
- Circuit Breakers
- Connecticut Electric
- Crouse-Hinds Cooper
- Eaton Cutler Hammer
- Federal Pacific
- Thomas Betts
- Westinghouse

Motor Controls
- Allen Bradley
- Appleton Electric
- Cutler Hammer
- E.M. & Wiegmann
- Joslyn Clark
- Killark Electric
- Moeller Electric
- NSI Industries
Transformers
- Dongan Electric
- Hammond Power

Absolutely Everything You Need to Know About a Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breaker
- 24 Jan, 2018
- Posted by: Circuit Breaker Wholesale
Do you know how a thermal magnetic circuit breaker works?
If not, it’s worth finding out as these popular options are probably going to be the best bet for your home or building.
How a Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breaker Works
Despite the name, it’s actually fairly easy to understand how a thermal magnetic circuit breaker works. You just have to understand how two other versions operate first.
How a Magnetic Circuit Breaker Works
The main difference between these two circuit breakers comes down to what makes them trip. In other words, the difference is in how they protect the home/building’s wiring.
In a magnetic circuit breaker , this is done with an electromagnet.
When an acceptable amount of current is throwing through the breaker, the electromagnet is unaffected. It’s calibrated to move the trip bar when sufficient magnetic force – via a strong enough current – is present.
As the current increases through the coil, it could eventually reach a threshold where it becomes powerful enough to pull the trip bar toward the electromagnet. This would open the contacts and stop the current.
In doing so, it prevents significant damage from occurring – including a fire.
Magnetic circuit breakers shut down immediately when the current becomes too powerful. The moment the magnetic current becomes strong enough, it automatically pulls the trip bar.
How a Thermal Circuit Breaker Works
A thermal circuit breaker accomplishes the same thing by using a bimetallic strip.
Again, as the current builds in power, it becomes hotter and hotter.
At some point, the temperature reaches a predetermined threshold for the breaker and actually damages the bimetallic strip to the point that it gives and breaks the connection.
Fortunately, when it cools down, the strip is able to be reset and normal operation can continue.
Unlike the magnetic version, a thermal circuit breaker works on a time delay. The heat must build until it is able to deform the strip enough to shut down operation.
As the name suggests, a thermal magnetic circuit breaker works by combining the two versions above.
It essentially leverages both forms to protect the conductors and other elements connected to the circuit breaker from the dangers of excessive current.
The main advantage of how a thermal magnetic circuit breaker works is that it gives you both instantaneous and time-delayed protection.
Instantaneous protection is good for interrupting currents that are extremely powerful but not part of normal operation, like line-line faults, line-ground faults, and short circuits. They must be interrupted right away or they could become dangerous, even fatal.
So why would you ever want a delayed response?
Some pieces of electrical equipment temporarily draw currents that exceed their rated values. This is part of their normal operation. Examples of this type of equipment include electric motors and HID lamps.
When started, they can pull extremely high inrush currents.
A magnetic circuit breaker would not allow this initial requirement, so these devices wouldn’t work.
Choose a Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breaker
The advantages of relying on a thermal magnetic circuit breaker should be fairly obvious. In short, they will keep your home or building safe without limiting the types of devices you can use. Given their popularity, you’ll also have no problem finding one that fits your unique needs.
- Air Conditioning
- Electrician
- Garage Door Installation
- Garage Door Repair
- Heating & Furnace
- HVAC Contractors
- Landscaping
- Pest Control
- Experiences
- Homeowner Login
- Join As a Pro
What Are Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breakers?
Are you looking to hire a:.
- Carpentry Pro
- Landscaping Pro
- Plumbing Pro
- Remodeling Pro
- Roofing Pro
- HVAC Contractors Pro

Pretty much everyone is familiar with the effect of a tripped breaker in the home. Suddenly, you have no electrical power in one or more outlets and you’re forced to head down to the basement or out to the garage to switch the electrical panel back on. This usually happens when too many appliances are plugged into one outlet or connected to the same electrical circuit. That’s what triggers the circuit breaker to kick in and protect you from potential electrical hazards.
But what is a circuit breaker exactly and why is it so important in your home? Let’s take a closer look.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
We’ll start by clearing up the difference between a circuit breaker’s function and its purpose . 1. Circuit Breaker Function. The function of an electrical circuit breaker is to “break” (that is, to discontinue) a circuit of electricity. It does this automatically when it detects:
* an electrical overload -- The power demand on one of the circuits is beyond its capacity, usually because you’ve got too many items plugged in at the same time.
* a short circuit – An electrical circuit is accidentally shortened when a live wire comes in contact with another part of the circuit (usually due to faulty insulation) and takes the path of least resistance. This can result in an electrical charge in an unexpected location ... for example, a light switch.
Once the electrical issue has been resolved, the circuit breaker can then be manually or automatically set to restart the flow of electricity.
2. Circuit Breaker Purpose . The purpose of the circuit breaker is to prevent damage from occurring. An overtaxed or malfunctioning electrical system can do a lot of harm to home appliances and electronics. Much more seriously, it can endanger you and your household, with the risk of electric shock, electrocution, or electrical fire .
Circuit breakers come in varying sizes and types and may be used to protect everything from household appliances and electronic devices to high-voltage circuits which service entire cities.
Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breaker Definition
In American homes today, thermal magnetic circuit breakers are the most common type. These are circuit breakers which utilize two components to detect electrical faults.
The first component is an electromagnet that is sensitive to large surges in electrical currents. Electrical surges can cause short-circuiting, which may seriously damage your valuable electrical appliances (such as a clothes dryer or an air conditioner) or large electronics (think DVD player or desktop computer). The electromagnet responds instantly to such dangerous situations by shutting off the flow of electricity so that your appliances are protected.
The second component used in a thermal magnetic circuit breaker is a thermal bimetallic strip that responds to prolonged low-level electrical surges or overloads of electrical currents. Excessive electrical currents will heat the bimetallic strip enough to bend it towards a trip bar that turns the circuit off.
Thermal magnetic circuit breakers are popular because they can quickly limit short-circuiting and then restart the flow of electricity when the surge has passed.
Circuit Breaker Safety
- Set thermal magnetic circuit breakers according to the manufacturer’s directions for safe and effective functioning.
- Limit electrical power usage to prevent stressing your circuits. (Fringe Benefit: This tip saves money on your utility bills, as well.) Try to keep heavy-consumption electrical devices, like space heaters , irons, toaster ovens, and hair dryers, on different circuits. Avoid overloading the system with multi-outlet extension cords. If at all possible, turn off appliances and electronics when not in use.
- Install GFCI (ground fault circuit interrupter outlets ) and test them monthly.
- Rethink your existing electrical system if you have frequent tripped breaker problems. Call a licensed electrician to assess the system and make any necessary upgrades.
Related Articles

Looking for a Pro? Call us at (866) 441-6648

Electrical Average Costs
- Replace Knob and Tube Wiring $6,625
- Upgrade an Electrical Panel $1,264
- Install a GFCI Outlet $190
Electricians Experiences

Pool Wiring Repair Eliminates A Potential Hazard

Look To Your Electrician For Advice On The Best Lighting System

Ceiling Fan Replacement By A Fast, Knowledgeable And Reasonable Electrician
Top cities covered by our electricians.
- Service Needed Select Service Needed Additions / Remodels / Major Renovations Air Conditioning & Heating Appliances Asphalt Paving Builders (New Home) Carpentry, Decks & Porches Carpet - Install / Clean Cleaning Services Concrete, Brick & Stone Countertops - Install / Repairs Doors Driveways, Patios, Walks, Floors Drywall Electrical / Generators Fences Flooring Garage - Build/Remodel Garage Doors, Openers Gutters Handyman Services Heating & Cooling Home Security Insulation Landscaping & Lawn Care Major Renovations Painting & Staining Pest Control / Termites Plumbing / Water Heaters / Gas Piping Recovery Services (Water, Fire, Etc) Roofing Septic System Services Siding Tile & Stone Tree Removal And Trimming Windows Other / Miscellaneous
Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breakers
Last time, one of the member of the community named Nasir told us about “Magnetic Circuit Breakers”. Today, he continues his tutorial series by telling us about another type of Circuit Breakers.
Remember you can send us articles of testimonies too by sending a mail to the team!
Thermal magnetic circuit breakers are just an advance form of the Magnetic Circuit Breakers we have studied before. The difference lays in the fact that Magnetic circuit breakers have a single mechanism which operates on a solenoid or an electromagnet, and the circuit trips when the magnetic field of the magnet becomes strong enough due to excessive current flowing in the circuit.
So first studying the basic principle of operation of a thermal magnetic circuit breakers which is that when excessive current flows through the circuit the heat sensing elements attached to the trip unit heat up and opens the contacts so that the flow of current is stopped immediately, preventing the circuit from damaging.
A thermal magnetic circuit breaker is shown in the figure below:
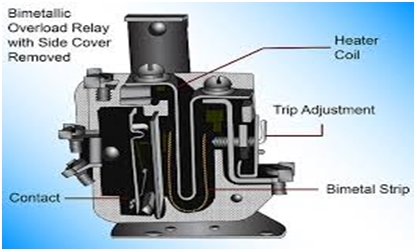
A thermal magnetic circuit breaker has two tripping mechanisms, on which the unit operates. These are:
- A bimetallic Switch
- An Electromagnet
Bimetal Switch
In this case, a bimetallic switch is attached to the trip unit of the circuit breaker. It acts as a heat sensor.
In case of some faulty wiring or another problem when an abnormally large amount of current tries to flow through the circuit, it first passes through the bimetal switch attached to the trip unit, as it is also a path of the circuit through which the current has to flow.
The bimetal switch heats up due to this large amount of current. Due to this heating, the bimetal switch bends and touches the trip bar on which it is mounted. This contact causes the trip bar to rotate, thus opening its contact with the circuit ahead. In this way the flow of current is stopped.
When the safe amount of current is restored, the switch cools down instantaneously and the contact of the trip unit with the circuit ahead is restored allowing the current to flow safely.

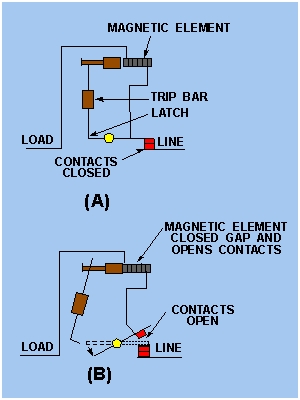
Electromagnet
In case of an electromagnet, a wire is wound on an iron core, thus forming an Electromagnet When a large amount of current tries to flow through the circuit the electromagnet starts generating a very strong magnetic field, whose value is directly proportional to the amount of the current.
This strong magnetic field has enough strength to attract the nearby armature, which then tries to move towards the electromagnet, touching the trip unit on its way.
When the trip unit comes in contact with the armature, it rotates in the same way as above, and hence its contact opens with the external circuit. When the value of current reduces and comes back to the safe value, the magnetic field also decreases and the original contact is maintained.
This mechanism is shown in the figure below:
Thermal magnetic circuit breakers are used for fast switching, like in places where the current has to be limited very quickly. Their switching operation is so fast that the circuit is opened or closed in just a matter of milliseconds.
This was all about the working mechanism of Thermal Magnetic Circuit Breakers. Up till now almost all the main types of the breakers have been discussed, which are commonly used now a days. So in the next we will discuss about disconnection the circuit breakers.
A house crt. rated at 15 A. Should it trip say when the ammeter reaches 15.2 or 15.5 or 16A. If so what adjustments are available to make it trip at any particular setting? The crt. is brand new and will not trip even at 40 amps. what causes can possibly cause this mulfunction?
Is there any method can also be applied to trip the breaker, due to loose connection whereby temperature rise happening on terminal, which thermal sensor can sense and trip the particular circuit? As such all magnetic & thermal breakers Trip under O/L & S/C. conditions I agree. To protect the Cables & equipment, to prevent from Fire why not manufacturer provide this arrangement too.?
Leave a Comment X
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

TM-D Thermal-Magnetic Trip Unit for 3P and 4P Circuit Breakers from 80 A to 250 A
Introduction
The TM-D thermal-magnetic trip unit is designed to protect conductors in commercial and industrial electrical distribution.
The trip unit exists in two configurations:
Description
The adjustment dials are on the front of the trip unit:
A Setting range for the TM-D thermal-magnetic trip unit
B Adjustment dial for the thermal protection pickup Ir
C Adjustment dial for the magnetic protection pickup Im (for TM-D 200/250 only)
Setting the Thermal Protection
The thermal protection pickup Ir is set by a 4-setting dial.
Turning the thermal protection adjustment dial (A) modifies the trip curve as shown (B) .
The following table shows the values of the pickup Ir (in amperes) for thermal protection (values indicated on the dial) with respect to every trip unit rating, relative to the position of the dial Ir.
Setting the Magnetic Protection on Trip Units with In from 80 A to 160 A
For trip units rated below 200 A, the magnetic protection pickup cannot be adjusted and equals the value shown below:
Setting the Magnetic Protection on Trip Units with In from 200 A to 250 A
For trip units rated between 200 A and 250 A, the magnetic protection pickup Im is set using a 6-setting dial.
Turning the magnetic protection adjustment dial ( A) modifies the trip curve as shown (B) .
The following table shows the values of the pickup Im(in amperes) for magnetic protection (values indicated on the dial), relative to the position of the Im dial:
Example of Application
Protection of a feed with the following characteristics:
o Power supplied by a 1,250 kVA transformer - 400 V, 4%
o Protection of a distribution box located 15 m away, the loads on which are mainly for lighting (incandescent bulbs), heating, and small machines
The value of the calculated rated current (load consumption) is In = 175 A.
The following illustration shows the installation diagram:
Calculations performed on the installation in accordance with the regulations can be used to determine the characteristics of the appropriate Compact NSX circuit breaker to install (calculations performed using the Ecodialsoftware).
The following table presents the circuit breaker selection:
The following table shows the trip unit protection settings:
DOCA0140EN-01
© 2020 Schneider Electric. All rights reserved.

CBI-electric (Circuit Breaker Industries)
Purposefully differentiated.
Tel + 27 11 928 2000 Private Bag X2016, Isando 1600 1 Tripswitch Drive, Elandsfontein, Gauteng, 1401 [email protected] [email protected] (Outside Africa) [email protected] (USA) [email protected] (Australia)

Thermal-Magnetic Principles
Normal load operation, thermal (inverse time) trip mechanism..
The thermal trip mechanism operates in response to overload conditions. The mechanism includes a bimetal element located behind the trip bar. The bimetal element is part of the current carrying path. When there is an overload, the increased current flow heats the bimetal and causes it to bend. As the bimetal bends, it touches and rotates the trip bar causing the circuit breaker to trip. The time needed for the bimetal to bend and trip the circuit breaker varies inversely with the current.
Short Circuit Operation
Magnetic (instantaneous) trip mechanism..
The magnetic trip mechanism operates when there is a high current (short circuit) in the current path. The mechanism includes an electromagnet and an armature. When high level current passes through the conductor, the magnetic field strength of the electromagnet rapidly increases and attracts the armature. As the top of the armature is drawn to the electromagnet, the armature rotates the trip bar causing the circuit breaker to trip.
- The Fuchs-type thermal-magnetic circuit breakers are ideal for upstream cascading breaker systems.
- Thermal-magnetic breakers can be mounted in any position. The tripping characteristic does not change.
- Magnetic only tripping circuit breakers are available, ideally suitable for motor short circuit protection.
- Specially designed breakers for class 2 co-ordination with contactors and overload relays.
Search form
News headlines.
- SA’s Solar Power Surge Raises Safety Concerns: Seven tips for rooftop safe...
- The Silent Threat in the Workplace: Is your business safe from electrical...
- Load Shedding vs Load Curtailment: Counting the costs for industry
- Could Industrial IoT Help Combat the Costs of Illegal Power Connections?
- Johannesburg Faces Water Crisis, But Saving Electricity Could Be the Key
CBI-electric Offices
- Français - French
- 中文 - Chinese (Simplified)
- Español - Spanish (Castillian)
- Cybersecurity Safety Notice
- About the Book
- Pact Series Master Range
- ComPact NSX Range
- Operating the Circuit Breaker
- EcoStruxure Power Commission Software
- De-Energizing the Circuit Breaker
- Environmental Conditions
- Front Face Description
- Opening, Closing, and Resetting the Circuit Breaker
- Testing the Circuit Breaker
- Locking the Circuit Breaker
- Testing a Circuit Breaker With Direct Rotary Handle
- Locking a Circuit Breaker With Direct Rotary Handle
- Testing a Circuit Breaker With Extended Rotary Handle
- Locking a Circuit Breaker With Extended Rotary Handle
- Opening, Closing, and Resetting a Circuit Breaker With Motor Mechanism
- Opening, Closing, and Resetting Circuit Breakers With Communicating Motor Mechanism
- Plug-in Circuit Breaker
- Withdrawable Circuit Breaker
- Accessories
- Electrical Auxiliary Device Summary
- Indication Contacts
- Wireless Indication Auxiliary
- SDTAM Module ( MicroLogic 2 M and 6 E-M )
- 24 Vdc Power Supply Connector
- BSCM Breaker Status Control Module
- Insulated NSX Cord
- Control Auxiliaries
- PowerTag Energy M250/M630
- Applications
- Fault Currents in Electrical Distribution
- Protection Against Overcurrents in Electrical Distribution
- Protection Against Ground Faults
- Protection for Motor-Feeders
- Thermal-Magnetic Trip Unit Summary
- TM-D Thermal-Magnetic Trip Unit for 1P and 2P Circuit Breakers
- TM-D Thermal-Magnetic Trip Unit for 1P Circuit Breakers 250 A
- TM-D Thermal-Magnetic Trip Unit for 3P and 4P Circuit Breakers up to 63 A
TM-D Thermal-Magnetic Trip Unit for 3P and 4P Circuit Breakers from 80 A to 250 A
- TM-G Thermal-Magnetic Trip Unit
- MA Magnetic Trip Unit
- Earth-Leakage Protection by VigiPacT Add-on
- Characteristics of MicroLogic Electronic Trip Units
- MicroLogic 2 Electronic Trip Units
- MicroLogic 4 Electronic Trip Units
- MicroLogic 1.3 M Electronic Trip Unit
- MicroLogic 2 M Electronic Trip Unit
- MicroLogic 2 G Electronic Trip Unit
- MicroLogic 2 AB and 4 AB Electronic Trip Units
- MicroLogic Maintenance Interfaces
- Pocket Battery
- Service Interface Connected to a PC
- Stand-Alone USB Maintenance Interface
- USB Maintenance Interface Connected to a PC
- Commissioning
- Maintaining the Circuit Breaker During Operation
- Responding to a Trip
- Troubleshooting
- ComPact NSX 100-250 - Distribution Protection Tripping Curves
- ComPact NSX 100-250 - Motor-Feeder Protection Tripping Curves
- ComPact NSX 400-630 - Distribution Protection Tripping Curves
- ComPact NSX 400-630 - Motor-Feeder Protection Tripping Curves
- ComPact NSX 100-630 - Reflex Tripping
- ComPact NSX 100-630 - Limitation Curves
For the best experience of this site, please enable Javascript for the www.productinfo.schneider-electric.com domain.
Introduction
The TM-D thermal-magnetic trip unit is designed to protect conductors in commercial and industrial electrical distribution.
Description
The adjustment dials are on the front of the trip unit:
A Setting range for the TM-D thermal-magnetic trip unit
B Adjustment dial for the thermal protection pickup Ir
C Adjustment dial for the magnetic protection pickup Ii (for TM-D 200/250 only)
Setting the Thermal Protection
The thermal protection pickup Ir is set by a 4-setting dial.
Turning the thermal protection adjustment dial (A) modifies the trip curve as shown (B) .
The following table shows the values of the pickup Ir (in amperes) for thermal protection (values indicated on the dial) with respect to every trip unit rating, relative to the position of the dial Ir .
Setting the Magnetic Protection on Trip Units with In from 80 A to 160 A
For trip units rated below 200 A, the magnetic protection pickup cannot be adjusted and equals the value shown below:
Setting the Magnetic Protection on Trip Units with In from 200 A to 250 A
For trip units rated between 200 A and 250 A, the magnetic protection pickup Ii is set using a 6-setting dial.
Turning the magnetic protection adjustment dial (A) modifies the trip curve as shown (B) .
The following table shows the values of the pickup Ii (in amperes) for magnetic protection (values indicated on the dial), relative to the position of the Ii dial:
Example of Application
Power supplied by a 1,250 kVA transformer - 400 V, 4%
Protection of a distribution box located 15 m away, the loads on which are mainly for lighting (incandescent bulbs), heating, and small machines
The value of the calculated rated current (load consumption) is In = 175 A.
The following illustration shows the installation diagram:
Calculations performed on the installation in accordance with the regulations can be used to determine the characteristics of the appropriate ComPact NSX circuit breaker to install (calculations performed using the Ecostruxure Power Design – Ecodial software).
The following table presents the circuit breaker selection:
The following table shows the trip unit protection settings:
Show QR code for this page
Was this helpful?
Contact Information
Legal information.
The information provided in this document contains general descriptions, technical characteristics and/or recommendations related to products/solutions.
This document is not intended as a substitute for a detailed study or operational and site-specific development or schematic plan. It is not to be used for determining suitability or reliability of the products/solutions for specific user applications. It is the duty of any such user to perform or have any professional expert of its choice (integrator, specifier or the like) perform the appropriate and comprehensive risk analysis, evaluation and testing of the products/solutions with respect to the relevant specific application or use thereof.
The Schneider Electric brand and any trademarks of Schneider Electric SE and its subsidiaries referred to in this document are the property of Schneider Electric SE or its subsidiaries. All other brands may be trademarks of their respective owner.
This document and its content are protected under applicable copyright laws and provided for informative use only. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise), for any purpose, without the prior written permission of Schneider Electric.
Schneider Electric does not grant any right or license for commercial use of the document or its content, except for a non-exclusive and personal license to consult it on an "as is" basis.
Schneider Electric reserves the right to make changes or updates with respect to or in the content of this document or the format thereof, at any time without notice.
To the extent permitted by applicable law, no responsibility or liability is assumed by Schneider Electric and its subsidiaries for any errors or omissions in the informational content of this document, as well as any non-intended use or misuse of the content thereof.
© 2022 Schneider Electric
- Get custom product tools and services
- Access training
- Manage support cases
- Create and manage your orders (authorised partners only)
Welcome to the Schneider Electric Website
Search FAQs
How does a thermal magnetic trip unit work, released for: schneider electric new zealand.
Discuss this topic with experts
Start here!
Find answers now. Search for a solution on your own, or connect with one of our experts.
Contact Support
Reach out to our customer support team to receive more information, technical support, assistance with complaints and more.
Where to buy?
Easily find the nearest Schneider Electric distributor in your location.
Search topic-related frequently asked questions to find answers you need.
Contact Sales
Start your sales enquiry online and an expert will connect with you.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The trip unit is the part of the circuit breaker that determines when the contacts will open automatically. In a thermal-magnetic circuit breaker, the trip unit includes elements designed to sense the heat resulting from an overload condition and the high current resulting from a short circuit. In addition, some thermal magnetic circuit ...
The thermomagnetic trip unit consists of two parts: The thermal trip unit - Made up by a bimetal thermal device which actuates the opening of a circuit breaker with a delay depending on the overcurrent value. This trip unit is intended for the protection against overloads. The magnetic trip unit - Made up by an electromagnetic device, with ...
Resolution: Thermal magnetic trip units trip under short circuit conditions instantaneously, with no intentional delay. Below the instantaneous trip current, they have a delay established to protect conductors while allowing momentary current surges such as for motor starting and transformer inrush. In some cases, they have adjustable ...
Thermal Magnetic Trip Action. As the name implies, a thermal magnetic trip unit combines the features of a thermal unit and a magnetic unit, as shown in Fig. 5. As a result, the time current curve, as shown in Fig. 6, combines the performance characteristics. Here, Points 1 and 2 show both the thermal and magnetic action for a typical 100A MCCB.
As the name suggests, a thermal magnetic circuit breaker works by combining the two versions above. It essentially leverages both forms to protect the conductors and other elements connected to the circuit breaker from the dangers of excessive current. The main advantage of how a thermal magnetic circuit breaker works is that it gives you both ...
The trip unit cover is factory sealed to prevent tampering with the calibration. Tables 1-1 and 1-2 list catalog num-bers and electrical data for trip units. Thermal Trip: In accordance with standards require-ments the thermal element trips the circuit breaker with-in 2 hours for an overload of 135 percent and trips in less time for higher over ...
This is an older video of mine but shows the basics of a thermal magnetic circuit breaker and how it works. A cut-away breaker was used to show the thermal ...
Thermal-magnetic trip units protect against overcurrents and short-circuits using tried and true techniques. But today, installation optimisation and energy efficiency have become decisive factors and electronic trip units offering more advanced protection functions combined with measurements are better suited to these needs. When there is an ...
In American homes today, thermal magnetic circuit breakers are the most common type. These are circuit breakers which utilize two components to detect electrical faults. The first component is an electromagnet that is sensitive to large surges in electrical currents. Electrical surges can cause short-circuiting, which may seriously damage your ...
Robert Repas. Thermal-magnetic circuit breakers contain two different switching mechanisms, a bimetal switch and an electromagnet. The bimetal serves as a means of handling overcurrents. The ...
Thermal-magnetic trip units are designed to provide protection for distribution or for specific applications. Identification. Type of protection. TM-D. Thermal-magnetic trip unit. TM-G. Thermal-magnetic trip unit with low pickup (for protecting generators, very long feeds) MA. Magnetic-only trip unit (for example, for protecting motors ...
The function of the trip unit is to trip the operating mechanism in the event of a short circuit or a prolonged overload of current. Basics Of Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) - EATON. 1. Electromechanical (thermal magnetic) trip unit. Traditional molded case circuit breakers use electromechanical (thermal magnetic) trip units.
Learn What is MCB circuit breaker, How the MCB Miniature circuit breaker works, and types B, C, and D of the MCB types and uses explained in this video tutor...
This strong magnetic field has enough strength to attract the nearby armature, which then tries to move towards the electromagnet, touching the trip unit on its way. When the trip unit comes in contact with the armature, it rotates in the same way as above, and hence its contact opens with the external circuit. When the value of current reduces ...
MCCB circuit breaker working principle is explained in this video. The difference between magnetic & thermal trip is explained in this video tutorial. Full f...
The thing is, we don't know what trip unit you might have. It could be thermal-mag, it could be mag-only. In either case the three separate dials are always the Magnetic Trips providing only the Short Circuit protection, thermal trips are what provide the Over Current protection and on MCCBs must be fixed in order to be UL listed.
A Setting range for the TM-D thermal-magnetic trip unit. B Adjustment dial for the thermal protection pickup Ir. C Adjustment dial for the magnetic protection pickup Im (for TM-D 200/250 only). Setting the Thermal Protection. The thermal protection pickup Ir is set by a 4-setting dial. Turning the thermal protection adjustment dial (A) modifies the trip curve as shown (B).
As the top of the armature is drawn to the electromagnet, the armature rotates the trip bar causing the circuit breaker to trip. Features: The Fuchs-type thermal-magnetic circuit breakers are ideal for upstream cascading breaker systems. Thermal-magnetic breakers can be mounted in any position. The tripping characteristic does not change.
Tables 1-1 and 1-2 list catalog num-bers and electrical data for trip units. Thermal Trip: In accordance with UL standards require-ments the thermal element trips the circuit breaker with-in 2 hours for an overload of 135 percent and trips in less time for higher overloads. For all currents in excess of the magnetic setting, the tripping action ...
The TM-D thermal-magnetic trip unit is designed to protect conductors in commercial and industrial electrical distribution. The trip unit exists in two configurations: 3P, 3D. 4P, 3D. Description. The adjustment dials are on the front of the trip unit: A Setting range for the TM-D thermal ...
The thermal magnetic trip unit consists of two parts: The thermal trip unit - Made up of a bimetallic thermal device which actuates the opening of a circuit breaker with a delay depending on the overcurrent value; for overload protection.. The magnetic trip unit - Made up of an electromagnetic device, with a fixed (fixed instantaneous trip) or adjustable (adjustable instantaneous trip ...
Issue:How does a thermal-magnetic trip unit work in a circuit breaker?Product Line:Circuit BreakersEnvironment:Miniature and Molded Case Thermal-Magnetic Circuit trip no…
The Westinghouse/Cutller Hammer KT3400T Trip unit for the KD and HKD frame has the 3 dials so you can set the instantainous trip for each phase. We always set the settings at 10 (high) This is 10 times the thermal rating (4000 Amps) Adjusting these settings will not affect the thermal triping at all. Sincerely, joe