
Essays About Journeys: Top 5 Examples and 7 Easy Prompts
Essays about journeys require recounting the events of your travel. Discover our guide with examples and prompts to help you write your essay.
No two journeys are the same, and various factors will always be at play. It’s the reason many documents their expedition through different mediums. Writing about journeys is similar to telling a real-life story that influenced your character or perspective.
Writing essays about journeys helps to develop your writing and observation skills as you recall and pick the highlights of your travel. Sharing your experiences can entice readers to take on a journey themselves. So, aim to inspire with this exciting essay topic.
5 Essay Examples
1. the best journey in my life by suzanne pittman, 2. road trips: everything you need for a comfortable journey by car by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 3. the first day of my journey to adulthood by anonymous on papersowl.com, 4. life is a journey essay by anonymous on paperwritings.com, 5. long essay on train journey by prasanna, 1. reasons to go on a journey, 2. trip vs. journey, 3. how to enjoy long journeys, 4. my most memorable journey, 5. what makes a journey meaningful, 6. my dream journey, 7. a hero’s journey.
“I had to save a lot of money because I wanted very much to go on this journey with my friends. We planned our trip to take us around Europe. We were going to stop in various parts of Europe with family members and friends.”
The essay mimics Pittman’s travel itinerary during her journey in Europe. She includes all the trip details from the first to the last day and makes the readers feel as if they’re traveling with them. Pittman also offers some travel tips to help anyone who wants to visit Europe on a budget. These tips include staying with friends and relatives and taking comfortable train rides despite long distances.
“With proper planning, everything else seems effortless. You need to consider all factors when planning in order for you to enjoy a successful, stress-free adventure.”
The author believes that the primary purpose of traveling is to relax and have fun. They use the essay to teach how to plan car trips properly. Travelers must learn to budget and estimate expenses, including accommodation, gas, activities, and food. Picking a transportation means is also crucial as one needs to consider factors such as capacity, range, and utility.
“Although things didn’t go how I planned I’m still in college bettering myself and furthering my education. Anything is possible with a good support system and positive mindset.”
The essay narrates how the author’s journey into adulthood becomes a mini-vacation in Georgia after their top university rejects their enrollment. This rejection offers the opportunity to understand many great life lessons. Despite having five other universities to choose from, the writer realizes they only provide free tuition for the first semester. Ultimately, the author receives a full scholarship to a university closer to home.
“All people have the same journey to take – their life. As well as in the other journeys, there may be some inconveniences, disappointments and joys, and a lot depends on how we plan this particular journey and what attitude we develop towards it.”
In this essay, the writer shares that the best way to go on a life journey is with the most joy and minor damage you can endure. It’s constant work to continuously improve one’s life while developing positive qualities and thinking. But in doing so, you’ll have a solid foundation to achieve what you want out of life. However, the author still reminds the readers that they should always be ready to face unexpected events and deal with them in the best way possible.
“These days, people prefer traveling via airplanes because it is time-saving. But going by plane gets boring and monotonous. Train journeys are a relief from the monotony.”
For Prasanna, whether it’s a short or extended tour, a train journey offers an exciting travel experience. She talks about the local and regional trains in India, which are often overcrowded but still used by many as they are the cheapest, safest, and fastest mode of transport in the country. She also mentions that you’ll never get hungry when riding their local trains because of the vendors who sell Indian delicacies.
7 Prompts for Essays About Journeys

Everyone has different motives for traveling. Some go on a journey to appreciate beautiful sceneries, while some move to attend family or work-related gatherings. Some do so to run away from problems. For this prompt, research the common reasons to travel. You can also interview people on why they go on a journey and add any personal experiences.
It’s a trip when a person travels from one point to another without any transfers. Meanwhile, a journey is a more extended voyage that includes transfers and several trips. Compare and contrast trips and journeys to make your readers understand their similarities and differences. You can also have the advantages and disadvantages of each in your paper.
If writing an essay sounds like a lot of work, simplify it. Write a simple 5 paragraph essay instead.
The idea of having a long journey and discovering new things is exciting. However, the excitement can disappear when you’re far away from home. This is especially true for longer and farther travels. This prompt will help readers have a safer, more affordable, and more enjoyable trip by discussing the best long-distance travel tips. You can present an imaginary itinerary with estimated costs to make the essay more digestible.
Write about an unforgettable journey you’ve had through this prompt. Include the purpose of your travel, how you planned it, and if your timetable was followed. Share what you’ll improve on next time to make your journey even better; you can also talk about your companions and the activities that make the adventure worthwhile.
Journeys become meaningful when they enrich lives. It can be because of the destination, the people you are with, or the travel’s goal. Use this prompt to suggest how journeys improve us as humans. You can section your piece based on an individual’s objectives. For example, someone who wants to recharge and get away from the city will find meaning in going to a location far from technology.

Although traveling can be tiring, 43% of travelers appreciate the experience they gain. Think of journeys you desire to be in and add your reasons. Then, you can share your plan on how to make it happen. For instance, you want to tour Southeast Asia and visit countries like the Philippines, Vietnam, and Thailand. To make this dream journey come true, you’ll save for an entire year and work around a tight budget.
It’s normal to see the main character in a movie or novel go through a character arc before they become a true hero. Use this prompt to explain a hero’s journey and why the character must go through it. To give you an idea, Peter Parker was a shy and introverted kid who lived an everyday life before becoming Spider-Man. This makes him relatable to the audience and lets them understand his decisions in the following scenes.
For more examples, check out our guide to movies that follow the hero’s journey .
You can also talk about real-life heroes, such as doctors and firefighters. Interview someone with that profession and ask them why they decided to have their current career.

Maria Caballero is a freelance writer who has been writing since high school. She believes that to be a writer doesn't only refer to excellent syntax and semantics but also knowing how to weave words together to communicate to any reader effectively.
View all posts
Essay on Train Journey for Students and Children
500+ words essay on train journey.
First of all, a journey refers to traveling from one place to another. When it comes to journeys, train journeys take the top spot. A train journey certainly is a wonderfully joyous occasion. Furthermore, train journeys fill individuals with a feeling of intense excitement. This mode of the journey is best when the travel distance is long. A train journey creates an aura that cannot be experienced with other types of journeys.

My Experience of Journey by Train
I have always been an avid supporter of train journeys. My involvement with train journeys began in childhood . I live in Lucknow and from here I have undertaken many train journeys. Furthermore, since childhood, I have paid several visits to the hill station of Almora to meet my relatives. Almora is a hill station located in the state of Uttarakhand. Most noteworthy, Almora is situated in the Himalayan mountain region. Due to this, trains cannot travel directly to Almora. Consequently, Kathgodam is the last town station accessible by trains before the mountain range begins.
The trip from Lucknow to kathgodam is quite a lively experience. I have always ensured the reservation of my seats beforehand. So, my train journey begins from Lucknow railway station. As the train undergoes motion and leaves the Lucknow railway station, my excitement begins to rise. Moreover, as the train gathers speed, a thrilling feeling overtakes me.
My train journey from Lucknow to Kathgodam is probably 8-10 hours duration. However, I enjoy every minute of it in spite of the journey being so long. Furthermore, all along the journey, one can purchase items of food and drinks. I almost always purchase meals and refreshments at least twice in the journey.
When slumber overtakes me, I make use of the sleeping berth. I personally find sleeping on the train berth very comfortable. When I wake after a deep sleep, mountains are visible from a distance. Moreover, as the train approaches Kathgodam with menacing speed, the view of mountains gets bigger and bigger. Also, my amusement greatly rises as I see the Himalayas draw closer. Finally, as the train stops at Kathgodam, my delightful train journey comes to an end.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Why Do I Like to Travel by Train?
Comfort is one of the biggest advantages of a train journey. Most noteworthy, one can move freely in a train cabin. Furthermore, in trains, there is a possibility of an ample foot room. Moreover, trains offer comfortable sleeping berths. All of this makes the train journey a relaxing experience.
Beautiful sightseeing is another noteworthy benefit of train journeys. As the train travels, one can enjoy the views of the countryside, farms, forests , factories, etc. This makes train journeys more comprehensive than journeys by air or road.
Train journeys offer a variety of opportunities to pass time. Furthermore, the train offers a sociable environment. In train journeys, conversations between passengers almost always take place. One can make new friends with traveling passengers on the train easily. Also, one can spend time in a handsome manner on a train journey. In a train journey, one can spend time reading something, listening to music, watching videos, sleeping/resting comfortably, etc.
To sum it up, train journeys are truly one of a kind. The train journey offers uniqueness like no other journey. Most noteworthy, the charm of such a journey is unmatchable. The train journey certainly offers an unforgettable rich experience.
Q1 Why does the writer sleeps so deeply in trains?
A1 The writer sleeps deeply in trains because he finds sleeping on the train berth very comfortable.
Q2 What makes train journeys so journeys so comfortable?
A2 Trains journeys certainly are very comfortable. First of all, one can move freely in a train cabin. Furthermore, there is ample foot room possibility and comfortable sleeping berths on the train.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Improve your writing in one of the largest and most successful writing groups online
Join our writing group!
The Hero’s Journey Ultimate Writing Guide with Examples

by Alex Cabal
What do Star Wars , The Hobbit , and Harry Potter have in common? They’re all examples of a story archetype as old as time. You’ll see this universal narrative structure in books, films, and even video games.
This ultimate Hero’s Journey writing guide will define and explore all quintessential elements of the Hero’s Journey—character archetypes, themes, symbolism, the three act structure, as well as 12 stages of the Hero’s Journey. We’ll even provide a downloadable plot template, tips for writing the Hero’s Journey, and writing prompts to get the creative juices flowing.
What is the Hero’s Journey?
The Hero’s Journey is a universal story structure that follows the personal metamorphosis and psychological development of a protagonist on a heroic adventure. The protagonist goes through a series of stages to overcome adversity and complete a quest to attain an ultimate reward—whether that’s something tangible, like the holy grail, or something internal, like self confidence.
In the process of self-discovery, the archetypal Hero’s Journey is typically cyclical; it begins and ends in the same place (Think Frodo leaving and then returning to the Shire). After the epic quest or adventure has been completed by overcoming adversity and conflict—both physical and mental—the hero arrives where they once began, changed in some as they rose to meet the ultimate conflict or ordeal of the quest.
Joseph Campbell and Christopher Vogler
The Hero’s Journey has a long history of conversation around the form and its uses, with notable contributors including Joseph Campbell and the screenwriter Christopher Vogler , who later revised the steps of the Hero’s Journey.
Joseph Campbell’s “monomyth” framework is the traditional story structure of the Hero’s Journey archetype. Campbell developed it through analysis of ancient myths, folktales, and religious stories. It generally follows three acts in a cyclical, rather than a linear, way: a hero embarks on a journey, faces a crisis, and then returns home transformed and victorious.
Campbell’s ideation of the monomyth in his book The Hero With a Thousand Faces was influenced by Carl Jung’s perspective of psychology and models of self-transformation , where the Hero’s Journey is a path of transformation to a higher self, psychological healing, and spiritual growth.
While Campbell’s original take on the monomyth included 17 steps within the three acts, Christopher Vogler, in his book The Writer’s Journey , refined those 17 steps into 12 stages—the common formula for the modern structure many writers use today.
It’s also worth checking out Maureen Murdock’s work on the archetype, “The Heroine’s Journey.” This takes a look at the female Hero’s Journey, which examines the traditionally masculine journey through a feminist lens.
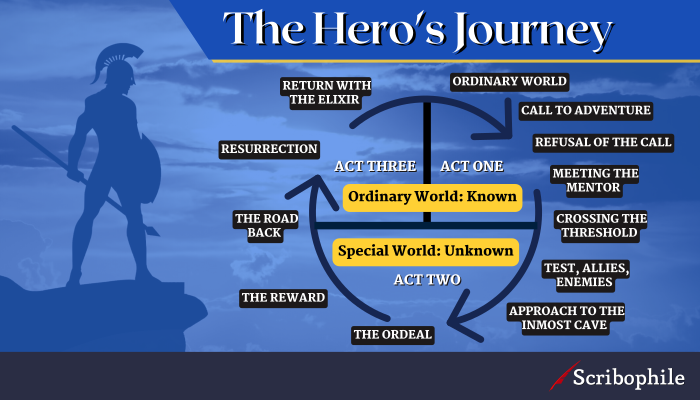
Hero’s Journey diagram: acts, steps, and stages
Below, you can see the way Volger’s Hero’s Journey is broken into twelve story beats across three acts.
Why is the Hero’s Journey so popular?
The structure of the Hero’s Journey appears in many of our most beloved classic stories, and it continues to resonate over time because it explores the concept of personal transformation and growth through both physical and mental trials and tribulations. In some sense, every individual in this mythic structure experiences rites of passage, the search for home and the true authentic self, which is mirrored in a protagonist’s journey of overcoming obstacles while seeking to fulfill a goal.
Additionally, the Hero’s Journey typically includes commonly shared symbols and aspects of the human psyche—the trickster, the mother, the child, etc. These archetypes play a role in creating a story that the reader can recognize from similar dynamics in their own relationships, experiences, and familiar world. Archetypes allow the writer to use these “metaphorical truths”—a playful deceiver, a maternal bond, a person of innocence and purity—to deeply and empathetically connect with the reader through symbolism. That’s why they continue to appear in countless stories all around the world.
Hero’s Journey character archetypes
Character archetypes are literary devices based on a set of qualities that are easy for a reader to identify, empathize with, and understand, as these qualities and traits are common to the human experience.
It should be noted that character archetypes are not stereotypes . While stereotypes are oversimplifications of demographics or personality traits, an archetype is a symbol of a universal type of character that can be recognized either in one’s self or in others in real life.
The following archetypes are commonly used in a Hero’s Journey:
The hero is typically the protagonist or principal point-of-view character within a story. The hero transforms—internally, externally, often both—while on their journey as they experience tests and trials and are aided or hindered by the other archetypes they encounter. In general, the hero must rise to the challenge and at some point make an act of sacrifice for the ultimate greater good. In this way, the Hero’s Journey represents the reader’s own everyday battles and their power to overcome them.
Heroes may be willing or unwilling. Some can be downright unheroic to begin with. Antiheroes are notably flawed characters that must grow significantly before they achieve the status of true hero.
The mentor often possesses divine wisdom or direct experience with the special world, and has faith in the hero. They often give the hero a gift or supernatural aid, which is usually something important for the quest: either a weapon to destroy a monster, or a talisman to enlighten the hero. The mentor may also directly aid the hero or present challenges to them that force internal or external growth. After their meeting, the hero leaves stronger and better prepared for the road ahead.
The herald is the “call to adventure.” They announce the coming of significant change and become the reason the hero ventures out onto a mysterious adventure. The herald is a catalyst that enters the story and makes it impossible for the hero to remain in status quo. Existing in the form of a person or an event, or sometimes just as information, they shift the hero’s balance and change their world.
The Threshold Guardian
This archetype guards the first threshold—the major turning point of the story where the hero must make the true commitment of the journey and embark on their quest to achieve their destiny. Threshold guardians spice up the story by providing obstacles the hero must overcome, but they’re usually not the main antagonist.
The role of the threshold guardian is to help round out the hero along their journey. The threshold guardian will test the hero’s determination and commitment and will drive them forward as the hero enters the next stage of their journey, assisting the development of the hero’s character arc within the plot. The threshold guardian can be a friend who doesn’t believe in the hero’s quest, or a foe that makes the hero question themselves, their desires, or motives in an attempt to deter the hero from their journey. Ultimately, the role of the threshold guardian is to test the hero’s resolve on their quest.
The Shape Shifter
The shape shifter adds dramatic tension to the story and provides the hero with a puzzle to solve. They can seem to be one thing, but in fact be something else. They bring doubt and suspense to the story and test the hero’s ability to discern their path. The shape shifter may be a lover, friend, ally, or enemy that somehow reveals their true self from the hero’s preconceived notion. This often causes the hero internal turmoil, or creates additional challenges and tests to overcome.
The shadow is the “monster under the bed,” and could be repressed feelings, deep trauma, or festering guilt. These all possess the dark energy of the shadow. It is the dark force of the unexpressed, unrealized, rejected, feared aspects of the hero and is often, but not necessarily, represented by the main antagonist or villain.
However, other characters may take the form of the shadow at different stages of the story as “foil characters” that contrast against the hero. They might also represent what could happen if the hero fails to learn, transform, and grow to complete their quest. At times, a hero may even succumb to the shadow, from which they will need to make sacrifices to be redeemed to continue on their overall quest.
The Trickster
The trickster is the jester or fool of the story that not only provides comic relief, but may also act as a commentator as the events of the plot unfold. Tricksters are typically witty, clever, spontaneous, and sometimes even ridiculous. The trickster within a story can bring a light-hearted element to a challenge, or find a clever way to overcome an obstacle.

Hero’s Journey themes and symbols
Alongside character archetypes, there are also archetypes for settings, situations, and symbolic items that can offer meaning to the world within the story or support your story’s theme.
Archetypes of themes, symbols, and situations represent shared patterns of human existence. This familiarity can provide the reader insight into the deeper meaning of a story without the writer needing to explicitly tell them. There are a great number of archetypes and symbols that can be used to reinforce a theme. Some that are common to the Hero’s Journey include:
Situational archetypes
Light vs. dark and the battle of good vs. evil
Death, rebirth, and transformation in the cycle of life
Nature vs. technology, and the evolution of humanity
Rags to riches or vice versa, as commentary on the material world and social status
Wisdom vs. knowledge and innocence vs. experience, in the understanding of intuition and learned experience
Setting archetypes
Gardens may represent the taming of nature, or living in harmony with nature.
Forests may represent reconnection with nature or wildness, or the fear of the unknown.
Cities or small towns may represent humanity at its best and at its worst. A small town may offer comfort and rest, while simultaneously offering judgment; a city may represent danger while simultaneously championing diversity of ideas, beings, and cultures.
Water and fire within a landscape may represent danger, change, purification, and cleansing.
Symbolic items
Items of the past self. These items are generally tokens from home that remind the hero of where they came from and who or what they’re fighting for.
Gifts to the hero. These items may be given to the hero from a mentor, ally, or even a minor character they meet along the way. These items are typically hero talismans, and may or may not be magical, but will aid the hero on their journey.
Found items. These items are typically found along the journey and represent some sort of growth or change within the hero. After all, the hero would never have found the item had they not left their everyday life behind. These items may immediately seem unimportant, but often carry great significance.
Earned rewards. These items are generally earned by overcoming a test or trial, and often represent growth, or give aid in future trials, tests, and conflicts.
The three act structure of the Hero’s Journey
The structure of the Hero’s Journey, including all 12 steps, can be grouped into three stages that encompass each phase of the journey. These acts follow the the external and internal arc of the hero—the beginning, the initiation and transformation, and the return home.
Act One: Departure (Steps 1—5)
The first act introduces the hero within the ordinary world, as they are—original and untransformed. The first act will typically include the first five steps of the Hero’s Journey.
This section allows the writer to set the stage with details that show who the hero is before their metamorphosis—what is the environment of the ordinary world? What’s important to the hero? Why do they first refuse the call, and then, why do they ultimately accept and embark on the journey to meet with the conflict?
This stage introduces the first major plot point of the story, explores the conflict the hero confronts, and provides the opportunity for characterization for the hero and their companions.
The end of the first act generally occurs when the hero has fully committed to the journey and crossed the threshold of the ordinary world—where there is no turning back.
Act Two: Initiation (Steps 6—9)
Once the hero begins their journey, the second act marks the beginning of their true initiation into the unfamiliar world—they have crossed the threshold, and through this choice, have undergone their first transformation.
The second act is generally the longest of the three and includes steps six through nine.
In this act, the hero meets most of the characters that will be pivotal to the plot, including friends, enemies, and allies. It offers the rising action and other minor plot points related to the overarching conflict. The hero will overcome various trials, grow and transform, and navigate subplots—the additional and unforeseen complexity of the conflict.
This act generally ends when the hero has risen to the challenge to overcome the ordeal and receives their reward. At the end of this act, it’s common for the theme and moral of the story to be fully unveiled.
Act Three: Return (Steps 10—12)
The final stage typically includes steps 10—12, generally beginning with the road back—the point in the story where the hero must recommit to the journey and use all of the growth, transformation, gifts and tools acquired along the journey to bring a decisive victory against their final conflict.
From this event, the hero will also be “reborn,” either literally or metaphorically, and then beginning anew as a self-actualized being, equipped with internal knowledge about themselves, external knowledge about the world, and experience.
At the end of the third act, the hero returns home to the ordinary world, bringing back the gifts they earned on their journey. In the final passages, both the hero and their perception of the ordinary world are compared with what they once were.
The 12 steps of the Hero’s Journey
The following guide outlines the 12 steps of the Hero’s Journey and represents a framework for the creation of a Hero’s Journey story template. You don’t necessarily need to follow the explicit cadence of these steps in your own writing, but they should act as checkpoints to the overall story.
We’ll also use JRR Tolkien’s The Hobbit as a literary example for each of these steps. The Hobbit does an exemplary job of following the Hero’s Journey, and it’s also an example of how checkpoints can exist in more than one place in a story, or how they may deviate from the typical 12-step process of the Hero’s Journey.

1. The Ordinary World
This stage in the Hero’s Journey is all about exposition. This introduces the hero’s backstory—who the hero is, where they come from, their worldview, culture, and so on. This offers the reader a chance to relate to the character in their untransformed form.
As the story and character arc develop, the reader is brought along the journey of transformation. By starting at the beginning, a reader has a basic understanding of what drives the hero, so they can understand why the hero makes the choices they do. The ordinary world shows the protagonist in their comfort zone, with their worldview being limited to the perspective of their everyday life.
Characters in the ordinary world may or may not be fully comfortable or satisfied, but they don’t have a point of reference to compare—they have yet to leave the ordinary world to gain the knowledge to do so.
Step One example
The Hobbit begins by introducing Bilbo in the Shire as a respectable and well-to-do member of the community. His ordinary world is utopian and comfortable. Yet, even within a village that is largely uninterested in the concerns of the world outside, the reader is provided a backstory: even though Bilbo buys into the comforts and normalcy of the Shire, he still yearns for adventure—something his neighbors frown upon. This ordinary world of the Shire is disrupted with the introduction of Gandalf—the “mentor”—who is somewhat uncomfortably invited to tea.
2. Call to Adventure
The call to adventure in the Hero’s Journey structure is the initial internal conflict that the protagonist hero faces, that drives them to the true conflict that they must overcome by the end of their journey.
The call occurs within the known world of the character. Here the writer can build on the characterization of the protagonist by detailing how they respond to the initial call. Are they hesitant, eager, excited, refusing, or willing to take a risk?
Step Two example
Bilbo’s call to adventure takes place at tea as the dwarves leisurely enter his home, followed by Gandalf, who identifies Bilbo as the group’s missing element—the burglar, and the lucky 14th member.
Bilbo and his ordinary world are emphasized by his discomfort with his rambunctious and careless guests. Yet as the dwarves sing stories of old adventures, caverns, and lineages, which introduce and foreshadow the conflict to come, a yearning for adventure is stirred. Though he still clings to his ordinary world and his life in the Shire, he’s conflicted. Should he leave the shire and experience the world, or stay in his comfortable home? Bilbo continues to refuse the call, but with mixed feelings.

3. Refusal of the Call
The refusal of the call in the Hero’s Journey showcases a “clinging” to one’s original self or world view. The initial refusal of the call represents a fear of change, as well as a resistance to the internal transformation that will occur after the adventure has begun.
The refusal reveals the risks that the protagonist faces if they were to answer the call, and shows what they’ll leave behind in the ordinary world once they accept.
The refusal of the call creates tension in the story, and should show the personal reasons why the hero is refusing—inner conflict, fear of change, hesitation, insecurity, etc. This helps make their character clearer for the reader.
These are all emotions a reader can relate to, and in presenting them through the hero, the writer deepens the reader’s relationship with them and helps the reader sympathize with the hero’s internal plight as they take the first step of transformation.
Step Three example
Bilbo refuses the call in his first encounter with Gandalf, and in his reaction to the dwarves during tea. Even though Bilbo’s “Tookish” tendencies make him yearn for adventure, he goes to bed that night still refusing the call. The next morning, as Bilbo awakes to an empty and almost fully clean hobbit home, he feels a slight disappointment for not joining the party, but quickly soothes his concerns by enjoying the comfort of his home—i.e. the ordinary world. Bilbo explores his hesitation to disembark from the ordinary world, questioning why a hobbit would become mixed up in the adventures of others, and choosing not to meet the dwarves at the designated location.
4. Meeting the Mentor
Meeting the mentor in the Hero’s Journey is the stage that provides the hero protagonist with a guide, relationship, and/or informational asset that has experience outside the ordinary world. The mentor offers confidence, advice, wisdom, training, insight, tools, items, or gifts of supernatural wonder that the hero will use along the journey and in overcoming the ultimate conflict.
The mentor often represents someone who has attempted to overcome, or actually has overcome, an obstacle, and encourages the hero to pursue their calling, regardless of the hero’s weaknesses or insecurities. The mentor may also explicitly point out the hero’s weaknesses, forcing them to reckon with and accept them, which is the first step to their personal transformation.
Note that not all mentors need to be a character . They can also be objects or knowledge that has been instilled in the hero somehow—cultural ethics, spiritual guidance, training of a particular skill, a map, book, diary, or object that illuminates the path forward, etc. In essence, the mentor character or object has a role in offering the protagonist outside help and guidance along the Hero’s Journey, and plays a key role in the protagonist’s transition from normalcy to heroism.
The mentor figure also offers the writer the opportunity to incorporate new information by expanding upon the story, plot, or backstory in unique ways. They do this by giving the hero information that would otherwise be difficult for the writer to convey naturally.
The mentor may accompany the hero throughout most of the story, or they may only periodically be included to facilitate changes and transformation within them.
Step Four example
The mentor, Gandalf, is introduced almost immediately. Gandalf is shown to be the mentor, firstly through his arrival from—and wisdom of—the outside world; and secondly, through his selection of Bilbo for the dwarven party by identifying the unique characteristics Bilbo has that are essential to overcoming the challenges in the journey. Gandalf doesn’t accompany Bilbo and the company through all of the trials and tribulations of the plot, but he does play a key role in offering guidance and assistance, and saves the group in times of dire peril.

5. Crossing the Threshold
As the hero crosses the first threshold, they begin their personal quest toward self-transformation. Crossing the threshold means that the character has committed to the journey, and has stepped outside of the ordinary world in the pursuit of their goal. This typically marks the conclusion of the first act.
The threshold lies between the ordinary world and the special world, and marks the point of the story where the hero fully commits to the road ahead. It’s a crucial stage in the Hero’s Journey, as the hero wouldn’t be able to grow and transform by staying in the ordinary world where they’re comfortable and their world view can’t change.
The threshold isn’t necessarily a specific place within the world of the story, though a place can symbolize the threshold—for example a border, gateway, or crossroads that separate what is safe and “known” from what is potentially dangerous. It can also be a moment or experience that causes the hero to recognize that the comforts and routine of their world no longer apply—like the loss of someone or something close to the hero, for example. The purpose of the threshold is to take the hero out of their element and force them, and the reader, to adapt from the known to the unknown.
This moment is crucial to the story’s tension. It marks the first true shift in the character arc and the moment the adventure has truly begun. The threshold commonly forces the hero into a situation where there’s no turning back. This is sometimes called the initiation stage or the departure stage.
Step Five example
The threshold moment in The Hobbit occurs when the party experiences true danger as a group for the first time. Bilbo, voted as scout by the party and eager to prove his burglar abilities, sneaks upon a lone fire in the forest where he finds three large trolls. Rather than turn back empty-handed—as he initially wants to—Bilbo chooses to prove himself, plucking up the courage to pickpocket the trolls—but is caught in the process. The dwarves are also captured and fortunately, Gandalf, the mentor, comes to save the party.
Bilbo’s character arc is solidified in this threshold moment. He experiences his first transformation when he casts aside fear and seeks to prove himself as a burglar, and as an official member of the party. This moment also provides further characterization of the party as a whole, proving the loyalty of the group in seeking out their captured member.
Gandalf’s position as the mentor is also firmly established as he returns to ultimately save all of the members of the party from being eaten by trolls. The chapter ends with Bilbo taking ownership of his first hero talisman—the sword that will accompany him through the rest of the adventure.
6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
Once the hero has crossed the threshold, they must now encounter tests of courage, make allies, and inevitably confront enemies. All these elements force the hero to learn the new ways of the special world and how it differs from the hero’s ordinary world—i.e. how the rules have changed, the conditions of the special world vs. the ordinary world, and the various beings and places within it.
All these elements spark stages of transformation within the hero—learning who they can trust and who they can’t, learning new skills, seeking training from the mentor, and overcoming challenges that force and drive them to grow and transform.
The hero may both succeed and fail at various points of this stage, which will test their commitment to the journey. The writer can create tension by making it clear that the hero may or may not succeed at the critical moment of crisis. These crises can be external or internal.
External conflicts are issues that the character must face and overcome within the plot—e.g. the enemy has a sword drawn and the hero must fight to survive.
Internal conflicts occur inside the hero. For example, the hero has reached safety, but their ally is in peril; will they step outside their comfort zone and rise to the occasion and save their friend? Or will they return home to their old life and the safety of the ordinary world?
Tests are conflicts and threats that the hero must face before they reach the true conflict, or ordeal, of the story. These tests set the stage and prime the hero to meet and achieve the ultimate goal. They provide the writer the opportunity to further the character development of the hero through their actions, inactions, and reactions to what they encounter. The various challenges they face will teach them valuable lessons, as well as keep the story compelling and the reader engaged.
Allies represent the characters that offer support to the protagonist along the journey. Some allies may be introduced from the beginning, while others may be gained along the journey. Secondary characters and allies provide additional nuance for the hero, through interactions, events, and relationships that further show who the hero is at heart, what they believe in, and what they’re willing to fight for. The role of the allies is to bring hope, inspiration, and further drive the hero to do what needs to be done.
Enemies represent a foil to the allies. While allies bring hope and inspiration, enemies will provide challenges, conflicts, tests, and challenges. Both allies and enemies may instigate transformative growth, but enemies do so in a way that fosters conflict and struggle.
Characterization of enemies can also enhance the development of the hero through how they interact and the lessons learned through those interactions. Is the hero easily duped, forgiving, empathetic, merciful? Do they hold a grudge and seek revenge? Who is the hero now that they have been harmed, faced an enemy, and lost pieces of their innocent worldview? To answer that, the hero is still transforming and gestating with every lesson, test, and enemy faced along the way.
Step Six example
As the plot of The Hobbit carries on, Bilbo encounters many tests, allies, and enemies that all drive complexity in the story. A few examples include:
The first major obstacle that Bilbo faces occurs within the dark and damp cave hidden in the goblin town. All alone, Bilbo must pluck up the wit and courage to outriddle a creature named Gollum. In doing so, Bilbo discovers the secret power of a golden ring (another hero talisman) that will aid him and the party through the rest of the journey.
The elves encountered after Bilbo “crosses the threshold” are presented as allies in the story. The hero receives gifts of food, a safe place to rest, and insight and guidance that allows the party to continue on their journey. While the party doesn’t dwell long with the elves, the elves also provide further character development for the party at large: the serious dwarf personalities are juxtaposed against the playful elvish ones, and the elves offer valuable historical insight with backstory to the weapons the party gathered from the troll encounter.
Goblins are a recurring enemy within the story that the hero and party must continue to face, fight, and run from. The goblins present consistent challenges that force Bilbo to face fear and learn and adapt, not only to survive but to save his friends.

7. Approach to the Inmost Cave
The approach to the inmost cave of the Hero’s Journey is the tense quiet before the storm; it’s the part of the story right before the hero faces their greatest fear, and it can be positioned in a few different ways. By now, the hero has overcome obstacles, setbacks, and tests, gained and lost allies and enemies, and has transformed in some way from the original protagonist first introduced in the ordinary world.
The moment when the hero approaches the inmost cave can be a moment of reflection, reorganization, and rekindling of morale. It presents an opportunity for the main characters of the story to come together in a moment of empathy for losses along the journey; a moment of planning and plotting next steps; an opportunity for the mentor to teach a final lesson to the hero; or a moment for the hero to sit quietly and reflect upon surmounting the challenge they have been journeying toward for the length of their adventure.
The “cave” may or may not be a physical place where the ultimate ordeal and conflict will occur. The approach represents the momentary period where the hero assumes their final preparation for the overall challenge that must be overcome. It’s a time for the hero and their allies, as well as the reader, to pause and reflect on the events of the story that have already occurred, and to consider the internal and external growth and transformation of the hero.
Having gained physical and/or emotional strength and fortitude through their trials and tests, learned more rules about the special world, found and lost allies and friends, is the hero prepared to face danger and their ultimate foe? Reflection, tension, and anticipation are the key elements of crafting the approach to the cave.
Step Seven example
The approach to the cave in The Hobbit occurs as the party enters the tunnel of the Lonely Mountain. The tunnel is the access point to the ultimate goal—Thorin’s familial treasure, as well as the ultimate test—the formidable dragon Smaug. During this part of the story, the party must hide, plot, and plan their approach to the final conflict. It’s at this time that Bilbo realizes he must go alone to scout out and face the dragon.
8. The Ordeal
The ordeal is the foreshadowed conflict that the hero must face, and represents the midpoint of the story. While the ordeal is the ultimate conflict that the hero knows they must overcome, it’s a false climax to the complete story—there’s still much ground to cover in the journey, and the hero will still be tested after completing this, the greatest challenge. In writing the ordeal phase of the Hero’s Journey, the writer should craft this as if it actually were the climax to the tale, even though it isn’t.
The first act, and the beginning of the second act, have built up to the ordeal with characterization and the transformation of the hero through their overcoming tests and trials. This growth—both internal and external—has all occurred to set the hero up to handle this major ordeal.
As this stage commences, the hero is typically faced with fresh challenges to make the ordeal even more difficult than they previously conceived. This may include additional setbacks for the hero, the hero’s realization that they were misinformed about the gravity of the situation, or additional conflicts that make the ordeal seem insurmountable.
These setbacks cause the hero to confront their greatest fears and build tension for both the hero and the reader, as they both question if the hero will ultimately succeed or fail. In an epic fantasy tale, this may mean a life-or-death moment for the hero, or experiencing death through the loss of an important ally or the mentor. In a romance, it may be the moment of crisis where a relationship ends or a partner reveals their dark side or true self, causing the hero great strife.
This is the rock-bottom moment for the hero, where they lose hope, courage, and faith. At this point, even though the hero has already crossed the threshold, this part of the story shows how the hero has changed in such a way that they can never return to their original self: even if they return to the ordinary world, they’ll never be the same; their perception of the world has been modified forever.
Choosing to endure against all odds and costs to face the ordeal represents the loss of the hero’s original self from the ordinary world, and a huge internal transformation occurs within the hero as they must rise and continue forth to complete their journey and do what they set out to do from the beginning.
The ordeal may also be positioned as an introduction to the greater villain through a trial with a shadow villain, where the hero realizes that the greatest conflict is unveiled as something else, still yet to come. In these instances, the hero may fail, or barely succeed, but must learn a crucial lesson and be metaphorically resurrected through their failure to rise again and overcome the greater challenge.
Step Eight example
Bilbo must now face his ultimate challenge: burgle the treasure from the dragon. This is the challenge that was set forth from the beginning, as it’s his purpose as the party’s 14th member, the burglar, anointed by Gandalf, the mentor. Additional conflicts arise as Bilbo realizes that he must face the dragon alone, and in doing so, must rely on all of the skills and gifts in the form of talismans and tokens he has gained throughout the adventure.
During the ordeal, Bilbo uses the courage he has gained by surmounting the story’s previous trials; he’s bolstered by his loyalty to the group and relies upon the skills and tools he has earned in previous trials. Much as he outwitted Gollum in the cave, Bilbo now uses his wit as well as his magical ring to defeat Smaug in a game of riddles, which ultimately leads Smaug out of the lair so that Bilbo can complete what he was set out to do—steal the treasure.

The reward of the Hero’s Journey is a moment of triumph, celebration, or change as the hero achieves their first major victory. This is a moment of reflection for both the reader and the hero, to take a breath to contemplate and acknowledge the growth, development, and transformation that has occurred so far.
The reward is the boon that the hero learns, is granted, or steals, that will be crucial to facing the true climax of the story that is yet to come. The reward may be a physical object, special knowledge, or reconciliation of some sort, but it’s always a thing that allows for some form of celebration or replenishment and provides the drive to succeed before the journey continues.
Note that the reward may not always be overtly positive—it may also be a double-edged sword that could harm them physically or spiritually. This type of reward typically triggers yet another internal transformation within the hero, one that grants them the knowledge and personal drive to complete the journey and face their remaining challenges.
From the reward, the hero is no longer externally driven to complete the journey, but has evolved to take on the onus of doing so.
Examples of rewards may include:
A weapon, elixir, or object that will be necessary to complete the quest.
Special knowledge, or a personal transformation to use against a foe.
An eye-opening experience that provides deep insight and fundamentally changes the hero and their position within the story and world.
Reconciliation with another character, or with themselves.
No matter what the reward is, the hero should experience some emotional or spiritual revelation and a semblance of inner peace or personal resolve to continue the journey. Even if the reward is not overtly positive, the hero and the reader deserve a moment of celebration for facing the great challenge they set out to overcome.
Step Nine example
Bilbo defeats the dragon at a battle of wits and riddles, and now receives his reward. He keeps the gifts he has earned, both the dagger and the gold ring. He is also granted his slice of the treasure, and the Lonely Mountain is returned to Thorin. The party at large is rewarded for completing the quest and challenge they set out to do.
However, Tolkien writes the reward to be more complex than it first appears. The party remains trapped and hungry within the Mountain as events unfold outside of it. Laketown has been attacked by Smaug, and the defenders will want compensation for the damage to their homes and for their having to kill the dragon. Bilbo discovers, and then hides, the Arkenstone (a symbolic double edged reward) to protect it from Thorin’s selfishness and greed.

10. The Road Back
The road back in the Hero’s Journey is the beginning of the third act, and represents a turning point within the story. The hero must recommit to the journey, alongside the new stakes and challenges that have arisen from the completion of the original goal.
The road back presents roadblocks—new and unforeseen challenges to the hero that they must now face on their journey back to the ordinary world. The trials aren’t over yet, and the stakes are raised just enough to keep the story compelling before the final and ultimate conflict—the hero’s resurrection—is revealed in the middle of the third act.
The hero has overcome their greatest challenge in the Ordeal and they aren’t the same person they were when they started. This stage of the story often sees the hero making a choice, or reflecting on their transformed state compared to their state at the start of the journey.
The writer’s purpose in the third act is not to eclipse the upcoming and final conflict, but to up the stakes, show the true risk of the final climax, and to reflect on what it will take for the hero to ultimately prevail. The road back should offer a glimmer of hope—the light at the end of the tunnel—and should let the reader know the dramatic finale is about to arrive.
Step Ten example
What was once a journey to steal treasure and slay a dragon has developed new complications. Our hero, Bilbo, must now use all of the powers granted in his personal transformation, as well as the gifts and rewards he earned on the quest, to complete the final stages of the journey.
This is the crisis moment of The Hobbit ; the armies of Laketown are prepared for battle to claim their reward for killing Smaug; the fearless leader of their party, Thorin, has lost reason and succumbed to greed; and Bilbo makes a crucial choice based his personal growth: he gives the Arkenstone to the king as a bargaining chip for peace. Bilbo also briefly reconnects with the mentor, Gandalf, who warns him of the unpleasant times ahead, but comforts Bilbo by saying that things may yet turn out for the best. Bilbo then loyally returns to his friends, the party of dwarves, to stand alongside them in the final battle.
11. Resurrection
The resurrection stage of the Hero’s Journey is the final climax of the story, and the heart of the third act. By now the hero has experienced internal and external transformation and a loss of innocence, coming out with newfound knowledge. They’re fully rooted in the special world, know its rules, and have made choices that underline this new understanding.
The hero must now overcome the final crisis of their external quest. In an epic fantasy tale, this may be the last battle of light versus darkness, good versus evil, a cumulation of fabulous forces. In a thriller, the hero might ultimately face their own morality as they approach the killer. In a drama or romance, the final and pivotal encounter in a relationship occurs and the hero puts their morality ahead of their immediate desires.
The stakes are the highest they’ve ever been, and the hero must often choose to make a sacrifice. The sacrifice may occur as a metaphoric or symbolic death of the self in some way; letting go of a relationship, title, or mental/emotional image of the self that a hero once used as a critical aspect of their identity, or perhaps even a metaphoric physical death—getting knocked out or incapacitated, losing a limb, etc.
Through whatever the great sacrifice is, be it loss or a metaphoric death, the hero will experience a form of resurrection, purification, or internal cleansing that is their final internal transformation.
In this stage, the hero’s character arc comes to an end, and balance is restored to the world. The theme of the story is fully fleshed out and the hero, having reached some form of self-actualization, is forever changed. Both the reader and the hero experience catharsis—the relief, insight, peace, closure, and purging of fear that had once held the hero back from their final transformation.
Step Eleven example
All the armies have gathered, and the final battle takes place. Just before the battle commences, Bilbo tells Thorin that it was he who gave the Arkenstone to the city of men and offers to sacrifice his reward of gold for taking the stone. Gandalf, the mentor, arrives, standing beside Bilbo and his decision. Bilbo is shunned by Thorin and is asked to leave the party for his betrayal.
Bilbo experiences a symbolic death when he’s knocked out by a stone. Upon awakening, Bilbo is brought to a dying Thorin, who forgives him of his betrayal, and acknowledges that Bilbo’s actions were truly the right thing to do. The theme of the story is fully unveiled: that bravery and courage comes in all sizes and forms, and that greed and gold are less worthy than a life rich in experiences and relationships.

12. Return with the Elixir
The elixir in the Hero’s Journey is the final reward the hero brings with them on their return, bridging their two worlds. It’s a reward hard earned through the various relationships, tests, and growth the hero has experienced along their journey. The “elixir” can be a magical potion, treasure, or object, but it can also be intangible—love, wisdom, knowledge, or experience.
The return is key to the circular nature of the Hero’s Journey. It offers a resolution to both the reader and the hero, and a comparison of their growth from when the journey began.
Without the return, the story would have a linear nature, a beginning and an end. In bringing the self-actualized hero home to the ordinary world, the character arc is completed, and the changes they’ve undergone through the journey are solidified. They’ve overcome the unknown, and though they’re returning home, they can no longer resume their old life because of their new insight and experiences.
Step Twelve example
The small yet mighty hero Bilbo is accompanied on his journey home by his mentor Gandalf, as well as the allies he gathered along his journey. He returns with many rewards—his dagger, his golden ring, and his 1/14th split of the treasure—yet his greatest rewards are his experience and the friends he has made along the way. Upon entering the Shire Bilbo sings a song of adventure, and the mentor Gandalf remarks, “My dear Bilbo! Something is the matter with you, you are not the hobbit you were.”
The final pages of The Hobbit explore Bilbo’s new self in the Shire, and how the community now sees him as a changed hobbit—no longer quite as respectable as he once was, with odd guests who visit from time to time. Bilbo also composes his story “There and Back Again,” a tale of his experiences, underlining his greatest reward—stepping outside of the Shire and into the unknown, then returning home, a changed hobbit.
Books that follow the Hero’s Journey
One of the best ways to become familiar with the plot structure of the Hero’s Journey is to read stories and books that successfully use it to tell a powerful tale. Maybe they’ll inspire you to use the hero’s journey in your own writing!
The Lord of the Rings trilogy by J. R. R. Tolkien.
The Harry Potter series by J. K. Rowling.
The Earthsea series by Ursula K. Le Guin.
The Odyssey by Homer.
Siddhartha by Herman Hesse.
Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen.
Writing tips for the Hero’s Journey
Writing a Hero’s Journey story often requires planning beforehand to organize the plot, structure, and events of the story. Here are some tips to use the hero’s journey archetype in a story:
Use a template or note cards to organize and store your ideas. This can assist in ensuring that you tie up any loose ends in the plot, and that the cadence of your story is already outlined before you begin writing.
Use word count goals for writing different sections of your story. This can help you keep pace while you plan and write the first draft. You can always revise, edit, and add in detail at later stages of development, but getting the ideas written without bogging them down with details can assist in preparing your outline, and may perhaps provide additional inspiration and guidance along the way.
Lean into creativity and be flexible with the 12 steps. They don’t need to occur in the exact order we’ve listed above, but that ordering can offer great checkpoint moments for your story.
Invest in characterization and ensure that your main character is balanced with credible strengths and weaknesses. A perfect, pure hero has no room to grow. A one-dimensional villain who relies on the trope of “pure evil” without any motivations for their actions is boring and predictable.
Ensure tension and urgency is woven into the story. An epic tale to the grocery store for baby formula may still be fraught with danger, and the price of failure is a hungry child. Without urgency, tension, and risk, a Hero’s Journey will fall flat.
Be hard on your characters. Give them deep conflicts that truly test their nature, and their mental, physical, and spiritual selves. An easy journey isn’t a memorable one.
Have a balance of scenes that play on both positive and negative emotions and outcomes for the hero to create a compelling plot line that continues to engage your reader. A story that’s relentlessly positive doesn’t provide a pathway for the hero to transform. Likewise, a story that’s nothing but doom, strife, and turmoil, without a light at the end of the tunnel or an opportunity for growth, can make a story feel stagnant and unengaging.
Reward your characters and your reader. Personal transformation and the road to the authentic self may be grueling, but there’s peace or joy at the end of the tunnel. Even if your character doesn’t fully saved the world, they—and the reader—should be rewarded with catharsis, a new perspective, or personal insight at the end of the tale.
Hero’s Journey templates
Download these free templates to help you plan out your Hero’s Journey:
Download the Hero’s Journey template template (docx) Download the Hero’s Journey template template (pdf)
Prompts and practices to help you write your own Hero’s Journey
Use the downloadable template listed below for the following exercises:
Read a book or watch a movie that follows the Hero’s Journey. Use the template to fill in when each step occurs or is completed. Make note of themes and symbols, character arcs, the main plot, and the subplots that drive complexity in the story.
When writing, use a timer set to 2—5 minutes per section to facilitate bursts of creativity. Brainstorm ideas for cadence, plot, and characters within the story. The outline you create can always be modified, but the timer ensures you can get ideas on paper without a commitment; you’re simply jotting down ideas as quickly as you can.
Use the downloadable template above to generate outlines based on the following prompts.
A woman’s estranged mother has died. A friend of the mother arrives at the woman’s home to tell her that her mother has left all her belongings to her daughter, and hands her a letter. The letter details the mother’s life, and the daughter must visit certain places and people to find her mother’s house and all the belongings in it—learning more about her mother’s life, and herself, along the way.
The last tree on earth has fallen, and technology can no longer sustain human life on Earth. An engineer, having long ago received alien radio signals from a tower in their backyard, has dedicated their life to building a spaceship in their garage. The time has come to launch, and the engineer must select a group of allies to bring with them to the stars, on a search for a new life, a new home, and “the others” out there in the universe.
A detective is given a new case: to find a much-talked-about murderer. The twist is, the murderer has sent a letter to the detective agency, quietly outing a homicidal politician who is up for re-election and is a major financial contributor to the police. In the letter, the murderer states that if the politician doesn’t come clean about their crimes, the murderer will kill the politician on the night of the election. The detective must solve the case before the election, and come to terms with their own feelings of justice and morality.
Get feedback on your writing today!
Scribophile is a community of hundreds of thousands of writers from all over the world. Meet beta readers, get feedback on your writing, and become a better writer!
Join now for free

Related articles

What is the Mentor Archetype? Definition and Examples

What Is a Dramatic Question? (And Why You Need One for Your Story)

Myth in Literature: Definition, and Using Myths to Explore New Ideas
What is Plot? Definition, Examples & 10+ Types of Story Plots

What is Suspense? Definition & Examples in Literature

What is a Static Character? Definition and Examples
The Sitting Bee
Short Story Reviews
The Journey by Barrie Hough
In The Journey by Barrie Hough we have the theme of friendship, fear, connection, helplessness, control, equality and perseverance. Narrated in the third person by an unnamed narrator it becomes clear to the reader after reading the story that Hough may be exploring theme of friendship. Thembi and Johan have a very special connection with one another despite the fact that Johan can at times be difficult to understand because of his stutter. Despite this Thembi remains by Johan’s side as a friend would do and challenges Johan to better himself. This may be important as by challenging himself Johan manages to reach his goal of speaking without stuttering. Though at first he is annoyed with Thembi later on in the story it becomes clear that all Thembi’s challenges have been worth it. Johan also feels connected to Thembi because like him she is an outsider and may not necessarily be accepted by the other students in the school. Though Thembi does appear to be able to stand up for herself and has the skills to verbally defend herself. She is after all a member of the school debating society.
By not going into too much detail about the other students in the school Hough also manages to keep the reader focused on the fledgling relationship between Thembi and Johan and the pressure that Johan feels he is under in order to please Thembi. At one stage in the story Thembi gets angry with Johan and considers his demands to be unreasonable. When the reality is Thembi is only trying to help Johan who unfortunately feels helpless when it comes to his speech. However it is noticeable that Johan does not give up. Instead he perseveres and shows resilience. Beating the challenge that has been put before him by Thembi. This too could be significant as Hough may be suggesting that others who may feel stifled by life can succeed if they only try that little bit harder and persevere. Like Johan they too can overcome the obstacles that life puts in front of them regardless of how difficult they might feel the task at hand is. In reality everybody should have hope in their life for it is hope for something better that helps at times to pull a person into a new and brighter day.
What is also interesting about Johan’s fears is the fact that he knows that should he not talk to Thembi without stuttering. He will not have the opportunity to kiss her. It being clear to the reader that Johan likes Thembi as one would like a girlfriend. In many ways the story could be seen as a story of a young teenage boy overcoming adversity and getting the girl he loves. Something which is not necessarily a reality for most people. Thembi has everything that Johan needs and he knows this. He just needs to be patient and to be able to control his speech. Without losing his temper because he finds the task at hand so difficult. Though Johan may not know it. Thembi only has Johan’s best interests at heart. She wants him to succeed as she too knows what it is like to be on the outside of society. By challenging Johan Thembi is also making sure that Johan advances in life and that one obstacle at least has been cleared. Having a speech impediment can leave a person feeling insecure within themselves because of society’s cruelties. Whether society means to be cruel is not important. What is important is that someone like Johan can lose all confidence if they are ridiculed by their peers.
The end of the story is also interesting as the reader senses how happy both Thembi and Johan are. Thembi’s faith in Johan has been rewarded and Johan has manged to control his speech. Hough possibly suggesting that things in the future will be good for both Thembi and Johan. Johan will get to kiss Thembi for the first time. Something which will further connect both Thembi and Johan. If anything Johan, thanks to Thembi, can hold his head high and be full of confidence. No longer will he be ostracized by his peers and if he is he has the confidence to now stand up for himself should the need arise. By challenging Johan. Thembi has managed to give him back control over his life. It is as though Johan is starting life all over again but this time he is everybody’s equal. He does not have to isolate himself in fear of being ridiculed by his peers. Just as there is a new South Africa. There is a new Johan. Johan gets the girl, gets control back of his life and gets to see the dawning of a new and equal South Africa.
- The Apprentice by Odun Balogun
- Next Door by Tobias Wolff
- The Little Match Girl by Hans Christian Andersen
- First Confession by Frank O’Connor
22 comments
Thembi’ home language
What is the setting of the story
School and Johan’s home
Mid 1990’s on May during mandelas inauguration
At school after the first democratic elecrions
They are at school
How did johan and thembi become friends
Ok so Johan made Thembi feel welcome when everyone was discriminating her
Thanks Freddy.
Can l please have the the elements of the story
What are the genres and types of a short story is this
What does thembi mean when he says life’s not a musical?
What illustrate that barry hough is using a third person limited narrator to tell the story
A third person narrator uses he/she when referring to characters. A limited narrator does not know more than the reader nor do they know everything.
What ‘quiet language’ that Johan can read
Directions from Thembi’s house to Johan’s house
Okay what is the plot main event of the story please get back to me sap
I think you made a mistake or maybe can you please explain this line for me
“At one stage in the story Thembi gets angry with Thembi and considers her demands to be unreasonable”
Thanks Kholofelo. You’re right.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments via e-mail
Currently you have JavaScript disabled. In order to post comments, please make sure JavaScript and Cookies are enabled, and reload the page. Click here for instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your browser.
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Life Journey
The Journey Of Life: Life Is A Journey
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Inspiration

Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
- Essay On Train Journey
Train Journey Essay
500+ words essay on train journey.
A journey by train is the most common thing in today’s modern world. Since all of us need to travel far distances, we need transportation for that. Trains come out to be the best and most economical option among all transportation facilities available. The journey by train makes us feel pleasure and fills us with excitement. All of us must have gone on a vacation with family by taking a journey by train. In this essay on a train journey, I am going to share my first time travelling experience by train. You can also check out the list of CBSE Essays . Practise writing “a Train Journeyssay” to boost your writing skills.
A Journey by Train Essay
A train is not just a transport vehicle. It connects people; it provides access to jobs, communities and goods. It delivers vital social services. Trains are the backbone of the transportation system, which help in creating a sustainable economy. We have often read books and magazines that mention the beautiful experience of train journeys. By reading them, our heart fills with adventure, thrill and happiness.
My First Experience of Train Journey
A journey by train always excites me. It is fun to travel by train. I have been travelling by train since my childhood. The first time I experienced the train journey was when I was studying in Class 6. During my summer vacation, my parents planned to visit Nainital. My father had already booked the train tickets for AC3 Class two months before.
We were staying in Lucknow, and from there, our train journey began. We reached Lucknow Charbagh Station one hour before the train departure time. Lucknow station was 7-8 km far away from our home. So, my father booked a taxi, and we reached Lucknow station. After reaching the station, my father checked for the train timing and platform number on which the train had to arrive. The train was on time, and we had to go to platform number 5. We did not have much luggage, so we did not take coolies. My father took 2 suitcases, and my mother took one bag. Before going to platform number 5, we purchased some chips, water bottles and biscuits.
The station was crowded with people. There were tea stalls, food counters, coolies and many other passengers like us waiting for their train. I could hear a lot of noise in the station, which was due to train announcements, coolies and tea sellers. Hearing the noise and looking at the trains as 1 hour passed, I didn’t get to know. Now, it was time for our train to arrive. We comfortably entered the train and reached our seats. My seat was in the lower berth, so I was happy that I could see all the views from my window seat.
The train gave a hooter sound, and then it started. I was so excited and filled with curiosity and enthusiasm. As the train has taken up speed, I feel as if trees and homes are moving along with us. I asked my mother, “Is it really happening?” Then, my mother replied, “Trees and homes are not moving. As we are sitting in the train and the train is moving at a fast speed, that is why things around us seem to be moving along with us. In reality, we are moving, and other things are static in their respective places.” Then, I understood the concept. For some time, I was peacefully enjoying the scene from my window.
On the train, my experience was very joyful. In our front seat, there was also one family. We played the ludo game, name the places and antakshari. In between the games, we also had snacks and lunch. The train had stopped at the major station, and people were getting down and sitting up on the train. As the train stops at any station, many of the food sellers enter the train to sell their items and get down when the train starts running. This process repeats at every station where the train stops.
Finally, after 10 hours of travelling, it was time for the Kathgodam station to arrive, where we had to get down. Before the Kathgodam station, I could see the mountains and greenery from the window seat. At that time, I got to know that we had come to Hill station to enjoy our summer vacation. We got down in Kathgodam station, and from there, we booked a taxi for Nainital. After 2 hours of road journey, we reached Nainital.
Nainital is such a beautiful place. It is surrounded by mountains all around. From the mountains, a lake called “Nani Lake” was flowing, which increased the beauty of Nainital. The temperature of the Nainital was so pleasant that we felt relieved from summer and heat. We did many activities like boat riding and mountain climbing. We have visited many sites and also done a lot of shopping. After spending 3 days in Nainital, we again took a train from Kathgodam station to Lucknow and came back home. The experience was awesome for me. I will never forget this enjoyable journey by train.
Students must have found this essay on “Train Journey” useful for improving their essay writing skills. They can get the study material and the latest update on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams, at BYJU’S.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling
- Admission help
- Custom essay help
- Writing assignment
- College essay
- Coursework writing
- Custom writing
- Dissertation writing
- Homework help
- Personal statement
- Proofreading
- School papers
- Speech writing
- Thesis help
- Lab report writing
- Ghostwriting
- Book report
- Book review
- Movie review
- Testimonials
- 1-929-999-5210 Copied!
- Write my essay
Personal Essay on Life Is a Journey
Life is a journey essay.
All people have the same journey to take – their life . As well as in the other journeys, there may be some inconveniences, disappointments and joys, and a lot depends on how we plan this particular journey and what attitude we develop towards it. I will try to show my vision of the best way to go through this path with as much joy as possible and with minimum of harm.

When you work on the strong foundation and achieve certain progress in it, you can work on all the other aspects. In life there are lots of them, and you should always be ready that life involves a lot of unexpected events and you have to be ready to perceive them in the right way. If you learn how to…

Journey of the Magi Summary & Analysis by T. S. Eliot
- Line-by-Line Explanation & Analysis
- Poetic Devices
- Vocabulary & References
- Form, Meter, & Rhyme Scheme
- Line-by-Line Explanations

"Journey of the Magi" is a poem by T.S. Eliot, first published in 1927 in a series of pamphlets related to Christmas. The poem was written shortly after Eliot's conversion to the Anglican faith. Accordingly, though the poem is an allegorical dramatic monologue that inhabits the voice of one the magi (the three wise men who visit the infant Jesus), it's also generally considered to be a deeply personal poem. Indeed, the magus in the poem shares Eliot's view that spiritual transformation is not a comfort, but an ongoing process—an arduous journey seemingly without end. The magus's view on the birth of Jesus—and the shift from the old ways to Christianity—is complex and ambivalent.
- Read the full text of “Journey of the Magi”

The Full Text of “Journey of the Magi”
“journey of the magi” summary, “journey of the magi” themes.

Spiritual Death and Rebirth
Line-by-line explanation & analysis of “journey of the magi”.
'A cold coming ... ... dead of winter.'

And the camels ... ... girls bringing sherbet.
Lines 11-16
Then the camel ... ... had of it.
Lines 17-20
At the end ... ... was all folly.
Lines 21-25
Then at dawn ... ... in the meadow.
Lines 26-31
Then we came ... ... might say) satisfactory.
Lines 32-36
All this was ... ... Birth or Death?
Lines 36-39
There was a ... ... Death, our death.
Lines 40-43
We returned to ... ... of another death.
“Journey of the Magi” Symbols

Biblical Imagery
- Line 23: “running stream”
- Line 24: “three trees on the low sky”
- Line 25: “an old white horse”
- Line 26: “vine-leaves”
- Line 27: “pieces of silver”
- Line 28: “empty wine-skins”
“Journey of the Magi” Poetic Devices & Figurative Language
Alliteration.
- Line 1: “cold coming”
- Line 4: “ways,” “deep,” “weather”
- Line 5: “dead,” “winter”
- Line 9: “summer,” “slopes”
- Line 10: “silken”
- Line 11: “camel,” “cursing”
- Line 12: “wanting,” “women”
- Line 18: “Sleeping,” “snatches”
- Line 19: “singing,” “saying”
- Line 20: “That this”
- Line 21: “dawn,” “down,” “valley”
- Line 22: “snow,” “smelling,” “vegetation”
- Line 27: “Six,” “door dicing,” “silver”
- Line 31: “say) satisfactory.”
- Line 35: “were we,” “way”
- Line 37: “doubt,” “death”
- Line 38: “But,” “different,” “Birth”
- Line 39: “bitter,” “Death,” “death”
- Line 42: “gods”
- Line 43: “glad”
- Lines 1-5: “'A cold coming we had of it, / Just the worst time of the year / For a journey, and such a long journey: / The ways deep and the weather sharp, / The very dead of winter.'”
- Lines 17-20: “At the end we preferred to travel all night, / Sleeping in snatches, / With the voices singing in our ears, saying / That this was all folly.”
- Line 4: “The,” “the weather”
- Line 5: “The very dead”
- Line 6: “And,” “camels,” “sore,” “refractory”
- Line 9: “The summer palaces,” “the terraces”
- Line 10: “the silken,” “bringing sherbet”
- Line 11: “Then,” “men,” “grumbling”
- Line 12: “running,” “liquor,” “women”
- Line 13: “n,” “ight-fires”
- Line 15: “high prices”
- Line 16: “time”
- Line 18: “Sleeping in”
- Line 19: “With,” “singing in,” “saying”
- Line 20: “this,” “all folly”
- Line 22: “below,” “snow,” “smelling,” “vegetation”
- Line 23: “stream,” “beating”
- Line 24: “three trees,” “low”
- Line 25: “And an,” “ old,” “meadow”
- Line 26: “vine”
- Line 27: “dicing”
- Line 28: “wine”
- Line 29: “no information,” “so”
- Line 30: “too soon”
- Line 31: “place,” “you,” “say”
- Line 41: “ease”
- Line 42: “people”
- Line 3: “journey, and”
- Line 6: “galled, sore-footed, refractory”
- Line 9: “slopes, the”
- Line 12: “away, and”
- Line 13: “out, and”
- Line 19: “ears, saying”
- Line 22: “Wet, below,” “line, smelling”
- Line 29: “information, and”
- Line 30: “evening, not”
- Line 31: “place; it”
- Line 32: “ago, I”
- Line 33: “again, but”
- Line 35: “This: were”
- Line 36: “Death? There”
- Line 37: “doubt. I”
- Line 38: “different; this”
- Line 39: “us, like Death, our”
- Line 40: “places, these”
- Line 41: “here, in”
- Line 2: “Just,” “ worst”
- Line 4: “ways deep,” “the weather sharp,”
- Line 7: “Lying down in,” “melting snow”
- Line 8: “There were,” “ times ,” “we regretted”
- Lines 9-10: “The summer palaces on slopes, the terraces, / And the silken girls bringing sherbet.”
- Lines 11-12: “Then the camel men cursing and grumbling / and running away, and wanting their liquor and women,”
- Line 13: “night,” “-fires,” “out,” “shelters”
- Line 14: “cities hostile,” “towns”
- Line 15: “villages dirty ,” “high,” “ prices”
- Line 16: “hard,” “had”
- Line 17: “travel all”
- Line 18: “Sleeping in snatches”
- Line 19: “With the voices singing,” “our ears, saying”
- Line 20: “That this was all folly”
- Lines 21-25: “Then at dawn we came down to a temperate valley, / Wet, below the snow line, smelling of vegetation; / With a running stream and a water-mill beating the darkness, / And three trees on the low sky, / And an old white horse galloped away in the meadow.”
- Line 32: “All,” “long”
- Lines 33-35: “set down / This set down / This”
- Line 35: “were we led all,” “way”
- Line 37: “evidence,” “doubt,” “death”
- Line 38: “different,” “Birth”
- Line 39: “Hard,” “bitter,” “Death,” “death”
- Line 42: “alien people,” “gods”
- Line 43: “glad,” “death”
Polysyndeton
- Line 11: “and”
- Line 12: “and,” “and,” “and”
- Line 13: “And,” “and”
- Line 14: “And,” “and”
- Line 15: “And,” “and”
- Line 23: “and”
- Line 24: “And”
- Line 25: “And”
- Line 3: “journey,” “journey”
- Line 36: “Birth or Death,” “Birth”
- Line 37: “ birth and death,”
- Line 38: “Birth”
- Line 39: “ Death, our death”
- Line 43: “death”
Rhetorical Question
- Lines 35-36: “were we led all that way for / Birth or Death?”
- Lines 4-5: “The ways deep and the weather sharp, / The very dead of winter.'”
- Lines 11-16: “Then the camel men cursing and grumbling / and running away, and wanting their liquor and women, / And the night-fires going out, and the lack of shelters, / And the cities hostile and the towns unfriendly / And the villages dirty and charging high prices: / A hard time we had of it.”
- Line 22: “Wet, below the snow line, smelling of vegetation;”
- Lines 24-25: “And three trees on the low sky, / And an old white horse galloped away in the meadow.”
“Journey of the Magi” Vocabulary
Select any word below to get its definition in the context of the poem. The words are listed in the order in which they appear in the poem.
- The Old Dispensation
- (Location in poem: )
Form, Meter, & Rhyme Scheme of “Journey of the Magi”
Rhyme scheme, “journey of the magi” speaker, “journey of the magi” setting, literary and historical context of “journey of the magi”, more “journey of the magi” resources, external resources.
Eliot's Reading — The poem read by its author.
Lancelot Andrewes's Sermon — The 1622 Christmas sermon of the British bishop Lancelot Andrewes, which Eliot adapted for the poem's opening.
A Documentary on the Poet — A BBC production about Eliot's life and work.
Eliot and Christianity — An article exploring Eliot's relationship with his religion.
More Poems and Eliot's Biography — A valuable resource on Eliot's life and work from the Poetry Foundation.
LitCharts on Other Poems by T. S. Eliot
Four Quartets: Burnt Norton
La Figlia Che Piange
Morning at the Window
Portrait of a Lady
Rhapsody on a Windy Night
The Hollow Men
The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock
The Waste Land
Ask LitCharts AI: The answer to your questions

Home — Essay Samples — Literature — Hero's Journey — The Hero’s Journey: A Short Story
The Hero's Journey: a Short Story
- Categories: Fiction Hero's Journey Short Story
About this sample

Words: 680 |
Published: Mar 16, 2024
Words: 680 | Page: 1 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 777 words
3 pages / 1847 words
4 pages / 1725 words
4.5 pages / 1980 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Hero's Journey
The monomyth, also known as the hero's journey, is a narrative pattern that appears in many myths, legends, and stories across different cultures. It was first outlined by Joseph Campbell in his book "The Hero with a Thousand [...]
The concept of the hero has been a prevalent and enduring theme. Heroes are often portrayed as individuals who exhibit courage, strength, and selflessness in the face of adversity. One such hero who has captured the hearts and [...]
The epic poem Beowulf, which is believed to have been written in the late 10th century, tells the story of a great Scandinavian warrior named Beowulf who comes to the aid of King Hrothgar of the Danes. The poem is filled with [...]
Is it their bravery in the face of danger, their selflessness in helping others, or their unwavering commitment to a cause? The concept of heroism has been a topic of debate for centuries, with different cultures and societies [...]
In the Disney movie Toy Story, Woodie, Andy’s cowboy toy, is an example of an universal hero who follows the twelves steps of The Hero’s Journey. The journey all begins with the introduction of the ordinary world, the toys’ life [...]
The hero’s journey is a classic storytelling framework that has been used for centuries to outline the trials and tribulations of a protagonist as they embark on a transformative quest. One of the most famous examples of the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Search Journey with Jesus Website
Translate journey with jesus website.
- The Peace Dove
Ray: make a link to my book reviews of Picturing the Bible, and in the upper right module teaser text a link to my review of Hildegard of Bingen: A Spiritual Reader
Lectionary essay for the May 19, 2024 RCL Pentecost Sunday
TITLE: The Peace Dove
Images and descriptions for the lectionary essay: use the five images from here, https://journeywithjesus.net/essays/3637-20090525JJ
Image for upper left module: use the second image from here, https://journeywithjesus.net/essays/3637-20090525JJ
Poem for upper right module: O Comforting Fire of Spirit , Hildegard of Bingen, https://journeywithjesus.net/poemsandprayers/590-hildegard-of-bingen-o-comforting-fire-of-spirit
Image for upper right module: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hildegard_of_Bingen#/media/File :Hildegard_von_Bingen.jpg
Teaser text for upper right module: Hildegard of Bingen (1098–1179) was a German Benedictine abbess, writer, music composer, philosopher, mystic, visionary, medical writer-practitioner, and scientist. See Hildegard of Bingen: A Spiritual Reader .
Weekly Prayer at end of essay: make poem title below a link to the poetry archive version, https://journeywithjesus.net/poemsandprayers/150-veni-creator-spiritus
Acts 2:1–21 or Ezekiel 37:1–14 Psalm 104:24–34, 35b Romans 8:22–27 or Acts 2:1–21 John 15:26–27; 16:4b–15
Pentecost Sunday
From Our Archives
Debie Thomas, When You Send Forth Your Spirit (2021); Debie Thomas, When the Spirit Comes (2018); and Debie Thomas, Against Christianese: Pentecost Sunday (2015).
For Sunday May 19, 2024 Pentecost Sunday
Lectionary Readings ( Revised Common Lectionary , Year B)
Acts 2:1–21 or Ezekiel 37:1–14 Psalm 104:24–34, 35b Romans 8:22–27 or Acts 2:1–21 John 15:26–27; 16:4b–15
This Week's Essay
I once told a film critic that when I watch a movie, I listen for a single sentence that captures the entire film. "I do the same thing," said Scott, "but I look for an image." We Christians are people of the Book who worship the Word made flesh. It took a while, but Christians also became people of images, and in those images we've expressed our faith as much as in words.
In his marvelous book Picturing the Bible: The Earliest Christian Art , Jeffrey Spier explains how the early Jesus movement first expressed itself in visual forms. Art and architecture flourished in classical Greece and Rome, of course, but we Christians were slow to express our faith pictorially. In fact, says Spier,"no churches, decorated tombs, nor indeed Christian works of art of any kind datable before the third century are known." This might have been because the earliest Christians were a persecuted and illicit sect comprised largely of people from lower socio-economic classes. They also inherited Judaism's ambivalence toward art rooted in the prohibition against graven images in Exodus 20:4.
But around the year 200, "purely Christian images began to appear." The forty catacombs in and around Rome, along with the discovery of a house church at Dura Europos in Syria dated to 240 AD, show how the earliest Christian art was not merely decorative but intentionally devotional; its purpose was not "objective beauty" but an "expression of faith." In the first decades of the third century, genuine Christian art appears on seal rings, tombs, clay lamps, engraved gems, and in one instance a marble statuette. A hundred years after that, Christian art adorned belt buckles and Bible covers, plates and coins, intricate mosaics and ornate crosses.
Just as Christians portrayed Jesus as a shepherd, fish, anchor, or a lamb, the five images in this essay illustrate how the Holy Spirit was represented by a dove. The symbolism of the dove hearkens back to when Noah sent a dove out from the ark to see if the flood waters had receded. When the dove returned, "there in its beak was a freshly plucked olive leaf" (Genesis 8:11). At last, peace and safety for the whole earth! In all three synoptic gospels, when John baptized Jesus, the Spirit descended upon him as a dove. The illuminated Rabbula Gospel from the sixth century (see below), like thousands of similar images thereafter, reminds us that Pentecost celebrates the descent of the dove and the peace of God's Spirit for all the world.
Is there anything we need more today in our violent world? Peace in Palestine, peace in Ukraine, peace in Sudan, and around the world.
The earliest Christian writers didn't say much about art and images, and Spier believes that their hostility toward visual representations has been exaggerated. Most early Christian art drew upon well-known Bible texts like Noah, Daniel in the lion's den, Moses, Jonah, Adam and Eve, and Abraham. In perhaps the earliest textual reference to Christian art, Clement of Alexandria (150–215) wrote that Christians could also borrow pagan symbols as long as they were appropriate. Swords and bows would be inappropriate, he said, because they signaled war and violence, but a dove was suitable, said Clement, " since we follow peace ."
Truly "pentecostal" believers are people of peace. "Seek peace and pursue it," wrote the ancient psalmist (Psalm 34:14). "Make every effort to live in peace with all people," says Hebrews 12:14. "Make every effort to do what leads to peace," wrote Paul (Romans 14:19). As followers of the Prince of Peace (Isaiah 9:6) and the "Lord of peace," we wish every person "peace at all times and in every way" (1 Thessalonians 3:16). "Blessed are the peacemakers," said Jesus (Matthew 5:9).
There's a fascinating commentary about the work of the Spirit in the life of Israel's first king, Saul. We read in 1 Samuel 10:6 that when the Spirit of the Lord came upon Saul, “he was changed into another person." This Pentecost I'm praying the Peace Prayer ascribed to Saint Francis of Assisi (1182–1226). It captures the radical "change into another person" for which I pray:
Lord, make me an instrument of your peace. Where there is hatred, let me sow love; Where there is error, truth; Where there is injury, pardon; Where there is doubt, faith; Where there is despair, hope; Where there is darkness, light; And where there is sadness, joy. O Divine Master, grant that I may not so much seek To be consoled as to console; To be understood as to understand; To be loved as to love. For it is in giving that we receive; It is in pardoning that we are pardoned; It is in self-forgetting that we find; And it is in dying to ourselves that we are born to eternal life. Amen.
We don't know the actual author of this famous prayer, and it was not until the 1920s that it was even ascribed to Saint Francis. By one account the prayer was found in 1915 in Normandy, written on the back of a card of Saint Francis. But it certainly expresses his longing to be an instrument of peace in our violent world.
The second sentence of the Bible reads that the primordial soup of pre-creation was tohu wa-bohu— a formless or unformed waste. A shapeless, futile and empty void. Darkness and desolation covered the watery deep. Things were chaotic. But then a "great wind" ( ruach elohim ) blew over the waters. The simplest way to read this is a "strong and stormy wind," but interpreters have never been able to resist the translation that the ruach elohim is the very wind, breath, or Spirit of the living God.
Like a dove, or a tender and protective mother, God's Spirit hovers, broods, or flutters over the watery chaos. This word rachaph is used only two other times in the Hebrew Old Testament, both in Deuteronomy 32:11. When God found his people in a "howling wasteland of a wilderness," he encircled, shielded or guarded them — "like an eagle that stirs up its nest and hovers over its young." And so the dove of God's Spirit broods and blows over our own little lives, and over all creation and history, longing to bring peace and protection.
The Spirit of God forms the formless. He breathes spirit into matter. He creates purpose, order and meaning out of our chaos. He fills the empty void with beauty and goodness. He turns darkness into light, night into day, the evening into a new morning. God calls those things that don't exist into existence. And in Romans 8 for this week, the Spirit intercedes for all the bondage, decay, groans, pains, frustrations and futility of "the whole creation."
In the New Testament, the Spirit is called the paraclete , literally, one called alongside to help, encourage, and comfort. And in the earliest art of the first believers, the Spirit is a dove of peace descending into our lives to bring the presence of God's shalom , that is, anything and everything that nourishes human wholeness and well-being.
Weekly Prayer Veni, Creator Spiritus , "Come, Creator Spirit!" Attributed to the German Benedictine monk and priest Rabanus Maurus (776–856). Come, Holy Spirit, Creator blest, and in our souls take up Thy rest; come with Thy grace and heavenly aid to fill the hearts which Thou hast made. O comforter, to Thee we cry, O heavenly gift of God Most High, O fount of life and fire of love, and sweet anointing from above. Thou in Thy sevenfold gifts are known; Thou, finger of God's hand we own; Thou, promise of the Father, Thou Who dost the tongue with power imbue. Kindle our sense from above, and make our hearts o'erflow with love; with patience firm and virtue high the weakness of our flesh supply. Far from us drive the foe we dread, and grant us Thy peace instead; so shall we not, with Thee for guide, turn from the path of life aside. Oh, may Thy grace on us bestow the Father and the Son to know; and Thee, through endless times confessed, of both the eternal Spirit blest. Now to the Father and the Son, Who rose from death, be glory given, with Thou, O Holy Comforter, henceforth by all in earth and heaven. Amen.
Dan Clendenin: [email protected]
Image credits: (1) Yale Divinity Digital Image & Text Library ; (2–4) JesusWalk.com ; and (5) Wikimedia.org .
Support us on Patreon!

Latest Essays
- Ascending with Christ
- Everyone Born of God Overcomes the World
- We Love Because He First Loved Us

Essay on Journey of My Life
Students are often asked to write an essay on Journey of My Life in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Journey of My Life
Beginning of journey.
My life journey began in a small town. My parents taught me love, respect, and the importance of hard work. They instilled in me the value of education.
Academic Life
School was an exciting place for me. I enjoyed learning new things every day. My teachers played a significant role in shaping my character and intellect.
Life wasn’t always easy. I faced many challenges, but they made me stronger. Each difficulty was a stepping stone towards personal growth.
Future Aspirations
I dream of becoming a scientist. I am working hard to make my dream come true. Life is a journey, and I am excited about the path ahead.
250 Words Essay on Journey of My Life
The early years.
The journey of my life began in a small town, brimming with life and culture. I was a curious child, always eager to learn more about the world around me. This curiosity became the foundation for my lifelong pursuit of knowledge.
Academic Pursuits
As I grew older, my academic interests began to take shape. I was particularly drawn to literature and science, two fields that seemed to offer endless possibilities for exploration. I delved into the works of great authors while simultaneously unraveling the mysteries of the universe.
Overcoming Challenges
However, my journey was not without its challenges. I faced academic hardships, personal losses, and moments of self-doubt. But these trials only served to strengthen my resolve. I learned to view challenges as opportunities for growth and self-improvement.
Life at College
My college years were a time of great personal and intellectual growth. I was exposed to a diverse range of perspectives and ideas, which broadened my worldview and deepened my understanding of various subjects. These experiences shaped me into a more thoughtful and empathetic individual.
Looking Forward
As I embark on the next chapter of my life, I carry with me the lessons I’ve learned and the experiences I’ve gained. I am eager to continue my journey, to learn, grow, and contribute to society in meaningful ways.
In conclusion, the journey of my life has been a rich tapestry of experiences, filled with learning, growth, and resilience. It’s a journey that continues to inspire and shape me, and I look forward to what lies ahead.
500 Words Essay on Journey of My Life
The genesis of my journey.
Life is often compared to a journey, filled with ups and downs, twists and turns. My journey began in a small town, where the essence of community and solidarity was deeply ingrained in me. My parents, both educators, instilled in me the importance of knowledge and the power it holds. They taught me that education is not just about acquiring degrees but about understanding the world around us.
The Pursuit of Knowledge
As I grew older, my thirst for knowledge intensified. I was particularly drawn to the sciences, finding solace in the logic and clarity they provided. I spent countless hours pouring over textbooks, trying to decipher the language of the universe. It was during my high school years that I developed a deep appreciation for physics and its ability to explain the world in such a precise manner. This fascination led me to pursue a degree in Physics at university.
Stepping into Adulthood
University life was a stark contrast to my sheltered upbringing. I was suddenly exposed to a diverse range of ideas, cultures, and perspectives. It was overwhelming, yet exhilarating. I learned to navigate this new world, making mistakes, learning from them, and growing as an individual. I made lifelong friendships, experienced heartbreak, and discovered my passion for research during these transformative years.
Embracing Challenges
Post-university, I faced the harsh realities of adulthood. I struggled to find a job that aligned with my passion and skills. It was a challenging period, filled with self-doubt and uncertainty. However, I held onto the belief that every experience, good or bad, contributes to our growth. I eventually landed a job as a research assistant at a renowned institute. It was a demanding job, but it allowed me to delve deeper into my field of interest.
Continuing the Journey
Looking back, I realize that each stage of my life has been a journey in itself, shaping me into the person I am today. As I continue this journey, I am guided by my passion for knowledge and my desire to contribute positively to the world. I understand that there will be more challenges ahead, but I am ready to face them with courage and determination.
In conclusion, the journey of my life has been a beautiful amalgamation of experiences, each one teaching me invaluable lessons. I believe that life is not about the destination, but the journey itself. It’s about embracing every moment, every experience, and using them to become the best version of ourselves. As I continue on this journey, I look forward to what lies ahead, ready to embrace the unknown with an open mind and a resilient spirit.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Life Is a Journey
- Essay on My First Train Journey
- Essay on An Unforgettable Journey
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The Essence of Buddhist Philosophy: a Journey into the Depths of Existence
This essay about Buddhist philosophy explores its core tenets, including the Four Noble Truths, impermanence, interconnectedness, and mindfulness. It highlights how these concepts offer insights into the nature of suffering and the human condition, providing a practical guide for living a meaningful and fulfilling life. Through mindfulness practices and ethical conduct, individuals can cultivate wisdom and compassion, ultimately transcending the limitations of the ego to find inner peace and liberation from suffering.
How it works
In the vast expanse of human thought and spirituality, few philosophies have resonated as deeply and enduringly as Buddhism. Rooted in the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, the Buddha, this ancient tradition offers profound insights into the nature of existence and the human condition. Embarking on a journey through the core tenets of Buddhism unveils a tapestry of wisdom that continues to inspire seekers of truth and inner peace across the ages.
At the heart of Buddhist philosophy lies the profound recognition of suffering as an inherent aspect of human existence.
Known as dukkha, this pervasive sense of dissatisfaction and discontent arises from the ceaseless craving and attachment that characterize much of human experience. Whether it manifests as physical pain, emotional turmoil, or existential angst, suffering permeates the fabric of life, casting a shadow over even the most fleeting moments of joy.
Yet, within the depths of suffering lies the seed of liberation. The Four Noble Truths, articulated by the Buddha, illuminate the path to freedom from suffering. These truths serve as signposts along the journey of self-discovery, inviting individuals to confront the root causes of their suffering with courage and clarity. Through the transformative power of insight and introspection, practitioners come to understand that liberation is not a distant ideal but a tangible possibility in the here and now.
Central to the Buddhist path is the cultivation of mindfulness – a state of present-moment awareness that serves as a gateway to profound insight and inner peace. Through mindfulness practices such as meditation and contemplation, individuals learn to observe the fluctuations of their minds with non-judgmental awareness, cultivating a deep understanding of the impermanent and interconnected nature of reality. In the stillness of mindful awareness, the ceaseless chatter of the ego begins to fade, revealing the profound truth of our interconnectedness with all beings and the natural world.
Impermanence, or anicca, lies at the very heart of Buddhist philosophy. This fundamental principle asserts that all phenomena, from the grandest cosmic events to the most mundane everyday experiences, are subject to constant change and flux. Nothing remains static or permanent; everything is in a perpetual state of becoming. Embracing impermanence allows individuals to release their grip on the fleeting pleasures of the world and find solace in the timeless flow of existence.
In the intricate web of existence, interconnectedness – or pratityasamutpada – weaves the threads of causality that bind all phenomena together. According to this profound teaching, nothing exists in isolation; every thought, word, and action sends ripples through the fabric of reality, shaping the course of our lives and the destiny of the cosmos. Recognizing our interconnectedness with all beings fosters a deep sense of compassion and empathy, inspiring us to act with kindness and generosity towards others.
The Buddhist path is not merely a theoretical framework but a practical guide for living a life of meaning and purpose. The Eightfold Path, comprising ethical conduct, mental discipline, and wisdom, offers a roadmap for navigating the complexities of human existence with grace and integrity. By cultivating virtues such as compassion, generosity, and wisdom, individuals align themselves with the fundamental principles of reality, paving the way for a life of profound fulfillment and inner peace.
In conclusion, the teachings of Buddhism offer a profound and timeless wisdom that speaks to the deepest aspirations of the human spirit. Through its exploration of suffering, impermanence, interconnectedness, and mindfulness, Buddhism provides a roadmap for transcending the limitations of the ego and discovering the boundless potential of our true nature. As we embark on this journey of self-discovery and transformation, may we find solace in the timeless truths that have illuminated the path of countless seekers throughout the ages.
Cite this page
The Essence of Buddhist Philosophy: A Journey into the Depths of Existence. (2024, May 12). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-buddhist-philosophy-a-journey-into-the-depths-of-existence/
"The Essence of Buddhist Philosophy: A Journey into the Depths of Existence." PapersOwl.com , 12 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-buddhist-philosophy-a-journey-into-the-depths-of-existence/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Essence of Buddhist Philosophy: A Journey into the Depths of Existence . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-buddhist-philosophy-a-journey-into-the-depths-of-existence/ [Accessed: 14 May. 2024]
"The Essence of Buddhist Philosophy: A Journey into the Depths of Existence." PapersOwl.com, May 12, 2024. Accessed May 14, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-buddhist-philosophy-a-journey-into-the-depths-of-existence/
"The Essence of Buddhist Philosophy: A Journey into the Depths of Existence," PapersOwl.com , 12-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-buddhist-philosophy-a-journey-into-the-depths-of-existence/. [Accessed: 14-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Essence of Buddhist Philosophy: A Journey into the Depths of Existence . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-essence-of-buddhist-philosophy-a-journey-into-the-depths-of-existence/ [Accessed: 14-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
The Incredible Journey
44 pages • 1 hour read
A modern alternative to SparkNotes and CliffsNotes, SuperSummary offers high-quality Study Guides with detailed chapter summaries and analysis of major themes, characters, and more.
Chapter Summaries & Analyses
Chapters 1-2
Chapters 3-8
Chapters 9-11
Character Analysis
Symbols & Motifs
Important Quotes
Essay Topics
Discussion Questions
How are animals similar to humans? How are they different? Write a compare/contrast essay that uses concrete details in order to form your argument.
According to The Incredible Journey , what specific characteristics distinguish domestic animals from wild ones? Use specific examples in your answer. You may want to contrast one of the domesticated animals against one of the wild animals that they encounter during their journey.
What is Burnford communicating about the bond that exists, specifically, between children and their pets? Use specific plot points, quotes, or character traits in your answer.

Don't Miss Out!
Access Study Guide Now
Featured Collections
Action & Adventure
View Collection
Action & Adventure Reads (Middle Grade)
Canadian Literature
Juvenile Literature
Loyalty & Betrayal
The Journey
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
In Medicine, the Morally Unthinkable Too Easily Comes to Seem Normal

By Carl Elliott
Dr. Elliott teaches medical ethics at the University of Minnesota. He is the author of the forthcoming book “The Occasional Human Sacrifice: Medical Experimentation and the Price of Saying No,” from which this essay is adapted.
Here is the way I remember it: The year is 1985, and a few medical students are gathered around an operating table where an anesthetized woman has been prepared for surgery. The attending physician, a gynecologist, asks the group: “Has everyone felt a cervix? Here’s your chance.” One after another, we take turns inserting two gloved fingers into the unconscious woman’s vagina.
Had the woman consented to a pelvic exam? Did she understand that when the lights went dim she would be treated like a clinical practice dummy, her genitalia palpated by a succession of untrained hands? I don’t know. Like most medical students, I just did as I was told.
Last month the Department of Health and Human Services issued new guidance requiring written informed consent for pelvic exams and other intimate procedures performed under anesthesia. Much of the force behind the new requirement came from distressed medical students who saw these pelvic exams as wrong and summoned the courage to speak out.
Whether the guidance will actually change clinical practice I don’t know. Medical traditions are notoriously difficult to uproot, and academic medicine does not easily tolerate ethical dissent. I doubt the medical profession can be trusted to reform itself.
What is it that leads a rare individual to say no to practices that are deceptive, exploitative or harmful when everyone else thinks they are fine? For a long time I assumed that saying no was mainly an issue of moral courage. The relevant question was: If you are a witness to wrongdoing, will you be brave enough to speak out?
But then I started talking to insiders who had blown the whistle on abusive medical research. Soon I realized that I had overlooked the importance of moral perception. Before you decide to speak out about wrongdoing, you have to recognize it for what it is.
This is not as simple as it seems. Part of what makes medical training so unsettling is how often you are thrust into situations in which you don’t really know how to behave. Nothing in your life up to that point has prepared you to dissect a cadaver, perform a rectal exam or deliver a baby. Never before have you seen a psychotic patient involuntarily sedated and strapped to a bed or a brain-dead body wheeled out of a hospital room to have its organs harvested for transplantation. Your initial reaction is often a combination of revulsion, anxiety and self-consciousness.
To embark on a career in medicine is like moving to a foreign country where you do not understand the customs, rituals, manners or language. Your main concern on arrival is how to fit in and avoid causing offense. This is true even if the local customs seem backward or cruel. What’s more, this particular country has an authoritarian government and a rigid status hierarchy where dissent is not just discouraged but also punished. Living happily in this country requires convincing yourself that whatever discomfort you feel comes from your own ignorance and lack of experience. Over time, you learn how to assimilate. You may even come to laugh at how naïve you were when you first arrived.
A rare few people hang onto that discomfort and learn from it. When Michael Wilkins and William Bronston started working at the Willowbrook State School in Staten Island as young doctors in the early 1970s, they found thousands of mentally disabled children condemned to the most horrific conditions imaginable: naked children rocking and moaning on concrete floors in puddles of their own urine; an overpowering stench of illness and filth; a research unit where children were deliberately infected with hepatitis A and B.
“It was truly an American concentration camp,” Dr. Bronston told me. Yet when he and Dr. Wilkins tried to enlist Willowbrook doctors and nurses to reform the institution, they were met with indifference or hostility. It seemed as if no one else on the medical staff could see what they saw. It was only when Dr. Wilkins went to a reporter and showed the world what was happening behind the Willowbrook walls that anything began to change.
When I asked Dr. Bronston how it was possible for doctors and nurses to work at Willowbrook without seeing it as a crime scene, he told me it began with the way the institution was structured and organized. “Medically secured, medically managed, doctor-validated,” he said. Medical professionals just accommodated themselves to the status quo. “You get with the program because that’s what you’re being hired to do,” he said.
One of the great mysteries of human behavior is how institutions create social worlds where unthinkable practices come to seem normal. This is as true of academic medical centers as it is of prisons and military units. When we are told about a horrific medical research scandal, we assume that we would see it just as the whistle-blower Peter Buxtun saw the Tuskegee syphilis study : an abuse so shocking that only a sociopath could fail to perceive it.
Yet it rarely happens this way. It took Mr. Buxtun seven years to convince others to see the abuses for what they were. It has taken other whistle-blowers even longer. Even when the outside world condemns a practice, medical institutions typically insist that the outsiders don’t really understand.
According to Irving Janis, a Yale psychologist who popularized the notion of groupthink, the forces of social conformity are especially powerful in organizations that are driven by a deep sense of moral purpose. If the aims of the organization are righteous, its members feel, it is wrong to put barriers in the way.
This observation helps explain why academic medicine not only defends researchers accused of wrongdoing but also sometimes rewards them. Many of the researchers responsible for the most notorious abuses in recent medical history — the Tuskegee syphilis study, the Willowbrook hepatitis studies, the Cincinnati radiation studies , the Holmesburg prison studies — were celebrated with professional accolades even after the abuses were first called out.
The culture of medicine is notoriously resistant to change. During the 1970s, it was thought that the solution to medical misconduct was formal education in ethics. Major academic medical centers began establishing bioethics centers and programs throughout the 1980s and ’90s, and today virtually every medical school in the country requires ethics training.
Yet it is debatable whether that training has had any effect. Many of the most egregious ethical abuses in recent decades have taken place in medical centers with prominent bioethics programs, such as the University of Pennsylvania , Duke University , Columbia University and Johns Hopkins University , as well as my own institution, the University of Minnesota .
One could be forgiven for concluding that the only way the culture of medicine will change is if changes are forced on it from the outside — by oversight bodies, legislators or litigators. For example, many states have responded to the controversy over pelvic exams by passing laws banning the practice unless the patient has explicitly given consent.
You may find it hard to understand how pelvic exams on unconscious women without their consent could seem like anything but a terrible invasion. Yet a central aim of medical training is to transform your sensibility. You are taught to steel yourself against your natural emotional reactions to death and disfigurement; to set aside your customary views about privacy and shame; to see the human body as a thing to be examined, tested and studied.
One danger of this transformation is that you will see your colleagues and superiors do horrible things and be afraid to speak up. But the more subtle danger is that you will no longer see what they are doing as horrible. You will just think: This is the way it is done.
Carl Elliott ( @FearLoathingBTX ) teaches medical ethics at the University of Minnesota. He is the author of the forthcoming book “The Occasional Human Sacrifice: Medical Experimentation and the Price of Saying No,” from which this essay is adapted.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Episode 125. From Leftism to Liberty, a Personal Journey with Michael Rectenwald The Forge of Freedom
Show Notes Episode 125. From Leftism to Liberty, a Personal Journey with Michael Rectenwald Michael Rectenwald, a former NYU professor and now a presidential candidate on the Libertarian Party ticket, discusses his journey from leftism to libertarianism. He speaks about his awakening to the problems of the woke left and the suppression of free speech on college campuses. Rectenwald explains how his study of economics, particularly the works of Ludwig von Mises, led him to reject socialism and embrace libertarianism. He emphasizes the importance of individual liberty and the need to decentralize power. Rectenwald also shares his motivation for running for president and his vision for a society based on maximum liberty and private property. Chapters 00:00 Introduction: Michael Rectenwald's Background 03:53 Awakening to the Problems of the Woke Left 09:18 Rejecting Socialism: Embracing Libertarianism 15:31 The Importance of Individual Liberty and Decentralization Takeaways Michael Rectenwald's journey from leftism to libertarianism was sparked by his opposition to the woke left and the suppression of free speech on college campuses. His study of economics, particularly the works of Ludwig von Mises, led him to reject socialism and embrace libertarianism. Rectenwald emphasizes the importance of individual liberty and the need to decentralize power. He is running for president on a platform of maximum liberty and private property. Resources Dr. Michael Rectenwald on X: "Allow me to reintroduce myself." https://twitter.com/RecTheRegime/status/1786008528135524748 From Leftism to Liberty, a Personal Journey | SpringerLink https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-29608-6_60#citeas From Leftism to Liberty, a Personal Journey — Michael Rectenwald https://www.michaelrectenwald.com/essays/from-leftism-to-liberty-a-personal-journey From Leftism to Liberty, a Personal Journey https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ck6bl_mOq2cu0EmfG7w7gFvf61uG2E7_/view Michael Rectenwald: books, biography, latest update https://www.amazon.com/stores/author/B001KC6JIY Michael Rectenwald 2024 https://rectenwald2024.com/bio/ https://rectenwald2024.com/issues/ Michael Rectenwald on the Tom Woods Show https://tomwoods.com/ep-1771-michael-rectenwald-on-the-american-dystopia/ https://tomwoods.com/ep-2169-the-great-reset-and-woke-capitalism-with-michael-rectenwald/ https://tomwoods.com/ep-2371-michael-rectenwald-and-tom-woods-on-ayn-rand-rfk-lockdown-victims-and-personal-productivity/ https://tomwoods.com/ep-2404-anti-marx-anti-war-with-michael-rectenwald/ 1. The Success of Socialist Ideas | Mises Institute https://mises.org/online-book/socialism-economic-and-sociological-analysis/introduction/1-success-socialist-ideas 2. The Crisis of Civilization | Mises Institute https://mises.org/online-book/socialism-economic-and-sociological-analysis/conclusion-historical-significance-modern-socialism/2-crisis-civilization Socialism: An Economic and Sociological Analysis: Ludwig von Mises, J. Kahane: 9780913966631: Amazon.com: Books https://www.amazon.com/Socialism-Sociological-Ludwig-von-Mises/dp/0913966630 Rectenwald, M. (2023). From Leftism to Liberty, a Personal Journey. In: Cavallo, J.A., Block, W.E. (eds) Libertarian Autobiographies. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-29608-6_60 Tags #MichaelRectenwald #RecTheRegime #NYU #leftism #libertarianism #freespeech #woke #ideology #socialism #LudwigvonMises #Mises #individualliberty #decentralization #presidentialcampaign #liberty #freedom #forgeoffreedom DISCLAIMER: This podcast is for informational purposes only and should not be considered legal, medical, or financial advice. The views expressed in this podcast are those of the hosts and guests and do not necessarily reflect the views of any organizations or individuals they may mention. The hosts and guests are not lia
- Episode Website
- More Episodes
Top Podcasts In Education

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Summary. ' The Journey ' by Mary Oliver tells of the emotional and mental turmoil someone endured to end one unhealthy life and begin anew in a different world. In the first lines of this piece the speaker addresses "you". The second person narration means that the reader is included in the poem. They are part of the story and are ...
7 Prompts for Essays About Journeys. 1. Reasons To Go On A Journey. For this prompt, research and discuss the common reasons to travel. Everyone has different motives for traveling. Some go on a journey to appreciate beautiful sceneries, while some move to attend family or work-related gatherings.
In conclusion, every journey is a story waiting to be told, and every story is a journey waiting to be taken. It's the journey, not the destination, that shapes us. 500 Words Essay on An Unforgettable Journey The Prelude to the Journey. Every journey is a mosaic of experiences, a tapestry of memories woven together over time.
500 Words Essay on A Memorable Journey Introduction. Every journey leaves an indelible mark on the canvas of our lives, but some journeys are so profound that they transform us completely. These are the journeys that we remember, cherish, and narrate to others as a memorable journey. This essay is an exploration of such a journey, one that was ...
Published: Sep 7, 2023. Table of contents. Exploring oneself is a lifelong journey filled with unique experiences, challenges, and growth. In this essay, I will take you on a comprehensive journey through my life, sharing insights into my background, values, interests, and aspirations. This narrative is a snapshot of who I am and the factors ...
It focuses on the narrator's struggles, resilience, and personal growth. This essay example follows a clear and chronological structure. It also traces the author's journey from a challenging childhood to his college years. The key idea that emerges from the essay is the transformative power of forgiveness.
500+ Words Essay on Train Journey. First of all, a journey refers to traveling from one place to another. When it comes to journeys, train journeys take the top spot. A train journey certainly is a wonderfully joyous occasion. Furthermore, train journeys fill individuals with a feeling of intense excitement.
A sudden and unexpected journey, promising adventure and peril. A test of character, strength, and skill. An ultimate battle that tests the hero's resolve. A triumphant return home. If this sounds familiar, that's because this exact narrative template has inspired countless stories from ancient myths to modern television shows and movies ...
Long Essay on Train Journey 500 words in English. Journey by Train essay is usually given to classes 7, 8, 9, and 10. A train journey is one of the most exciting travel experiences. It can usually be of two types, short trips and long, overnight tours. Children are very fond of train journeys because of the pure pleasure of getting window seats.
This ultimate Hero's Journey writing guide will define and explore all quintessential elements of the Hero's Journey—character archetypes, themes, symbolism, the three act structure, as well as 12 stages of the Hero's Journey. We'll even provide a downloadable plot template, tips for writing the Hero's Journey, and writing prompts ...
In The Journey by Barrie Hough we have the theme of friendship, fear, connection, helplessness, control, equality and perseverance. Narrated in the third person by an unnamed narrator it becomes clear to the reader after reading the story that Hough may be exploring theme of friendship. Thembi and Johan have a very special connection with one ...
The journey of my life is a story of struggle and obsession at every stage of my life. Framing things positively is an art. This art is very necessary for growth in life. Talking about my very stage after being born in a very mediocre family. The family earns tightly for its survival in this cruel world.
A Journey by Train Essay. A train is not just a transport vehicle. It connects people; it provides access to jobs, communities and goods. It delivers vital social services. Trains are the backbone of the transportation system, which help in creating a sustainable economy.
In this essay I want to talk about the most memorable journey of my life. It began at home as we packed things for an exciting trip for our anniversary. We already booked the hotel room and made a bucket list of exciting places to visit. We were so energized in light of the fact that my wife and I were going to Bali.
Life Is a Journey Essay. All people have the same journey to take - their life. As well as in the other journeys, there may be some inconveniences, disappointments and joys, and a lot depends on how we plan this particular journey and what attitude we develop towards it. I will try to show my vision of the best way to go through this path ...
Learn More. "Journey of the Magi" is a poem by T.S. Eliot, first published in 1927 in a series of pamphlets related to Christmas. The poem was written shortly after Eliot's conversion to the Anglican faith. Accordingly, though the poem is an allegorical dramatic monologue that inhabits the voice of one the magi (the three wise men who visit the ...
Published: Mar 16, 2024. The hero's journey is a common narrative structure found in literature, mythology, and folklore. It follows the path of a hero as they embark on a transformative adventure, facing various trials and challenges along the way. This narrative structure, popularized by scholar Joseph Campbell, has been used to analyze and ...
This Week's Essay. THANK YOU to Michael Fitzpatrick for a six-week series of lectionary essays from Easter to Pentecost. Michael was a regular staff writer for JWJ from 2020 to 2023. He is a U. S. Army veteran and philosopher. He served five years in the Army as a Chaplain's Assistant, which included two deployments to Iraq during 2004-05 and ...
500 Words Essay on Journey of My Life The Genesis of My Journey. Life is often compared to a journey, filled with ups and downs, twists and turns. My journey began in a small town, where the essence of community and solidarity was deeply ingrained in me. My parents, both educators, instilled in me the importance of knowledge and the power it holds.
Essay Example: In the vast expanse of human thought and spirituality, few philosophies have resonated as deeply and enduringly as Buddhism. Rooted in the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, the Buddha, this ancient tradition offers profound insights into the nature of existence and the human condition ... Embarking on a journey through the core ...
Essay Topics. 1. How are animals similar to humans? How are they different? Write a compare/contrast essay that uses concrete details in order to form your argument. 2. According to The Incredible Journey, what specific characteristics distinguish domestic animals from wild ones? Use specific examples in your answer.
A Journey of My Life - Short Essay. A Journey of my Life Everything has a history. Everyone has their own endeavor. It depends on how they take it, how they overcome each situation and how they will face each circumstance that made their endeavor meaningful. As a student, I am leaving a very simple yet a fruitful life.
My Life My Journey Essay. Decent Essays. 3133 Words. 13 Pages. Open Document. As a very small child I don't remember too much, but the things that I do remember were seen through a child's eyes that has made me the person that I am today and I will always have those memory's with me until my last breath on this earth.
Here is the way I remember it: The year is 1985, and a few medical students are gathered around an operating table where an anesthetized woman has been prepared for surgery.
Show Notes Episode 125. From Leftism to Liberty, a Personal Journey with Michael Rectenwald Michael Rectenwald, a former NYU professor and now a presidential candidate on the Libertarian Party ticket, discusses his journey from leftism to libertarianism. He speaks about his awakening to the pr…