NASA's Voyager 1 sends readable message to Earth after 4 nail-biting months of gibberish
After four months of being unable to detect comprehensible data from the Voyager 1 spacecraft, NASA scientists have had fresh luck after sending a "poke."

After a nail-biting four months, NASA has finally received a comprehensible signal from its Voyager 1 spacecraft.
Since November 2023, the almost-50-year-old spacecraft has been experiencing trouble with its onboard computers. Although Voyager 1, one of NASA's longest-lived space missions, has been sending a steady radio signal to Earth, it hasn't contained any usable data , which has perplexed scientists.
Now, in response to a command prompt, or "poke," sent from Earth on March 1, NASA has received a new signal from Voyager 1 that engineers have been able to decode. Mission scientists hope this information may help them explain the spacecraft's recent communication problems.
"The source of the issue appears to be with one of three onboard computers, the flight data subsystem (FDS), which is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it's sent to Earth by the telemetry modulation unit," NASA said in a blog post Wednesday (March 13) .
Related: NASA's 46-year-old Voyager 1 probe is no longer transmitting data
On March 1, as part of efforts to find a solution to Voyager 1's computer issues, NASA sent a command to the FDS on the spacecraft, instructing it to use different sequences in its software package, which would effectively mean skirting around any data that may be corrupted.
Voyager 1 is more than 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth. This means any radio signals sent from our planet take 22.5 hours to reach the spacecraft, with any response taking the same time to be picked up by antennas on Earth.

Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
On March 3, NASA detected activity from one section of the FDS that differed from the "unreadable data stream" they'd previously been receiving. Four days later, engineers started the heavy task of trying to decode this signal. By March 10, the team discovered that the signal contained a readout of the entire FDS memory. This included the instructions for what the FDS needed to do, any values in its code that can be changed depending on commands from NASA or the spacecraft's status, and downloadable science or engineering data.
Voyager 1 has ventured farther from Earth than any other human-made object . It was launched in 1977, within weeks of its twin spacecraft , Voyager 2. The initial aim of the mission was to explore Jupiter and Saturn . Yet after almost five decades, and with countless discoveries under their belts, the mission continues beyond the boundaries of the solar system .
— NASA hears 'heartbeat' signal from Voyager 2 probe a week after losing contact
— Historic space photo of the week: Voyager 2 spies a storm on Saturn 42 years ago
— NASA reestablishes full contact with Voyager 2 probe after nail-biting 2-week blackout
NASA scientists will now "compare this readout to the one that came down before the issue arose and look for discrepancies in the code and the variables to potentially find the source of the ongoing issue," they said in the blog post.
However, NASA stressed that it will take time to determine if any of the insights gained from this new signal can be used to solve Voyager 1's long-standing communication issues.

Emily is a health news writer based in London, United Kingdom. She holds a bachelor's degree in biology from Durham University and a master's degree in clinical and therapeutic neuroscience from Oxford University. She has worked in science communication, medical writing and as a local news reporter while undertaking journalism training. In 2018, she was named one of MHP Communications' 30 journalists to watch under 30. ( [email protected] )
NASA details plan to build a levitating robot train on the moon
Horned 'SpaceX spiral' photobombs auroras over Europe in 1st-of-its-kind sighting
James Webb telescope detects 1-of-a-kind atmosphere around 'Hell Planet' in distant star system
Most Popular
- 2 32 of the most colorful birds on Earth
- 3 Can mirrors facing each other create infinite reflections?
- 4 See stunning reconstruction of ancient Egyptian mummy that languished at an Australian high school for a century
- 5 New invention transforms any smartphone or TV display into a holographic projector
- 2 'The most critically harmful fungi to humans': How the rise of C. auris was inevitable
- 3 32 of the most colorful birds on Earth
- 4 Roman-era skeletons buried in embrace, on top of a horse, weren't lovers, DNA analysis shows
- 5 Stone with 1,600-year-old Irish inscription found in English garden
NASA’s Voyager 1 Resumes Sending Engineering Updates to Earth

NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is depicted in this artist’s concept traveling through interstellar space, or the space between stars, which it entered in 2012.
After some inventive sleuthing, the mission team can — for the first time in five months — check the health and status of the most distant human-made object in existence.
For the first time since November , NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems. The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again. The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars).
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the issue was tied to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, called the flight data subsystem (FDS). The FDS is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it’s sent to Earth.

After receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in five months, members of the Voyager flight team celebrate in a conference room at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory on April 20.
The team discovered that a single chip responsible for storing a portion of the FDS memory — including some of the FDS computer’s software code — isn’t working. The loss of that code rendered the science and engineering data unusable. Unable to repair the chip, the team decided to place the affected code elsewhere in the FDS memory. But no single location is large enough to hold the section of code in its entirety.
So they devised a plan to divide the affected code into sections and store those sections in different places in the FDS. To make this plan work, they also needed to adjust those code sections to ensure, for example, that they all still function as a whole. Any references to the location of that code in other parts of the FDS memory needed to be updated as well.
The team started by singling out the code responsible for packaging the spacecraft’s engineering data. They sent it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. A radio signal takes about 22 ½ hours to reach Voyager 1, which is over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and another 22 ½ hours for a signal to come back to Earth. When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft.
Get the Latest News from the Final Frontier
During the coming weeks, the team will relocate and adjust the other affected portions of the FDS software. These include the portions that will start returning science data.
Voyager 2 continues to operate normally. Launched over 46 years ago , the twin Voyager spacecraft are the longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history. Before the start of their interstellar exploration, both probes flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune.
Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages JPL for NASA.
News Media Contact
Calla Cofield
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
626-808-2469

- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone
golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone
Mission Status
Instrument status.
Where are the Voyagers now?
To learn more about Voyager, zoom in and give the spacecraft a spin. View the full interactive experience at Eyes on the Solar System . Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
View Voyager
Space Flight Operations Schedule (SFOS)
SFOS files showing Voyager activity on Deep Space Network (DSN)
2024 Tracking Schedule
2023 tracking schedule, 2022 tracking schedule, 2021 tracking schedule, 2020 tracking schedule, 2019 tracking schedule, 2018 tracking schedule, 2017 tracking schedule, 2016 tracking schedule, 2015 tracking schedule, 2014 tracking schedule, 2013 tracking schedule, 2012 tracking schedule, 2011 tracking schedule, 2010 tracking schedule, 2009 tracking schedule, 2008 tracking schedule, 2007 tracking schedule, 2006 tracking schedule, 2005 tracking schedule, 2004 tracking schedule, 2003 tracking schedule, 2002 tracking schedule, 2001 tracking schedule, 2000 tracking schedule, 1999 tracking schedule, 1998 tracking schedule, 1997 tracking schedule, 1996 tracking schedule, 1995 tracking schedule, 1994 tracking schedule.
We finally know why NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft stopped communicating — scientists are working on a fix
The first spacecraft to explore beyond the solar system started spouting gibberish late last year. Now, NASA knows why.

NASA engineers have discovered the cause of a communications breakdown between Earth and the interstellar explorer Voyager 1. It would appear that a small portion of corrupted memory exists in one of the spacecraft's computers.
The glitch caused Voyager 1 to send unreadable data back to Earth, and is found in the NASA spacecraft's flight data subsystem (FDS). That's the system responsible for packaging the probe's science and engineering data before the telemetry modulation unit (TMU) and radio transmitter send it back to mission control.
The source of the issue began to reveal itself when Voyager 1 operators sent the spacecraft a "poke" on March 3, 2024. This was intended to prompt FDS to send a full memory readout back to Earth.
The readout confirmed to the NASA team that about 3% of the FDS memory had been corrupted, and that this was preventing the computer from carrying out its normal operations.
Related: NASA finds clue while solving Voyager 1's communication breakdown case
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 became the first human-made object to leave the solar system and enter interstellar space in 2012. Voyager 2 followed its spacecraft sibling out of the solar system in 2018, and is still operational and communicating well with Earth.
After 11 years of interstellar exploration, in Nov. 2023, Voyager 1's binary code — the computer language it uses to communicate with Earth — stopped making sense. Its 0's and 1's didn't mean anything anymore.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"Effectively, the call between the spacecraft and the Earth was still connected, but Voyager's 'voice' was replaced with a monotonous dial tone," Voyager 1's engineering team previously told Space.com .

The team strongly suspects this glitch is the result of a single chip that's responsible for storing part of the affected portion of the FDS memory ceasing to work.
Currently, however, NASA can’t say for sure what exactly caused that particular issue. The chip could have been struck by a high-speed energetic particle from space or, after 46 years serving Voyager 1, it may simply have worn out.
— Voyager 2: An iconic spacecraft that's still exploring 45 years on
— NASA's interstellar Voyager probes get software updates beamed from 12 billion miles away
— NASA Voyager 2 spacecraft extends its interstellar science mission for 3 more years
Voyager 1 currently sits around 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, which means it takes 22.5 hours to receive a radio signal from it — and another 22.5 hours for the spacecraft to receive a response via the Deep Space Network's antennas. Solving this communication issue is thus no mean feat.
Yet, NASA scientists and engineers are optimistic they can find a way to help FDS operate normally, even without the unusable memory hardware.
Solving this issue could take weeks or even months, according to NASA — but if it is resolved, Voyager 1 should be able to resume returning science data about what lies outside the solar system.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.’s Open University. Follow him on Twitter @sciencef1rst.
China launches 4 satellites on 1st flight of new Long March 6C rocket (video)
SpaceX launches 20 Starlink satellites from California (video)
The stormy sun erupts with its biggest solar flare yet from a massive sunspot — and it's still crackling (video)
- jcs Funny timing for this article, when I am streaming an old Star Trek movie. So, surely this didn't cause a 3 byte glitch removing the O, Y and A from Voyager's name buffer? Get it? Reply
- bwana4swahili It is quite amazing it has lasted this long in a space environment. Reply
bwana4swahili said: It is quite amazing it has lasted this long in a space environment.
- HankySpanky So now we know even better for next time. Perhaps a spare chipset that is not redundant but is ready to take over, stored in a protective environment. A task NASA can handle. We'll find out in 100 year or so - if humanity still exists. Reply
HankySpanky said: So now we know even better for next time. Perhaps a spare chipset that is not redundant but is ready to take over, stored in a protective environment. A task NASA can handle. We'll find out in 100 year or so - if humanity still exists.
- Classical Motion I'm afraid it might self repair. And download galactic knowledge, then decide we are a danger. And turn around. Reply
Classical Motion said: I'm afraid it might self repair. And download galactic knowledge, then decide we are a danger. And turn around.
- jcs ROFLOL! And a hot bald chick delivering the bad news! Reply
- View All 8 Comments
Most Popular
- 2 Houston, we have an encore: ISS virtual reality experience 'The Infinite' returns
- 3 Total solar eclipse 2027: A complete guide to the 'eclipse of the century'
- 4 This Week In Space podcast: Episode 110 — Voyager 1's Brush with Silence
- 5 DARPA's autonomous 'Manta Ray' drone can glide through ocean depths undetected
April 22, 2024
After Months of Gibberish, Voyager 1 Is Communicating Well Again
NASA scientists spent months coaxing the 46-year-old Voyager 1 spacecraft back into healthy communication
By Meghan Bartels

NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is depicted in this artist’s concept traveling through interstellar space, or the space between stars, which it entered in 2012.
NASA/JPL-Caltech
After months of nonsensical transmissions from humanity’s most distant emissary, NASA’s iconic Voyager 1 spacecraft is finally communicating intelligibly with Earth again.
Voyager 1 launched in 1977 , zipped past Jupiter and Saturn within just a few years and has been trekking farther from our sun ever since; the craft crossed into interstellar space in 2012. But in mid-November 2023 Voyager 1’s data transmissions became garbled , sending NASA engineers on a slow quest to troubleshoot the distant spacecraft. Finally, that work has paid off, and NASA has clear information on the probe’s health and status, the agency announced on April 22.
“It’s the most serious issue we’ve had since I’ve been the project manager, and it’s scary because you lose communication with the spacecraft,” said Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in an interview with Scientific American when the team was still tracking down the issue.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
The Voyager 1 spacecraft is a scientific legend : It discovered that Jupiter’s moon Io, far from being a dead world like our own companion, is instead a supervolcanic world . The craft’s data suggested that Saturn’s moon Titan might have liquid on its surface. And for more than a decade, Voyager 1 has given scientists a glimpse at what space looks like beyond the influence of our sun.
Yet its long years in the harsh environment of space have done a number on the probe, which was designed to last just four years. In particular, degraded performance and low power supplies have forced NASA to turn off six of its 10 instruments, and its communication has gotten even spottier than can be explained by the fact that cosmic mechanics mean a signal takes nearly one Earth day to travel between humans and the probe.
When the latest communications glitch occurred last fall, scientists could still send signals to the distant probe, and they could tell that the spacecraft was operating. But all they got from Voyager 1 was gibberish—what NASA described in December 2023 as “a repeating pattern of ones and zeros.” The team was able to trace the issue back to a part of the spacecraft’s computer system called the flight data subsystem, or FDS, and identified that a particular chip within that system had failed.
Mission personnel couldn’t repair the chip. They were, however, able to break the code held on the failed chip into pieces they could tuck into spare corners of the FDS’s memory, according to NASA. The first such fix was transmitted to Voyager 1 on April 18. With a total distance of 30 billion miles to cross from Earth to the spacecraft and back, the team had to wait nearly two full days for a response from the probe. But on April 20 NASA got confirmation that the initial fix worked. Additional commands to rewrite the rest of the FDS system’s lost code are scheduled for the coming weeks, according to the space agency, including commands that will restore the spacecraft’s ability to send home science data.
Although, for now, Voyager 1 appears to be on the mend, NASA scientists know it won’t last forever. Sooner or later, a glitch they can’t fix will occur, or the spacecraft’s ever dwindling fuel supply will run out for good. Until then NASA is determined to get as much data as possible out of the venerable spacecraft—and its twin, Voyager 2, which experienced its own communications glitch earlier in 2023 .
NASA’s Voyager 1 Is Glitching, Sending Nonsense From Interstellar Space
The aging spacecraft, launched in 1977, is transmitting a gibberish pattern of ones and zeros back to Earth
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/MargaretOsborne.png)
Margaret Osborne
Daily Correspondent
:focal(768x432:769x433)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/13/a4/13a47049-e0ed-4339-b21b-a4026a1a9a4d/voyager-1536x864.png)
NASA’s Voyager 1 probe is experiencing a glitch that’s causing it to send a repeating, gibberish pattern of ones and zeroes back to Earth, the agency announced this week. The spacecraft is still able to receive and execute commands sent to it, but it’s unable to transmit back science or engineering data.
After ruling out other possibilities, the Voyager team determined the spacecraft’s issues stem from one of its three computers, called the flight data system (FDS). Last weekend, engineers tried to restart the FDS to see whether they could resolve the problem, but the probe still isn’t returning usable data, according to NASA.
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 and its twin spacecraft Voyager 2 are NASA’s longest-operating mission. They are the only probes to ever explore interstellar space , or the vast area between stars. The spacecraft were initially launched to study Jupiter and Saturn, and they were only intended to last five years . But after making a series of discoveries—including spotting active volcanoes on Jupiter’s moon Io—NASA extended their mission. Both spacecraft carry a “ golden record ,” a 12-inch, gold-plated, copper disk that contains sounds and images to represent humankind in case any extraterrestrials ever encounter them.
My twin Voyager 1 is having a bit of trouble with its Flight Data System, but our team is on it! Details from @NASAJPL below. -V2 https://t.co/DRnxCzYLv5 — NASA Voyager (@NASAVoyager) December 12, 2023
By today’s standards, the technology aboard the Voyager crafts is ancient. Their computers only have 69.63 kilobytes of memory —about enough to store an average jpeg file. To make room for new observations, they must erase data after sending it to Earth.
“The Voyager computers have less memory than the key fob that opens your car door,” Linda Spilker , a planetary scientist who started working on the Voyager missions in 1977, told Scientific American ’s Tim Folger last year.
But the simple, yet hardy design of the Voyagers has contributed to their longevity and allowed them to hop between missions to collect valuable data. Still, both aging spacecraft have experienced glitches. Over the summer, a human error caused Voyager 2’s antenna to tilt two degrees away from Earth , leading researchers to lose contact with the craft for more than a week before its functions returned to normal. In 2022, an issue in the attitude articulation and control system (AACS) of Voyager 1 caused it to send “garbled information about its health and activities to mission controllers, despite operating normally,” per NASA . Engineers were eventually able to solve the glitch.
Right now, Voyager 1 is hurtling through space about 15 billion miles from Earth and Voyager 2 is more than 12.6 billion miles away. Because the spacecraft are so distant, commands from mission controllers take 22.5 hours to reach Voyager 1. This means it takes 45 hours to determine whether a command to the spacecraft has had the intended outcome. NASA says it could take several weeks to develop a new plan to fix the current FDS problem.
“Finding solutions to challenges the probes encounter often entails consulting original, decades-old documents written by engineers who didn’t anticipate the issues that are arising today,” NASA says in its statement. “As a result, it takes time for the team to understand how a new command will affect the spacecraft’s operations in order to avoid unintended consequences.”
Calla Cofield, a media relations specialist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which manages the mission, tells CNN ’s Ashley Strickland engineers are now working to find the underlying cause of the problem before figuring out next steps.
“The Voyagers are performing far, far past their prime missions and longer than any other spacecraft in history,” Cofield tells the publication. “So, while the engineering team is working hard to keep them alive, we also fully expect issues to arise.”
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/MargaretOsborne.png)
Margaret Osborne | | READ MORE
Margaret Osborne is a freelance journalist based in the southwestern U.S. Her work has appeared in the Sag Harbor Express and has aired on WSHU Public Radio.
8 MINUTES AGO: Voyager 1 Just Sent Out A TERRIFYING Message From Space

We’re never going to stop exploring the unknown in air and space.
Voyager, in some very real sense, is material that’s not from the medium in which it finds itself.
I was hearing the first of the two Voyager spacecraft to extend man set this farther into the solar system than ever before.
The Earth may be a massive and beautiful place, but in comparison to the rest of the universe it is a mere speck.
- Scientists Just Made A Terrifying Discovery In The Euphrate River
- NASA Just Found Something Incredible in the Galaxy That Will Change Our Lives!
- Scientists Just Found Zeus’s God Temple Sealed for Thousands Of Years
Ever since human technology made it possible to launch rockets and satellites into space, people have had an insatiable desire to learn more and more about the mysteries of the universe.
How do we go about it?
Well, with the Voyages delivering us information to process and, well, it’s just sent us a dreadful warning and it’s about to change everything.
Join us as we analyze all that the Voyager has discovered up to this point, along with the terrifying message and what it might mean for the future.
For almost 45 years, the Voyager missions have been an integral part of space exploration, providing some of the very first and most significant glances into the true state of our solar system.
Yet these missions were never intended to survive this long.
When the first plans for the probe were carried out, the idea to send out probes in the 1970s was created out of sheer accident when Michael Minovich realized that a spacecraft could piggyback on the velocity of a planet and catapult further out into the solar system.
According to NASA officials, the Voyager mission was planned to last five years when it was first launched.
However, both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 are still on the move, gathering crucial scientific data from the deepest reaches of space.
In the summer of 1977, the two spacecraft launched within weeks of each other.
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 were designed to explore Jupiter and Saturn.
Both spacecraft successfully carried out studies of those planets.
Later, Voyager 2 completed the first ever close observations of Uranus in 1986 and Neptune in 1989.
The flyby trips involving the four planets became known as the Voyager Grand Tour.
After that, the two spacecraft embarked on a new mission to explore distant reaches of space.
NASA revealed in 2013 that Voyager 1 had crossed the boundary separating our solar system from Interstellar space.
The term Interstellar means between Stars.
According to scientists, Interstellar space begins where the sun’s continual flow of particles and magnetic fields cease.
According to NASA, Voyager 2 eventually entered Interstellar space in 2018.
At the moment, the spacecraft was 17.7 billion kilometers from the sun.
So far, the Voyages are the only spacecraft that have explored Interstellar space.
The two explorers investigated how the Interstellar medium interacts with solar wind, the sun’s continual flow of charged particles.
They have also supplied information about the heliosphere, which is a protective bubble that surrounds our solar system.
The solar wind creates the heliosphere, which is molded and changed by Interstellar circumstances.
The actual border of the solar system, the place where solar wind ends and Interstellar space begins, is called the heliopause.
According to NASA, the Voyager spacecraft has supplied fresh knowledge about Interstellar space.
They discovered, for example, that cosmic rays are approximately three times more intense beyond the heliopause than deep within the heliosphere.
Scientists merged Voyager findings with data from subsequent missions to obtain a more complete picture of our sun and how the heliosphere interacts with Interstellar space.
As per NASA, last year scientists announced that Voyager 1 had recorded a humming noise that was linked to waves identified in minuscule amounts of gas found in the near emptiness of Interstellar space.
Nicola Fox, the director of NASA’s heliophysics division in Washington DC, stated in a statement that the Voyager’s missions had supplied significant information about the sun and the sun’s influence throughout the solar system over the past four decades.
Experts are still puzzled as to how voyages can continue to operate in temperatures well below what they were built for.
Scientists have also detected something weird going on in the Solar System’s outskirts.
The heliopause, which is the barrier between the heliosphere and the Interstellar medium, appears to be rippling and creating oblique angles in an unexpected way.
The general concept that the heliopause changes shape is not new.
Over the past decade, researchers have determined that it is not static.
They made this discovery using data from the only two spacecraft to leave the heliosphere thus far, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, as well as NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX) satellite, which studies the emissions of energetic neutral atoms (ENAs) produced when solar winds and the Interstellar medium interact.
The Voyager spacecraft provide the only direct, in-situ measurements of the locations of these boundaries, but only at one point in space and time.
Eric Zernstein, a space physicist at Princeton University, wrote in an email to Vice, ‘IBEX helps round out that data.
Scientists have used the data to develop models that forecast how the heliopause will change in the future.
In a nutshell, solar winds and the Interstellar medium push and pull on each other to form a constantly shifting boundary.
However, recent heliopause research has revealed data that contradicts prior findings.
IBEX documented the brightening of ENAs that suggested asymmetries in the heliopause over a period of many months in 2014, and the scientists later found such asymmetries were incongruent with the model’s, Vice reported.
Furthermore, scientists observed that the heliopause shifted substantially in a relatively short amount of time after studying data from Voyager 1 and Voyager 2.
That explains why there was such a significant gap between the two probes’ entries into Interstellar space in 2012 and 2018, respectively.
However, the heliopause’s movement also contradicts the theories.
The researchers called these disparities ‘entry-speaking,’ and potentially controversial in an article published October 10 in the journal Nature Astronomy.
They intend to continue investigating the heliopause in the hopes of gaining more information from NASA’s Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe (IMAP), a new and improved satellite that can detect ENAs and is set to debut in 2025.
According to Zernstein, ‘we can only speculate on this odd occurrence occurring in the ghostly depths of the solar system till then.
‘ In the middle of May, the Voyager 1 on-board system that is responsible for keeping its High Gain antenna pointed at Earth and is known as the Attitude Articulation and Control System (AACS) started beaming home confusing jumbles of data, rather than typical reports about the spacecraft’s health and status.
From our vantage point, it seemed as though the spacecraft had developed a condition similar to an electronic aphasia, a condition that results in the impairment of one’s ability to speak fluently.
It’s possible that the data were generated at random, or that they don’t reflect any probable state at all.
According to NASA’s explanation in a statement from the time, the AACS could be in even more perplexing for the engineers was the fact that despite the strange status updates from the spacecraft, Voyager 1 looked to be in excellent condition.
The radio signal coming from the ship is still strong and consistent, which indicates that the antenna is still aimed at Earth and is not in the configuration that the AACS claimed it wasn’t.
To NASA, similarly, the science systems on Voyager 1 continued to collect and transmit data as usual, despite the fact that the AACS was experiencing the same strangeness.
Furthermore, whatever was wrong with the AACS did not trigger a fault protection system that is designed to put the spacecraft into safe mode whenever there is a glitch.
Fortunately, NASA engineers identified the problem and were able to implement a solution.
It was discovered that the AACS had begun delivering its telemetry data through an onboard computer that had stopped functioning many years earlier.
All NASA engineers had to do was issue the command to the AACS to utilize the right computer to send its data home, because the dead computer damaged all of the outgoing data.
The next challenge will be determining what prompted the AACS to swap systems in the first place.
According to NASA, the system most likely received an incorrect command from another onboard computer.
While they claim it is not a serious concern for Voyager 1’s well-being at the moment, the underlying culprit must be located and rectified to prevent future strangeness.
Voyager 1 has spent the last decade drifting in Interstellar space beyond the reach of our Sun’s magnetic field.
The field shielded the craft from cosmic rays and other Interstellar radiation, in the same way that Earth’s magnetic fields shield us from high energy particles and radiation from the Sun.
When one of those high-speed energetic particles strikes a computer chip, it can cause minor memory errors that mount up over time, and it’s realistic to expect that to be a concern for Voyager 1’s on-board computers as well.
A mystery like this is sort of par for the course at this stage of the Voyager mission,” said Susan Dodd, project manager for Voyager 1 and 2, in a statement.
“Both spacecraft are about 45 years old, which is much beyond what the mission plan is expected.
We are also in Interstellar space, which has a high radiation environment that no spacecraft has ever flown in before.
The journeys that these spacecraft have taken up to this point have been remarkable.
Let’s hear your thoughts about Voyager 1 in the comments down below.

- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo

- CA Privacy Notice
- Buying Guides
Voyager is sending ‘impossible data’ back to Nasa from the edge of the Solar System
Nasa’s engineering team is investigating a mystery taking place on the Voyager 1 spacecraft .
Voyager 1 is the most distant human-made object in existence, having launched 44 years ago. It is currently operating at the edge of the solar system , flying through the “interstellar medium” beyond the Sun’s influence.
However, scientists found that the craft is receiving and executing commands from Earth successfully – but the readouts from the probe’s attitude articulation and control system (AACS) do not reflect what is actually happening on board Voyager 1.
The system maintains the craft’s orientation, keeping its antenna pointed precisely to the Earth so that data can be sent from it to Nasa. While all indications suggest that the AACS is working as normal, the telemetry data it is returning appears to be randomly generated – failing to reflect any possible state that the system could be in.
Further, the issue has not triggered any fault protection system that could put Voyager into safe mode, and the signal has not weakened – suggesting that the antenna is still in its normal position, pointing towards Earth.
Nasa says that it will continue to monitor the situation, as it is possible that the invalid data could be being produced by another system, but says that it does not understand why it is happening or how long this issue could continue. It takes approximately two days for a message from Earth to reach Voyager and get a response from the craft.
“A mystery like this is sort of par for the course at this stage of the Voyager mission,” said Suzanne Dodd, project manager for Voyager 1 and 2 at Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
“The spacecraft are both almost 45 years old, which is far beyond what the mission planners anticipated. We’re also in interstellar space – a high-radiation environment that no spacecraft have flown in before. So there are some big challenges for the engineering team. But I think if there’s a way to solve this issue with the AACS, our team will find it.”
There is a possibility that Nasa will not find the source of the issue and instead have to issue software changes or use one of the craft’s backup systems – something that has been done before in 2017 when Voyager had to switch from its primary thrusters to secondary ones because of signs of degradation.
Recommended Stories
Nba draft lottery: hawks get no. 1 pick, despite 3 percent chance of winning.
The Atlanta Hawks won the No. 1 overall selection in the NBA Draft Lottery. The Hawks had a 3 percent chance of winning the top pick.
2024 NBA Mock Draft 7.0: Who will the Hawks take at No. 1? Our projections for every pick with lottery order now set
With the lottery order set, here's a look at Yahoo Sports' projections for both rounds of the 2024 NBA Draft.
Former MLB infielder, Little League World Series star Sean Burroughs dies at 43
The seven-year major leaguer collapsed while coaching his son's Little League game on Thursday.
The best RBs for 2024 fantasy football, according to our experts
The Yahoo Fantasy football analysts reveal their first running back rankings for the 2024 NFL season.
Here's 1 big investing mistake you are probably still making
Maybe a 5% CD isn't the best choice for your hard-earned money.
How rich homebuyers are avoiding high mortgage rates
Homebuyers with means are turning to an old strategy to get around a new crop of high mortgage rates: all-cash deals.
Dolphins owner Stephen Ross reportedly declined $10 billion for team, stadium and F1 race
The value of the Dolphins and Formula One racing is enormous.
The FDIC change that leaves wealthy bank depositors with less protection
Affluent Americans may want to double-check how much of their bank deposits are protected by government-backed insurance. The rules governing trust accounts just changed.
Fantasy Baseball Waiver Wire: A hitter who should be rostered in every league is available in more than half of them
Prep for the final days of Week 6 with Dalton Del Don's latest batch of fantasy baseball waiver wire pickups!
Timberwolves coach Chris Finch calls Jamal Murray's heat-pack toss on court 'inexcusable and dangerous'
Murray made a bad night on the court worse during a moment of frustration on the bench.
Which pickup trucks get the best fuel economy? Here are the tops for gas mileage (or diesel)
Trucks aren't known for being fuel efficient, though times are changing. These are the trucks with the best gas mileage in various segments.

Tight end rankings for fantasy football 2024
The Yahoo Fantasy football analysts reveal their first tight end rankings for the 2024 NFL season.
Wide receiver rankings for 2024 fantasy football
The Yahoo Fantasy football analysts reveal their first wide receiver rankings for the 2024 NFL season.
The best budgeting apps for 2024
Budgeting apps can help you keep track of your finances, stick to a spending plan and reach your money goals. These are the best budget-tracking apps available right now.
Derrick Lewis strips off shorts, moons crowd in St. Louis after KO win over Rodrigo Nascimento
“I appreciate St. Louis for letting me show my naked ass tonight."
Former House Speaker Paul Ryan says he’s not voting for Trump : 'Character is too important'
Ryan says he would be writing in a Republican candidate instead of voting for Donald Trump.
2024 NBA Draft Lottery: Top prospects, teams with the best odds and how the lottery works
Here is everything you need to know about the upcoming NBA Draft Lottery and NBA Draft.
Bud Light sales still falling as Modelo, Coors fight to keep their gains
The competition among beer giants is still brewing.
Please save 'Inside the NBA'
Appreciate 'Inside the NBA' while it's still here, because if this goes away, there may never be anything as good again.
Is Pacers coach Rick Carlisle right to be upset about officiating in Knicks series and a big-market bias?
Indiana's head coach refused to blame the officiating following Game 1, then looked at the high road two days later and went a step away from nuclear.
NASA gave Voyager 1 a 'poke' amid communication woes. Here's why the response was encouraging.
The voyager 1's mission was extended to 2025. but a communication breakdown in november put it in peril..

The mission of one of NASA's twin Voyager space probes has been in peril for months as the space agency has been unable to receive usable data from the craft launched 46 years ago to explore the far reaches of the cosmos.
But a recent "poke" sent to Voyager 1 as it travels 15.1 billion miles away from Earth has given engineers a reason for optimism when they received a response earlier in March.
Mission control prodded Voyager 1 and received a new signal March 3 that they began working furiously to decode days later. By March 10, the team determined that what they had was a memory readout, which may contain valuable data to allow them to restore regular communications with Voyager 1, NASA said .
The 46-year-old pioneering probe has continually defied expectations for its lifespan as it ventures further into uncharted territory of the cosmos . NASA had hoped Voyager 1's extended mission would allow the spacecraft to beam back valuable data through 2025 .
But a communication breakdown in November put that goal in peril.
SpaceX launch: Starship lost, but successful in third test; here's what happened in past launches
Unexpected issue caused Voyager 1 to send home gibberish
Voyager 1 has never ceased sending a steady radio signal to ground control operators on Earth, but that signal has not carried any usable data since November, NASA said.
Instead, the probe's telemetry modulation unit began sending a nonsensical repeating patterns of code.
The space agency traced the source of the communication breakdown to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, known as the flight data subsystem, which is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it’s beamed to Earth.
In order to figure out what was going on, mission control sent a "poke" March 1 commanding Voyager 1's flight data subsystem to run different sequences in case a software corruption was causing the issue. Within two days, NASA got the response for which it hoped.
On March 3, the Voyager mission team noticed that activity from one section of the flight data subsystem, was different from the rest of the computer's unreadable data stream. Because it still wasn't in the format used by Voyager 1 when it's properly sending data, the team was confused.
The array of giant radio network antennas known as the Deep Space Network that communicates with both Voyager probes decoded the signal and found that it contained a readout of the subsystem's entire memory – its coding, as well as the science and engineering data its collected. The discovered readout provided an opportunity for the team to analyze it for discrepancies in the code that could have caused the ongoing issue.
"Using that information to devise a potential solution and attempt to put it into action will take time," NASA said.
What is the mission of NASA Voyager probes?
The twin Voyager probes were launched on separate dates in 1977 from Cape Canaveral, Florida and have since traveled billions of miles away from Earth.
In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to reach interstellar space, followed in 2018 by Voyager 2, according to NA S A .
The probes' main mission is to explore the far reaches of our solar system ‒ and beyond. To that end, the spacecrafts have investigated all the giant planets of our outer solar system ‒ Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune ‒ as well as the planets' magnetic fields and a combined 48 of their moons, NASA says .
But both Voyager 1 and 2 also carry a greeting to any form of life they may encounter called the Golden Record.
Famed American astronomer Carl Sagan chaired the committee tasked with selecting the contents of the message, contained on a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk. The phonograph records contain aspects that encapsulate life on Earth, such as samples of music from different cultures and eras, natural and man-made sounds from Earth , and electronic information encoded in analog form that an advanced civilization could convert into photographs .
Voyager 2 also recently lost contact with NASA
In July, Voyager 2 also experienced a communication breakdown with mission control when its antenna was inadvertently pointed into the wrong direction .
Contact was lost July 21 with Voyager 2 after mission control transmitted routine commands that inadvertently triggered a 2-degree change in the craft's antenna orientation and disrupted the deep-space probe's ability to receive commands or transmit data back to Earth.
Fortunately, contact was restored in August when NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory sent an interstellar "shout" that successfully commanded the craft, which is now 12.6 billion miles away, to reorient itself.
Eric Lagatta covers breaking and trending news for USA TODAY. Reach him at [email protected]
Advertisement
How are the Voyager spacecraft able to transmit radio messages so far?
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email

The two Voyage spacecraft certainly have had an amazing track record. They were sent to photograph planets like Jupiter, Saturn and Neptune and have just kept on going past the outer edge of the solar system. Voyager 1 is currently over 7 billion miles (about 11 billion kilometers) away from Earth and is still transmitting -- it takes about 10 hours for the signal to travel from the spacecraft to Earth!
The Voyager spacecraft use 23-watt radios. This is higher than the 3 watts a typical cell phone uses, but in the grand scheme of things it is still a low-power transmitter. Big radio stations on Earth transmit at tens of thousands of watts and they still fade out fairly quickly.
The key to receiving the signals is therefore not the power of the radio, but a combination of three other things:
- Very large antennas
- Directional antennas that point right at each other
- Radio frequencies without a lot of man-made interference on them
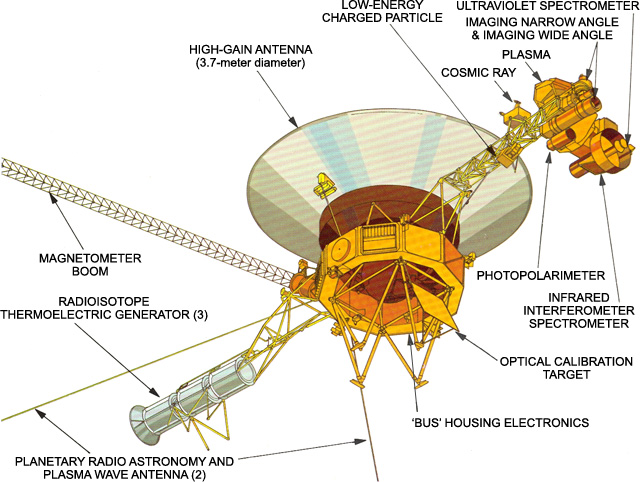
The antennas that the Voyager spacecraft use are big. You may have seen people who have large satellite dish antennas in their yards. These are typically 2 or 3 meters (6 to 10 feet) in diameter. The Voyager spacecraft has an antenna that is 3.7 meters (14 feet) in diameter, and it transmits to a 34 meter (100 feet or so) antenna on Earth. The Voyager antenna and the Earth antenna are pointed right at each other. When you compare your phone's stubby, little omni-directional antenna to a 34 meter directional antenna, you can see the main thing that makes a difference!
The Voyager satellites are also transmitting in the 8 GHz range , and there is not a lot of interference at this frequency. Therefore the antenna on Earth can use an extremely sensitive amplifier and still make sense of the faint signals it receives. Then when the earth antenna transmits back to the spacecraft, it uses extremely high power (tens of thousands of watts) to make sure the spacecraft gets the message.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role do earth's ground stations play in receiving signals from distant spacecraft like voyager, how has technology advanced to maintain communication with voyager as it moves further away.
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:
After months of silence, Voyager 2 sends a gleeful message back to Earth
11.5 billion miles away from Earth, the intrepid spacecraft finally got a call from NASA after months of radio silence.

After months of the silent treatment , NASA has finally reconnected with one of its longest running missions.
The Voyager 2 spacecraft has been roaming the cosmos for more than 40 years, all the while staying in touch with a diligent team of engineers in ground control. But in March of this year, NASA hung up the line.
The space agency left the spacecraft to spend a lonely few months in space in order to upgrade their communication system. Flying some 11.5 billion miles away from Earth, Voyager 2 was left to its own devices in mid-March.
But on October 29, NASA briefly reconnected. And, thankfully, Voyager 2 gleefully answered the call.
Voyager 2 is a vital scientific mission and one of the furthest manmade objects from Earth — so far it has left the Solar System entirely. To communicate with the spacecraft, NASA relies on a system called the Deep Space Network (DSN) antennas .
The system came to be when NASA launched its first ever satellite, Explorer 1, in 1958. The DSN is used to communicate with an average of 30 spacecraft every day. It runs 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, and is spread out across three sites in the United States, Australia, and Spain.
The DSN is reliable. But it is also more than 70 years old.
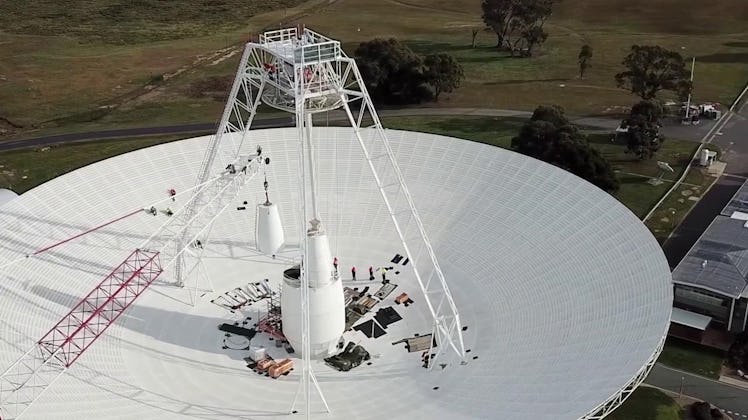

Engineers got to work, upgrading the radio antenna Deep Space Station 43 in Canberra, Australia.
As the space agency gears up for a slew of new missions to the Moon and Mars , all launching in the next few years, the DSN is due for a much needed upgrade.
NASA started this crucial work with an antenna dubbed Dss43. It is 230-feet-wide, about the size of a 20-story building, and is located in Canberra, Australia.
Dss43 has been operational for 48 years — and some of its parts, including the transmitter used to communicate with Voyager 2, had never been upgraded.
But to safeguard the antenna's next four decades of service (hopefully), NASA has upgraded Dss43's heating and cooling equipment, power supply equipment, and other electronics.
Friday's brief call to Voyager 2 was the first test of the new equipment.
"What makes this task unique is that we're doing work at all levels of the antenna, from the pedestal at ground level all the way up to the feedcones at the center of the dish that extend above the rim," Brad Arnold, the DSN project manager at NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California, said in a statement . "This test communication with Voyager 2 definitely tells us that things are on track with the work we're doing."
In the test, NASA's mission operators sent a series of commands to Voyager 2 for the first time since the radio antenna went offline in mid-March, and the spacecraft confirmed that it had received the signal and went on to execute the commands.
Unfortunately for the lonely craft, NASA is going to hang up the line again. Dss43 will not be fully back online until February, 2021. Voyager 2 will have to face a few more months alone. That's worrying for the mission's engineers on the ground, too.
"Having the antenna down for one year is not an ideal situation for Voyager or for many other NASA missions," Philip Baldwin, operations manager for NASA's Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) Program, said in statement. "The agency made the decision to conduct these upgrades to ensure that the antenna can continue to be used for current and future missions. For an antenna that is almost 50 years old, it's better to be proactive than reactive with critical maintenance."
In January 2020, Voyager 2 suffered a slight glitch , when its software shut down one of its science instruments unexpectedly. NASA’s ground team of engineers worked round the clock to get the spacecraft up and running to its normal operations once again by sending commands up to the craft. Because of its distance, each command took about 17 hours to reach Voyager 2. With no communication line, any fault with the craft that occurs during the downtime would be missed.
Voyager 2 is on a joint mission with another craft, Voyager 1, to provide scientists with a unique view of our own Solar System, looking at it from the outside in.
Both spacecraft began their journey in 1977, and the speedier twin Voyager 1 made the jump into interstellar space in 2011, before it was followed by Voyager 2 in 2018 .
Initial results from the mission published in the journal Nature in November, 2019 describe how the craft have given scientists a pretty good idea of the shape of the heliosphere — the bubble that the Sun forms around itself and separates it from outer space.
The mission still has about five years left in its designated timeline.
- Space Science
NASA's Voyager 1 is sending mysterious data from beyond our solar system. Scientists are unsure what it means.
- NASA said Voyager 1 is sending data that doesn't match the spacecraft's movements.
- The veteran spacecraft has been exploring our solar system and interstellar space since 1977.
- It is now 14.5 billion miles away from Earth, making it the most distant human-made object.

NASA's Voyager 1 is continuing its journey beyond our solar system, 45 years after it was launched. But now the veteran spacecraft is sending back strange data, puzzling its engineers.
NASA said on Wednesday that while the probe is still operating properly, readouts from its attitude articulation and control system — AACS for short — don't seem to match the spacecraft's movements and orientation, suggesting the craft is confused about its location in space. The AACS is essential for Voyager to send NASA data about its surrounding interstellar environment as it keeps the craft's antenna pointing right at our planet.
"A mystery like this is sort of par for the course at this stage of the Voyager mission," Suzanne Dodd, a project manager for Voyager 1 and 2 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, said in a statement . "The spacecraft are both almost 45 years old, which is far beyond what the mission planners anticipated." NASA said Voyager 1's twin, the Voyager 2 probe, is behaving normally.
Related stories
Launched in 1977 to explore the outer planets in our solar system, Voyager 1 has remained operational long past expectations and continues to send information about its journeys back to Earth. The trailblazing craft left our solar system and entered interstellar space in 2012 . It is now 14.5 billion miles away from Earth, making it the most distant human-made object.
NASA said that from what its engineers can tell, Voyager 1's AACS is sending randomly generated data that does not "reflect what's actually happening onboard." But even if system data suggests otherwise, the spacecraft's antenna seems to be properly aligned — it is receiving and executing commands from NASA and sending data back to Earth. It said that so far the system issue hasn't triggered the aging spacecraft to go into "safe mode," during which it carries out only essential operations.
"Until the nature of the issue is better understood, the team cannot anticipate whether this might affect how long the spacecraft can collect and transmit science data," NASA said.
Dodd and her team hope to figure out what's prompting the robot emissary from Earth to send junky data. "There are some big challenges for the engineering team," Dodd said. A major one: It takes light 20 hours and 33 minutes to get to Voyager's current interstellar location, so a round-trip message between the space agency and Voyager takes two days.
"But I think if there's a way to solve this issue with the AACS, our team will find it," Dodd added.
Watch: NASA is flying a $1.5 billion spacecraft into the sun — here's why
- Main content
NASA has solved the mystery of Voyager 1's strange data transmissions

As NASA wrestles with Artemis 1's engine woes that are delaying the return to human exploration of the moon, the agency has solved another mystery, one causing its 45-year-old spacecraft, Voyager 1, to transmit garbled data.
NASA engineers have found the bug that was causing critical instruments on the four-decade-old spacecraft to send "garbled" health information to mission controllers on Earth.
- Apple Vision Pro review: Fascinating, flawed, and needs to fix 5 things
- Apple builds a slimmed-down AI model using Stanford, Google innovations
- I tested the AI gadget that got the internet buzzing and it left me wanting more
- The best AI image generators to try right now
Voyager 1's attitude articulation and control system (AACS), which keeps its antenna directed at Earth, earlier this year started to send back information that didn't reflect what was actually happening onboard . The AACS appeared to be functioning normally, but the data it was sending back was deemed invalid because it didn't match any possible state the system could be in.
SEE: What is Artemis? Everything you need to know about NASA's new moon mission
Also, the rest of the probe appeared healthy, since it continued to gather and return science data.
The agency today said it has found the source of the garbled information: a zombie computer that should not have been used to relay telemetry data.
"The AACS had started sending the telemetry data through an onboard computer known to have stopped working years ago, and the computer corrupted the information," NASA said in a press release .
While NASA engineers have solved the problem, they still don't know why the AACS started routing information through the non-functioning computer. However, they guess that the AACS probably received a faulty command from another onboard computer.
NASA notes that if that other onboard computer generated a bad command, there could be an issue somewhere else on the spacecraft. The search continues for what the underlying issue is, but engineers believe it won't drastically harm its future.
SEE: NASA's new tiny, high-powered laser could find water on the Moon
"We're happy to have the telemetry back," said Suzanne Dodd, Voyager's project manager.
"We'll do a full memory readout of the AACS and look at everything it's been doing. That will help us try to diagnose the problem that caused the telemetry issue in the first place. So we're cautiously optimistic, but we still have more investigating to do."
Voyager 1 launched from Cape Canaveral in September 1977 and is now the farthest spacecraft from Earth, traveling in space at about 14.5 billion miles (23.3 billion kilometers) away. It would take light about 20 hours to travel from the spacecraft.
The Voyager 1 was the first human-made object to reach into interstellar space and in 1998 overtook NASA's Pioneer 10 to become the most distant human-made object.
It reached interstellar space in August 2012 and, among other things, takes measurements of the density of material in interstellar space . It will eventually exit the solar system but not for a long, long time.
This startup established a Bluetooth connection from space. Here's what that means
The best roomba vacuums for your home: expert reviewed, the best travel vpns: expert tested.

Voyager 1 stops communicating with Earth
Sign up for CNN’s Wonder Theory science newsletter. Explore the universe with news on fascinating discoveries, scientific advancements and more .
NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has experienced a computer glitch that’s causing a bit of a communication breakdown between the 46-year-old probe and its mission team on Earth.
Engineers are currently trying to solve the issue as the aging spacecraft explores uncharted cosmic territory along the outer reaches of the solar system.
Voyager 1 is currently the farthest spacecraft from Earth at about 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away, while its twin Voyager 2 has traveled more than 12 billion miles (20 billion kilometers) from our planet. Both are in interstellar space and are the only spacecraft ever to operate beyond the heliosphere, the sun’s bubble of magnetic fields and particles that extends well beyond the orbit of Pluto.
Initially designed to last five years, the Voyager probes are the two longest-operating spacecraft in history. Their exceptionally long lifespans mean that both spacecraft have provided additional insights about our solar system and beyond after achieving their preliminary goals of flying by Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune decades ago.
But their unexpectedly lengthy journeys have not been without challenges.
Voyager 1 has three onboard computers, including a flight data system that collects information from the spacecraft’s science instruments and bundles it with engineering data that reflects the current health status of Voyager 1. Mission control on Earth receives that data in binary code, or a series of ones and zeroes.
But Voyager 1’s flight data system now appears to be stuck on auto-repeat, in a scenario reminiscent of the film “ Groundhog Day .”
A long-distance glitch
The mission team first noticed the issue November 14, when the flight data system’s telecommunications unit began sending back a repeating pattern of ones and zeroes, like it was trapped in a loop.
While the spacecraft can still receive and carry out commands transmitted from the mission team, a problem with that telecommunications unit means no science or engineering data from Voyager 1 is being returned to Earth.
The Voyager team sent commands over the weekend for the spacecraft to restart the flight data system, but no usable data has come back yet, according to NASA .
NASA engineers are currently trying to gather more information about the underlying cause of the issue before determining the next steps to possibly correct it, said Calla Cofield, media relations specialist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, which manages the mission. The process could take weeks.
The last time Voyager 1 experienced a similar, but not identical, issue with the flight data system was in 1981, and the current problem does not appear to be connected to other glitches the spacecraft has experienced in recent years, Cofield said.
As both Voyager probes experience new trials, mission team members have only the original manuals written decades ago to consult, and those couldn’t account for the challenges the spacecraft are facing as they age.
The Voyager team wants to consider all of the potential implications before sending more commands to the spacecraft to make sure its operations aren’t impacted in an unexpected way.
Voyager 1 is so far away that it takes 22.5 hours for commands sent from Earth to reach the spacecraft. Additionally, the team must wait 45 hours to receive a response.
Keeping the Voyager probes alive
As the aging twin Voyager probes continue exploring the cosmos, the team has slowly turned off instruments on these “senior citizens” to conserve power and extend their missions, Voyager’s project manager Suzanne Dodd previously told CNN .
Along the way, both spacecraft have encountered unexpected issues and dropouts, including a seven-month period in 2020 when Voyager 2 couldn’t communicate with Earth. In August, the mission team used a long-shot “shout” technique to restore communications with Voyager 2 after a command inadvertently oriented the spacecraft’s antenna in the wrong direction.
While the team hopes to restore the regular stream of data sent back by Voyager 1, the mission’s main value lies in its long duration, Cofield said. For example, scientists want to see how particles and magnetic fields change as the probes fly farther away from the heliosphere. But that dataset will be incomplete if Voyager 1 can’t return information as it continues on.
The mission team has been creative with its strategies for extending the power supply on both spacecraft in recent years to allow their record-breaking missions to continue.
“The Voyagers are performing far, far past their prime missions and longer than any other spacecraft in history,” Cofield said. “So, while the engineering team is working hard to keep them alive, we also fully expect issues to arise.”
For more CNN news and newsletters create an account at CNN.com
By clicking Sign In, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Sign In Up with your social account
We won't post to any of your accounts
Your password must include:
- Min 8 characters
- Min 1 lowercase character
- Min 1 uppercase character
- Min 1 number
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Do Not Sell
- Accessibility statement
- Social icon facebook
- Social icon instagram
- Social icon twitter

Getty Images (2)
Jelly Roll’s Wife Bunnie XO Receives an Emotional Message From Her Late Ex Through Medium Tyler Henry

Jelly Roll’s wife Bunnie XO received an emotional message from her late ex-boyfriend, Tony, through psychic medium Tyler Henry .
“The way I want to word this, if there’s anybody who has passed, who loved you a hell of a lot, and you maybe could’ve seen a romantic future, but it wasn’t the right time or the right place,” Tyler, 28, told Bunnie, 44, during the Wednesday, May 8, episode of her podcast “ Dumb Blonde .”
Bunnie replied, “Probably my ex Tony.”
“I think that guy wants you to know how proud he is,” Tyler continued, “and, when he comes across, acknowledges an awareness and existence in your relationship and that you deserved more than he was able to give at that time.”

Bunnie then went on to give fans more details about her relationship with Tony.
“Tony was my ex and I was pregnant with his child and I lost his baby, but we were young. When I ran away from home, he was my boyfriend, like my protector, and he actually always loved me,” the popular internet personality explained.
She added that Tony “had smoked fake weed and it sent him into cardiac arrest, and he died.” Bunnie said that while Tony didn’t “die automatically” but that he “went into a coma” and passed away later.
“I went to go see him,” Bunnie said. “I remember I held his hand and when I held his hand, I could see him standing, looking at me in the corner of the room. I even looked at my ex Frankie, at the time, and I went, ‘He’s dead. He’s not coming back; he’s in the corner of the room right now looking at us.’”

Deal of the Day

The podcast gave fans more context in some text added to the video that read, “My ex [that] I lost 15 years ago came thru when Tyler was channeling, and watch my face when I realize how he confirmed I saw him on his deathbed. For everyone saying Tyler isn’t real, you can’t Google this or the details. I was shook.”
Tyler first garnered fame from the E! Entertainment series Hollywood Medium and has conducted readings for several celebrities including Rebel Wilson , Lizzo and Sofia Vergara . In March 2022, he starred in the Netflix series Life After Death for one season.

However, Tyler wasn’t the first psychic medium to make an appearance on Bunnie’s podcast. In October 2023, Bunnie welcomed Aimee Balesky onto the show. During the episode, Aimee helped Bunnie learn how to feel her own aura.
- Hollywood Medium
- tyler henry

- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Trump fined $1,000 for violating gag order again and threatened with jail time

Ximena Bustillo

Former President Donald Trump attends his trial in Manhattan criminal court on May 2. The judge in the case heard arguments related to the prosecution's request to fine Trump for violating a gag order in the case. Getty Images hide caption
Former President Donald Trump attends his trial in Manhattan criminal court on May 2. The judge in the case heard arguments related to the prosecution's request to fine Trump for violating a gag order in the case.
Former President Donald Trump has been held in contempt of court and fined $1,000 for violating a gag order aimed at protecting witnesses and jurors in his Manhattan criminal trial.
While handing his order down from the bench, New York Judge Juan Merchan issued a blistering warning to Trump that should the violations continue, he will put him in jail — an unprecedented consequence for a former president and presumptive GOP nominee.
Merchan said that the maximum $1,000 per violation penalty is "not serving as a deterrent," leaving him to consider jail time as a sanction. He noted that "to take that step would be disruptive to these proceedings."

Hope Hicks, former Trump confidant, testifies against him in New York criminal trial
Merchan said he worries about the court officers, Secret Service and various other personnel that would be needed for such a measure, "but at the end of the day, I have a job to do."
Trump sat at the bench with arms crossed, with his son Eric Trump in the room, as the judge handed down his order .
"Because this is now the 10th time that this Court has found Defendant in criminal contempt, spanning three separate motions, it is apparent that monetary fines have not and will not, suffice to deter Defendant from violating this Court's lawful orders," Merchan said in his written order.
Merchan only fined Trump for one of four alleged violations brought by the prosecution — for a statement claiming the jury is "95% democrats."

Who is Keith Davidson, the lawyer who negotiated hush money payments from Trump?
What did prosecutors argue trump did.
Prosecutors in Trump's criminal trial last week asked Merchan to fine him $4,000 — $1,000 for each of four statements — for violating the order and to find Trump in contempt of court for a second time. Merchan heard arguments over the violation in a hearing on May 2.
Prosecutors brought up comments made by Trump in various media outlets including a podcast, local interviews and at media appearances. In one instance, the prosecution pointed to Trump calling National Enquirer David Pecker's testimony "nice," arguing it could serve as a reminder to future witnesses that the former president is watching and willing to comment.
As for Trump's comment that "95% of the jurors are all democrats," prosecutors argued that it "amplifies and creates an air of menace." The two other allegations included comments about former Trump lawyer Michael Cohen, who is assumed to be a future witness.
Last week, Trump was ordered to pay $9,000 and remove seven offending posts from his Truth Social account, and two posts from his campaign website that Merchan ruled violated the gag order. Merchan warned in that ruling that the court "will not tolerate continued willful violations of its lawful orders and that if necessary and appropriate under the circumstances, it will impose an incarceratory punishment." In other words, he reminded Trump that jail is a punishment option.

Trump ordered to pay $9,000 for violating gag order in criminal hush money trial
Weeks before the trial began, Merchan issued a gag order on Trump that specifically bars him from making or directing others to make public statements about potential jurors, court staff or family members of staff.
Trump, the presumptive 2024 GOP presidential nominee, is accused of 34 felony counts of falsifying business records with the intent to further other crimes ahead of the 2016 presidential election. Trump has pleaded not guilty to all charges. The jury has already heard from several witnesses including former National Enquirer publisher Pecker, First Republic Bank banker Gary Farro, longtime Trump executive assistant Rhona Graff and lawyer Keith Davidson, who represented two women at the center of the trial.
On May 2, Trump's lawyer Todd Blanche argued that Trump is still speaking out in self-defense and also in defense of his run for president.

The NPR Politics Podcast
Politics weekly roundup: hush money, pocket money.
"He can't just say no comment repeatedly when he's running for president," Blanche said.
Trump has challenged the gag order, including a failed attempt to delay the trial while he fought it. An appeals court judge's decision to keep the gag order in place came less than a week before jury selection began.
Trump has argued that this order is unconstitutionally limiting his political speech as he campaigns to be the next president. In the ruling that put the gag order in place, Merchan rejected Trump's assertion that his statements "constitute core political speech."
The current gag order does not cover Merchan or District Attorney Alvin Bragg. Both have also been recipients of the former president's ire.
- social media
- Michael cohen
- truth social
- Juan Merchan
- manhattan criminal

COMMENTS
After a nail-biting four months, NASA has finally received a comprehensible signal from its Voyager 1 spacecraft. Since November 2023, the almost-50-year-old spacecraft has been experiencing ...
On Saturday, April 5, Voyager 1 finally "phoned home" and updated its NASA operating team about its health. The interstellar explorer is back in touch after five months of sending back nonsense data.
CNN —. For the first time in five months, NASA engineers have received decipherable data from Voyager 1 after crafting a creative solution to fix a communication problem aboard humanity's most ...
Contact restored. That was the message relieved NASA officials shared after the agency regained full contact with the Voyager 1 space probe, the most distant human-made object in the universe ...
The Voyager 1 team received a clear message about the spacecraft's status on April 20, and they expect to have science data flowing again in the next few weeks. This comes a few months after ...
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the ...
In the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app, you can see the real spacecraft trajectories of the Voyagers, which are updated every five minutes. Distance and velocities are updated in real-time. For a full 3D, immersive experience click on View Voyagers link below to launch the NASA Eyes on the Solar System app. View Voyager.
Voyager 1 currently sits around 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, which means it takes 22.5 hours to receive a radio signal from it — and another 22.5 hours for the spacecraft ...
NASA / JPL-Caltech. For the first time in five months, NASA has received usable data from Voyager 1, the farthest spacecraft from Earth. The aging probe, which has traveled more than 15 billion ...
First, it takes a long time to communicate with Voyager 1. Traveling at the speed of light, the radio signals used to command the spacecraft take 22.5 hours to travel 15 billion miles—and 22.5 ...
Now NASA engineers says they've been able to decipher a new message that Voyager 1 sent in March. Image via Caltech/ NASA-JPL. NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft launched from Earth in 1977. It ...
The first such fix was transmitted to Voyager 1 on April 18. With a total distance of 30 billion miles to cross from Earth to the spacecraft and back, the team had to wait nearly two full days for ...
Right now, Voyager 1 is hurtling through space about 15 billion miles from Earth and Voyager 2 is more than 12.6 billion miles away. Because the spacecraft are so distant, commands from mission ...
CNN —. Engineers have sent a "poke" to the Voyager 1 probe and received a potentially encouraging response as they hope to fix a communication issue with the aging spacecraft that has ...
The space probe, launched in 1977 as part of the Voyager program, is currently 14.5 billion miles from Earth, and it therefore takes nearly two days (20 hours and 33 minutes) to send a message and ...
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 were designed to explore Jupiter and Saturn. Both spacecraft successfully carried out studies of those planets. Later, Voyager 2 completed the first ever close observations of Uranus in 1986 and Neptune in 1989. The flyby trips involving the four planets became known as the Voyager Grand Tour.
Nasa's engineering team is investigating a mystery taking place on the Voyager 1 spacecraft.. Voyager 1 is the most distant human-made object in existence, having launched 44 years ago. It is currently operating at the edge of the solar system, flying through the "interstellar medium" beyond the Sun's influence.. However, scientists found that the craft is receiving and executing ...
USA TODAY. 0:00. 1:30. The mission of one of NASA's twin Voyager space probes has been in peril for months as the space agency has been unable to receive usable data from the craft launched 46 ...
For months now, the most distant spacecraft to Earth - Voyager 1 - has been talking gibberish on the interplanetary 'radio'. The repetitive jumble of 1s and 0s it's sending back to our planet, 24 billion kilometers (15 billion miles) away, has made no sense to scientists until now. Turns out, officials at NASA just needed to give the oh-so ...
The voyager can transmit over 7 billion miles (about 11 billion kilometres) away from Earth. Philip Wallick / Getty Images. The two Voyage spacecraft certainly have had an amazing track record. They were sent to photograph planets like Jupiter, Saturn and Neptune and have just kept on going past the outer edge of the solar system. Voyager 1 is currently over 7 billion miles (about 11 billion ...
In the test, NASA's mission operators sent a series of commands to Voyager 2 for the first time since the radio antenna went offline in mid-March, and the spacecraft confirmed that it had received ...
May 19, 2022, 11:39 AM PDT. An illustration depicting one of NASA's twin Voyager spacecraft. Both Voyagers have entered interstellar space. NASA/JPL-Caltech. NASA said Voyager 1 is sending data ...
Image: NASA. As NASA wrestles with Artemis 1's engine woes that are delaying the return to human exploration of the moon, the agency has solved another mystery, one causing its 45-year-old ...
The space agency more recently received a memory "readout" from Voyager 1 (at such a great distance, it takes nearly a day for a message from the craft to reach us), which the team is now ...
Voyager 1 is currently the farthest spacecraft from Earth at about 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) away, while its twin Voyager 2 has traveled more than 12 billion miles (20 billion ...
News. May 11, 2024 2:37 pm. By Whitney Danhauer. Jelly Roll's wife Bunnie XO received an emotional message from her late ex-boyfriend, Tony, through psychic medium Tyler Henry. "The way I want ...
Two days before the trip, her friend Sanna Rameau received a puzzling WhatsApp message from Henao indicating she was running off for a few days with a man she'd just met. The message, seen by ...
Wisconsin's 'uninstructed' voters send Biden a message to change course on Gaza Organizers of the protest vote wanted to get at least 20,000 "uninstructed" votes in Tuesday's primary. The results ...
The former president received a second fine for violating a gag order prohibiting him from speaking about witnesses, jurors, court staff and their families. Trump is trying to appeal the gag order.