
- Diversity Inclusion
- Advisory Panel
- Our Audience
- Private Tourism Academies
- Tourism Ambassador Training
- Destination Training
- Tourism Keynote Speakers
- Sponsorship
- Business Class Podcast
- Skill & Knowledge
- Product Training
- Our Technology
- Become An Instructor
- Sponsorship Opportunities
- Product Training & Promotion
- Hire Us To Speak


The Evolution of Travel Agencies: A Historical Perspective
The history of travel agencies is a compelling narrative that has witnessed significant transformations over the years. This article explores the evolution of travel agencies from their early beginnings to the present day, highlighting key milestones and shifts in the industry.
Early Travel Arrangements:
Before the establishment of travel agencies, individuals took charge of their travel arrangements directly with transportation providers and accommodations. This process was often cumbersome and time-consuming, requiring considerable effort from the traveler.
Emergence of Travel Agencies:
In the 19th century, the concept of travel agencies began to take shape. Thomas Cook & Son, founded in 1841 by Thomas Cook, is recognized as one of the earliest travel agencies. Initially focusing on organizing railway outings, the agency later expanded its services to include international travel.
Growth and Globalization:
As transportation infrastructure grew and global travel became more accessible, the role of travel agencies expanded. They became intermediaries between travelers and various service providers, offering packaged tours and simplifying the booking process.
Technology and Online Booking:
The late 20th century witnessed a transformative shift with the advent of technology. The rise of the internet allowed travelers to research and book their trips online, reducing dependence on traditional brick-and-mortar travel agencies.
Specialization and Niche Markets:
As the travel industry diversified, agencies began specializing in specific niches such as adventure travel, luxury vacations, or eco-tourism. This specialization enabled agencies to cater to the unique preferences of different traveler segments.
Challenges and Adaptation:
The advent of online booking platforms and direct-to-consumer options presented challenges to the traditional travel agency model. However, many agencies have adapted by leveraging technology to enhance customer service, offering personalized experiences and providing expertise in complex travel arrangements.
Conclusion:
While the travel agency landscape has undergone significant changes, agents continue to play a crucial role, particularly for complex or customized trips. Their expertise and personalized service add substantial value, contributing to a resurgence in specific segments of the industry. The role of travel agencies continues to evolve in response to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements, ensuring their relevance in the dynamic world of travel.

Disclaimer: Opinions expressed in this article The opinions and viewpoints expressed in this article are intended to provide an insightful exploration of the history and evolution of tourism ambassadors. However, it is essential to note that these opinions do not necessarily reflect those of the author or the Tourism Academy. The article aims to present a comprehensive overview of the topic based on available information and research, but individual perspectives may vary. Please consider multiple sources and viewpoints when you understand the subject matter.
Leave a comment
Related articles, us travel's geoff freeman on leadership and industry transformation, family travel association: transforming travel agent accreditation with the tourism academy, unveiling the spirit of travel with bud geissler, 2024 american bus association marketplace chair.
Join Us On YouTube!

Matsumoto Castle, Nagano, Japan
A Brief History of Travel and Tourism
Utilizing the widest definition of the word, human beings have been travelling since the dawn of time. No matter one’s beliefs about the creation of humans, everyone can agree our species began in some single locale, likely Africa or the Middle East , and ‘travelled’ outwards, settling new lands. However, most of this ‘travel’ was done out of necessity and war, often without the intent of return. It wouldn’t be until Antiquity, or the glory days of the Greek and Roman empires, that tourism, or leisure travel, would be introduced.
Aristocratic Tourism
In those days, tourism was a privilege almost entirely confined to the wealthy, who travelled largely for cultural exploration. One has to remember, the Greek and Roman upper classes were people who prided themselves on artistic, scientific, and philosophical pursuits. It follows, then, that these early travellers largely sought to learn the arts, languages, and cultures of their destinations.

Soon enough, travelling for leisure’s sake began to gain popularity; from the Roman Empire arises some of the earliest examples of travel resorts and spas in the world. Though they documented their experiences most thoroughly, the elite Europeans were not the only ones travelling in ancient times. In eastern Asia , it was popular for nobles to travel across the countryside for the religious and cultural experience it offered, oftentimes stopping at temples and sacred sites during their travels.

Religious Tourism
During the Middle Ages, travel took on a new meaning. Although leisurely travel was still reserved for the upper class, it became more and more common for members of the upper and even lower classes to embark on pilgrimages. Most of the major religions at the time, including the Islamic, Judaic, and Christian traditions, encouraged their practitioners to conduct pilgrimages.

Largely unaided by technology, most of these journeys were done on foot, often occasionally with a beast of burden to carry supplies. The wealthy were able to afford other forms of travel including horseback and ship. Furthermore, the Middle Ages saw the emergence of connected shipping routes. As ports grew, travel opportunities increased, and the dock was typically the start of any long-distance travel during the Middle Ages.

The Grand Tour
Travel continued to exist in this way for some time: the rich travelled primarily for cultural and leisure reasons, while the poor travelled largely for religious reasons, if at all. The next major development travel underwent was the establishment of the Grand Tour. Undertaken by the elite men of Western and Northern European countries , the Grand Tour took young travellers across Europe in a “rite of passage” meant to educate the wealthy after they finished their education but before adulthood. Historians cite this tradition as the origin of the modern tourism industry and indicate that the tradition had become well established in European culture by the 1660s.

Like many traditions, the Grand Tour eventually developed a rigid structure. Tourists were expected to follow a set itinerary and travelled with a tutor. The Grand Tour typically began in England, moved south through France into Switzerland and Italy. After spending a few months in Italy, the traveller and his tutor moved upwards through Germany and into Holland before returning to England. These trips utilized the most advanced travel technology of the day, including ships and collapsable coaches, and it wasn’t entirely uncommon for the traveller and tutor to be waited on by a handful of servants.

Tourism For The Masses
The Grand Tour remained a popular cultural phenomenon amongst the rich until the 1840s, which saw the advent of the first widespread railway system across system Europe. Immediately, this innovation opened the possibility of embarking on a Grand Tour to the middle classes, and soon it became more popular for middle and even working-class citizens to travel for leisure.
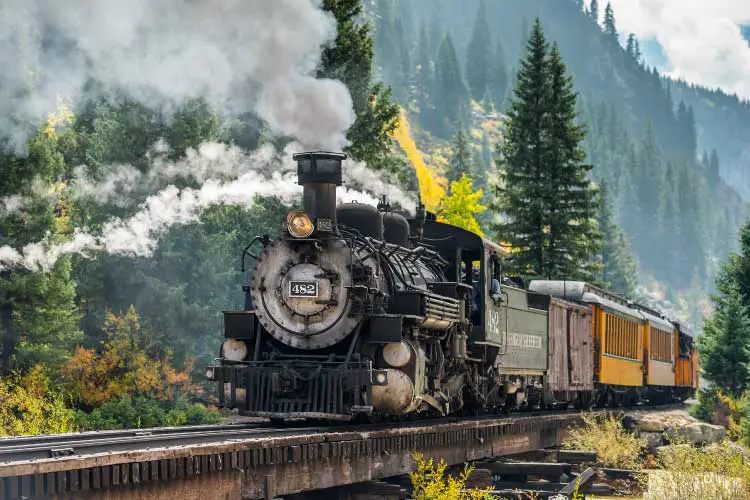

More importantly, the implementation of railway systems across Europe and the United States positioned the world for the Industrial Revolution. The United Kingdom is often cited as the first country to actively promote leisure time to its industrial class, and as a result, the country had a strong impact on the early development of the tourism industry. One hugely influential player in the history of travel and tourism was Englishmen Thomas Cook, who established the first-ever travel agency to provide ‘inclusive individual travel’ in the 1840s.

This means that travellers move independently in their travels, but all the food, lodging, and travel expenses were set at a fixed price for a predetermined length of time. This allowed travellers to take any route they fancied throughout Europe without having to ascertain food or lodging ahead of time. This fact, coupled with the falling ticket prices of railways, meant that long-distance travel was dramatically cheaper and faster than ever before. This not only further lowered the barriers to leisure travel but also drastically increased the incidences of business-related travel. As one can imagine, Cook’s Tours became massively popular, and the company remains successful today as the Thomas Cook Group.

In short, the introduction of a widespread railway system gifted a massive boost to the tourism industry; this boon would largely reflect that the aeroplane would have in the early-20th century. More so than any other technological development, the aeroplane opened the floodgates of mass international tourism. Behemoth multinational airlines such as Pan Am, Delta, and American Airlines arose during the 1900s, and suddenly the physical boundaries between cities were rendered useless. It has become possible for a traveller to get nearly anywhere on the globe in less than 48 hours, for a price that most middle and working-class members can achieve.

Today, travel stands as one of the most economically important leisure activities in the world. The tourism market is so large that it has split into an astounding number of niche markets, including ecotourism , backpacking, and historical tourism. As of the writing of this article, there have even been a handful of trips into orbit around Earth branded as “space tourism”, a new and exciting chapter in the history of travel and tourism. The story of tourism displays a remarkable connection to the technology that makes travel possible. Transportation innovations like the train and aeroplane have eliminated the difficulties and lowered the costs of long-distance travel, and planet Earth has truly become a smaller place because of it.

© Textbook Travel 2024 ⋅ View Privacy Policy


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview
Learning Objectives
- Specify the commonly understood definitions of tourism and tourist
- Classify tourism into distinct industry groups using North American Industry Classification Standards (NAICS)
- Define hospitality
- Gain knowledge about the origins of the tourism industry
- Provide an overview of the economic, social, and environmental impacts of tourism worldwide
- Understand the history of tourism development in Canada and British Columbia
- Analyze the value of tourism in Canada and British Columbia
- Identify key industry associations and understand their mandates
What Is Tourism?
Before engaging in a study of tourism , let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure ( United Nations World Tourism Organization , 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure).
Definition of Tourist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” (LinkBC, 2008, p.8). The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 156 countries and over 400 affiliates such as private companies and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website : http://www2.unwto.org/.
NAICS: The North American Industry Classification System
Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business — whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground — are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

The Hospitality Industry
When looking at tourism it’s important to consider the term hospitality . Some define hospitality as “t he business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, ¶ 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry. You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4, respectively.
Before we seek to understand the five industry groupings in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Global Overview
Origins of tourism.
Travel for leisure purposes has evolved from an experience reserved for very few people into something enjoyed by many. Historically, the ability to travel was reserved for royalty and the upper classes. From ancient Roman times through to the 17th century, young men of high standing were encouraged to travel through Europe on a “grand tour” (Chaney, 2000). Through the Middle Ages, many societies encouraged the practice of religious pilgrimage, as reflected in Chaucer’s Canterbury Tales and other literature.
The word hospitality predates the use of the word tourism , and first appeared in the 14th century. It is derived from the Latin hospes , which encompasses the words guest, host , and foreigner (Latdict, 2014). The word tourist appeared in print much later, in 1772 (Griffiths and Griffiths, 1772). William Theobald suggests that the word tour comes from Greek and Latin words for circle and turn, and that tourism and tourist represent the activities of circling away from home, and then returning (Theobald, 1998).
Tourism Becomes Business
Cox & Kings, the first known travel agency, was founded in 1758 when Richard Cox became official travel agent of the British Royal Armed Forces (Cox & Kings, 2014). Almost 100 years later, in June 1841, Thomas Cook opened the first leisure travel agency, designed to help Britons improve their lives by seeing the world and participating in the temperance movement. In 1845, he ran his first commercial packaged tour, complete with cost-effective railway tickets and a printed guide (Thomas Cook, 2014).
The continued popularity of rail travel and the emergence of the automobile presented additional milestones in the development of tourism. In fact, a long journey taken by Karl Benz’s wife in 1886 served to kick off interest in auto travel and helped to publicize his budding car company, which would one day become Mercedes Benz (Auer, 2006). We take a closer look at the importance of car travel later this chapter, and of transportation to the tourism industry in Chapter 2.
Fast forward to 1952 with the first commercial air flights from London, England, to Johannesburg, South Africa, and Colombo, Sri Lanka (Flightglobal, 2002) and the dawn of the jet age, which many herald as the start of the modern tourism industry. The 1950s also saw the creation of Club Méditérannée (Gyr, 2010) and similar club holiday destinations, the precursor of today’s all-inclusive resorts.
The decade that followed is considered to have been a significant period in tourism development, as more travel companies came onto the scene, increasing competition for customers and moving toward “mass tourism, introducing new destinations and modes of holidaying” (Gyr, 2010, p. 32).
Industry growth has been interrupted at several key points in history, including World War I, the Great Depression, and World War II. At the start of this century, global events thrust international travel into decline including the September 11, 2001, attack on the World Trade Center in New York City (known as 9/11), the war in Iraq, perceived threat of future terrorist attacks, and health scares including SARS, BSE (bovine spongiform encephalopathy), and West Nile virus (Government of Canada, 2006).
At the same time, the industry began a massive technological shift as increased internet use revolutionized travel services. Through the 2000s, online travel bookings grew exponentially, and by 2014 global leader Expedia had expanded to include brands such as Hotels.com, the Hotwire Group, trivago, and Expedia CruiseShip Centers, earning revenues of over $4.7 million (Expedia Inc., 2013).
A more in-depth exploration of the impact of the online marketplace, and other trends in global tourism, is provided in Chapter 14. But as you can already see, the impacts of the global tourism industry today are impressive and far reaching. Let’s have a closer look at some of these outcomes.
Tourism Impacts
Tourism impacts can be grouped into three main categories: economic, social, and environmental. These impacts are analyzed using data gathered by businesses, governments, and industry organizations.
Economic Impacts
According to a UNWTO report, in 2011, “international tourism receipts exceeded US$1 trillion for the first time” (UNWTO, 2012). UNWTO Secretary-General Taleb Rifai stated this excess of $1 trillion was especially important news given the global economic crisis of 2008, as tourism could help rebuild still-struggling economies, because it is a key export and labour intensive (UNWTO, 2012).

Tourism around the world is now worth over $1 trillion annually, and it’s a growing industry almost everywhere. Regions with the highest growth in terms of tourism dollars earned are the Americas, Europe, Asia and the Pacific, and Africa. Only the Middle East posted negative growth at the time of the report (UNWTO, 2012).
While North and South America are growing the fastest, Europe continues to lead the way in terms of overall percentage of dollars earned (UNWTO, 2012):
- Europe (45%)
- Asia and the Pacific (28%)
- North and South America (19%)
- Middle East (4%)
Global industry growth and high receipts are expected to continue. In its August 2014 expenditure barometer, the UNWTO found worldwide visitation had increased by 22 million people in the first half of the year over the previous year, to reach 517 million visits (UNWTO, 2014a). As well, the UNWTO’s Tourism 2020 Vision predicts that international arrivals will reach nearly 1.6 billion by 2020 . Read more about the Tourism 2020 Vision : http://www.e-unwto.org/doi/abs/10.18111/9789284403394
Social Impacts

In addition to the economic benefits of tourism development, positive social impacts include an increase in amenities (e.g., parks, recreation facilities), investment in arts and culture, celebration of First Nations people, and community pride. When developed conscientiously, tourism can, and does, contribute to a positive quality of life for residents.
However, as identified by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP, 2003a), negative social impacts of tourism can include:
- Change or loss of indigenous identity and values
- Culture clashes
- Physical causes of social stress (increased demand for resources)
- Ethical issues (such as an increase in sex tourism or the exploitation of child workers)
Some of these issues are explored in further detail in Chapter 12, which examines the development of Aboriginal tourism in British Columbia.
Environmental Impacts
Tourism relies on, and greatly impacts, the natural environment in which it operates. Even though many areas of the world are conserved in the form of parks and protected areas, tourism development can have severe negative impacts. According to UNEP (2003b), these can include:
- Depletion of natural resources (water, forests, etc.)
- Pollution (air pollution, noise, sewage, waste and littering)
- Physical impacts (construction activities, marina development, trampling, loss of biodiversity)
The environmental impacts of tourism can reach outside local areas and have an effect on the global ecosystem. One example is increased air travel, which is a major contributor to climate change. Chapter 10 looks at the environmental impacts of tourism in more detail.
Whether positive or negative, tourism is a force for change around the world, and the industry is transforming at a staggering rate. But before we delve deeper into our understanding of tourism, let’s take a look at the development of the sector in our own backyard.
Canada Overview
Origins of tourism in canada.
Tourism has long been a source of economic development for our country. Some argue that as early as 1534 the explorers of the day, such as Jacques Cartier, were Canada’s first tourists (Dawson, 2004), but most agree the major developments in Canada’s tourism industry followed milestones in the transportation sector: by rail, by car, and eventually, in the skies.
Railway Travel: The Ties That Bind

The dawn of the railway age in Canada came midway through the 19th century. The first railway was launched in 1836 (Library and Archives Canada, n.d.), and by the onset of World War I in 1914, four railways dominated the Canadian landscape: Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), Canadian Northern Railway (CNOR), the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR), and the Grand Trunk Pacific (GTP). Unfortunately, their rapid expansion soon brought the last three into near bankruptcy (Library and Archives Canada, n.d.).
In 1923, these three rail companies were amalgamated into the Canadian National Railway (CNR), and together with the CPR, these trans-continentals dominated the Canadian travel landscape until other forms of transportation became more popular. In 1978, with declining interest in rail travel, the CPR and CNR were forced to combine their passenger services to form VIA Rail (Library and Archives Canada, n.d.).
The Rise of the Automobile
The rising popularity of car travel was partially to blame for the decline in rail travel, although it took time to develop. When the first cross-country road trip took place in 1912, there were only 16 kilometres of paved road across Canada (MacEachern, 2012). Cars were initially considered a nuisance, and the National Parks Branch banned entry to automobiles, but later slowly began to embrace them. By the 1930s, some parks, such as Cape Breton Highlands National Park, were actually created to provide visitors with scenic drives (MacEachern, 2012).
It would take decades before a coast-to-coast highway was created, with the Trans-Canada Highway officially opening in Revelstoke in 1962. When it was fully completed in 1970, it was the longest national highway in the world, spanning one-fifth of the globe (MacEachern, 2012).
Early Tourism Promotion
As early as 1892, enterprising Canadians like the Brewsters became the country’s first tour operators, leading guests through areas such as Banff National Park (Brewster Travel Canada, 2014). Communities across Canada developed their own marketing strategies as transportation development took hold. For instance, the town of Maisonneuve in Quebec launched a campaign from 1907 to 1915 calling itself “Le Pittsburg du Canada.” And by 1935 Quebec was spending $250,000 promoting tourism, with Ontario, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia also enjoying established provincial tourism bureaus (Dawson, 2004).
National Airlines
Our national airline, Air Canada, was formed in 1937 as Trans-Canada Air Lines. In many ways, Air Canada was a world leader in passenger aviation, introducing the world’s first computerized reservations system in 1963 ( Globe and Mail , 2014). Through the 1950s and 1960s, reduced airfares saw increased mass travel. Competitors including Canadian Pacific (which became Canadian Airlines in 1987) began to launch international flights during this time to Australia, Japan, and South America ( Canadian Geographic, 2000). By 2000, Air Canada was facing financial peril and forced to restructure. A numbered company, owned in part by Air Canada, purchased 82% of Canadian Airline’s shares, with the result of Air Canada becoming the country’s only national airline ( Canadian Geographic, 2000).
Parks and Protected Areas
A look at the evolution of tourism in Canada would be incomplete without a quick study of our national parks and protected areas. The official conserving of our natural spaces began around the same time as the railway boom, and in 1885 Banff was established as Canada’s first national park. By 1911, the Dominion Forest Reserves and Parks Act created the Dominion Parks Branch, the first of its kind in the world (Shoalts, 2011).
The systemic conservation and celebration of Canada’s parks over the next century would help shape Canada’s identity, both at home and abroad. Through the 1930s, conservation officers and interpreters were hired to enhance visitor experiences. By 1970, the National Park System Plan divided Canada into 39 regions, with the goal of preserving each distinct ecosystem for future generations. In 1987, the country’s first national marine park was established in Ontario, and in the 20 years that followed, 10 new national parks and marine conservation areas were created (Shoalts, 2011).
The role of parks and protected areas in tourism is explored in greater detail in Chapter 5 (recreation) and Chapter 10 (environmental stewardship).
Global Shock and Industry Decline
As with the global industry, Canada’s tourism industry was impacted by world events such as the Great Depression and the World Wars.
More recently, global events such as 9/11, the SARS outbreak, and the war in Iraq took their toll on tourism receipts. Worldwide arrivals to Canada dropped 1% to 694 million in 2003, after three years of stagnant growth. In 2005, spending reached $61.4 billion with domestic travel accounting for 71% (Government of Canada, 2006).
Tourism in Canada Today
In 2011, tourism created $78.8 billion in total economic activity and 603,400 jobs. Tourism accounted for more of Canada’s gross domestic product (GDP) than agriculture, forestry, and fisheries combined (Tourism Industry Association of Canada, 2014).
Spotlight On: The Tourism Industry Association of Canada (TIAC)
Founded in 1930 and based in Ottawa, the Tourism Industry Association of Canada (TIAC) is the national private-sector advocate for the industry. Its goal is to support policies and programs that help the industry grow, while representing over 400 members including airports, concert halls, festivals and events, travel services providers, and businesses of all sizes. For more information, visit the Tourism Industry Association of Canada’s website : http://tiac.travel/About.html
Unfortunately, while overall receipts from tourism appear healthy, and globally the industry is growing, according to a recent report, Canada’s historic reliance on the US market (which traditionally accounts for 75% of our market) is troubling. Because three out of every four international visitors to Canada originates in the United States, the 55% decline in that market since 2000 is being very strongly felt here. Many feel the decline in American visitors to Canada can be attributed to tighter passport and border regulations, the economic downturn (including the 2008 global economic crisis), and a stronger Canadian dollar (TIAC, 2014).
Despite disappointing numbers from the United States, Canada continues to see strong visitation from the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Australia, and China. In 2011, we welcomed 3,180,262 tourists from our top 15 inbound countries (excluding the United States). Canadians travelling domestically accounted for 80% of tourism revenues in the country, and TIAC suggested that a focus on rebounding US visitation would help grow the industry (TIAC, 2014).
Spotlight On: The Canadian Tourism Commission
Housed in Vancouver, Destination Canada , previously the Canadian Tourism Commission (CTC), is responsible for promoting Canada in several foreign markets: Australia, Brazil, China, France, Germany, India, Japan, Mexico, South Korea, the United Kingdom, and the United States. It works with private companies, travel services providers, meeting professionals, and government organizations to help leverage Canada’s tourism brand, Canada. Keep Exploring . It also conducts research and has a significant image library (Canadian Tourism Commission, 2014). For more information, visit Destination Canada website : http://en.destinationcanada.com/about-ctc.
As organizations like TIAC work to confront barriers to travel, the Canadian Tourism Commission (CTC) is active abroad, encouraging more visitors to explore our country. In Chapter 8, we’ll delve more into the challenges and triumphs of selling tourism at home and abroad.
The great news for British Columbia is that once in Canada, most international visitors tend to remain in the province they landed in, and BC is one of three provinces that receives the bulk of this traffic (TIAC, 2012). In fact, BC’s tourism industry is one of the healthiest in Canada today. Let’s have a look at how our provincial industry was established and where it stands now.
British Columbia Overview
Origins of tourism in bc.
As with the history of tourism in Canada, it’s often stated that the first tourists to BC were explorers. In 1778, Captain James Cook touched down on Vancouver Island, followed by James Douglas in 1842, a British agent who had been sent to find new headquarters for the Hudson’s Bay Company, ultimately choosing Victoria. Through the 1860s, BC’s gold rush attracted prospectors from around the world, with towns and economies springing up along the trail (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009).
Railway Travel: Full Steam Ahead!
The development of BC’s tourism industry began in earnest in the late 1800s when the CPR built accommodation properties along itsnewly completed trans-Canada route, capturing revenues from overnight stays to help alleviate their increasing corporate debt. Following the 1886 construction of small lodges at stops in Field, Rogers Pass, and Fraser Canyon, the CPR opened the Hotel Vancouver in May 1887 (Dawson, 2004).
As opposed to Atlantic Canada, where tourism promotion centred around attracting hunters and fishermen for a temporary infusion of cash, in British Columbia tourism was seen as a way to lure farmers and settlers to stay in the new province. Industry associations began to form quickly: the Tourist Association of Victoria (TAV) in February 1902, and the Vancouver Tourist Association in June of the same year (Dawson, 2004).
Many of the campaigns struck by these and other organizations between 1890 and 1930 centred on the province’s natural assets, as people sought to escape modern convenience and enjoy the environment. A collaborative group called the Pacific Northwest Travel Association (BC, Washington, and Oregon) promoted “The Pacific Northwest: The World’s Greatest Out of Doors,” calling BC “The Switzerland of North America.” Promotions like these seemed to have had an effect: in 1928, over 370,000 tourists visited Victoria, spending over $3.5 million (Dawson, 2004).
The Great Depression and World War II
As the world’s economy was sent into peril during the Great Depression in the 1930s, tourism was seen as an economic solution. A newly renamed Greater Victoria Publicity Bureau touted a “100 for 1” multiplier effect of tourism spending, with visitor revenues accounting for around 13.5% of BC’s income in 1930. By 1935, an organization known as the TTDA (Tourist Trade Development Association of Victoria and Vancouver Island) looked to create a more stable industry through strategies to increase visitors’ length of stay (Dawson, 2004).
In 1937, the provincial Bureau of Industrial and Tourist Development (BITD) was formed through special legislation with a goal of increasing tourist traffic. By 1938, the organization changed its name to the British Columbia Government Travel Bureau (BCGTB) and was granted a budget increase to $105,000. This was soon followed by an expansion of the BC Tourist Council designed to solicit input from across the province. And in 1939, Vancouver welcomed the King and Queen of England and celebrated the opening of the Lions Gate Bridge, activities that reportedly bolstered tourism numbers (Dawson, 2004).
The December 1941 Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in Hawaii had negative repercussions for tourism on the Pacific Rim and was responsible for an era of decreased visitation to British Columbia, despite attempts by some to market the region as exciting. From 1939 to 1943, US visits to Vancouver (measured at the border) dropped from over 307,000 to approximately 183,600. Just two years later, however, that number jumped to 369,250, the result of campaigns like the 1943 initiative aimed at Americans that marketed BC as “comrades in war” (Dawson, 2004).

Post-War Rebound
We, with all due modesty, cannot help but claim that we are entering British Columbia’s half-century, and cannot help but observe that B.C. also stands for BOOM COUNTRY. – Phil Gagliardi, BC Minister of Highways, 1955 (Dawson, 2004, p.190)
A burst of post-war spending began in 1946, and although short-lived, was supported by steady government investment in marketing throughout the 1950s. As tourism grew in BC, however, so did competition for US dollars from Mexico, the Caribbean, and Europe. The decade that followed saw an emphasis on promoting BC’s history, its “Britishness,” and a commodification of Aboriginal culture. The BCGTB began marketing efforts to extend the travel season, encouraging travel in September, prime fishing season. It also tried to push visitors to specific areas, including the Lower Fraser Valley, the Okanagan-Fraser Canyon Loop, and the Kamloops-Cariboo region (Dawson, 2004).

In 1954, Vancouver hosted the British Empire Games, investing in the construction of Empire Stadium. A few years later, an increased emphasis on events and convention business saw the Greater Vancouver Tourist Association change its name in 1962 to the Greater Vancouver Visitors and Convention Bureau (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009).
The ski industry was also on the rise: in 1961, the lodge and chairlift on Tod Mountain (now Sun Peaks) opened, and Whistler followed suit five years later (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009). Ski partners became pioneers of collaborative marketing in the province with the foundation of the Ski Marketing Advisory Committee (SMAC) supported by Tod Mountain and Big White, evolving into today’s Canada’s West Ski Area Association (Magnes, 2010). This pioneer spirit was evident across the ski sector: the entire sport of heliskiing was invented by Hans Gosmer of BC’s Canadian Mountain Holidays, and today the province holds 90% of the world’s heliskiing market share (McLeish, 2014).
The concept of collaboration extended throughout the province as innovative funding structures saw the cost of marketing programs shared between government and industry in BC. These programs were distributed through regional channels (originally eight regions in the province), and considered “the most constructive and forward looking plan of its kind in Canada” (Dawson 2004, p.194).
Tourism in BC continued to grow through the 1970s. In 1971, the Hotel Room Tax Act was introduced, allowing for a 5% tax to be collected on room nights with the funds collected to be put toward marketing and development. By 1978, construction had begun on Whistler Village, with Blackcomb Mountain opening two years later (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009). Funding programs in the late 1970s and early 1980s such as the Canada BC Tourism Agreement (CBCTA) and Travel Industry Development Subsidiary Agreement (TIDSA) allowed communities to invest in projects that would make them more attractive tourism destinations. In the mountain community of Kimberley, for instance, the following improvements were implemented through a $3.1 million forgivable loan: a new road to the ski resort, a covered tennis court, a mountain lodge, an alpine slide, and nine more holes for the golf course (e-Know, 2011).
Around the same time, the “Super, Natural British Columbia” brand was introduced, and a formal bid was approved for Vancouver to host a fair then known as Transpo 86 (later Expo 86). Tourism in the province was about to truly take off.
Expo 86 and Beyond
By the time the world fair Expo 86 came to a close in October 1986, it had played host to 20,111,578 guests. Infrastructure developments, including rapid rail, airport improvements, a new trade and convention centre at Canada Place (with a cruise ship terminal), and hotel construction, had positioned the city and the province for further growth (PricewaterhouseCooopers, 2009). The construction and opening of the Coquihalla Highway through to 1990 enhanced the travel experience and reduced travel times to vast sections of the province (Magnes, 2010).
Take a Closer Look: The Value of Tourism
Tourism Vancouver Island, with the support of many partners, has created a website that directly addresses the value of tourism in the region. The site looks at the economics of tourism, social benefits of tourism, and a “what’s your role?” feature that helps users understand where they fit in. Explore the Tourism Vancouver Island website : http://valueoftourism.ca/.
By 2000, Vancouver International Airport (YVR) was named number one in the world by the International Air Transport Association’s survey of international passengers. Five years later, the airport welcomed a record 16.4 million passengers (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009).
Going for Gold

In 2003, the International Olympic Committee named Vancouver/Whistler as the host city for the 2010 Olympic and Paralympic Winter Games. Infrastructure development followed, including the expansion of the Sea-to-Sky Highway, the creation of Vancouver Convention Centre West, and the construction of the Canada Line, a rapid transport line connecting the airport with the city’s downtown.
As BC prepared to host the Games, its international reputation continued to grow. Vancouver was voted “Best City in the Americas” by Condé Nast Traveller magazine three years in a row. Kelowna was named “Best Canadian Golf City” by Canada’s largest golf magazine, and BC was named the “Best Golf Destination in North America” by the International Association of Golf Tour Operators. Kamloops, known as Canada’s Tournament City, hosted over 100 sports tournaments that same year, and nearby Sun Peaks Resort was named the “Best Family Resort in North America” by the Great Skiing and Snowboarding Guide in 2008 (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2009).
By the time the Vancouver 2010 Olympic and Paralympic Games took place, over 80 participating countries, 6,000 athletes, and 3 billion viewers put British Columbia on centre stage.
Spotlight On: Destination British Columbia
Destination BC is a Crown corporation founded in November 2012 by the Government of British Columbia. Its mandate includes marketing the province as a tourist destination (at home and around the world), promoting the development and growth of the industry, providing advice and recommendations to the tourism minister on related matters, and enhancing public awareness of tourism and its economic value to British Columbia (Province of British Columbia, 2013b).
Tourism in BC Today
Building on the momentum generated by hosting the 2010 Winter Olympic Games, tourism in BC remains big business. In 2012, the industry generated $13.5 billion in revenue.
The provincial industry is made up of over 18,000 businesses, the majority of which are SMEs (small to medium enterprises), and together they employ approximately 127,300 people (Tourism Industry Association of BC, 2014). It may surprise you to learn that in British Columbia, tourism provides more jobs than high tech, oil and gas, mining, and forestry (Porges, 2014).
Spotlight On: The Tourism Industry Association of BC
Founded in 1993 as the Council of Tourism Associations, today the Tourism Industry Association of BC (TIABC) is a not-for-profit trade association comprising members from private sector tourism businesses, industry associations, and destination marketing organizations (DMOs). Its goal is to ensure the best working environment for a competitive tourism industry. It hosts industry networking events and engages in advocacy efforts as “the voice of the BC tourism industry.” Students are encouraged to join TIABC to take advantage of their connections and receive a discount at numerous industry events. For more information, visit the Tourism Industry Association of BC’s website : http://www.tiabc.ca/student-membership
One of the challenges for BC’s tourism industry, it has long been argued, is fragmentation. Back in September 1933, an article in the Victoria Daily Times argued for more coordination across organizations in order to capitalize on what they saw as Canada’s “largest dividend payer” (Dawson, 2004). Today, more than 80 years later, you will often hear BC tourism professionals say the same thing.
On the other hand, some experts believe that the industry is simply a model of diversity, acknowledging that tourism is a compilation of a multitude of businesses, services, organizations, and communities. They see the ways in which these components are working together toward success, rather than focusing on friction between the groups.
Many communities are placing a renewed focus on educating the general public and other businesses about the value of tourism and the ways in which stakeholders work together. The following case study highlights this in more detail:
Take a Closer Look: Tourism Pays in Richmond, BC
The community of Richmond, BC, brings to life the far-reaching positive economic effects of tourism in action. Watch the short video called “Tourism Pays” to see what we mean!: http://vimeo.com/31624689

Throughout the rest of this textbook, you’ll have a chance to learn more about the history and current outlook for tourism in BC, with in-depth coverage of some of the triumphs and challenges we’ve faced as an industry. You will also learn about the Canadian and global contexts of the tourism industry’s development.
As we’ve seen in this chapter, tourism is a complex set of industries including accommodation, recreation and entertainment, food and beverage services, transportation, and travel services. It encompasses domestic, inbound, and outbound travel for business, leisure, or other purposes. And because of this large scope, tourism development requires participation from all walks of life, including private business, governmental agencies, educational institutions, communities, and citizens.
Recognizing the diverse nature of the industry and the significant contributions tourism makes toward economic and social value for British Columbians is important. There remains a great deal of work to better educate members of the tourism industry, other sectors, and the public about the ways tourism contributes to our province.
Given this opportunity for greater awareness, it is hoped that students like you will help share this information as you learn more about the sector. So let’s begin our exploration in Chapter 2 with a closer look at a critical sector: transportation.
- British Columbia Government Travel Bureau ( BCGTB) : the first recognized provincial government organization responsible for the tourism marketing of British Columbia
- Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) : a national railway company widely regarded as establishing tourism in Canada and BC in the late 1800s and early 1900s
- Destination BC: the provincial destination marketing organization (DMO) responsible for tourism marketing and development in BC, formerly known as Tourism BC
- Destination Canada: the national government Crown corporation responsible for marketing Canada abroad, formerly known as the Canadian Tourism Commission (CTC)
- Destination marketing organization (DMO): also known as a destination management organization; includes national tourism boards, state/provincial tourism offices, and community convention and visitor bureaus
- Diversity: a term used by some in the industry to describe the makeup of the industry in a positive way; acknowledging that tourism is a diverse compilation of a multitude of businesses, services, organizations, and communities
- Fragmentation: a phenomenon observed by some industry insiders whereby the tourism industry is unable to work together toward common marketing and lobbying (policy-setting) objectives
- Hospitality: the accommodations and food and beverage industry groupings
- North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) : a way to group tourism activities based on similarities in business practices, primarily used for statistical analysis
- Tourism: the business of attracting and serving the needs of people travelling and staying outside their home communities for business and pleasure
- Tourism Industry Association of BC ( TIABC) : a membership-based advocacy group formerly known as the Council of Tourism Associations of BC (COTA)
- Tourism Industry Association of Canada (TIAC): the national industry advocacy group
- Tourist: someone who travels at least 80 kilometres from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or pleasure or other reasons; can be further classified as domestic, inbound, or outbound
- United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) : UN agency responsible for promoting responsible, sustainable, and universally accessible tourism worldwide
- List the three types of tourist and provide an example of each.
- What is the UNWTO? Visit its website, and name one recent project or study the organization has undertaken.
- List the five industry groups according to the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). Using your understanding of tourism as an industry, create your own definition and classification of tourism. What did you add? What did you take out? Why?
- In 2011, how much money was generated by tourism worldwide? What percentage of this money was collected in Europe? Where was the least amount of money collected?
- According to UNEP, what are the four types of negative environmental tourism impact? For each of these, list an example in your own community.
- What major transportation developments gave rise to the tourism industry in Canada?
- Historically, what percentage of international visitors to Canada are from the United States? Why is this an important issue today?
- Name three key events in the history of BC tourism that resonate with you. Why do you find these events of interest?
- Watch the video in the “Take a Closer Look” feature on Richmond. Now think about the value of tourism in your community. How might this be communicated to local residents? List two ways you will contribute to communicating the value of tourism this semester.
- Choose one article or document from the reference list below and read it in detail. Report back to the class about what you’ve learned.
Case Study: Tourism – Canada’s Surprise Blind Spot
In a 2014 episode of the Voice of Canadian Business , the Canadian Chamber of Commerce’s podcast, host Mary Anne Carter sat down with Greg Klassen, the CTC’s president and CEO, and Michele Saran, executive director of Business Events Canada. Their discussion highlighted the reasons Canada is struggling to remain competitive within the sector, and underscores the role and impact Canada’s tourism industry has on the economy.Listen to the 14-minute podcast on tourism in Canada and answer the following questions: www.chamber.ca/media/pictures-videos/140407-podcast-tourism/
- Why are governments around the world starting to invest in tourism infrastructure? What does this mean for the competitive environment for Canada’s tourism product?
- How do we compare to the United States as a destination for business travel?
- According to Greg, why is the $200 million investment in Brand USA a “double-edged sword” for tourism in Canada? What is beneficial about this? Why does it make things more difficult?
- What is the relationship between tourism and people’s understanding of a country’s image?
- What ranking is Canada’s brand? What other industries are affected by this brand?
- Describe one activity the CTC participates in to sell Canadian tourism product abroad.
- Name two “sectors of excellence” for Canada. Why is the CTC focussing their business events sales strategies on these industries?
- What does the CTC consider to be the benefits of Vancouver hosting the 2014 and 2015 TED conferences?
Brewster Travel Canada. (2014). About Us – Brewster History . Retrieved from http://www.brewster.ca/corporate/about-brewster/brewster-history/
British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training . (2013a). BC Stats: Industry Classification . Retrieved from http://www.bcstats.gov.bc.ca/StatisticsBySubject/BusinessIndustry/IndustryClassification.aspx
British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training. (2013b). Bill 3 – 2013: Destination BC Corp Act . Retrieved from https://www.leg.bc.ca/39th5th/1st_read/gov03-1.htm
Canadian Geographic . (2000, September). Flying through time: Canadian aviation history . Retrieved from http://www.canadiangeographic.ca/magazine/so00/aviation_history.asp
Canadian Tourism Commission. (2014). About the CTC. Retrieved from http://en-corporate.canada.travel/about-ctc
Chaney, Edward. (2000). The evolution of the grand tour: Anglo-Italian cultural relations since the Renaissance . Portland OR: Routledge.
Cox & Kings. (2014). About us – History. Retrieved from http://www.coxandkings.co.uk/aboutus-history
Dawson, Michael. (2004). Selling British Columbia: Tourism and consumer culture, 1890-1970 . Vancouver, BC: UBC Press.
Discover Hospitality. (2015). What is hospitality? Retrieved from http://discoverhospitality.com.au/what-is-hospitality/
e-Know. (2011, November). Ogilvie’s past in lock step with last 50 years of Kimberley’s history. Retrieved from www.e-know.ca/news/ogilvie’s-past-in-lock-step-with-last-50-years-of-kimberley’s-history/
Expedia, Inc. (2013). Expedia: Annual report 2013. [PDF] Retrieved from http://files.shareholder.com/downloads/EXPE/3546131959x0x750253/48AF365A-F894-4E9C-8F4A-8AB11FEE8D2A/EXPE_2013_Annual_Report.PDF
Flightglobal. (2002). Sixty years of the jet age. Retrieved from http://www.flightglobal.com/features/jet-age/
Globe and Mail, The. (2014, March 28). Ten things you don’t know about Air Canada. Retrieved from http://www.theglobeandmail.com/life/travel/travel-news/10-things-you-likely-dont-know-about-air-canada/article17725796/?page=all
Government of Canada. (2006). Building a national tourism strategy. [PDF] Retrieved from https://www.ic.gc.ca/eic/site/034.nsf/vwapj/tourism_e.pdf/$FILE/tourism_e.pdf
Government of Canada. (2013, July 5). Appendix E: Tourism industries in the human resource module . Retrieved from http://www.statcan.gc.ca/pub/13-604-m/2013072/appe-anne-eng.htm
Griffiths, Ralph, Griffiths, G. E. (1772). Pennant’s tour in Scotland in 1769. The Monthly Review; or, Literary Journal XLVI : 150 . Retrieved from Google Books .
Gyr, Ueli. (2010, December 3). The history of tourism: Structures on the path to modernity. European History Online (EHO). Retrieved from http://ieg-ego.eu/en/threads/europe-on-the-road/the-history-of-tourism
Latin definition for hospes, hospitis. (2014).In Latdict – Latin Dictionary and Grammar Resources . Retrieved from http://www.latin-dictionary.net/definition/22344/hospes-hospitis
Library and Archives Canada. (n.d.). Ties that bind: Essay. A brief history of railways in Canada. Retrieved from http://www.collectionscanada.gc.ca/trains/021006-1000-e.html
LinkBC. (2008). Transforming communities through tourism: A handbook for community tourism champions. [PDF] Retrieved from http://linkbc.ca/siteFiles/85/files/TCTT.pdf
MacEachern, A. (2012, August 17). Goin’ down the road: The story of the first cross-Canada car trip. The Globe and Mail . Retrieved from http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/national/goin-down-the-road-the-story-of-the-first-cross-canada-car-trip/article4487425/
McLeish. (2014, July 23). History of heliskiing in Canada. Retrieved from www.lastfrontierheli.com/news/1607/history-of-heliskiing-in-canada/
Magnes, W. (2010, May 26). The evolution of British Columbia’s tourism regions: 1970-2010 [PDF] . Retrieved from http://linkbc.ca/siteFiles/85/files/LinkBCMagnesPaper2011.pdf
Porges, R. (2014, September). Tell me something I don’t know: Promoting the value of tourism. Tourism Drives the Provincial Economy . Presentation hosted by the Tourism Industry Association of BC, Vancouver, BC.
PricewaterhouseCooopers, LLC. (2009). Opportunity BC 2020: Tourism sector. [PDF] Prepared for the BC Business Council. Retrieved from http://www.bcbc.com/content/558/2020_200910_Mansfield_Tourism.pdf
Shoalts, A. (2011, April). How our national parks evolved: From Grey Owl to Chrétien and beyond, 100 years of Parks Canada. Canadian Geographic . Retrieved from http://www.canadiangeographic.ca/magazine/apr11/national_parks_evolution.asp
Theobald, William F. (1998). Global Tourism (2nd ed.). Oxford, England: Butterworth–Heinemann, pp. 6-7.
Thomas Cook Group of Companies. (2014). Thomas Cook history. Retrieved from http://www.thomascook.com/thomas-cook-history/
Tourism Industry Association of BC. (2014). Value of tourism toolkit: Why focus on the value of tourism? Retrieved from http://www.tiabc.ca/value-of-tourism-toolkit
Tourism Industry Association of Canada. (2014, October 14). Travel industry poised to boost Canadian exports: US market and border efficiencies central to growth potential . Retrieved from http://tiac.travel/cgi/page.cgi/_zine.html/TopStories/Travel_Industry_Poised_to_Boost_Canadian_Exports_US_Market_and_Border_Efficiencies_Central_to_Growth_Potential
Tourism Industry Association of Canada, HLT Advisory. (2012). The Canadian tourism industry: A special report [PDF] . Retrieved from http://www.hlta.ca/reports/The_Canadian_Tourism_Industry_-_A_Special_Report_Web_Optimized_.pdf
United Nations and World Tourism Organization. (1995). Recommendations on tourism statistics. [PDF] Retrieved from http://unstats.un.org/unsd/newsletter/unsd_workshops/tourism/st_esa_stat_ser_M_83.pdf
United Nations Environment Programme. (2003a). Negatives Socio-cultural impacts from tourism . Retrieved from http://www.unep.org/resourceefficiency/Business/SectoralActivities/Tourism/FactsandFiguresaboutTourism/ImpactsofTourism/Socio-CulturalImpacts/NegativeSocio-CulturalImpactsFromTourism/tabid/78781/Default.aspx
United Nations Environment Programme. (2003b). Tourism’s three main impact areas. Retrieved from http://www.unep.org/resourceefficiency/Business/SectoralActivities/Tourism/TheTourismandEnvironmentProgramme/FactsandFiguresaboutTourism/ImpactsofTourism/EnvironmentalImpacts/TourismsThreeMainImpactAreas/tabid/78776/Default.aspx
United Nations World Tourism Organization. (2008). Understanding tourism: Basic glossary . Retrieved from http://media.unwto.org/en/content/understanding-tourism-basic-glossary
United Nations World Tourism Organization. (2012, May 7). International tourism receipts surpass US$ 1 trillion in 2011. Retrieved from http://media.unwto.org/en/press-release/2012-05-07/international-tourism-receipts-surpass-us-1-trillion-2011
United Nations World Tourism Organization. (2014a). UNWTO world tourism barometer, 12 [PDF] (1). Retrieved from http://dtxtq4w60xqpw.cloudfront.net/sites/all/files/pdf/unwto_barom14_04_august_excerpt_0.pdf
United Nations World Tourism Organization. (2014b). Who we are. Retrieved from http://www2.unwto.org/content/who-we-are-0
Attributions
Figure 1.1 Selkirk College and Nelson by LinkBC is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.2 Capilano University’s Team by LinkBC is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.3 Vancouver Island University by LinkBC is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.4 Canadian Pacific 4-4-0 A-2-m No 136 by Peter Broster is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.5 Vancouver Island University by LinkBC is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.6 Switzerland vs. Canada by s.yume is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Figure 1.7 CTC’s Boardroom by LinkBC is used under a CC-BY 2.0 license.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC Copyright © 2015 by Capilano University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Call us to tailor your perfect holiday South Glos: 01454 634070
- Call us to tailor your perfect holiday Bristol: 0117 428 0570
- Call us to tailor your perfect holiday Bath: 01225 418100
- Book an appointment
- Meet the team
- Why use a travel agent?
- What makes us special
- Travel Trust Association
- Bristol Film Festival
- Interactive cruise finder
- Interactive brochure rack
- Travel to the EU
- Travel Insurance
- Latest Offers

Welcome to our blog! Discover the latest travel insights and goings on with the team.
A brief history of the travel agent

In 1841, Thomas Cook received a commission from Midland Railway to organise the transportation of member of temperance society.
He founded an agency in his own name and partnered with his son, establishing the package tour holiday.
In the early 20th Century, airline numbers grew exponentially, which in turn resulted in an increase in demand for travel agents. Agents were primarily used by middle and uppr class customers who had a lot of disposible income to spend on holidays.
During WWII, the travel industry took a big hit, unsurprisingly. However, during the post-war years, when income was still very low, travel agents were forced to react to the market demands and create cheaper packages which fell in line with reduced airfares.
Once this happened, travel became much more accessible to all demographics, and the British search for some summer sun began.
Like any industry, travel agents have had their ups and their downs. The most recent being the dawn of the internet nullifying the requirement of a travel agent for many people. Agents have needed to respond an ensure their value-added remains despite the wealth of information accessible at the fingertips of many.
Share this blog post:
- Staff travels
- Travel Advice

Many of the flights and flight-inclusive holidays on this website are financially protected by the ATOL scheme. But ATOL protection does not apply to all holiday and travel services listed on this website. Please ask us to confirm what protection may apply to your booking. If you do not receive an ATOL Certificate then the booking will not be ATOL protected. If you do receive an ATOL Certificate but all parts of your trip are not listed on it, those parts will not be ATOL protected. Please see our booking conditions for information, or for more information about financial protection and the ATOL Certificate go to: www.atol.org.uk/ATOLCertificate

- Music & Dance
- TV & Movies
- Food Culture
- Restaurants
- Aromatherapy
- Healthy Living
- Educational
- Life Stories
- Famous People
- Expensive Products
- Product Reviews
- Empires and Kingdoms
- Prehistoric and Early Civilizations
- Pre-Columbian
- Colonial Period
- American Revolution
- Civil War Era
- Civil Rights
- US Presidents
- The Middle East
- People in History
- Statues & Monuments
- Historic Mysteries
- History Questions
- Chinese Mythology
- Japanese Mythology
- Greek Mythology
- Norse Mythology
- Roman Mythology
- African Mythology
- Native American Mythology
- Mythical Creatures
- Superstitions
- Buddhist Mythology
- Christianity
- African Folk
- Paganism & Wicca
- Prayer Beads
A Brief History of Travel

In our modern world, global travel has become so easy that it’s easy to forget that mass tourism is a relatively new occurrence. At least it is for the masses. But why do we travel? And when did travel become ‘a thing’? Have we always been travelling, or is it really just a modern invention?
Today, tourism is a huge industry, supporting millions, perhaps billions of people around the world. From airlines and taxi drivers, to restaurants, hotels and bloggers, tourism plays an integral part in our modern global economy. And this economy has been growing at a staggering rate throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. In 1980 there were just over 280 million tourism arrivals around the globe. By 2018, there were an estimated 1.4 billion tourist arrivals, with the money spent on travel accounting for around 10.4% of global GDP.
But it wasn’t always like this.
Table of Contents
Travel in the Ancient World
For most of human history, travel had been undertaken either as part of exploration or trade. Or, sometimes, both together. Military conquests or the spreading of a religious word have spurred people to reach out across the region to either subjugate or enlighten the neighbours – and on occasion to dominate distant lands.
However, travel for pleasure has always been there in the background, albeit usually for the more fortunate monied classes. In ancient Greece, there are examples of people travelling to watch the original Olympic Games, or to question the Oracle at Delphi. There were also other games less famous than the Olympics which would attract visitors from far and wide. At the time, there was an extensive network of inns across Greece designed for travellers to stay the night, although they were basic by today’s standards with no bathrooms, toilets or catering facilities.
Well-to-do Egyptians too would explore ancient marvels (some of which were ancient even in 1000BCE). The Pyramids and the Acropolis were draws for tourists even in pre-modern times, and those who could afford to visit ancient sites would take time out with their slaves and entourages to go and explore. Visitors came from Greece and Rome to marvel at the scale of the pyramids of Giza, which were the world’s largest man made structures for thousands of years.
But it was perhaps the Romans who first took holidays or vacations in a way that might seem familiar to us today. The nobility of ancient Rome would escape the stifling heat of the city in summer and head to either the cooler hills, or the seaside. Sicily, Capri and the north of Italy were all favourite haunts, although some would even travel as far as Egypt or Greece for these excursions.
In fact the Romans also pioneered the spa holiday, often travelling to find thermal baths for health benefits. Around these spas would spring up additional services including restaurants, gambling dens and even prostitution. Roman travel was made relatively easy by their great network of roads and shipping routes across the territory. However, with the collapse of the Roman Empire, tourism in the Mediterranean took a break for a while.
Ancient Tourism in Asia
The ancient Silk Route is still well known today as a network of paths and shipping lanes leading from China to the Western lands. Although it was clearly a trade network, travellers would have traversed the steppes of central Asia perhaps for enlightenment or other benefits.
Srinagar in Kashmir, northern India holds an interesting example of the possibilities of the age. The city hosts a tomb said to be that of a pilgrim from the Middle East who arrived around 2000 years ago. It is said that the tomb houses the body of Jesus Christ, who survived the crucifixion and fled to India to live a life of quiet contemplation. Although the tomb is officially the resting place of a Muslim preacher called Youza Asaph, the speculation around the Jesus story is still quite strong.
Although this might be controversial for some, even if it isn’t the body of Christ, the fact of the matter is that people did make such a huge journey even in antiquity. This could have been to spread their own gospel, or to study Buddhism (the dominant religion at the time).
China too has a history of classical travellers, such as Hsuan Tsang, born around 607CE. Although it was illegal to travel outside of China around this time, between 627-643, Tsang travelled along the Silk Route, to Samarkand and Tashkent (both in modern Uzbekistan), and eventually visited Benares in India on a Buddhist pilgrimage. He even recorded his travels in a book, Great Tang Records on the Western Regions.
Zheng He is another famous example of a Chinese traveller, although he was more a diplomat acting at the behest of the Emperor of the time. Born in Yunan to a Muslim family, He led expeditions as far afield as the Arabian Peninsula, the Horn of Africa and Sri Lanka. Zheng He bought back many exotic treasures to the emperors including spices, wild animals and minerals and was even rumoured to have reached the American continent and Australia.
His ships were also famous, mainly for being huge. Although time may have blurred the truth, rumours of the time suggest that his flagship was many times bigger than any other wooden ship of the time.
Conquests, Pilgrimages and Persecution
Back in Europe, there was undoubtedly tourism during the middle ages, that is the years between the 5th and 15th century. Much of it would have centered around religious observances, for example pilgrimages to distant temples and the tombs of Saints.
With the conquest of Spain by the Muslims, many would come from as far away as Baghdad or Damascus to enjoy the lifestyle in this lush distant land.
With Muslims so far flung, the pilgrimage to Mecca would have been one of the main reasons for pilgrims to travel huge distances. From Al Andalus (Spain) or Morocco, all the way to Arabia, or even in the case of Zhang He, visiting from China, Mecca was probably one of the biggest destinations for travellers for hundreds of years.
And, with the religious theme being kept, the Crusades inspired a whole generation of European noblemen to head to their own holy land of Jerusalem and Palestine to defend against the invading Muslims. Although the Crusades are illustrated as battles and sieges, in fact there is evidence of some co-existence and even sharing of knowledge.
Moving towards the modern age, with the discovery of America by Europeans in 1492, people began to eye the new world more as a new frontier and the chance for a new beginning. Travel to the Americas was, at first, less about travel and more about escaping persecution, poverty and hardship in Europe.
The 16th, 17th and 18th centuries saw lots of movement, through forced migration such as slavery or displacement as well as colonising Asia, Australia, parts of Africa and the Americas. And with the opening of shipping routes, an increased exposure to foreign cultures through newspapers and books and more awareness of the world around us, a new era was about to begin…
The Birth of Tourism
Tourism as we would recognise it today started around the 17th or 18th century. Well to do Europeans would set off on a Grand Tour of classical cities across the continent, taking in stops in Paris, Vienna, Prague, Florence, Rome, Venice and London, among many others. In this respect, the modern travel trail isn’t quite so modern as it would seem.
Famous poets such as Britain’s Lord Byron spent two years travelling the Mediterranean, enjoying copious amounts of wine and seducing the locals. In-keeping with this style of travel, the Grand Tour tended to be reserved for the nobles and more monied classes. These ‘tourists’ would then return with tall tales of the riches of far off lands and often publish memoirs, poems and other forms of media, a precursor to Instagram posts perhaps?
Arguably, mass tourism as we know it today took shape when Thomas Cook, a British businessman, started organising mass tours from his base in Leicester. At first, his ‘travel agency’ would organise excursions across England. His first, in 1841, was from Leicester in England, to Loughborough, a town just 11 miles away. His next ‘tour’ was to Liverpool, and by 1856 he was organising tours to Scotland, Italy, Egypt and even the United States – surely a milestone in the history of travel and tourism as we know it.
Today, Thomas Cook is still a household brand name in the UK, with the company offering holiday packages across the world.
The Sky is the Limit
Of course, air travel changed everything. From days, or even weeks to reach a destination, suddenly far flung cities were within just a few hours reach.
The first commercial air link, in 1914, was between St Petersburg and Tampa, both in Florida, USA. By 1919, many nations began setting up commercial airlines, some of which are still in operation today. KLM (Royal Dutch Airlines), Czech Airlines, Avianca and Qantas are a few of the founding transcontinental airline companies who are still flying the skies.
Although air travel was slow at first, as anyone who has seen an Indian Jones movie would understand, it was still a lot faster than travelling by boat or train. And, of course, it was expensive. Air travel was the preserve of the rich, and the glamour associated with air travel is still something people come to expect.
Today, of course, budget airlines rule the skies and everyone can fly around the world for what amounts to pocket change. Anyone can fly away for a city break getaway for the weekend, or perhaps to live as a digital nomad in a more exotic city. Ryanair in Europe, AirAsia in Asia and JetBlue of the USA make travel much more accessible for everyone, although perhaps to the detriment of that glamorous image.
Now, the world is struggling with the effects of over-tourism, with protests in popular locations such as Barcelona and Venice. But, the double edged sword means that the tourist dollar is still welcomed, even if those excessive tourists are not. So where next for tourism?
Are people looking for more independent and unique experiences? Or perhaps we’re going to start looking to the stars… One thing is for sure, the history of travel is still being written.
Share This Article!
About the author: oliver lynch.

Interesting stuff. Have you read the mentioned book ‘Great Tang Records on the Western Regions’? I am wondering if it is any good?
Hey Walter, I actually haven’t read it and I couldn’t find a Kindle edition (not quite ready to splash out $50 on a print copy). Let me know if you find a copy and what you think of it…
Leave A Comment Cancel reply

OUR HISTORY Four Decades in the Travel Business
The travel agent’s story, second generation owner, mark moorhead:.

They were handling leisure travel for a lot of Carmel residents, many of whom were business owners or managers. Pleased with the agency, many of those clients requested The Travel Agent see to their corporate travel needs as well. We added on personnel and so forth; the agency continued to grow.
“As the city grew, so did the agency.”
In 1989, my folks asked me to come on board. The business was growing and they were excited about its future, but they were in their mid to late sixties by this point. So they brought me in and made me an offer. We were living in Phoenix at the time, and although we loved Arizona, we felt Carmel/Indy was an ideal place to raise the boys. And up we came.
Since I’d run and owned businesses in the past, I had some experience and familiarity. I came in and learned the trade. They slowly worked themselves out as I worked myself in and eventually took over.
“The key is to find the advisor and relationship that works for you.”
I believe that the concept of specialization in business has really come to fruition over the last two or three decades. The knowledge of our advsiors spans the globe; we build relationships with not only our clients, but locals around the world to help facilitate your travel dreams.
Our agents specialize in creating unique and custom itinerary’s built around your needs, desires and wishes on any of the 7 continents. We take the time to listen to your unique requests and bring those to reality by utilizing our partnerships and knowledge from around the world.
The key is to find the advisor and relationship that works for you. Once that is found, our customers don’t leave us. Even if they move to Colorado or retire to Florida, with today’s technology the relationship can continue. We are building our business as a result of our specialization and our relationships.
Let us put our experience to work for you.
- Switzerland
- Galapagos Islands
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Extraordinary Journeys
- How This Works
- Helpful Links
- Our History
- Testimonials
- Corporate Travel

History of the Travel Agent Industry
Leave a comment cancel reply, privacy overview.


Art & Culture Travel Blog
History of travelling: how people started to travel.
- Tea Gudek Šnajdar
- Cultural Tourism

Although we often have a feeling like people are travelling for the last few decades only, the truth is – people are travelling for centuries. Old Romans were travelling to relax in their Mediterranean villas. At the same time, people in Eastern Asia wandered for cultural experiences. I’ve got so fascinated with the history of travelling, that I did my own little research on how people started to travel. And here is what I’ve learned.
History of travelling
I was always curious about the reason people started to travel. Was it for pure leisure? To relax? Or to learn about new cultures, and find themselves along the way?
I wanted to chaise the reason all the way to its source – to the first travellers. And hopped to find out what was the initial motivation for people to travel.
According to linguists, the word ‘travel’ was first used in the 14th century. However, people started to travel much earlier.
While looking at the history of travelling and the reasons people started to travel, I wanted to distinguish the difference between travellers and explorers. Most of the time, when thinking about travel in history, people like Marco Polo or Christopher Columbus are coming to mind. However, they weren’t really travellers in a modern sense. They were explorers and researchers. So, to really learn about how people started to travel, I wanted to focus on ordinary people. Travellers like you and me, if you wish.
Romans and their roads

First people who started to travel for enjoyment only were, I’m sure you won’t be surprised, old Romans. Wealthy Romans would often go to their summer villas. And it was purely for leisure. They could, of course, start doing that because they invented something quite crucial for travelling – roads. Well developed network of roads was the reason they could travel safely and quickly.
However, there is another reason that motivated people in Antiquity to travel. And I was quite amazed when I learned about it.
It was a desire to learn. They believed travelling is an excellent way to learn about other cultures, by observing their art, architecture and listening to their languages.
Sounds familiar? It seems like Romans were the first culture tourists.
⤷ Read more : 20 Archaeological sites you have to visit in Europe
Travelling during the Middle Ages
It may come by surprise, but people started to wander more during the Middle Ages. And most of those journeys were pilgrimages.
Religion was the centre of life back in the Middle Ages. And the only things that connected this world with the saints people were worshipping, were the relics of saints. Pilgrims would often travel to another part of the country, or even Europe to visit some of the sacred places.
The most popular destinations for all those pilgrims was Santiago de Compostela, located in northwest Spain. People would travel for thousands of kilometres to reach it. To make a journey a bit easier for them, and to earn money from the newly developed tourism, many guest houses opened along the way. Pilgrims would often visit different towns and churches on their way, and while earning a ticket to heaven, do some sightseeing, as well.
Wealthy people were travelling in the caravans or by using the waterways. What’s changing in the Middle Ages was that travel wasn’t reserved only for the rich anymore. Lower classes are starting to travel, as well. They were travelling on foot, sleeping next to the roads or at some affordable accommodations. And were motivated by religious purposes.
⤷ TIP : You can still find many of those old pilgrim’s routes in Europe. When in old parts of the cities (especially in Belgium and the Netherlands ), look for the scallop shells on the roads. They will lead you to the local Saint-Jacob’s churches. Places dedicated to that saint were always linked to pilgrims and served as stops on their long journeys. In some cities, like in Antwerp , you can follow the scallop shell trails even today.
Below you can see one of the scallop shells on a street and Saint-Jacques Church in Tournai , Belgium.

Grand Tours of the 17th century
More impoverished people continued to travel for religious reasons during the following centuries. However, a new way of travelling appeared among wealthy people in Europe.
Grand tours are becoming quite fashionable among the young aristocrats at the beginning of the 17th century. As a part of their education (hmmm… culture tourists, again?) they would go on a long journey during which they were visiting famous European cities. Such as London , Paris , Rome or Venice, and were learning about their art, history and architecture.
Later on, those grand tours became more structured, and they were following precisely the same route. Often, young students would be accompanied by an educational tutor. And just to make the things easier for them, they were allowed to have their servants with them, too.
One of those young aristocrats was a young emperor, Peter the Great of Russia. He travelled around western Europe and has spent a significant amount of his time in the Netherlands. The architecture of Amsterdam and other Dutch cities definitely inspired a layout of the new city he has built – Saint Petersburg . So, travelling definitely remains an essential part of education since Roman times.
⤷ Read more : 15 Best museums in Europe you have to visit this year
The railway system and beginning of modern travel in the 19th century

Before the railway system was invented, people mostly travelled on foot (budget travel) or by water (the first-class travel at that time). However, when in the 1840s, an extensive network of railways was built, people started to travel for fun.
Mid-19th century definitely marks a real beginning of modern tourism. It’s the time when the middle class started to grow. And they have found a way to travel easily around Europe.
It’s coming by no surprise that the first travel agency, founded by Thomas Cook in England, was established at that time, too. He was using recently developed trains together with a network of hotels to organise his first group trips.
⤷ Read more : The most interesting European myths and legends
History of travelling in the 20th century
Since then, things started to move quickly. With the development of transportation, travelling became much more accessible. Dutch ships would need around a year to travel from Amsterdam to Indonesia. Today, for the same trip, we need less than a day on a plane.
After the Second World War, with the rise of air travel, people started to travel more and more. And with the internet and all the cool apps we have on our smartphones, it’s easier than ever to move and navigate your way in a new country. Mass tourism developed in the 1960s. But, with the new millennium, we started to face the over-tourism.
We can be anywhere in the world in less than two days. And although it’s a great privilege of our time, it also bears some responsibilities. However, maybe the key is to learn from history again and do what old Romans did so well. Travel to learn, explore local history and art, and be true culture tourists.
History of Travelling , How people started to travel , Travel
An official website of the United States government Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
A Brief History of the FAA
The modern age of powered flight began in 1903 when Orville Wright made the first sustained, powered flight on December 17 in a plane he and his brother Wilbur built. This twelve-second flight led to the development of the first practical airplane in 1905 and launched worldwide efforts to build better flying machines. As a result, the early 20th century witnessed myriad aviation developments as new planes and technologies entered service. During World War I, the airplane also proved its effectiveness as a military tool and, with the advent of early airmail service, showed great promise for commercial applications.
Despite limited post-World War I technical developments, early aviation remained a dangerous business. Flying conditions proved difficult since the only navigation devices available to most pilots were magnetic compasses. Pilots flew 200 to 500 feet above ground so they could navigate by roads and railways. Low visibility and night landings were made using bonfires on the field as lighting. Fatal accidents were routine.
The Air Mail Act of 1925 facilitated the creation of a profitable commercial airline industry, and airline companies such as Pan American Airways, Western Air Express, and Ford Air Transport Service began scheduled commercial passenger service. By the mid-1930s, the four major domestic airlines that dominated commercial travel for most of the 20th century began operations: United, American, Eastern, and Transcontinental and Western Air ( TWA ).
As air travel increased, some airport operators, hoping to improve safety, began providing an early form of air traffic control ( ATC ) based on visual signals. Early controllers stood on the field and waved flags to communicate with pilots. Archie League, the system's first flagmen, began work in the late 1920s at the airfield in St. Louis, Missouri.
Origins of the FAA
Birth of federal aviation agency, from agency to administration, labor organizes, evolving duties, air traffic control automation, deregulation, labor unrest, technological innovation, organizational restructuring, creation of faa's air traffic organization ( ato ), the next generation air transportation system (nextgen), enhancing capacity, safety first, last, and always.
Aviation industry leaders believed the airplane could not reach its full commercial potential without federal action to improve and maintain safety standards. At their urging, the Air Commerce Act was passed in 1926. This landmark legislation charged the Secretary of Commerce with fostering air commerce, issuing and enforcing air traffic rules, licensing pilots, certifying aircraft, establishing airways, and operating and maintaining aids to air navigation. A new Aeronautics Branch in the Department of Commerce assumed primary responsibility for aviation oversight, and William P. MacCracken, Jr., became its first director.
In 1934, the Department of Commerce renamed the Aeronautics Branch the Bureau of Air Commerce to reflect the growing importance of aviation to the nation. In one of its first acts, the Bureau encouraged a group of airlines to establish the first air traffic control centers (Newark, New Jersey; Cleveland, Ohio; and Chicago, Illinois) to provide en route air traffic control. In 1936, the Bureau took over these centers. Early en route controllers tracked the position of planes using maps and blackboards and little boat-shaped weights that came to be called "shrimp boats." They had no direct radio link with aircraft, but used telephones to stay in touch with airline dispatchers, airway radio operators, and airport traffic controllers. Although en route ATC became a federal responsibility, local government authorities continued to operate airport towers. While the Department of Commerce worked to improve aviation safety, a number of high profile accidents called the department's oversight responsibilities into question. A 1931 crash that killed all on board, including popular University of Notre Dame football coach Knute Rockne, elicited public calls for greater federal oversight of aviation safety. Four years later, a DC-2 crash killed U.S. Senator Bronson Cutting of New Mexico.
To ensure a federal focus on aviation safety, President Franklin Roosevelt signed the Civil Aeronautics Act in 1938. The legislation established the independent Civil Aeronautics Authority ( CAA ), with a three-member Air Safety Board that would conduct accident investigations and recommend ways of preventing accidents. The legislation also expanded the government's role in civil aviation by giving CAA power to regulate airline fares and determine the routes individual carriers served. In 1940, President Roosevelt split the CAA into two agencies, the Civil Aeronautics Administration, which went back to the Department of Commerce, and the Civil Aeronautics Board ( CAB ). The offshoot of the original CAA retained responsibility for ATC , airman and aircraft certification, safety enforcement, and airway development. CAB responsibilities included safety rulemaking, accident investigation, and economic regulation of the airlines.
On the eve of America's entry into World War II, for defense purposes, CAA extended its ATC system to include operation of airport towers. In the postwar era, ATC became a permanent federal responsibility at most airports. The postwar era also witnessed the advent of commercial jets. The British Overseas Aircraft Corporation introduced the first commercial jet service in 1952. The 36-seat Comet flew at 480 miles per hour. The top cruising speed of the DC-3 piston aircraft, in comparison, was about 180 miles per hour. By the mid-1950s, U.S. companies began designing and building their own jet airliners.
On June 30, 1956, a Trans World Airlines Super Constellation and a United Air Lines DC-7 collided over the Grand Canyon, Arizona, killing all 128 occupants of the two airplanes. The collision occurred while the aircraft were flying under visual flight rules in uncongested airspace. The accident dramatized the fact that, even though U.S. air traffic had more than doubled since the end of World War II, little had been done to mitigate the risk of midair collisions.
On May 21, 1958, Senator A. S. "Mike" Monroney (D-OK) introduced a bill to create an independent Federal Aviation Agency to provide for the safe and efficient use of national airspace. Two months later, on August 23, 1958, the President signed the Federal Aviation Act, which transferred the Civil Aeronautics Authority's functions to a new independent Federal Aviation Agency responsible for civil aviation safety. Although the Federal Aviation Agency technically came into existence with the passage of the act, it actually assumed its functions in stages. Under the provisions of the act, the Federal Aviation Agency would begin operations 60 days after the appointment of the first Federal Aviation Agency Administrator. On November 1, 1958, retired Air Force General Elwood "Pete" Quesada became the first Federal Aviation Agency Administrator. Sixty days later, on December 31, the Federal Aviation Agency began operations.
With no dedicated office space for the Federal Aviation Agency, employees of the growing agency were housed in several widely dispersed buildings around Washington, DC, including some "temporary" buildings of World War II vintage. The Federal Aviation Agency worked to obtain a headquarters building to consolidate employees in one location, and on November 22, 1963, the Federal Aviation Agency's Washington headquarters staff began moving into the newly completed Federal Office Building 10A, at 800 Independence Avenue, SW. Excitement about the new building quickly evaporated on move day as employees heard the news that President Kennedy had been assassinated in Texas.
President Johnson, concerned about the lack of a coordinated transportation system, believed a single department was needed to develop and carry out comprehensive transportation policies and programs across all transportation modes. In 1966, Congress authorized the creation of a cabinet department that would combine major federal transportation responsibilities. This new Department of Transportation ( DOT ) began full operations on April l, 1967. On that day, the Federal Aviation Agency became one of several modal organizations within DOT and received a new name, the Federal Aviation Administration ( FAA ). At the same time, CAB's accident investigation function was transferred to the new National Transportation Safety Board.
In January 1968, New York controllers formed an employee organization, the Professional Air Traffic Controllers Organization, or PATCO . Within six months, PATCO had a national membership of over 5,000 controllers. To highlight difficult working conditions and growing national airspace system ( NAS ) congestion, in July 1968, the PATCO chairman announced "Operation Air Safety," which he described as a campaign to maintain FAA prescribed separation standards between aircraft. A period of discord between management and PATCO culminated in a 1970 "sickout" by 3,000 controllers. Although controllers subsequently gained additional wage and retirement benefits, tensions between the union and management did not ease.
In February 1972, the National Association of Air Traffic Specialists ( NAATS ) became the exclusive representative for all flight service station specialists, those controllers who supported general aviation pilots. FAA and NAATS concluded an agency-wide collective bargaining agreement on June 1, 1972, the first such contract between FAA and a national labor organization.
Almost from its creation, the agency found itself faced with a number of unexpected challenges. In 1961, for example, the first series of aircraft hijackings in the U.S. occurred. In August of that year, the federal government began employing armed guards, border patrolmen recruited from the U.S. Immigration and Naturalization Service, on civilian planes. In September, President Kennedy signed an amendment to the Federal Aviation Act of 1958, which made it a crime to hijack an aircraft, interfere with an active flight crew, or carry a dangerous weapon aboard an air carrier aircraft. To help enforce the act, a special corps of FAA safety inspectors began training for duty aboard airline flights. In March 1962, Attorney General Robert Kennedy swore in FAA's first "peace officers," as special U.S. deputy marshals. These men worked as safety inspectors for the FAA flight standards organization and carried out their role as armed marshals on flights only when specifically requested to do so.
FAA responsibilities increased even more in the late 1960s. An economic boom brought with it growing concerns about pollution and noise. Aviation, on the cutting edge of technological innovation, became an early area of environmental concern for the public, especially as more and more airplanes traversed the NAS . In 1968, Congress vested in FAA's Administrator the power to prescribe aircraft noise standards.
With continued growth in the nation's airspace, it quickly became evident that airport safety and capacity had to be increased to prevent system delays. Between mid-1959 and mid-1969, the number of aircraft operations at FAA's ATC towers had increased by 112 percent. Schedule delays cost the air carriers millions of dollars annually, not to mention the cost to passengers over and above inconvenience and discomfort. The Airport and Airway Development Act of 1970 placed the agency in charge of a new airport aid program funded by a special aviation trust fund and made FAA responsible for safety certification of airports served by air carriers.
Realizing the need for continued ATC system modernization to keep up with technological developments, FAA began modernizing the NAS in the mid-1960s. The civilian ATC system being replaced by NAS En Route Stage A was essentially a manually operated system employing radar, general purpose computers, radio communications, and air traffic controllers. For terminal airspace, the FAA was developing the automated radar traffic control system ( ARTS ).
To help monitor and even restrict flights moving from one air route traffic control center to another, FAA established the Central Flow Control Facility at its Headquarters. Opened in April 1970, the new facility collected and correlated systemwide air traffic and weather data, detected potential trouble spots, and suggested solutions. On July 29, FAA established the Air Traffic Control Systems Command Center to integrate the functions of the Central Flow Control Facility, Airport Reservation Office, the Air Traffic Service Contingency Command Post, and Central Altitude Reservation Facility.
The Airline Deregulation Act, signed on October 24, 1978, created a highly competitive airline industry. Deregulation increased FAA workload exponentially. The FAA had to certify every new airline, and there were hundreds of applications after deregulation that FAA had to review and approve or disapprove. In the immediate years after the deregulation act, FAA flight standards and other offices focused primarily on the new applicants.
By the time airline deregulation became law, FAA had achieved a semi-automated air traffic control system based on a marriage of radar and computer technology. Despite its effectiveness, however, the air traffic control system required enhancement to keep pace with the increased volumes of traffic that resulted from the new, deregulated environment.
The labor contract between FAA and PATCO expired in March 1981. Formal contract negotiations had begun in February, but those ended after 37 negotiating sessions. Informal talks, however, continued until June 17, when PATCO rejected a Reagan Administration contract proposal. After the failure of last minute negotiations, on August 3, approximately 12,300 members of the 15,000-member PATCO went on strike, grounding about 35 percent of the nation's 14,200 daily commercial flights. Approximately four hours after the strike began, President Reagan issued the strikers a firm ultimatum – return to work within 48 hours or face permanent dismissal. After expiration of the grace period, FAA fired approximately 11,400 controllers. Most of those fired appealed the action, and FAA eventually reinstated 440 as a result of their appeals.
The strike and dismissals drastically curtailed FAA's controller workforce. To keep the airways open, approximately 3,000 air traffic controller supervisory personnel worked at controlling traffic. FAA assigned assistants to support the controllers, and accelerated the hiring and training of new air traffic personnel. Military controllers arrived at FAA facilities soon after the strike began, and about 800 were ultimately assigned to the agency.
In the aftermath of the strike, PATCO disbanded and the controllers remained without a union until June 19, 1987, when the National Air Traffic Controllers Association became the exclusive representative of terminal and center controllers.
During this time, FAA electronics technicians unionized. On December 29, 1981, the Professional Airway Systems Specialists ( PASS ) became the exclusive representative of the technicians. FAA and PASS concluded their first national labor agreement during fiscal year 1984.
Aviation system disruptions in the aftermath of the PATCO strike led many in FAA to come to the realization that the agency needed a systematic, long-term plan for modernization. In January 1982, FAA publicly released the first annual National Airspace System ( NAS ) Plan, a comprehensive 20-year blueprint for a state-of-the-art traffic control and air navigation system to accommodate projected growth in air travel.
As the modernization program evolved, problems in developing ambitious automation systems prompted a change in strategy. FAA shifted its emphasis from the advanced automation system toward enhancing the ATC system through more manageable, step-by-step improvements through the new Free Flight program. At the same time, the agency worked to speed the application of the Global Positioning System satellite technology to civil aeronautics.
In February 1991, FAA replaced the NAS Plan with the more comprehensive Capital Investment Plan. The new plan incorporated the NAS plan projects and included higher levels of automation as well as new radar, communications, and weather forecasting systems.
FAA also addressed a wide variety of technical issues as the rapid evolution of aeronautics continued. The Aviation Safety Research Act of 1988, for example, mandated greater emphasis on long-range research planning and on study of such issues as aging aircraft structures and human factors affecting safety. FAA engineers and scientists also investigated areas such as human performance in aeronautical tasks, improvement of runways, and the effects of corrosion on aircraft structures.
In November 1995, DOT transferred the commercial space transportation office to the FAA . Originally established within DOT in 1984, the new FAA office regulated the U.S. commercial launch industry, licensed commercial launch operations to ensure public health and safety and the safety of property, and protected national security and foreign policy interests of the United States during commercial launch operations. It also issued licenses for commercial launches of orbital and suborbital rockets.
The fiscal year 1996 DOT appropriations bill, signed in November 1995, included important provisions for FAA personnel and procurement reform. FAA began the mandated reforms by first creating a new acquisition management system designed to reduce the time and cost of acquiring systems and services. FAA then placed all employees into a new personnel system intended to speed recruitment and reward outstanding employees, while dealing effectively with substandard performance. While the agency was no longer subject to certain Office of Personnel Management rules, its employees continued to enjoy a range of legal protections that applied to other federal workers.
In June 1998, FAA began testing a new compensation plan called core compensation, which replaced the traditional grade and step base pay method with a structure of pay bands, the value of which were determined by comparison with similar jobs in government and private industry. The program also linked compensation with performance. On April 23, 2000, FAA transferred approximately 6,500 employees into the core compensation system.
On September 11, 2001, nineteen radical Islamic extremists with the group al Qaeda penetrated security at three major airports, seized four U.S. domestic airliners, and turned three of the aircraft into missiles that destroyed the World Trade Center in New York City and damaged the Pentagon in Arlington, Virginia. Passengers on the fourth plane fought the hijackers, causing the plane to crash in a Pennsylvania field. To prevent any further hijackings, FAA immediately put a ground stop on all traffic for the first time in U.S. aviation history. In the overnight hours of September 11, members of FAA's Flight Standards Service developed an initial lead identifying the names of potential hijackers and provided those names to the FBI . The tragic events of this day radically changed the FAA . On November 19, 2001, the president signed the Aviation and Transportation Security Act, which among other provisions, established a new agency responsible for aviation security – the Transportation Security Administration ( TSA ), within DOT . FAA remained responsible for aviation security until February 13, 2002, when TSA took over those responsibilities. The November 2002, passage of the Homeland Security Act moved TSA into the new Department of Homeland Security on March 1, 2003.
In April 2000, President Clinton signed into law the Wendell H. Ford Aviation Investment and Reform Act for the 21st Century, which contained a provision mandating the appointment of a chief operating officer. In a December executive order, the president directed FAA to create a performance-based organization that focused solely on efficient operation of the ATC system.
In June 2003, FAA selected its first ATO Chief Operating Officer ( COO ), Russell Chew. With the COO in place, FAA went forward with a major reorganization of its air traffic and research and acquisition organizations. On November 18, 2003, the Secretary of Transportation announced initial details of the new ATO business structure. The ATO consolidated FAA's air traffic services, research and acquisitions, and Free Flight Program activities into a smaller, more efficient organization with a strict focus on providing the best service for the best value to the aviation industry and the traveling public.
The ATO officially began operations on February 8, 2004. It consisted of five major service units: En Route & Oceanic; Terminal; Flight Services; System Operations; and, Technical Operations. Also included within the organization's top level are five staff-level business groups: Safety; Communications; Operations Planning; Finance; and Acquisition and Business Services. In 2008, the ATO consolidated the service units and staff offices into four business units, each led by a senior vice president.
In line with other agency efforts to improve efficiency, in December 2005, the COO restructured ATO administrative and support functions in the field. In June 2006, he instituted a new ATO Service Center structure. Three service centers replaced the nine service area offices within En Route, Terminal, and Technical Operations. Each of the service centers was made up of five functional groups: administrative services, business services, safety assurance, system support, and planning and requirements. A sixth group, engineering services, was a shared resource and remained in place in the existing locations.
With the ATO structure in place, the agency's first COO resigned from FAA on February 23, 2007. Administrator Marion Blakey assigned COO responsibilities to Deputy Administrator Robert Sturgell as collateral duties until a new COO came on board. On October 1, 2007, Administrator Blakey hired the agency's second COO , Hank Krakowski.
The Vision 100 – Century of Aviation Reauthorization Act, signed into law in December 2003, endorsed the concept of a Next Generation Air Transportation System (NextGen). The following month, the DOT Secretary announced plans for a new, multi-year, multi-agency effort to develop an air transportation system for the year 2025 and beyond. He subsequently established a Joint Planning and Development Office ( JPDO ) at the FAA comprised of representatives from FAA , National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the Departments of Transportation, Defense, Homeland Security, and Commerce, and the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy to create and carry out an integrated plan for NextGen. On December 15, 2004, DOT unveiled the Integrated Plan for the Next Generation Air Transportation System, which laid out goals, objectives, and requirements necessary to create the NextGen system.
When constraints in en route airspace and the airspace surrounding U.S. airports began to result in flight delays and schedule disruptions, FAA began to look for immediate solutions while continuing NextGen activities. To improve capacity, FAA began implementing a number of new concepts. The Required Navigation Performance ( RNP ) concept, for example, would take advantage of new onboard technologies for precision guidance to help transition the NAS from reliance on airways running over ground-based navigation aids to a point-to-point navigation concept. FAA also implemented the use of Reduced Vertical Separation Minima ( RVSM ), which reduced the minimum vertical separation between aircraft from 2,000 feet to 1,000 feet for all properly equipped aircraft flying between 29,000 feet and 41,000 feet. This increased the routes and altitudes available and allowed more efficient routings that would save time and fuel.
Between 2001 and 2007, aviation witnessed one of its safest periods for scheduled air carriers. Not counting the terrorist activities of September 11, 2001, there were only three fatal accidents in 2001; none in 2002; two in 2003; one in 2004; three in 2005; two in 2006; and none in 2007. Fatal accidents became rare events with only .01 accidents per 100,000 flight hours or .018 accidents per 100,000 departures.
Thanks to the work of FAA , over the past 50 years, aviation has become central to the way we live and do business, linking people from coast to coast and connecting America to the world. In fact, FAA has created the safest, most reliable, most efficient, and most productive air transportation system in the world.
To ensure aviation's future viability, FAA is now working with its federal and industry partners to develop a flexible aerospace system that fully responds to the changing needs of businesses and customers in the 21st century. The strength of the NextGen system depends on lower costs, improved service, greater capacity, and smarter security measures. That is why FAA has defined a vision of the future that integrates achievements in safety, security, efficiency, and environmental compatibility.
Last updated: Monday, November 15, 2021
Collecting Soviet History
History of the Soviet Union with an emphasis on its state security services and their role in maintaining cohesion throughout the USSR. The Cheka and NKVD gradually evolved into the KGB and MVD. Collectively, these agencies enabled the Soviet structure to remain in place as long as it did, and longer than it might have otherwise. (Note: For best results, please read in chronological order starting with the "Introduction" in the column on the right side of the page under "Archive of Chapters")
The Bolshevik
08 march 2011, nkvd honored employee badges and documents, no comments:, post a comment.
Moscow tours, business travel to moscow, tour guide service, interpreting service
- Our Service
- Our Photo Album
Moscow tours, business travel to Moscow, tour guide service, interpreting service
We are here to navigate you through Moscow and beyond. We specialize in private and customer-tailored tours for individuals and groups.
Tour options include:
- Moscow tours in 1 day/2days/3days (Red Square tour, Kremlin tour, metro tour, panoramic city tour, etc);
- Moscow panoramic city tour / night Moscow by legendary retro cars ;
- Layover tours in Moscow;
- Moscow cultural heritage tours, Moscow themed tours;
- Russian home hosted visits (visit to the Russian dacha);
- Russian culinary classes;
- Moscow-St.Peterburg tour package. Two Russian capitals in one week;
- Moscow-St.Petersburg educational tours for students and children;
- Russian towns of the Golden Ring (Sergiev Posad, Suzdal, Vladimir); Trips out of Moscow
- Shore excursions (Moscow/St.Petersburg)
- Russian honeymoon tours, photo walks in Moscow;
- Moscow tours for children
- Christmas time in Moscow;
- AK-47 shooting tour, tank T-34 ride, segway tour, fishing in Moscow region.
- Group Tours ( offers for travel agencies)
We are officially endorsed by Moscow Government to guide in most iconic tourist attractions of Russia’s capital such as Red Square, St. Basil’s Cathedral, museums of the Moscow Kremlin, the Tretyakov Art Gallery, etc.
We love our city and are ready to share with you our in-depth knowledge of Moscow, this old but very dynamic and amazing city. We will be glad to provide context and fun in equal measure opening up your eyes to Russian history, culture and art.
We know how to make the most of your time while you are here and will be delighted to turn your stay in Moscow into a life experience.
Why book with us?
- We love what we do.
- We highly value responsibility and individual approach.
- Our friendly booking service will help plan your itinerary according to your wishes. We are very flexible and design the tours individually for every customer.
- We are officially recognized by Moscow Government.
- Our training, qualifications, experience and personality will ensure that your visit to Moscow is a great success.
We take part in BBC series of documentaries "World's Busiest Cities"(Moscow)

Buy Tickets to the Bolshoi Theatre

Other special offers...
Interpreting and assistance at exhibitions and conferences, our garage ( vehicles+drivers), where to stay in moscow, what and where to eat in moscow, visa support, learning and discovery, our partners (trips to st.petersburg).
Copyright 2015 - Moscow Navigator
Ukraine-Russia war latest: Putin more confident than ever after inauguration speech; plot to 'kill Zelenskyy' stopped
Vladimir Putin has been officially sworn in as Russian president for a new six-year term, although many Western nations did not attend. The ruler seems more confident than ever. Elsewhere, Ukraine says it has foiled a plot to kidnap and kill President Zelenskyy.
Tuesday 7 May 2024 19:09, UK

- Putin sworn in again as president | Claims Russia would work with West
- 'We elect our president': Kremlin defends 'purely democratic' Russia
- Ivor Bennett analysis: Painted as a modern-day Tsar, Putin seems more confident than ever
- Plot to 'kidnap and kill Zelenskyy' stopped, Ukraine says
- Many nations boycott Putin's inauguration ceremony
- Putin has 85% approval rating - here's why
- Big picture : What you need to know as a new week begins
- Your questions answered: Why can't Ukraine destroy key Crimean bridge?
- Live reporting by Lauren Russell and Ollie Cooper
We're pausing our live coverage of the war in Ukraine for the time being - thanks for tuning in.
Before you go, here is a recap of today's developments.
- Vladimir Putin was officially sworn in again as Russian president, marking the start of his fifth term in office;
- During his inaugural speech, Mr Putin said he is willing to work with the West, but it is down to them to cooperate with Russia;
- Two people have been arrested after Ukraine's intelligence agency foiled a plot to assassinate President Volodymyr Zelenskyy;
- The widow of former Putin critic Alexei Navalny criticised Mr Putin on the day of his inauguration calling him a murderer and a liar.
By Ivor Bennett , Moscow correspondent
Held inside the throne room of the Tsars, the ceremony felt almost like a coronation rather than an inauguration.
And that was part of the point. The symbolism was key.
Andreyevsky Hall, where Vladimir Putin took the oath of office, is dripping with gold.
It oozes power.
I think this was an attempt to paint him as a modern-day Tsar, who is the rightful ruler of Russia.
The other aim was to add the stamp of electoral legitimacy to his leadership, and his policies.
The Kremlin’s chief spokesman Dmitry Peskov told me beforehand that this was just part of the "democratic" political process (see our 13.35 post).
The speech was typical Putin - talking up Russia's greatness, blaming the West for Moscow's isolation and doubling down on his current path of conflict abroad and a crackdown at home.
He said he ranks the safety of the Russian people "above all else".
Translation - we're in this for the long haul.
But whose fault is Russia’s status as a global pariah?
Not ours, he said.
This was all part of the Kremlin's narrative to portray the West as the aggressor, and Russia as the victim.
What might concern people both at home and abroad was the tone of the speech.
For example, he gave a thinly veiled warning that protest will not be tolerated, saying it’s important "not to forget the tragic price of internal turmoil", adding that Russia must be "absolutely resistant" to it.
And the last line: "We will overcome all obstacles and bring all our plans to life."
Vladimir Putin seems more confident than ever.
Polish Prime Minister Donald Tusk has said Europe needs to spend "big money" in order to prevent other powers in the world from "raising a hand against it".
Speaking at a conference in the Polish city of Katowice, Mr Tusk called on European countries to take joint action to increase spending on defence by at least €100bn (£85bn).
"Europe must be prepared in the next dozen or so months and the entire next five years for a situation in which no power in the world will dare raise a hand against it," he said.
"Big money will move the war away from Europe's borders for a long time, perhaps permanently."
He also repeated the idea of building a common European air defence system - saying Europe has "more initiatives than real actions".
Due to the war in Ukraine, Poland is strengthening its defence capabilities, allocating over 4% of its GDP.
Ursula von der Leyen, president of the European Commission, agreed Europe must spend more on defence and declared that if she remains in office for another term she will propose new defence projects.
A Russian national has been sanctioned in the UK, US and Australia for his alleged role as the creator of the most prolific ramsomware group in the world.
The sanctions target Dmitry Khoroshev who has been identified as one of the leaders of LockBit, the ransomware group responsible for extorting over $1bn from thousands of victims globally.
In the US, Khoroshev has been charged with 26 counts of allegedly developing and administering a malicious cyber scheme.
The UK's foreign office said the LockBit group was behind attacks on over 200 UK businesses and major public server providers and 25% of all global ransomware attacks.
Pro-Russian Chechen forces are baring the brunt of the frontlines in Ukraine and training Russian troops behind the scenes, the UK's Ministry of Defence says.
Around 9,000 personnel are currently serving within the Pro-Russian Chechen forces in Ukraine, which has been pushed back onto the frontline since the withdrawal of Russia's private military company, Wagner, the MoD said in its daily intelligence update.
At the start of the Ukraine war in 2022, Chechen forces became known as "TikTok troops" for their presence on social media.
But, they have since provided personnel and given training to Russians at The Special Forces University in Gudermes, Chechnya.
The MoD said troops receive up to 10 days' training at the so-called university.
Chechnya has historically always supported Russia's military action in Ukraine.
Ukraine and Russia have accused each other of using banned toxins on the battlefield.
The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), which is in The Hague, said that all accusations were "insufficiently substantiated".
But it added: "The situation remains volatile and extremely concerning regarding the possible re-emergence of use of toxic chemicals as weapons."
Neither side has asked the OPCW to investigate the alleged use of chemical weapons.
Last week, Russia denied allegations from the US that it had used the choking agent chloropicrin against Ukrainian troops and utilised riot control agents "as a method of warfare".
Under the Chemical Weapons Convention, any toxic chemical used with the purpose of causing harm or death is considered a chemical weapon.
We've been covering the fifth inauguration of Vladimir Putin as Russian president.
The ceremony took place in Moscow's Grand Kremlin Palace, and our correspondent Ivor Bennett was there to experience the entire event.
He also interviewed Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov about the state of democracy in Russia and the lack of opposition during the presidential election back in March.
Bennett asked Mr Peskov: "Western leaders and Western governments believe that Vladimir Putin has turned Russia into a dictatorship, why do you think that’s not the case?"
Mr Peskov replied: "This is not the case.
"It's just propaganda, it's rough propaganda, nothing else."
He went on to say Russia was "purely democratic", adding: "We choose our power. We elect our power. We elect our president. We vote for the president or don’t want to vote for the president.
"And we insist that we have the right to do it the way we want to do it.
"And we don’t want a third country to interfere in our choices, in our preferences."
Pressed on whether the lack of opposition to Vladimir Putin in Russia was democratic, Mr Peskov said: "But there is opposition inside the country, of course the conditions are much tougher here because we are in war conditions."
Mr Peskov used the word "war" twice in the interview - typically, the Kremlin refers to its invasion of Ukraine as a "special military operation" - a term he also used once.
Ivor Bennett then asked if it was even more important for the public to have the right to speak out in wartime.
"No, to the contrary. It needs tougher measures to ensure the victory, to ensure that we reach our goals," Mr Peskov replied.
Asked whether this was democratic, Mr Peskov insisted: "It is, it is."
He added that the Western media in Europe and the US exists in the "same circumstances".
Dozens of demonstrators gathered outside The Hague's Peace Palace in The Netherlands to protest the inauguration of President Vladimir Putin.
The protesters, many of whom had travelled from Germany, carried a giant carnival float that showed a caricature of the Russian leader with blood on his hands in a striped prison uniform.
They also held Ukrainian flags and placards saying: "Putin to The Hague" - which is the home of the International Court of Justice.
Dina Musina, who works for a Berlin-based charity that supports Russian prisoners, said they need to "raise awareness about Putin's crimes internationally".
A plot to assassinate President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has been uncovered by Ukraine's state security service (SBU).
The SBU claimed two agents who were posing as Ukrainian state guard servicemen were tasked by Moscow to figure out a way to capture Mr Zelenskyy and later kill him.
They also planned to kill other high-ranking Ukrainian officials, the SBU said in a statement on Telegram .
Head of the SBU, Vasyl Malyuk, described the plot as a "gift to Putin before the inauguration".
The SBU said two suspects have been detained after an investigation gradually documented their alleged criminal actions.
Ukrainian claims that plots to kill Mr Zelenskyy are not new.
The president said in 2022 there had been at least 10 attempts to assassinate him since the start of the war.
The widow of former Putin critic Alexei Navalny has criticised President Vladimir Putin on the day of his fifth inauguration as Russian leader.
In a video posted on YouTube shortly before the ceremony took place in Moscow, Yulia Navalnaya called Mr Putin a liar, a thief and a murderer.
She added that the war in Ukraine is "bloody and senseless" and no one wants it apart from the Russian leader.
"Huge sums of money are stolen from all of us every day to fund bombings of peaceful cities, riot police beating people with batons, propagandists spreading lies. And also for [the elite's] own palaces, yachts and private jets," she said.
"And as long as this continues, we can't stop the fight."
Having been exiled from Russia, Ms Navalnaya has vowed to continue the work of her late husband, who died in an Arctic penal colony on 16 February.
She has accused Mr Putin of having him killed, an accusation which the Kremlin has always denied.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


COMMENTS
The history of travel agencies is a compelling narrative that has witnessed significant transformations over the years. This article explores the evolution of travel agencies from their early beginnings to the present day, highlighting key milestones and shifts in the industry. Early Travel Arrangements:
A travel agency is a private retailer or public service that provides travel and tourism-related services to the general public on behalf of accommodation or travel suppliers to offer different kinds of travelling packages for each destination. ... In 1758, Cox & Kings became the first travel agency in modern history. In 1840, ...
The evolution of the travel advisor profession just might be an example of Darwinism at its finest. It's a story of adaptation, survival and revival that has pushed the profession to not just iterate, but to be born anew. Today, advisors — nee agents — serve as the de facto gatekeepers of insider knowledge about destinations and supplier ...
The history of professional travel agency may be traced back to 1841 when Thomas ... That brief success gave him ample solace to think for deepening his aim and interest to enlarge the scope of travel business in Europe. This turnaround has laid foundation of his future travel business. He later described this period as one
A Brief History of Travel and Tourism. Culture. Utilizing the widest definition of the word, human beings have been travelling since the dawn of time. No matter one's beliefs about the creation of humans, everyone can agree our species began in some single locale, likely Africa or the Middle East, and 'travelled' outwards, settling new lands.
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services. As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.
Another significant corporation connected to the travel industry is Cox & Kings. Although the corporation was founded in 1758, a year before Thomas Cook, but its first activities were focused on managing the affairs of British officers deployed abroad. Brief History of Tourism: The earliest travel agencies were founded in the 19th century.
1931 - ASTA Is Founded. 3/18. "Since its founding on April 20, 1931, as the American Steamship and Tourist Agents Association, ASTA has remained true to the mission outlined by its founding members," ASTA said. "In 1931, more than 60 agents joined an association that promised to protect and promote the mutual interests of its members, maintain ...
Main Body. Chapter 1. History and Overview. Learning Objectives. Specify the commonly understood definitions of tourism and tourist. Classify tourism into distinct industry groups using North American Industry Classification Standards (NAICS) Define hospitality. Gain knowledge about the origins of the tourism industry.
Brownell Travel markets itself as the oldest tour operator in the United States, having arranged an archaeology-focused trip to Switzerland for 10 American travellers in 1887 (at a time when Grover Cleveland, the only man to serve two non-consecutive terms as US president, was in the White House). The Polytechnic Touring Association - which ...
A brief history of the travel agent. In 1841, Thomas Cook received a commission from Midland Railway to organise the transportation of member of temperance society. He founded an agency in his own name and partnered with his son, establishing the package tour holiday. In the early 20th Century, airline numbers grew exponentially, which in turn ...
And this economy has been growing at a staggering rate throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. In 1980 there were just over 280 million tourism arrivals around the globe. By 2018, there were an estimated 1.4 billion tourist arrivals, with the money spent on travel accounting for around 10.4% of global GDP. But it wasn't always like this.
1871: The official name of the company becomes Thomas Cook & Son. 1872/73: Thomas Cook organizes and leads the world's first round-the-world tour. The journey takes 222 days and covers more than ...
In 1845, Cook arranged travel for 165,000 people without the aid of any technology. Consider for a moment, that the ball point pen had not been invented yet, the telegraph was not yet commercially available in the UK until 1846 and the telephone would not be patented for another thirty years. Cook managed all that customer and booking data with ...
The Travel Agent's Story. Second Generation Owner, Mark Moorhead: My parents started The Travel Agent in 1979. My father had just taken early retirement, the nest was empty, and they were both ready for their next adventure. She had experience in the industry from her work at an agency downtown; he had great business acumen. It was a perfect fit.
History of the Travel Agent Industry. February 25, 2015 by Kristy Feldman. Travel Agent history, travel agent, travel agent industry, travel agent industry history. 6 Travel Agent Training Options.
In spite of the controversy, over 95 percent of travel agents subscribed to a CRS in 1989, and 75 percent of airline tickets were booked through a travel agency, according to the DOJ. 1990s: Global Distribution Systems Emerge & the Internet Changes Everything. In 1992, the DOT addressed gaps in the Civil Aeronautics Board's 1984 rules.
However, when in the 1840s, an extensive network of railways was built, people started to travel for fun. Mid-19th century definitely marks a real beginning of modern tourism. It's the time when the middle class started to grow. And they have found a way to travel easily around Europe. It's coming by no surprise that the first travel agency ...
A Brief History of the FAA. The modern age of powered flight began in 1903 when Orville Wright made the first sustained, powered flight on December 17 in a plane he and his brother Wilbur built. This twelve-second flight led to the development of the first practical airplane in 1905 and launched worldwide efforts to build better flying machines.
History Company M-Travel operates at the travel market since 1994. Main directions of the company's activity are international tourism, air ticket sale, organization of business trips, sightseeing programs, foreign training, and medical treatment at the leading thermal resorts of the world.
History of the Soviet Union with an emphasis on its state security services and their role in maintaining cohesion throughout the USSR. The Cheka and NKVD gradually evolved into the KGB and MVD. Collectively, these agencies enabled the Soviet structure to remain in place as long as it did, and longer than it might have otherwise.
The badges were originally made from brass with silver plating, then were made from solid silver and later back to silver plating with at least a shiny sword blade and gold plating on the hilt and hand guard of the sword. Though the basic design continued to be used throughout the history of the USSR mostly with the NKVD and the MVD, there is ...
We specialize in private and customer-tailored tours for individuals and groups. Moscow Tours. Business trips to Moscow. Eco-tours, hikings in Moscow region. Trips to the towns of the Golden Ring of Russia. MoscowNavigator International Travel Club. St. Petersburg tours. Tour options include: Moscow tours in 1 day/2days/3days (Red Square tour ...
A Russian national has been sanctioned in the UK, US and Australia for his alleged role as the creator of the most prolific ramsomware group in the world.