Unique visitors
CREATED FOR:
The ‘Unique visitors’ metric shows the number of visitor IDs for the dimension item. It is one of the most common metrics used when determining traffic, as it gives a high-level overview of the popularity of a dimension item. For example, a visitor can come to your site every day for a month, but they still count as a single unique visitor.
If you use Cross-device analytics , this metric is replaced with the Unique devices metric.

Daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, and yearly unique visitors
Analysis Workspace treats unique visitors based on the granularity of the report. For example, if you use the Day dimension, you’ll see daily unique visitors for each dimension item. However, for the report total, it is deduplicated unique visitors for the freeform table’s date range.
How this metric is calculated
This metric counts the number of unique visitor ID’s for a given dimension item. It uses multiple advanced mechanisms to identify unique visitors, since there are several ways to identify them. The following table lists the ways a visitor is identified, along with its priority. Some hits can have multiple visitor identification methods; in these cases the higher priority method is used.
Behavior that affects unique visitor count
Unique visitor identifiers are typically stored in a browser cookie. A new unique visitor is counted if they perform any of the following:
- Clears their cache at any time
- Opens a different browser on the same computer. One unique visitor is counted per browser.
- The same person browsing your site on different devices. A separate unique visitor is counted per device. You can use Cross-device analytics to combine visitors together using the People metric.
- Opens a private browsing session (such as Chrome’s Incognito tab).
A new unique visitor is not counted, as long as the cookie identifier is preserved:
- Closes their browser for an extended period
- Upgrades their browser to the latest version
When should I use hits, visits or visitors in my Adobe Analytics Segments
This past week I got asked this question and although I have no doubts when I am creating my Adobe Analytics (AA) segments I still could not give a clear answer. Later on that day, I stoped and thought about my logical mechanism to create the segment. This is how I choose.
Problem that I am trying to solve Segments is a very powerful and useful tool in AA. It allows you to create variables that were not available before. And because it is so useful, some analysts forget that they should be created to solve problems and not expand variables.
For example, let’s create a situation where I am asked to filter all conversions for a specific product, here called product bazinga. The checkout url for my commerce variables are all the same after a parameter but they all differ in the product name. No need to say that the product name is not shared in this data layer setup. This is how the confirmation url would like:
When someone buys the product cozinga: www.companyfic.com/cozinga/checkout/orderconfirmation
And when someone buys the bazinga product we: www.companyfic.com/bazinga/checkout/orderconfirmation
This case it’s a no brainer because I want to filter all pages that contain the string bazinga and the string orderconfirmation. And when the user hits these pages. It does not matter for me what they do after, before, in a different day. All care is that hit.
Basically I defined my problem. Defined the view I was trying to focus on and then it is clear which option I should choose.
Variables involved in the report
Now that the product is clear, looking at the variables you will be selecting in this report is also pretty useful. If the variables are more related to the hit, page views, time on page, scroll down then that’s what you are looking for. If the variables are more related to the visit (such as revenue, basket size, day of the order) then you should definitely use visit. The same with visitor.
Hit : I am focus on the page and what happens in that page. Anything after or before does not influence my segment. Ex: Page isolation, bounce rate in pages, product analysis.
Visits : I am focus on that visit, pages only matter in a visit level. Ex. what is number of page views for the product bazinga that comes SEM traffic source.
Visitors : I have a broad focus and I am interested in users. It does matter what users did in a previous visit. Ex. I want to know how many users from BC bought the product bazinga in the last 30 days.
Be careful when using segments that were created for different purpose, it might influence results. Ex. If you have your bazinga purchase segment and the business asks you to answer a question related to traffic source, you might have a higher number than you were supposed to. You are applying a hit segment to a problem that requires a visit segment for instance.
About: Andresa de Andrade
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How do Varying Definitions of Site “Visit” Impact My Business Reporting?
Hannah alexander.
A visit is universally defined as a singular visitor or user on a website. However, different platforms use varying parameters and terms when reporting visits. For example, Adobe Analytics and Google Analytics differ in how each counts traffic.
The following should help you better understand how to report visits by analytics platform:
Adobe Analytics
Adobe Analytics recognizes a new visit as whenever one of these instances occurs:
- Additional tabs within the same browser do NOT count as unique visits.
- A user can close a tab—or even restart their computer—then reopen a tab in the same browser within 30 minutes and this will still count as the same visit!
- New activity occurs on a new platform or device
- A visit will continue into the next day if the above parameters are met. Further, the visit would occur for each time it took place—if a visit took place from 11:55 p.m. on June 1 to 12:05 a.m. on June 2, Adobe Analytics will count for both of those days when reporting at a daily granular level.
- More than 2,500 hits in the same location (browser, tab, device, etc.) within 12 hours.
- Adobe Analytics will not count a new visit if the campaign source or referring domain changes; it retains its original referral source for the visit period.
Visits End When:
- Click volume indicates potential bot activity, preventing a new visit.
- More than 100 hits detected in 100 seconds
- Manually terminated visits are not counted.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics defines a Session (same as a “visit” in Adobe Analytics) as the period of time a user is active on a site or app.
- New sessions are registered starting at 12 a.m. the following day.
- New sessions begin when the campaign source or referring domain changes.
- Users that leave a site and return within 30 minutes are counted as part of the original session.
- Manual session override allowed via the use of Session Control .
- The three outlier detection methods used in Adobe Analytics logic do not account for bot activity (i.e., more than 12 inactive hours, 2,500 hits, or 100 hits in 100 seconds).
When Google Analytics Sessions End:
- Sessions expire each day at 11:59 p.m.
- By default, if a user is inactive for 30 minutes or more, any future activity is attributed to a new session.
What Does This Mean for Me?
- You will need to manually filter out bots in Google Analytics (unless configuration options are already set up to exclude bots and spiders).
- Daily visits in Adobe Analytics are not mutually exclusive—a visit can stay continuous across multiple days. This means the total visit count could be less than the sum of the daily visit counts . In Google, session count and the sum of the daily session counts are the same (visits always end at 11:59 p.m.).
- You should configure each platform to use the same Time Zone. Google Analytics will end your session at 11:59 p.m. for the set Time Zone.
- The free version of Google Analytics will provide sampled data if the dataset includes more than 500k sessions within a given date range. Make sure your reports are unsampled.
Keep an eye out for future blog posts about the key differences between web analytics platforms.
And if your business is considering a transition to Google Analytics 4, now’s the time! Here’s an overview of GA4 benefits:
Why Your Business Needs Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
Contact Evolytics for more information. We’ve got the expertise to lead you in the right direction with your analytics reporting:
Get in touch with an Evolytics expert.
Share this post:

Hannah Alexander, Associate Director of Experimentation & Strategy, leads the Experimentation & Strategy practice at Evolytics, inclusive of A/B Testing, personalization, Conversion Rate Optimization and strategy planning for clients such as Vail, Sephora, HSBC and Realtor.com. She is an Adobe Analytics certified expert who is further known at Evolytics for having developed the Evolytics Hybrid Analytics Workforce Team, designed to help new-to-analytics employees develop a personalized analytics career path.
Privacy Overview
Compare Return Visits and Visit Number greater than 1
On this page
Definition of reports
Comparison of reports.
某些 Creative Cloud 应用程序、服务和功能在中国不可用。

Visit Number: Each visit is assigned a visit number based on a virtual cookie. Each new visit increments this number by one. The Visit Number report does not include non-cookied visitors.
Return visits: The number of visits where visit number is greater than 1. The Return Visits report includes non-cookied visitors.
Users sometimes compare Return Visits to the sum of Visit Numbers greater than 1:
- Comparing these reports in the latest version of Adobe Analytics: Because of the ability to track non-cookied visitors, these metrics are extremely close, if not identical.
- Return Visits is greater than the sum of Visit Number < 1: The Return Visits report includes non-cookied visitors while the Visit Number report does not. Because of this, Return Visits can be higher in SiteCatalyst 14.
- Return Visits is lower than the sum of Visit Number < 1: This comparison is impossible in reporting. All circumstances where visit number < 1 are also counted in the Return Visits report.
Legal Notices | Online Privacy Policy
Language Navigation
A Beginner’s Guide to Adobe Analytics
While most digital analysts understand Google Analytics, many can find Adobe Analytics to be a complete mystery. If you are one of those people, you’ve come to the right place. Let’s dig into Adobe Analytics and get you up to speed!
In this post, we'll cover the following Adobe Analytics beginner topics:
- The program formerly known as “Omniture”
What is Adobe Analytics?
Why use adobe analytics.
- Adobe Entry Page vs. Google Analytics Landing Page
- Adobe Success Events vs. Google Analytics Goal Completions
Differences in Dimensions and Metrics Scope
- Adobe Analytics Report Navigation
- Standard Adobe Reports
Upcoming Adobe Analytics Tips
Similar to tools like Google Analytics 360 , Adobe Analytics offers notable benefits and features (avoiding sampling, custom tracking flexibility, etc.), justifying the notable yearly cost associated to it.
- Becoming familiar with Adobe will naturally expand your analytics skills! While many elements of Google Analytics tracking are applicable to Adobe; Adobe's new features, tools, and caveats will deepen and enrich your analytics knowledge base.
- If you understand the features within Adobe Analytics, you will save yourself time as well as others by quickly solving complex analysis problems, creating expansive and actionable reporting, and setting up strategic tracking.
Comparing Dimensions and Metrics in Google Analytics vs Adobe Analytics
Now that we’ve established why Adobe Analytics is important, let’s look at some high-level dimension and metrics differences between Google Analytics and Adobe Analytics, and establish why the scope of dimensions and metrics is so critical to understanding any analytics set-up.

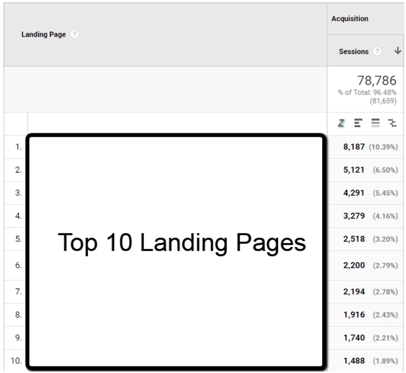
Adobe Analytics Entry Page vs. Google Analytics Landing Page
Looking at Adobe data, one of the first things you will likely notice is that sessions are now visits, and landing page is now entry page. As these are two extremely visible aspects of Google Analytics and Adobe Analytics, it’s important to note the high-level naming difference.
Google Analytics

Adobe Analytics

Google Analytics Goal Completions vs. Adobe Success Events
Another notable difference is GA goal completions vs. Adobe success events. For Google Analytics, each goal completion is counted once per session, where in Adobe, each success event counts each time the item occurs in a visit.
For example, if a conversion/success event in each platform is playing a video on the site, and you watch 5 videos in a single session/visit, in Google Analytics that will trigger only 1 video play goal completion, but in Adobe Analytics that will trigger 5 video play success events. When you think of Adobe success events, think of total events in Google Analytics.
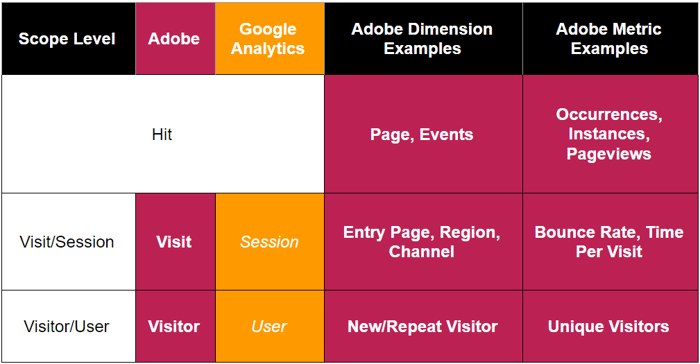
An important aspect of all analytics is the scope of dimensions and metrics. Scope affects data collection, aggregation, and even the way you analyze data.
Ensure that you are matching the correct dimensions and metrics by scope when doing analysis, otherwise you run the risk of misleading your report stakeholders which leads to poor decisions based on this data.
So what are these scopes, and how do they differ between Google Analytics & Adobe?
Adobe Analytics and Google Analytics Hits:
- Definition: The building block upon which all other data is formed. Measures each individual interaction on the site (think pageviews, events).
- Google Analytics vs. Adobe Analytics: Standard across Google Analytics and Adobe.
- Main Takeaway Tip: You want to match hit dimensions to hit metrics (i.e. page with pageviews).
Adobe Analytics Visit / Google Analytics Session:
- Definition: Multiple hits make up a session/visit. The most heavily featured scope across both platforms.
- Google Analytics vs. Adobe Analytics: Different in naming across Google Analytics (session) & Adobe (visit).
- Main Takeaway Tip: These session/visit-level items can occur once in this scope, such as entry page, region, etc. Should match session/visit dimensions with session/visit metrics (i.e. entry page with visits and bounce rate, etc.)
Adobe Analytics Visitor / Google Analytics User:
- Definition: While multiple hits make up a session/visit, multiple sessions/visits make up a visitor/user.
- Google Analytics vs. Adobe Analytics: Different in naming across Google Analytics (user) & Adobe (visitor).
- Main Takeaway Tip: This typically is the most hidden scope in both platforms, but can provide powerful analysis, allowing you to be more audience-focused . Should match visitor/user dimensions with visitor/user metrics (i.e. new/repeat visitor with unique visitors).
See a more visual example of this breakdown below:
Now that you understand the scope of dimensions and metrics and how they differ between Adobe and Google Analytics, you are ready to jump into the Adobe interface. Let’s do it!
Navigation of the Adobe Analytics Interface
Once you’ve logged into the Adobe interface, you’ll be presented with the layout of report options (may differ slightly by account), which we will break down piece-by-piece:
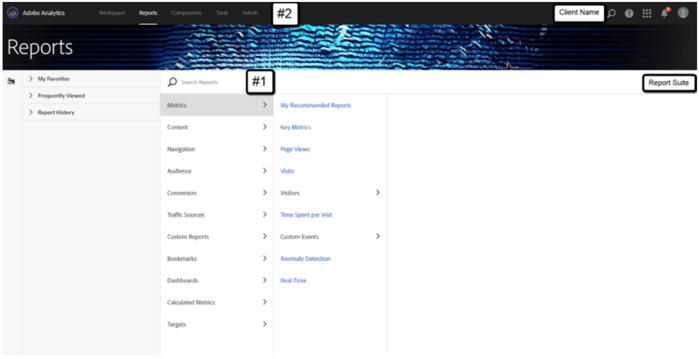
#1: Adobe Analytics Report Navigation
The search reports and navigation element allows you to find what report you want, either through typing in the report name or navigating through the sections. Let’s see how we can find the entry page report with both options:
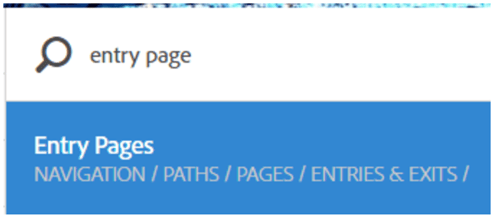
#1A: Search Option
By typing in the report name itself, you’ll see which reports have this naming, and then can select the report that is more relevant to you. See below for the entry page report:
#1B: Navigation Option
In this case, we don’t type the report name in, but rather click through the report structure to find it. You’ll notice that under the search option, this shows the same route that we use in the navigation structure to reach the report.
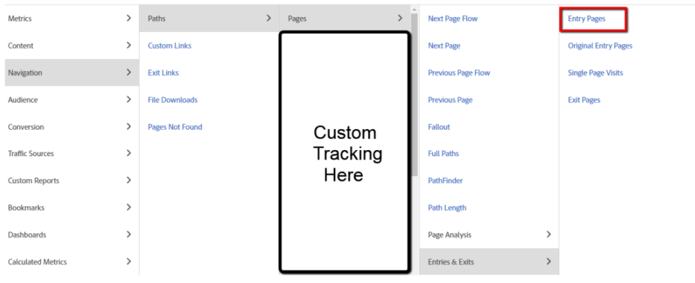
#2: Top-Nav Bar
The top-nav allows you to easily navigate between Adobe’s interface. When you first log in to Adobe Analytics, this default to opening on the reporting tab. You could update in the future to land on the Workspace option as well. You could also not see the Workspace option if you don’t have access to this area (granted under your user-level rights).
Let’s break down each of the options available in this area.
- Workspace : This links to Adobe’s Analysis Workspace tool, which I’ll expand on in a future post. Some pretty amazing report, analysis, and visualization capabilities with this tool.
- Reports : Your current view, allowing you to pick among report options.
- Components : Allows you to manage segments, create calculated metrics, manage scheduled reports, etc.
- Tools : Allows you to access non-Workspace Adobe tools, such as Report Builder & Ad-Hoc Analysis . Report Builder is an add-on to Microsoft Excel, and is very useful for report automation. It functions in a similar manner as the Google Sheets Add-On does with the Google Analytics API . I’ll expand on Report Builder usage in a future post as well.
- Admin : Depending on your user access (either admin or user), this allows you to create new users, update Adobe report suite configuration settings, etc.
- Report Suite : On the far right of the screen (on the same level as the report search), you can change the Adobe report suite you are viewing (think Google Analytics account or property). For more advanced users, Adobe offers other types of report suites: Virtual and Global/Roll-Up being some of the major options.
Standard Adobe Analytics Report
Now that we know the basic interface, let’s explore a simple report (entry pages):

On the upper left-hand side, with the three icons, you have the options to (from top-to-bottom):

- View Reports : Navigate away from the current report
- Apply Segments : You can apply multiple segments at once (will find the overlap of all segments), and create and manage segments (which align to the dimension and metric scopes you choose!)

- "Entry Pages Report" - Name of the report
- The Star - Favorite the report to come back to for future reference (under your login)
- Cloud with Arrow - Download the report (Excel, PDF, etc.)
- Envelope - Send the report via email
- Book - Bookmark the report
- Speedometer - Add to an Adobe dashboard (less useful than Adobe’s other reporting options [Analysis Workspace being the main] in my opinion)
- Three Dots - contains more options, one of which is a quick link option (great for sharing reports with others - allow for them to come directly to the report upon login)
- The Cylinder - Which Report Suite the data is pulling from
- The Calendar - Allows for changing date ranges, and comparing dates (Adobe also allows you preset ranges - last month, last week, etc.). You can also create custom date ranges to fit your reporting needs
One last tip for the report layout: You can use these reports to drill down further based on what you have selected. This is located as shown below:

Want to see what channels drove visits to these entry pages? How about a breakdown by mobile device type? What can the regional data tell you about your paid targeting efforts? The possibilities are nearly endless. Go explore!
With these tools, you now how have the ability to:
- Understand how Adobe Analytics functions, why it is important, and how it differs from Google Analytics.
- Navigate the Adobe Analytics interface and basic reports.
Now that you have this knowledge, if you have the opportunity, get in there and explore! What questions do you have based on what you’ve found? What are the hidden gems of Adobe Analytics that you use? Let me know in the comments!
However, truthfully, this is just the tip of the iceberg in relation to Adobe Analytics knowledge. To truly understand what Adobe offers, you’ll want to understand the following topics as well:
- eVars (custom conversion) vs. sProps (custom traffic) : How custom tracking with Adobe fundamentally works.
- Adobe’s Pathing & Fallout Tools : How Adobe’s PathFinder and Full Paths reports differ from Google Analytics’ pathing efforts, and how you can integrate pathing and fallout reporting into Analysis Workspace.
- Adobe Analysis Workspace : How Adobe’s main reporting and analysis tool is competing against Google Data Studio , and how it provides one of the most flexible and powerful interfaces of all major data analysis tools.
- Adobe Report Builder : How Adobe’s reporting automation tool stacks up against Google’s options, and how to most easily integrate it into your Excel reporting set-up.
Stay tuned for more information on these areas in future posts. If you’re ready for level two, check out The Definitive Guide to Adobe Analysis Workspace . Happy data digging!

We love helping marketers like you.
Sign up for our newsletter to receive updates and more:
Related Posts
Sign in to Community
Sign in to view all badges
Expand my Community achievements bar.

Adobe Analytics
Visit expiration - mobile app (con't).
- Mark as New
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
Solved! Go to Solution.
Total Likes

View solution in original post
- All forum topics
- Previous Topic
- Certifications
- Instructor-led training
- View all learning options
Documentation
- Documentation home
- Experience Cloud release notes
- Document Cloud release notes
- Community home
- Community Advisors
- Experience League Showcase
- Advertising
- Audience Manager
- Campaign Classic v7 & Campaign v8
- Campaign Standard
- Experience Cloud
- Experience Manager Sites & More
- Experience Platform
- Journey Optimizer
- Real-Time Customer Data Platform
- Creative Cloud
- Document Cloud
- Marketo Engage
- Experience Cloud support
- Document Cloud support
- Community forums
- Adobe Developer
- Adobe status
Adobe account
- Log in to your account
- Corporate responsibility
- Investor Relations
- Supply chain
- Trust Center
- Diversity & Inclusion
- COVID-19 Responses

COMMENTS
The 'Visits - All Visitors' metric is comparable to the 'Visits' metric in other Analytics tools. The 'Visits' metric in Data Warehouse excludes visitors that don't have persistent cookies. Adobe recommends using 'Visits - All Visitors' in Data Warehouse requests where visits are desired as a metric. A sequence of page views ...
The 'Visits - All Visitors' metric is comparable to the 'Visits' metric in other Analytics tools. The 'Visits' metric in Data Warehouse excludes visitors that don't have persistent cookies. Adobe recommends using 'Visits - All Visitors' in Data Warehouse requests where visits are desired as a metric. A sequence of page views ...
Admin. The 'Unique visitors' metric shows the number of visitor IDs for the dimension item. It is one of the most common metrics used when determining traffic, as it gives a high-level overview of the popularity of a dimension item. For example, a visitor can come to your site every day for a month, but they still count as a single unique ...
Page Views, Visits, and Visitors. This brief video will give you some basic info on understanding these staples to understanding Web site traffic.
While this action is technically part of the same browsing session, Adobe considers this action two separate visits. In general a visit will be counted for both web and mobile SDK implementation. It will always start on first servercall/hit sent to adobe analytics for a specific unique visitor ID and be closed when one of the condition above is ...
The same with visitor. Hit: I am focus on the page and what happens in that page. Anything after or before does not influence my segment. Ex: Page isolation, bounce rate in pages, product analysis. Visits: I am focus on that visit, pages only matter in a visit level. Ex. what is number of page views for the product bazinga that comes SEM ...
to gain points, level up, and earn exciting badges like the new
A visit is universally defined as a singular visitor or user on a website. However, different platforms use varying parameters and terms when reporting visits. For example, Adobe Analytics and Google Analytics differ in how each counts traffic. The following should help you better understand how to report visits by analytics platform:
however to throw some water on this. if you create a visit or visitor segment and only pages C & D qualify then in that report C will get the entry credit because that is the page where you entered the 'segment;' (think of reports without segmentation as being in the 'all pages (no segment)' segment.
Users sometimes compare Return Visits to the sum of Visit Numbers greater than 1: Comparing these reports in the latest version of Adobe Analytics: Because of the ability to track non-cookied visitors, these metrics are extremely close, if not identical. Return Visits is greater than the sum of Visit Number < 1: The Return Visits report includes non-cookied visitors while the Visit Number ...
Analogy for Reporting Period, Unique Visitors, Visits and Pageviews. A good way to think about these four definitions in Adobe Analytics (Reporting Period, Unique Visitors, Visits and Pageviews) is with a brick-and-mortar analogy. Scenario. Imagine that John owns a store. The store is open during the workweek, Monday to Friday.
Visit Number equal to 1 is New and Visit Number greater than 1 is Return. Create a segment on visits level. In the report you can check how many interactions coming from new vs return. How they are performing. Create a report. New visits and Return visits are dimensions
Definition: The building block upon which all other data is formed. Measures each individual interaction on the site (think pageviews, events). Google Analytics vs. Adobe Analytics: Standard across Google Analytics and Adobe. Main Takeaway Tip: You want to match hit dimensions to hit metrics (i.e. page with pageviews).
Foundational Metrics in Adobe Analytics. This video helps provide a conceptual description of basic visitor metrics in Adobe Analytics and how they relate to each other. You will also walk through several example use cases for when to use Page Views, Visits, and Unique Visitors in reporting. For more info in the documentation, please see Page ...
The 'Unique visitors' metric shows the number of visitor IDs for the dimension item. It is one of the most common metrics used when determining traffic, as it gives a high-level overview of the popularity of a dimension item. For example, a visitor can come to your site every day for a month, but they still count as a single unique visitor.
From the topic "Visit Expiration - Mobile App", we learned that the visit definition is based on Adobe Analytics Server's calculation and we could customize it via Virtual Report Suite, as below,
A visit is one session on the website and is unique. Occurrences are the total number of pageviews and events that fire on a page. Occurrences are not unique and a visit is unique within a defined time frame. ... Occurrences is the number of adobe analytics web beacons. So if a page lazy loads and you are sending a beacon each lazy load is an ...