- Quick Links
- Make An Appointment
- Our Services
- Price Estimate
- Price Transparency
- Pay Your Bill
- Patient Experience
- Careers at UH

Schedule an appointment today

Thailand Travel Requirements & Vaccinations
Thailand is a country located in Southeast Asia on the Indochinese peninsula. Officially known as the Kingdom of Thailand, it was formerly known as Siam. Thai is the official language of Thailand with English being spoken in most of the larger cities and tourist destinations. Thailand is home to some of the most popular and luxurious resorts in Asia.
The terrain of Thailand varies greatly and ranges from mountainous regions in the north, to plateaus in the east and river valleys in much of the interior. Despite the geographical variations, most of Thailand experiences a tropical wet and dry (savanna) climate which is comprised of three distinct seasons:
- Summer or pre-monsoon season lasts from mid-February to mid-May and is characterized by warm, dry temperatures.
- Rainy or southwest monsoon season lasts from mid-May to mid-October and is defined by an abundance of rain.
- Winter or northeast monsoon season is mid-October through mid-February and comes with dry, mild weather conditions.
Thailand has a vast array of attractions and activities to offer visitors, including:
- Bangkok and the many historical, natural and cultural sights it has to offer
- Trekking and adventure travel in the forested mountain regions
- Archaeological sites, Buddhist temples and museums
- Clear blue/green shallow waters on sandy beaches along the coast
- A diverse wildlife system
Recommended Vaccinations for Thailand Travel
- Hepatitis A
- Japanese encephalitis
*Rabies vaccination is typically only recommended for very high risk travelers given that it is completely preventable if medical attention is received within 7 – 10 days of an animal bite.
Travelers may also be advised to ensure they have received the routine vaccinations listed below. Some adults may need to receive a booster for some of these diseases:
- Measles, mumps and rubella (MMR)
- Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis)
Older adults or those with certain medical conditions may also want to ask about being vaccinated for shingles and/or pneumonia.
This information is not intended to replace the advice of a travel medicine professional. Not all of the vaccines listed here will be necessary for every individual.
Talk to the experts at UH Roe Green Center for Travel Medicine & Global Health to determine how each member of your family can obtain maximum protection against illness, disease and injury while traveling, based on age, health, medical history and travel itinerary.
Make an Appointment
To schedule a pre-travel consultation call, 216-844-8500 .
Please note: You must be physically located in Ohio for a virtual consultation
What Can You Do to Help?
Make a gift to support urgent patient care at University Hospitals.
Update May 10, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory July 24, 2023
Thailand - level 1: exercise normal precautions.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Exercise normal precautions in Thailand. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Reconsider travel to:
- Yala, Pattani, Narathiwat, and Songkhla provinces due to civil unrest associated with ongoing insurgent activities.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Thailand.
If you decide to travel to Thailand:
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Thailand.
- Have evacuation plans that do not rely on U.S. government assistance.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Yala, Pattani, Narathiwat, and Songkhla Provinces – Level 3: Reconsider Travel
Periodic violence directed mostly at Thai government interests by a domestic insurgency continues to affect security in the southernmost provinces of Yala, Pattani, Narathiwat, and Songkhla. In Songkhla, the insurgency is most active in the districts of Chana, Thepha, Nathawat, and Saba Yoi. U.S. citizens are at risk of death or injury due to the possibility of indiscriminate attacks in public places.
The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in these provinces as U.S government employees must obtain special authorization to travel to these provinces.
Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
6 months from date of entry required
One page is required per entry stamp; please note endorsement pages are not considered blank passport page
No, if your stay is less than 30 days
Yellow fever may be required if arriving from certain countries with yellow fever
Embassies and Consulates
U.S. Embassy Bangkok 95 Wireless Road Bangkok 10330 Thailand Telephone: + (66) (2) 205-4049, 02-205-4049 (within Thailand) Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(66) (2) 205-4000, 02-205-4000 (within Thailand) Fax: +(66) (2) 205-4103, 02-205-4103 (within Thailand) Email: [email protected]
CONSULATE
U.S. Consulate General Chiang Mai 387 Witchayanond Road Chiang Mai 50300 Thailand Telephone: +(66) (53) 107-777, 053-107-777 (within Thailand) Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(66) 81-881-1878, 081-881-1878 (within Thailand) Fax: +(66) (53) 252-633, 053-252-633 (within Thailand) Email: [email protected]
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Visit the Royal Thai Embassy website for the most current visa information.
- U.S. citizen tourists entering Thailand for fewer than 30 days do not require a visa.
- We strongly recommend that your passport be valid for at least six months beyond the date of your arrival in Thailand to avoid possible denied entry.
- Thai immigration officials or airline staff may ask for your onward/return ticket.
- Business travelers, U.S. government employees travelling on official business, teachers, retirees, and those planning to stay longer than 30 days should check with the Royal Thai Embassy about visa requirements .
- If you overstay your visa, you will be fined. Depending on the length of overstay, you may also be arrested, detained, deported at your own expense, and banned from re-entering Thailand.
We strongly recommend you carry a copy of your U.S. passport identification page and current Thai visa to help avoid detention by the Thai immigration police.
Thailand’s entry/exit information is subject to change without notice. For the most current information, please see The Royal Thai Police Immigration Bureau .
You can find detailed information on vaccinations and other health precautions on the CDC website .
HIV/AIDS Restrictions: Some HIV/AIDS entry restrictions exist for visitors to and foreign residents of Thailand. However, these restrictions are generally not enforced. Please verify this information with the Royal Thai Embassy before you travel.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction and customs regulations on our websites.
COVID-19 Requirements: There are no COVID-related entry requirements for U.S. citizens.
Safety and Security
Terrorism: Terrorist groups and those inspired by such organizations are intent on attacking U.S. citizens abroad. Terrorists are increasingly using less sophisticated methods of attack – including knives, firearms, and vehicles – to more effectively target crowds. Frequently, their aim is unprotected or vulnerable targets, such as:
- High-profile public events (sporting contests, political rallies, demonstrations, holiday events, celebratory gatherings, etc.)
- Hotels, clubs, and restaurants frequented by tourists
- Places of worship
- Shopping malls and markets
- Public transportation systems (including subways, buses, trains, and scheduled commercial flights)
For more information, see our Terrorism page.
Periodic acts of violence in Thailand remain a concern. In August 2019, several small explosions and related arson events occurred in various locations throughout Bangkok resulting in no deaths but some injuries and minor property damage. Several small-scale bombings occurred near some tourist locations in the far Southern provinces in August 2016 and December 2018. In August 2015, an explosion near the Erawan Shrine in downtown Bangkok killed at least 20 people and injured more than 100. The U.S. Department of State assesses there is a continued risk of terrorism in Southeast Asia, including in Thailand.
If a protest or demonstration is expected to pass near the U.S. Embassy or Consulate facilities, Embassy and Consulate entrances and functions may be restricted. The U.S. Embassy in Bangkok’s website , Facebook, and Twitter sites and the U.S. Consulate General in Chiang Mai’s website , Facebook , and Twitter sites post information about local events that may affect Embassy functions. Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive security and safety messages.
Far Southern Thailand: Periodic violence directed mostly at Thai government interests by a domestic insurgency continues to affect security in the southernmost provinces of Yala, Pattani, Narathiwat, and Songkhla. U.S. citizens are at risk of death or injury due to the possibility of indiscriminate attacks in public places. Martial law is in force in this region.
The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in these provinces. Travel to this region by U.S government employees must be reviewed and approved in advance. For more information on terrorist threats against U.S. citizens worldwide and steps to take as a result of these threats, please see the Worldwide Caution .
- Crimes of opportunity, such as pick-pocketing, bag-snatching, and burglary, occur in Thailand.
- Violent crimes against foreigners are relatively rare. However, murders, rapes, and assaults against foreigners do occur.
- Sexually motivated violence, committed by either Thai citizens or foreigners, is most likely to occur after time spent at bars, clubs, and parties, on beaches, or in remote/isolated areas. The Thai police response will differ from an investigation in the United States; investigating officials have publicly discredited people who have reported being the victim of crimes . In addition to making a report at the police jurisdiction in which the crime occurred, we advise contacting the Embassy and engaging a local attorney if you are a victim of an assault.
- When traveling alone, exercise caution, stay near other travelers, and ensure friends or family know how to contact you.
- Taxi and “tuk-tuk” drivers may attempt to charge excessive fares or refuse passengers. You should either request the driver use the meter or agree on the fare beforehand.
- At the airport use only public transportation from the airport’s official pick-up area, cars from the limousine counters, or a car from your hotel.
- Rental scams do occur in Thailand. Many rental motorbike, jet ski, and car companies will hold your passport until you pay for real or fictitious damages. We advise against using your passport as collateral.
- Exorbitant bar tab scams occur in Thailand. Some bars and entertainment venues will charge exorbitant prices for drinks or unadvertised cover charges and threaten violence if you don’t pay.
- Other scams involving gems, city tours, entertainment venues, and credit cards are common, especially in tourist areas.
International Financial Scams: See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information.
Internet romance and financial scams are prevalent in Thailand. Scams are often initiated through Internet postings/profiles or by unsolicited emails and letters. Scammers almost always pose as U.S. citizens who have no one else to turn to for help. Common scams include:
- Romance/Online dating
- Money transfers
- Grandparent/Relative targeting
- Free Trip/Luggage
- Work permits/job offers
Victims of Crime: U.S. citizen victims of crime are encouraged to contact the U.S. Embassy or Consulate for assistance. Report crimes to the local police by calling 191 or the Tourist Police at 1155 and contact the U.S. Embassy at +66 (0) 2-205-4049 or Consulate at +(66) (53) 107-777. Remember that only local officials have the authority to investigate and to prosecute a crime.
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence are encouraged to contact the U.S. Embassy or Consulate for assistance. Report crimes to the local police by calling 191 or the Tourist Police at 1155 and contact the U.S. Embassy at +66 (0) 2-205-4049 or Consulate at +(66) (53) 107-777. Remember that only local officials have the authority to investigate and to prosecute a crime.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Help you find appropriate medical care
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent
- Explain the local criminal justice process in general terms
- Provide a list of local attorneys
- Provide our information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution
- Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home
- Replace a stolen or lost passport
Tourism: The tourism industry is unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities do not commonly occur. Hazardous areas/activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is typically available only in/near major cities. First responders are generally unable to access areas outside of major cities and to provide urgent medical treatment. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Conditions at the Bangkok Immigration Detention Center (IDC): Conditions in immigration detention centers (IDCs) where authorities detain foreign nationals who violate immigration laws remain poor and most are overcrowded. IDCs, administered by the Immigration Police Bureau, which reports to the Royal Thai Police (RTP), are not subject to many of the regulations that govern the regular prison system. U.S. citizen detainees often complain of stark, austere living conditions, overcrowding, and unhealthy conditions. Personal security is poor. In addition, the main IDC in Bangkok does not dependably provide adequate medical or mental health care. In 2019, two U.S. citizens died while in custody at the Bangkok IDC. Deportations are self-funded and it may take up to two weeks for Thai authorities to process a case before deportation. Detainees must have funds to purchase a phone card and do not have access to the internet. Prior approval and a security escort are required to visit a Western Union or an ATM machine.
- Please see the Immigration Act B.E. 1979 for more information about Thai Immigration violations.
- Please see the Department of State’s Report on Human Rights Practices for Thailand for further information.
Lèse majesté (Royal Insult): Thais hold the monarchy in the highest regard. Making a critical or defamatory comment about the royal family is punishable by a prison sentence of up to 15 years per offense. As an example, purposely tearing Thai bank notes, which carry an image of the King, may be considered a lèse majesté offense.
- Prostitution is illegal in Thailand. Serious consequences include criminal conviction and imprisonment, particularly in the case of child prostitution.
- Commercial surrogacy is banned.
- Personal use of even non-lethal military equipment, such as protective vests and night vision scopes, is prohibited.
- Illegal drugs carry severe penalties. Expect long jail sentences under harsh conditions, heavy fines, or even execution for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs.
- Shoplifting can result in large fines and lengthy detention followed by deportation.
- Domestic Issues: Local police are reluctant to become involved in domestic issues. You may call the Family Services Emergency hotline by dialing 1300 from any Thai phone.
- Possessing counterfeit or pirated goods is a crime in Thailand. For more information see the intellectual property section of the U.S. Department of Justice website .
Customs may enforce strict regulations on Buddha images, firearms, bullets and/or bullet casings, bullet-proof vests, night vision devices and other para-military type equipment, explosives, drugs, radios, books, and recordings, which might be cultural property and/or considered harmful to the public interest.
Faith-Based Travelers: See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTI Travelers: There are no known legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or the organization of LGBTI events in Thailand. However, LGBTI groups report that in the case of sexual crimes, police tend to downplay sexual abuse claims from LGBTI victims.
See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers Who Require Accessibility Assistance. Sidewalks and street crossings are not suitable for travelers with mobility issues. Newly constructed buildings, facilities, and transportation equipment should be accessible by law for persons with mobility issues. However, enforcement of these provisions is not uniform.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: Some victims of sexual assault or domestic violence find that Thai authorities do not handle such cases with as much sensitivity or consideration for privacy as they would expect in the United States. See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
Ambulance services are:
- not present throughout the country or are unreliable in most areas except for Bangkok and other major cities.
- Injured or seriously ill travelers may prefer to take a taxi or private vehicle to the nearest major hospital rather than wait for an ambulance.
Medical treatment is generally adequate in Thailand’s urban areas. In Bangkok, Chiang Mai, Phuket, and Pattaya, good facilities exist for routine, long-term, and emergency health care. Basic medical care is available in rural areas, but English-speaking providers are rare.
Medical tourism is an established and rapidly growing industry. You should consult with your local physician before traveling and also refer to information on medical tourism from CDC.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
Medicine for personal use is allowed as long as the amount does not exceed a 30-day supply and you bring the medicine with you. Do not mail medicine to Thailand without first confirming it will be allowed into the country.
If traveling with prescription medication, check with Thailand Customs and the Thailand Food and Drug Administration to ensure the medication is legal in Thailand. Always, carry your prescription medication in original packaging with your doctor’s prescription.
The following diseases are present:
- Chikungunya
- Japanese encephalitis
- Tuberculosis:
- Hepatitis A and B
- Melioidosis
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Air Quality: The air quality in Thailand varies considerably and fluctuates with the seasons, but seasonal smog is a problem. In recent years the air quality in Bangkok, Chiang Mai, Khon Kaen, Lampang, Nan, and Samut Sakhon have exceeded Thai and U.S. government daily standards for fine particulate matter (PM 2.5) for a portion of the year. In Chiang Mai and other northern provinces, annual agricultural burning, approximately February through late April, and forest fires cause days with unhealthy to hazardous air quality based on the U.S. index. In Bangkok environs, airborne dust and auto pollutants are prevalent in the cooler, dry period (December-February). Anyone who travels where pollution levels are high is at risk. People at the greatest risk from air pollution exposure include:
- Infants, children, and teens
- People over 65 years of age
- People with lung disease such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema;
- People with heart disease
- People who work or are active outdoors
For Bangkok and Chiang Mai, U.S. Mission Thailand is reporting the U.S. EPA’s Air Quality Index (AQI) calculated from PM2.5 data captured by monitors owned and maintained by the Royal Thai Government. The information and advice on health protection measures to take is available
Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates.
The U.S. Embassy maintains a list of doctors and hospitals . We do not endorse or recommend any specific medical provider or clinic.
Health facilities in general:
- Adequate health facilities are available in Bangkok and other major cities but health care in rural areas may be below U.S. standards.
- Hospitals and doctors require payment “up front” prior to service or admission. Credit card payment is not always available.
- Medical staff at public hospitals may speak little or no English.
- Patients bear all costs for transfer to or between hospitals.
- Psychological and psychiatric services are limited, even in the larger cities, with hospital-based care only available through government institutions.
Medical Tourism and Elective Surgery:
- Medical tourism is a rapidly growing industry. People seeking health care overseas should understand that medical systems operate differently from those in the United States and are not subject to the same rules and regulations. Anyone interested in traveling for medical purposes should consult with their local physician before traveling and visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information on Medical Tourism.
- We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation in the event of unforeseen medical complications.
- Your legal options in case of malpractice are very limited in Thailand.
- Although Thailand has many elective/cosmetic surgery facilities that are on par with those found in the United States, the quality of care varies widely. If you plan to undergo surgery in Thailand, make sure that emergency medical facilities are available and professionals are accredited and qualified.
Pharmaceuticals:
- Exercise caution when purchasing medication overseas. Pharmaceuticals, both over the counter and requiring prescription in the United States, are often readily available for purchase with little controls. Counterfeit medication is common and may prove to be ineffective, the wrong strength, or contain dangerous ingredients. Medication should be purchased in consultation with a medical professional and from reputable establishments.
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration are responsible for rules governing the transport of medication back to the United States. Medication purchased abroad must meet their requirements to be legally brought back into the United States. Medication should be for personal use and must be approved for usage in the United States. Please visit the U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration websites for more information.
Assisted Reproductive Technology and Surrogacy:
- If you are considering traveling to Thailand to have a child through use of assisted reproductive technology (ART) or surrogacy, please see our ART and Surrogacy Abroad page .
- Surrogacy is illegal for foreigners in Thailand, subject to complex local regulation. For additional information, visit the Government of Thailand’s website for information on foreigner surrogacy.
- If you decide to pursue parenthood in Thailand via assisted reproductive technology (ART) with a gestational mother, be prepared for long and unexpected delays in documenting your child’s citizenship. Be aware that individuals who attempt to circumvent local law risk criminal prosecution.
Water Quality:
- In many areas, tap water is not potable. Bottled water and beverages are generally safe, although you should be aware that many restaurants and hotels serve tap water unless bottled water is specifically requested. Be aware that ice for drinks may be made using tap water.
Adventure Travel:
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Adventure Travel .
COVID-19 Testing: For the most current list of COVID-19 testing locations in Thailand approved by the Ministry of Public Health, please visit: http://service.dmsc.moph.go.th/labscovid19 . Testing is paid for by U.S. citizens.
The Ministry of Public Health provides a list of 44 laboratories approved to conduct COVID-19 testing found here .
Please Note : Same-day Covid-19 testing is available at most private hospitals throughout Thailand. Please reference this list of testing locations and contact the provider directly to inquire about COVID-19 testing options, scheduling, cost, and other information.
COVID-19 Vaccines: The COVID-19 vaccine is available for U.S. citizens to receive in Thailand. According to Thai authorities, both private and public hospitals are providing COVID-19 vaccines. More information on a list of hospitals in Thailand is available here .
The Bang Rak Vaccination and Health Center, the Institute of Dermatology, and the Bamrasnaradura Infectious Diseases Institute are currently providing free bivalent vaccines to non-Thai citizens on a walk-in basis.
Visit the FDA's website to learn more about FDA-approved vaccines in the United States.
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety:
- Traffic accidents are common in Thailand. According to the World Health Organization , in 2018, Thailand had one of the world’s highest traffic-related fatality rates. Bangkok and some parts of Chiang Mai have heavy traffic.
- Reckless driving: Speeding, reckless passing, and failure to obey other traffic laws are common in all regions of Thailand. Traffic moves on the left. Some drivers move illegally against the traffic. Scooters and motorbikes commonly drive on the sidewalks during rush hour and other periods of heavy traffic. Commercial drivers commonly consume alcohol, amphetamines, and other stimulants.
- Accidents involving motorcycles can be deadly . Riders may incur serious injuries when they are not wearing helmets or proper clothing and footwear. According to the World Health Organization, in 2016, 74 percent of traffic fatalities involved riders of 2-and 3-wheeled vehicles. Use of motorcycle helmets is mandatory, but this law is sporadically enforced.
- Use a pedestrian bridge to cross the road where one is available, including in front of the U.S. Embassy on Wireless Road and on Sukhumvit Road, where many pedestrians have been killed and several U.S. citizens seriously injured. Look carefully in both directions before crossing streets, even when using a marked crosswalk.
- If you have a traffic accident, you should contact your insurance company for guidance in dealing with the other party and the police.
- Emergency vehicles: Congested roads and a scarcity of ambulances can make it difficult for accident victims to receive timely medical attention
Traffic Laws:
- Driving under influence is punishable by law . If you are found to be intoxicated, you could be jailed for a minimum of two years and subject to a fine.
- Bribes are illegal. If you are found guilty, you could be imprisoned up to five years, face severe fines, or both.
- Lack of ID.
- Not obeying traffic laws and traffic signals.
- Driving slowly in regular lanes of traffic.
- If you are involved in a traffic accident, you should contact your auto insurance company for guidance .
Public Transportation:
- Mass transit: In Bangkok, the BTS elevated "Skytrain," “Airport Rail Link” mass transit, and the underground MRT systems are reliable, inexpensive, air conditioned, and often faster than Bangkok traffic.
- Bus system: Bangkok also has an extensive bus system, but buses can be overcrowded and are often driven with little or no regard for passenger safety.
- For hire vehicles: Cities outside of Bangkok typically have only rudimentary public transportation and usually do not have metered taxis. In many cases, motorcycle taxis, tuk-tuks, bicycle-powered rickshaws, and pick-up trucks will be the only options available for travelers without their own transport.
- Smartphone-based for-hire vehicle service exist in Bangkok and other large cities. Those affiliated with registered taxis, such as Grab Taxi, Line Taxi, and All Thai Taxi are legal, but their affiliated car services are under legal review.
See our Road Safety page for more information.
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Thailand’s Civil Aviation Authority as not being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Thailand’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Thailand should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the NGA broadcast warnings .
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Thailand . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, thailand map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
Thailand to Drop More COVID-19 Restrictions for Travelers — What to Know
Starting May 1, the Southeast Asian country will no longer require vaccinated visitors to get tested before arrival or during their trip or quarantine.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/alison-fox-author-pic-15f25761041b477aaf424ceca6618580.jpg)
Thailand will eliminate pre-arrival testing for all visitors next month as the country becomes the latest to ease pandemic-related restrictions.
Starting May 1, the Southeast Asian country will no longer require visitors to get tested before coming or upon arrival, regardless of their vaccination status, according to the Tourism Authority of Thailand . While fully vaccinated travelers will be able to come into the country and travel freely without any quarantine restrictions or mandatory hotel stays, the rules will be slightly different for unvaccinated travelers.
Visitors who are not fully vaccinated and arrive without a negative COVID-19 test will be required to book a minimum 5-day stay in an approved hotel, quarantine, and get tested with a PCR test on day 5 of their trip. Alternatively, unvaccinated travelers may skip quarantine and travel freely throughout Thailand if they arrive in the country with a negative COVID-19 PCR test taken within 72 hours of their trip.
All travelers to Thailand must still register for a Thailand Pass online and obtain an insurance policy with a minimum coverage of $10,000, which is less than the previous requirement of $20,000.
Before May 1, vaccinated international visitors must pay for at least one night in a government-approved hotel, take a PCR test upon arrival, take a rapid antigen self-test on day 5 of their trip, and obtain an insurance policy with at least $20,000 in coverage. Thailand eliminated the pre-arrival test for vaccinated travelers earlier this month.
Thailand first started welcoming international tourists quarantine-free as part of its Phuket Sandbox program in July 2021, but required them to remain on the island. In November, Thailand then allowed tourists to visit the rest of the country quarantine-free , but tightened border restrictions again in December amid the emergence of the omicron variant.
In February, the country once again brought back its "Test & Go Thailand Pass" program , allowing vaccinated international visitors to travel to any part of the country and skip quarantine.
Thailand joins several other countries around the world in eliminating pandemic-related measures for vaccinated visitors, including Canada and Australia , which each dropped pre-arrival testing for vaccinated travelers. Some destinations have taken it even further, eliminating pandemic-era travel rules altogether, regardless of vaccination status, including Iceland , Ireland , the United Kingdom , and Aruba .
Alison Fox is a contributing writer for Travel Leisure. When she's not in New York City, she likes to spend her time at the beach or exploring new destinations and hopes to visit every country in the world. Follow her adventures on Instagram .
Related Articles
Thailand loosens entry restrictions as omicron worries ease
BANGKOK – Thailand will ease entry requirements for vaccinated visitors from all countries next month as concerns about the omicron variant of the coronavirus decline, officials said Thursday.
The country's tourism-dominated economy was devastated by travel restrictions imposed in 2020 to fight the spread of coronavirus. The number of foreign tourists has remained low despite a relaxation of the restrictions last year.
Fully vaccinated travelers will be able to enter the country under the "Test and Go" program if they undergo an RT-PCR test on arrival and spend a night in a pre-booked hotel while awaiting results, and then have a second test and hotel stay five days later. The visitor is responsible for the costs of the tests and hotels.
Visitors must also download a tracking app.
►Traveling to Hawaii?: You might soon need a COVID booster to bypass testing or quarantine.
Learn more: Best travel insurance
►Free COVID-19 tests are on their way: Will they work for travel?
An earlier "Test and Go" program with a single RT-PCR test was introduced in November as virus cases declined in Thailand and vaccination rates surged, but was suspended in December after the omicron variant was judged a threat.
The scheduled Feb. 1 revival of the program, with the addition of the second test, was announced Thursday after a meeting of the government's Center for COVID-19 Situation Administration chaired by Prime Minister Prayuth Chan-Ocha.
"The country will benefit from both Thai and foreign visitors as well as investors who help stimulate the economy," center spokesperson Taweesin Visanuyothin said.
The center also agreed to ease COVID-19 prevention measures in 25 provinces that have had tight restrictions.
Prayuth said on his Facebook page that the actions were taken in response to a better-than-expected situation with the omicron variant, and to promote economic recovery while maintaining health safety.
The government also currently allows entry to visitors who quarantine for seven to 10 days in approved hotels or join "sandbox" programs in areas such as the resort island of Phuket where they have freedom of movement during a seven-day quarantine period.
Thailand reported 8,129 new COVID-19 cases and 19 deaths on Thursday, bringing its total confirmed cases to 2,353,062 and related deaths to 21,987.
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Section 2 - Interactions Between Travel Vaccines & Drugs
- Section 2 - Travelers’ Diarrhea
Yellow Fever Vaccine & Malaria Prevention Information, by Country
Cdc yellow book 2024.
Author(s): Mark Gershman, Rhett Stoney (Yellow Fever) Holly Biggs, Kathrine Tan (Malaria)
The following pages present country-specific information on yellow fever (YF) vaccine requirements and recommendations, and malaria transmission information and prevention recommendations. Country-specific maps are included to aid in interpreting the information. The information in this chapter was accurate at the time of publication; however, it is subject to change at any time due to changes in disease transmission or, in the case of YF, changing entry requirements for travelers. Updated information reflecting changes since publication can be found in the online version of this book and on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Travelers’ Health website. Recommendations for prevention of other travel-associated illnesses can also be found on the CDC Travelers’ Health website .
Yellow Fever Vaccine
Entry requirements.
Entry requirements for proof of YF vaccination under the International Health Regulations (IHR) differ from CDC’s YF vaccination recommendations. Under the IHR, countries are permitted to establish YF vaccine entry requirements to prevent the importation and transmission of YF virus within their boundaries. Certain countries require proof of vaccination from travelers arriving from all countries ( Table 5-25 ); some countries require proof of vaccination only for travelers above a certain age coming from countries with risk for YF virus transmission. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines areas with risk for YF virus transmission as countries or areas where YF virus activity has been reported currently or in the past, and where vectors and animal reservoirs exist.
Unless issued a medical waiver by a yellow fever vaccine provider, travelers must comply with entry requirements for proof of vaccination against YF.
WHO publishes a list of YF vaccine country entry requirements and recommendations for international travelers approximately annually. But because entry requirements are subject to change at any time, health care professionals and travelers should refer to the online version of this book and the CDC Travelers’ Health website for any updates before departure.
CDC Recommendations
CDC’s YF vaccine recommendations are guidance intended to protect travelers from acquiring YF virus infections during international travel. These recommendations are based on a classification system for destination-specific risk for YF virus transmission: endemic, transitional, low potential for exposure, and no risk ( Table 2-08 ). CDC recommends YF vaccination for travel to areas classified as having endemic or transitional risk (Maps 5-10 and 5-11 ). Because of changes in YF virus circulation, however, recommendations can change; therefore, before departure, travelers and clinicians should check CDC’s destination pages for up-to-date YF vaccine information.
Duration of Protection
In 2015, the US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices published a recommendation that 1 dose of YF vaccine provides long-lasting protection and is adequate for most travelers. The recommendation also identifies specific groups of travelers who should receive additional doses, and others for whom additional doses should be considered (see Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 26, Yellow Fever ). In July 2016, WHO officially amended the IHR to stipulate that a completed International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis is valid for the lifetime of the vaccinee, and YF vaccine booster doses are not necessary. Moreover, countries cannot require proof of revaccination (booster) against YF as a condition of entry, even if the traveler’s last vaccination was >10 years ago.
Ultimately, when deciding whether to vaccinate travelers, clinicians should take into account destination-specific risks for YF virus infection, and individual risk factors (e.g., age, immune status) for serious YF vaccine–associated adverse events, in the context of the entry requirements. See Sec. 5, Part 2, Ch. 26, Yellow Fever , for a full discussion of YF disease and vaccination guidance.

Table 2-08 Yellow fever (YF) vaccine recommendation categories 1
Malaria prevention.
The following recommendations to protect travelers from malaria were developed using the best available data from multiple sources. Countries are not required to submit malaria surveillance data to CDC. On an ongoing basis, CDC actively solicits data from multiple sources, including WHO (main and regional offices); national malaria control programs; international organizations; CDC overseas offices; US military; academic, research, and aid organizations; and the published scientific literature. The reliability and accuracy of those data are also assessed.
If the information is available, trends in malaria incidence and other data are considered in the context of malaria control activities within a given country or other mitigating factors (e.g., natural disasters, wars, the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic) that can affect the ability to control malaria or accurately count and report it. Factors such as the volume of travel to that country and the number of acquired cases reported in the US surveillance system are also examined. In developing its recommendations, CDC considers areas within countries where malaria transmission occurs, substantial occurrences of antimalarial drug resistance, the proportions of species present, and the available malaria prophylaxis options.
Clinicians should use these recommendations in conjunction with an individual risk assessment and consider not only the destination but also the detailed itinerary, including specific cities, types of accommodations, season, and style of travel, as well as special health conditions (e.g., pregnancy). Several medications are available for malaria prophylaxis. When deciding which drug to use, consider the itinerary and length of trip, travelers’ previous adverse reactions to antimalarials, drug allergies, medical history, and drug costs. For a thorough discussion of malaria and guidance for prophylaxis, see Sec. 5, Part 3, Ch. 16, Malaria .
Entry requirements : Required for travelers ≥9 months old arriving from countries with risk for YF virus transmission; this includes >12-hour airport transits or layovers in countries with risk for YF virus transmission. 1
CDC recommendations : Not recommended
- Primarily the provinces that border Burma, Cambodia (few cases in Buri Ram Province), and Malaysia (few cases in Satun Province) Also, the provinces of Phitsanulok and Ubon Ratchathani (bordering Laos), and Surat Thani (especially in the rural forest and forest-fringe areas of these provinces)
- Rare to few cases in other parts of Thailand, including the cities of Bangkok (the capital), Chiang Mai, and Chiang Rai, or on the islands of Koh Pha Ngan, Koh Samui, or Phuket
- No malaria transmission on the islands of Krabi Province (Ko Lanta, Koh Phi, Koh Yao Noi, Koh Yao Yai) or in Pattaya City
- Chloroquine and mefloquine
- P. vivax (80%)
- P. falciparum (<20%)
- P. knowlesi 6 , P. malariae , and P. ovale (rare)
- Provinces that border Burma, Cambodia (except Buri Ram Province), and Malaysia (except Satun Province); the provinces of Phitsanulok, Ubon Ratchathani, and Surat Thani: Atovaquone-proguanil, doxycycline, tafenoquine 3
- All other areas with malaria transmission (including the provinces of Buri Ram and Satun): No chemoprophylaxis recommended (insect bite precautions and mosquito avoidance only) 4
Related Maps
Map 2-16 malaria prevention in thailand, other vaccines to consider.
See Health Information for Travelers to Thailand .
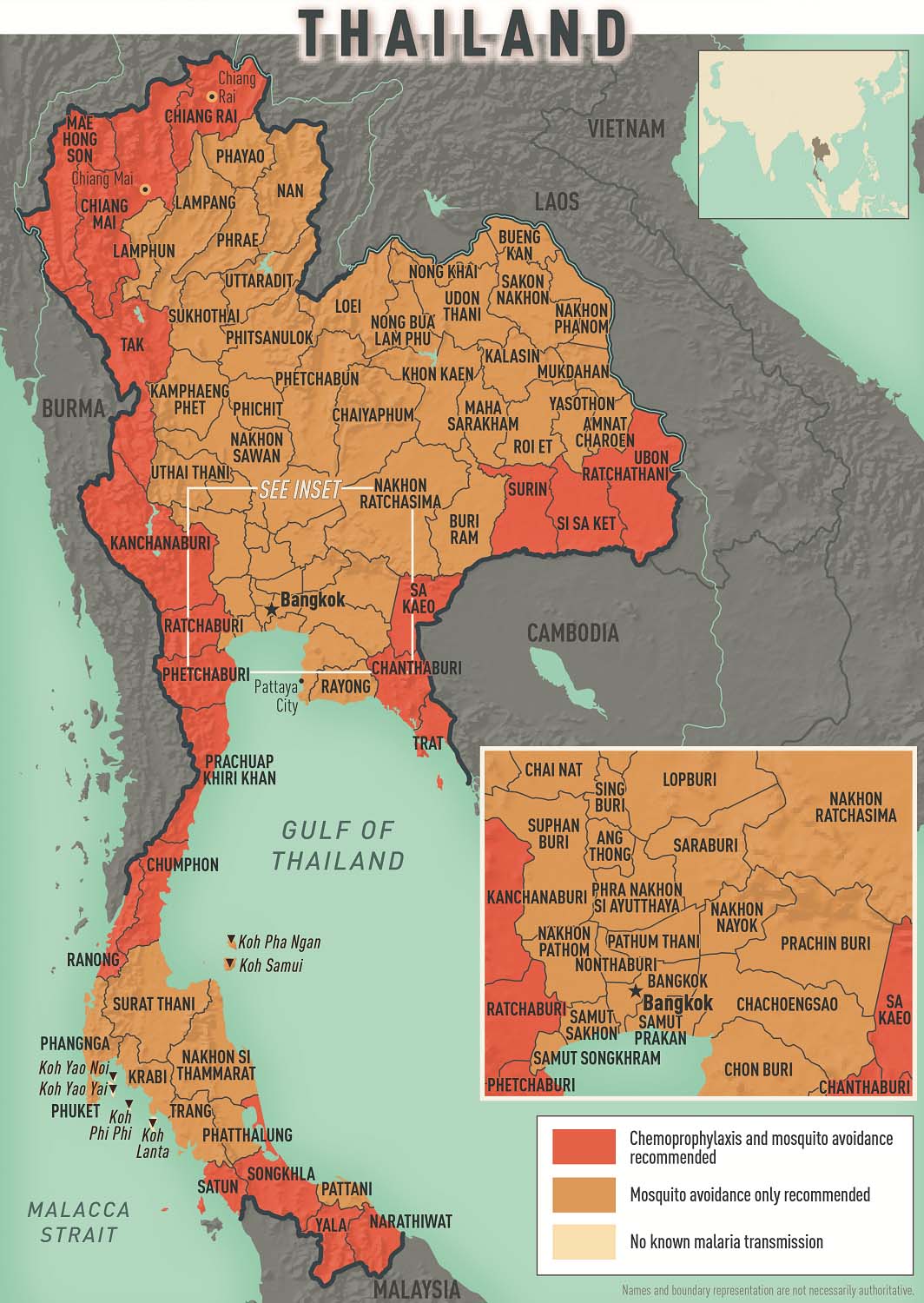
View Larger
1 Current as of November 2022. This is an update of the 2010 map created by the Informal WHO Working Group on the Geographic Risk of Yellow Fever.
2 Refers to Plasmodium falciparum malaria, unless otherwise noted.
3 Tafenoquine can cause potentially life-threatening hemolysis in people with glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. Rule out G6PD deficiency with a quantitative laboratory test before prescribing tafenoquine to patients.
4 Mosquito avoidance includes applying topical mosquito repellant, sleeping under an insecticide-treated mosquito net, and wearing protective clothing (e.g., long pants and socks, long-sleeve shirt). For additional details on insect bite precautions, see Sec. 4, Ch. 6, Mosquitoes, Ticks & Other Arthropods.
5 Primaquine can cause potentially life-threatening hemolysis in people with G6PD deficiency. Rule out G6PD deficiency with a quantitative laboratory test before prescribing primaquine to patients.
6 P. knowlesi is a malaria species with a simian (macaque) host. Human cases have been reported from most countries in Southwest Asia and are associated with activities in forest or forest-fringe areas. P. knowlesi has no known resistance to antimalarials.
Yellow Fever Maps
2 In 2017, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) expanded its YF vaccination recommendations for travelers going to Brazil because of a large YF outbreak in multiple states in that country. Please refer to the CDC Travelers’ Health website for more information and updated recommendations.
3 YF vaccination is generally not recommended for travel to areas where the potential for YF virus exposure is low. Vaccination might be considered, however, for a small subset of travelers going to these areas who are at increased risk for exposure to YF virus due to prolonged travel, heavy exposure to mosquitoes, or inability to avoid mosquito bites. Factors to consider when deciding whether to vaccinate a traveler include destination-specific and travel-associated risks for YF virus infection; individual, underlying risk factors for having a serious YF vaccine–associated adverse event; and destination entry requirements.
The following authors contributed to the previous version of this chapter: Mark D. Gershman, Emily S. Jentes, Rhett J. Stoney (Yellow Fever) Kathrine R. Tan, Paul M. Arguin (Malaria)
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Symptoms and Complications
- How It Spreads
- Plan for Travel
- Measles Cases and Outbreaks
- Measles Resources
- Clinical Overview
- For Health Departments
- Lab Testing
Clinical Overview of Measles
- Measles is one of the most contagious diseases. MMR vaccine provides the best protection.
- Isolate infected patients for 4 days after they develop a rash and follow airborne precautions in healthcare settings.
- Report suspected measles cases to your local health department.
- Laboratory confirmation is essential for all sporadic measles cases and all outbreaks.
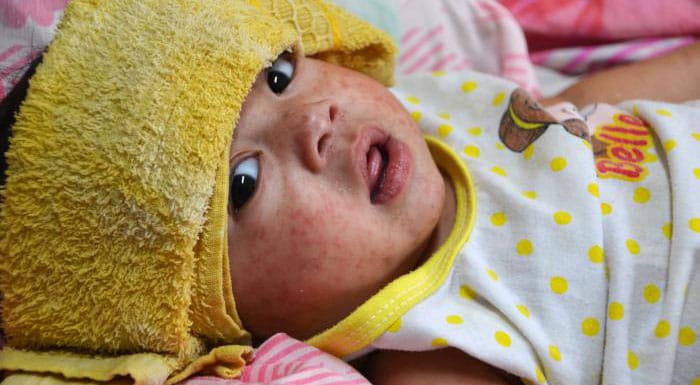
Clinical features
Measles is an acute viral respiratory illness. It is characterized by:
- A prodrome of fever (as high as 105°F), malaise, and cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis (three "C"s)
- A pathognomonic enanthema (Koplik spots)
- Followed by a maculopapular rash
The rash usually appears about 14 days after a person is exposed. The rash spreads from the head to the trunk to the lower extremities.
Patients are considered to be contagious from 4 days before to 4 days after the rash appears. Sometimes immunocompromised patients do not develop the rash.
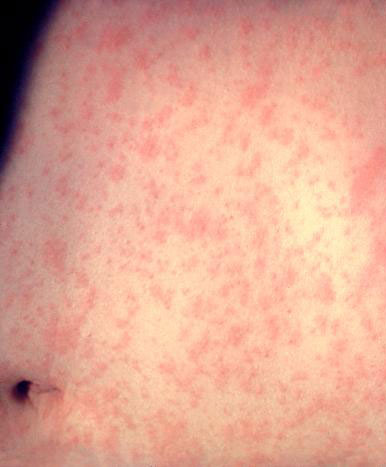
Photos of Measles
Measles is caused by a single-stranded, enveloped RNA virus with 1 serotype. It is classified as a member of the genus Morbillivirus in the Paramyxoviridae family. Humans are the only natural hosts of measles virus.
How it spreads
Measles is one of the most contagious of all infectious diseases. Up to 9 out of 10 susceptible people with close contact to a measles patient will develop measles.
The virus is transmitted by:
- Direct contact with infectious droplets.
- Airborne spread when an infected person breathes, coughs, or sneezes.
Measles virus can remain infectious in the air for up to 2 hours after an infected person leaves an area.
Disease rates
Prior to vaccination introduction:
The live measles vaccine was licensed in 1963. In the decade before, an average of 549,000 measles cases and 495 measles deaths were reported annually in the United States. However, it is likely that 3 to 4 million people on average were infected with measles annually; most cases were not reported. Of the reported cases, approximately:
- 48,000 people were hospitalized from measles.
- 1,000 people developed chronic disability from acute encephalitis caused by measles annually.
Post-vaccine era:
In 2000, measles was declared eliminated from the United States. However, cases and outbreaks still occur every year in the United States. This is because measles is still commonly transmitted in other countries in Europe, the Middle East, Asia, the Americas, and Africa.
Since 2000, the annual number of cases has ranged from a low of 37 in 2004; to a high of 1,282 in 2019. The majority of cases in the United States have been among people who are not vaccinated against measles.
Measles vaccination
Measles can be prevented with measles-containing vaccine, which is primarily administered as the combination measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. The combination measles-mumps-rubella-varicella (MMRV) vaccine can be used for children aged 12 months through 12 years for protection against all four viruses. Single-antigen measles vaccine is not available.
- One dose of MMR vaccine is approximately 93% effective at preventing measles.
- Two doses are approximately 97% effective.
Almost everyone who does not respond to the measles component of the first dose of MMR vaccine at age 12 months or older will respond to the second dose. Therefore, the second dose of MMR is administered to address primary vaccine failure. 1
Administration recommendations
For children:
CDC recommends routine childhood immunization for MMR vaccine starting with the first dose at 12 through 15 months of age, and the second dose at 4 through 6 years of age or at least 28 days following the first dose.
The MMRV vaccine is also available to children 12 months through 12 years of age; the minimum interval between doses is three months.
For students:
Students at post-high school educational institutions without evidence of measles immunity need two doses of MMR vaccine, with the second dose administered no earlier than 28 days after the first dose.
For international travelers:
People 6 months of age or older who will be traveling internationally should be protected against measles. Before traveling internationally,
- Infants 6 through 11 months of age should receive one dose of MMR vaccine. A
- Children 12 months of age or older should have documentation of two doses of MMR vaccine (the first dose of MMR vaccine should be administered at age 12 months or older; the second dose no earlier than 28 days after the first dose). B
- Teenagers and adults born during or after 1957 without evidence of immunity against measles should have documentation of two doses of MMR vaccine, with the second dose administered no earlier than 28 days after the first dose.
For healthcare personnel:
Healthcare personnel should have documented evidence of immunity against measles, according to the ACIP recommendations for immunizing personnel.
For adults:
People who are born during or after 1957 who do not have evidence of immunity against measles should get at least one dose of MMR vaccine.
Some people should not get MMR or MMRV vaccine.
MMR Vaccine Information for Healthcare Providers
Who Should NOT Get Vaccinated with MMR
Prevention in healthcare settings
While the most important measure to prevent measles transmission in all settings is ensuring community immunization, core measles prevention in healthcare settings requires a multi-faceted approach.
Diagnosis and laboratory testing
Testing recommendations for measles.
Consider measles in patients presenting with febrile rash illness and clinically compatible measles symptoms, especially if they recently traveled internationally; or were exposed to a person with febrile rash illness. Healthcare providers are required to report suspected measles cases to their local health department.
Laboratory confirmation is essential for all sporadic measles cases and all outbreaks. The most common methods for confirming measles infection are:
- Detection of measles-specific IgM antibody in serum.
- Measles RNA by RT-PCR in a respiratory specimen.
Obtain both a serum sample and a throat swab (or nasopharyngeal swab) from patients suspected to have measles at first contact with them. Urine samples may also contain virus. When feasible to do so, collecting both respiratory and urine samples can increase the likelihood of detecting measles virus.
Molecular analysis can also be conducted to determine the genotype of the measles virus. Genotyping is used to map the transmission pathways of measles viruses. The genetic data can help to link or unlink cases and can suggest a source for imported cases. Genotyping is the only way to distinguish between wild-type measles virus infection and a rash caused by a recent measles vaccination.
Patient management
There is no specific antiviral therapy for measles. Medical care is supportive and to help relieve symptoms and address complications such as bacterial infections.
For severe measles
Severe measles cases among children, such as those who are hospitalized, should be treated with vitamin A. Vitamin A should be administered immediately on diagnosis and repeated the next day. The recommended age-specific daily doses are:
- 50,000 IU for infants younger than 6 months of age
- 100,000 IU for infants 6–11 months of age
- 200,000 IU for children 12 months of age and older
World Health Organization: Measles and Vitamin A Guidance
Red Book: Measles
Infected people should be isolated for 4 days after they develop a rash; airborne precautions should be followed in healthcare settings. Because of the possibility (albeit low) of MMR vaccine failure in healthcare providers exposed to infected patients, providers should observe airborne precautions in caring for patients with measles.
The preferred placement for patients who require airborne precautions is in a single-patient airborne infection isolation room (AIIR). Regardless of presumptive immunity status, all healthcare staff entering the room should use respiratory protection consistent with airborne infection control precautions. This includes use of an N95 respirator or a respirator with similar effectiveness in preventing airborne transmission.
Evidence of immunity
Acceptable presumptive evidence of immunity against measles includes at least one of the following:
- Written documentation of adequate vaccination:
- One or more doses of a measles-containing vaccine administered on or after the first birthday for preschool-age children and adults not at high risk
- Two doses of measles-containing vaccine for school-age children and adults at high risk, including college students, healthcare personnel, and international travelers
- Laboratory evidence of immunity A
- Laboratory confirmation of measles
- Birth before 1957
Healthcare providers and health departments should not accept verbal reports of vaccination without written documentation as presumptive evidence of immunity.
Post-exposure prophylaxis
People exposed to measles who cannot readily show that they have evidence of immunity against measles should be offered post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP).
To potentially provide protection or modify the clinical course of disease among susceptible persons, administer one of these:
- MMR vaccine within 72 hours of initial measles exposure.
- Immunoglobulin (IG) within 6 days of exposure.
Do not administer MMR vaccine and IG simultaneously, as this practice invalidates the vaccine.
Please refer to the following references for additional information on post-exposure prophylaxis:
ACIP Recommendations: Prevention of Measles, Rubella, Congenital Rubella Syndrome, and Mumps (2013)
ACIP General Recommendations on Immunization (2011)
Complications
Common complications from measles include otitis media, bronchopneumonia, laryngotracheobronchitis, and diarrhea.
Even in previously healthy children, measles can cause serious illness requiring hospitalization.
- 1 out of every 1,000 measles cases will develop acute encephalitis, which often results in permanent brain damage.
- 1 to 3 out of every 1,000 children who become infected with measles will die from respiratory and neurologic complications.
- Behavioral and intellectual deterioration.
- Seizures that generally develop 7 to 10 years after measles infection.
Who is at risk
People at high risk for complications include:
- Infants and children aged <5 years
- Adults aged >20 years
- Pregnant people
- People with weakened immune systems, such as from leukemia and HIV infection
Measles importation and outbreaks
Measles cases occur as a result of importations by people who were infected while in other countries; and from subsequent transmission that may occur from those importations. Measles is more likely to spread and cause outbreaks in communities where groups of people are unvaccinated.
Outbreaks in countries to which Americans often travel can directly contribute to an increase in measles cases in the United States. In recent years, measles importations have come from frequently visited countries and countries where large outbreaks were reported. These include but not limited to the Philippines, Ukraine, Israel, Thailand, Vietnam, England, France, Germany, and India.
International travelers
Resources and tools, measles update.
Be on Alert for Travel-Related Measles | AMA Ed Hub
Testing tools
Measles is a mandatory, immediately notifiable disease., webinars & trainings.
We Must Maintain Measles Elimination in the United States: Measles Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Prevention (presented August 17, 2023)
PowerPoint presentations
An Introduction to Measles
Clinical Factsheets

Measles Clinical Diagnosis Fact Sheet
Measles Clinical Features and Diagnosis
Cdc expert commentary.
Measles in the US: 5 Things to Know | Medscape
- Infants who get one dose of MMR vaccine before their first birthday should get two more doses according to the routinely recommended schedule (one dose at 12 through 15 months of age and another dose at 4 through 6 years of age or at least 28 days later).
- The measles-mumps-rubella-varicella (MMRV) vaccine is also available to children 12 months through 12 years of age. If used in place of MMR vaccine, the first dose should be administered at age 12 months or older, and the second dose no earlier than three months after the first dose. MMRV should not be administered to anyone older than 12 years of age.
- CDC. Prevention of Measles, Rubella, Congenital Rubella Syndrome, and Mumps, 2013: Summary Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) . MMWR 2013;62(RR04);1-34.
- Siegel JD, Rhinehart E, Jackson M, Chiarello L, and the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee, 2007 Guidelines for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings .
Measles (Rubeola)
Measles is one of the most contagious diseases and can be dangerous in babies and young children. The best protection against measles is the MMR vaccine.
For Everyone
Health care providers, public health.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6-11 months, according to CDC's measles vaccination recommendations for international travel. Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book. Rabies: Rabid dogs are commonly found in Thailand.
Review the Country Security Report for Thailand. Have evacuation plans that do not rely on U.S. government assistance. Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel. Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler's Checklist. Yala, Pattani, Narathiwat, and Songkhla Provinces ...
Thailand Information and Travel Advisory page from travel.state.gov. CDC page on COVID-19; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Travel Recommendations by Country. Enroll in Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive health updates from the American Citizens Services unit in Thailand.
Trek through mountainous regions, explore archaeological sites and discover a diverse wildlife system when you visit Thailand. Be sure to visit the experts at UH Roe Green Center for Travel Medicine & Global Health to get your CDC travel immunizations and booster shots before your trip.
Bangkok CNN —. Thailand has relaxed its quarantine restrictions and is reopening to vaccinated travelers arriving from several dozen countries and territories, providing a much-needed boost for ...
Health Alert: U.S. Embassy Bangkok, Thailand (December 5, 2021) Location: Thailand. Event: On December 6, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) will implement a one-day COVID-19 testing requirement for travelers over age two coming to the United States. Regardless of vaccination status or nationality, any individual coming to the United States must show a negative pre-departure ...
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
All travelers to Thailand must still register for a Thailand Pass online and obtain an insurance policy with a minimum coverage of $10,000, which is less than the previous requirement of $20,000.
Fully vaccinated travelers will be able to enter under the "Test and Go" program if they take a RT-PCR test on arrival and spend a night in a hotel. ... Thailand reported 8,129 new COVID-19 cases ...
Telephone: +66 053 107 700. +66 2 205 4000 (after hours) Email: [email protected]. State Department - Consular Affairs. 888-407-4747 or 202-501-4444. Thailand Country Information. Enroll in Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts.
CDC Yellow Book 2024. Preparing International Travelers. Author (s): Mark Gershman, Rhett Stoney (Yellow Fever) Holly Biggs, Kathrine Tan (Malaria) The following pages present country-specific information on yellow fever (YF) vaccine requirements and recommendations, and malaria transmission information and prevention recommendations.
For more health recommendations for international travel, visit the CDC Yellow Book. Every year, millions of US residents travel to countries where malaria is present. About 2,000 cases of malaria are diagnosed in the United States annually, mostly in returned travelers. Travelers to sub-Saharan Africa have the greatest risk of both getting ...
Protect your child and family when traveling in the United States or abroad by: Getting the shots required for all countries you and your family plan to visit during your trip. Making sure you and your family are up-to-date on all routine U.S. vaccines. Staying informed about travel notices and alerts and how they can affect your family's ...
You should plan to be fully vaccinated at least 2 weeks before you depart. If your trip is less than 2 weeks away and you're not protected against measles, you should still get a dose of the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine. The MMR vaccine protects against all 3 diseases. Two doses of MMR vaccine provide 97% protection against measles.
Clinical features. Measles is an acute viral respiratory illness. It is characterized by: A prodrome of fever (as high as 105°F), malaise, and cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis (three "C"s) A pathognomonic enanthema (Koplik spots) Followed by a maculopapular rash. The rash usually appears about 14 days after a person is exposed.