic barely dropped during the first year of the pandemic, going from just over 12 million crossings in 2019 to 11.5 million in 2020. The border was never closed to essential truck cargo traffic. While not everyone is eager to cross the border, overall traffic numbers are climbing. The Federal Highway Administration announced this week that motorists in the U.S. drove 282.5 billion miles in June 2021. That's 35.7 billion more miles than they drove in June 2020 and almost as many as the 284.5 billion miles driven in June 2019.
Sebastian Blanco has been writing about electric vehicles, hybrids, and hydrogen cars since 2006. His articles and car reviews have appeared in the New York Times, Automotive News , Reuters, SAE, Autoblog, InsideEVs, Trucks.com, Car Talk, and other outlets. His first green-car media event was the launch of the Tesla Roadster, and since then he has been tracking the shift away from gasoline-powered vehicles and discovering the new technology's importance not just for the auto industry, but for the world as a whole. Throw in the recent shift to autonomous vehicles, and there are more interesting changes happening now than most people can wrap their heads around. You can find him on Twitter or, on good days, behind the wheel of a new EV.

.css-190qir1:before{background-color:#000000;color:#fff;left:0;width:50%;border:0 solid transparent;bottom:48%;height:0.125rem;content:'';position:absolute;z-index:-10;} News .css-188buow:after{background-color:#000000;color:#fff;right:0;width:50%;border:0 solid transparent;bottom:48%;height:0.125rem;content:'';position:absolute;z-index:-10;}

Mercedes-AMG Reveals 805-HP PHEV GT63 Coupe

Shelby Super Snake Unveiled with 830 Horsepower

Cybertruck Recalled Due to Unintended Acceleration

Test: Rivian R1T Shows How Cold Affects EV Range

Nissan Reveals Striking New Qashqai SUV for Europe

2025 Mustang GTD Order Applications Are Now Open

2025 GMC Terrain Teases Assertive New Front End

NHTSA Upgrades Probe Into 3 Million Hondas

Hybrid-Only 2025 Toyota Camry Starts At $29,495

Corvette Engineering Icon Tadge Juechter to Retire

Jeep Recon, Wagoneer S EVs Could Get Gas Versions
Canada-U.S. border rules and restrictions during the COVID-19 pandemic explained
The rules are complicated and sometimes change. here's what you need to know now.
Social Sharing
Confused over Canada-U.S. border restrictions during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Perhaps you're wondering why you see U.S. licence plates in a local parking lot when the Canada-U.S. land border is closed to tourists.
Or you're stumped why your neighbour was able to fly to New York last week, but you can't make the five-minute drive across the Windsor-Detroit border to visit family.
Here's what you need to know about current Canada-U.S. border restrictions and how they may impact you.
Canada-U.S. land border rules
To help stop the spread of the novel coronavirus, Canada and the U.S. agreed to close their shared land border to non-essential traffic starting on March 21. The agreement is reviewed every 30 days. So far, the border closure has been extended three times.
The current end date is July 21 , and that date could be extended once again, particularly if the number of COVID-19 cases in some U.S. states continues to spike.
"I honestly don't think the border will open until the end of the year," said U.S. immigration lawyer Len Saunders. "Especially when you hear about more [COVID-19] cases in Arizona and Texas and all these southern states."
- B.C. closing Peace Arch park at Canada-U.S. border due to 'significant' number of visitors
The Canada-U.S. land border remains open to people making trips for essential reasons, such as for work or school.
On June 9, the Canadian government loosened its border restrictions to allow American visitors with immediate family in Canada to enter the country. Note that a boyfriend or girlfriend doesn't qualify as family and a common-law partner only qualifies if that person has lived with their significant other for at least a year.
Visiting family members must stay in Canada for at least 15 days and self-quarantine for 14 days upon arrival.

The land border closure continues to frustrate many cross-border couples who can't meet Canada's requirements for reuniting with family.
Last year, Ian Geddes of Blaine, Wash., married Birgit Heinbach of Surrey, B.C. Until Heinbach gets her U.S. immigrant visa, the two are separated by the border.
Geddes said he can't get enough time off work right now to complete a 14-day quarantine in Canada — before he can hang out with his wife and her son.
- Engaged Canadian-American couples kept apart despite new exemption for cross-border families
"It's just a really tough situation," said Geddes, who wishes the Canadian government would waive the self-quarantine requirement for immediate family.
"You should be allowed to cross into a country and see your wife," he said. "Give us some kind of a concession."
You can fly to the U.S.
Some Canadians may be surprised to learn they can still fly to the U.S. during the pandemic, even though the same rule doesn't apply on the other side of the border.
With the exception of immediate family, Canada currently restricts all foreigners — including Americans — from visiting the country for non-essential travel via any mode of transportation.
The U.S., however, only prohibits visitors from entering its country if they've been in Brazil, China, Iran, Ireland, the U.K. or 26 European countries in the Schengen Area 14 days prior.

Because of the bilateral agreement to close the Canada-U.S. land border, the only way Canadians can currently travel to the U.S. is by air . Saunders said dozens of his Canadian clients have flown to the U.S. with no complications during the land border closure.
"There's a back door wide open," said Saunders, whose office sits close to the Canadian border in Blaine, Wash. "They can just go in through the airport, and so that's what people are doing in droves."
- Canadians can still travel to the U.S. during the COVID-19 pandemic — just not by car
Canadian air passengers also likely won't have to self-isolate for 14 days upon arrival in the U.S. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that international travellers do so, but it's not a requirement unless specified by a particular region or state.
When Canadians return home, they must self-isolate for 14 days — as per federal rules .
WATCH | What adjusted border rules mean for families eager to reunite:

U.S.- Canada border restrictions loosened, allowing some families to reunite
Heinbach plans to fly to the U.S. in August to visit Geddes in Blaine. It's a frustrating solution for the couple because, even though they live in different countries, their homes are only eight kilometres apart — typically a 10-minute drive, depending on border traffic.
But now Heinbach must fly from Vancouver to Seattle to visit Geddes in Blaine — a journey of more than three hours by plane and car.
"It just doesn't make sense," said Geddes.
U.S. licence plates in Canada
Some Banff, Alta., residents have complained that they've recently spotted American tourists and U.S. licence plates in the resort town.
"Two days ago, I saw four people get out of a car, out of a Texas vehicle," Banff resident Nina Stewart told CBC News on June 12. "They were laughing and joking about how easy it was to get into Banff."
- Air Canada apologizes after barring passenger from flying to U.S. to see terminally ill husband
Canada allows Americans to drive through the country to Alaska for essential reasons, such as for work or returning to their home. However, they're not to make unnecessary stops along the way.
RCMP said officers fined seven Americans this week who were supposed to be driving straight to Alaska, but instead were caught taking in the sights at Banff National Park. The fines, issued under the Alberta Health Act, were for $1,200 each.
"As much as you'd want to stop and see the sights ... that's just inappropriate," said Fraser Logan, spokesperson for the RCMP in Alberta.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Business reporter
Based in Toronto, Sophia Harris covers consumer and business for CBC News web, radio and TV. She previously worked as a CBC videojournalist in the Maritimes where she won an Atlantic Journalism Award for her work. Contact: [email protected]
- @sophiaharrisCBC
Related Stories
- Stewart, B.C., mayor calls for around-the-clock border staffing
- Federal carbon tax protesters slow traffic at Sask.'s borders with Alberta, Manitoba for 2nd day
- Denver is a city overwhelmed with migrants from the southern U.S. border
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

COVID-19 international travel advisories
If you plan to visit the U.S., you do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
- As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
- As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific COVID-19 travel rules from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel.
LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
U.S.-Canada Border Crossing: What You Need to Know
Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
Table of Contents
Who can travel from the U.S. to Canada?
How many border crossings are there between the u.s. and canada, checklist for a u.s.-canada border crossing, special cases for alaska residents, if you want to cross the u.s.-canada border ….
Borders between the U.S. and Canada recently reopened to travelers more than a year after having closed due to COVID-19. Now, many who are eager to explore our neighbor to the north are left wondering what’s involved in a border crossing and what guidelines they’ll need to adhere to for a successful journey.
If you’re anxious to visit Montreal, Toronto, Vancouver or Calgary, here’s what to know to plan your U.S.-Canada border crossing, whether by land, air or sea.
Currently, Canadian borders are open to all U.S. citizens wishing to enter regardless of vaccination status. However, the requirements for entry will vary based on your vaccination status.
Fully vaccinated travelers no longer need to provide a negative COVID test for entry, but must still use the ArriveCAN app to submit mandatory entry information, including proof of vaccination, at least 72 hours prior to arrival and/or before boarding a cruise ship destined for Canada.
Not fully vaccinated? You won’t be able to visit Canada if you’re traveling for discretionary or leisure purposes. If you don't qualify as a fully vaccinated traveler but still need to travel to Canada for reasons other than leisure, you’ll be required to quarantine for 14 days, take a molecular COVID test, and register for a COVID test upon your arrival in the country, which you can do in advance to save time.
» Learn more: What COVID test is required for travel?
There are more than 100 land border crossings between the U.S. and Canada, and wait time to cross can vary widely.
At most crossings, how long you wait depends on the time of day and the day of the week. Some crossings have little to no delay at off-peak travel times, and others, like Buffalo, New York, can log wait times around 40 minutes.
If you want to set appropriate expectations for how long it takes to cross the U.S.-Canada border, check the Government of Canada website , which is updated hourly.
» Learn more: Need a passport for a trip? Give yourself a big time cushion
If you're fully vaccinated and traveling to Canada, whether by car, plane or boat, you still have to follow certain protocols. To meet entry requirements, you must:
Have no symptoms of COVID-19.
Have received all doses of a COVID-19 vaccine at least 14 full days before you enter Canada.
Upload your proof of vaccination in ArriveCAN , an app that provides border crossing info and stores important documentation.
Have your required entry documents.
NOTE: As of April 1, 2022, fully vaccinated travelers no longer need to provide a negative test for entry.
» Learn more: 4 differences between a passport book and card
If you don’t meet all the requirements of a fully vaccinated traveler, you’ll have to quarantine for 14 days upon arrival. You may also be selected for a random arrival test at some airports and land crossings. These may take place at the airport or a designated testing site, or you may be provided with a do-it-yourself kit that you can send in once you arrive at your final destination.
If you live in Alaska, you may sometimes have to drive through Canada to get to certain regions of the state. Unvaccinated Alaska residents who must pass through Canada for necessary purposes (i.e. not for leisure or recreation) may do so without pre-entry and arrival COVID tests, but they must remain in their vehicle while driving through Canada. They'll also likely be given a specimen collection kit when they cross a land border into Canada.
If you're leaving Alaska to travel to the lower forty-eight, or if you're returning to Alaska after being in another state, you may also be granted special permission to pass through Canada. However, if you’re not fully vaccinated you will need a negative COVID molecular test result to enter. You'll also need proof that you live in Alaska if you’re driving north, or proof of residence or employment in the lower forty-eight if driving south.
The key to a successful U.S.-Canadian border crossing is preparation. Make sure you know what documentation and information you need well in advance of your arrival at the border or the airport. Ensure everything is in order and uploaded to the ArriveCAN app, and be patient. Above all, travel safely.
How to maximize your rewards
You want a travel credit card that prioritizes what’s important to you. Here are our picks for the best travel credit cards of 2024 , including those best for:
Flexibility, point transfers and a large bonus: Chase Sapphire Preferred® Card
No annual fee: Bank of America® Travel Rewards credit card
Flat-rate travel rewards: Capital One Venture Rewards Credit Card
Bonus travel rewards and high-end perks: Chase Sapphire Reserve®
Luxury perks: The Platinum Card® from American Express
Business travelers: Ink Business Preferred® Credit Card

on Chase's website
1x-5x 5x on travel purchased through Chase Travel℠, 3x on dining, select streaming services and online groceries, 2x on all other travel purchases, 1x on all other purchases.
60,000 Earn 60,000 bonus points after you spend $4,000 on purchases in the first 3 months from account opening. That's $750 when you redeem through Chase Travel℠.

1.5%-6.5% Enjoy 6.5% cash back on travel purchased through Chase Travel; 4.5% cash back on drugstore purchases and dining at restaurants, including takeout and eligible delivery service, and 3% on all other purchases (on up to $20,000 spent in the first year). After your first year or $20,000 spent, enjoy 5% cash back on travel purchased through Chase Travel, 3% cash back on drugstore purchases and dining at restaurants, including takeout and eligible delivery service, and unlimited 1.5% cash back on all other purchases.
$300 Earn an additional 1.5% cash back on everything you buy (on up to $20,000 spent in the first year) - worth up to $300 cash back!

on Capital One's website
2x-5x Earn unlimited 2X miles on every purchase, every day. Earn 5X miles on hotels and rental cars booked through Capital One Travel, where you'll get Capital One's best prices on thousands of trip options.
75,000 Enjoy a one-time bonus of 75,000 miles once you spend $4,000 on purchases within 3 months from account opening, equal to $750 in travel.


Travelling to the United States
Planning a trip to the United States? Here are the answers to some common questions from travellers aiming for a smooth border crossing.
Do I need to be vaccinated to enter the United States?
No. As of May 12, 2023, you no longer need to be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States, regardless of whether you arrive by car, train, boat or plane.
What are the requirements for entering the United States by air?

To enter the United States by air, you must present a valid Canadian passport or NEXUS card (even for a simple connection). Children also must have one of these two documents.
As a traveller, you are responsible for ensuring that you meet the requirements, which are outlined on travel.gc.ca .
Sherpa, the tool you need.
Important information about your trip: health restrictions, entry requirements, and more

What are the requirements for entering the United States by car or boat?
Any Canadian citizen aged 16 or older must present either of the following documents when entering the United States by land (or sea):
- a valid passport ;
- a membership card for an expedited border crossing program like NEXUS;
- an Enhanced Identification Card proving Canadian citizenship; or
- a Secure Certificate of Indian Status.
Canadian citizens aged 15 or under who are accompanied and those aged 16 or 17 who are travelling to the U.S. by land or sea with a school or other organized group (under the supervision of an adult and with consent from a parent or guardian) may present the original or a copy of their birth certificate, or a Canadian citizenship card or certificate.
The NEXUS card helps frequent travellers get across the border faster. Travellers must apply to get one. A NEXUS card can be used instead of a passport to enter or leave the U.S. by land or sea. It can also be used at self-service checkpoints when returning to Canada by air.
See border wait times
Plan your trips to avoid waiting in line for hours. The tables are updated on the hour, 24/7:
Canadian customs
U.S. customs
What are the requirements for returning to Canada?

COVID-19–related requirements to return to Canada (vaccination status, random testing, isolation/quarantine) were lifted by the Canadian government. The ArriveCAN app is still available, but its use is now optional. Travellers can also use it to fill out their customs declarations.
However, the government reserves the right to reinstate certain border measures should the situation become a concern again. For more information or to find out what you need to know before crossing the border, visit the Canadian government website .
What travel insurance is recommended for the United States?
If you’re planning a trip to the U.S., even for just a day, you should purchase emergency medical travel insurance before leaving. But for even better protection against the unexpected, it’s wise to add trip cancellation and interruption insurance.
Thinking of visiting the U.S. more than once this year or travelling abroad elsewhere? Consider getting annual travel insurance . It will cover you for all your trips, all year long—making your life easier.
What about snowbirds heading to the United States?
All Canadian travellers—including snowbirds—must comply with the entry requirements for their means of travel. To help you prepare for your trip, see our comprehensive report on snowbirds .
What can I bring home to Canada after a stay in the U.S. (personal exemptions)?
Food, alcoholic beverages, and gifts are some of the things you can bring home from a trip to the United States or elsewhere. It’s important to understand these personal exemptions so you can avoid paying duties and taxes or having prohibited items confiscated.
Similarly, you should know what foods you can and cannot bring into the United States by land. Regulations on the entry of animals and animal products into the U.S. change frequently based on disease outbreaks in various parts of the world.
Important travel information
Check out our helpful information and travelling tips related to Covid-19 , including health measures for before, during, and after a trip, cancellation policies, travel insurance, and more.
Have a criminal record? You probably won’t be allowed to enter the United States (or even stop over), even if you have received a pardon in Canada. To obtain a waiver (fees apply) or for further information, contact the U.S. Consulate General . Note that a waiver is not required if you have a record of impaired driving with no aggravating factors (no injuries or deaths).
CAA-Quebec Travel Insurance: The ideal choice!
Request a quote.

Language selection
- Français fr
Latest border and travel measures
This news release may not reflect the current border and travel measures. Check COVID-19: Travel, testing and borders for the latest requirements to enter Canada.
Important notice
Note that information and resources on the coronavirus (COVID-19) are available on Canada.ca. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/coronavirus-disease-covid-19.html
Government of Canada's first phase to easing border measures for travellers entering Canada
From: Public Health Agency of Canada
News release
Today, the Government of Canada is announcing the details of the first phase of its approach to easing border measures for travellers entering Canada. These cautious adjustments are now possible because of the successes of the vaccine roll out in Canada and Canadians following public health measures.
June 21, 2021 | Ottawa | Public Health Agency of Canada
The Government of Canada is taking a responsible, precautionary approach at the border by continually monitoring available data and scientific evidence to protect the health and safety of Canadians.
Beginning July 5, 2021 at 11:59 p.m. EDT, fully vaccinated travellers who are permitted to enter Canada will not be subject to the federal requirement to quarantine or take a COVID-19 test on day-8. In addition, fully vaccinated travellers arriving by air will not be required to stay at a government-authorized hotel.
To be considered fully vaccinated, a traveller must have received the full series of a vaccine — or combination of vaccines — accepted by the Government of Canada at least 14 days prior to entering Canada. Currently, those vaccines are manufactured by Pfizer, Moderna, AstraZeneca/COVISHIELD, and Janssen (Johnson & Johnson). Travellers can receive their vaccine in any country, and must provide documentation supporting their vaccination in English, French or with a certified translation.
For these new measures to apply to them, fully vaccinated travellers must still meet all other mandatory requirements, including pre- and on-arrival testing. Continued testing will allow public health experts to keep monitoring positivity rates at the border, monitor for variants of concern, and make further adjustments to border measures as needed.
Fully vaccinated travellers must also be asymptomatic, have a paper or digital copy of their vaccination documentation, and provide COVID-19-related information electronically through ArriveCAN prior to arrival in Canada. They must still present a suitable quarantine plan, and be prepared to quarantine, in case it is determined at the border that they do not meet all of the conditions required to be exempt from quarantine. As with all other exempt travellers, they will be required to follow public health measures in place, such as wearing a mask when in public, keep a copy of their vaccine and test results, as well as a list of close contacts for 14 days after entry to Canada.
For travellers who are not fully vaccinated, there are no changes to Canada’s current border measures. They must continue to adhere to the current testing and federal quarantine requirements, which have been effective in reducing importation and transmission of COVID-19 and variants in Canada, and provide COVID-19-related information electronically through ArriveCAN before arriving in Canada. Unvaccinated air travellers must also book a three-night stay at a government-authorized hotel before their departure to Canada.
The Government of Canada’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic will continue to prioritize the health and safety of Canadians. As vaccination, case counts and hospitalization rates evolve, the Government of Canada will continue to consider further targeted measures at the borders—and when to lift or adjust them—to keep Canadians safe and the economy running.
“The cautious adjustments announced today are only possible because of the tremendous efforts of Canadians, and additional ones will only happen if we continue to protect each other. Thank you to all those who have stepped up to get their first and second dose. If you haven’t, get vaccinated when it’s your turn, follow up for your second dose, and continue to follow public health measures.” The Honourable Patty Hajdu Minister of Health
“This is the first phase of our precautionary approach to easing Canada’s border measures. At this time we are not opening up our borders any further. The Government of Canada continues to work globally through the World Health Organization as well as closely with the provinces, territories, Indigenous partners and American authorities on moving forward toward reopening in a way that is safe for both countries.” The Honourable Dominic LeBlanc President of the Queen’s Privy Council for Canada and Minister of Intergovernmental Affairs
“At this time, the Government of Canada continues to strongly advise Canadians to avoid non-essential travel. Although the future is looking brighter than it has for a long time with COVID-19 cases on a downward trend and vaccination efforts going well across the country, we can’t let our guard down. Our phased approach to easing border measures is guided by facts, scientific evidence, and the advice of our public health experts. In all that we’re doing in response to this pandemic, our top priority continues to be the health, safety and security of all Canadians.” The Honourable Bill Blair Minister of Public Safety and Emergency Preparedness
"Our government continues to closely monitor traveller positivity rates upon entry to Canada, to help protect Canadians. Today, we announced that we will be eliminating pre-departure temperature screening for international travellers coming to Canada. Also, given the number of COVID-19 cases continue to be very high in India, we have extended our flight restrictions for this country. We will continue to assess the evolving situation and determine appropriate action going forward.” The Honourable Omar Alghabra Minister of Transport Canada
“The safety and security of Canadians remains our top priority as we look to support the careful and safe arrival of new permanent residents to Canada over the next year. These new permanent residents will finally be able to start their new life in Canada and Canada will benefit from their skills when we pivot to post-pandemic economic recovery. At the same time, we’ll continue to offer protection to those who need it most, and keep our place as a global leader in providing a safe haven for refugees.” The Honourable Marco Mendicino Minister of Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada
Quick facts
For all travellers coming to Canada, planning in advance to ensure all mandatory requirements are met is crucial. In addition, some provinces and territories may have their own entry restrictions in place. Check and follow both the federal and any provincial or territorial restrictions and requirements before travelling.
Fully vaccinated travellers who wish to be considered for the eased quarantine and testing requirements must meet all criteria, including the electronic submission of their vaccination documentation, in English or French, into ArriveCAN prior to arrival at the port of entry.
A person who submits false information on vaccination status could be liable to a fine of up to $750,000 or six months imprisonment or both, under the Quarantine Act , or prosecution under the Criminal Code for forgery. Violating any quarantine or isolation instructions provided to travellers by a screening officer or quarantine officer when entering Canada is also an offence under the Quarantine Act and could lead to a $5,000 fine for each day of non-compliance or for each offence committed, or more serious penalties, including six months in prison and/or $750,000 in fines. Non-compliant air travellers may also be subject to fines of up to $5,000 for each offence committed under the Aeronautics Act.
The Government of Canada is extending, until July 21, 2021,11:59 p.m. EDT, the temporary travel restrictions on discretionary (non-essential) international travel and with the US. Travellers who are currently eligible to enter Canada include Canadian citizens, permanent residents and persons registered under the Indian Act , as well as some foreign nationals who are allowed to enter Canada under the current entry prohibitions ( Prohibition of Entry into Canada from the United States; Prohibition of Entry into Canada from any Country other than the United States ).
The Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) restricting all direct commercial and private passenger flights to Canada from India will be extended until July 21, 2021, as well as the Interim Order Respecting Certain Requirements for Civil Aviation Due to COVID-19 requiring air passengers who depart India to Canada via an indirect route to obtain a COVID-19 pre-departure test from a third country before continuing their journey to Canada. The NOTAM and Interim Order will not be extended for Pakistan at this time.
The existing international flight restrictions that funnel scheduled international commercial passenger flights into four Canadian airports (Montréal-Trudeau International Airport, Toronto Pearson International Airport, Calgary International Airport and Vancouver International Airport) will be maintained in this first phase of re-opening.
Currently, foreign nationals who hold a valid Confirmation of Permanent Residence approved on or before March 18, 2020 are allowed to enter Canada. As of June 21, 2021, any foreign national who holds a valid Confirmation of Permanent Residence will be allowed to travel to Canada. Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada will work with applicants who have a Confirmation of Permanent Residence that is expiring or has expired.
Related products
- Backgrounder: Phase I of easing border measures for travellers entering Canada
- Backgrounder: Individuals approved for permanent residence may travel to Canada as of June 21
- Infographic - Fully vaccinated travellers entering Canada during COVID-19
Associated links
- COVID-19: Travel, testing, quarantine and borders
- COVID-19: Summary data about travellers, testing and compliance
- COVID-19 measures, updates, and guidance for aviation
Thierry Bélair Office of the Honourable Patty Hajdu Minister of Health 613-957-0200
Media Relations Public Health Agency of Canada 613-957-2983 [email protected]
Public Inquiries: 1-833-784-4397
Page details
- Open access
- Published: 19 April 2024
A methodology for estimating SARS-CoV-2 importation risk by air travel into Canada between July and November 2021
- Rachael M. Milwid 1 , 6 na1 ,
- Vanessa Gabriele-Rivet 1 , 6 na1 ,
- Nicholas H. Ogden 1 , 3 , 6 ,
- Patricia Turgeon 1 , 3 , 6 ,
- Aamir Fazil 2 ,
- David London 4 ,
- Simon de Montigny 5 &
- Erin E. Rees 1 , 3 , 6
BMC Public Health volume 24 , Article number: 1088 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
261 Accesses
16 Altmetric
Metrics details
Estimating rates of disease importation by travellers is a key activity to assess both the risk to a country from an infectious disease emerging elsewhere in the world and the effectiveness of border measures. We describe a model used to estimate the number of travellers infected with SARS-CoV-2 into Canadian airports in 2021, and assess the impact of pre-departure testing requirements on importation risk.
A mathematical model estimated the number of essential and non-essential air travellers infected with SARS-CoV-2, with the latter requiring a negative pre-departure test result. The number of travellers arriving infected (i.e. imported cases) depended on air travel volumes, SARS-CoV-2 exposure risk in the departure country, prior infection or vaccine acquired immunity, and, for non-essential travellers, screening from pre-departure molecular testing. Importation risk was estimated weekly from July to November 2021 as the number of imported cases and percent positivity (PP; i.e. imported cases normalised by travel volume). The impact of pre-departure testing was assessed by comparing three scenarios: baseline (pre-departure testing of all non-essential travellers; most probable importation risk given the pre-departure testing requirements), counterfactual scenario 1 (no pre-departure testing of fully vaccinated non-essential travellers), and counterfactual scenario 2 (no pre-departure testing of non-essential travellers).
In the baseline scenario, weekly imported cases and PP varied over time, ranging from 145 to 539 cases and 0.15 to 0.28%, respectively. Most cases arrived from the USA, Mexico, the United Kingdom, and France. While modelling suggested that essential travellers had a higher weekly PP (0.37 – 0.65%) than non-essential travellers (0.12 – 0.24%), they contributed fewer weekly cases (62 – 154) than non-essential travellers (84 – 398 per week) given their lower travel volume. Pre-departure testing was estimated to reduce imported cases by one third (counterfactual scenario 1) to one half (counterfactual scenario 2).
Conclusions
The model results highlighted the weekly variation in importation by traveller group (e.g., reason for travel and country of departure) and enabled a framework for measuring the impact of pre-departure testing requirements. Quantifying the contributors of importation risk through mathematical simulation can support the design of appropriate public health policy on border measures.
Peer Review reports
Government public health organisations are responsible for assessing the risk of importation of infectious diseases (e.g. [ 1 ]). To be effective, such risk assessments can use modelling methods that integrate data on incoming travel volumes from source endemic/epidemic locations through the global travel network, and country-specific epidemiological and vaccine coverage data [ 2 , 3 ]. In addition to assessing the spatio-temporal risk of importation, models can also be used to quantify the effectiveness of specific prevention strategies prior to their implementation, or post-hoc as a means of on-going evaluation and support for preparedness [ 4 ]. This can be accomplished by comparing estimated importation rates with measures in place against scenarios in which border measures are removed.
SARS‑CoV‑2, the causative agent of COVID-19, spread rapidly across the world resulting in nearly 300 million reported cases and 5.5 million reported deaths by the end of 2021 [ 5 ]. From March 2020 to September 2022, the Canadian government implemented border measures to slow the importation of COVID-19 cases arising from international air travel [ 6 ] (Fig. 1 ). These measures included restrictions on foreign nationals entering Canada [ 6 ], flight suspensions from selected countries [ 7 ], vaccination requirements to enter Canada [ 8 ], pre-departure molecular testing for SARS-CoV-2 within 72 h of departure [ 9 ], quarantine and further testing upon entry into Canada [ 10 , 11 ], and post-entry testing. Some travellers were exempt from some or all of the border measures depending on their reason for travel (e.g. providing an essential service) [ 12 ].
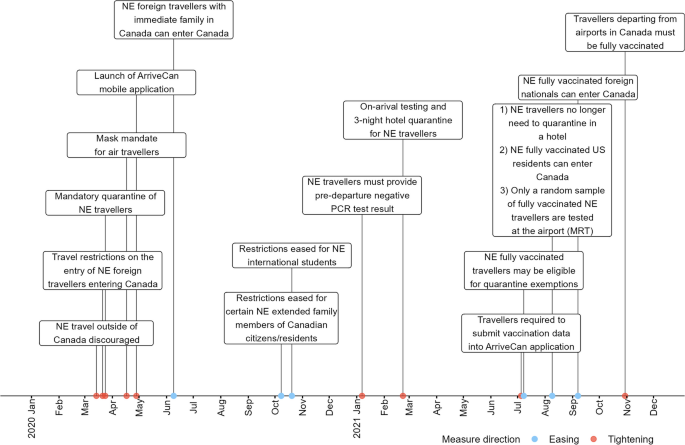
Summary of Canadian border measures implemented and eased in 2020–2021 [ 6 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. NE = Non-essential
During the COVID-19 pandemic, importation models were used to estimate the number of imported cases from domestic and international travel, and assess the impact of border measures [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. In Canada, mathematical models were developed within the first few months of the pandemic to assess the impact of importation on local COVID-19 transmission in specific provinces (e.g. Québec and Ontario [ 19 ], and Newfoundland and Labrador [ 20 ]). At the national-level, an importation modelling method was implemented by the Public Health Agency of Canada’s (PHAC) modelling team to assess possible rates of importation of cases throughout the pandemic, with and without border measures. This study aimed to describe the mathematical model developed by PHAC and estimate the weekly importation risk from air travellers into Canadian airports from July to November 2021 as measured by the number of travellers infected with SARS-CoV-2 (i.e. imported cases) and percent positivity, PP (i.e. imported cases normalised by total travel volume). In addition, the impact of pre-departure testing of non-essential travellers to reduce importation risk was assessed by comparing estimated imported cases against counterfactual scenarios.
The model operates at a daily time step to estimate the weekly number of air travellers arriving infected with SARS-CoV-2 at the airport-level from July to November 2021. The model was adapted from a mathematical model previously used to estimate importation risk of dengue and COVID-19 [ 2 , 18 ]. The key model adaptations adjusted for underreporting in COVID-19 case counts, accounted for the impacts of vaccination and pre-departure testing for SARS-CoV-2 to reduce importation risk, and stratified importation risk by SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOC) and variants of interest (VOI).
Air travel volume data
Model input for air travel volumes was derived from two data sources. Daily travel volumes from each country of departure (i.e. the country from which travel to Canada was initiated) to Canada were derived using Canada Border Services Agency’s (CBSA) Advanced Passenger Information in combination with the overall passage data from CBSA (Additional File 1 ). Monthly travel volumes for each itinerary from the origin airport to the final Canadian destination airport were obtained from the International Air Transport Authority (IATA) [ 21 ]. Finally, the CBSA travel volumes were distributed in proportion to the IATA travel volumes to derive model input at the daily and airport levels.
Traveller groups
In the model, travellers were stratified as essential or non-essential based on their reason for travel. Non-essential travellers, which included those who travelled for personal reasons (e.g. tourism, education), were assumed to have a negative pre-departure molecular test result three days prior to their scheduled departure [ 11 ], while essential travellers were exempt from that requirement. Between November 2020 and October 2022, non-essential travellers were required to submit COVID-19 related information [ 22 , 23 ] via the Government of Canada’s (GoC) digital ArriveCan platform at each entry into Canada. This data source, in combination with the CBSA ContactTrace program, were used to derive the weekly country-specific proportions of non-essential travellers in the model ([ 24 ]; Additional file 1 ).
Travellers were also characterized as being Canadian or foreign residents to distinguish their place of residence as being in Canada or another country, respectively. In the model, Canadian residents were assumed to have spent all their time in Canada, except for the period in which they travelled to a non-Canadian country where they could become infected with COVID-19 and then import the infection into Canada. This time spent outside of Canada was assumed to follow a normal distribution with a mean of 15 days and a standard deviation of 2 days according to recent estimates [ 25 ]. Foreign residents were assumed to reside and spend their time only in the country of departure before travel to Canada. This was the country in which they could be infected with SARS-CoV-2 prior to entering Canada. Model input for the country-specific weekly proportions of Canadian and foreign residents were derived from CBSA’s Advanced Passenger Information data (for essential travellers) and ArriveCan and ContactTrace data (for non-essential travellers, Additional file 1 ).
Finally, travellers were stratified by vaccination status to account for any vaccine-induced immunity. For non-essential travellers, the weekly country-specific distributions of vaccine statuses were derived from the ArriveCan and ContactTrace data and could be one of: unvaccinated, partially vaccinated with a GoC approved vaccine, partially vaccinated with a non-GoC approved vaccine, fully vaccinated with GoC approved vaccines, fully vaccinated with non-GoC approved vaccines or fully vaccinated with a mixture of GoC approved and non-GoC approved vaccines. Hereafter, partially vaccinated refers to vaccination with one dose of a two dose vaccine regime while fully vaccinated refers to one dose of a one dose vaccine regime or two doses of a two dose vaccine regime. The vaccination status of essential travellers was not available from the ArriveCan data because these travellers were not required to provide proof of vaccination during the study period. Model input for the daily distributions of vaccination statuses in essential travellers were assumed to follow the vaccine coverage for the country of departure (foreign resident travellers) or for Canada (Canadian resident travellers) as reported by Our World in Data (OWD; [ 5 ]). Vaccination status for essential travellers in the model included only unvaccinated, partially vaccinated or fully vaccinated because OWD did not provide information on vaccine type for us to distinguish between GoC approved or otherwise.
Correcting for underreporting of COVID-19 cases
Reported COVID-19 case data were likely underestimated due to asymptomatic transmission, incomplete testing and imperfect test sensitivity and reporting systems [ 26 ]. We derived country-specific correction factors to inflate case data and better reflect the true prevalence (Additional File 1 ). A semi-Bayesian probabilistic bias approach was used to estimate the number of true cases at the country level, using reported case data and testing rates [ 27 ]. We adapted the method to also account for the evolving population-level immunity due to previous COVID-19 infections and increasing vaccination rates. True case counts were estimated from March to August 2020 and then monthly thereafter to reduce instability in estimates caused by sparse case data at the onset of the pandemic and low testing rates [ 27 ]. The estimated true case count was divided by the reported case count [ 5 , 28 , 29 ] in order to obtain country-specific correction factors for each time period from March 2020 onwards. Finally, a regression modelling approach was implemented using the country-level Gross National Income (GNI) as a predictor [ 30 ] and the calculated correction factor as the dependent variable. This regression model was used to impute the missing correction factors for countries that did not have case, testing, or vaccination data. The GNI was used as a proxy for the effectiveness of the country surveillance system to detect, test and report COVID-19 cases [ 30 ].
Model formulation
The probability of a traveller arriving in Canada infected with SARS-CoV-2 accounts for the vaccination status of the traveller and potential immunity acquired from a previous infection in their country of residence ( cr ). For simplicity, it was assumed that infection- and vaccine-induced immunity did not wane from the beginning of the pandemic until the end of the study period, and prior infections provided complete immunity against re-infection. The probability of a traveller having infection-acquired immunity on any given day d and in country of residence cr \(({Pinf}_{cr,d})\) was calculated as the cumulating proportion of residents reported to have had COVID-19 given the 2020 country population size [ 5 , 31 , 32 ]. For an essential traveller, the probability of vaccine-acquired protection \((Pvac{c\_E}_{cr,d})\) on any given day d and in country of residence cr , was equal to:
where \({VE}_{cr,status}\) , vaccine effectiveness, is the probability that a traveller had complete immunity against infection which varied according to COVID-19 vaccination status (partially or fully vaccinated) and the cr for the assumed type of vaccine (mRNA vaccines or others) (Additional file 1 : Table A2); and \(Pro{p}_{cr,d, status}\) represents the proportion of the population in country \(cr\) for each vaccination status on day d . Since vaccination status information was available for non-essential travellers, their probability of vaccine-acquired protection \((Pvac{c\_NE}_{cr,status})\) was equal to the associated vaccine effectiveness \({VE}_{cr,status}\) .
The probability of a traveller arriving in Canada infected with SARS-CoV-2 depended on their risk of exposure in the country of departure, cd , prior to departure for Canada. The daily probability of infection \(({\beta }_{cd,d})\) for a susceptible person on a given day d in country cd was calculated as the number of new cases (corrected for underreporting) out of the total susceptible population (i.e. the proportion of the population that was not immune to infection with COVID-19 due to prior infection or vaccination). Based on this daily probability of infection, the probability of a traveller arriving in Canada infected with SARS-CoV-2 was calculated according to the traveller’s reason for travel (i.e. essential or non-essential). For an essential traveller, the probability of importation, ( \({P\_E}_{s,cd,cr};\) Eq. 2 and Additional file 1 ), on travel day s was based on the traveller’s probability of acquiring infection on any of the n days prior to departure to Canada, given that they did not have infection-acquired protection \(\left(1-{Pinf}_{cr,d}\right)\) or vaccine-acquired protection \(\left(1-{Pvacc\_E}_{cr,d}\right)\) . Here n represents the sum of the latent and infectious periods for SARS-CoV-2 infections (Table 1 ). The probability of importation for a non-essential traveller, ( \({P\_NE}_{s,cd,cr, status}\) ; Eq. 3 and Additional file 1 ), was based on the traveller’s probability of acquiring infection on any of the ( n - \(\mu\) ) days prior to the test day and receiving a false negative test result on test day, or not being infected on test day and acquiring infection after completing the test prior to departure. Here \(\mu\) represents the number of days between the test and travel days (i.e. set at three days in the model). An estimated molecular test sensitivity ( se ) of 60% was implemented, which represented the mean value when accounting for the variation in sensitivity with respect to time since infection ([ 33 , 34 ]; Additional file 1 ). Similar to essential travellers, the probability of importation for non-essential travellers is conditional on not having infection-acquired protection \(\left(1-{Pinf}_{cr,d}\right)\) or vaccine-acquired protection \(\left(1-{Pvacc\_NE}_{cr,status}\right)\) .
where \({t}_{c}\) is the number of days spent in the country of departure \(cd\) prior to leaving for Canada. For foreign residents, it was assumed that \({{\text{t}}}_{{\text{c}}}>{\text{n}}\) .
Finally, the total number of importations ( \({I}_{w}\) ) for every epi-week, w , was calculated using the probability of air travellers arriving infected ( \({P}_{k,\upgamma ,s}\) ) for each airport-level origin–destination travel route ( k ), each travel group (γ, i.e. Canadian or foreign resident, vaccination status, essential or non-essential traveller) and each day of the week ( \(s\) ), and the corresponding travel volume ( \({v}_{k,\upgamma ,s}\) ):
Importation estimates were stratified by VOCs and VOIs listed by the USA Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It was assumed that the proportion of variants reported in the GISAID database [ 39 ] for each country during a three-week period (including the week modelled and the two prior weeks) was the same proportion that would be observed in infected travellers arriving in Canada from these countries.
Modelling importation risk and counterfactual scenarios
We used the model to estimate importation risk from July 11 to November 27, 2021 under the assumption that all non-essential travellers were required to have a negative molecular pre-departure test result three days prior to departure for Canada. As well as being our most probable estimate of the true importation risk given the testing requirements that were in effect during the modelled time period, these model estimates formed our baseline to compare with two counterfactual scenarios. Model output is presented by country of departure, SARS-CoV-2 variant and traveller groups. In addition, the number of infected travellers arriving at each of Canada’s four largest airports (Toronto Pearson, Montréal-Trudeau, Vancouver International, and Calgary International) as their final destination are presented. Finally, we mapped country-level model outputs in terms of the cumulative number of importations, percent positivity, and travel volumes for the total study period using ArcGIS Pro version 2.9.0 (ESRI, Redlands, CA).
Two counterfactual scenarios were simulated from July 11 to November 27, 2021 to measure the impact of pre-departure testing on non-essential travellers to reduce importation risk as compared to the baseline. For counterfactual scenario 1, fully vaccinated (with or without GoC approved vaccines) non-essential travellers were not tested, and for counterfactual scenario 2 there was no testing of any non-essential travellers. For both counterfactual scenarios, the model was run for all non-essential travellers, whereas outputs from the baseline scenario were used for essential travellers. The weekly percent change in the total number of imported cases for each counterfactual scenario was compared to the baseline scenario.
Model stochasticity was implemented through the distributions of parameter input values for vaccine effectiveness, latent and infectious periods, and for Canadian travellers, travel duration. For each of these parameters, a value was randomly chosen from a pre-defined distribution (Table 1 ) for every category of traveller, with these categories consisting of unique combinations of origin–destination airport pathway, essential status and day. The baseline and counterfactual scenarios were simulated 50 times. We only present the mean results because the confidence intervals were too narrow to visualise in the plots. All model simulations and analyses were conducted in R version 4.1.0 [ 40 ].
The importation model estimated that a total of 7,863 infected travellers entered Canada by air from July 11 to November 27, 2021. Most cases originated from the USA (2,890 cases), the country with the highest incoming travel volume to Canada (1.46 million travellers) and a PP of 0.198% (Fig. 2 a, b). Other countries with a high risk of importation were Mexico (1,034 cases; 0.414% PP; 249,462 travellers), the United Kingdom (429 cases; 0.277% PP; 154,715 travellers), and France (335 cases, 0.145% PP; 230,295 travellers) (Fig. 2 ). The relative ranking of contributing countries evolved over time, and differed between destination airports (Figs. 2 and 3 , and Fig. A2 in Additional file 1 ).
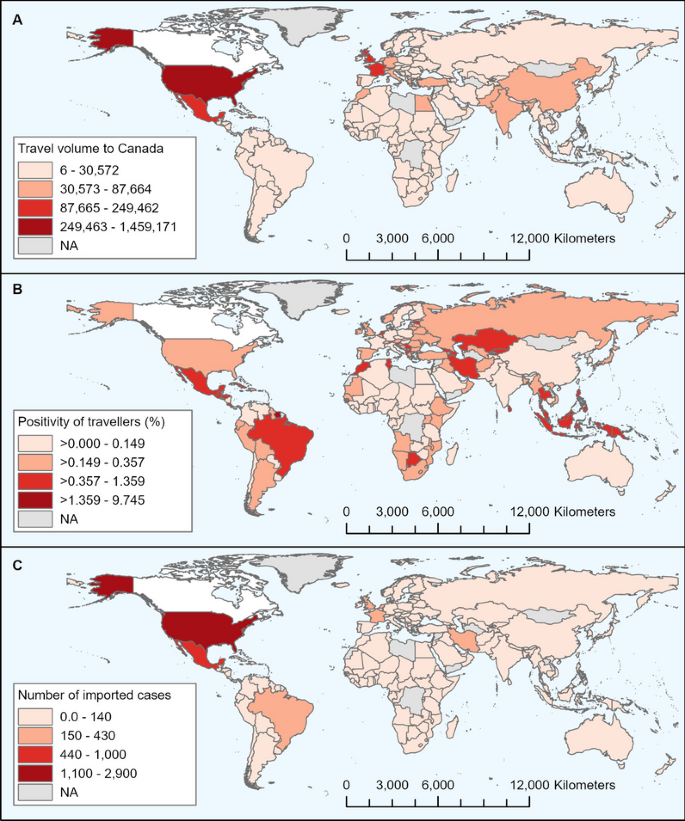
Maps illustrating results at the country of departure level from July 11, 2021 to November 27, 2021 for A estimated travel volume to Canada, and model estimates for B COVID-19 percent positivity of travellers entering Canada, and C number of imported COVID-19 cases to Canada. The destination country, Canada, is shown in white. Countries in grey either have unavailable travel volume data and/or reported case counts
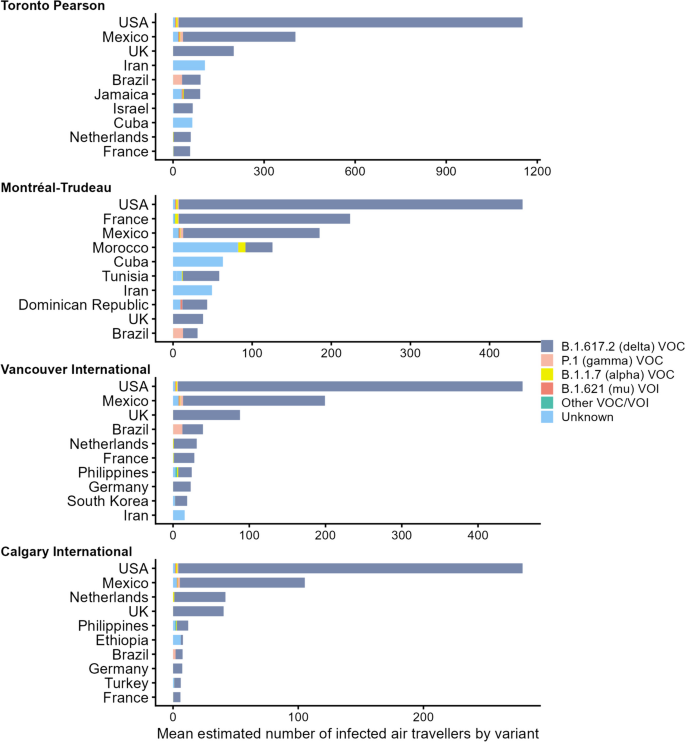
Model output for the mean number of SARS-CoV-2 infected air travellers by variant and country of departure arriving at their final destination in one of the four largest Canadian airports, as estimated from July 11 to November 27, 2021
The composition of SARS-CoV-2 variants also varied between airports and through time. Throughout the study period the Delta variant was modelled to be the predominant infectious agent in travellers arriving at the Canadian destination airports. There were also estimated contributions from the Gamma, Mu, and Alpha variants, especially prior to August (Fig. 3 ; Fig. A2 in Additional file 1 ).
Output from the importation model suggests that the number of imported cases and PP also varied over time. There was a peak in August, followed by a decrease until the end of October, and a subsequent increase in November (Fig. 4 ). In the baseline scenario, the mean weekly number of imported cases ranged from 145 to 539 cases and PP ranged from 0.15 to 0.28%. Most cases were imported by non-essential travellers (range: 84–398 per week), who comprised the largest proportion of travel volume (range: 79–90% per week) and populations with full vaccination status (range: 67–92% per week). In contrast, essential travellers had fewer imported cases (range: 62–154 per week), with a smaller travel volume (range: 10–21% per week) and populations of full vaccination status (range: 29–76% per week). Despite having lower importation numbers, the PP in essential travellers was consistently higher (range: 0.37–0.65% per week) than non-essential travellers (range: 0.12–0.24% per week).
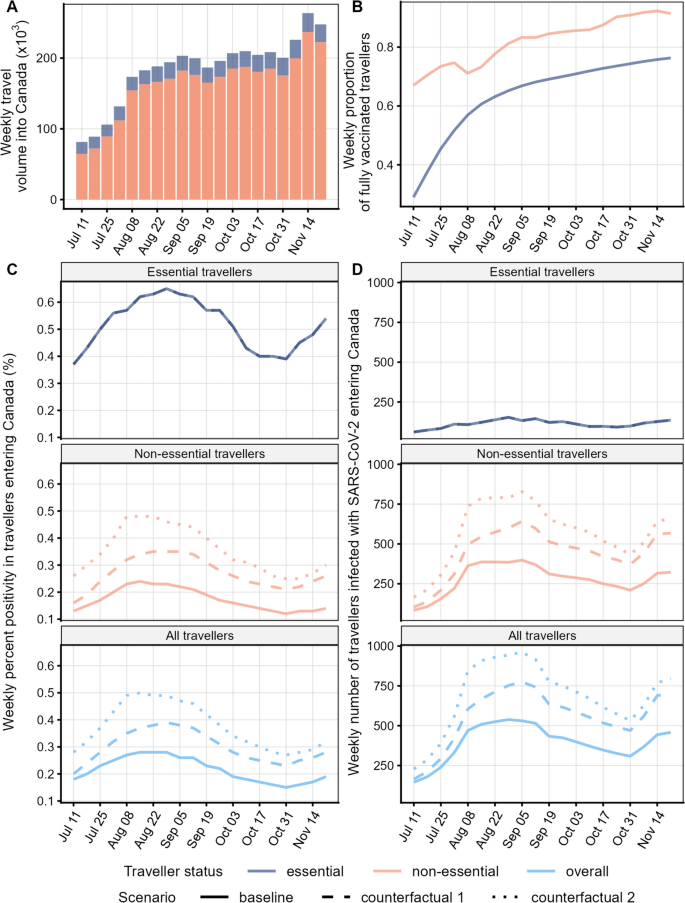
Weekly model inputs for the study period (July to November 2021) for A estimated travel volumes into Canada for essential and non-essential travellers, B proportions of fully vaccinated travellers estimated for essential travellers given global vaccine coverage [ 5 ] and reported for non-essential travellers [ 23 ], and model output for C percent positivity and D number of imported COVID-19 cases into Canada as stratified into essential and non-essential travellers and combined (overall) for the baseline scenario (pre-departure testing of all non-essential travellers), counterfactual scenario 1 (no pre-departure testing of fully vaccinated non-essential travellers) and counterfactual scenario 2 (no pre-departure testing of any non-essential travellers). In C ) and D ), the essential traveller curve is identical for all three scenarios since the model for essential travellers was not repeated for the counterfactual scenarios
The counterfactual analysis suggested that pre-departure testing in non-essential travellers reduced importation risk. Compared to the baseline scenario, the risk of importation in non-essential travellers was greater in the counterfactual scenarios, with up to 775 weekly importations (PP ≤ 0.38%) when fully vaccinated travellers were exempt from pre-departure testing (counterfactual scenario 1), and up to 961 weekly imported cases (PP ≤ 0.47%) when all non-essential travellers were exempt from testing (counterfactual 2; Fig. 4 ). Pre-departure testing in the baseline scenario averted 30% of cases occurring over the study period compared to counterfactual scenario 1, with 12 to 36% of cases prevented weekly (Fig. 5 ). Even more cases (43%) were prevented when comparing the baseline scenario to counterfactual scenario 2, with 36 to 45% of cases prevented weekly (Fig. 5 ). The percentage of cases averted in counterfactual scenario 1 increased with time, especially between July and September. For counterfactual scenario 2 the temporal trends on the impact of testing were less pronounced (Fig. 5 ).
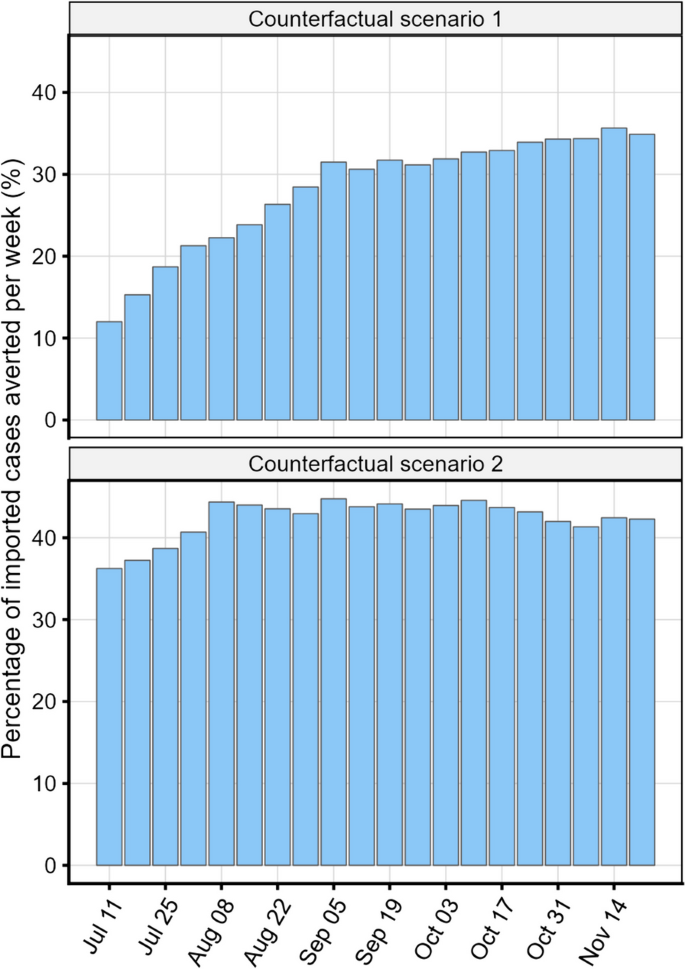
Weekly percentage of infected travellers averted from arriving at Canadian airports from July to November 2021 when comparing the baseline scenario (pre-departure testing of all non-essential travellers) to counterfactual scenario 1 (no pre-departure testing of fully vaccinated non-essential travellers) and to counterfactual scenario 2 (no pre-departure testing of any non-essential travellers)
A mathematical model estimating the importation risk of COVID-19 into Canada by combining detailed travel volume data with the evolving global epidemiological landscape and country-specific levels of vaccine- and infection-acquired immunity is presented in this study. The study results suggest that the risk, as measured through the number of travellers arriving infected with SARS-CoV-2 and PP, varied over time by country and Canadian destination airports. Considering the entire study period, the highest overall number of imported COVID-19 cases were estimated to originate from the USA, Mexico, UK, and France. Findings from this study highlight the differential impact of essential and non-essential travellers on COVID-19 importations between July and November 2021. Notably, results from the counterfactual modelling analyses support the effectiveness of pre-departure molecular testing in all non-essential travellers to reduce the number of imported COVID-19 cases.
Flexibility in the model structure and detailed importation risk profiles allow for more nuanced assessments supporting evidence-based policy decision making. By including COVID-19 variant data and detailed travel volumes at the airport level, the model provides a comprehensive characterisation of importation risk by country of departure, variant and point of entry throughout Canada. Furthermore, estimates of importation risk at the airport level allows an evidence-based assessment of the risk and the potential impact on transmission dynamics in the region where the airport is located. In the case of an emergent VOC, the model outputs could be valuable to help target surveillance and on-arrival response efforts towards locations where passengers at higher risk are landing.
Our modelling approach enabled a comprehensive understanding of importation risk through two measures. The PP represents the mean individual-level probability of importation for a given traveller group or country. The number of imported cases provides insight on the level of risk that the traveller group or country poses to Canada by considering the relative importance of both PP and travel volume. The distinction in measures helps interpret the potential roles of different traveller groups or countries on importation risk. For example, model results suggest that essential travellers had a substantially higher PP than non-essential travellers during the study period. This difference can largely be attributed to pre-departure testing requirements for non-essential travellers as supported by results from the counterfactual analyses. However, despite higher PP in essential travellers than non-essential travellers, the overall number of imported cases from essential travellers was low because there were far fewer essential travellers. Another example from the country-level perspective has the opposite conclusion. Model output indicated that travellers from the USA contributed the highest number of imported cases because travel volumes from the USA were higher than any other country, despite the PP of travellers from the USA being lower compared to other countries (e.g. Mexico, Brazil). We found using both measures together is more revealing of importation risk than relying on one alone.
As in [ 41 ], which demonstrates the effectiveness of the pre-departure testing program, our model suggests that there would have been nearly twice as many importations estimated to occur in the absence of a pre-departure testing requirement (counterfactual scenario 2). It is important to note that model results are expected to be conservative in terms of the impact of pre-departure testing, given that the mean test sensitivity chosen in our model (i.e. 60%) fell on the lower range of plausible values. The temporal increase in the surplus cases that would have occurred had non-essential fully vaccinated travellers not undergone pre-departure testing (counterfactual scenario 1) can be attributed in part to a growing proportion of non-essential travellers becoming fully vaccinated through time. With vaccination, a larger number of travellers were exempt from the pre-departure testing requirement in counterfactual scenario 1, resulting in increased importations compared to the baseline scenario. The observed temporal increase in fully vaccinated travellers could be explained by the following factors: 1) increased second dose uptake within the Canadian population [ 42 ], 2) permitting fully vaccinated non-essential citizens and permanent residents of the US with a GoC approved vaccine to enter Canada for discretionary travel, with exceptions, effective August 9, 2021, and 3) extending factor #2 on September 7, 2021 to all other countries [ 8 , 14 ]. Consequently, toward the end of the study period, the difference in the impact of removing pre-departure testing in fully vaccinated non-essential travellers as opposed to all non-essential travellers was relatively small. While this analysis highlights the impact of the pre-departure testing program, it also demonstrates the versatility of the model in assessing and comparing the relative influence of different prevention strategies.
Although evaluating the impact of international COVID-19 importations on the local spread in Canada is beyond the scope of this paper, it has been explored previously in different contexts. Results from modelling studies suggest that case importation may have played an important role in local dynamics during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic and for emergent variants [ 19 , 20 , 43 ] or in countries with low prevalence and limited public health measures in place to restrict domestic spread [ 44 ]. However, international travel restrictions appear to be less effective once the disease is widespread and outbreaks are self-sustaining in the destination country [ 43 , 45 , 46 ]. In that specific context, imported cases would have a relatively small contribution to local transmission dynamics. As such, the impact of international travel restrictions relies on complex and dynamic factors, and requires evaluation and adaptation to the evolving local and global epidemiological situation, while also taking into account their economic and social costs. Previous work evaluating the potential impact of the border re-opening on disease spread within Canada [ 47 ] has been performed using an agent-based model [ 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 ]. However, further analyses would be needed to fully assess the impact of the pre-departure testing requirements on local transmission dynamics among the Canadian population.
Despite the strengths of our modelling approach there are important limitations to consider. First, for the study presented, we did not have access to border testing data for validating model results. Furthermore, as with any highly data driven model, error in input data will decrease accuracy of model output. For instance, the combination of multiple datasets to obtain air travel volume could have led to biased model inputs by traveller group. However, these data sources had the advantage of accounting for Notices to Airmen (NOTAMs) on flight suspensions from specific countries during the study period. Furthermore, the model relies on robust global surveillance data. Poor data quality and quantity can result in biased outcomes, especially in countries with limited testing capacities and unreliable reporting systems. A strength of the current model is the incorporation of a modified semi-Bayesian probabilistic bias approach, implemented to correct the number of reported cases by adjusting for under-ascertainment [ 27 ]. Although the country-specific case count estimates from this methodology align well with other published estimates (Fig. A1 in Additional file 1 ), a minimal amount of data is still required to produce reliable results.
Other limitations arise from the model assumptions. First, by assuming that there was complete protection against reinfection and no-waning in post-infection- and vaccine-induced immunity, model output could underestimate importation risk. Secondly, it was assumed that Canadian travellers only visit one country (the country of departure) and for a limited period prior to departure for Canada and that foreign travellers remain in their respective country of departure without travelling to other countries throughout the pandemic. We justify these assumptions because travel was greatly reduced during the pandemic [ 52 , 53 ]. Also, we erred on a simplified model structure in the absence of having complete data on travel history prior to departure for Canada. These assumptions likely reduced the accuracy in estimating travellers’ probabilities for vaccine- (for foreign essential travellers) and infection-acquired protection (for all travellers) and probabilities of exposure in the country of departure prior to travel. It is however difficult to know if the resulting error over- or underestimated importation risk. Finally, the model assumed that the traveller population was represented by the underlying country population in terms of the vaccination coverage (for essential travellers only), age demographics and socio-economic landscape, which could potentially lead to bias in terms of estimated exposure risk. For instance, travellers departing from countries with large wealth and income inequalities may have higher quality housing (i.e. less overcrowding) and better access to vaccination, and hence lower SARS-CoV-2 exposure compared to the general population from which model estimates for infection probabilities were calculated [ 54 ].
Our mathematical model provided a detailed COVID-19 importation risk profile for air travellers arriving at Canadian airports from international departures. Model outputs indicated travel groups and countries contributing high importation risk as measured by the number of imported cases and PP. Essential travellers were estimated to contribute fewer importations than non-essential travellers. Furthermore, model results suggest that pre-departure molecular testing in non-essential travellers likely led to lower numbers of imported cases and PP than when compared to counterfactual scenarios that were more lenient. The model we present here was applied to a Canadian COVID-19 context, including an assessment of pre-departure testing, but could be adapted to other similar infectious diseases and border measures, such as vaccination mandates on specific traveller groups and flight suspensions from high-risk countries. As the rate of emerging infectious diseases continues to increase with global environmental change [ 55 ], versatile tools such as this importation risk model can help support evidence-based border policy development.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from CBSA, IATA, and GISAID but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of CBSA, IATA, and GISAID.
Abbreviations
Canada Border Services Agency
International Air Transport Authority
Government of Canada
Gross National Income
Our World in Data
Percent Positivity
Variants of concern
Variants of interest
Notice to Airmen
Dudouet P, Gautret P, Larsen CS, Díaz-Menéndez M, Trigo E, von Sonnenburg F, et al. Chikungunya resurgence in the Maldives and risk for importation via tourists to Europe in 2019–2020: A GeoSentinel case series. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020;36:101814.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Liebig J, Jansen C, Paini D, Gardner L, Jurdak R. A global model for predicting the arrival of imported dengue infections. PLoS One. 2019;14(12):e0225193.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yuan B, Nishiura H. Estimating the actual importation risk of dengue virus infection among Japanese travelers. PLoS One. 2018;13(6):e0198734.
Sharun K, Tiwari R, Natesan S, Yatoo MI, Malik YS, Dhama K. International travel during the COVID-19 pandemic: implications and risks associated with “travel bubbles.” J Travel Med. 2020;27(8):taaa184.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ritchie H, Mathieu E, Rodés-Guirao L, Appel C, Giattino C, Ortiz-Ospina E, et al. Coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19). Our World in Data. 2020.
Google Scholar
Government of Canada. Timeline - CBSA border measures 2021. Updated April 23, 2021. Available from: https://www.publicsafety.gc.ca/cnt/trnsprnc/brfng-mtrls/prlmntry-bndrs/20210907/05-en.aspx . Accessed 11–02–2022.
Transport Canada. Trasportation in Canada 2021; comprehensive report. 2021.
Government of Canada. Travel Advisory: Reminder – On September 7, new measures for fully vaccinated international travellers to Canada will come into force 2021. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/border-services-agency/news/2021/09/travel-advisory-reminder--on-september-7-new-measures-for-fully-vaccinated-international-travellers-to-canada-will-come-into-force.html . Accessed 29 July 2022.
Government of Canada. Statement from the Chief Public Health Officer of Canada on January 7, 2021. Ottawa, ON, Canada. 2021. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/news/2021/01/statement-from-the-chief-public-health-officer-of-canada-on-january-7-2021.html . Accessed 16 Jan 2023.
Government of Canada. Travellers’ testing, isolation and quarantine obligations. 2021. Available from: https://www.publicsafety.gc.ca/cnt/trnsprnc/brfng-mtrls/prlmntry-bndrs/20210722/020/index-en.aspx . Accessed 16 Jan 2023.
Government of Canada. COVID-19; Canada border testing program: understanding the data. 2023. Available from: https://health-infobase.canada.ca/covid-19/border-testing-data/technical-notes.html . Accessed 30 Aug 2023.
Government of Canada. Orders in council 2021. Available from: https://orders-in-council.canada.ca/attachment.php?attach=40875&lang=en . Accessed 31 Aug 2023.
Institut national de santé publique du Québec (INSPQ). Ligne du temps COVID-19 au Québec 2022. Available from: https://www.inspq.qc.ca/covid-19/donnees/ligne-du-temps . Accessed: 29 April 2022.
Government of Canada. Travel Advisory: REMINDER – On August 9th, new public health measures will come into force affecting travel to Canada 2021. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/border-services-agency/news/2021/08/travel-advisory-reminder--on-august-9th-new-public-health-measures-will-come-into-force-affecting-travel-to-canada.html . Accessed 29 July 2022.
Canadian Institute for Health Information. Canadian COVID-19 intervention timeline. 2022. Available from: https://www.cihi.ca/en/canadian-covid-19-intervention-timeline . Accessed: 11-02-2022.
Han X, Xu Y, Fan L, Huang Y, Xu M, Gao S. Quantifying COVID-19 importation risk in a dynamic network of domestic cities and international countries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118(31):e2100201118.
Menkir TF, Chin T, Hay JA, Surface ED, De Salazar PM, Buckee CO, et al. Estimating internationally imported cases during the early COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):311.
Liebig J, Najeebullah K, Jurdak R, Shoghri AE, Paini D. Should international borders re-open? The impact of travel restrictions on COVID-19 importation risk. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):1573.
Godin A, Xia Y, Buckeridge DL, Mishra S, Douwes-Schultz D, Shen Y, et al. The role of case importation in explaining differences in early SARS-CoV-2 transmission dynamics in Canada-A mathematical modeling study of surveillance data. Int J Infect Dis. 2021;102:254–9.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Hurford A, Rahman P, Loredo-Osti JC. Modelling the impact of travel restrictions on COVID-19 cases in Newfoundland and Labrador. R Soc Open Sci. 2021;8(6):202266.
International Air Transport Association (IATA). Air Traffic Statstics. 2021. Available from: https://www.iata.org/en/services/statistics/air-transport-stats/ . Cited 2022.
Government of Canada. ArriveCan awareness toolkit 2020. Available from: http://www.amb-canada.fr/pdf/ArriveCan_EN.pdf . Accessed: 11–02–2022.
Government of Canada. ArriveCAN. Version 2.21 2021. Available from: Use ArriveCAN for a faster border experience - Canada.ca.
Canada Border Services Agency. Contact Trace. Version 3.9.2. 2021.
Messenger JC, Lee S, McCann D. Working time around the world: Trends in working hours, laws, and policies in a global comparative perspective. Abingdon: Routledge; 2007.
Dougherty BP, Smith BA, Carson CA, Ogden NH. Exploring the percentage of COVID-19 cases reported in the community in Canada and associated case fatality ratios. Infect Dis Model. 2021;6:123–32.
PubMed Google Scholar
Wu SL, Mertens AN, Crider YS, Nguyen A, Pokpongkiat NN, Djajadi S, et al. Substantial underestimation of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the United States. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1–10.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Centers for Disease Control Prevention. COVID-19 Response. COVID-19 case surveillance public data access, summary, and limitations 2021. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/cases-in-us.html . Accessed 29 Sept 2021.
Dong E, Du H, Gardner L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20(5):533–4.
The World Bank. GNI per capita, Atlas method (2019) 2019. Available from: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GNP.PCAP.CD . Accessed: 13 Sept 2023.
United States Census Bureau. Table 2. Resident population for the 50 states, the Distric of Columbia, and Puerto Rico: 2020 CENSUS. Available from: https://www.census.gov/data/tables/2020/dec/2020-apportionment-data.html . Accessed 02-01-2023.
The World Bank. Population, total - Tuvalu. Available from: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL?locations=TV . Accessed 29 Sept 2021.
Johansson MA, Wolford H, Paul P, Diaz PS, Chen T-H, Brown CM, et al. Reducing travel-related SARS-CoV-2 transmission with layered mitigation measures: symptom monitoring, quarantine, and testing. BMC Med. 2021;19:1–13.
Article Google Scholar
Zhen W, Smith E, Manji R, Schron D, Berry GJ. Clinical evaluation of three sample-to-answer platforms for detection of SARS-CoV-2. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;58(8):e00783-e820.
Cevik M, Bamford C, Ho A. COVID-19 pandemic—a focused review for clinicians. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26(7):842–7.
Weiss A, Jellingsø M, Sommer MOA. Spatial and temporal dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EBioMedicine. 2020;58:102916.
Woodruff A, Walsh KL, Knight D, Irizarry-Alvarado JM. COVID-19 infection: strategies on when to Discontinue isolation, a retrospective study. Am J Infect Control. 2020;48(9):1032–6.
Hellou MM, Górska A, Mazzaferri F, Cremonini E, Gentilotti E, De Nardo P, et al. Nucleic-acid-amplification tests from respiratory samples for the diagnosis of coronavirus infections: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;27:341–51.
Shu Y, McCauley J. GISAID: from vision to reality. Eurosurveillance. 2017;22(13):30494. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2017.22.13.30494 .
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2020.
Kiang MV, Chin ET, Huynh BQ, Chapman LA, Rodríguez-Barraquer I, Greenhouse B, et al. Routine asymptomatic testing strategies for airline travel during the COVID-19 pandemic: a simulation study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21(7):929–38.
Noah L. COVID-19 tracker canada 2020. Available from: COVID19Tracker.ca. Accessed 10–04–2022.
Arino J, Boëlle P-Y, Milliken E, Portet S. Risk of COVID-19 variant importation–how useful are travel control measures? Infect Dis Model. 2021;6:875–97.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hanly MJ, Churches T, Fitzgerald O, Post JJ, MacIntyre CR, Jorm L. The impact of re-opening the international border on COVID-19 hospitalisations in Australia: a modelling study. Med J Aust. 2022;216(1):39–42.
Russell TW, Wu JT, Clifford S, Edmunds WJ, Kucharski AJ, Jit M. Effect of internationally imported cases on internal spread of COVID-19: a mathematical modelling study. Lancet Public Health. 2021;6(1):e12–20.
Shiraef MA, Friesen P, Feddern L, Weiss MA. Did border closures slow SARS-CoV-2? Sci Rep. 2022;12:1709.
Public Health Agency of Canada. COVID-19: PHAC modelling group report. 2021.
Ogden NH, Turgeon P, Fazil A, Clark J, Gabriele-Rivet V, Tam T, et al. Counterfactuals of effects of vaccination and public health measures on COVID-19 cases in Canada: What could have happened? Can Commun Dis Rep. 2022;48(7/8):292–302.
Gabriele-Rivet V, Spence KL, Ogden NH, Fazil A, Turgeon P, Otten A, et al. Modelling the impact of age-stratified public health measures on SARS-CoV-2 transmission in Canada. R Soc Open Sci. 2021;8(11):210834.
Ng V, Fazil A, Waddell LA, Turgeon P, Otten A, Ogden NH. Modelling the impact of shutdowns on resurging SARS-CoV-2 transmission in Canada. R Soc Open Sci. 2021;8(5):210233.
Ng V, Fazil A, Waddell LA, Bancej C, Turgeon P, Otten A, et al. Projected effects of nonpharmaceutical public health interventions to prevent resurgence of SARS-CoV-2 transmission in Canada. CMAJ. 2020;192(37):E1053–64.
Sun X, Wandelt S, Zhang A. How did COVID-19 impact air transportation? A first peek through the lens of complex networks. J Air Transp Manag. 2020;89:101928.
Goulias KG. Special issue on understanding the relationships between COVID-19 and transportation. Transportation Letters. 2021;13(5–6):327–30.
Patel JA, Nielsen F, Badiani AA, Assi S, Unadkat V, Patel B, et al. Poverty, inequality and COVID-19: the forgotten vulnerable. Public Health. 2020;183:110–1.
Baker RE, Mahmud AS, Miller IF, Rajeev M, Rasambainarivo F, Rice BL, et al. Infectious disease in an era of global change. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022;20(4):193–205.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Samir Mechai for his help in processing the weekly GISAID data on the COVID-19 variants, Dige Guan for providing aggregated data from ArriveCan and ContactTrace, David Champredon for support in the calculation of a mean test sensitivity estimate and Christopher Bell, Kerry Watkins, Rachel Rodin, Elizabeth Harris, Daniele Curtis, and Shirley Bryan for providing critical review and comments on the manuscript.
Not applicable.
Author information
Rachael M. Milwid and Vanessa Gabriele-Rivet contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Authors and Affiliations
Public Health Risk Sciences Division, National Microbiology Laboratory, Public Health Agency of Canada, St-Hyacinthe, QC, Canada
Rachael M. Milwid, Vanessa Gabriele-Rivet, Nicholas H. Ogden, Patricia Turgeon & Erin E. Rees
Public Health Risk Sciences Division, National Microbiology Laboratory, Public Health Agency of Canada, Guelph, Guelph, ON, Canada
Aamir Fazil
Department of Pathology and Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Université de Montréal, Saint-Hyacinthe, QC, Canada
Nicholas H. Ogden, Patricia Turgeon & Erin E. Rees
Physique Des Particules, Université de Montréal, Faculté Des Arts Et Des Sciences, Montréal, QC, Canada
David London
Emergency Management Branch, Global Public Health Intelligence Network Tiger Team, Public Health Agency of Canada, Ottawa, ON, Canada
Simon de Montigny
Epidemiology of Zoonoses and Public Health Research Unit, Faculté de médecine vétérinaire, Université de Montréal, Saint-Hyacinthe, QC, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ER, NO, VG-R, and RMM designed the study. ER, VG-R and RMM contributed to the model development and analysis. DL contributed to the equation formation and SDM provided support with interpretation of the results. VG-R, RMM and ER wrote the manuscript and ER, NO, VG-R, AF, PT, DL and SDM edited the final manuscript. VG-R and RMM contributed equally to this work and share first authorship. ER is the senior author.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Vanessa Gabriele-Rivet .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
This file contains a detailed description of the methods, data sources and additional results.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Milwid, R.M., Gabriele-Rivet, V., Ogden, N.H. et al. A methodology for estimating SARS-CoV-2 importation risk by air travel into Canada between July and November 2021. BMC Public Health 24 , 1088 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18563-1
Download citation
Received : 16 September 2023
Accepted : 09 April 2024
Published : 19 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18563-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Importation risk
- Mathematical model
- Pre-departure molecular testing
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Skip to main content
- Skip to site information
Language selection
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
Entering Canada
On this page, by private boat, required identification, permanent residents, travelling with children, you and the border services officer.
Whether you’re returning home or visiting, you’ll follow the same 3 steps to enter Canada:
Step 1. Pre-arrival: Use Advance Declaration or complete a Declaration Card
If you’re arriving by air at one of Canada’s participating international airports, you can save time at the border. Submit your customs and immigration declaration online using Advance Declaration up to 72 hours before you arrive in Canada.
If you choose not to submit your declaration in advance, you can complete it at an airport kiosk or eGate. If you’re landing at an airport without kiosks or eGates, you’ll receive a Declaration Card on board the aircraft or other conveyance. Read the instructions and complete the card before you arrive. Have it ready to present to Canadian officials at the airport, along with your identification and other travel documents. If you're travelling with children, please have their documentation ready as well.
If using a Declaration Card, detach and discard the instructions. To help us serve you faster, do not fold the card.
Everyone arriving in Canada must complete a declaration. You can list up to 4 people living at the same residence on one card, or 8 people per Advance Declaration submission.
The Declaration Card or Advance Declaration submission tells us what we need to know about you, your travels and what you’re bringing into the country.
Connecting to another flight
If you’re connecting to another flight or travelling on to another destination and re-boarding the same plane, follow the signs. At some airports, you may have to check your baggage and have it screened again.
If you travel frequently our trusted traveller programs can help
If you're a member of a trusted traveller program, you can skip Step 2 and go directly to the automated kiosks or eGates for faster processing.
Step 2. Arrival: First CBSA checkpoint
When you arrive at the terminal, follow the signs to the first Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) checkpoint, also called “primary inspection.”
If you used Advance Declaration, go to a kiosk or eGate to retrieve your confirmed declaration receipt. Up to 5 people may use a kiosk as a group upon arrival.
Next, a border services officer will examine your:
- Declaration Card or Advance Declaration kiosk receipt
- your identification
- other travel documents
The officer may ask you a series of questions to determine:
- your immigration status
- the type of any goods you're bringing with you
- your duty-free allowance
- your personal exemption entitlements
Goods not properly declared that are restricted or prohibited in Canada can, under the law, be seized.
Newcomer or coming to Canada to study or work
If you’re a newcomer to Canada, coming to study or work in Canada, you may need to present further documentation. The officer will help guide you through this process. You may ask the officer for help if you don’t speak English or French well.
Step 3. Baggage and second CBSA checkpoint
Go to the baggage claim area. If you must pay duty and taxes, you can pay at most major airports while waiting for your luggage.
Once you’ve picked up your luggage:
- go to the next CBSA checkpoint
- Declaration Card, Advance Declaration kiosk or eGate receipt
- receipt, if you paid duty and taxes for your goods
The officer may direct you to a secondary inspection area.
Here, officers may ask you:
- for detailed information about your travels
- to present your luggage and goods for examination
This is a normal part of the travelling process. Your cooperation is appreciated and helps us ensure the safety of Canada, its economy and its residents.
If you’re arriving by land, follow the signs to the first checkpoint, also called “primary inspection.” Here, a border services officer will examine your identification and other travel documents and take your verbal declaration.
Visit U.S. to Canada border wait times for estimated wait times at certain locations.
If you’re arriving by private boat, go directly to a designated marine telephone reporting site and call the CBSA Telephone Reporting Centre (TRC) at 1-888-226-7277 to obtain clearance.
Private boaters that meet certain conditions may report to the CBSA by calling the TRC using cell phone from their location in Canadian waters.
Learn more about reporting requirements for private boaters.
Make sure you carry proper identification for yourself and any children travelling with you to help confirm your legal right to enter Canada. Canada has introduced a new entry requirement, known as an Electronic Travel Authorization (eTA), for certain international travellers who fly to Canada.
Read about the changes and how they may affect you.
The Government of Canada recommends that Canadian citizens travel with a valid Canadian passport because it’s the only reliable and universally accepted travel and identification document available to Canadians for the purpose of international travel.
International transportation companies such as airlines may require travellers to present a passport before boarding. Canadian citizens may face delays or may not be allowed to board the plane or other conveyance if they present other documents such as a:
- Enhanced Driver's License (EDL)/Enhanced Identification Card (EIC)
- NEXUS card (used where the program is available)
- Free and Secure Trade (FAST) card used in FAST lanes
- Canadian citizenship card
- Certificate of Indian Status
- Birth certificate in combination with either a driver's licence or a government-issued photo identification
Permanent residents (immigrants living in Canada who are not yet Canadian citizens) need a valid permanent resident card to return to Canada. Check the expiry date on your card.
Note that a Certificate of Canadian Citizenship is not a travel document.
See Canadian Citizenship for further details.
Parents who share custody of their children should bring copies of the legal custody documents to the border when travelling with their children.
A consent letter should be used for all cross-border travel when a child is travelling:
- with only 1 parent or guardian
- in the care of friends or relatives
- with a group, such as a sports, school, musical or religious group
Example of a consent letter to permit travel by a child with a single custodian or parent.
When travelling with a group of vehicles, parents or guardians should arrive at the border in the same vehicle as the children.
Adults who aren’t parents or guardians should have written permission from the parents or guardians to supervise the children. The consent letter should include addresses and telephone numbers where the parents or guardian can be reached.
Border officers watch for missing children, and may ask detailed questions about the children who are travelling with you.
You may occasionally find yourself going through a more detailed inspection. In some cases, this simply means that you may have to complete a form. In other cases, the border services officer will need to identify the goods you’re bringing into the country or examine your luggage.
Border services officers are legally entitled to examine your luggage as part of their responsibility to protect Canada's safety, economy and environment. You are responsible for opening, unpacking and repacking your luggage.
By making your goods easily accessible for inspection and having your receipts handy, you will be helping the CBSA to help you. It’s a good idea to keep all your receipts for accommodation and purchases, and for any repairs done to, or parts bought for, your vehicle. The border services officer may ask to see them as evidence of the length of your stay and of the value of the goods or repairs.
If you disagree with the amount of duty and taxes that you have to pay, please ask to speak with the CBSA superintendent on duty. A consultation can often resolve the issue quickly and without cost. If you’re still not satisfied, our officers can tell you how to make a formal appeal.
Border services officers may arrest an individual for an offence under the Criminal Code (for example, impaired driving, outstanding arrest warrants, stolen property, abductions/kidnappings) and for infractions under other acts of Parliament (for example, the Customs Act , the Immigration and Refugee Protection Act ).
If you’re arrested, you may be compelled to attend court in Canada. You should note that anyone arrested in Canada is protected by and will be treated in accordance with the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms .
Related links
- Bringing goods to Canada
- Traveller entry requirements
- Travel documents
- Programs for trusted travellers
- Travelling as a dual citizen

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
COVID-19 test. All foreign nationals entering the United States by land are required to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test result taken within 72 hours of crossing the border. The test must be a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) or a viral antigen test. You will need to show proof of the negative test result to the CBP officer at the ...
Updated Date: April 21, 2022 Since January 22, 2022, DHS has required non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide proof of vaccination upon request.
Proof of COVID-19 vaccination is not required. Pre-board testing is not required. COVID-19 pre-entry and arrival tests are not required. Quarantine after you enter Canada is not required. Using ArriveCAN is not required, but. to save time at the border, you can use Advance Declaration in ArriveCAN to submit your customs and immigration ...
The United States and Canada have limited non-essential travel at our shared land ports of entry. "Non-essential" travel includes travel that is considered tourism or recreational in nature. "Essential travel" still permitted includes: work and study, critical infrastructure support, economic services and supply chains, health ...
Updated Date: April 21, 2022 As of Thursday, April 21, 2022, DHS will extend COVID-19-related land border entry requirements. Non-U.S. travelers seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders are required to be fully vaccinated against COVID-19 and provide proof of vaccination upon request.
If the test is more than 72 hours old when they re-enter Canada, they will be required to get a new pre-arrival molecular test in the United States. Unvaccinated or partially vaccinated travellers who are eligible to enter Canada must continue to follow pre-arrival, arrival and Day-8 molecular COVID-19 testing requirements, and quarantine for ...
These requirements are: proof of approved COVID-19 vaccination(s) at least 14 days prior to entry to Canada, proof of a negative COVID-19 PCR test within 72 hours prior to arrival, and submittal of travel information in Canada's ArriveCAN travel app. Travelers must be asymptomatic upon arrival. Travelers are encouraged to hand carry original ...
With the COVID-19 restrictions at the border to remain in place for at least another month, some Canadians may need a primer on what those rules are.. Public Health Agency of Canada announced that ...
All travellers, regardless of vaccination status, will still require a pre-entry COVID-19 molecular test result. However effective August 9, 2021, the Government of Canada is adjusting its post-arrival testing strategy for fully vaccinated travellers. Using a new border testing surveillance program at airports and land border crossings, fully ...
More than 112 million vehicles crossed from Canada to the U.S. in 2019, but the number dropped to 68.5 million in 2020. The drop was mostly due to lower numbers of personal vehicles and buses, as ...
Canadians can still travel to the U.S. during the COVID-19 pandemic — just not by car Canadian air passengers also likely won't have to self-isolate for 14 days upon arrival in the U.S.
If crossing the U.S.- Mexico border by car: remain extremely vigilant; ... Canadian citizens don't require visitor, business, transit or other visas to enter the United States from Canada but there are some exceptions. Canadians Requiring Visas ... COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, ...
To help keep people in Canada safe, the Government of Canada put in place border measures to reduce the risk of the importation and transmission of COVID-19 and new variants in Canada related to international travel. Today, the Government of Canada announced it is extending current border measures for travellers entering Canada. Requirements ...
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S. As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19. As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
Checklist for a U.S.-Canada border crossing. If you're fully vaccinated and traveling to Canada, whether by car, plane or boat, you still have to follow certain protocols. To meet entry ...
To enter the United States by air, you must present a valid Canadian passport or NEXUS card (even for a simple connection). Children also must have one of these two documents. As a traveller, you are responsible for ensuring that you meet the requirements, which are outlined on travel.gc.ca. Sherpa, the tool you need.
The Government has announced travel restrictions due to concerns over the Omicron variant and is re-instating COVID-19 testing on all air travellers entering the country with the exception of the United States. Response . The Government of Canada continues to make cautious adjustments to its border approach using scientific evidence and data.
November 19, 2021. Today, the Government of Canada announced upcoming adjustments to Canada's border measures. This backgrounder provides additional context to support travellers in understanding COVID-19 testing and vaccine requirements, as well as other border measures, which are an important part of Canada's response to the global COVID ...
Use Advance Declaration in ArriveCAN to submit your customs and immigration declaration before flying into Canada. Government of Canada's official one-stop-shop for comprehensive international travel information.
On September 7, 2021, provided that Canada's COVID-19 epidemiology remains favourable, the Government intends to open Canada's borders for discretionary travel by travellers from any country who have been fully vaccinated with Government of Canada-accepted vaccines at least 14 days prior to entering Canada and who meet specific entry ...
The Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) restricting all direct commercial and private passenger flights to Canada from India will be extended until July 21, 2021, as well as the Interim Order Respecting Certain Requirements for Civil Aviation Due to COVID-19 requiring air passengers who depart India to Canada via an indirect route to obtain a COVID-19 pre ...
During the COVID-19 pandemic, importation models were used to estimate the number of imported cases from domestic and international travel, and assess the impact of border measures [16,17,18,19].In Canada, mathematical models were developed within the first few months of the pandemic to assess the impact of importation on local COVID-19 transmission in specific provinces (e.g. Québec and ...
Proof of COVID-19 vaccination is not required. Pre-board testing is not required. COVID-19 pre-entry and arrival tests are not required. Quarantine after you enter Canada is not required. Using ArriveCAN is not required, but. to save time at the border, you can use the ArriveCAN customs and immigration feature to complete your declaration in ...
Step 1. Pre-arrival: Use Advance Declaration or complete a Declaration Card. If you're arriving by air at one of Canada's participating international airports, you can save time at the border. Submit your customs and immigration declaration online using Advance Declaration up to 72 hours before you arrive in Canada.