

We apologize for the inconvenience...
To ensure we keep this website safe, please can you confirm you are a human by ticking the box below.
If you are unable to complete the above request please contact us using the below link, providing a screenshot of your experience.
https://ioppublishing.org/contacts/
Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification
More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

Some searches may not work properly. We apologize for the inconvenience.
The Nature And Development Of Visitor Attractions
In: handbook of tourism economics analysis, new applications and case studies.
- Author & abstract
- Related works & more
Corrections
(The University of Limerick, Ireland)
Suggested Citation
Download full text from publisher.
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
Destination Image Gaps Between Official Tourism Websites and User-Generated Content
- Conference paper
- First Online: 23 January 2016
- Cite this conference paper

- Estela Marine-Roig 3 &
- Salvador Anton Clavé 4
5608 Accesses
10 Citations
The aim of this paper is to analyse and compare destination image on official tourism websites with the image expressed by tourists in travel blogs and reviews in order to assess image congruency and identify image gaps at different geographical brand levels. This is done through a massive computerized semi-automatic content analysis of attraction factors and geographical elements on official tourism websites and in 46,576 travel blogs and review entries about Catalonia and its sub-regional brands. Our results show relative image congruency at regional level, but significant image gaps at sub-regional levels, indicating the need for coordinated image policies at different geographical levels.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

A Framework for Destination Image Analytics

The Effect of Asymmetrical Image Projections on Online Destination Branding

The Adoption of Pinterest for Destination Marketing: The Case of Austrian Destinations
Andreu, L., Bigne, J. E., & Cooper, C. (2001). Projected and perceived image of Spain as a tourist destination for British travellers. Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing, 9 (4), 47–67.
Article Google Scholar
Anton Clavé, S. (2010). Identity and tourism. Between image and perception. Paradigmes, 5 , 156–165.
Google Scholar
Bandyopadhyay, R., & Morais, D. (2005). Representative dissonance: India’s Self and Western image. Annals of Tourism Research, 32 (4), 1006–1021.
Bastida, U., & Huan, T. C. (2014). Performance evaluation of tourism websites’ information quality of four global destination brands: Beijing, Hong Kong, Shanghai, and Taipei. Journal of Business Research, 67 (2), 167–170.
Bui, T. L. H. (2011). Congruency between the projected and perceived destination image of Vietnam. Journal of International Business Research, 10 (2), 1–13.
Chen, H. J., Yung, C. Y., & Wang, M. H. (2008). Perception gaps between tourist blogs and travel information on destination image. 26th EuroCHRIE Conference , Oct. 12–14, Dubai.
Choi, S., Lehto, X. Y., & Morrison, A. M. (2007). Destination image representation on the web: Content analysis of Macau travel related websites. Tourism Management, 28 (1), 118–129.
Crompton, J. L. (1979). An assessment of the image of the Mexico as a vacation destination and the influence of geographical location upon the image. Journal of Travel Research, 17 (4), 18–23.
Dinnie, K. (2008). Nation branding: Concepts, issues, practice . Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Dragova, S., Petrovskaya, K., & Egger, R. (2014). Measuring the perceived image of Lithuania through its destination management organization website. In Z. Xiang & I. Tussyadiah (Eds.), Information and communication technologies in tourism 2014 (pp. 679–691). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-03973-2_49 .
Echtner, C. M., & Ritchie, J. R. B. (2003). The meaning and measurement of destination image. Journal of Tourism Studies, 14 (1), 37–48.
Eurobarometer. (2015). Flash Eurobarometer 414: Preferences of Europeans towards tourism . Brussels, Belgium: European Commission.
Eurostat. (2014). Tourism. In Eurostat regional yearbook 2014 (pp. 187–210). Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union.
Fernández-Cavia, J., & Huertas-Roig, A. (2009). City brands and their communication through Web sites: Identification of problems and proposals for improvement. In M. Gasco-Hernandez & T. Torres-Coronas (Eds.), Information communication technologies and city marketing: Digital opportunities for cities around the world (pp. 26–49). Hershey, EEUU: Idea Group Inc.
Chapter Google Scholar
Fernández-Cavia, J., Rovira, C., Díaz-Luque, P., & Cavaller, C. (2014). Web Quality Index (WQI) for official tourist destination websites. Proposal for an assessment system. Tourism Management Perspectives, 9 , 5–13.
Gartner, W. C. (1994). Image formation process. Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing, 2 (2-3), 191–216.
Govers, R. (2010). Destination eBrands. 17th International Conference on Information Technology and Travel & Tourism . Lugano: ENTER 2010.
Kim, S., & Lehto, X. Y. (2013). Projected and perceived destination brand personalities: The case of South Korea. Journal of Travel Research, 52 (1), 117–130.
Krizman, D. & Belullo, A. (2007). Internet – An agent of Tourism destination image formation: Content and correspondence analysis of Istria travel related websites. 4th International Conference: Global Challenges for Competitiveness: Business and Government Perspective (pp. 541–556). Pula: Juraj Dobrila University of Pula, Department of Economics and Tourism.
Leung, D., Law, R., van Hoof, H., & Buhalis, D. (2013). Social media in tourism and hospitality: A literature review. Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing, 30 (1-2), 3–22.
Litvin, S. W., Goldsmith, R. E., & Pan, B. (2008). Electronic word-of-mouth in hospitality and tourism management. Tourism Management, 29 (3), 458–468.
Mackay, K. J., & Fesenmaier, D. R. (1997). Pictorial element of destination in image formation. Annals of Tourism Research, 24 (3), 537–565.
Marine-Roig, E. (2014). A webometric analysis of travel blogs and reviews hosting: The case of Catalonia. Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing, 31 (3), 381–396. doi: 10.1080/10548408.2013.877413 .
Marine-Roig, E. (2015). Identity and authenticity in destination image construction. Anatolia – An International Journal of Tourism and Hospitality Research, 26 (4), 574–587. doi: 10.1080/13032917.2015.1040814 .
Marine-Roig, E., & Anton Clavé, S. (2015a). A method for analysing large-scale UGC data for tourism: Application to the case of Catalonia. In I. Tussyadiah & A. Inversini (Eds.), Information and communication technologies in tourism (pp. 3–17). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-14343-9_1 .
Marine-Roig, E. & Anton Clavé, S. (2015b). Tourism analytics with massive user-generated content: A case study of Barcelona. Journal of Destination Marketing and Management . doi: 10.1016/j.jdmm.2015.06.004 .
Mercille, J. (2005). Media effects on image: The case of Tibet. Annals of Tourism Research, 32 (4), 1039–1055.
Moura, F., Gnoth, J., & Deans, K. R. (2014). Localizing cultural values on tourism destination websites: The effects on users’ willingness to travel and destination image. Journal of Travel Research, 54 (4), 528–542.
Perry, M. (1978). Comparison of tourist destinations image as perceived by travellers and travel agents. Journal of the School of Business Administration, 1 (3).
Rodríguez-Molina, M. A., Frías-Jamilena, D. M., & Castañeda-García, J. A. (2015). The contribution of website design to the generation of tourist destination image: The moderating effect of involvement. Tourism Management, 47 , 303–317.
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness [Grant id.: MOVETUR CSO2014-51785-R].
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Business Administration and Economic Management of Natural Resources (AEGERN), University of Lleida, Catalonia, Spain
Estela Marine-Roig
Research Group on Territorial Analysis and Tourism Studies (GRATET), Rovira i Virgili University, Catalonia, Spain
Salvador Anton Clavé
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Estela Marine-Roig .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of Tourism, Bournemouth University, Poole, Dorset, United Kingdom
Alessandro Inversini
HES-SO Valais, Sierre, Valais, Switzerland
Roland Schegg
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Marine-Roig, E., Clavé, S.A. (2016). Destination Image Gaps Between Official Tourism Websites and User-Generated Content. In: Inversini, A., Schegg, R. (eds) Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2016. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28231-2_19
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28231-2_19
Published : 23 January 2016
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-28230-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-28231-2
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Tourism Destination Image Analysis Integrating a Visual Methodology

2019, e-Review of Tourism Research (eRTR)
Tourism Destination Image Analysis: Integrating a Visual Methodology Tourism destination image analysis and methodology has developed greatly over the decades. However, the integration of a visual methodology within word-based studies has remained limited. As a result, destination image promoters and marketers have struggled to interpret text-based results into useful promotional material. Thus, the aim of this qualitative study is to proposes a visually integrated methodology using open-ended questions, projective questions and projective drawings to analyse a destination's image. In the conclusion, the Triangulation Analysis of a Tourism Destination Image model is proposed to visually assist researchers and destination image marketers when analysing and promoting a destination's image.
Related Papers
Amfiteatru Economic
Nicolae Teodorescu
The problematic area of the tourism destination image has a high expansion in marketing, the efforts of its conceptualization and phenomenalism being remarkable among specialists. In this context, the authors propose a systemic approach, the result of which refers to a model regarding the image research of a tourism destination, whose validation has been attained using Transalpina destination. The model created by the authors envisages morphological features and specific functional relationships, which are consistent with the marketing theory, and, in context, with the consumer behaviour theory. The conceptual-methodological solutions are magnified by applicative-experimental validations, which enhance the theoretical and practical valences of the created model. The main direction of developing the elaborated model consists in efforts of formalization and abstracting, in the perspective offered by several scientific disciplines.
International journal of tourism research
Deepak Bisht
Steven Pike
The analysis of destination image is relatively recent. However, in almost three decades since the first studies emerged, the topic has become one of the most popular in the tourism research literature. A review of 142 destination image papers, published in the literature during the period 1973 -2000, was undertaken to provide destination image researchers with a reference guide to the context, method and focus of previous studies.
International Journal of Research and Innovation in Social Science
DR. I PUTU GDE SUKAATMADJA, SE, MP
The development of the image of the destination continues to grow so that research is needed that can determine future research gaps. This rapid development inspired us to conduct a recent literature review on destination image. In this study we update the literature review introduced in previous studies (Li et al., 2015) and define research gaps to be conducted. To achieve the objectives of this study, the researcher details the image research of selected destinations from 2012-2019 which was carried out to review the latest findings. The result is a brief summary of the destination image research based on the attributes used, analysis, number of samples and type of sample.
Asli D.A. Tasci
Annals of Faculty of Economics
Ban Olimpia
Destination Management and Marketing
Adina Nicoleta Candrea
As the tourism marketplace is currently highly competitive, Destination Management Organizations (DMOs) need to have a thorough understanding of the actual perception of their destinations and even of the desired perception they should have to adequately implement measures to alter or maintain such images. In this context, the present chapter provides an overview of tourist destination image evaluation, from both a theoretical and empirical perspective. It outlines the role of conducting research in order to evaluate destination image as key strategic information which has to be provided to DMOs. The chapter provides a theoretical framework to destination image evaluation as well as a case study on the evaluation of a Romanian city's image as a tourist destination.
Journal of Travel Research
Tourism Management
Nina K Prebensen
Jun (Justin) Li
Research on destination image has progressed quite significantly over the past decade. Analyzing these advancements was our main inspiration to create an updated literature review on destination image. In this paper, we update the literature reviews on destination image introduced in the former review papers (Chon, 1990; Echtner & Ritchie, 1991; Gallarza et al., 2002; Pike, 2002) and establish research gaps that have to be researched in the future. The goals were to execute an in-depth review of the relevant literature, to take a look at the current findings associated with the challenge of destination image and also to identify the methodological issues and implications of new information for potential research in the future. To achieve these goals, a detailed investigation of selected destination image research released from 1991‒2011 was performed to review the latest findings. The result is a brief summary of the relevant literature developed on the subject of destination image, in the last 20 years.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 13 May 2024
The influence of rural tourism landscape perception on tourists’ revisit intentions—a case study in Nangou village, China
- Yuxiao Kou 1 &
- Xiaojie Xue 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 620 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1454 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental studies
Rural tourism development has an important impact on optimizing the rural industrial structure and stimulating local economic growth. China’s Rural Revitalization Strategy has promoted the development of rural tourism nationwide and emphasized Chinese characteristics in the process of local development. Based on the theoretical analysis of landscape perception, this article uses the external Landscape Perception→Satisfaction→Revisit Intention influence path as a theoretical research framework to construct a structural equation model to analyze the willingness of tourists to revisit rural tourism destinations. We selected Nangou Village, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province, as a key model village for rural revitalization, and conducted an empirical analysis. The empirical analysis results show that landscape perception has a significant positive impact on satisfaction and revisit intention. Tourist satisfaction has a significant positive impact on revisit intention and plays an intermediary role between landscape perception and revisit intention. The five dimensions of natural ecology, historical culture, leisure recreation, research experience, and integral route under landscape perception are all significantly positively correlated with revisit intention, with historical culture and integral route having the greatest impact on landscape perception. The survey about Nangou Village verifies the relationship between landscape perception, satisfaction, and tourists’ revisit intention. Based on the objective data analysis results, this study puts forward suggestions for optimizing Nangou Village’s tourism landscapes and improving tourists’ willingness to revisit from three aspects: deeply excavating rural historical and cultural resources, shaping the national red culture brand, and creating rural tourism boutique routes. It is hoped that the quantitative research method of landscape perception theory in Nangou Village can also provide a reference and inspiration for similar rural tourism planning.
Similar content being viewed by others
Impact of ecological presence in virtual reality tourism on enhancing tourists’ environmentally responsible behavior
Evaluating the potential of suburban and rural areas for tourism and recreation, including individual short-term tourism under pandemic conditions
A geographical perspective on the formation of urban nightlife landscape
Introduction.
Rural tourism, which originated in Europe in the mid-19th century (He, 2003 ), has constructed a new type of urban–rural relationship—the attachment of the cities to the countryside and the integration of the countryside with the city (Liu, 2018 ). In the 1990s, with the continuous improvement of China’s urbanization level, rural tourism began to rise in response to the demand for returning to nature and simplicity (Guo and Han, 2010 ). The main body of rural tourism (i.e., the main target) is urban residents, and its object is a combination of enjoying the agricultural ecological environment, agricultural production activities, and traditional folk customs. These are presented through tourism industry planning and landscape product design, which is based on the unique production, life, and ecological resources in the countryside, and integrates sightseeing, participation, leisure, vacation, recuperation, entertainment, shopping, and other tourism activities (Zhang, 2006 ).
Rural tourism development is of great significance for optimizing the industrial structure in rural areas, realizing the linked development of primary, secondary, and tertiary industries, increasing farmers’ income, stimulating rural economic development, and accelerating the integration of urban and rural areas (Lu et al., 2019 ). Since the implementation of the Rural Revitalization Strategy, China has taken increasing rural tourism as one of the important ways to achieve it (Yin and Li, 2018 ) and has launched construction projects nationwide.
Rural tourism in China started with self-organized agritainment, with farming experiences and sightseeing leisure as the main projects (Guo et al., 2000 ). Early studies have found that rural tourism projects embodying regional characteristics, folklore, and participatory farming activities present stronger competitive advantages in terms of higher rates of tourists’ participation and revisit rates (Wang et al., 2005 ). In the process of the “localization” of rural tourism in China, rural tourism has undergone a top-down evolution. Since the central government’s comprehensive deployment of new rural construction in 2006, national departments and local governments have issued a series of policies to promote the development of rural tourism, leisure agriculture, and culture, which have promoted the prosperity of diversified, high-quality, and distinctive practices of rural tourism nationwide (Ma et al., 2007 ). The rural revitalization strategy is a crucial national policy at present in China, driving various initiatives such as the construction of beautiful countryside and the development of the rural tourism industry. This policy has given rise to trends like the inheritance of local culture, the promotion of green ecological concepts, and the integration of industries. However, there are still challenges encountered, such as the homogenization in tourism development and the necessity to coordinate the development of industries, culture, ecology, and economy. Under the policy guidance of developing the agricultural economy and revitalizing national culture, China has explored rural tourism landscape products that fit the national cultural context and market demand of the country. Its characteristics are mainly reflected at two levels: First, it focuses on the integration of ethnic and regional cultural perspectives. Rural tourism planning focuses on identifying geographical cultural aspects (Sun et al., 2008 ), integrating traditional Chinese red culture and local characteristics (Huang, 2003 ) into tourism landscape products, and creating Chinese cultural brands. Second, we should focus on upgrading traditional sightseeing, farming, folk customs, and leisure tourism projects, develop in-depth experiential research projects, and create a comprehensive boutique tourism route (Chen et al., 2021 ).
With the prosperity of rural tourism, the related research has gradually increased. Zhai ( 2015 ) pointed out that unique cultural and geographical landscapes are not only objects that should be emphasized and protected in the construction of the countryside but also important resources for the development of rural tourism. Zhang and Wang ( 2018 ) believed that the essence of rural tourism is the cultural experience of tourists in the countryside. Chen ( 2020 ) studied the “local sentiment” from an anthropological perspective as an important factor in promoting the development of China’s rural tourism market. Xu and Tang ( 2016 ) argued that local characteristics are essential for rural landscape construction, proposing the planning and construction strategy of “livability, suitability for industry, suitability for tourism, and suitability for culture”. Shi ( 2021 ) pointed out the significance of ecological esthetics theory to the planning and design of rural tourism landscapes and proposed the strategy of integrating local characteristics with ecological features and improving the ecosystems through artistic techniques. Most of the research has focused on the development and upgrading strategies of Chinese rural tourism landscapes from the supply-side perspective but lacks studies on what kind of experience and value tourists expect from the demand-side perspective, and the research methods lack scientific quantitative analyses.
Satisfaction and revisit intention are used to evaluate the perception and experience of rural landscapes, which directly reflect tourists’ actual feelings about the resource endowment, operational management effectiveness, social and cultural environment, and rural landscape planning in the area (Zhang et al., 2014 ). Landscape perception emphasizes the mutual influence of tourists’ perception of the tourism environment (Echtner and Ritchie, 1993 ), recognition of the location (Middleton and Hawkins, 1998 ), preferences (Zhang et al., 2017 ), and other aspects, while the revisit intention reflects tourists’ willingness to experience an activity again (Xu et al., 2014 ). Strengthening tourists’ revisit intention in rural tourism is of great significance for stabilizing and increasing rural income and promoting sustainable development in rural areas. It is an important measure of whether the quality and style of rural areas have been improved and whether rural revitalization has been promoted (Li et al., 2022 ). Therefore, based on the objective data analysis results of tourists’ perception and satisfaction with rural tourism landscapes and their revisit intention, we can objectively and reasonably propose upgrading and optimization strategies for rural landscapes. The relationship diagram is shown in Fig. 1 .
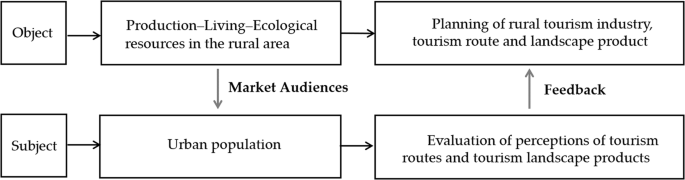
The figure illustrates the interaction between subject and object in rural tourism.
This study selected Nangou Village in Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province, as the research object. Based on the construction of traditional rural tourism facilities, Nangou Village has developed a certain number of distinctive tourism products that integrate production, learning, and research based on the Ansai folk culture and revolutionary humanistic resources in the region. However, as a key model village in China’s rural revitalization strategy, Nangou Village is still exploring a new round of optimization and upgrading. On the basis of the theory of landscape perception and a demonstrated impact mechanism between landscape perception and satisfaction, as well as revisit intention, combined with the perception results, this article proposes feasible strategies for the planning, design, and optimization of the tourism industry in Nangou Village.
Theoretical foundation
Landscape perception theory.
Landscape perception theory originated in the 1950s and is an independent theory developed for environmental psychology research. It combines the research paradigms and methods of environmental psychology and human geography (Deng, 2006 ) and aims to study people’s preferences (Guo et al., 2004 ), perception (Crompton, 1979 ; Fan et al., 2014 ), and satisfaction levels (Tribe and Snaith, 1998 ; Chi and Qu, 2008 ) of the objective environment. Ervin Zube et al. ( 1982 ) integrated the existing research paradigms of landscape perception—expert paradigm, psychophysical paradigm, cognitive paradigm, and empirical paradigm—and further proposed a theoretical model to unify humans, landscapes, and the results of their interaction into a closed loop. Landscape perception is essentially a process in which the human brain acquires environmental information through the sensory systems and then processes it (Purcell, 1987 ). In the interactive relationship between people and landscapes, the landscape is the perceived object while people are the main subjects of the environmental perception. The perception of landscapes is related to individual differences, involving experiences, memories, cognitive level, and social–cultural backgrounds (Qin, 2022 ; Cosgrove, 1984 ).
Based on subjective feelings and psychological evaluations of the surrounding environment, landscape perception further affects individuals’ emotions and environmental behaviors. An emotional state is a psychological product of individuals’ acceptance of external stimuli, combined with their own experiences and cognition, which is an important driving force that can promote individuals’ interactive behavioral responses. Motloch ( 2000 ) proposed that landscape perception will also generate emotional load after observation, recognition, and meaning attribution. Song ( 2013 ) summarizes it as a process of landscape stimulation, generation of feelings, sublimation of cognition, and emotional response. For such emotional reactions, scholars commonly use satisfaction and place identity to measure the positive affective state generated by landscape perception (Baker and Crompton, 2000 ). Behavioral responses are subjective reactions of people to approach or avoid external stimuli, which are especially influenced by their emotional state (Bitner, 1992 ; Mehrabian and Russell, 1974 ). Gobster ( 2008 ) argues that landscape perception is reflected both in cognitive and emotional aspects and that landscape preferences and emotional experiences can affect environmental behavior. Ostoić et al. ( 2017 ) believe that landscape perception emphasizes the mutual influence of tourists’ perceptions, recognition, preferences, and other aspects of the tourism environment, which can directly reflect the effectiveness of the tourism environment’s planning and design, and thus affect tourists’ behavior. In short, there are interactions between landscape environmental stimuli, emotional states, and behavioral responses, and landscape perception has a significant impact on an individual’s sense of environmental responsibility, environmental protection intention, and intention to revisit a destination (Wu et al., 2019 ).
Landscape perception and satisfaction, revisit intention
Satisfaction is a comprehensive feeling experienced by tourists during and after visiting a tourist destination (Chon, 1989 ). It can be an evaluation of a single dimension such as landscape products, tourism services, transportation accessibility, etc., or a comprehensive measure of overall satisfaction in multiple dimensions (Cole and Scott, 2004 ; Sailesh et al., 2023 ). Among them, the physical landscape environment is one of the most important dimensions that affects overall satisfaction (Chi and Qu, 2009 ). Oliver ( 1980 ) proposed the “expectation discrepancy model”, which refers to the process in which tourists form certain expectations based on their previous experiences before traveling, and then compare their expectations with their actual feelings during the travel process to determine their level of satisfaction. If the expectations are met, the tourists are satisfied; otherwise, they are not. The tourism landscape studied in this article is an important component in the study of tourist destination satisfaction, which directly affects the tourists’ selection of tourist destinations, consumption of tourism products and services, and willingness to revisit.
Behavioral intention is the result of rational cognitive processing of situational information by tourists, resulting from psychological comparison and judgment (perception value or satisfaction). In the existing research, tourists’ behavioral intentions are often described as tourists’ recommendation behavior and revisiting intention. Revisit intention refers to the behavioral intention of tourists to visit the destination again in the future (Hung and Petrick, 2011 ). Chen proposed that revisit intention should include two levels of behavioral intention: the intention of the tourists themselves to revisit this place, and the intention to recommend this place to their acquaintances. Xiu, on this basis, included whether tourists would prioritize this attraction in their travel choices into the evaluation indexes of revisit intention (Guo, 2016 ). In addition, some scholars have demonstrated that destination image perception, especially landscape perception, is a direct driver of tourists’ recommendation behavior and intention (Chew and Jahari, 2013 ; Nisco et al., 2015 ; Prayag et al., 2017 ), and satisfaction with the tourism destination is one of the strongest factors affecting revisiting behavior (Campo-Martínez et al., 2010 ; Humagain and Singleton, 2021 ).
In summary, the relationship between landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention has been demonstrated in relevant studies. In spite of this, it remains necessary to further the research on the influence paths of these three factors. For example, Xu et al. ( 2023 ) took the Qilian Village landscape renovation project as the subject of a case study to identify users’ perceptions of landscape characteristics through structural equation modeling. Although they explored the impact of landscape perception on satisfaction, no further study was conducted on users’ behavioral intentions via the influence paths. Similarly, Qu et al. ( 2023 ), referring to the ancient villages in southern Anhui as an example, explored the path to high-quality development of rural tourism from the perspective of the authenticity of rural landscapes. Despite the SPSS data analysis conducted to verify the positive correlation between satisfaction and revisit intention, they ignored the optimization strategies of landscape as the carrier of tourism, which thus affects the applicability of this research. Additionally, in China, there are few papers that quantitatively present tourists’ landscape demands and support planning strategies, with most research focusing on the subjective discussions of tourism landscape planning strategies from the perspective of the supply side. In conclusion, it remains imperative to conduct further research on the strategies of optimizing the design of rural tourism landscapes based on a complete demonstration of the influence paths of landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention, with the results of quantitative data analysis as guidance.
Research hypotheses
Landscape perception theory has been widely applied in tourism-related research and has gradually permeated into the research on rural tourism landscapes (Yang et al., 2022 ; Fan, 2020 ). The rural tourism landscape studied in this article, perceived as a physical environment, usually includes rural ecological landscapes, authentic historical and cultural landscapes, agricultural leisure and entertainment facilities, and experiential red revolutionary landscapes, and it also involves diachronic overall tourism routes.
Some scholars have explored the rationality of the path mechanism of the landscape perception–satisfaction–revisit intention in related studies, and they used the relevant results as a strategic basis for optimizing the development of rural tourism. For example, Acharya et al. ( 2023 ) showed that the better the tourism ecological environment is, the higher the satisfaction and revisit intention of tourists are, and the path from the ecological environment to the revisit intention of tourists needs to be connected by satisfaction. Geng et al. ( 2010 ) analyzed and demonstrated the positive impact of rural natural landscape satisfaction and sightseeing route satisfaction on tourists’ revisit intention using logistic model analysis. Queiroz ( 2017 ) found that cultural experiences can better reflect the authenticity of rural areas, and tourist satisfaction can be improved through the enhancement of cultural facilities, thereby promoting tourists’ willingness to revisit. Yang et al. ( 2022 ) believe that developing recreational activities with rural characteristics can stimulate tourists’ interest and participation, thereby enhancing their satisfaction and willingness to return. Zhou et al. ( 2016 ) posited that recreational facilities and entertainment activities are both important factors that attract tourists to choose rural tourism; in addition, a higher attractiveness of the tourism landscape increases the satisfaction of tourists, creating a greater impact on revisit intention.
Some scholars have further proposed and demonstrated that satisfaction plays a mediating role in the impact path of tourists’ landscape perception on their revisit intention. For example, Kim et al. ( 2013 ) conducted a survey in rural areas and found that satisfaction plays an intermediary role between tourists’ rural image perception and tourists’ revisit intention.Tu et al. ( 2017 )proposed that the internal mechanism of tourists’ behavioral intentions based on destination image perception may be achieved through the mediating effect of positive emotions such as satisfaction. Meng ( 2018 ) argued that in rural tourism, rural landscapes, and related service facilities are important manifestations of rurality, which affect tourists’ satisfaction with their travel experience and indirectly affect their revisit intention.
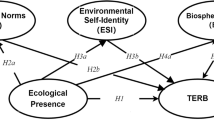
In summary, this study took Nangou Village as a research sample to explore the influence mechanism between rural tourism landscape perception and its associated satisfaction and revisit intention, and the following hypotheses were made (Fig. 2 ).
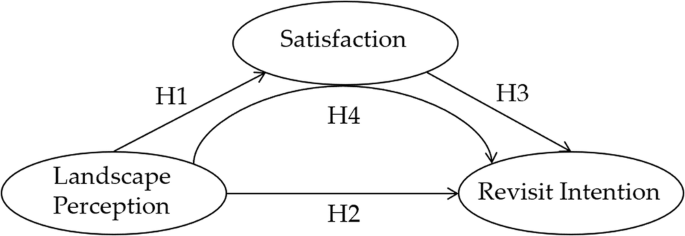
The figure presents the hypothesized relationship between the three variables.
Hypothesis 1 (H1) . Rural tourism landscape perception will positively affect the overall satisfaction of rural tourism.
Hypothesis 2 (H2) . Rural tourism landscape perception will positively affect the rural tourism revisit intention.
Hypothesis 3 (H3) . Rural tourism satisfaction will positively affect the rural tourism revisit intention.
Hypothesis 4 (H4) . Satisfaction will act as a mediator in the relationship between rural tourism landscape perception and revisit intention.
Study design
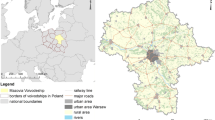
Nangou Village, the research object of this study, is located in Gaoqiao Town, Ansai District, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province, China, covering approximately 1716 hectares with seven natural villages under its jurisdiction, which are typical loess hilly villages (Fig. 3 ). As a key model village for rural revitalization, Nangou Village has a good natural ecological foundation and abundant agricultural and regional culture resources and has achieved preliminary linkages between the primary, secondary, and tertiary industries. In the first rural tourism development, Nangou Village built the Nangou Paradise for sightseeing and its supporting facilities, the Nangou Soil and Water Conservation Demonstration Park of Ansai District of Yan’an City, and the Agricultural Picking Experience Park, the red military camps based on Yan’an Red Culture, and various characteristic landscape pieces under the influence of Ansai’s unique regional culture, which form a comprehensive cultural tourism village. With the deepening of rural revitalization in China, Nangou Village will serve as a key area for the Ansai District to build a five-billion-level cultural tourism industry cluster, further expanding and upgrading the existing tourism landscape facilities. Therefore, this article aims to propose a scientific strategy for the upgrading and transformation of Nangou Village through subjective evaluation methods.
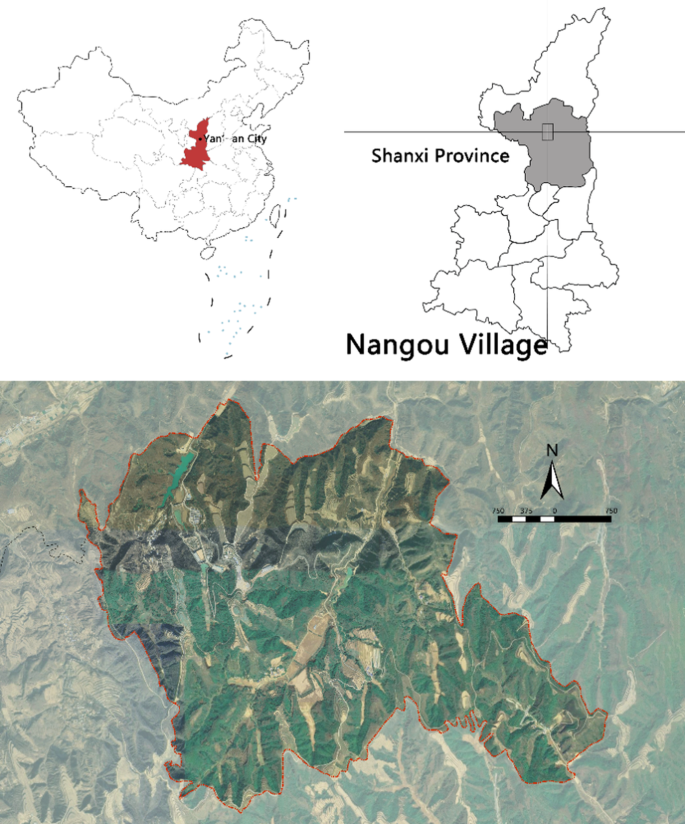
The figure presents the geographic location of the Nangou village.
Evaluation index construction
Based on the analysis and organization of the existing literature and the construction of the theoretical framework mentioned earlier, this study constructed evaluation indicators for three variables: landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention (Table 1 ).
LP—The research on rural tourism landscape perception is not yet perfect; this study tentatively divided the LP scale into five dimensions on the basis of previous research and combined with a review of the literature. Among them, the Natural Ecology sub-dimension involves the evaluation of the rural landscape’s pastoral characteristics, the quality of the ecological environment, and the integration of landscape facilities and natural ecology (Xie et al., 2002 ; Marianna et al., 2023 ). The Historical Culture sub-dimension involves the evaluation of the regional history and culture of the rural tourism landscapes, the recognizability of the cultural symbols, and the authenticity of the cultural preservation (Huang et al., 2015 ). The Leisure Recreation sub-dimension involves the evaluation of the suitability, attractiveness, and abundance of recreational facilities in rural tourism landscapes (Yuan, 2017 ). The Research Experience sub-dimension involves the evaluation of the attractiveness, abundance, brand value, and impressiveness of the research experiences for tourists (Fan and Liu, 2016 ; Wang and Wang, 2010 ; Huang et al., 2018 ). The Integral Route sub-dimension involves the evaluation of the prominent theme features in the routes, an abundance of scenarios and experiences, and the attractiveness of the integral route (Li, 2003 ; Yan, 2021 ).
SA—This is the evaluation of whether the overall quality and experience of the rural tourism landscapes meet expectations. Here, the overall satisfaction, expectation, and competitiveness of rural tourism landscape quality and experience are used as the evaluation indexes (Chen, 2012 ; Wang et al., 2005 ).
RI—This is the evaluation of tourists’ loyalty to rural tourism destinations, with loyalty, willingness to revisit, and recommendation behavior as the evaluation indexes (Wang et al., 2006 ; Stylos et al., 2015 ).
Questionnaire design and collection
The questionnaire was designed in four parts. The first part covers the demographic characteristics, including gender, age, education level, and occupation. The second part is the evaluation of cultural image perception, while the third part is the evaluation of environmental design, and the fourth part is the evaluation of place perception. The items in these last three parts corresponded to the evaluation indexes shown in Tables 2 – 4 , respectively, and a 5-point Likert scale was used to rank the perception level.
In November 2022, the study conducted a field survey in Nangou village, complemented by an online questionnaire from November 15, 2022, through September 12, 2023. The introduction section of the questionnaire included the research objectives, the anticipated societal benefits, and the scope of information that would be collected. Before proceeding, participants were asked to review this introduction; their agreement to participate was taken as informed consent. In total, the study received 344 valid responses, serving as the sample data. The sample size satisfies the requirements for structural equation modeling that a desirable sample size should be over 200, with at least ten responses correlating to each variable under observation (Barrett, 2007 ).
Quantitative analysis methods
The data were analyzed using SPSS (version 27.0) and AMOS 27.0. Frequency analysis of the demographic characteristics and reliability analysis were conducted.
In this study, structural equation modeling (SEM) was used as the core method, and the three concepts of landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention were set as latent variables, and SEM was utilized to verify the hypotheses on the relationship between the three aspects. First, a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was introduced to test whether the relationship between the factors and the corresponding measurement items was as expected, and to further revise the relationship model between the latent variables and the indicator question items and between the indicator question items (Li and Chen, 2010 ). Second, the interaction mechanism between the latent variables was analyzed by SEM to verify or falsify the research hypotheses (Gu et al., 2022 ). Finally, the bootstrap method was used to validate and analyze the indirect effects (Wen and Ye, 2014 ).

Results analysis
Demographic variables and statistical results of travel characteristics.
Using SPSS software to analyze the demographic characteristics of the 354 questionnaires, the sample was found to be well-balanced in terms of gender. The age distribution was broad and predominantly consisted of young and middle-aged people. The occupational status covered various fields, while most respondents had received middle and higher levels of education. The middle-income group accounted for a larger proportion of the sample, which is a good representation of the population (Fig. 4 ).
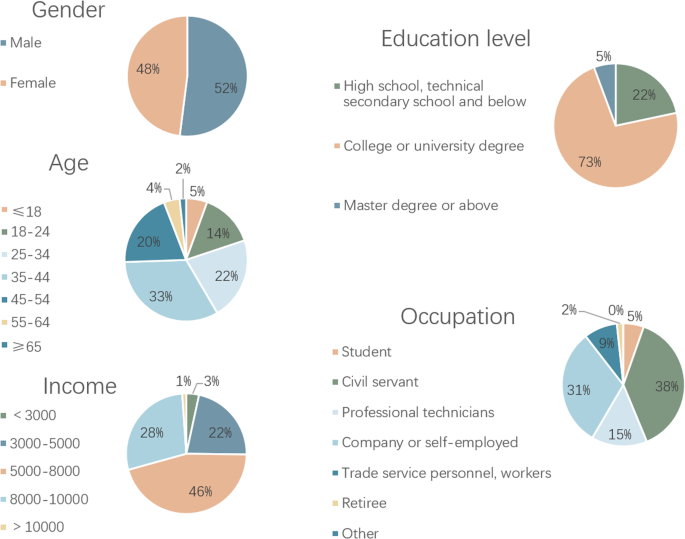
The figure presents the statistical results of the demographic variables for the 354 questionnaires.
The survey results showed that tourists preferred to choose research experience and historical culture landscape projects at the destination, followed by natural ecology and leisure recreation. In terms of tour length and size, tourists who chose one-day and two-person tours accounted for most of the tourists, and very few tourists chose multiday tours. The majority of tourists who came to this destination came as a unit, and the least frequent response was as individual tourists. The majority of tourists visited this village for the first time, and the number of tourists choosing to revisit the place again was very few (Fig. 5 ).
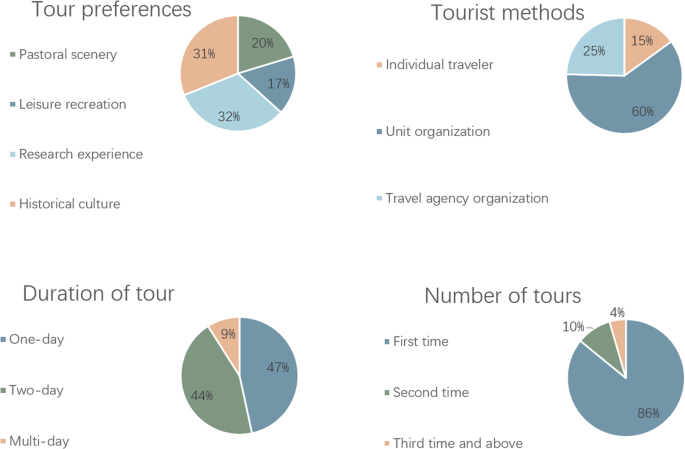
The figure presents the statistical results of the travel characteristics for the 354 questionnaires.
Reliability analysis results
In this study, the latent variables were tested using Cronbach’s α (Table 2 ), which showed that the Cronbach’s α values of landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention were 0.898, 0.803, and 0.845, respectively, and the scales’ overall Cronbach’s α value was 0.913. The Cronbach’s α values of the sub-dimensions under landscape perception ranged from 0.805 to 0.863, which are all greater than 0.8. In summary, the reliability test coefficients of each sub-dimension scale exceed 0.7, which indicates that the internal consistency of the data was good (Eisinga et al., 2013 ).
Latent variable evaluation results
As shown in Fig. 6 , the overall average landscape perception score was 3.748, which is close to a good level. Comparing the average evaluation score, the five latent variables can be ranked as NE > HC > RE > LR > IR, with scores of 3.976, 3.906, 3.889, 3.836, and 3.826, respectively. The overall average score for satisfaction was 3.625, between average and satisfactory. The overall average score for revisit intention was 3.452, between average and willing, but not reaching the desired level.
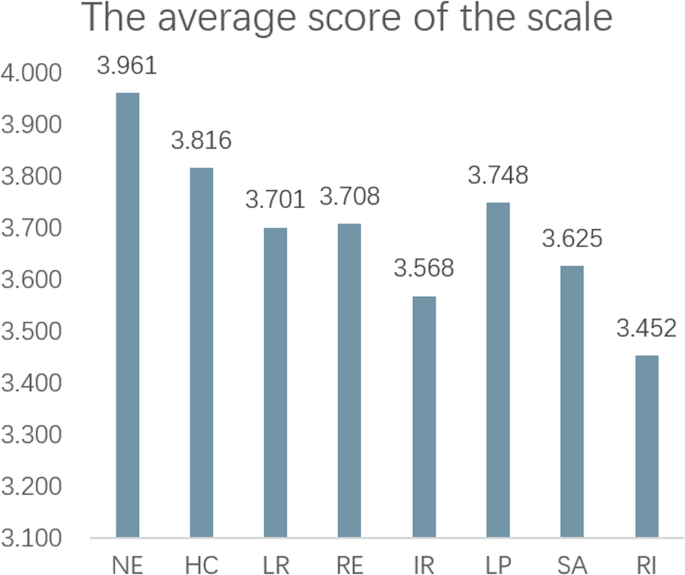
The figure presents the statistical results of the latent variable average scores. NE Natural Ecology, HC Historical Culture, LR Leisure Recreation, RE Research Experience, IR Integral Route, LP Landscape Perception, SA Satisfaction, RI Revisit Intention.
This study examined the relationship between the latent and observed variables in the measurement model through CFA to determine the reasonableness of the scale construction by convergent and discriminant validity. For convergent validity, there are usually three discriminating criteria: (1) standardized factor loadings are all greater than 0.5 (Bailey and Ball, 2006 ); (2) average variance extracted (AVE) is greater than 0.5 (Bagozzi and Yi, 1988 ); and (3) composite reliability (CR) is greater than 0.7 (Fornell and Larcker, 1981 ). Satisfying the above criteria indicates good convergent validity. As shown in Table 3 , the standardized factor loading ranged from 0.686 to 0.891, which meets the criterion of greater than 0.5. The minimum value of CR was greater than 0.8, which is greater than the threshold value of 0.7, and the AVEs were all greater than 0.5, which indicates that the scale has a good convergent validity.
For discriminant validity, if the correlation coefficients between a factor and the other factors are all less than the square root of its AVE value, it indicates good discriminant validity between the factors (Hair et al., 2010 ). As shown in Table 4 , the correlation coefficients between landscape perception and the two factors of its sub-dimension are only slightly larger than the square root of the AVE, and the square root of the AVE values of the rest of the factors is higher than the correlation coefficients between the factor and the other factors, which indicates that the present scale has good discriminant validity.
Theoretical model validation
Under the premise of ensuring the reliability and validity of the measurement model, structural modeling was further performed to verify the hypothesized relationships among the three variables of landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention. First, the results of model fit showed that CMID/DF = 1.097, GFI = 0.949, AGFI = 0.936, CFI = 0.995, TLI (NNFI) = 0.994, RMSEA = 0.017, and SRMR = 0.037 (Table 5 ), and all the indexes were in line with the standard, which indicated that the model had a good fit (Hayduk, 1987 ; Scott and Willits, 1994 ).
This study further used AMOS 27 to establish a structural model and measure the causal relationships between the three latent variables, LP, SA, and RI. As shown in Table 6 and Fig. 7 , (1) Landscape perception has a positive and significant effect on Satisfaction, with a path coefficient of 0.559 ( P < 0.001); (2) Landscape perception has a positive and significant effect on Revisit Intention, with a path coefficient of 0.434 ( P < 0.001); and (3) Landscape Satisfaction had a positive and significant effect on Revisit Intention, with a path coefficient of 0.377 ( P < 0.001) (Cabrera-Nguyen, 2010 ). This proves that hypotheses H1, H2, and H3 are supported.
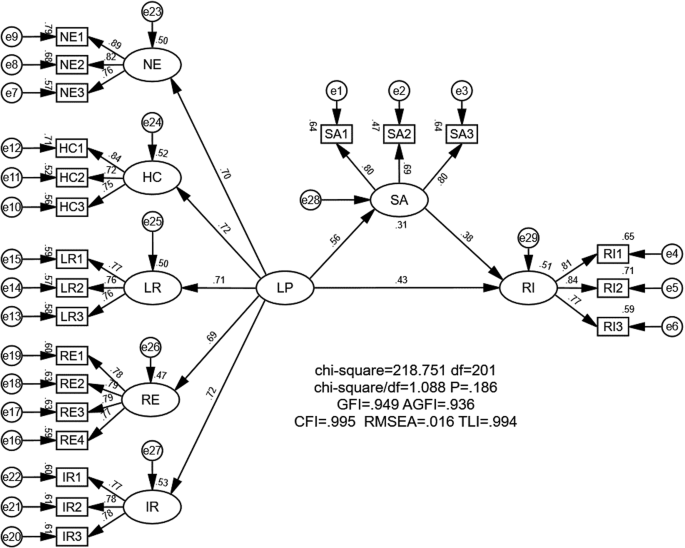
NE Natural Ecology, HC Historical Culture, LR Leisure Recreation, RE Research Experience, IR Integral Route, LP Landscape Perception, SA Satisfaction, RI Revisit Intention.
Mediation analysis of satisfaction
This study adopted the bootstrap method suggested by McKinnom to test the possible mediating effect of SA in the relationship between LP and RI, and the bootstrap sample size was set at 5000 (MacKinnon et al., 2002 ). Usually, if the bootstrap confidence interval does not contain 0, then the corresponding indirect, direct, or total effect exists (MacKinnon et al., 2004 ). The test results show that at a 95% confidence level, the confidence interval of indirect effect was [0.141, 0.314], the confidence interval of direct effect was [0.456, 0.755], and the confidence interval of total effect was [0.682, 0.961], which all exclude 0, indicating that the indirect effect exists, and the ratio of the indirect effect was 0.27. The results of the mediation test support hypothesis H4 (Table 7 ).
Discussion and recommendations
Coupling relationship among lp, sa, and ri.
This study established a hypothesis model based on the a priori theory of the influencing relationship between Landscape Perception→Satisfaction→Revisit Intention, and explored and confirmed the influence paths of LP on SA and RI with Nangou Village as the research object. In the SEM results, the coefficient of LP’s influence path on SA was 0.559, and the coefficient of LP’s influence path on RI was 0.434. LP influences tourists’ revisit intention to the destination through the overall satisfaction of the tourist landscapes, which confirms that the landscape quality and experience of the destination is an important influencing factor that affects tourists’ satisfaction, which then enhances tourists’ revisit intention. This result is consistent with that of many previous studies, such as those conducted by Cao ( 2019 ) and Li ( 2022 ), in which quantitative analysis is conducted under different contexts to investigate the influence paths of landscape perception. Their research also confirms that tourists’ perception of the landscape contributes to enhancing satisfaction and revisiting intention. At present, the intention to revisit Nangou Village has not reached the desired level. Based on the LP → SA → RI influence path, this study concludes that it is necessary to upgrade the tourism landscapes as a whole in the new round of rural tourism planning, to effectively improve the attractiveness of the destination from the environmental level.
Coupling relationship among LP and its sub-variables
Different from previous studies, we defined LP as a second-order variable containing five sub-dimensions: natural ecology, historical culture, leisure recreation, research experience, and integral route. The fitted data showed that the five sub-variables were an accurate representation of the LP structure. In the results of the structural equation, all five latent variables involved in the LP dimension showed significant positive correlations with LP ( P < 0.01), and the influence path was IR > HC > LR > NE > RE. In the correlation analysis, IR, HC, LR, RE, and IR also showed significant positive correlations with revisit intention, with correlation coefficients in the order of NE > IR > HC > LR > RE (Table S1 ), and the correlation coefficients in the order of IR > LR > LR > RE (Table 2 ). All of these results emphasize the important influence of historical culture and integral route on landscape perception and revisit intention. In the actual evaluation of landscape perception, the evaluation results of the five sub-dimensions did not reach a satisfactory level; therefore, in order to further increase the revisit intention of the destination, it is necessary to upgrade the landscapes of Nangou Village in all dimensions as a whole, and in particular, it should focus on upgrading the historical culture, the integral routes, as well as the facilities of the research experience that tourists are more inclined to choose.
Recommendations
Deeply excavating rural historical and cultural resources.
Rural tourism itself is a large-scale cultural exchange; any tourism product or tourism mode has its own cultural connotation, which is a necessary condition to attract tourism (Li and Wang, 1999 ). Rural culture is both productive and fragile; therefore, cultural protection and inheritance in rural tourism development is essential. Emphasizing the characteristic regional culture can not only improve the visibility, dissemination, and attractiveness of rural tourism destinations, but also enhance the vitality, efficiency, and effectiveness of rural development. The rural landscapes are both the end product of rural tourism and the carrier of rural culture. Based on the principle of protecting the authenticity of rural culture, integrating the elements of native culture into the tourism landscape designs of traditional villages and optimizing the tourism content is conducive to strengthening the attractiveness of traditional villages to tourists (Sun and Zhang, 2020 ). The results of the survey on the preference of tourism types in Nangou Village show that the historical culture and landscapes are popular aspects. Meanwhile, the SEM model results show that historical culture is an important factor influencing tourists’ revisit intention. Therefore, future tourism planning in Nangou Village should strengthen the development of vernacular cultural landscapes and highlight its own distinct characteristics. The tourism landscapes developed in the first round in Nangou Village have problems such as low cultural taste and inconspicuous characteristics. The new tourism planning for Nangou Village should sufficiently mobilize the regional cultural resources of the Ansai District, utilizing the region’s primitive village landscapes and folk cultural resources to create a rich “composite vernacular complex” type of landscape facilities. For example, we could introduce traditional activities such as horse riding, cattle riding, and Paper Cuttings with Ansai characteristics to the local culture experience hall; renovate cave dwelling homestays with distinctive Shaanxi characteristics; and integrate agricultural and folk activities such as tasting farmhouse meals and picking agricultural products into the homestay experience. In summary, the new tourism landscape should showcase the inherent qualities of Nangou Village, such as locality, authenticity, and humanity, from four aspects: food, housing, transportation, and work.
Shaping the National Red Culture Brand
Red cultural resources, as the Chinese excellent culture refined during the revolutionary era, play a prominent role in enhancing national self-confidence and building a strong nation. Meanwhile, the red tourism industry, which inherits and carries forward the red culture, has also become a unique path in China’s rural revitalization (Liu, 2020 ). The purpose of rural red tourism is to jointly develop traditional green ecological resources and red resources with humanistic characteristics. Through the development model of red and green integration, we can carry forward the narrative and dissemination power of the red spirit concept. At the same time, based on the comprehensive development of red tourism routes, sites, events, symbols, and other resources, we can enhance the popularity of rural tourism brands, expand market entities, and attract more visitors (Hong, 2021 ). Nangou Village is located in the red Yan’an revolutionary hometown, which occupies a place in China’s revolutionary history. In the first round of development, Nangou Village built red culture experience facilities, mainly serving units with red education and training needs in the surrounding areas. However, Nangou Village has insufficient scheduling of classic resources such as red sites, red stories, red history, and red characters, and has not established a more competitive and penetrating red tourism culture brand that serves a comprehensive audience. Therefore, we suggest that Nangou Village expand the scale of red travel facilities, create multi-dimensional red tourism experience scenarios, enhance the cultural connotation of red tourism scenic spots, and create educational and training routes with prominent themes of the red spirit. In addition, rural culture, red tourism resources, and natural ecological resources should be integrated under specific local conditions, for example, temperature-controlled greenhouses, characteristic agricultural planting, folk culture experiences, and other projects around the red tourism areas can be incorporated. This is conducive to enhancing the “red tourism integration” brand effect for its greater influence on surrounding facilities. Therefore, the connection between the cultural dimension and tourists’ perception of landscapes can be reinforced. In turn, it enhances the favorability and visibility of the “Red Yan’an” brand, which gives full play to its economic potential while promoting the inheritance of red cultural genes.
Creating rural tourism boutique routes
Rural tourism boutique routes are an arrangement and scientific organization of characteristic tourism landscapes, which is an important strategy for rural tourism destinations to attract tourists. The creation of boutique tourism routes is based on the integration of regional resources, forming a “string of points into a line, with a line leading to the surface, the overall promotion” of the joint development of the countryside, which is able to better utilize and display rural resources, and promote the integrated development of industries and the cultivation of new business models (You, 2014 ; Wang, 2015 ). According to the SEM results, it can be seen that the integral route sub-dimension of Nangou Village had the greatest impact on landscape perception. However, at present, tourists gave the lowest rating for aspect, which affected their satisfaction and led to a low willingness to revisit. At present, the tourism landscape projects in Nangou Village have problems, such as dispersion, small scales, individual operations, a single rural tourism product, and imperfect industrial and economic structures. Therefore, the upgrading strategy should incorporate the cultural theme of “Ansai Five Business Cards” into the integral tourism routes, and form the regional tourism development routes, rural tourism routes, and red knowledge education and training routes in the Greater Nangou area, which rely on the characteristic resources of Nangou Village. Moreover, it should connect the regional construction with the routes, and form a diversified tourism industry integrating “agricultural science popularization + folklore experience + parent-child amusement + leisure agriculture”. Finally, the tourism route planning should make full use of the Nangou Village brand, taking rural culture and tourism as the engine to optimize and expand primary industries, achieve coordinated development of the village and urban economy, and focus on the development of tertiary industries, in order to cooperate with the new rural industrial development system in Nangou Village.
Conclusions
With the gradual evolution of urbanization and the extensive promotion of China’s Rural Revitalization Strategy, rural tourism has become more and more popular and has developed rapidly. Landscape perception is the process of human interactions with the landscape, and the positive or negative results of this perception will directly affect the satisfaction of the tourists with the destination, thus affecting the tourists’ revisit intention. This study was based on the theory of landscape perception, and selected Nangou Village as the research object, on the basis of validating the influencing relationship of Landscape Perception→Satisfaction→Revisit Intention, to put forward reasonable suggestions for the optimization and upgrading of Nangou Village. The results of the research show the following: (1) Tourists’ landscape perception significantly influences tourists’ satisfaction and revisit intention. (2) Tourists’ satisfaction with the destination plays an intermediary role in the influence of landscape perception on revisit intention. (3) Landscape perception contains five dimensions (natural ecology, historical culture, leisure recreation, research experience, and integral route), all of which significantly influence tourists’ satisfaction and revisit intention. Among these dimensions, historical culture and integral route have the greatest influence, which indicates that the cultural and integral nature of the landscape is the core element that drives tourists to generate positive emotions. (4) Tourists prefer landscape projects with historical culture and research experience. (5) The overall landscape planning of Nangou Village was not evaluated highly, and it needs to be upgraded in a focused way. Using the empirical results as a reference, this study proposes strategies for upgrading the tourism landscapes of Nangou Village: deeply excavate rural historical and cultural resources, shape the national red culture brand, and create rural tourism boutique routes. Therefore, exploring the factors affecting revisit intention and thinking about the construction of rural tourism landscape perception elements can provide theoretical guidance for solving the next stage of rural tourism planning in Nangou Village and providing a direction for the construction of beautiful villages in the future.
The methodology of empirical research as applied in this study, along with the corresponding data analysis conducted in the case study of Nangou Village, aims to reveal the influencing factors for revisit intention. By adopting a reverse-thinking approach to constructing the elements of rural tourism landscape perception, theoretical guidance is provided for the next phase of rural tourism planning in Nangou Village. Meanwhile, it gains the strategic insights crucial for local governments and collaborative planning agencies to develop, manage, and market rural tourism destinations. Additionally, the research methods used in this study provide a reference for relevant government and planning agencies to carry out rural tourism planning. Firstly, rural tourism relies heavily on tourism landscape facilities as its primary support system. Therefore, rural tourism is supposed to focus on increasing the attention paid to tourists’ demands from the perspective of the supply side. This can be achieved by constructing landscape perception scales that are more tailored to the advantages and characteristics of tourism destinations. Through the surveys of rural tourism landscape perception elements based on combined scale analysis, tourists’ expectations and demands can be better satisfied. Thus, their satisfaction and revisit intention can be enhanced. Secondly, in the practice of rural tourism marketing, the SEM (structural equation modeling) quantitative results of landscape perception, satisfaction, and revisit intention can be referenced to guide targeted promotion and advertising efforts for landscape elements perceived more strongly by tourists. In this way, the attractiveness to tourist groups can be improved. Lastly, planning agencies can apply the scale developed in this study to measure the satisfaction level of rural tourism industries in tourists’ minds at various stages. By assessing the scores in different dimensions, planning agencies can better identify their strengths and weaknesses, which enables them to maintain their advantages while making improvement.
Some limitations should be noted, which need to be addressed in the future. Firstly, the division of landscape perception dimensions in this study was somewhat subjective and innovative, and there are some immaturity issues. Secondly, the data collection time was short, which may not represent the average situation throughout the year. Finally, this article intended to propose optimization suggestions for Nangou Village at the landscape level, but this should be integrated with the industrial transformation, planning and propaganda, and enhancing service quality and other influencing factors of tourism destinations in the overall tourism planning.
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material ( S2 . Dataset), further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Acharya S, Mekker M, Jonas DV (2023) Linking travel behavior and tourism literature: investigating the impacts of travel satisfaction on destination satisfaction and revisit intention. Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect 17:100745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trip.2022.100745
Article Google Scholar
Bagozzi RP, Yi Y (1988) On the evaluation of structural equation models. J Acad Market Sci 16(1):74–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02723327
Bailey R, Ball S (2006) An exploration of the meanings of hotel brand equity. Serv Ind J 26:15–38. https://doi.org/10.1080/02642060500358761
Baker DA, Crompton JL (2000) Quality, satisfaction and behavioral intentions. Ann Tour Res 27:785–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-7383(99)00108-5
Barrett P (2007) Structural equation modelling: adjudging model fit. Pers Individ Differ 42:815–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2006.09.018
Bitner MJ (1992) Servicescapes: the impact of physical surroundings on customers and employees. J Market 56:57–71. https://doi.org/10.1177/002224299205600205
Cabrera-Nguyen P (2010) Author guidelines for reporting scale development and validation results in the Journal of the Society for Social Work and Research. J Soc Soc Work Res 01:99–103. https://doi.org/10.5243/jsswr.2010.8
Campo-Martínez S, Garau-Vadell JB, Martínez-ruiz MP (2010) Factors influencing repeat visits to a destination: the influence of group composition. Tour Manag 31:862–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2009.08.013
Cao YL (2019) A study of the effect of perceived rurality on revisit intention. Master’s Thesis. Xi’an International Studies University, Xi’an, China
Google Scholar
Chen B (2020) Rural complex and rural revitalization: approaches and prospects of Chinese rural anthropology. Guangxi Ethnic Stud 06:94–102. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-454X.2020.06.012
Chen CW, Jin ML, Jin HX, Cheng QY (2021) Beautiful country quality line construction based on region linkage—a case study of the construction practice of Yiwu “Colorful Huaxi”. Chin Landsc Archit 37(2):12–19. https://doi.org/10.19775/j.cla.2021.02.0012
Article CAS Google Scholar
Chen JH (2012) The research of tourist satisfaction in urban wetland park tourism resort based on tourism experience. Master’s Thesis. Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China
Chew YET, Jahari SA (2013) Destination image as a mediator between perceived risks and revisit intention: a case of post-disaster Japan. Tour Manag 40:382–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2013.07.008
Chi CG, Qu H (2008) Examining the structural relationships of destination image, tourist satisfaction and destination loyalty: an integrated approach. Tour Manag 29:624–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2007.06.007
Chi CGQ, Qu H (2009) Examining the relationship between tourists’ attribute satisfaction and overall satisfaction. J Hosp Market Manag 18:4–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/19368620801988891
Chon K (1989) Understanding recreational travelers’ motivation, attitude and satisfaction. Tour Rev 44(1):3–7. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb058009
Cole ST, Scott D (2004) Examining the mediating role of experience quality in a model of tourist experiences. J Travel Tour Market 16:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1300/J073v16n01_08
Cosgrove D (1984) Social formation and symbolic landscape. Groom Helm, London, GBR. pp. 56–84
Crompton JL (1979) An assessment of the image of Mexico as a vacation destination and the influence of geographic allocation upon that image. J Travel Res 17(4):18–23. https://doi.org/10.1177/004728757901700404
Deng W (2006) Landscape perception: towards landscape semiology. World Archit 07:47–50. https://doi.org/10.16414/j.wa.2006.07.009
Echtner CM, Ritchie JRB (1993) The measurement of destination image: an empirical assessment. J Travel Res 31(4):3–13. https://doi.org/10.1177/004728759303100402
Eisinga R, Grotenhuis M, Pelzer B (2013) The reliability of a two-item scale: Pearson, Cronbach, or Spearman-Brown? Int J Public Health 58(4):637–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-012-0416-3
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Fan J, Qiu HL, Wu XF (2014) Tourist destination image, place attachment and tourists’ environmentally responsible behavior: a case of Zhejiang tourist resorts. Tour Trib 29(1):55–66. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-5006.2014.01.006
Fan YH (2020) Research on the evaluation and perception of village landscape in western Sichuan based on the network content analysis method. Master’s Thesis. Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu, China
Fan YM, Liu H (2016) Landscape and village integrated beautiful village planning. Planners 32(04):97–100. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2016.04.016
Fornell C, Larcker DF (1981) Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J Market Res 18(1):39–50. https://doi.org/10.1177/002224378101800104
Geng XH, Wang XQ, Sun QS (2010) Eco-tourism, tourist satisfaction and revisit will: a case study of future Agro-park in Suzhou China. Ecol Econ 06:119–123
Gobster PH (2008) Yellowstone hotspot: reflections on scenic beauty, aesthetics, and ecology. Landscape J 27:291–308
Gu T, Hao E, Ma L, Liu X, Wang L (2022) Exploring the determinants of residents’ behavior towards participating in the sponge-style old community renewal of China: extending the theory of planned behavior. Land 11:1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081160
Guo HC (2016) Study on the experience value of mountain resort tourism, degree of satisfaction and revisit intention—a case of DaWei Mountain. Master’s Thesis. Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China
Guo HC, Han D (2010) Review on the development of rural tourism in China. Prog Geogr 29(12):1597–1605. https://doi.org/10.11820/dlkxjz.2010.12.018
Guo HC, Liu JP, Wang YC (2000) The study on development of tourism agriculture. Econ Geogr 20:119–124. https://doi.org/10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2000.02.025
Guo YZ, Zhang H, Song SL, Li L, Chen XL, Zhang L (2004) A study of market positioning of China’s outbound travel destinations. Tour Trib 19(4):27–32. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-5006.2004.04.010
Hair JFJ, Black WC, Babin BJ et al. (2010) Multivariate data analysis. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, USA. pp. 785-785
Hayduk LA (1987) Structural equation modeling with LISREL: essentials and advances. JHU Press, Maryland, USA
He JM (2003) A study on rural tourism overseas. Tour Trib 18:76–80. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-5006.2003.01.017
Hong Y (2021) Research on government functions in the integration and development of Yan’an Red Culture and tourism industry, Master’s Thesis, Yan’an University, Yan’an, China
Huang J (2003) Soil complex, family complex and agritourism development. Thinking 29(5):24–26. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-778X.2003.05.006
Huang SS, Fan Y, Xiong HG (2018) Study on the development path for red culture resources under the perspective of rural revitalization strategy. Price Month 09:90–94. https://doi.org/10.14076/j.issn.1006-2025.2018.09.16
Huang ZF, Lu L, Su Q, Zhang JH, Sun JX, Wan XC et al. (2015) Research and development of rural tourism under the background of new urbanization: theoretical reflection and breakthrough of predicament. Geogr Res 34(8):1409–1421. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlyj201508001
Humagain P, Singleton PA (2021) Examining relationships between COVID-19 destination practices, value, satisfaction and behavioral intentions for tourists’ outdoor recreation trips. J Dest Market Manag 22:100665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2021.100665
Hung K, Petrick JF (2011) The role of self- and functional congruity in cruising intentions. J Travel Res 50:100–112. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287509355321
Kim B, 김용기 GK, Hee Park S (2013) Effects of images of rural tourism on tourists’ satisfaction and revisit intention: case of Changpo and Woiam villages. J Tour Sci 37:303–324
Li D, Wang YQ, You YA, Chen YT (2022) Tourism involvement, destination image and willingness to revisit: a moderated intermediary role model. J Central China Normal University (Natural Sciences) 56(5):871–881. https://doi.org/10.19603/j.cnki.1000-1190.2022.05.017
Li JH (2022) Research on the effects of rurality perception on the tourists’ revisit intentions—taking Nostalgialove Hometown Taihang Water Town in Baoding as a study case. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University, Baoding, China
Li TY, Wang LY (1999) An introduction to tourism principles. Nankai University Press, Tianjin, China. pp. 34–50
Li W (2003) A discussion on the development and plan of rural tourism. Areal Res Dev 22(6):72–75. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-2363.2003.06.018
Article ADS Google Scholar
Li XJ, Chen XZ (2010) Factor analysis under the structural equation model. Sci Technol Eng 10:5708–5711+5727. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2010.23.022
Liu T (2020) Study on the practice path of Honghu Wetland Red Culture promoting rural rejuvenation, Master’s Thesis, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan, China
Liu YS (2018) Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China. Acta Geogr Sinica 73(04):637–650. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlxb201804004
Lu L, Ren YS, Zhu DC, Cheng JM, Yang XZ, Yang Z et al. (2019) The research framework and prospect of rural revitalization led by rural tourism. Geogr Res 38(01):102–118. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlyj020180454
Ma Y, Zhao L, Song H, Guo QX, Liu MJ (2007) Study on the Chinese rural tourism development pattern—a case of CHENGDU. Econ Geogr 27(2):336–339. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-8462.2007.02.035
MacKinnon DP, Lockwood CM, Hoffman JM, West SG, Sheets V (2002) A comparison of methods to test mediation and variable effects. Psychol Methods 07:83–104. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989x.7.1.83
MacKinnon DP, Lockwood CM, Willams J (2004) Confidence limits for the indirect effect; distribution of the product and resampling methods. Multivar Behav Res 39(1):99–128. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327906mbr3901_4
Marianna S, Solenè P, Bynum BB (2023) Resident connection to nature and attitudes towards tourism: findings from three different rural nature tourism destinations in Poland. J Sustain Tour 31:664–687. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1995399
Mehrabian A, Russell JA (1974) An approach to environmental psychology. The MIT Press, Cambridge, GBR
Meng XL (2018) Research on rural tourism destination image, perceived value and the relationship between revisit intention: based on the research on rural tourism in Zhejiang province. J Zhejiang Wanli Univ 31(01):8–15. https://doi.org/10.13777/j.cnki.issn1671-2250.2018.01.002
Middleton VTC, Hawkins R (1998) Sustainable tourism: a marketing perspective. Routledge Press, Boston, USA
Motloch JL (2000) Introduction to landscape design. John Wiley & Sons, New York, USA
Nisco AD, Mainolfi G, Marino V, Napolitano MR (2015) Tourism satisfaction effect on general country image, destination image, and post-visit intentions. J Vacat Market 21:305–317. https://doi.org/10.1177/1356766715577502
Oliver RL (1980) A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. J Market Res 17:460–469. https://doi.org/10.1177/002224378001700405
Ostoić SK, Van Den Bosch CCK, Vuletić D, Stevanov M, Živojinović I, Mutabdžija-Bećirović S et al. (2017) Citizens’ perception of and satisfaction with urban forests and green space: results from selected Southeast European cities. Urban Forest Urban Green 23:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2017.02.005
Prayag G, Hosany S, Muskat B, Del Chiappa G (2017) Understanding the relationships between tourists’ emotional experiences, perceived overall image, satisfaction, and intention to recommend. J Travel Res 56:41–54. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287515620567
Purcell AT (1987) Landscape perception, preference, and Schema discrepancy. Environ Plann B Plann Design 14:67–92. https://doi.org/10.1068/b140067
Qin R (2022) Research on children’s outdoor activity space design based on Landscape Perception—Take Tongle Bay of Changchun North Lake Park as an example. Master’s Thesis. Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China
Queiroz OT (2017) Ruralities as tourist attraction and cultural experience: the Santa Gertrudes farm. Rosa dos Ventos 9(3):447–456. https://doi.org/10.18226/21789061.v9i3p447
Qu GC, Zhao Y, An JH, Xu JY, Qian QQ, Chen MC (2023) Research on the path of high-quality development of rural tourism in southern Anhui based on the original authenticity of nostalgia. Gansu Agri (12):90–95. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-9019.2023.12.017
Sailesh A, Michelle M, Jonas VD (2023) Linking travel behavior and tourism literature: Investigating the impacts of travel satisfaction on destination satisfaction and revisit intention. Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect 17:100745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trip.2022.100745
Scott D, Willits FK (1994) Environmental attitudes and behavior: a Pennsylvania survey. Environ Behav 26(2):239–260. https://doi.org/10.1177/001391659402600206
Shi X (2021) Landscape design for rural tourism under the perspective of ecological aesthetics. Sichuan Drama (10):113–116
Song WY (2013) Outdoor event space landscape perception and its design research. Master’s Thesis. Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China
Stylos N, Vassiliadis AC, Bellou V, Andronikidis A (2015) Destination images, holistic images and personal normative beliefs: predictors of intention to revisit a destination. Tour Manag 53:40–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2015.09.006
Sun XH, Zhang X (2020) Research on adaptive design of traditional village landscape under the background of rural tourism. Design 33:158–160
Sun YH, Chen T, Wang YC (2008) Progress and prospects in research of the traditional rural cultural landscape. Prog Geogr 27(6):90–96. https://doi.org/10.11820/dlkxjz.2008.06.013
Tribe J, Snaith T (1998) From SERVQUAL TO HOLSAT: holiday satisfaction in Varadero, Cuba. Tour Manag 19:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-5177(97)00094-0
Tu HW, Xiong LY, Huang YM, Guo GX (2017) The effect of destination image on tourist behavior intention: an explanation based on the emotion appraisal theory. Tour Trib 32(2):32–41. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-5006.2017.02.009
Wang Q, Ding ZR, Zhang JH, Yang XZ (2006) Study on the model of tourist satisfaction index about tourism environment: a case study of Huangshan Mountain. Geogr Res 25(1):171–181. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2006.01.020
Wang X, Gu CLMei H (2005) Tourist attraction customer satisfaction index model. Acta Geogr Sinica 60(5):807–816. 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2005.05.012
Wang XR, Wang SJ (2010) The research on customer satisfaction of leisure agriculture garden. Chin Agri Sci Bull 26(13):413–419
CAS Google Scholar
Wang YC, Xu CX, Guo HC (2005) Discussions on the new trends of rural tourism development in China. Arid Land Geogr 28(6):862–868. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6060.2005.06.025
Wang ZJ (2015) Study on the planning and design of beautiful rural top line, Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou, China
Wen ZL, Ye BJ (2014) Analyses of mediating effects: the development of methods and models. Adv Psychol Sci 22(5):731–745. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00731
Wu D, Shen CY, Wang EX, Hou YY, Yang J (2019) Impact of the perceived authenticity of heritage sites on subjective well-being: a study of the mediating role of place attachment and satisfaction. Sustainability 11(21):6148. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11216148
Xie HL, Liu LM, Li L (2002) An inquiry analysis on rural development of ecotourism. Ecol Econ 12:69–71. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-4407.2002.12.022
Xu JQ, Zeng Q, Li C (2023) Perception and evaluation of beautiful rural landscape characteristics from the perspective of regional culture-taking Qilian village landscape improvement project as an example. Agri Technol 43(01):89–94. https://doi.org/10.19754/j.nyyjs.20230115023
Xu WH, Tang LZ (2016) Research on the “Four Desirable” strategy in beautiful countryside planning and construction. Chin Landsc Archit 32(09):20–23
Xu YF, Liu MH, Zhang CY (2014) The influence mechanism of tourist loyalty based on perceived destination attributes. Econ Geogr 34(8):167–172
Yan R (2021) Research and application of tourism route optimization based on improved genetic algorithm, Master’s Thesis, North Minzu University, Yinchuan, China https://doi.org/10.27754/d.cnki.gbfmz.2021.0000944
Yang F, Fen J, Xie SY (2022) A study on the evaluation of tourist satisfaction and its influence on the intention to revisit destination: taking 5A scenic spots in Wuhan as examples. J Central China Normal Univ (Natural Sciences) 56(1):116–126. https://doi.org/10.19603/j.cnki.1000-1190.2022.01.013
Yang W, Fan B, Tan J, Lin J, Shao T (2022) The spatial perception and spatial feature of rural cultural landscape in the context of rural tourism. Sustainability 14:4370
Yin Y, Li XQ (2018) The development of mobile internet and the changes of the elderly life. J Chin Acad Gov 05:182–186+193. https://doi.org/10.14063/j.cnki.1008-9314.20181023.026
You JM (2014) The research on the development of rural tourism resources in Zhejiang province based on the construction of beautiful countryside, Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou, China
Yuan Y (2017) Planning and construction of rural complex oriented tourism areas: Siliangjiang Rural Tourism Area Planning (2017–2021) example. Planners 33(12):136–143. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2017.12.020
Zhai YZ (2015) Regional Cultural Studies Rural Cultural Tourism Landscape Design. Master’s Thesis. Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, China
Zhang D (2006) Study on tourist perceived value of rural tourism. Master’s Thesis. Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Zhang H, Fu X, Ca LA, LU L (2014) Destination image and tourist loyalty: a meta-analysis. Tour Manag 40(1):213–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2013.06.006
Zhang L, Wang SL (2018) Study on the visitors experience of tourism products in historical and cultural rural tourism. Art Design 06:142–143. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0412-3662.2018.06.037
Zhang Y, Van Den Berg AE, Van Dijk T, Weitkamp G (2017) Quality over quantity: contribution of urban green space to neighborhood satisfaction. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(5):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14050535
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zhou Y, He JH, Rong H (2016) Satisfaction evaluation of tourist and influence factors analysis in rural tourism. Bus Manag J 38(07):156–166. https://doi.org/10.19616/j.cnki.bmj.2016.07.014
Zube EH, Sell JL, Taylor JG (1982) Landscape perception: research, application and theory. Landsc Plann 9:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3924(82)90009-0
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Academy of Agricultural Planning and Engineering, MARD of China “Study on the transformation of rural space and planning response in the suburbs of Xi'an from the perspective of social change”, grant number XC2X2DKT-20230916 and by the Shaanxi Provincial Science and Technology Project of China “Study on Reshaping the Spatial Value of Cultural Memory of Industrial Heritage and the Path of Local Identity”, grant number 2022JM-289.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Art and Design, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, China
Yuxiao Kou & Xiaojie Xue
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, YK and XX; methodology, XX; software, YK; validation, YK and XX; formal analysis, YK; investigation, YK; resources, XX; data curation, YK; writing—original draft preparation, YK; writing—review and editing, XX; visualization, YK; supervision, XX; project administration, XX; funding acquisition, XX All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xiaojie Xue .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of the primary author’s institution, School of Art and Design, Xi’an University of Technology. All procedures involving human participants in the research were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable standards.
Informed consent
The informed consent was obtained from all participants before the study started.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supporting material, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kou, Y., Xue, X. The influence of rural tourism landscape perception on tourists’ revisit intentions—a case study in Nangou village, China. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 620 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03129-8
Download citation
Received : 21 December 2023
Accepted : 24 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03129-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Visual analysis of tourism image research from the perspective of culture
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
Importance Of Tourism In Tourism
Attraction Infrastructure A tourist attraction is a place of interest where tourists visit, typically for its inherent or exhibited natural or cultural value, historical significance, offering leisure, recreation, adventure and amusement. On the other hand the term tourist destination refers to the geographic area that is different from the place of the permanent residence of a tourist, where tourist activity is implemented and tourist products are consumed. It is possible to define it as a location of tourist consumption (Cavlek et al., 2011). Research on tourist attractions has been undertaken from different approaches and with different definitions of what an attraction is and how it functions. Attractions are the pivotal element of tourism development; evidence shows that tourists are more likely to be motivated to visit destinations that have such resources that can satisfy their needs (Richards, 2006). Wanhill (2008a) used the term imagescape to represent the attraction product concept (the concept of attraction product is further explored in 2.4). Imagescape condenses history and culture in time and space into marketable entertainment experiences (Wanhill, 2008b). According to Pearce (1991) tourist attraction is a named site with a specific human or natural feature which is the focus of visitor and management attention. Kyle and Chick (2002) refer attraction to the perceived importance or interest in an activity or a product, and the pleasure that derives from
Family Fun In Hawaii Rhetorical Techniques
Tourism websites are created to advertise specific locations and to aid customers in their decision of where to travel. In order for a customer to travel to the destination advertised, these websites have to grab and maintain a customer’s attention. The images capture exquisite moments of Hawaii that could be defined as adventurous, pleasurable, and/or astonishing; in addition, the accompanying text delivers a well-thought description of each image by integrating visual imagery within each section. With these specific images and well-thought descriptions displayed on the tourism website for Hawaii, a representation of how people should imagine Hawaii is formed. The authors exploit the imagination of how Hawaii’s beaches, volcanoes, golf courses,
Similarities Between Lennon And Folley
Lennon and Folley also discussed in their book the different actions that might constitute or comprise dark tourism. Even though many factors may motivate a person to visit a dark tourism site, “It is those who visit due to serendipity” (Lennon and Folley 2000:p.23) is still the basis of dark tourism. This still did not stop them from conceding the fact that different motivators still play a big role in this form of tourism. Some motivators may include the personal connection between the visitor and the destination (Mudzanani 2014:p.165), gratitude, education, humility and superiority (2010:p.25) or emotionally visceral experiences (Kang et.al:2012).
Push-Pull Theory
Fakeye and Crompton (1991) suggest six pull factors, they are social opportunities; natural and cultural amenities; bars and evening entertainment; physical amenities and recreation activities; infrastructure, foods, and friendly people; natural and cultural amenities. The study that giving by Fakeye and Crompton (1991) was based on a sample of people visit to a renamed winter place called Texas, and they used 32 attribute items. Hence, Hu and Ritchie (1993) used other relative 16 attribute items, and found the change on across group and their purpose for travel as well as their purpose of travel with family members. In addition, Kim et al (2000) gave 4 destination attributes, they are physical environment; entertainment; high profiles entertainment opportunities; infrastructure. Turnbull and Uysal (1995) also explored six pull factors, but they are different from Fakeye and Crompton’s research.
Importance Of Tourism In Europe
Are you planning to have a special vacation that you can never forget? Do you decide that your next trip destination will be Europe? Are you curious to know more about Europe? So, this article is definitely what you are looking for, as it would help you a lot to know more information about Europe, and would guide you while you are preparing your traveling plan.
The Importance Of Tourism
In this paper I will demonstrate that ethical tourism is the better option that guarantees a stable economic growth while keeping cultural integrity and environmental protection. Even though mass tourism accounts for the rise in employment and gross national product, its economic benefits become marginal as social and environmental costs increase. I will show that ecotourism and pro-poor tourism, as forms of ethical and responsible tourism, contribute to the conservation of the wildlife heritage and to the development of a sustainable growth. Mass tourism concerns all those activities that include shifting of large groups of tourists, high volume of sales, utilization of holiday packages and development of infrastructure and transportation systems. After the second World War, mass tourism increased substantially.
Identity And Identity In Tourism
IDENTIFY AND RESEARCH A TOURISM ATTRACTION Introduction Tourism has experienced continued growth and extensive diversification and competition on the last decades, becoming one of the fastest growing economic sectors in the world and by consequence, one of the main income sources for many developing countries. “Every time we travel we are part of a global movement that has the power to drive inclusive development, to create jobs and to build the sustainable societies we want for our future,” says the actual UNWTO¹ Secretary General, Taleb Rifai. “This movement also contributes to build mutual understanding and to safeguard our shared natural and cultural heritage,” he completes. A sustainable and responsible approach to tourism means that neither the natural environment nor the socio-cultural organisation of the host communities would be compromised by the arrival of tourists.
Relationship Between Hospitality And Tourism Industry
Nowadays hospitality and tourism industry is one of the main industry in this world. A lot of people need a place to escape from their routines or even just to stay overnight as they having a business trip to other places. We call these people as customer or guest. Human mobility from one place to another , both in the country and from and abroad is very high. Human mobility is not only related to business activities but also recretional activities.
Social, Social And Economic Benefits Of Tourism
Benefits of Tourism Tourism is an important activity that people has undertaken for a very long time in the most countries around the world. In recent time it has been recognized as an important social and economic phenomenon. As well as its direct effect it has indirect effects both on the society and at the individual level. . The interaction between tourists and poor communities can provide a number of intangible and practical benefits. These can range from increased awareness of cultural, environmental, and economic issues and values, on both sides, to mutual benefits from improved local investment in infrastructure.
Travel Behavior
This media product refers to travel behaviour which involves the way in which tourists behave according to their attitudes prior to, the duration of as well as the aftermath of travelling. Background regarding travel behaviour may assist in marketing and product planning as well as enhancement which can increase the number of tourists to tourism products such as resorts. However, it was discovered that very little research was conducted regarding the travel behaviour of tourists visiting South African resorts. The purpose of the study was to determine the travel behaviour and more so the travel motivation of tourists visiting resorts. The tourist industry is considered one of the largest and fastest growing industries in the world and as a
Tourism: The Four Different Perspectives Of Tourism
Therefore, tourism may be defined as the activities, processes and outcomes by the relationship and interaction among the tourist, government, suppliers of the tourism, the host communities and the environment that surrounding the destination which involved in attracting and accommodating of the visitors (Goeldner & Ritchie, 2009). According to Goelner & Ritchie (2009), there are four different perspectives of tourism can be identified from the tourist, business operator who providing goods and services, government of the host destination area and the local community. The first group is the tourists or visitors. They are the group who search for various travel experiences and satisfaction physically and psychologically.
Write An Essay On The Benefits Of Tourism To A Country
Over the past few decades, tourism has experienced the sustained growth and deepening diversification to become one of the fastest growing economic sectors over the world. Nowadays, the business volume of tourism can be said to be equals to or even surpasses the business volume of food products, automobiles or oil exports. Tourism plays an important role in almost every country due to it has a greater impact on the development of country economy. The main benefits of tourism are creating extra money for national income and creating more career opportunities for locals. One of the easiest benefits to determine is the career opportunities that the tourism brings.
Importance Of Tourism Behaviour
“Tourism Behaviour understanding includes the idea and knowledge of the different factors which are by no other means very obvious because the effects which do shape the activities and tastes of tourism are often highly embedded in the cultural and the personal biography of the individual that the whole of subject is not known of how actually they were made.” (Seaton, 1996). Figure.1. The tourism system.
The Importance Of Film Tourism
Film tourism is a blooming sector among the tourism industry. It describes the effects that film and TV-productions can have on our travel decisions as they inspire people to experience the screened places firsthand. Not only is film tourism an excellent vehicle for destination marketing, it also presents new product development opportunities, such as location tours, film museums, exhibitions and the theming of existing tourist attractions with a film connection. (Film-tourism.com, 2014) Following with the prevalence of Korean dramas and soaps, many people are long for the romantic scenes and actors shown in the television.
Evolution Of Tourism
Tourism can be considered one of the most significant economic and social phenomena of the twentieth and twenty-first century. The evolving of the tourist’s behavior has triggered a series of changes in the way of operating the tourism businesses. From traditional travel agencies, hotels and airlines up to the online tour operators. All tour operators have had to adapt to the changes of the individual as a traveler and this has led to continuous development of strategies by the agents.
Tourism And Leisure Time
The concept brings proofs on how people spend their time, in which areas and for which purposes. (Nash, 1960, cited in Morgan…). As the people spend their time on different activities, one of those activities is tourism. As well as leisure, tourism has many definitions; we will use one of those which reflect main idea. Tourism is a
More about Importance Of Tourism In Tourism
Related topics.
- World Tourism Organization
- Cultural tourism

Tourism Pictures
Download free tourism images.
Browse premium images on iStock | Claim your discount now


COMMENTS
Handbook of Tourism Economics, pp. 259-279 (2013) The variety of visitor attractions is large and there are endless variations in terms of the product concept. However, the latter is inextricably bound up with the assessment of market potential and vice-versa. Thus, while there is a clear demand for entertainment attractions, success is related ...
Tourist activities could be varied among cities within the same country, which presents challenges for tourism management organizations in developing countrywide management strategies (Heung & Quf ...
The tourist is the end consumer seeking experience and justifying with his Imagescape. The Imagescape could be different for the same destination in different people's mind. The destination management companies work in order to continue, refine, or modify the current destination image to increase the tourist flow.
1. Introduction. Given the intangible nature of tourism products, tourists heavily rely on imagining their future travel scenarios that could occur at destinations when evaluating and making travel decisions (Salazar, 2012).For example, when seeing a tourism landscape photograph, tourists might envision the processes of sightseeing and their feelings before the trip actually begins.
Suggested Citation. Stephen Wanhill, 2013. " The Nature And Development Of Visitor Attractions ," World Scientific Book Chapters, in: Clement A Tisdell (ed.), Handbook of Tourism Economics Analysis, New Applications and Case Studies, chapter 12, pages 259-279, World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.. Handle: RePEc:wsi:wschap:9789814327084_0012.
& Jacobsen, 2003), experiencescape (O'Dell and Billing, 2005) and imagescape ... Tourism is an exemplar of the experience economy (Oh et al., 2007;Pine & Gilmore, 1999): it typifies a ...
Chapter 12 in Handbook of Tourism Economics:Analysis, New Applications and Case Studies, 2013, pp 259-279 from World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd. ... Location is also linked to market assessment and the imagescape; heritage attractions may have little choice as to their location, whereas created entertainments have the possibility of ...
Introduction. As repeatedly proven in tourism research, tourists consume not only spaces but also images (Fierro & Aranburu, 2019) that provide a source of meaningful experiences, including the hedonic, utilitarian, and social consumption of destinations (Hosany & Gilbert, 2010).For decades, the main reason for the analysis of destination image has been its influence on tourist decision-making ...
The Tourism industry is widespread and includes several stakeholders in overall channel of tourist circuit. The industry is full of diversities and experiences in diversities. ... The Imagescape ...
1. Introduction. Tourism Destination Image (TDI) is the sum of people's views and impressions of a tourism destination (Balomenou et al., 2017).A positive destination image boosts the area's competitiveness and improves visitor satisfaction and loyalty (Chi & Qu, 2008).Building an attractive and well-experienced tourism image is crucial for destinations to broaden the international tourism ...
2.1. Attractions compatibility. According to Nelson's (Citation 1958) theory of cumulative attraction, multiple attractions in an area will draw more visitors than if such attractions were widely scattered (Hernández et al., Citation 2021; Lue et al., Citation 1993).A key component of cumulative attraction is the principle of compatibility, which is measured in terms of the number of shared ...
m Websites and User-Generated ContentEstela Marine-Roig and Salvador Anton Clave ́Abstract The aim of this paper is to analyse and compare destination image on official tourism websites with the image expressed by tourists in travel blogs and reviews in order to as. ess image congruency and identify image gaps at different geographical brand ...
Literature Review Tourism destination image has been studied for several decades (Tasci, Gartner, & Cavusgil, 2007), with tourism directors and academics expending extensive amounts of resources in understanding how a tourist constructs, stores, and visualises a destination (Kock, Josiassen, & Assaf, 2016).
The tourism landscape studied in this article is an important component in the study of tourist destination satisfaction, which directly affects the tourists' selection of tourist destinations ...
To date, there has been no comprehensive review of studies on the evolution and applications of experiencescapes, despite their critical role in forming tourism experiences. This study addresses the gap by discussing the emergence, nature, development and potential of experiencescapes and presents implications for future research.
This study collected the relevant literature in the field of tourism image in CNKI and web of Science (WOS) in recent ten years, drew the knowledge map through CiteSpace citation analysis software, and statistically analyzed the literature source, author, organization, research status and revealed the research status and trend of tourism image from the perspective of culture. At present ...
This model provides the basis for the detailed synthesis of the destination image paradigm, as addressed throughout this chapter. This is done from a "3-TDS" gap perspective, confronting host-guest (supply-and-demand) perspectives, based on the idea of the fi ve-gap service quality analysis model by Parasuraman et al. (1985: 44) and with ...
Imagescape condenses history and culture in time and space into marketable entertainment experiences (Wanhill, 2008b). According to Pearce (1991) tourist attraction is a named site with a specific human or natural feature which is the focus of visitor and management attention.
1 U.S. Travel Service, United States Department of Commerce, Mar kel Research of Attitudes of potential Travelers to the U.S.A., 1962, 108p. 2 Herta Herzog, "What Is a Product?:" Consumer Behavior and the Behavioral Sciences, ed. Steuart H. Britt (New York: john Wiley and Sons, Inc., 1967), pp. 353-355. 3 Edward J. Mayo, "Regional Images and ...
Virtually untouched by modern tourism, the district is celebrated for its dramatic black and green sand beaches, tropical fruit and coffee farms and popular Punalu'u Bake Shop.
namche nepal crossing. rome Italy Pictures & Images trevi fountain. belgien brüssel urban. hijab Turkey Images & Pictures tourists. washington washington monument united states. palma spain Palm Tree Pictures & Images. marienplatz münchen germany. morocco essaouira restaurant.