- Publications
- Key Findings
- Interactive Data and Economy Profiles
- Full report

Travel & Tourism Development Index 2021: Rebuilding for a Sustainable and Resilient Future

4. Key findings

Several key findings have been identified in the Travel & Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2021 results and research. First, the need for T&T development has never been greater as it plays a critical role in helping the global economic recovery by supporting the livelihoods of some of the populations hardest hit by the pandemic and by building resilience, especially when it comes to lower-income countries. Moreover, by investing in the factors that help drive T&T, many economies can leverage tourism to further their overall development. The need for T&T development has never been greater as it plays a critical role in helping the global economic recovery.
Second, the key findings show not only how ongoing challenges such as reduced capacity and labour shortages are tempering the recovery but also how shifting demand has created opportunities, forcing many T&T businesses and destinations to adapt, highlighting the sector’s impressive flexibility. Third, the analysis explores in more detail how various aspects and drivers of T&T development can be more thoughtfully and effectively considered and employed to bolster the recovery and build a more inclusive, sustainable and resilient T&T sector.
4.1 The need for Travel and Tourism development has never been greater
The case for t&t development.
As already alluded to in the global context section above, the T&T sector’s significant contribution to global economic and social development makes its recovery and long-term growth paramount. In 2019, the sector’s direct, indirect and induced output accounted for about 10% of global GDP. Moreover, for many emerging economies, T&T is a major source of export revenue, foreign exchange earnings and investment. On average, out of the economies covered by the TTDI, T&T contributed 70% more towards the exports of middle-income economies than to the exports of high-income economies in 2019. 10 Consequently, restoring T&T sector growth will be particularly vital for developing economies’ recovery. For instance, the World Bank forecasts that emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs) will not return to pre-pandemic economic output trends until after 2023, with more than 80% of tourism-reliant EMDEs still below their 2019 economic output at the end of 2021. 11 Recent concerns about the slowdown in globalization and trade due to the impact of the pandemic and geopolitical tensions 12 further enforce how important T&T is for global connectivity.
It is also important to note that T&T is vital not only to overall economic performance but also to the livelihood of some of the populations and businesses most vulnerable to, and hardest hit by, the pandemic. This sector contributed to about 10% of global jobs in 2019, 13 employs almost twice as many women as other sectors, has a large share of youth employment and is a major source of jobs for minorities, migrants, informal workers and low-skilled workers. 14 Moreover, SMEs account for more than 80% of T&T businesses. 15 Unsurprisingly, research has shown that T&T growth can support social progress and create opportunities and well-being for communities. 16 Consequently, investing in T&T could not only mitigate the impact of the pandemic but also improve socioeconomic progress and resilience.

Enabling the T&T development landscape
With the case for T&T’s recovery and development clear, it will be critical to focus on and invest in the factors and policies (beyond the critical need for vaccine distribution) that can help enable these goals, many of which are measured by the TTDI. World Economic Forum research shows that TTDI performance correlates with direct T&T GDP, international tourist arrivals and receipts. 17
Figure 3: Travel and Tourism economic and enabling development landscape

Figure 3 can help us understand which economies are likely to be best positioned from a T&T recovery and resiliency point of view, and which may need to prioritize greater investment in T&T enabling factors. This is illustrated by comparing the TTDI scores to economic dependence on T&T. Low- and middle-income economies tend to score below the TTDI average, indicating a potential constraining factor for their economic recovery. In particular, economies in the bottom-right quadrant would gain the most by investing in the drivers of T&T development because they are more dependent on the sector for economic development. Such investment will help their economic recovery by enabling stronger tourism growth as well as supporting their overall economies to be more robust and resilient. On the other hand, while economies in the bottom left are less dependent on T&T, their below-average TTDI score may indicate that their conditions are leading to an underuse of the sector’s ability to drive development, weakening their economic potential – a resiliency issue in itself.
Higher TTDI scores for economies in the top two quadrants indicate that they are more mature markets and are best positioned for the sector’s recovery. Countries in the top-left quadrant are in a more optimal position from a resiliency point of view as they have favourable conditions for T&T operations but are also less reliant on it for their overall economic performance. However, that is not to say that T&T does not play an important role in their overall economic development, especially at the local level and for specific segments of the labour force and SMEs. Meanwhile, economies in the top-right quadrant, like those below them, have also been more vulnerable to the impact of the pandemic, especially given that analysis shows they are typically more reliant on the export of T&T services. These factors may limit their ability to recover economically from the pandemic, but they are also better positioned to generate tourism-led economic growth as international tourism returns. In general, for the most mature T&T countries such as those higher in the top quadrants, sector performance and resilience may be less about making major improvements in aspects of T&T development such as infrastructure and more about continuously calibrating their T&T strategies to adapt to changing demand dynamics, local needs and overall T&T trends.
Figure 4: TTDI 2021 pillar performance

Figure 4 shows in more detail what gaps remain to achieving improved T&T performance and development for various countries. High-income economies and countries in the Europe and Eurasia (Europe) and Asia-Pacific (APAC) regions tend to lead the overall index in results. Among the largest differentiators between index leaders and laggards are: the distribution and promotion of natural, cultural and non-leisure assets and activities; the availability of quality transport and tourist service infrastructure; the degree of international openness; and favourable factors such as (increasingly important) ICT readiness and health and hygiene. However, as shown in the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report 2019, because T&T growth is so dependent on factors such as infrastructure and health and hygiene, which if improved bring benefits to more than the tourism sector, sector leaders can play a valuable role in encouraging investment that benefits a country’s economy as a whole. This is especially true for developing economies that have innate natural and cultural assets around which to mobilize investment. 18 The next section detailing key findings will use the TTDI results to discuss the T&T challenges and opportunities created over the past few years, as well as examining how various drivers of T&T development can be employed to bolster T&T recovery and build a more inclusive, sustainable and resilient T&T sector, thereby unleashing its potential for economic and social progress.
4.2 Recovery challenges and shifting demand dynamics
The results highlight difficult operating conditions.
While varying greatly based on local, segment, national and regional conditions, the TTDI results and research help highlight some of the various and common operational challenges the T&T sector faces in its recovery.
With T&T activities being severely restricted over the past few years, the greatest decline in index performance has come from the contraction of related operations and investment. As such, average scores fell in the Air Transport Infrastructure (-9.4%), Prioritization of Travel and Tourism (-6.7%) and Tourist Service Infrastructure (-1.5%) pillars. Air route capacity and airport connectivity plummeted, especially in more mature and high-income economies. Similarly, the decline in tourist service infrastructure reflects initially reduced capacity in the accommodation and related segments. The average number of per capita short-term rental units dropped by about one-fifth between mid-2019 and 2021 across economies ranked in the index. 19 While not reflected in the TTDI results, STR data indicates that, over a similar timespan, the number of hotel rooms did not recover to pre-pandemic levels in many countries. 20 In line with these trends, both T&T capital investment and government T&T expenditures also fell. The decline in sector capacity has also been compounded by the fact that most businesses are SMEs and do not have the means to survive prolonged drops in demand or restrictions on person-to-person contact. The disproportionate impact of the pandemic on the sector is indicated by the direct T&T contribution to global GDP falling from 3.2% to 1.6% and the contribution to global employment falling from 3.8% to 3.1% between 2019 and 2020. 21
Figure 5: Select pillar 2019 to 2021 average score change

Yet, as demand resumes in line with easing travel restrictions and somewhat improving COVID-19 conditions, the initial reductions in capacity increase the potential for supply-side constraints. In advanced economies, in particular, rising demand, earlier layoffs that disproportionality hit T&T, and competition for talent with other sectors have resulted in widespread labour shortages. A WTTC report focusing on the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Spain, Italy and Portugal estimates that the T&T sectors in these countries experienced staff shortfalls ranging from 9% to 18% in 2021. 22 The interconnected nature of the T&T supply chain and ecosystem has also created challenges. Hotels, airlines, car rental firms, tour operators, cruise lines and others all form a chain of service providers dependent on each other along the traveller journey. Bankruptcies or other disruption issues at any point along this chain have the potential to negatively affect the others.
"In addition to labour shortages and capacity constraints, the sector has also been exposed to broader global disruptions that are complicating recovery."
Over the course of the pandemic, growth in merchandise trade coincided with production, worker, equipment and space shortages to create a global supply-chain crisis. For instance, hotels have faced shortages of items ranging from slippers for clients to kitchen equipment. 23
The recent outbreak of war in Ukraine and resulting sanctions and travel restrictions related to Russia have added further pressure on the recovery. Airlines around the world have had to reroute operations, increasing travel times and costs. Meanwhile, the still fragile recovery in international tourism demand could be tempered by increased hesitancy among travellers when it comes to visiting Europe. 24 Many T&T economies in Europe, Eurasia and beyond may also be hard hit due to reduced demand from Russia and Ukraine. Combined, these two economies account for about 3% of international tourism spending, with Russia having been a major source of visitors to destinations ranging from Azerbaijan, Georgia and Turkey to Israel, the United Arab Emirates and Thailand. 25
While not yet fully reflected in the TTDI’s Price Competitiveness pillar, rising travel demand, the stated labour, capacity and other shortages, global supply-chain disruptions and rises in fuel prices and inflation caused by factors such as the war in Ukraine will likely increase costs and service prices throughout the entire T&T supply chain and ecosystem. For example, as of 13 May 2022, jet fuel prices were more than double what they were a year ago, 26 and if they remain high, airline yields and ticket prices will likely rise. 27 Recent UNWTO analysis cites how conflict-induced uncertainty, higher energy and food prices and inflation, in general, are putting pressure on consumer purchasing power and tempering global economic growth, potentially affecting T&T sector performance. Moreover, as economies such as the United States combat inflation by increasing interest rates, consumer demand and T&T investment may be further hit by the rising cost of credit. 28
The pandemic shifts demand dynamics, creating opportunities and driving adaptation
With travel restrictions still common and traveller confidence hampered by pandemic concerns, the past few years have also seen a shift in demand trends in global T&T. According to the UNWTO Panel of Experts, the major trends driving the T&T recovery include domestic tourism, travel close to home, open-air activities, nature-based products and rural tourism. 29 The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) data shows that, on average for the 117 economies covered by the index, domestic spending’s share of T&T spending increased from 50.8% in 2019 to 62.6% in 2020 as domestic demand fared better than collapsing international demand. 30 Moreover, current projections for 2021 show that domestic spending growth is expected to substantially outpace international spend in every region outside of the Caribbean and Middle East. 31
The TTDI results further reinforce the shift in demand dynamics that the world has witnessed. The second most improved pillar is Natural Resources (+2.5% average score increase). While this was driven largely by an expansion in the number of recognized UNESCO World Heritage natural sites and protected areas, such as national parks, the greatest improvement has come from destinations’ ability to garner interest in nature-related segments as illustrated by the 20.8% average growth in natural tourism Digital Demand value, a measure of online searches for topics such as natural wonders, outdoor activities and rural accommodation.

On the other hand, the Non-Leisure Resources pillar had one of the greatest declines in average performance (-1.9%) as business travel declined. While this sector is recovering, it has rebounded at a slower rate than leisure, with factors such as workplace flexibility and the availability of virtual alternatives for in-person meetings tempering demand and potentially leading to some permanent loss in corporate travel. This will force many T&T segments to adapt. For example, operators in the meetings, incentives, conferences and events (MICE) area may have to rely more on smaller and hybrid events. 32 T&T businesses and destinations are increasingly looking to capture opportunities offered by the changing nature of work. Over the course of the pandemic, more businesses have gone virtual, and an increasing share of the labour force is becoming independent.
"In 2020, 10.9 million Americans said they were digital nomads, a 49% increase from 2019."
This sample of independent workers is also increasingly willing to travel. A recent survey showed that the share of US independent workers doing business outside the country jumped from 12% in 2013 to 28% in 2020. 33 Additionally, the trend in “bleisure” travel – the addition of leisure activities to business trips – is also growing. 34
To cater to these growing markets, T&T businesses will have to become more flexible and create new, innovative products. For instance, some major hospitality groups are creating new long-stay properties that include kitchens and living spaces, while other have introduced packages that offer reduced rates for those staying longer, which include IT and boardroom services. 35 Furthermore, while virtual business may require less office space, corporations and their employees may need options for occasional company meetings and events that the sector could provide. However, it is important to note that these new market opportunities are primarily for the high-end travel market and are not likely to replace the overall loss in business travel. Lastly, T&T operators have also had to introduce more flexible booking and cancellation policies in order to address uncertainty about travel regulations and the pandemic, in addition to increased consumer desire to make last-minute changes or to add leisure stays to their business trips. 36
From a destination point of view, many governments have also adapted to changing conditions to take advantage of shifting demand dynamics. For one thing, many countries have provided various incentives to boost domestic tourism. For example, Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea and Japan have rolled out various programmes that provide discounts, coupons and subsidies for domestic travel. 37 Meanwhile, Aruba targeted the digital nomad market through extended work visas and other benefits via its One Happy Workation programme. 38 The trends towards more rural and nature-based tourism also offer an opportunity for less-developed economies to harness the benefits of T&T given that the distribution and quality of natural assets are less tied to overall economic development, with Natural Resources being one of the few pillars where non- high-income economies typically outperform high- income countries (see Figure 6).
Figure 6: Composition of top quartile, by income group

Overall, the above adaptations to shifting demand and COVID-19 conditions help highlight how flexible T&T business and destinations can be in times of crisis. As the sector rebuilds and addresses future risks, its adaptability will become more crucial than ever. In particular, as can be seen in the key findings that follow, the shift to domestic and nature-based travel, as well as other trends, coincides with an increased emphasis on sustainable and safe travel. Therefore, T&T development will have to become increasingly sustainability-oriented.
4.3 Building back better
Given the current challenges, shifting demand dynamics and future opportunities and risks, it is vital that T&T development strategies are employed to rebuild the sector in a more inclusive, sustainable and resilient manner.
Restoring and accelerating international openness and consumer confidence, including investment in health and security
For starters, as travel restrictions are removed, ensuring that T&T markets are open to visitors and investors will become vital. In particular, it is important that the historical trend of ever greater international openness in T&T continues. Reduced visa requirements fuel international tourism and additional air service agreements open up markets to more airlines, routes, competition and, ultimately, better service (see Figure 7). Given the recent decline in international route capacity and travel demand, prioritizing visa and air service agreement liberalization will be important – with those economies most dependent on tourism exports and lacking large domestic markets standing to benefit the most. Financial openness and an increase in regional trade agreements can also help to facilitate necessary cross-border investment in T&T and beyond, which may also help encourage more international and intra-regional travel.
TTDI results indicate that Western, Southern and Northern Europe are usually the most internationally open subregions due to the close integration that the European Union, the Schengen Area and similar blocs and agreements provide. Such systems allow T&T operators to benefit from factors such as a larger and more diverse consumer base and common market rules. It is also important to recognize that despite the pandemic and disrupted global trade, 83 economies ranked in the index increased their number of regional trade agreements in force between 2019 and 2021. Relevant recent developments include the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), which came into force in 2021. Combined with related efforts such as the Free Movement Protocol and Single African Air Transport Market (SAATM), the sub-Saharan Africa region has the potential to unlock its untapped T&T potential and grow its underdeveloped intra- regional T&T market and air route capacity. 39
Figure 7: Correlation between air service agreement liberalization and air transport infrastructure, 2019

Endnotes 40 , 41
Of course, the pandemic, along with the recent rise in geopolitical tensions, also highlights just how important health and security conditions are to protecting the openness on which T&T relies and to restoring consumer confidence in travel. Economies with sophisticated healthcare systems are better equipped to mitigate the impact of pandemics on T&T and the wider economy by protecting their populations, including the T&T workforce and visitors, thus reducing the need for travel and lockdown restrictions. Meanwhile, access to clean water and sanitation facilities helps prevent diseases or their spread. Lastly, consumers and business travellers are likely to remain more sensitive to the health and hygiene conditions at destinations for some time. A recent survey shows that the majority of travellers consider safety protocols, restrictions and cleanliness to be key factors in travel decision- making. 42 In the short term, T&T business, destinations and international organizations have responded to these issues via actions such as the introduction of various protocols and certifications. For instance, the World Travel & Tourism Council has introduced the Safe Travels protocols and certification stamp that can be used by T&T to show customers they are following standardized global health and hygiene practices. 43
In general, underdeveloped health and hygiene infrastructure and access represents an acute challenge for many developing countries, with low- and lower-middle-income economies scoring 50.0% and 25.6% below average in the Health and Hygiene pillar. These states lack physicians and hospital beds (in terms of ratio to population size) and access to basic sanitation and drinking water, and such issues, combined with lower vaccination rates, mean that these economies will struggle to recover at the same pace as others and will have difficulty building adequate resilience against future health security risks. It is therefore crucial for the success of the global T&T sector that the challenges related to vaccine distribution and roll-out are addressed in an equitable and inclusive fashion. While further effort is required, public-private cooperation can provide a useful avenue to address this challenge. For example, the World Economic Forum’s Supply Chain & Transport Industry Action Group community, which consists of leading supply-chain companies, is supporting UNICEF and the COVAX Vaccine Distribution programme with “planning, preparedness and prioritized transportation and distribution of COVID-19 vaccines and related supplies”. 44

The above-mentioned introduction of travel bans, flight-route adjustments, increasing fuel and food prices and potentially hindered international travel demand caused by the war in Ukraine have also shown the degree to which international T&T can be affected by geopolitical tension and conflict. Overall, it is well established that crime and security issues such as terrorism and conflict have a negative impact on tourist arrivals and sector revenue. 45 The 2021 TTDI data shows that economies in the Americas, sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia tend to score the lowest for safety and security, thereby creating a further obstacle to the future development of T&T in these areas.
On the other hand, research has also shown that a sustainable and open tourism sector can be resilient to violence and conflict and that it may help foster positive peace, namely the “attitudes, institutions and structures that create and sustain peaceful societies”. More specifically, the mechanisms through which tourism can accomplish this include cultural and information exchange, encouragement of tolerance, better government functioning, human capital development, and local and cross-border economic gain that can reduce the risks to peace. 46 It is now more important than ever to leverage the T&T sector’s potential for peace through sustainable development.
"It is crucial for the success of the global T&T sector that the challenges related to vaccine distribution and roll- out are addressed in an equitable and inclusive fashion. While further effort is required, public- private cooperation can provide a useful avenue to address this challenge."
Building favourable and inclusive labour, business and socioeconomic conditions
Over the course of the pandemic, the T&T sector has received substantial support in the form of debt financing, tax policies, assistance with business costs, public-sector investment, employment support, incentivization of tourism demand and easing of regulations. 47 In the future, continued investment in human capital and the creation of more favourable labour, business and socioeconomic conditions will be vital components in making the sector more inclusive, addressing ongoing challenges such as labour shortages and driving T&T growth and resilience.
Factors such as accessible and quality education and staff training, supportive hiring and firing practices, programmes to source skilled labour, flexible working arrangements and efforts to improve labour productivity can help equip T&T companies with a workforce that can improve operating efficiency, provide quality services, maintain flexibility in the face of evolving business needs and challenges and take advantage of the growing role of ICT tools. For example, according to the World Economic Forum’s The Future of Jobs Report 2020 , skills gaps in the local labour market were the number one barrier to adoption of new technologies in the transport and storage, and consumer sectors, the two sectors most closely tied to T&T. 48 Furthermore, according to the WTTC, factors such as facilitation of labour mobility, upskilling and reskilling and promotion of education are vital elements in addressing the current labour shortage. 49 Meanwhile, the past few years have shown how important policy stability, access to credit and creating more business- friendly regulatory and tax environments have been in supporting the T&T sector, especially SMEs that typically do not have the same resources and access to capital as larger firms. 50
The 2021 TTDI results partially reflect some efforts by policy-makers to support their economies, with the average Business Environment score climbing 1.7% since 2019. In particular, perceptions of the burden of government regulations and SME access to finance were areas that saw some of the largest improvements. The average Human Resource and Labour Market pillar also improved by 1.5% between 2019 and 2021, due to overall progress made in areas such as staff training. Nonetheless, less developed economies still score well below the TTDI average for most indicators for both pillars.
The pandemic has also highlighted how important an economy’s socioeconomic resilience is for the T&T sector. In general, the ability of an economy to support its population through social protections such as unemployment and maternity benefits, keep youth employed or in training, effectively uphold workers’ rights and support a diverse and inclusive workforce may potentially help strengthen employee productivity, expand the labour pool and make it more resilient to risks such as pandemics. 51 This is particularly true for the T&T sector because it provides income for a large number of youth, women, informal workers, the self-employed and small enterprises, who do not always have access to social or worker protections. Figure 8 shows that there is a relationship between socioeconomic resilience and conditions and labour productivity in T&T. Recent survey data also reinforces how important issues such as benefits and working conditions are for attracting talent and addressing the ongoing labour shortage in the sector. One poll of former US hospitality workers showed that more than half won’t return to their old jobs and over a third are not planning on returning to the industry as they seek higher pay, better working conditions and benefits, and more flexibility. 52
Figure 8: Correlation between socioeconomic resilience and conditions and tourism labour productivity

The 2021 TTDI results show that, across the board, socioeconomic resilience has tended to improve due to the expansion of social protection coverage and spending in line with global efforts to mitigate the impact of COVID-19. High-income economies do tend to score far higher on the Socioeconomic Resilience and Conditions pillar, putting them in a better position to deal with future challenges and maximize their workforce potential. Conversely, low- and lower-middle-income countries have far lower socioeconomic resilience due to more limited social protection, higher rates of youth not in education, employment or training (NEET), fewer workers rights and greater inequality of opportunity for all. As a result, the T&T sector in these economies may face more obstacles to recovery and may be more vulnerable to future risks.
While rising interest rates and debt levels represent a growing obstacle, government responses to the pandemic demonstrated their capacity to provide more comprehensive socioeconomic support, and the benefits of doing so, albeit during an unprecedented situation. While the pandemic has certainly disproportionately affected SMEs, entrepreneurs or more vulnerable populations, strengthening such mechanisms, especially in the T&T sector, could have compound benefits for the sector and economies as a whole.
The growing role of environmental sustainability
In the coming years, the success of T&T businesses and destinations will be increasingly tied to their ability to manage and operate under ever greater ecological and environmental threats. According to surveys conducted for the World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report 2022 , environmental risks represent half of the top 10 global risks, with climate action failure, extreme weather and biodiversity role natural assets play in generating T&T demand and spend, these environmental risks represent a serious threat to long-term growth for the sector. Moreover, within this context, travellers increasingly value environmentally sustainable options. 54 df
The 2021 TTDI results indicate the extent of environmental sustainability threats and challenges. For instance, comparing the Natural Resources and Environmental Sustainability pillar scores helps to pinpoint where some of the greatest risks to nature-based tourism might lie. Out of the 30 economies that rank in the top quartile for natural resources, 17 score below the global average for environmental sustainability and eight rank in the bottom 25.
Figure 9 provides a regional view of the challenge. While most economies in the Americas and Asia- Pacific and almost half of those in sub-Saharan Africa score above average for natural resources, they commonly underperform in environmental sustainability, making it a critical problem for future T&T development. Environmental issues differ in these regions, but some examples include elevated climate-related risk (as measured by the Global Climate Risk Index), air and sea pollution, deforestation, poor wastewater treatment and inadequate preservation policies. In the Middle East and North Africa, common problems include water stress and air pollution. On the other hand, economies in the Europe and Eurasia region are world leaders in environmental sustainability, accounting for more than half of countries in the TTDI that score above average for this pillar. Combined with the fact that natural resources are not its greatest strength or dependency, the region and its tourism sector may be the better positioned to deal with future ecological risks.
Figure 9: Share of regional economies scoring above average for natural resources and environmental sustainability

Nonetheless, while there are some economies that have better environmental conditions, the challenge is widespread and is not easing. The difference in average score between the top and bottom quartiles for the Environmental Sustainability pillar is the second-lowest among the pillars. Moreover, performance for many indicators in this pillar has been mixed. For example, scores for deforestation continued to worsen. On the other hand, efforts to preserve the environment and T&T-generating natural assets got a boost from continued expansion in the share of protected territories and the number of environmental treaties signed.

A recent UNWTO and One Planet report reiterated the importance of a healthy environment for T&T competitiveness and development and recommended several actions to help the T&T sector produce a greener recovery. This included biodiversity protection actions such as putting tourism at the forefront of conservation efforts and ensuring that the value tourism provides for conservation efforts via monitoring mechanisms and investing in nature-based solutions is captured. Climate action efforts in T&T can be accelerated through the likes of monitoring and reporting emissions from tourism operations, accelerating decarbonization through the development of low-carbon transport options and greener infrastructure, and engaging in carbon removal via the restoration of carbon-density ecosystems and carbon-removal technologies. Finally, circular economy actions are recommended.
These include investing in transforming tourism value chains by reducing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, remanufacturing, recycling and repurposing whenever possible; prioritizing sustainable food approaches such as local and organic procurement; creating sustainable menus and focusing on reducing food loss; and shifting towards a circularity of plastic in tourism. 55
At the World Economic Forum, efforts in this field are plentiful, and cover multistakeholder actions on decarbonizing transportation, accelerating action on plastics, ensuring the long-term, sustainable use of the ocean, and developing the circular economy. In particular, the Clean Skies for Tomorrow Coalition 56 is working with stakeholders in the aviation ecosystem, including buyers of corporate travel, to accelerate the production and use of sustainable aviation fuels, all while better distributing the green premium for these fuels. The Forum also hosts the Global Future Council on Sustainable Tourism, 57 a community of experts from academia, business, civil society and governments who are developing a set of principles for sustainable destinations to guide decision-making on rebuilding the sector in the wake of the pandemic. The Council is also researching customer behaviour changes that can incentivize the development and delivery of more sustainable travel products and services, articulating the value of investment in the blue and green economies in tourism, and providing guidance on the ambition of achieving net-zero emissions across the various verticals in the T&T sector.
Managing tourism demand and impact
Sustainable management of tourism demand that maximizes benefits for local communities, while also mitigating negative side effects such as overcrowding, will also become a vital component of T&T development as the sector recovers.
The TTCR 2019 discussed how long-term T&T growth was starting to put pressure on local infrastructure and housing, as well as degrading cultural and natural assets that attract visitors and fuelling uneven distribution of T&T benefits. This ultimately led to falling liveability standards for residents, local backlash against tourism and diminished visitor experience. 58 Although recent lockdowns and travel restrictions led to this sustainability challenge being discussed less, it is likely to become a more common topic as demand continues to recover. In many areas, the pandemic-fuelled travel demand push towards outdoor attractions, rural communities and secondary destinations has already revealed capacity constraints. For instance, the rise in nature travel had already led to more overcrowding at many national parks, with many US national parks monthly visitation number hitting all-time highs, leading to issue such as littering, wildlife disruption and traffic jams. 59 Visitors also show signs of wanting to reduce their footprint and improve the social impact on the destinations they visit, with just over half of global travellers in a recent survey indicating that they would be willing to switch their original destination for a lesser-known one if it led to a reduced footprint and greater community impact. 60
While issues such as overcrowding and other effects of T&T on communities are typically a local rather than national-level concern, the TTDI looks at the existence of, or risk related to, overcrowding and demand volatility, as well as the quality and impact of T&T via the T&T Demand Pressure and Impact pillar. In general, pillar results indicate that T&T Demand Pressure and Impact challenges affect economies of all levels of development. For instance, the difference in the average pillar score between low- and lower-middle-income and high-income economies covered by the index is just 0.8% and 2.5%, respectively.
High-income European countries tend to be some of the top TTDI performers and include rich cultural and non-leisure assets and quality transport and tourism infrastructure that allow for the absorption of large quantities of visitors. However, they still tend to score below average for the T&T Demand Pressure and Impact pillar due to factors such as shorter lengths of stay, higher seasonality and a very high level of concentration of interest in a small number of attractions, as shown by Tripadvisor page views and backed by at times unfavourable perceptions of the dispersions of tourism. Unsurprisingly, this region has often claimed headlines for tourism overcrowding. On the other hand, less-developed economies and those ranking lower on the TTDI tend to bring in fewer tourists, but still score below average for perception of tourism dispersion and town- and city-centre accessibility and crowding, an issue that may be partially explained by these economies’ typically below-average scores for transport infrastructure.
Figure 10: T&T Demand Pressure and Impact pillar component scores, 1–7 (best)

In summary, the relatively close distribution of T&T Demand Pressure and Impact pillar scores among economies of different incomes and tourist arrival levels highlights the fact that challenges such as overcrowding have less to do with visitor numbers and more to do with local conditions and policies.
Yet, as the sector rebuilds, there is an opportunity to use increasing domestic and nature-based T&T demand, consumers’ rising preference to manage their footprint and the need to address historical issues such as overcrowding by making investments and policies that help disperse T&T, thus making the sector more resilient. For one, proper care must be paid to developing transport, tourism, health and ICT infrastructure in rural, nature and secondary destinations. This can help funnel tourism and its benefits to more communities, make them more attractive destinations and increase their capacity to absorb more visitors. Within urban centres, improved road and public transport infrastructure and access to efficient, accessible, safe and affordable transport options can reduce the chances of overcrowding and lead to both greater liveability for residents and a better visitor experience (see Figure 11).
Figure 11: Correlation between public transport and quality of town and city centres

In general, TTDI 2021 results show an improvement in the Ground and Port Infrastructure pillar (+2.2%) since 2019. In particular, middle-income economies have experienced some of the strongest growth in areas such as perceptions of road quality and efficiency of train services. Nevertheless, as already alluded to, less-developed economies still have gaps in their infrastructure, ranging from lower road and rail density to a lack of access to efficient and quality public transport. Combined with lower marks for factors such as tourist and health infrastructure, these economies will face some of the greatest challenges in distributing tourism and its benefits throughout their communities. However, they also have the most to gain from overcoming these obstacles.
Aside from investment in infrastructure, policies are also a fundamental part of proper tourism demand management and dispersion. The above subsections of the key findings section explored how governments and destinations can institute policies to develop domestic and other forms of tourism. Moreover, there are specific efforts that can be made to manage T&T to prevent overcrowding and efficiently use a destination’s carrying capacity. For instance, the UNWTO has set out strategies and measures that can combat challenges such as these in cities. Some of these include the promotion of attractions and events that disperse visitors so they are not concentrated only in certain areas, time-based dynamic pricing, the creation of pedestrian-only zones, defining the carrying capacity of city areas, focusing on lower-impact visitor segments, ensuring local communities benefit from tourism, engaging with local stakeholders and monitoring the impact of tourism, including through the use of big data. 61
T&T stakeholders can also play a more active role in broader sustainable mobility efforts and trends that can help to reduce the sector’s environmental impact, manage demand and make destinations more attractive for visitors and residents. For example, the World Economic Forum’s Global New Mobility Coalition (GNMC) is a multistakeholder community for “accelerating the shift to a Shared, Electric and Autonomous Mobility (SEAM) system”. The synchronization of high-occupancy, electric and autonomous transport options can lead to better traffic flow, higher efficiency of road usage, more equitable mobility systems, better air quality, lower carbon emissions and improved grid resilience. More specifically, SEAM may reduce carbon emissions by 95%, improve mobility efficiency by 70% and decrease commuting costs by 40%. Given SEAM’s clear potential to create more sustainable destinations, a case can be made for T&T sector involvement this area. 62
The crucial role of digital technology
All of the aforementioned efforts to build back a better T&T sector will depend on effective leveraging of the growing role of digitalization in T&T.
More T&T services are being accessed by digital systems through online travel agencies (OTAs) and sharing economy platforms, direct online bookings, digital payment systems and mobile devices, and thus consumers tend to expect the greater convenience, increased options, reduced person- to-person contact and seamless experience that these systems provide. Furthermore, digitalization enables T&T businesses to gather consumer insights and preferences, optimize operations, cut transaction costs and automate processes. 63 Online platforms also enable T&T service providers, including SMEs, to reach beyond their local markets and connect with broader domestic and international markets. Due to the above- mentioned factors, it is not surprising that a positive relationship has been found between ICT readiness and international tourism receipts. 64 In the context of shifting demand dynamics, destinations with greater ICT readiness will be better positioned to diversify their markets and take advantage of trends such as the rising numbers of digital nomads and growth in nature-related travel. For instance, research shows a clear relationship between the ICT Readiness pillar and natural tourism online searches in economies with rich natural resources. 65
A recent report by the Asia Development Bank (ADB) and UNWTO outlines how the T&T sector can use big data and digitalization for better and more sustainable tourism management and recovery. Tourism-specific data coming from sources such as T&T operators and online platforms, and non-tourism-specific data coming from sources such as credit card transactions, mobility services and sensors can help T&T stakeholders track and manage the social, economic and environmental impacts of T&T, complement more traditional data-collection efforts, manage tourism flows and target preferred source markets, thereby helping to create smart destinations.

For instance, the Macao Government Tourism Office has worked with a major Chinese multinational technology company to “optimize visitors’ travel experiences before, during and after trips; obtain insights into travellers’ behaviour through in-depth analysis of big data; and monitor, divert and disperse visitor flows at tourist districts and congested areas”. The use of big data and various digital platforms and technology can also help seamless travel and act as health and security tools by enabling safety protocols, biosecurity technologies and digital health certificates, thereby boosting traveller confidence. However, the report also highlights the various barriers to greater use of big data and digitalization within the T&T sector. Some of these challenges include privacy concerns, data reliability, governance issues, disincentives for public-private collaboration, the digital divide, skills gaps and greater efforts to include SMEs. 66
Figure 12: ICT Readiness by economic income group, 2019–2021

Figure 12 helps to illustrate the digital divide among economic income groups. Developing economies typically lag when it comes to ICT infrastructure, internet connectivity and mobile network coverage, which hampers the use of digital platforms in financial services, transport and tourism activities. On the other hand, the ICT Readiness pillar is the most improved (+3.0%) since 2019 largely due to continued improvement in low- and middle-income economies. These results indicate that while high-income economies are best positioned to leverage digitalization and create smart destinations, developing economies are building capacity. In addition, as already mentioned, creating a more highly skilled labour force will be an essential element and challenge in maximizing the use of ICT tools in T&T.
The growing role of digitalization and, in particular, digital platforms, within the T&T space can also create other labour and socioeconomic challenges. Globally, the number of active digital labour platforms, which include ride-hailing taxi and delivery services, has grown from fewer than 200 in 2010 to at least 777 at the start of 2021. As stated, these platforms create new avenues for flexible employment for people, allow business to access wider markets and talent pools, improve productivity and provide convenience for customers. However, they could also lead to greater income and job insecurity. Commonly raised issues include less favourable working conditions, deficient social protection and employment benefits and a lack of access to fundamental rights of freedom of association and collective bargaining. 67 The growth in popularity of digital platforms offering short-term rentals has also led to concerns about residents’ access to housing at destinations where housing capacity is increasingly taken up by the T&T sector. 68 The concentration of market share in the hands of digital platforms may also lead to imbalances in the bargaining and pricing power of the various stakeholders, including workers and SMEs. 69
If proper efforts are made, from employee training and supporting SMEs’ use of ICT to fair and effective regulation of digital platforms and their impact on workers and destination communities, digitalization in T&T will become one of the driving forces in growing the sector’s role in inclusive, sustainable and resilient development. However, failing in these areas could also transform this key aspect of T&T operations into an increasingly acute barrier to future T&T growth.
4.4 Conclusion to the key findings
The COVID-19 pandemic and its impact have underscored the T&T sector’s vital role in global connectivity and development. In the coming years it will therefore be crucial for T&T stakeholders to devise strategies that make the sector more inclusive, sustainable and resilient.

As the TTDI 2021 results reveal, any such enterprise will require a comprehensive and holistic approach. Creating a better T&T economy is not just about improving infrastructure or offering favourable pricing. It also involves creating better health and hygiene conditions, ensuring natural resources are protected and that the workforce on which the sector depends has access to training and social protection. This necessitates the active participation and coordination of sector and non-sector business, employers and employees, government agencies ranging from tourism and health ministries to local authorities, environmental and conservation groups, and international organizations. Over the course of the pandemic, often uncoordinated travel restrictions and health protocols revealed the difficulty and necessity of such cooperation.
In the future, efforts will need to be made to devise common frameworks for defining and measuring T&T sustainability, including the creation of commonly accepted environment, social and governance metrics. The safe and ethical use of big data will prove fundamental to this cause. Moreover, in an increasingly complex and technology-enabled environment, it will be vital to ensure that developing economies, workers and SMEs are not left behind.
While these challenges may be difficult, the flexibility and adaptation the T&T sector has shown in the past few years also indicates that sector stakeholders are more than capable of rising to the occasion.
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
- SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
- Competitiveness
- Innovation and Investments
- ETHICS, CULTURE AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
- TECHNICAL COOPERATION
- UN Tourism ACADEMY
share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Sustainable development
"Tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities"
Sustainable tourism development guidelines and management practices are applicable to all forms of tourism in all types of destinations, including mass tourism and the various niche tourism segments. Sustainability principles refer to the environmental, economic, and socio-cultural aspects of tourism development, and a suitable balance must be established between these three dimensions to guarantee its long-term sustainability.
Thus, sustainable tourism should:
- Make optimal use of environmental resources that constitute a key element in tourism development, maintaining essential ecological processes and helping to conserve natural heritage and biodiversity.
- Respect the socio-cultural authenticity of host communities, conserve their built and living cultural heritage and traditional values, and contribute to inter-cultural understanding and tolerance.
- Ensure viable, long-term economic operations, providing socio-economic benefits to all stakeholders that are fairly distributed, including stable employment and income-earning opportunities and social services to host communities, and contributing to poverty alleviation.
Sustainable tourism development requires the informed participation of all relevant stakeholders, as well as strong political leadership to ensure wide participation and consensus building. Achieving sustainable tourism is a continuous process and it requires constant monitoring of impacts, introducing the necessary preventive and/or corrective measures whenever necessary.
Sustainable tourism should also maintain a high level of tourist satisfaction and ensure a meaningful experience to the tourists, raising their awareness about sustainability issues and promoting sustainable tourism practices amongst them.
COMMITTEE ON TOURISM AND SUSTAINABILITY (CTS)
Biodiversity
UN Tourism strives to promote tourism development that supports, in equal measure, the conservation of biodiversity, the social welfare and the economic security of the host countries and communities.
Climate Action
Tourism is both highly vulnerable to climate change while at the same time contributing to it. Threats for the sector are diverse, including direct and indirect impacts such as more extreme weather events, increasing insurance costs and safety concerns, water shortages, biodiversity loss and damage to assets and attractions at destinations, among others.
Global Tourism Plastics Initiative
The problem of plastic pollution in tourism is too big for any single organisation to fix on its own. To match the scale of the problem, changes need to take place across the whole tourism value chain.
Hotel Energy Solutions (HES)
Hotel Energy Solutions (HES) is a UN Tourism -initiated project in collaboration with a team of United Nations and EU leading agencies in Tourism and Energy .
Observatories (INSTO)
The UN Tourism International Network of Sustainable Tourism Observatories (INSTO) is a network of tourism observatories monitoring the economic, environmental and social impact of tourism at the destination level.
When responsibly planned and managed, tourism has demonstrated its capacity to support job creation, promote inclusive social integration, protect natural and cultural heritage, conserve biodiversity, generate sustainable livelihoods and improve human wellbeing. As the sector is experiencing tremendous growth, collective efforts to ensure its long-term sustainability are essential.
Resource Efficiency in Tourism
The report aims to inspire stakeholders and encourage them to advance the implementation of the SDGs through sustainable tourism.
Small Islands Developing States (SIDS)
Small Island Developing States face numerous challenges. For a significant number, their remoteness affects their ability to be part of the global supply chain, increases import costs - especially for energy - and limits their competitiveness in the tourist industry. Many are increasingly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change - from devastating storms to the threat of sea level rise.
Travel facilitation
Travel facilitation of tourist travel is closely interlinked with tourism development and can be a tool to foster increased demand and generate economic development, job creation and international understanding.
UNGA Sustainable Tourism Resolutions
The UN Tourism is regularly preparing reports for the General Assembly of the United Nations providing updates on sustainable tourism policies both from UN Tourism member States and States Members of the United Nations, as well as relevant agencies and programmes of the United Nations system.
unwto tourism highlights 2022
Un tourism | bringing the world closer.
Unwto 2021: a year in review, 2021: tourism united, resilient and determined.
2021 has been a year of learning and adapting for tourism. It has proven that only by working together can the sector overcome challenges and embrace opportunities.
Gathering the global tourism community and developing concrete actions, UNWTO has led tourism’s response with the vision of not only restarting, but doing so in a more inclusive, innovative and sustainable way.

January - March
As global tourism faced up to a second year of unprecedented crisis , UNWTO began 2021 by counting the cost so far . At the same time, however, the emergence of vaccines brought hope . The Global Tourism Crisis Committee met to explore what this meant for safe travel and the restart of tourism, while the announcement of the winners of the UNWTO Global Start-up Competition recognized the role culture and creativity will play in tourism’s restart and recovery .

April - June
Collaboration and innovation were the focusat the start of the second quarter. UNWTO partnered with IATA on a new Destination Tracker to give both tourists and destinations clear, impartial and trusted advice. And a new Start-up Competition was launched to find the best ideas for accelerating rural development through tourism. In May, the launch of the Best Tourism Villages by UNWTO generated significant interest from Members in every global region.

July - September
As destinations in Europe welcomed tourists back for the peak summer season, UNWTO highlighted the role of digital solutions for the safe restart of the sector. But UNWTO also looked ahead, to a more sustainable future , working with key partners to reduce plastic waste and consumption across every part of the sector. Together, we celebrated World Tourism Day around the theme of Tourism for Inclusive Growth, a message of solidarity and determination that was echoed on a global scale.

October - December
The final quarter of 2021 began with cautious optimism as UNWTO’s Barometer showed signs of improvement in tourist arrival numbers during the summer season in the northern hemisphere. A new partnership with Netflix will bring the message of tourism as a driver of opportunity to a massive global audience, while in November, UNWTO was tourism’s voice at COP26 and signatories to the landmark Glasgow Declaration keep growing. Finally, against the backdrop of the UNWTO General Assembly , the programme of work for the coming biennium was approved and 77% of Members voted to secure a second mandate for the Secretary-General from 2022-2025.
Growing and Moving Forward
UNWTO brings together political leaders from across the globe to deliver a strong, coordinated response. Governments, destinations, fellow UN agencies and international organizations met at key international events joining efforts to rethink tourism. Institutional coordination has proven crucial to find the solutions that build a smarter, greener and safer tourism.
Leaving Nobody Behind
The pledge to ‘ leave nobody behind ’ means nobody should miss out : Not now as we support the sector in the face of crisis, and not in the future as tourism starts again. Tourism is a proven driver of equality and opportunity. And that’s why we turn words into actions, delivering guidelines and action plans , to ensure everyone can enjoy the opportunities tourism brings.
A Shared Vision
Advancing the transformation of the tourism sector , partnerships are the only way forward. In 2021, UNWTO signed agreements with international organizations and the private sector to step our vision for the future of tourism: innovation , education , sustainability , green investment , rural development.
From business as usual to Covid-19
Looking to the future
- Regional Support Office for Asia and the Pacific (RSOAP)
- Member States in Asia and the Pacific
- SUSTAINABLE TOURISM OBSERVATORIES (INSTO)

World Tourism Barometer: September 2022
UNWTO updates World Tourism Barometer and reports international tourism back to 60% of pre-pandemic levels from January to July 2022

Below are excerpts from the September 2022 release of the UNWTO Tourism Barometer :
- The steady recovery reflects strong pent-up demand for international travel, especially in the months of June and July which are part of the Northern Hemisphere summer season. The easing or lifting of travel restrictions in an increasing number of countries also contributed to boost results.
- International tourist arrivals almost tripled (+172%) in January-July 2022 compared to the same period of 2021. Numbers climbed from -64% in January 2022 (versus 2019) to -28% in July, the strongest month since the start of the pandemic.
- Asia and the Pacific (+165%) saw arrivals more than double in the first seven months of 2022, though they remained 86% below 2019 levels.
- The ongoing recovery can also be seen in outbound tourism spending from major source markets. Expenditure from France was at -12% in January-July 2022 compared to 2019 while spending from Germany stood at -14%. International tourism spending remained at -10% in Belgium, -23% in Italy and -26% in the United States.
- The uncertain economic environment seems to have reversed prospects for a return to pre-pandemic levels in the near term. 61% of UNWTO Panel of Experts now see a potential return of international arrivals to 2019 levels in 2024 or later while those indicating a return to pre-pandemic levels in 2023 has diminished (27%) compared to the May survey (48%).

Know more about the global tourism sector performance from January to July 2022 by checking the UNWTO World Tourism Barometer Volume 20, Issue 5 .
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Regional Support Office in Asia and the Pacific (RSOAP)
Rsoap a to z.
- Sustainable Tourism Observatories(INSTO)
UNWTO A to Z
- About UNWTO
- Affiliate Members
- Member States
- Tourism in the 2030 Agenda
- World Tourism Day
- Technical Cooperation
- ASIA AND THE PACIFIC
- MIDDLE EAST
- RESOURCES/SERVICES
- Sustainable Development of Tourism
- Ethics, Culture and Social Responsibility
- Market Intelligence
- Tourism Data Dashboard
- Publications
- UNWTO Academy
Partners links

© UNWTO Regional Support Office for Asia and the Pacific (RSOAP)
- Course Catalog

TOURISM TRENDS 2022
11 Aug TOURISM TRENDS 2022
The situation for tourism remains rather unusual as a result of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
The crisis has marked a significant change for everyone, and above all for tourism, one of sectors hit hardest by the virus. 2020 was the year in which international tourism came to a near-complete standstill, and the only alternatives were domestic and local tourism.
2021 has seen some improvements, but only in a very subtle way as restrictions are still in place and many countries keep their borders fully or partially closed.
It is difficult to make an estimate for 2022 as it is not known how the pandemic will evolve. However, it is possible to talk about the new tourism trends that are likely to emerge over the coming year: – International travel with restrictions still maintained by both destinations and airlines in order to offer 100% security to the consumer.
– Reinforcement of COVID-19 testing; two years after the pandemic, COVID testing will still be in place as a preventive measure. – Conscious travel will be advocated. Travel to more distant destinations, but with prolonged durations of stay, as consumers look to enjoy as much of each place they visit as possible. – Green travel. Climate change is a problem that is present and growing. Consumers now are much more responsible and aware of the reality they live in on daily basis.
– A new trend is the “ed-ventures”. It is about combining education and holidays for the youngest members of the family. While adults may need to telework or attend meetings, their children can be doing workshops and learning in a playful way.
- Client log in
Metallurgicheskii Zavod Electrostal AO (Russia)
In 1993 "Elektrostal" was transformed into an open joint stock company. The factory occupies a leading position among the manufacturers of high quality steel. The plant is a producer of high-temperature nickel alloys in a wide variety. It has a unique set of metallurgical equipment: open induction and arc furnaces, furnace steel processing unit, vacuum induction, vacuum- arc furnaces and others. The factory has implemented and certified quality management system ISO 9000, received international certificates for all products. Elektrostal today is a major supplier in Russia starting blanks for the production of blades, discs and rolls for gas turbine engines. Among them are companies in the aerospace industry, defense plants, and energy complex, automotive, mechanical engineering and instrument-making plants.
Headquarters Ulitsa Zheleznodorozhnaya, 1 Elektrostal; Moscow Oblast; Postal Code: 144002
Contact Details: Purchase the Metallurgicheskii Zavod Electrostal AO report to view the information.
Website: http://elsteel.ru
EMIS company profiles are part of a larger information service which combines company, industry and country data and analysis for over 145 emerging markets.
To view more information, Request a demonstration of the EMIS service

Turn Your Curiosity Into Discovery
Latest facts.
11 Facts About National Numeracy Day May 22nd
9 Facts About Workers Memorial Day April 28th
40 facts about elektrostal.
Written by Lanette Mayes
Modified & Updated: 02 Mar 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett

Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to captivate you.
This article will provide you with 40 fascinating facts about Elektrostal, giving you a better understanding of why this city is worth exploring. From its origins as an industrial hub to its modern-day charm, we will delve into the various aspects that make Elektrostal a unique and must-visit destination.
So, join us as we uncover the hidden treasures of Elektrostal and discover what makes this city a true gem in the heart of Russia.
Key Takeaways:
- Elektrostal, known as the “Motor City of Russia,” is a vibrant and growing city with a rich industrial history, offering diverse cultural experiences and a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.
- With its convenient location near Moscow, Elektrostal provides a picturesque landscape, vibrant nightlife, and a range of recreational activities, making it an ideal destination for residents and visitors alike.
Known as the “Motor City of Russia.”
Elektrostal, a city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia, earned the nickname “Motor City” due to its significant involvement in the automotive industry.
Home to the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Elektrostal is renowned for its metallurgical plant, which has been producing high-quality steel and alloys since its establishment in 1916.
Boasts a rich industrial heritage.
Elektrostal has a long history of industrial development, contributing to the growth and progress of the region.
Founded in 1916.
The city of Elektrostal was founded in 1916 as a result of the construction of the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Located approximately 50 kilometers east of Moscow.
Elektrostal is situated in close proximity to the Russian capital, making it easily accessible for both residents and visitors.
Known for its vibrant cultural scene.
Elektrostal is home to several cultural institutions, including museums, theaters, and art galleries that showcase the city’s rich artistic heritage.
A popular destination for nature lovers.
Surrounded by picturesque landscapes and forests, Elektrostal offers ample opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and birdwatching.
Hosts the annual Elektrostal City Day celebrations.
Every year, Elektrostal organizes festive events and activities to celebrate its founding, bringing together residents and visitors in a spirit of unity and joy.
Has a population of approximately 160,000 people.
Elektrostal is home to a diverse and vibrant community of around 160,000 residents, contributing to its dynamic atmosphere.
Boasts excellent education facilities.
The city is known for its well-established educational institutions, providing quality education to students of all ages.
A center for scientific research and innovation.
Elektrostal serves as an important hub for scientific research, particularly in the fields of metallurgy, materials science, and engineering.
Surrounded by picturesque lakes.
The city is blessed with numerous beautiful lakes, offering scenic views and recreational opportunities for locals and visitors alike.
Well-connected transportation system.
Elektrostal benefits from an efficient transportation network, including highways, railways, and public transportation options, ensuring convenient travel within and beyond the city.
Famous for its traditional Russian cuisine.
Food enthusiasts can indulge in authentic Russian dishes at numerous restaurants and cafes scattered throughout Elektrostal.
Home to notable architectural landmarks.
Elektrostal boasts impressive architecture, including the Church of the Transfiguration of the Lord and the Elektrostal Palace of Culture.
Offers a wide range of recreational facilities.
Residents and visitors can enjoy various recreational activities, such as sports complexes, swimming pools, and fitness centers, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Provides a high standard of healthcare.
Elektrostal is equipped with modern medical facilities, ensuring residents have access to quality healthcare services.
Home to the Elektrostal History Museum.
The Elektrostal History Museum showcases the city’s fascinating past through exhibitions and displays.
A hub for sports enthusiasts.
Elektrostal is passionate about sports, with numerous stadiums, arenas, and sports clubs offering opportunities for athletes and spectators.
Celebrates diverse cultural festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal hosts a variety of cultural festivals, celebrating different ethnicities, traditions, and art forms.
Electric power played a significant role in its early development.
Elektrostal owes its name and initial growth to the establishment of electric power stations and the utilization of electricity in the industrial sector.
Boasts a thriving economy.
The city’s strong industrial base, coupled with its strategic location near Moscow, has contributed to Elektrostal’s prosperous economic status.
Houses the Elektrostal Drama Theater.
The Elektrostal Drama Theater is a cultural centerpiece, attracting theater enthusiasts from far and wide.
Popular destination for winter sports.
Elektrostal’s proximity to ski resorts and winter sport facilities makes it a favorite destination for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter activities.
Promotes environmental sustainability.
Elektrostal prioritizes environmental protection and sustainability, implementing initiatives to reduce pollution and preserve natural resources.
Home to renowned educational institutions.
Elektrostal is known for its prestigious schools and universities, offering a wide range of academic programs to students.
Committed to cultural preservation.
The city values its cultural heritage and takes active steps to preserve and promote traditional customs, crafts, and arts.
Hosts an annual International Film Festival.
The Elektrostal International Film Festival attracts filmmakers and cinema enthusiasts from around the world, showcasing a diverse range of films.
Encourages entrepreneurship and innovation.
Elektrostal supports aspiring entrepreneurs and fosters a culture of innovation, providing opportunities for startups and business development.
Offers a range of housing options.
Elektrostal provides diverse housing options, including apartments, houses, and residential complexes, catering to different lifestyles and budgets.
Home to notable sports teams.
Elektrostal is proud of its sports legacy, with several successful sports teams competing at regional and national levels.
Boasts a vibrant nightlife scene.
Residents and visitors can enjoy a lively nightlife in Elektrostal, with numerous bars, clubs, and entertainment venues.
Promotes cultural exchange and international relations.
Elektrostal actively engages in international partnerships, cultural exchanges, and diplomatic collaborations to foster global connections.
Surrounded by beautiful nature reserves.
Nearby nature reserves, such as the Barybino Forest and Luchinskoye Lake, offer opportunities for nature enthusiasts to explore and appreciate the region’s biodiversity.
Commemorates historical events.
The city pays tribute to significant historical events through memorials, monuments, and exhibitions, ensuring the preservation of collective memory.
Promotes sports and youth development.
Elektrostal invests in sports infrastructure and programs to encourage youth participation, health, and physical fitness.
Hosts annual cultural and artistic festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal celebrates its cultural diversity through festivals dedicated to music, dance, art, and theater.
Provides a picturesque landscape for photography enthusiasts.
The city’s scenic beauty, architectural landmarks, and natural surroundings make it a paradise for photographers.
Connects to Moscow via a direct train line.
The convenient train connection between Elektrostal and Moscow makes commuting between the two cities effortless.
A city with a bright future.
Elektrostal continues to grow and develop, aiming to become a model city in terms of infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life for its residents.
In conclusion, Elektrostal is a fascinating city with a rich history and a vibrant present. From its origins as a center of steel production to its modern-day status as a hub for education and industry, Elektrostal has plenty to offer both residents and visitors. With its beautiful parks, cultural attractions, and proximity to Moscow, there is no shortage of things to see and do in this dynamic city. Whether you’re interested in exploring its historical landmarks, enjoying outdoor activities, or immersing yourself in the local culture, Elektrostal has something for everyone. So, next time you find yourself in the Moscow region, don’t miss the opportunity to discover the hidden gems of Elektrostal.
Q: What is the population of Elektrostal?
A: As of the latest data, the population of Elektrostal is approximately XXXX.
Q: How far is Elektrostal from Moscow?
A: Elektrostal is located approximately XX kilometers away from Moscow.
Q: Are there any famous landmarks in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to several notable landmarks, including XXXX and XXXX.
Q: What industries are prominent in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal is known for its steel production industry and is also a center for engineering and manufacturing.
Q: Are there any universities or educational institutions in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to XXXX University and several other educational institutions.
Q: What are some popular outdoor activities in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal offers several outdoor activities, such as hiking, cycling, and picnicking in its beautiful parks.
Q: Is Elektrostal well-connected in terms of transportation?
A: Yes, Elektrostal has good transportation links, including trains and buses, making it easily accessible from nearby cities.
Q: Are there any annual events or festivals in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal hosts various events and festivals throughout the year, including XXXX and XXXX.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:

- Victor Mukhin

Victor M. Mukhin was born in 1946 in the town of Orsk, Russia. In 1970 he graduated the Technological Institute in Leningrad. Victor M. Mukhin was directed to work to the scientific-industrial organization "Neorganika" (Elektrostal, Moscow region) where he is working during 47 years, at present as the head of the laboratory of carbon sorbents. Victor M. Mukhin defended a Ph. D. thesis and a doctoral thesis at the Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology of Russia (in 1979 and 1997 accordingly). Professor of Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology of Russia. Scientific interests: production, investigation and application of active carbons, technological and ecological carbon-adsorptive processes, environmental protection, production of ecologically clean food.
Title : Active carbons as nanoporous materials for solving of environmental problems
Quick links.
- Conference Brochure
- Tentative Program

2022 has been the year to rethink tourism. Countries around the world turned UNWTO's vision for a greener, smarter and more inclusive sector into real action. 2020 showed the relevance of tourism for sustainable development. 2021 laid the foundations for the transformation of the sector. In 2022, we made it happen. 2022 began on a positive note.
According to the latest UNWTO World Tourism Barometer, international tourism saw a strong rebound in the first five months of 2022, with almost 250 million international arrivals recorded. This compares to 77 million arrivals from January to May 2021 and means that the sector has recovered almost half (46%) of pre-pandemic 2019 levels. UN ...
International Tourism Highlights, 2023 Edition - The Impact of COVID-19 on Tourism (2020-2022) ISBN (printed version): 978-92-844-2497-9 ISBN (electronic version): 978-92-844-2498-6 DOI: 10.18111/9789284424986 Published by the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), Madrid, Spain First published: September 2023 Revised and updated: October 2023
Find out the latest updates from the UNWTO on tourism trends, challenges and opportunities in 2022 and beyond. Learn about the UNWTO's activities, projects and partnerships in various regions and topics, such as sustainable tourism, gastronomy, investment and education.
International Tourism and COVID-19. Export revenues from international tourism dropped 62% in 2020 and 59% in 2021, versus 2019 (real terms) and then rebounded in 2022, remaining 34% below pre-pandemic levels. The total loss in export revenues from tourism amounts to USD 2.6 trillion for that three-year period. Go to Dashboard.
According to the latest UNWTO World Tourism Barometer, international tourist arrivals almost tripled in January to July 2022 (+172%) compared to the same period of 2021. This means t he sector recovered almost 60% of pre-pandemic levels. The steady recovery reflects strong pent-up demand for international travel as well as the easing or lifting ...
The time is now to seize this opportunity to rethink how we do tourism. The official World Tourism Day celebration will be held in Bali, Indonesia, on 27 September, highlighting the shift towards tourism being recognized as a crucial pillar of development. Wonderful Indonesia - Witness the 42nd World Tourism Day 2022 in Bali, Indonesia!
In terms of tourist numbers, the year 2022 is expected to close with over 900 million international arrivals, despite growing challenges pointing to a softening of the recovery pace. International tourist arrivals: 2020, 2021 and Scenarios for 2022 (monthly change over 2019,%) Source UNWTO World Tourism Barometer: November 2022 Press Release.
January - March. As global tourism faced up to a second year of unprecedented crisis, UNWTO began 2021 by counting the cost so far.At the same time, however, the emergence of vaccines brought hope.The Global Tourism Crisis Committee met to explore what this meant for safe travel and the restart of tourism, while the announcement of the winners of the UNWTO Global Start-up Competition ...
Below are excerpts from the latest World Tourism Barometer May 2022 issue: According to the latest UNWTO World Tourism Barometer, international tourism saw a 182% year-on-year increase in January-March 2022, with destinations worldwide welcoming an estimated 117 million international arrivals compared to 41 million in Q1 2021.
The UNWTO Elibrary is an online service from the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) with a broad coverage of tourism and related subject areas. ... International Tourism Highlights, 2023 Edition - The Impact of COVID-19 on Tourism (2020-2022) Revised and updated, October 2023. Released: December 2023.
The 7th UNWTO World Forum on Gastronomy Tourism will be held from Monday, December 12 to Thursday, December 15, 2022 (4 days).
The economic contribution of tourism (tourism direct gross domestic product) is estimated at US$1.9 trillion in 2021, above the US$1.6 trillion in 2020, but still well below the pre-pandemic value of US$ 3.5 trillion. The latest UNWTO Panel of Experts survey indicates that 61% of tourism professionals expect better performance in 2022 than in 2021.
Below are relevant points to the July 2022 World Tourism Barometer: Nearly 250 million international trips were recorded worldwide in the first five months of the year, more than three times the number of arrivals recorded in the same period of 2021 (77 million). Robust performance is also reflected in hotel occupancy rates.
2022-10-28. Below are excerpts from the September 2022 release of the UNWTO Tourism Barometer: The steady recovery reflects strong pent-up demand for international travel, especially in the months of June and July which are part of the Northern Hemisphere summer season. The easing or lifting of travel restrictions in an increasing number of ...
International tourism continues to outpace the global economy. 2. Driven by a relatively strong global economy, a growing middle class in emerging economies, technological advances, new business models, affordable travel costs and visa facilitation, international tourist arrivals grew 5% in 2018 to reach the 1.4 billion mark.
UNWTO Tourism Academy | TOURISM TRENDS 2022. The situation for tourism remains rather unusual as a result of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The crisis has marked a significant change for everyone, and above all for tourism, one of sectors hit hardest by the virus. 2020 was the year in which international tourism came to a near-complete ...
International Tourism Highlights, 2023 Edition - The Impact of COVID-19 on Tourism (2020-2022) Revised and updated, October 2023 Published: December 2023 Pages: 32
International Tourism Highlights, 2020 Edition. Published: January 2021 Pages: 23. eISBN: 978-92-844-2245-6 | ISBN: 978-92-844-2244-9. Abstract: 2019 was another year of strong growth, though international arrivals grew below the exceptional rates seen in 2017 (+7%) and 2018 (+6%). Demand was somewhat weaker for travel to advanced economy ...
Main Activities: Iron and Steel Mills and Ferroalloy Manufacturing | Nonferrous Metal (except Copper and Aluminum) Rolling, Drawing, and Extruding. Full name: Metallurgicheskii Zavod Electrostal AO Profile Updated: February 22, 2024. Buy our report for this company USD 29.95 Most recent financial data: 2022 Available in: English & Russian ...
40 Facts About Elektrostal. Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to ...
Catalysis Conference is a networking event covering all topics in catalysis, chemistry, chemical engineering and technology during October 19-21, 2017 in Las Vegas, USA. Well noted as well attended meeting among all other annual catalysis conferences 2018, chemical engineering conferences 2018 and chemistry webinars.
In the city of Elektrostal in Russia, a drone attack occurred. It's reported that no one was injured as a result of the incident. Additional details, including the particulars of the attack, potential motives or responsible parties, have not been provided. However, the fact that a drone was used as a means of attack underscores
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

U.S. Department of Commerce
- Fact Sheets
Was this page helpful?
Fact sheet: 2022 national travel and tourism strategy, office of public affairs.
The 2022 National Travel and Tourism Strategy was released on June 6, 2022, by U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina M. Raimondo on behalf of the Tourism Policy Council (TPC). The new strategy focuses the full efforts of the federal government to promote the United States as a premier destination grounded in the breadth and diversity of our communities, and to foster a sector that drives economic growth, creates good jobs, and bolsters conservation and sustainability. Drawing on engagement and capabilities from across the federal government, the strategy aims to support broad-based economic growth in travel and tourism across the United States, its territories, and the District of Columbia.
The federal government will work to implement the strategy under the leadership of the TPC and in partnership with the private sector, aiming toward an ambitious five-year goal of increasing American jobs by attracting and welcoming 90 million international visitors, who we estimate will spend $279 billion, annually by 2027.
The new National Travel and Tourism Strategy supports growth and competitiveness for an industry that, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, generated $1.9 trillion in economic output and supported 9.5 million American jobs. Also, in 2019, nearly 80 million international travelers visited the United States and contributed nearly $240 billion to the U.S. economy, making the United States the global leader in revenue from international travel and tourism. As the top services export for the United States that year, travel and tourism generated a $53.4 billion trade surplus and supported 1 million jobs in the United States.
The strategy follows a four-point approach:
- Promoting the United States as a Travel Destination Goal : Leverage existing programs and assets to promote the United States to international visitors and broaden marketing efforts to encourage visitation to underserved communities.
- Facilitating Travel to and Within the United States Goal : Reduce barriers to trade in travel services and make it safer and more efficient for visitors to enter and travel within the United States.
- Ensuring Diverse, Inclusive, and Accessible Tourism Experiences Goal : Extend the benefits of travel and tourism by supporting the development of diverse tourism products, focusing on under-served communities and populations. Address the financial and workplace needs of travel and tourism businesses, supporting destination communities as they grow their tourism economies. Deliver world-class experiences and customer service at federal lands and waters that showcase the nation’s assets while protecting them for future generations.
- Fostering Resilient and Sustainable Travel and Tourism Goal : Reduce travel and tourism’s contributions to climate change and build a travel and tourism sector that is resilient to natural disasters, public health threats, and the impacts of climate change. Build a sustainable sector that integrates protecting natural resources, supporting the tourism economy, and ensuring equitable development.
Travel and Tourism Fast Facts
- The travel and tourism industry supported 9.5 million American jobs through $1.9 trillion of economic activity in 2019. In fact, 1 in every 20 jobs in the United States was either directly or indirectly supported by travel and tourism. These jobs can be found in industries like lodging, food services, arts, entertainment, recreation, transportation, and education.
- Travel and tourism was the top services export for the United States in 2019, generating a $53.4 billion trade surplus.
- The travel and tourism industry was one of the U.S. business sectors hardest hit by the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent health and travel restrictions, with travel exports decreasing nearly 65% from 2019 to 2020.
- The decline in travel and tourism contributed heavily to unemployment; leisure and hospitality lost 8.2 million jobs between February and April 2020 alone, accounting for 37% of the decline in overall nonfarm employment during that time.
- By 2021, the rollout of vaccines and lifting of international and domestic restrictions allowed travel and tourism to begin its recovery. International arrivals to the United States grew to 22.1 million in 2021, up from 19.2 million in 2020. Spending by international visitors also grew, reaching $81.0 billion, or 34 percent of 2019’s total.
More about the Tourism Policy Council and the 2022 National Travel and Tourism Strategy
Created by Congress and chaired by Secretary Raimondo, the Tourism Policy Council (TPC) is the interagency council charged with coordinating national policies and programs relating to travel and tourism. At the direction of Secretary Raimondo, the TPC created a new five-year strategy to focus U.S. government efforts in support of the travel and tourism sector which has been deeply and disproportionately affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read the full strategy here
The end of development tourism: A new model for development cooperation
Subscribe to the sustainable development bulletin, patrick fine patrick fine nonresident senior fellow - global economy and development , center for sustainable development.
November 22, 2021
The time has come for international agencies, donors, and NGOs to adapt their business cultures and operating models to a new era of international development cooperation. The converging transformational forces of the COVID-19 pandemic and the movement to “decolonize development” have created new options for development partnerships to move away from the traditional use of expatriates in management and technical roles.
The first transformational force was the COVID-19 pandemic. By the middle of March 2020, international travel had shut down and organizations were scrambling to shift to remote work. While the capacity for virtual collaboration and remote work via video conferencing had been available for at least 10 years and there was some movement in this direction, the forced shift to a remote posture shattered cultural and perceived operational barriers to working remotely overnight. By May 2020, surprisingly few programs that had relied on external oversight and on-the-ground technical assistance had closed, and development organizations of all types (donors, multilateral development banks, NGOs) were expressing pride in how quickly they had adapted to collaborating and providing management and technical services virtually.
The converging transformational forces of the COVID-19 pandemic and the movement to “decolonize development” have created new options for development partnerships to move away from the traditional use of expatriates in management and technical roles.
The second transformational force that emerged in 2020 was the rise of a powerful movement around the need to “decolonize development.” While the decolonization critique is not new and echoes the 1970s outcry against “neo-colonialism,” the current manifestation has fired the passions of a new generation of development professionals caught up in the racial and social reckonings shaking the U.S. and Western Europe. In the context of international development, this translates into demands to address the power imbalances between donor nation and developing country organizations and professionals. In practical terms, it means greater transparency and local participation in how development assistance is programmed, greater local control over spending decisions, more use of local institutions and expertise, and achieving pay equity among international and national employees.
These two convergent forces have fundamentally changed the operating environment for international development organizations and cleared the path for more sustainable and cost-effective approaches to collaboration between international and local organizations, including the home office and country operations of large international organizations.
A new model for development cooperation
New approaches to project oversight and technical assistance are already embedding themselves in development organizations’ operations, but it would be useful for the development community to articulate these emerging practices as a preferred operating model guided by two simple principles:
First, whenever possible resident management and technical staff should be hired locally. The advantages here are well known: Local professionals possess the language and cultural skills and community networks essential to effective development work. Moreover, with the notable exception of most conflict-affected states, the excuse that local professionals are unavailable is no longer valid. A common and legitimate critique of international organizations is that the higher salaries and benefits they offer to expatriates are inherently inequitable, reinforce old colonial power imbalances, and can distort national labor markets. This first principle resolves these problems by eliminating differential treatment and employing all resident staff on a single set of terms and conditions of service that conform to the local labor market.
The second principle is that when external management and technical expertise are required, they should be provided virtually to the greatest extent possible. This recognizes that international collaboration is critical to addressing today’s development challenges, that complex endeavors frequently require highly specialized experience and skills, and that there is value in being part of larger international professional networks and initiatives.
Here it is worth digressing to address a weakness in the current decolonization narrative: the implication that donors need only provide the financing and leave recipient countries to handle the rest. This ignores the value of international collaboration in promoting innovation and technology transfer and in building capacity. All countries—rich and poor—are better off when they have economic, scientific, social, and institutional linkages to their neighbors and the larger international community. Going it alone is neither politically feasible nor practically desirable.
That said, the old argument that international organizations require expatriate on-the-ground presence to achieve results no longer holds water, thanks to the experience of working virtually over the last two years. However, embracing new practices does require changing organizational culture, as the allure of international travel and in-person collaboration are major motivators for many development professionals. While the approach proposed here does not eliminate all travel—certainly there is value in some in-person interaction (for example, to establish relationships, understand context, and conduct some types of research), the amount of international travel will greatly diminish. On the plus side, this will help international organizations reduce their carbon footprint, but as the new model takes hold, expect many U.S. and European development professionals to retire or change careers and many developing country counterparts to lament the reduction in opportunities to travel abroad.
So, what does this new model look like in practice?
It’s simple. All in-country positions are treated as local national positions with compensation and conditions of service geared to the local labor market. This doesn’t prevent an expatriate from competing for a position, but it removes the financial incentives to use expatriates.
Concurrently, short-term expatriate assignments, with rare exceptions, are virtual. This is far more economical, more environmentally friendly, and tilts power relations in favor of finding local employees while avoiding distortions to local labor markets.
Forty-five years ago, Ross Coggins’ satirical poem, “ The Development Set ,” summed up the contradictions and weaknesses inherent in the classic international development model. In 2020, the forced shift to remote work and a renewed and urgent concern about inequalities embedded in the development community’s traditional operating arrangements have created the conditions to replace “development tourism” with a new approach to development cooperation. Now, it is incumbent upon donors, multilateral institutions, and NGOs to take action.
Related Content
George Ingram
November 16, 2021
Justin Fugle
September 29, 2021
Global Economy and Development
Center for Sustainable Development
Tedros Adhanom-Ghebreyesus
May 9, 2024
Robin Brooks
Emily Gustafsson-Wright, Elyse Painter
May 8, 2024

About Tennessee Department of Tourist Development
Tennessee tourism generated $28.9 billion in domestic and international travel spending in 2022, according to recently released economic impact data from U.S. Travel Association and Tourism Economics. It also marks the largest visitor spending nationally in Tennessee’s history. Travelers in Tennessee spend an estimated $79 million per day. Travel in Tennessee generated $2.9 billion in state and local tax revenue. Travel and tourism is also the fourth largest employer in the state.
The department also operates 16 Welcome Centers along the interstate highway system in Tennessee. Each of the Welcome Centers is equipped with a toll-free telephone system allowing travelers to make hotel, motel, and campground reservations anywhere in Tennessee, as well as free Wi-Fi.
The great news as we plan for the next four years is that tourism is thriving in Tennessee. As world-class investors in lodging, attractions and restaurants see the business opportunity in Tennessee – so do we. - Commissioner Mark Ezell

Mission To increase the state’s economic viability and support the growth of tourism in all 95 counties by inspiring travel, developing programs and enhancing industry partnerships which drive job creation, tax revenue and new investments, thereby enriching the quality of life for every Tennessean.
Vision To be the global music destination of choice; a diverse American experience offering family fun, outdoor adventure, live entertainment, sporting events, festivals and a showcase of craftsmanship at the crossroads of rich history, local cuisine and renowned scenic beauty.
Order bulk vacation guides, transportation maps, Discover Tennessee Trails & Byways brochures and more.

Get the latest news and updates by following our TDTD Industry page on Facebook.

- Palm Beach County Visitor’s Guide
- Sports Facility Guide
- Art & Culture Magazine
- Focus on Film Newsletter
- Cultural Council for Palm Beach County
- Palm Beach County Film & Television
- Palm Beach County Sports Commission
- The Palm Beaches
- Discover The Palm Beaches
- Cultural Council For Palm Beach County
- Palm Beach County Convention Center
- Palm Beach County Environmental Resource Management
- Palm Beach International Airport
- Palm Beach County Film & Television Commission
- Florida State Statutes
- County Ordinances
- Bed Tax Collections
- Board of Directors
- Board Agendas
- Convention Center Study
- 2023 Equestrian Economic Impact
- Economic Impact of Reef Sports
- Economic Valuation of Lake Worth Lagoon
- Ecosystem Services Report
- Florida Economic Fishing Report
- Lake Worth Lagoon Management Plan
- 2023 MLB Spring Training Baseball Annual Benefits Report
- Annual Report
- Palm Beaches TV

- Protect Tourism Taxes to Generate a Maximum Return
- Determine the Success of each tourism program
- Provide leadership in marketing and development of local amenities for future economic benefit
- Advisory body to the Board of County Commissioners
- Ensure compliance with State & Local statutes

| Google Map |
Phone: 561-233-3130 Executive Director: Emanuel Perry
The Tourist Development Council (TDC) has oversight responsibility for the contracted marketing agencies which include Discover The Palm Beaches, the Cultural Council of Palm Beach County, the Palm Beach County Film & Television Commission and the Palm Beach County Sports Commission along with the Palm Beach County Convention Center operations. The development of the TDC Strategic Plan with the approval of the Board of County Commissioners provides a framework for use by all agencies in creating the marketing and promotion programs of tourism in Palm Beach County. This is accomplished by empowering collaborative partnerships of these agencies, advocating appropriate destination-defining developments and ensuring the continued steady growth of visitors to The Palm Beaches.
Tourism is among Palm Beach County's major industries generating an annual economic impact of $7.0 plus billion in the local economy, producing $45 million plus in bed-tax revenue, on lodging sales exceeding $700 million annually and supporting 60,000 plus tourism related jobs. The Tourist Development Tax and the current use is critically important to the management of Tourism Development in the Palm Beaches. The Tax which began in the 1980's to promote the tourism and the cultural economy by State Statute has served the State and County well.
We continue to grow the Palm Beach County economy through the managed investments in marketing, promotion, investments in beaches, a convention center and two Spring training baseball stadiums.
Annual Report
Commissioner Maria Sachs Chair TDC Mr. Jim Bronstien Vice Chair Mr. Daniel Hostettler Mr. Jim Mostad Commissioner Christina L. Romelus Mr. Donald P. Dufresne, Esq. Ms. Davicka Nicole Thompson Commissioner Kelly Shoaf County Administrator Verdenia C. Baker Deputy County Attorney Denise Coffman
Agency links.
- Cultural Council of Palm Beach County
- Discover the Palm Beaches
- Palm Beach County Film and Television Commission
Site Directory
- Things To Do
- Online Services
- Departments
Useful Links
- PBC Business Opportunities
- Volunteer Opportunities
- Publications
- Stay Connected!
- Web Site Disclaimer
- District Locator
- BCC Meetings

China’s tourism transportation carbon emissions: dynamic mechanisms and multi-regulatory strategies simulation
- Published: 10 May 2024

Cite this article

- Yun Tong 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Hao Li ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7572-9937 1 , 2 &
- Li Pang 1 , 2
Forecasting carbon emissions is regarded as the scientific basis for establishing milestone reduction targets and assessing the effectiveness of reduction strategies. This study aims to predict the tourism transportation carbon emissions (TTCE) in China until 2035 and to propose strategies for achieving the carbon peak target. Under the framework of environmental performance measurement, a system dynamics model of TTCE was constructed, filling a research gap. On this basis, we set up four single regulation scenarios and three combined regulation scenarios, and conducted systematic simulations of emission reduction effects. The results indicate that the “Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality” targets provide favorable external conditions for TTCE reduction. However, China’s tourism transportation sector still cannot meet its carbon peak target on schedule without intervention, and its carbon emissions will remain steadily increasing until at least 2035, reaching 464.83 Mt. Accelerating the optimization of the national energy structure and the promotion of new energy vehicles have brought benefits for TTCE reduction, but their effects are limited. Curbing aviation carbon emissions is the key to peak TTCE, which highlights that the government should encourage tourists to choose high-speed rail (trains) for medium-distance travel instead of aviation.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ahmad, S., Tahar, R. M., Muhammad-Sukki, F., Munir, A. B., & Rahim, R. A. (2016). Application of system dynamics approach in electricity sector modelling: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 56 , 29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.11.034
Article Google Scholar
Albalate, D., & Bel, G. (2012). High-speed rail: Lessons for policy makers from experiences abroad. Public Administration Review, 72 (3), 336–349. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6210.2011.02492.x
Becken, S., & Patterson, M. (2006). Measuring national carbon dioxide emissions from tourism as a key step towards achieving sustainable tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 14 (4), 323–338. https://doi.org/10.2167/jost547.0
CAAC–NDRC–MOT. (2021). The “14th Five-Year Plan” for civil aviation development . Retrieved from http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2022-01/07/5667003/files/d12ea75169374a15a742116f7082df85.pdf
Chang, K., Du, Z., Chen, G., Zhang, Y., & Sui, L. (2021). Panel estimation for the impact factors on carbon dioxide emissions: A new regional classification perspective in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 279 , 123637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123637
Article CAS Google Scholar
Chen, B., Chen, F., Ciais, P., Zhang, H., Lü, H., Wang, T., & Peters, W. (2022). Challenges to achieve carbon neutrality of China by 2060: Status and perspectives. Science Bulletin, 67 (20), 2030–2035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2022.08.025
China State Council. (2012). Development plan of energy conservation and new energy vehicle industry (2012–2020) . Retrieved from http://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2012-07/09/content_2179032.htm
China State Council. (2020). Development plan of new energy vehicle industry (2021–2035) . Retrieved from http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2020-11/02/content_5556716.htm
China State Council. (2021b). The “14th Five-Year Plan” for the development of modern integrated transport system . Retrieved from http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2022-01/18/content_5669049.htm
China State Council. (2021a). Outline of the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021–2025) for National Economic and Social Development and Vision 2035 of the People’s Republic of China . Retrieved from http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-03/13/content_5592681.htm
China State Council. (2021c). The action plan for carbon peaking by 2030 . Retrieved from http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-10/26/content_5644984.htm
China State Council. (2022). A circular on further optimizing and implementing the prevention and control measures of the novel coronavirus outbreak . Retrieved from http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-12/07/content_5730443.htm
Dietz, T., Shwom, R. L., & Whitley, C. T. (2020). Climate change and society. Annual Review of Sociology, 46 (1), 135–158. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-soc-121919-054614
Ding, H., Wang, J., Liao, W., Liang, T., & Dai, H. (2021). Site selection of self-driving and recreational vehicle camps in China: An investigation using analytic hierarchy process and entropy. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (english Edition), 8 (5), 762–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtte.2021.09.003
Dubois, G., & Ceron, J. P. (2006). Tourism/leisure greenhouse gas emissions forecasts for 2050: Factors for change in France. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 14 (2), 172–191. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669580608669051
Fang, K., Tang, Y., Zhang, Q., Song, J., Wen, Q., Sun, H., & Xu, A. (2019). Will China peak its energy-related carbon emissions by 2030? Lessons from 30 Chinese provinces. Applied Energy, 255 , 113852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113852
Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change, 12 (4), 283–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-3780(02)00044-4
Gössling, S. (2013). National emissions from tourism: An overlooked policy challenge? Energy Policy, 59 , 433–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.03.058
Gössling, S., & Michael Hall, C. (2008). Swedish tourism and climate change mitigation: An emerging conflict? Scandinavian Journal of Hospitality and Tourism, 8 (2), 141–158. https://doi.org/10.1080/15022250802079882
Gössling, S., Peeters, P., Ceron, J.-P., Dubois, G., Patterson, T., & Richardson, R. B. (2005). The eco-efficiency of tourism. Ecological Economics, 54 (4), 417–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2004.10.006
Gössling, S., Scott, D., & Hall, C. M. (2015). Inter-market variability in CO 2 emission-intensities in tourism: Implications for destination marketing and carbon management. Tourism Management, 46 , 203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2014.06.021
Gray, R. (2010). Is accounting for sustainability actually accounting for sustainability… and how would we know? An exploration of narratives of organisations and the planet. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 35 (1), 47–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aos.2009.04.006
Hafezi, M., Stewart, R. A., Sahin, O., Giffin, A. L., & Mackey, B. (2021). Evaluating coral reef ecosystem services outcomes from climate change adaptation strategies using integrative system dynamics. Journal of Environmental Management, 285 , 112082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112082
Howitt, O. J., Revol, V. G., Smith, I. J., & Rodger, C. J. (2010). Carbon emissions from international cruise ship passengers’ travel to and from New Zealand. Energy Policy, 38 (5), 2552–2560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2009.12.050
Hu, W., Dong, J., Hwang, B., Ren, R., Chen, Y., & Chen, Z. (2020). Using system dynamics to analyze the development of urban freight transportation system based on rail transit: A case study of Beijing. Sustainable Cities and Society, 53 , 101923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101923
Huang, Z., Cao, F., Jin, C., Yu, Z., & Huang, R. (2017). Carbon emission flow from self-driving tours and its spatial relationship with scenic spots—A traffic-related big data method. Journal of Cleaner Production, 142 , 946–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.129
IPCC. (2014). Climate change 2014: Synthesis report. Contribution of working groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change.
Jin, C., Cheng, J., Xu, J., & Huang, Z. (2018). Self-driving tourism induced carbon emission flows and its determinants in well-developed regions: A case study of Jiangsu Province, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 186 , 191–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.128
Jones, C. (2013). Scenarios for greenhouse gas emissions reduction from tourism: An extended tourism satellite account approach in a regional setting. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 21 (3), 458–472. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2012.708039
Kelly, C., Onat, N. C., & Tatari, O. (2019). Water and carbon footprint reduction potential of renewable energy in the United States: A policy analysis using system dynamics. Journal of Cleaner Production, 228 , 910–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.268
Khadaroo, J., & Seetanah, B. (2008). The role of transport infrastructure in international tourism development: A gravity model approach. Tourism Management, 29 (5), 831–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2007.09.005
Kim, E. E. K., Seo, K., & Choi, Y. (2022). Compensatory travel post COVID-19: Cognitive and emotional effects of risk perception. Journal of Travel Research, 61 (8), 1895–1909. https://doi.org/10.1177/00472875211048930
Koçak, E., Ulucak, R., & Ulucak, Z. Ş. (2020). The impact of tourism developments on CO 2 emissions: An advanced panel data estimation. Tourism Management Perspectives, 33 , 100611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2019.100611
Konan, D. E., & Chan, H. L. (2010). Greenhouse gas emissions in Hawaiʻi: Household and visitor expenditure analysis. Energy Economics, 32 (1), 210–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2009.06.015
Kumar, S., & Madlener, R. (2016). CO 2 emission reduction potential assessment using renewable energy in India. Energy, 97 , 273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.12.131
Kuo, N. W., & Chen, P. H. (2009). Quantifying energy use, carbon dioxide emission, and other environmental loads from island tourism based on a life cycle assessment approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 17 (15), 1324–1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2009.04.012
Lenzen, M., Sun, Y. Y., Faturay, F., Ting, Y. P., Geschke, A., & Malik, A. (2018). The carbon footprint of global tourism. Nature Climate Change, 8 (6), 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-018-0141-x
Li, D., Huang, G., Zhu, S., Chen, L., & Wang, J. (2021). How to peak carbon emissions of provincial construction industry? Scenario analysis of Jiangsu Province. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 144 , 110953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.110953
Li, G., Pu, K., & Long, M. (2023). High-speed rail connectivity, space-time distance compression, and trans-regional tourism flows: Evidence from China’s inbound tourism. Journal of Transport Geography, 109 , 103592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2023.103592
Li, L., Ye, F., Li, Y., & Tan, K. H. (2018b). A bi-objective programming model for carbon emission quota allocation: Evidence from the Pearl River Delta region. Journal of Cleaner Production, 205 , 163–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.069
Li, S., Cheng, Z., Tong, Y., & He, B. (2022). The interaction mechanism of tourism carbon emission efficiency and tourism economy high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Energies, 15 (19), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15196975
Li, W., An, C., & Lu, C. (2018a). The assessment framework of provincial carbon emission driving factors: An empirical analysis of Hebei Province. Science of the Total Environment, 637 , 91–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.419
Li, W., & Gao, S. (2018). Prospective on energy related carbon emissions peak integrating optimized intelligent algorithm with dry process technique application for China’s cement industry. Energy, 165 , 33–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.09.152
Lin, C. S., Liou, F. M., & Huang, C. P. (2011). Grey forecasting model for CO 2 emissions: A Taiwan study. Applied Energy, 88 (11), 3816–3820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.05.013
Lin, T. P. (2010). Carbon dioxide emissions from transport in Taiwan’s national parks. Tourism Management, 31 (2), 285–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2009.03.009
Liu, D., Yang, D., & Huang, A. (2021). LEAP-based greenhouse gases emissions peak and low carbon pathways in China’s Tourist Industry. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18 (3), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031218
Liu, S., Zhang, J., Liu, P., Xu, Y., Xu, L., & Zhang, H. (2023). Discovering spatial patterns of tourist flow with multi-layer transport networks. Tourism Geographies, 25 (1), 113–135. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616688.2020.1850849
Liu, X., Ma, S., Tian, J., Jia, N., & Li, G. (2015). A system dynamics approach to scenario analysis for urban passenger transport energy consumption and CO 2 emissions: A case study of Beijing. Energy Policy, 85 , 253–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.06.007
Liu, X., Ren, T., Ge, J., Liao, S., & Pang, L. (2022b). Heterogeneous and synergistic effects of environmental regulations: Theoretical and empirical research on the collaborative governance of China’s haze pollution. Journal of Cleaner Production, 350 , 131473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131473
Liu, Z., Lan, J., Chien, F., Sadiq, M., & Nawaz, M. A. (2022a). Role of tourism development in environmental degradation: A step towards emission reduction. Journal of Environmental Management, 303 , 114078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114078
Lundberg, K., Balfors, B., & Folkeson, L. (2009). Framework for environmental performance measurement in a Swedish public sector organization. Journal of Cleaner Production, 17 (11), 1017–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2009.01.011
Luo, F., Becken, S., & Zhong, Y. (2018). Changing travel patterns in China and ‘carbon footprint’implications for a domestic tourist destination. Tourism Management, 65 , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2017.09.012
Luo, F., Moyle, B. D., Moyle, C. L. J., Zhong, Y., & Shi, S. (2020). Drivers of carbon emissions in China’s tourism industry. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 28 (5), 747–770. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2019.1705315
Luo, X., Liu, C., & Zhao, H. (2023). Driving factors and emission reduction scenarios analysis of CO 2 emissions in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and surrounding cities based on LMDI and system dynamics. Science of the Total Environment, 870 , 161966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161966
Ma, X., Han, M., Luo, J., Song, Y., Chen, R., & Sun, X. (2021). The empirical decomposition and peak path of China’s tourism carbon emissions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28 (46), 66448–66463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14956-6
Meng, W., Xu, L., Hu, B., Zhou, J., & Wang, Z. (2017). Reprint of: Quantifying direct and indirect carbon dioxide emissions of the Chinese tourism industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 163 , S401–S409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.03.177
Ministry of Transport of China. (2021). Bulletin of Ministry of Transport of China (2011–2021) . Retrieved from https://www.mot.gov.cn/fenxigongbao/
National Bureau of Statistics of China. (2021). China statistical yearbook 2021 . China Statistics Press.
Google Scholar
Peeters, P., & Dubois, G. (2010). Tourism travel under climate change mitigation constraints. Journal of Transport Geography, 18 (3), 447–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2009.09.003
Peeters, P., van Egmond, T., & Visser, N. (2004). European tourism, transport and environment. Final Version . NHTV CSTT.
Perch-Nielsen, S., Sesartic, A., & Stucki, M. (2010). The greenhouse gas intensity of the tourism sector: The case of Switzerland. Environmental Science & Policy, 13 (2), 131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2009.12.002
Pham, H., Sutton, B. G., Brown, P. J., & Brown, D. A. (2020). Moving towards sustainability: A theoretical design of environmental performance measurement systems. Journal of Cleaner Production, 269 , 122273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122273
Pluchinotta, I., Pagano, A., Vilcan, T., Ahilan, S., Kapetas, L., Maskrey, S., Krivtsov, V., Thorne, C., & O’Donnell, E. (2021). A participatory system dynamics model to investigate sustainable urban water management in Ebbsfleet Garden City. Sustainable Cities and Society, 67 , 102709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.102709
Qiao, Q., Zhao, F., Liu, Z., Hao, H., He, X., Przesmitzki, S. V., & Amer, A. A. (2020). Life cycle cost and GHG emission benefits of electric vehicles in China. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 86 , 102418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2020.102418
Sun, Y. Y. (2016). Decomposition of tourism greenhouse gas emissions: Revealing the dynamics between tourism economic growth, technological efficiency, and carbon emissions. Tourism Management, 55 , 326–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.02.014
Sun, Y. Y., Lin, P. C., & Higham, J. (2020). Managing tourism emissions through optimizing the tourism demand mix: Concept and analysis. Tourism Management, 81 , 104161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104161
Sun, Z., Ma, Z., Ma, M., Cai, W., Xiang, X., Zhang, S., & Chen, L. (2022). Carbon peak and carbon neutrality in the building sector: A bibliometric review. Buildings, 12 (2), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12020128
Suryani, E., Chou, S.-Y., & Chen, C.-H. (2010). Air passenger demand forecasting and passenger terminal capacity expansion: A system dynamics framework. Expert Systems with Applications, 37 (3), 2324–2339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.07.041
Tang, B., Li, R., Yu, B., An, R., & Wei, Y. M. (2018). How to peak carbon emissions in China’s power sector: A regional perspective. Energy Policy, 120 , 365–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.04.067
Tang, C. C., Zha, J. P., Zhang, J. K., Tao, Y. G., Wang, L. G., Wang, L., & Han, Y. (2021). Dual-carbon goal of China’s tourism industry under high-quality development: Evaluation & prediction, major challenges and realization path. Journal of Chinese Ecotourism, 11 (4), 471–497. https://doi.org/10.12342/zgstly.20210084
Tao, Y., & Huang, Z. (2014). Review of accounting for carbon dioxide emissions from tourism at different spatial scales. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34 (5), 246–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2014.03.007
Tao, Y., Huang, Z., & Shi, C. (2015). Carbon dioxide emissions from regional tourism transport: A substitutional bottom-up analysis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35 (12), 4224–4233. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201309042211
Tsai, S. B. (2016). Using grey models for forecasting China’s growth trends in renewable energy consumption. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 18 (2), 563–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-1017-7
Tsai, S. B., Xue, Y., Zhang, J., Chen, Q., Liu, Y., Zhou, J., & Dong, W. (2017). Models for forecasting growth trends in renewable energy. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 77 , 1169–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.06.001
Ulibarri, N., Imperial, M. T., Siddiki, S., & Henderson, H. (2023). Drivers and dynamics of collaborative governance in environmental management. Environmental Management, 71 (3), 495–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-022-01769-7
UN-DESA. (2022). World population prospects 2022 . Retrieved from https://worldpopulationreview.com/countries/china-population
UNWTO-ITF. (2019). Transport-related CO2 emissions of the tourism sector: Modelling results . UNWTO.
UNWTO-UNEP-WMO. (2008). Climate change and tourism: Responding to global challenges . UNWTO.
Wang, H., Lu, X., Deng, Y., Sun, Y., Nielsen, C. P., Liu, Y., & McElroy, M. B. (2019). China’s CO 2 peak before 2030 implied from characteristics and growth of cities. Nature Sustainability, 2 (8), 748–754. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-019-0339-6
Wang, H., Shi, W., He, W., Xue, H., & Zeng, W. (2023). Simulation of urban transport carbon dioxide emission reduction environment economic policy in China: An integrated approach using agent-based modelling and system dynamics. Journal of Cleaner Production, 392 , 136221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136221
Wang, Z. X., Li, Q., & Pei, L. L. (2018). A seasonal GM(1,1) model for forecasting the electricity consumption of the primary economic sectors. Energy, 154 , 522–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.04.155
Wei, Y. X., Sun, G. N., Ma, L. J., & Li, J. (2012). Estimating the carbon emissions and regional differences of tourism transport in China. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (natural Science Edition), 40 (2), 76–84. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-4291.2012.02.017
Wu, J., Xu, M., & Zhang, P. (2018). The impacts of governmental performance assessment policy and citizen participation on improving environmental performance across Chinese provinces. Journal of Cleaner Production, 184 , 227–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.056
Xiang, Y., Zhou, H., Yang, W., Liu, J., Niu, Y., & Guo, J. (2017). Scale evolution of electric vehicles: A system dynamics approach. IEEE Access, 5 , 8859–8868.
Xiao, X., Zhang, J., Lu, J., & Yin, L. (2012). Analysis on spatial structure and scenarios of carbon dioxide emissions from tourism transportation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32 (23), 7540–7548. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201111301830
Xing, L., Xue, M., & Hu, M. (2019). Dynamic simulation and assessment of the coupling coordination degree of the economy–resource–environment system: Case of Wuhan City in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 230 , 474–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.09.065
Xu, G., Schwarz, P., & Yang, H. (2019). Determining China’s CO 2 emissions peak with a dynamic nonlinear artificial neural network approach and scenario analysis. Energy Policy, 128 , 752–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.01.058
Yang, H., Li, X., Ma, L., & Li, Z. (2021). Using system dynamics to analyse key factors influencing China’s energy-related CO 2 emissions and emission reduction scenarios. Journal of Cleaner Production, 320 , 128811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128811
Yang, L., & Lin, B. (2016). Carbon dioxide-emission in China׳ s power industry: Evidence and policy implications. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 60 , 258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.01.058
Yang, S., Duan, Z., & Jiang, X. (2023). Spatial dynamics and influencing factors of carbon rebound effect in tourism transport: Evidence from the Yangtze-river delta urban agglomeration. Journal of Environmental Management, 344 , 118431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118431
Ye, F., Xiong, X., Li, L., & Li, Y. (2021). Measuring the effectiveness of the Chinese Certified Emission Reduction scheme in mitigating CO 2 emissions: A system dynamics approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 294 , 125355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125355
Yu, X., Wu, Z., Wang, Q., Sang, X., & Zhou, D. (2020). Exploring the investment strategy of power enterprises under the nationwide carbon emissions trading mechanism: A scenario-based system dynamics approach. Energy Policy, 140 , 111409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111409
Yuan, C., Liu, S., & Fang, Z. (2016). Comparison of China’s primary energy consumption forecasting by using ARIMA (the autoregressive integrated moving average) model and GM(1,1) model. Energy, 100 , 384–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.02.001
Yue, Q., Chai, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, Q., Wang, H., Zhao, F., & Lu, Y. (2023). Analysis of iron and steel production paths on the energy demand and carbon emission in China’s iron and steel industry. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 25 (5), 4065–4085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02234-5
Zha, J., Dai, J., Ma, S., Chen, Y., & Wang, X. (2021). How to decouple tourism growth from carbon emissions? A case study of Chengdu, China. Tourism Management Perspectives, 39 , 100849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2021.100849
Zhang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Carbon tax, tourism CO 2 emissions and economic welfare. Annals of Tourism Research, 69 , 18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2017.12.009
Zhao, X., Ma, X., Chen, B., Shang, Y., & Song, M. (2022). Challenges toward carbon neutrality in China: Strategies and countermeasures. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 176 , 105959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105959
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Project of the National Social Science Foundation of China (21BJY194), the High-level Talent Project of Hainan Natural Science Foundation (722RC191).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of International Tourism and Public Administration, Hainan University, No. 58 Renmin Street, Meilan District, Haikou, 570228, China
Yun Tong, Hao Li & Li Pang
Hainan Province Holistic Tourism Research Base, Haikou, 570228, China
Academician Station of Hainan Province, Haikou, 570228, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hao Li .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
See Tables 5 and 6 .
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Tong, Y., Li, H. & Pang, L. China’s tourism transportation carbon emissions: dynamic mechanisms and multi-regulatory strategies simulation. Environ Dev Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04985-9
Download citation
Received : 23 March 2023
Accepted : 26 April 2024
Published : 10 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04985-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Tourism transportation carbon emissions
- Carbon peak target
- System dynamics
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

40 Facts About Elektrostal
Written by Lanette Mayes
Modified & Updated: 10 May 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett

Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to captivate you.
This article will provide you with 40 fascinating facts about Elektrostal, giving you a better understanding of why this city is worth exploring. From its origins as an industrial hub to its modern-day charm, we will delve into the various aspects that make Elektrostal a unique and must-visit destination.
So, join us as we uncover the hidden treasures of Elektrostal and discover what makes this city a true gem in the heart of Russia.
Key Takeaways:
- Elektrostal, known as the “Motor City of Russia,” is a vibrant and growing city with a rich industrial history, offering diverse cultural experiences and a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.
- With its convenient location near Moscow, Elektrostal provides a picturesque landscape, vibrant nightlife, and a range of recreational activities, making it an ideal destination for residents and visitors alike.
Known as the “Motor City of Russia.”
Elektrostal, a city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia, earned the nickname “Motor City” due to its significant involvement in the automotive industry.
Home to the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Elektrostal is renowned for its metallurgical plant, which has been producing high-quality steel and alloys since its establishment in 1916.
Boasts a rich industrial heritage.
Elektrostal has a long history of industrial development, contributing to the growth and progress of the region.
Founded in 1916.
The city of Elektrostal was founded in 1916 as a result of the construction of the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Located approximately 50 kilometers east of Moscow.
Elektrostal is situated in close proximity to the Russian capital, making it easily accessible for both residents and visitors.
Known for its vibrant cultural scene.
Elektrostal is home to several cultural institutions, including museums, theaters, and art galleries that showcase the city’s rich artistic heritage.
A popular destination for nature lovers.
Surrounded by picturesque landscapes and forests, Elektrostal offers ample opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and birdwatching.
Hosts the annual Elektrostal City Day celebrations.
Every year, Elektrostal organizes festive events and activities to celebrate its founding, bringing together residents and visitors in a spirit of unity and joy.
Has a population of approximately 160,000 people.
Elektrostal is home to a diverse and vibrant community of around 160,000 residents, contributing to its dynamic atmosphere.
Boasts excellent education facilities.
The city is known for its well-established educational institutions, providing quality education to students of all ages.
A center for scientific research and innovation.
Elektrostal serves as an important hub for scientific research, particularly in the fields of metallurgy, materials science, and engineering.
Surrounded by picturesque lakes.
The city is blessed with numerous beautiful lakes, offering scenic views and recreational opportunities for locals and visitors alike.
Well-connected transportation system.
Elektrostal benefits from an efficient transportation network, including highways, railways, and public transportation options, ensuring convenient travel within and beyond the city.
Famous for its traditional Russian cuisine.
Food enthusiasts can indulge in authentic Russian dishes at numerous restaurants and cafes scattered throughout Elektrostal.
Home to notable architectural landmarks.
Elektrostal boasts impressive architecture, including the Church of the Transfiguration of the Lord and the Elektrostal Palace of Culture.
Offers a wide range of recreational facilities.
Residents and visitors can enjoy various recreational activities, such as sports complexes, swimming pools, and fitness centers, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Provides a high standard of healthcare.
Elektrostal is equipped with modern medical facilities, ensuring residents have access to quality healthcare services.
Home to the Elektrostal History Museum.
The Elektrostal History Museum showcases the city’s fascinating past through exhibitions and displays.
A hub for sports enthusiasts.
Elektrostal is passionate about sports, with numerous stadiums, arenas, and sports clubs offering opportunities for athletes and spectators.
Celebrates diverse cultural festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal hosts a variety of cultural festivals, celebrating different ethnicities, traditions, and art forms.
Electric power played a significant role in its early development.
Elektrostal owes its name and initial growth to the establishment of electric power stations and the utilization of electricity in the industrial sector.
Boasts a thriving economy.
The city’s strong industrial base, coupled with its strategic location near Moscow, has contributed to Elektrostal’s prosperous economic status.
Houses the Elektrostal Drama Theater.
The Elektrostal Drama Theater is a cultural centerpiece, attracting theater enthusiasts from far and wide.
Popular destination for winter sports.
Elektrostal’s proximity to ski resorts and winter sport facilities makes it a favorite destination for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter activities.
Promotes environmental sustainability.
Elektrostal prioritizes environmental protection and sustainability, implementing initiatives to reduce pollution and preserve natural resources.
Home to renowned educational institutions.
Elektrostal is known for its prestigious schools and universities, offering a wide range of academic programs to students.
Committed to cultural preservation.
The city values its cultural heritage and takes active steps to preserve and promote traditional customs, crafts, and arts.
Hosts an annual International Film Festival.
The Elektrostal International Film Festival attracts filmmakers and cinema enthusiasts from around the world, showcasing a diverse range of films.
Encourages entrepreneurship and innovation.
Elektrostal supports aspiring entrepreneurs and fosters a culture of innovation, providing opportunities for startups and business development.
Offers a range of housing options.
Elektrostal provides diverse housing options, including apartments, houses, and residential complexes, catering to different lifestyles and budgets.
Home to notable sports teams.
Elektrostal is proud of its sports legacy, with several successful sports teams competing at regional and national levels.
Boasts a vibrant nightlife scene.
Residents and visitors can enjoy a lively nightlife in Elektrostal, with numerous bars, clubs, and entertainment venues.
Promotes cultural exchange and international relations.
Elektrostal actively engages in international partnerships, cultural exchanges, and diplomatic collaborations to foster global connections.
Surrounded by beautiful nature reserves.
Nearby nature reserves, such as the Barybino Forest and Luchinskoye Lake, offer opportunities for nature enthusiasts to explore and appreciate the region’s biodiversity.
Commemorates historical events.
The city pays tribute to significant historical events through memorials, monuments, and exhibitions, ensuring the preservation of collective memory.
Promotes sports and youth development.
Elektrostal invests in sports infrastructure and programs to encourage youth participation, health, and physical fitness.
Hosts annual cultural and artistic festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal celebrates its cultural diversity through festivals dedicated to music, dance, art, and theater.
Provides a picturesque landscape for photography enthusiasts.
The city’s scenic beauty, architectural landmarks, and natural surroundings make it a paradise for photographers.
Connects to Moscow via a direct train line.
The convenient train connection between Elektrostal and Moscow makes commuting between the two cities effortless.
A city with a bright future.
Elektrostal continues to grow and develop, aiming to become a model city in terms of infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life for its residents.
In conclusion, Elektrostal is a fascinating city with a rich history and a vibrant present. From its origins as a center of steel production to its modern-day status as a hub for education and industry, Elektrostal has plenty to offer both residents and visitors. With its beautiful parks, cultural attractions, and proximity to Moscow, there is no shortage of things to see and do in this dynamic city. Whether you’re interested in exploring its historical landmarks, enjoying outdoor activities, or immersing yourself in the local culture, Elektrostal has something for everyone. So, next time you find yourself in the Moscow region, don’t miss the opportunity to discover the hidden gems of Elektrostal.
Q: What is the population of Elektrostal?
A: As of the latest data, the population of Elektrostal is approximately XXXX.
Q: How far is Elektrostal from Moscow?
A: Elektrostal is located approximately XX kilometers away from Moscow.
Q: Are there any famous landmarks in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to several notable landmarks, including XXXX and XXXX.
Q: What industries are prominent in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal is known for its steel production industry and is also a center for engineering and manufacturing.
Q: Are there any universities or educational institutions in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to XXXX University and several other educational institutions.
Q: What are some popular outdoor activities in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal offers several outdoor activities, such as hiking, cycling, and picnicking in its beautiful parks.
Q: Is Elektrostal well-connected in terms of transportation?
A: Yes, Elektrostal has good transportation links, including trains and buses, making it easily accessible from nearby cities.
Q: Are there any annual events or festivals in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal hosts various events and festivals throughout the year, including XXXX and XXXX.
Elektrostal's fascinating history, vibrant culture, and promising future make it a city worth exploring. For more captivating facts about cities around the world, discover the unique characteristics that define each city . Uncover the hidden gems of Moscow Oblast through our in-depth look at Kolomna. Lastly, dive into the rich industrial heritage of Teesside, a thriving industrial center with its own story to tell.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:

Shapiro Administration Invests $200,000 in New PIDA Loan to Spur Tourism and Business Growth in Elk County
- May 8, 2024
PIDA has approved $11,428,160 in low interest loans that have resulted in $19,854,839 in private investment and supported 387 created and retained full-time jobs across PA in 2024 so far.
Tourism is one of the largest industries in Pennsylvania, and Governor Shapiro has proposed an $18 million increase in his 2024-25 budget to boost tourism and business marketing efforts.
Harrisburg, PA – Today, Department of Community and Economic Development (DCED) Secretary Rick Siger announced the approval of one new low-interest $200,000 loan through the Pennsylvania Industrial Development Authority (PIDA) to support tourism, business expansion, and boost the economy in Elk County.
The newly approved loan builds upon Governor Josh Shapiro’s commitment to create a stronger economy across Pennsylvania. Since 2023, PIDA has approved more than $56 million in low interest loans that have resulted in more than $165 million in private investment and created and retained over 1,520 full-time jobs.
PIDA provides low-interest loans and lines of credit for eligible businesses that commit to creating and retaining full-time jobs, as well as for the development of industrial parks and multi-tenant facilities. Loans can be used for: land and building acquisitions; construction and renovation costs; machinery and equipment purchases; working capital and accounts receivable lines of credits; multi-tenant facility projects; and industrial park projects.
“Tourism is one of the largest industries in Pennsylvania generating over $76 billion a year and supporting more than 486,000 jobs,” said Secretary Rick Siger. “The PIDA loan approved today will boost tourism in the heart of the Pennsylvania Wilds in Elk County and attract tourists from across the nation to this majestic region. The Shapiro Administration is working to transform Pennsylvania into an economic powerhouse and PIDA loans like this one give small businesses the tools to help make that happen.”
Wapiti Woods Lodge, LLC, through the North Central PA Regional Planning & Development Commission, was approved for a fifteen-year $200,000 loan at a 4.00-percent reset interest rate to help to assist with site improvements and construction of a lodge that will feature four bedrooms with a sleeping capacity for eight adults, 2.5 bathrooms, a full kitchen, laundry facilities, indoor and outdoor fireplaces, and extensive outdoor seating. This new lodge addresses an existing demand in the market for larger accommodations capable of hosting sizable groups which is currently unfulfilled by Wapiti Woods, LLC, and its ten cabins. The total project cost is $431,950.
Tourism is one of the largest industries in Pennsylvania, generating over $76 billion a year and supporting more than 486,000 jobs. Investing in tourism is a key component of the Governor’s economic development strategy – and the Governor proposed an $18 million increase in his 2024-25 budget to boost tourism and business marketing efforts. The Governor’s 2024-25 budget also calls for significant investments directly tied back to the Commonwealth’s ten-year economic development strategy and issues a strong call to action for partners across all sectors to join in with their support.
Other proposed economic development investments in the Governor’s budget include: $500 million in PA SITES funding to bring more commercial and industrial sites to Pennsylvania; $25 million for the Main Street Matters program to support small businesses and commercial corridors in communities across our Commonwealth; $20 million to support large-scale innovation and leverage Pennsylvania’s best-in-class research and development assets; and $3.5 million to create and launch the Pennsylvania Regional Economic Competitiveness Challenge to incentivize regional growth.
You can read Pennsylvania’s first economic development strategy in 20 years online. For more information on how the Governor’s proposed budget will create opportunity for all Pennsylvanians, visit Shapiro’s Budget website .
For more information about the Pennsylvania Industrial Development Authority or the Department of Community and Economic Development, visit the DCED website , and be sure to stay up-to-date with all of our agency news on Facebook , X , and LinkedIn .
MEDIA CONTACT: Governor’s Office, [email protected] , 717.783.1116 Penny Ickes, DCED, [email protected]
- DCED Funding PIDA Tags Governor Shapiro
Maldives Development Update 2024

The Maldives Development Update (MDU) has two main goals. First, it takes the pulse of the Maldivian economy by providing key developments over the past 12 months. Placing these in a global context, and based on these recent developments, it analyzes the outlook over the medium term. Second, every other edition of the MDU provides a more in-depth investigation of selected economic and policy issues. It has a wide audience including policymakers, policy analysts from think tanks or non-governmental organizations, and business and financial sector professionals interested in Maldives’ economic development.
Click here to download the latest Maldives Development Update (May, 2024).
RECENT ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
In 2023, the number of tourist arrivals reached a record-breaking figure of 1.88 million. Nevertheless, this did not result in higher GDP growth due to lower per-tourist spending and shorter stays. The Maldivian economy is estimated to have grown by 4% in 2023. Domestic inflation, at 2.9% in 2023, remained higher than the historical average of 0.5%. Price increases were experienced in the food, education, restaurant, and lodging services sectors. Food inflation could increase poverty by 0.4 percentage points, with atolls experiencing even higher rates.
Travel export receipts fell 6.8%, while merchandise imports remained elevated at $3.5 billion. This resulted in a current account deficit of 23.4% of GDP. High import costs and external debt repayments also weighed heavily on gross reserves, which fell to $551.1 million in January 2024. Failure to implement planned subsidy reforms, combined with rising recurrent and capital spending, resulted in a sharp increase in total expenditure and a fiscal deficit of 13.2% of GDP in 2023.
Tourism, which accounts for a quarter of the Maldives' economy, has experienced slower growth in 2023 due to a decline in average duration of stay and lower tourist spending. This slowdown has exposed underlying economic vulnerabilities in the Maldives.
These vulnerabilities stem from persistent large current account and fiscal deficits. The country relies heavily on imports while having limited official reserves, creating an unsustainable imbalance. Government support for struggling state-owned enterprises (SOEs), along with blanket subsidies, high capital spending, and a public health program, further exacerbate these pressures.
While these subsidies and in-kind transfers are crucial for boosting household incomes, their unsustainable nature raises concerns. When fiscal pressures mount, the Maldivian people's well-being could be negatively impacted. Additionally, infrastructure projects, although promising long-term growth, were financed through non-concessional external borrowing and sovereign guarantees. The rising cost of borrowing abroad has forced the government to turn towards domestic sources, increasing the domestic financial sector’s vulnerability to government debt.
The government recently announced its commitment to a fiscal reform agenda to address these economic vulnerabilities. This agenda includes reforms to subsidies, SOEs, the public health insurance scheme (Aasandha), and reprioritizing capital spending. These reforms offer a path towards a more resilient Maldivian economy.
The economy is projected to grow by 4.7% over the medium-term, supported by tourism, a decrease from the pre-pandemic average of 7.4%. This growth is based on expected fiscal adjustments, including subsidy reforms and reduced public expenditure and investments. This slowdown also means slower poverty reduction in 2024.
The fiscal deficit is expected to remain high in 2024 due to ambitious spending plans .The proposed fiscal reform package is expected to help but a more sustainable fiscal path requires a larger adjustment, particularly through cuts in non-essential capital and untargeted recurrent spending.
Inflation is expected to rise due to the removal of blanket subsidies, potentially driving poverty by 2.5 percentage points. The current account deficit is expected to remain high due to commodity price pressures and capital imports for infrastructure projects. Rising external financing needs, including debt servicing, are expected to sustain pressure on foreign exchange reserves.
Major downside risks include a shock to the tourism sector, limited domestic and external financing, and a widening current account deficit. To maintain macroeconomic stability, a major fiscal adjustment and a multi-year reform plan are required, along with a targeted transfer mechanism to offset welfare losses among vulnerable groups.

Rosatom Starts Production of Rare-Earth Magnets for Wind Power Generation
TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom has started gradual localization of rare-earth magnets manufacturing for wind power plants generators. The first sets of magnets have been manufactured and shipped to the customer.

In total, the contract between Elemash Magnit LLC (an enterprise of TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom in Elektrostal, Moscow region) and Red Wind B.V. (a joint venture of NovaWind JSC and the Dutch company Lagerwey) foresees manufacturing and supply over 200 sets of magnets. One set is designed to produce one power generator.
“The project includes gradual localization of magnets manufacturing in Russia, decreasing dependence on imports. We consider production of magnets as a promising sector for TVEL’s metallurgical business development. In this regard, our company does have the relevant research and technological expertise for creation of Russia’s first large-scale full cycle production of permanent rare-earth magnets,” commented Natalia Nikipelova, President of TVEL JSC.
“NovaWind, as the nuclear industry integrator for wind power projects, not only made-up an efficient supply chain, but also contributed to the development of inter-divisional cooperation and new expertise of Rosatom enterprises. TVEL has mastered a unique technology for the production of magnets for wind turbine generators. These technologies will be undoubtedly in demand in other areas as well,” noted Alexander Korchagin, Director General of NovaWind JSC.
For reference:
TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom incorporates enterprises for the fabrication of nuclear fuel, conversion and enrichment of uranium, production of gas centrifuges, as well as research and design organizations. It is the only supplier of nuclear fuel for Russian nuclear power plants. TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom provides nuclear fuel for 73 power reactors in 13 countries worldwide, research reactors in eight countries, as well as transport reactors of the Russian nuclear fleet. Every sixth power reactor in the world operates on fuel manufactured by TVEL. www.tvel.ru
NovaWind JSC is a division of Rosatom; its primary objective is to consolidate the State Corporation's efforts in advanced segments and technological platforms of the electric power sector. The company was founded in 2017. NovaWind consolidates all of the Rosatom’s wind energy assets – from design and construction to power engineering and operation of wind farms.
Overall, by 2023, enterprises operating under the management of NovaWind JSC, will install 1 GW of wind farms. http://novawind.ru
Elemash Magnit LLC is a subsidiary of Kovrov Mechanical Plant (an enterprise of the TVEL Fuel Company of Rosatom) and its main supplier of magnets for production of gas centrifuges. The company also produces magnets for other industries, in particular, for the automotive
industry. The production facilities of Elemash Magnit LLC are located in the city of Elektrostal, Moscow Region, at the site of Elemash Machine-Building Plant (a nuclear fuel fabrication facility of TVEL Fuel Company).
Rosatom is a global actor on the world’s nuclear technology market. Its leading edge stems from a number of competitive strengths, one of which is assets and competences at hand in all nuclear segments. Rosatom incorporates companies from all stages of the technological chain, such as uranium mining and enrichment, nuclear fuel fabrication, equipment manufacture and engineering, operation of nuclear power plants, and management of spent nuclear fuel and nuclear waste. Nowadays, Rosatom brings together about 350 enterprises and organizations with the workforce above 250 K. https://rosatom.ru/en/

U.S. Added Less New Wind Power in 2021 Than the Previous Year — Here’s Why
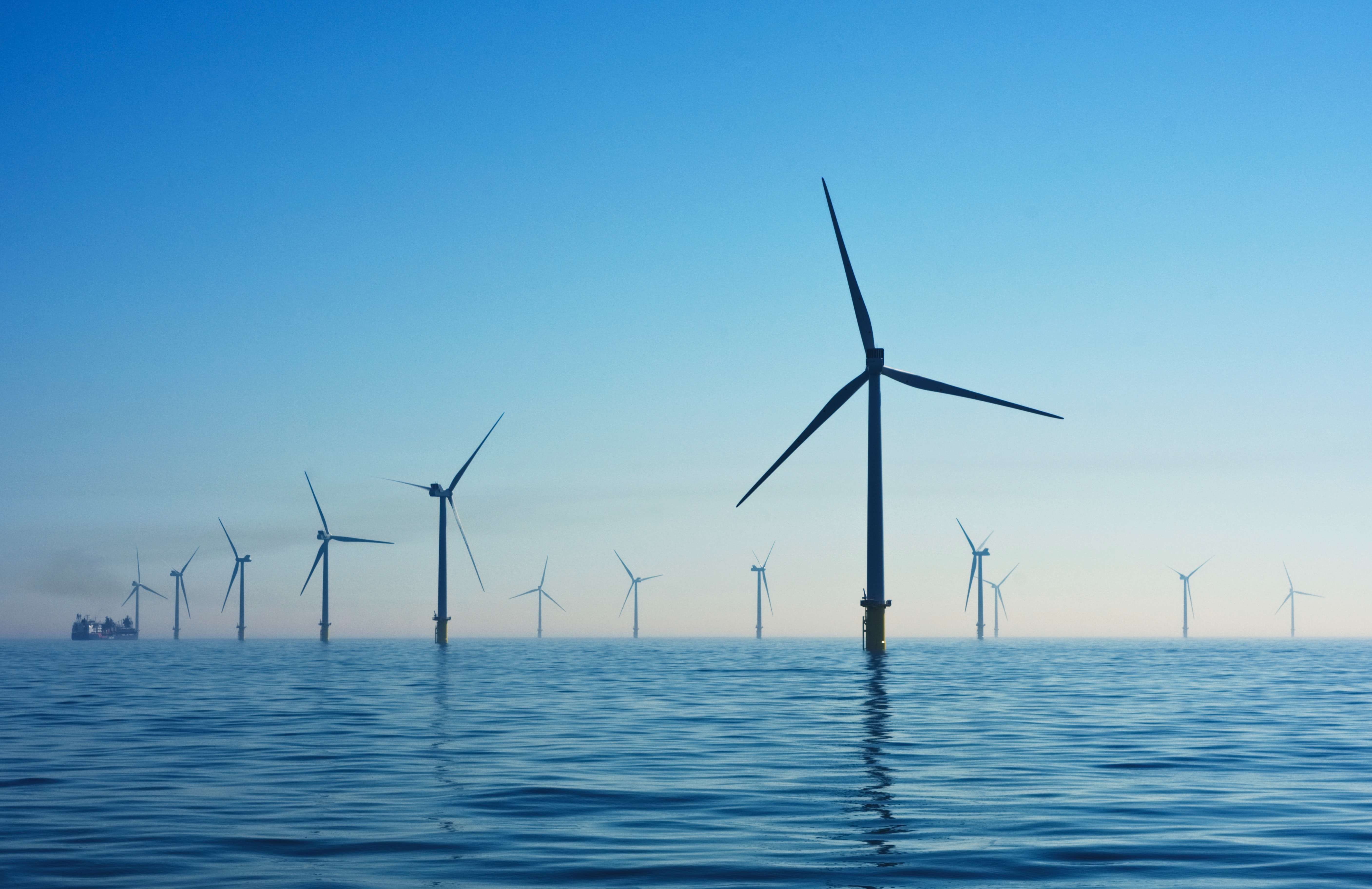

Finland Denies 16 Offshore Wind Bids

Japan's Chubu Completes Ecowende Buy-in

Vietnam's Largest Wind Power Plant Starts Operational

Trung Nam Group Inaugurates Wind Power Plant in Vietnam

Vietnam Plans to Double Wind Power Generation by 2030
Language selection
- Français fr
Government of Canada supports Oshawa-based tourism operator
From: Federal Economic Development Agency for Southern Ontario
News release
Canadian tourism organizations and attractions play a crucial role in showcasing our country’s unique history, geography, culture and experiences. By attracting domestic and international travelers, these destinations also contribute to good local jobs and economic growth in communities.
FedDev Ontario invests $125,000 in Treetop Eco-Adventure Park to develop new outdoor trampoline park
May 8, 2024 – Oshawa, Ontario
Canadian tourism organizations and attractions play a crucial role in showcasing our country’s unique history, geography, culture and experiences. By attracting domestic and international travelers, these destinations also contribute to good local jobs and economic growth in communities.
Today, the Honourable Filomena Tassi, Minister responsible for the Federal Economic Development Agency for Southern Ontario ( FedDev Ontario ), announced an investment of $125,000 for Treetop Eco-Adventure Park to expand operations at its Oshawa location.
With support from this investment through the Tourism Growth Program , Treetop Eco-Adventure Park, a high ropes and zipline ecological adventure park, will add a new outdoor trampoline attraction. This addition is expected to increase visitors to the area, resulting in spillover benefits for the local economy.
The Government of Canada is committed to supporting tourism businesses and organizations that attract visitors to the region while contributing to the local economy and positioning Canada as an all-season destination of choice.
“Tourism is an economic cornerstone in communities across southern Ontario, stimulating job creation and contributing significantly to the region's overall prosperity. The Government of Canada knows the value in supporting tourism businesses and organizations, like Treetop Eco-Adventure Park, who showcase the unique experiences and attractions southern Ontario has to offer.” - The Honourable Filomena Tassi, Minister responsible for the Federal Economic Development Agency for Southern Ontario
“Southern Ontario’s tourism industry is an incredibly important economic driver and provides jobs for Canadians from all walks of life. Through the Tourism Growth Program, the Government of Canada is supporting local organizations like Treetop Eco-Adventure Park. As we continue to invest in the industry, we’ll help bring more domestic and international visitors to the region to discover all that it has to offer.” - The Honourable Soraya Martinez Ferrada, Minister of Tourism
“Treetop Eco-Adventure Park is thrilled to rekindle its successful partnership with FedDev Ontario for our latest venture, IBounce—an interactive outdoor trampoline net park. With four dynamic game areas and five trampoline nets, we aim to captivate even more outdoor enthusiasts, inviting them to leap into boundless excitement amidst the scenic beauty of the Oak Ridges Moraine. Each bounce fosters a deeper connection with nature, reinforcing our commitment as stewards of Durham Region's second-largest forest and our passion for sharing its wonders in innovative and enjoyable ways.” - Karen Richards, Owner, Treetop Eco-Adventure Park
Quick facts
Treetop Eco-Adventure Park hosts up to 12,000 visitors every year and features 8 courses that entertain guests through Tarzan ropes, zip lines and a variety of different mid-air games for ages 3 and up.
Delivered by Canada’s regional development agencies, the Tourism Growth Program provides $108 million, over three years, directly to businesses and organizations to help diversify regional economies by investing in tourism products and experiences that will encourage visitation to and within Canada. In southern Ontario, FedDev Ontario is delivering over $30 million through the program.
Since 2015, the Government of Canada, through FedDev Ontario, has invested over $45 million in more than 85 projects with businesses and organizations in Durham region, estimated to create over 220 jobs and maintain over 750 jobs.
Since 2015, the Government of Canada, through FedDev Ontario, has invested over $415 million in more than 1,440 tourism-related businesses and organizations, estimated to create over 4,700 jobs and maintain over 20,000 jobs.
Associated links
- Treetop Eco-Adventure Park
- FedDev Ontario
- Tourism Growth Program in southern Ontario
Edward Hutchinson Press Secretary Office of the Minister responsible for the Federal Economic Development Agency for Southern Ontario [email protected]
Media Relations FedDev Ontario [email protected]
Stay Connected
Subscribe to FedDev Ontario's Southern Ontario Spotlight newsletter , featuring economic development news and updates from across the region.
Follow us on Twitter , Facebook , Instagram and LinkedIn for more information on how we are growing businesses, cultivating partnerships and building strong communities in southern Ontario.
Page details

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Showcased along 23 case studies from around the world, this two-volume report examines the role of tourism in each of the five pillars of the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, 2017: 1. Sustainable economic growth; 2. Social inclusiveness, employment and poverty reduction; 3. Resource efficiency, environmental protection ...
Several key findings have been identified in the Travel & Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2021 results and research.First, the need for T&T development has never been greater as it plays a critical role in helping the global economic recovery by supporting the livelihoods of some of the populations hardest hit by the pandemic and by building resilience, especially when it comes to lower ...
2.2 Tourism: a catalyst for development. From the viewpoint of development, understood in socio-economic terms, tourism becomes a. dynamic tool in the economic system, generating linkages created ...
Tourism has long been explored through the lens of development theory. David Harrison was one of the earlier academics to do so, subsequently turning his attention to critiquing the relevance of such theory to tourism, concluding that although much tourism research has been framed within it, development theory has contributed little if anything ...
Showcased along 23 case studies from around the world, this two-volume report examines the role of tourism in each of the five pillars of the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, 2017: 1. Sustainable economic growth; 2. Social inclusiveness, employment and poverty reduction; 3. Resource efficiency, environmental protection ...
Sustainable tourism development requires the informed participation of all relevant stakeholders, as well as strong political leadership to ensure wide participation and consensus building. Achieving sustainable tourism is a continuous process and it requires constant monitoring of impacts, introducing the necessary preventive and/or corrective ...
This flagship report addresses the changes needed in policies, business practices and consumer behaviour. Showcased along 23 case studies from around the world, this two-volume report examines the role of tourism in each of the five pillars of the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, 2017: 1. Sustainable economic growth; 2.
2022 has been the year to rethink tourism. Countries around the world turned UNWTO's vision for a greener, smarter and more inclusive sector into real action. 2020 showed the relevance of tourism for sustainable development. 2021 laid the foundations for the transformation of the sector. In 2022, we made it happen. 2022 began on a positive note....
The federal government will work to implement the strategy under the leadership of the TPC and in partnership with the private sector, aiming toward an ambitious five-year goal of increasing American jobs by attracting and welcoming 90 million international visitors, who we estimate will spend $279 billion, annually by 2027.. The new National Travel and Tourism Strategy supports growth and ...
In 1938, it was granted town status. [citation needed]Administrative and municipal status. Within the framework of administrative divisions, it is incorporated as Elektrostal City Under Oblast Jurisdiction—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts. As a municipal division, Elektrostal City Under Oblast Jurisdiction is incorporated as Elektrostal Urban Okrug.
The first transformational force was the COVID-19 pandemic. By the middle of March 2020, international travel had shut down and organizations were scrambling to shift to remote work.
Travelers' Daily Spend. Tennessee tourism generated $28.9 billion in domestic and international travel spending in 2022, according to recently released economic impact data from U.S. Travel Association and Tourism Economics. It also marks the largest visitor spending nationally in Tennessee's history. Travelers in Tennessee spend an estimated ...
Tourism is among Palm Beach County's major industries generating an annual economic impact of $7.0 plus billion in the local economy, producing $45 million plus in bed-tax revenue, on lodging sales exceeding $700 million annually and supporting 60,000 plus tourism related jobs. The Tourist Development Tax and the current use is critically ...
Tourist Development Council Appointment. This nine member council was created on March 23, 1992 by Ordinance No. 92-18 to meet monthly to make recommendations to the Board of County Commissioners regarding a proposed plan of uses for tourist development tax revenues, for the effective operation of the special projects or uses of the tourist development tax revenues, and to review all ...
Delivered by Canada's regional development agencies, the Tourism Growth Program is providing $108 million, over three years, directly to businesses and organizations to help diversify regional economies by investing in tourism products and experiences that will encourage visitation to and within Canada. In southern Ontario, FedDev Ontario is ...
Forecasting carbon emissions is regarded as the scientific basis for establishing milestone reduction targets and assessing the effectiveness of reduction strategies. This study aims to predict the tourism transportation carbon emissions (TTCE) in China until 2035 and to propose strategies for achieving the carbon peak target. Under the framework of environmental performance measurement, a ...
40 Facts About Elektrostal. Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to ...
Tourism is one of the largest industries in Pennsylvania, generating over $76 billion a year and supporting more than 486,000 jobs. Investing in tourism is a key component of the Governor's economic development strategy - and the Governor proposed an $18 million increase in his 2024-25 budget to boost tourism and business marketing efforts ...
Tourist Development. NOTE: The Department of Tourist Development and its employees do not accept, or consider, unsolicited sound recordings, musical compositions or any other creative materials. Please note that if, despite our policy, you submit unsolicited material to us, then the Department of Tourist Development has no obligation, and shall ...
Drive • 1h 3m. Drive from Elektrostal to Moscow 58.6 km. RUB 450 - RUB 700. Quickest way to get there Cheapest option Distance between.
Today, the Honourable Soraya Martinez Ferrada, Minister of Tourism and Minister responsible for the Economic Development Agency of Canada for the Regions of Quebec, announced the launch of the ITF's Signature Indigenous Tourism Experiences Stream (SITES). With $10 million in federal funding, SITES will support major Indigenous tourism ...
The city of Avondale is buzzing with activities dedicated to celebrating Economic Development, Tourism, and Small Business throughout May, as proclaimed by Mayor Kenn Weise. The city has launched ...
In 2023, the number of tourist arrivals reached a record-breaking figure of 1.88 million. Nevertheless, this did not result in higher GDP growth due to lower per-tourist spending and shorter stays. The Maldivian economy is estimated to have grown by 4% in 2023. Domestic inflation, at 2.9% in 2023, remained higher than the historical average of 0.5%. Price increases were experienced in the food ...
The Honourable Soraya Martinez Ferrada, Minister of Tourism and Minister responsible for the Economic Development Agency of Canada for the Regions of Quebec, will announce a new federal initiative to support Indigenous tourism and promote reconciliation. Minister Ferrada will be joined by Shannin Metatawabin, Chief Executive Officer of the National Aboriginal Capital Corporations Association ...
The Port of Seattle is pleased to announce its 2024-25 Tourism Marketing Support Program (TMSP) recipients. Thirty-eight organizations across the state received a total of $600,000 in matched marketing funds to help communities market their destinations while promoting Washington state as a destination for out-of-state visitors. Funding for the two-to-one match fund program was doubled this ...
Local security forces brought 15 men to a military enlistment office after a mass brawl at a warehouse of the Russian Wildberries company in Elektrostal, Moscow Oblast on Feb. 8, Russian Telegram channel Shot reported.. 29 people were also taken to police stations. Among the arrested were citizens of Kyrgyzstan. A mass brawl involving over 100 employees and security personnel broke out at the ...
Round table 2021. "Electrostal" Metallurgical plant" JSC has a number of remarkable time-tested traditions. One of them is holding an annual meeting with customers and partners in an extеnded format in order to build development pathways together, resolve pressing tasks and better understand each other. Although the digital age ...
We consider production of magnets as a promising sector for TVEL's metallurgical business development. In this regard, our company does have the relevant research and technological expertise for creation of Russia's first large-scale full cycle production of permanent rare-earth magnets," commented Natalia Nikipelova, President of TVEL JSC.
The Government of Canada knows the value in supporting tourism businesses and organizations, like Treetop Eco-Adventure Park, who showcase the unique experiences and attractions southern Ontario has to offer." - The Honourable Filomena Tassi, Minister responsible for the Federal Economic Development Agency for Southern Ontario
NASHVILLE, Tenn. (May 9, 2024) - Summer in Tennessee is known for its blockbuster music festivals, family road trips and delicious cuisine. But if you're interested in the great outdoors, waterfall chasing is the pastime you'll want to enjoy this summer. From May until September, Tennessee's waterfalls deliver stunning views, an escape from the heat and beautiful natural swimming holes.