- Ulubione stacje paliw
- Ustawienia konta
- Gorące tematy
- Sprawdź VIN przed zakupem!
- Ile kosztuje Cię auto?
- Wyszukiwarka aut
- Poznaj usterki przed zakupem
- AutoCentrum
- Motosłownik
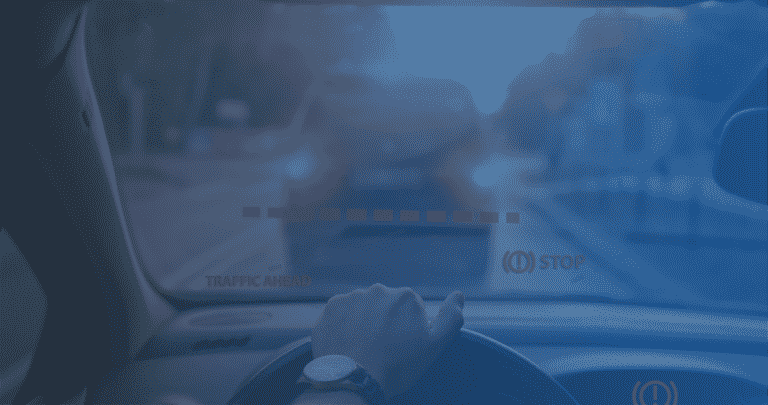
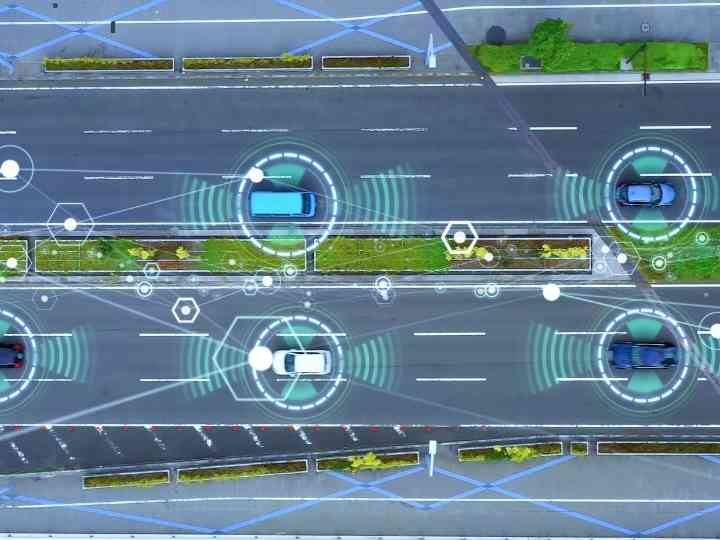
- ACC (Adaptive Cruise Control) ACC (Adaptive Cruise Control)

ACC (Adaptive Cruise Control) - co to jest?
ACC (z ang. Adaptive Cruise Control), jest to rozbudowana wersja tempomatu pierwszej generacji CCS (z ang. Cruising Control System), określana mianem adaptacyjnego lub aktywnego tempomatu. Obecnie w pojazdach możemy spotkać dwie kolejne generacje adaptacyjnych tempomatów. Aktywne tempomaty różnią się one od siebie przede wszystkim stopniem redukowania prędkości, aż do pełnego zatrzymania włącznie.
Tempomat CCS
Za pomocą przycisku, umieszczonego zazwyczaj przy kole kierownicy, zatwierdzana jest wybrana prędkość jazdy. Sterownik pobiera sygnał prędkości jazdy z czujników w kołach i sterując mocą silnika utrzymuje tę zadaną prędkość. Przerwanie działania tempomatu odbywa się poprzez naciśniecie pedału hamulca – po naciśnięciu na pedał przyspieszenia (przy włączonym tempomacie), samochód przyspieszy, a po puszczeniu pedału gazu zwolni naturalnie z zamkniętą przepustnicą do zadanej prędkości.
Adaptacyjny tempomat I generacji
Wczesne wersje ACC korzystają ze specjalnego czujnika (radaru), umieszczanego za atrapą chłodnicy. Jego zasięg obejmuje około 100 metrów drogi na pasie przed pojazdem. W razie wykrycia zbyt małego dystansu od auta poprzedzającego, system obniży prędkość samochodu do minimalnej prędkości wynoszącej 30-50 km/h . Do pełnego jej wytracenia i zatrzymania pojazdu potrzebna jest ingerencja kierowcy, informowanego sygnałem alarmowym o konieczności nacisku na pedał hamulca. Poniżej minimalnej prędkości tempomat się wyłącza.
Adaptacyjny tempomat II generacji
Urządzenia te umożliwiają nie tylko maksymalne wytracenie prędkości, ale również całkowite zatrzymanie samochodu. Oprócz zamontowanego z przodu samochodu czujnika radarowego długiego zasięgu (zakres jego efektywnego działania został zwiększony dwukrotnie, w porównaniu z aktywnymi tempomatami pierwszej generacji), ACC drugiej generacji wyposażony jest również dodatkowo w czujnik radarowy krótkiego zasięgu. Jest on w stanie śledzić nawet ponad 30 ruchomych obiektów jednocześnie (na przestrzeni od 0,2 do 30 metrów przed pojazdem).
W momencie wystąpienia krytycznej sytuacji (np. nagłego hamowania auta poprzedzającego), wysyłany jest sygnał potrzebny do pełnego zadziałania układu hamulcowego i w konsekwencji zatrzymania samochodu. Dzieje się tak równiez w normalnym ruchu drogowym, na przykład podczas jazdy w korku tempomat doprowadza do zatrzymania pojazdu.
Najbardziej rozbudowane wersje tempomatów ACC drugiej generacji współpracują ponadto z innymi układami zamontowanymi w pojazdach, m.in. z systemem Start&Stop , umożliwiającym wyłączanie silnika i ponowne ruszanie oraz układem PreSafe, osuszającym hamulce i napinającym pasy w celu uchronienia przed skutkami ewentualnej kolizji. Najnowsze wersje adaptacyjnych tempomatów są w stanie zatrzymać pojazd, a jeśli pojazd poprzedzający po zatrzymaniu w ciągu ok. 3 s ruszy z miejsca, również tempomat wprawi pojazd w ruch.
Obecnie coraz częściej tempomaty adaptacyjne łączy się z systemami niezależnymi od ruchu pojazdu , m.in. układem nawigacji satelitarnej , w celu zwiększenia wydajności lub bezpieczeństwa jazdy. Przykładowo uwzględnia wzniesienia do lekkiej redukcji prędkości, a na zjazdach ją zwiększa. Podczas szybkiej jazdy, np. drogą ekspresową, tempomat zmniejsza prędkość przed łukami. Są również tempomaty dostosowujące się do ograniczeń prędkości na drodze.
- Wskaźnik kontroli ciśnienia w oponach
- BAP - Barometric Air Pressure Sensor
- OPC - Opel Performace Center
Szukaj wg kategorii
- Bezpieczeństwo
- Diagnostyka / elektronika
- Instytucje / technologie
- Nadwozia / pojazdy
- Prowadzenie / zawieszenie
Szukaj alfabetycznie
Lista haseł.
- 4WD - Four Wheel Drive
- 4WS - Four Wheel Steering
- A/D - Auto Drive
- A/D Converter - Analog to Digital Converter
- AAC - Auxiliary Air Control
- AAP - Auxiliary Air Pump
- AAS - Auto Adjusting Suspension
- AAV - Auxiliary Air Valve
- ABC - Active Body Control
- ABCM - Antilock Brake Control Module
- ABD - Automatic Blocking of Differential
- ABS (Anti-Lock Breaking System)
- ACC (Adaptive Cruise Control)
- ACC-SCU - Zespół czujnika radarowego ze sterownikiem adaptacyjnej regulacji prędkości jazdy
- ACD - Active Center Differential
- ACEA - Association des Constructeurs Europeens d’Automobiles
- ACIS - Acoustic Control Induction System
- ACL - Air Cleaner
- ACMC - Air Conditioning Magnetic Clutch
- ACP - Aircon Pressure
- ACR - Automatic Code Reader
- ACRS - Air Cushion Restraint System
- ACS - After Crash System
- ACT - Air Charge Temperature Sensor
- Active Suspension (zawieszenie aktywne)
- ACV - Air Control Valve
- ADAC - Allgemeiner Deutscher Automobil-Club
- ADC - Active Damper Control
- ADC - Analog to Digital Converter
- ADK - AbstandDistanzKontrolle
- ADM - Automatic Drivetrain Management
- ADR - Automatic Distance Regulation
- ADS - Advanced Disk System
- ADU - Airbag Diagnostic Unit
- ADW - Analog-Digital Wandler
- AED - Automatic Enrichment Device
- AFL - Adaptive Front/Forward Lighting
- AFM - Air Flow Meter
- AFR (A/F) - Air to Fuel Ratio
- AFS - Active Front Steering
- AFS - Air Flow Sensor
- AFV - Alternative Fuel Vehicle
- AG - Automatische Getriebe
- AGB - Automatischer Geswindigkeits Begrenzer
- AGM - Absorbent Glass Matt
- AGS - Adaptive GetriebeSteuerung
- AHC - Active Height Control
- AHR - Active Head Restraint
- AI - Air Injection
- AIMA - Association of International Automobile Manufactures
- Airmatic DC - Airmatic Dual Control
- AIRS - Air Injection Reaction System
- AIS - Air Induction System
- AIS MOTOR - Automatic Idle Speed Motor
- AIV - Air Induction Valve
- AK - Automatische Kupplung
- Akcyza na LPG
- AKEK - Automatische Kindersitzerkennung
- AKF - AktivKohleFilter
- AKR - Antiklopfregelung
- AKS - Automatische Kupplung System
- AKSE - Automatische Kindersitzerkennung
- Aktywne czujniki
- Akumulator litowo-jonowy
- AL - Active Lenkung
- ALB - Anti - Lock - Breaking
- ALB - Automatischer Lastabhangiger Bremskraftregle
- ALC - Automatic Level Control
- ALCL - Assembly Line Communications Link
- ALDL - Assmebly Line Diagnostic Link
- ALG - Achlastgeber
- ALL - Automatic Load Leveling
- ALR - Automatic Locking Retractor
- ALT - Alternator
- ALWR - Automatische Leucht Weiten Regelung
- AMG - Aufrecht Melcher Großaspach
- Amortyzator
- AMR - Antriebs Momenten Regelung
- AMT - Automated Manual Transmission
- AMVAR - Elektroniczny system zmiennej amortyzacji
- ANC - Active Noise Control
- AOS - Automotive Occupancy Sensing
- AP - Accelerator Pedal
- AP - Air Pump
- Aparat zapłonowy (rozdzielacz)
- APB - Automatic Parking Brake
- APC - Accelerometer Pilot Control
- API - American Petroleum Institute
- APS - Absolute Pressure Sensor
- APS - Accelerator Pedal Sensor
- APS - Acoustic Parking System
- APS - Adaptive Pneumatic Suspension
- APV - All Purpose Vehicle
- AQS - Air Quality Sensor
- Aquaplaning (akwaplancja)
- ARF - AbgasRuckFuhrung
- ARR - AbgasRuckfuhrRegelung
- ARS - Advanced Restraint System
- ART - Abstands Regelungs Tempomat
- ARTS - Adaptive Restraint Technology System
- AS - AbschleppSchutz
- AS - Air Suction
- ASB - Active Sensor Bearing
- ASBS - Anti-Schleuder-Brems-System
- ASC - Acceleration Skid Control, Anti Skid Control, Anti-Slipping Control
- ASC - Active Stability Control, Automatic Stability Control
- ASC+T - Automatic Stability Control plus Traction
- ASCD - Automatic Speed Control Device
- ASD - Automatic Shut - Down
- ASD - Automatisches Sperr Differential
- ASDM - Airbag System Diagnostic Module
- ASF - Audi Space Frame
- Asferyczne lusterko zewnętrzne
- ASG - Automatic Stop and Go
- ASG (Automated Shift Gearbox)
- ASIC - Application Specific Integrated Circuit
- ASM - Alarm Siren Module
- ASM - Auto Shift Manual
- ASPV - Air Suspension Pressure Valve
- ASS - Active Service System
- ASSP - Application Specific Standard Product
- ASSYST - Active Service System
- AST - Automated Shift Transmission
- ASV - Air Suction Valve
- Asystent parkowania
- Asystent podjazdu
- Asystent zjazdu
- AT - Automatic Transmission
- ATC - Adaptive/Automatic Transmission Control
- ATC - Automatic Temperature Control
- ATC - Automatic Traction Control
- ATCM - Automatic Transmission Control Module
- ATCS - Active Torque Control System
- ATF - Automatic Transmission Fluid
- ATI - Advanced Turbo Intercooling
- ATL - Abgastturbolader
- ATM - Actuator Test Mode
- ATR - Abgastemperaturregulung
- ATR - Automatic Transmission Relay
- ATS - Air Temperature Sensor
- ATV - All Terrain Vehicle
- ATWS - Anti Theft Warning System
- ATX - Automatic Transaxle
- AU - Abgasuntersuchung
- Auto Hold - automatyczny hamulec postojowy
- Autocasco - polisa AC
- Automatyczna skrzynia biegów
- AVAC - Advanced Vehicle Analysis Computer
- AVE - Average
- AVG/AVE - Average
- AVOM - Analog VOLT/OHM Meter
- AVS - Adaptive Variable Suspension
- AVT - Active Valve Train
- AWC - All Wheel Control
- AWD - All Wheel Drive
- AWS - All Wheel Steering
- AWS - Anti Whiplash Seat
- AYC - Active Yaw Control
- BAC - Bypass Air Control
- Backfire (eksplozja niekontrolowana)
- BACV - Bypass Air Control Valve
- Bagażnik dachowy
- Bagnet olejowy
- Bar (ciśnienie)
- BARO - Barometric Pressure Sensor
- BAS - Brake Assist
- BAS - Brake Assist (Asystent hamowania)
- BAT MS - Battery Managemet System
- BATT - Battery
- BBDC - Before Bottom Dead Centre
- BBW - Brake by Wire
- BC - Board Computer
- BCDD - Boost Control Deceleration Device
- BCM - Body Control Module
- BDC - Bottom Dead Centre
- BDD - Battery Disconnect Device
- BDE - Benzin Direkteinsspritzung
- BDW - Brake Disc Wiping
- Belka skrętna
- BEV - Battery Electric Vehicle
- Bezpieczeństwo bierne
- Bezpieczeństwo czynne
- Bezpieczniki samochodowe
- Bezpośredni wtrysk paliwa
- Bezwładnościowe pasy bezpieczeństwa
- Bęben hamulcowy
- BI-litronic
- BID - Breakerless Inducive Discharge
- Bieg jałowy
- Bimetalowy włącznik
- BKV - Bremskraftverstarker
- BLIS - Blind Spot Information System
- Blok silnika
- Blokada mechanizmu różnicowego
- Blokada tylnego mostu
- BM - Board Monitor
- BMS - Battery Management System
- BOB - Breakout Box
- Boczne poduszki powietrzne
- Bokser (boxer)
- BOO Switch - Brake On/Off Switch
- BOV - zwór blow off valve
- BP - Barometric Pressure
- BP - Brake Pedal
- BPC - Boost Pressure Control
- BPS - Barometric Pressure Sensor
- BPV - Back Pressure Transducer Valve
- BPV - Battery Positive Voltage
- BPV - By-Pass Valve, bypass (zawór obejściowy)
- BPW - Base Pulse Width
- BRA - Brake
- BRK - Brake
- BSU - Bosch Smoke Unit
- BSW - Brake Switch
- BTCS - Brake Traction Control System
- BTDC - Before Top Dead Centre
- BVSV - Bimetal Vacuum Switching Valve
- CA - Cranking Amps
- CA - Crankshalf Aangle
- CAA - Clean Air Act
- CAB - Controller Anti - Lock Brake
- CAC - Charge Air Cooler
- CAD - Computer Aided Design
- CAGS - Computer Aided Gear Shift
- CAI - Cold Air Intake
- CAL - Computer Aided Lighting
- CAM - Camshaft
- CamInCam (CIC)
- CAN - Control Area Network
- CANPSV - Canister Purge Solenoid Valve
- CARB - California Air Resources Board
- CARB - Carburrettor
- CARE - Auto - Concept for Advanced Recycling and Environment - Automotive
- CARIN - Car Information and Navigation System
- Cartronic - Car Electronic
- CAS - Collision Avoidance System
- CAT - Catalyst
- CATC - Catalytic Converter
- CATS - Computer Active Technology Suspension
- CB - Choke Breaker
- CB - Citizens Band
- CB - Contact Breaker
- CBC - Cornering Brake Control
- CBS - Combined Braking System
- CC - Catalytic Converter
- CC - Coupe - Cabrio
- CC - Cubic Centimeter
- CCA - Cold Crankking Amps
- CCC - Computer Command Control
- CCM - Check Control Module
- CCMC - Committee of Common Market, Automobile Constructors
- CCP - Charcoal Canister Purge
- Ccp controlled canister purge
- CCS - Cruise Control System
- CCV - Closed Crankcase Ventilation
- CDC - Compact Disc Changr
- CDC - Continuous Damping Control
- CDCV - Canister Drain Cut Valve
- CDI - Capacitor Discharge Ignition
- CDI - Common Rail Direct (Diesel) Injection
- CDM - Calibration Data Manager
- CDM - Control and Diagnostic Module
- CDP - Compact Disc Player
- CDR - Crankcase Depression Regulator Valve
- CDS - Computer Diagnostic System
- CDS - Crankshaft Delay Sensor
- CDTI - Common rail Diesel Turbo Injection
- Centralny zamek
- Cewka zapłonowa
- Check engine - Sprawdź silnik!
- CID - Cylinder Identyfication Device
- Cięgno Bowdena
- Cięgno elastyczne
- Ciśnienie doładowania
- Ciśnienie oleju
- Ciśnienie wtrysku
- City Safety
- CKD - Completely Knocked-Down
- Climatic - Klimatyzacja półautomatyczna
- Climatronic - Klimatyzacja automatyczna
- CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) - sprężony gaz ziemny
- Coming/Leaving Home - Funkcja odprowadzania
- Common rail (wspólna szyna)
- Comprex - Rodzaj turbosprężarki
- Corner - Funkcja doświetlania zakrętów
- CR - Common Rail
- Crash - test
- CRS - Common Rail System
- Cruise control adaptacyjny
- CVH - Compound Valve angle Hemispherical combustion chamber
- CVT - Continuously Variable Transmission
- CVTC - Continuously Variable Timing Control
- Cykl Atkinsona
- Cykl Millera
- Czołowe poduszki powietrzne
- Czujnik deszczu
- Czujnik jakości powietrza
- Czujnik parkowania
- Czujnik położenia wału korbowego (Crank Angle Sensor)
- Czujnik poziomu oleju
- Czujnik spalania stukowego
- Czujnik świateł
- Czujnik zderzeniowy
- Czujnik zmierzchu
- Czynne bezpieczeństwo
- D - Drive Position
- D4 - Direct injection 4 stroke gasoline engine
- DAC - Driver Alert Control
- DCI - Diesel Common Rail Injection
- DHP - Drive Horse Power - moc na kołach
- DIN - Deutsche Industrie Norm
- DIS - Direct Ignition System
- DIS - Distributorless Ignition System
- DIS - Driver Information System
- DKZ - dwumasowe koło zamachowe
- Docieranie silnika
- DOHC - Double Over Head Camshaft
- Dolny martwy punkt
- Doładowanie
- DPF - Diesel Particulate Filter
- Drążek reakcyjny (Panharda)
- Drążek skrętny
- Drążek ustalający
- Droga hamowania
- Drut grzany
- DSA - Dual Stage Airbag
- DSC - Dynamic Stability Control
- DSG - Direct Shitf Gearbox
- DSR - Digital Service Register
- DSR - Dynamic Steering Response
- DSTC - Dynamic Stability and Traction Control
- DTC - Diagnostic Trouble Code
- DTC - Dynamic Traction Control
- DTM - Deutsche Tourenwagen Masters
- Dummy (dummies), Hybrid 3
- DV - zawór dump valve
- Dyferencjał
- Dynamiczne doświetlanie zakrętów
- E-gas - Elektroniczny pedał przyspieszania
- EAI - Electronic Advance Ignition
- EAP - Electronic Accelerator Pedal
- EAS - Electronic Air Suspension
- EAS - Electronic Assisted Steering
- EBA - Emergency Brake Assist
- EBCA - Electronic Brake Control Assistance
- EBD - Electronic Brakeforce Distribution
- EBS - Electronic Braking System
- EBV - Electronische Bremskraft Verteilung
- ECC - Electronic Climate Control
- ECE - Economic Commission for Europe
- ECU - Electronic Control Unit
- EDL - Electronic Differential Locking
- EDS - Electronic Differential System/Elektronische DifferentialSperre
- EEC - Evaporative Emission Control
- EFE - Early Fuel Evaporation
- EFI - Electronic Fuel Injection
- EGI - Electronic Gas Injection
- EGO - Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor
- EGR - Exhaust Gas Recirculation
- EHB - ElektroHydraulische Bremse
- Elektroniczny pedał przyspieszania
- Elektrozawór
- Elektryczny hamulec postojowy EPB
- EMB - Electromechanical Breaking System
- Energia kinetyczna
- EOBD - European On Board Diagnostic
- EPS - Electronic Power Steering System
- ESC - Electronic Stability Control
- ESP (ESC, VSC, DSC)
- ETC - Electronic Throttle Control
- Euro-NCAP - European New Car Assessment Programme
- Euroconector
- EVA - Emergency Valve Assistance
- Evap System - Evaporative Emission System
- EZEV - Equivalent Zero Emission Vehicle
- Facelifting
- Fazy rozrządu
- FF - Freiflachentechnik
- FIA - Federation Internatiole de I’Automobile
- Film grzany
- Filtr cząstek stałych
- Filtr fazy ciekłej
- Filtr fazy lotnej
- Filtr oleju
- Filtr paliwa
- Filtr powietrza
- Filtr przeciwpyłkowy
- Fotele klimatyzowane
- FPS - Fire Prevention System
- Front Assist
- FSI - Fuel Stratified Injection
- Funkcja gala
- FWD - Front Wheel Drive
- Gaźnik (karburator)
- GDI - Gasoline Direct Injection
- Generator HHO
- Geometria kół
- Głębokość brodzenia
- Głowica silnika
- GPS - Global Positioning System
- Grzybek zaworu
- GT - Gran Turismo
- GTI - Gran Tourer Injection
- Gwarancja mobilności
- HAC - Hill Start Assist Control
- Hak holowniczy
- Halogenowy cykl
- Hamulec bębnowy
- Hamulec elektromechaniczny
- Hamulec najazdowy
- Hamulec postojowy (ręczny)
- Hamulec tarczkowy
- Hamulec tarczowy
- Hamulec taśmowy
- HBA - Hydraulic Brake Assist
- HDC - Hill Descent Control
- HDI - High Pressure Direct Injection
- HHC - Hill Hold Control
- Hill holder
- Holowanie pojazdu
- Holzgas - Generator Imberta
- HPI - High Pressure Injection
- HSA - Hill Start Assist
- HUD - Head-up Display
- Hybrydowy napęd
- Hydroplaning
- HYGE - High Impulse Generator
- I-CTDI - Inteligent Common rail Turbocharged Direct Injection
- I-DTEC - Inteligent Diesel Technology
- IC - Inflatable Curtain
- ICs - Integrated Circuits
- IDE - Injection Directe Essence
- Immobiliser
- Indeks nośności
- Indeks prędkości
- Infotainment
- Inteligentna poduszka powietrzna
- Intercooler
- JTD - uniJet Turbo Diesel
- JTS - Jet Thrust Stoichiometric
- Kadłub silnika
- Kanał dolotowy
- Katalizator (konwerter lub reaktor katalityczny)
- Kategoria AM prawa jazdy
- Kąt natarcia
- Kąt pochylenia koła
- Kąt rampowy
- Kąt rozwidlenia
- Kąt wyprzedzenia wtrysku
- Kąt wyprzedzenia zapłonu
- Kąt zejścia
- KERS - Kinetic Energy Recovery System
- KESSY - Keyless Entry Start and Exit System
- Kierownica wielofunkcyjna
- KJS - Konkursowa Jazda Samochodem
- Klatka bezpieczeństwa
- Klimatyzacja
- Klimatyzacja (A/C - Air Conditioning)
- Klocki hamulcowe
- KM (koń mechaniczny)
- Koce grzewcze
- Kolektor dolotowy o zmiennej geometrii
- Kolektor ssący (dolotowy)
- Kolizja drogowa
- Kolo zamachowe
- Kolumna kierownicy
- Kolumna MacPhersona
- Kolumna resorująca
- Koło pasowe
- Koło pierścieniowe
- Koło słoneczne
- Koło zamachowe dwumasowe
- Koło zębate
- Kombilimuzyna
- Komora spalania
- Komora wirowa
- Komora wstępna
- Kompresor (sprężarka klimatyzacji)
- Komputer pokładowy
- Korektor siły hamowania
- KOZ - Kąt opóźnienia zapłonu
- Krzyżaki wału napędowego
- Ksenony (ksenonowe oświetlenie)
- Kurtynowe poduszki powietrzne
- Lakier wodorozpuszczalny
- Lane Assist
- LED - Light Emitting Diodes
- LEV - Low Emission Vehicle
- Leżakowanie opon
- Liczba cetanowa (LC)
- Liczba oktanowa
- Liczba zasadowa TBN (Total Basic Number)
- Light assistant
- LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas)
- LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas)
- LSD - Limited Slip Differential
- Lusterko fotochromatyczne
- Luz zaworowy
- Łańcuch rozrządu
- Łańcuchy śniegowe
- Łącznik stabilizatora
- Łożysko koła
- Łożysko oporowe
- M+S - Mud and Snow
- MAP - Manifold Absolute Pressure sensor
- Masa resorowana i nieresorowana
- Masy nieresorowane
- MAT - Manifold Air Temperature
- Mata wygłuszająca
- Max inflation
- MBA - Mechanical Brake Assistant
- MDI - Mobile Device Interface
- Mechanizm różnicowy
- Mieszanka paliwowo - powietrzna
- Mieszanka stechiometryczna
- MIL - Malfunction Indicator Light
- Miska olejowa
- MKD - Medium Knocked Down
- Moment obrotowy
- Most napędowy
- Mover (urządzenie manewrowe)
- MPI - Multi Point Injection
- MPV - Multi Purpose Vehicle
- MSR - Motor Schleppmoment Regulung
- Multiplikator
- Multitronic
- Myjnia parowa
- Nadsterowność
- Nadwozie ocynkowane
- Nagrzewnica
- Napęd hydrauliczny
- Napęd pneumatyczny
- Napinacz pasa bezpieczeństwa
- NASCAR - National Assocation for Stock Car Auto Racing
- Nawigacja satelitarna
- Nm - Niutonometr
- NOS - Nitrous Oxide System
- NVA - Night Vision Assistant
- OBD - On Board Diagnostics
- Obieg oleju
- Obieg w układzie chłodzenia
- Ochrona antykorozyjna nadwozia
- Ochrona pieszego
- Odpowietrznik
- Odzysk energii
- Ogniwo paliwowe
- Ogranicznik napięcia pasa
- Ogrzewanie postojowe
- OHC - Over Head Camshaft
- OHV - Over Head Valves
- Olej silnikowy
- ON - Olej napędowy
- Opona diagonalna
- Opona radialna
- Opona samouszczelniająca się
- Opory ruchu
- Oznaczenie opon
- Oznaczenie RF
- Oznaczenie XL
- Paliwo zimowe
- Pałąki przeciwkapotażowe
- Pas bezpieczeństwa
- Pasek klinowy (wieloklinowy)
- Pasek rozrządu
- PCU - Power Control Unit
- PDC - Park Distance Control
- PDR (Paintless Dent Repair)
- Pedały bezpieczne
- Pencil coils
- Pirotechniczne napinacze pasów
- Płyn hamulcowy
- Płyta podłogowa
- Podgrzewana szyba przednia
- Podparcie lędźwiowe i boczne
- Podsterowność
- Poduszka kolanowa
- Poduszka powietrzna (airbag)
- Poduszki powietrzne
- Pojemność bagażnika
- Pojemność skokowa
- Pompa oleju
- Pompa paliwa
- Pompa wtryskowa
- Pompowanie azotem
- Pompowtryskiwacz
- Popychacze hydrauliczne
- Poziomowanie karoserii
- Półautomatyczna skrzynia biegów
- Półosie napędowe
- Przegroda czołowa
- Przekaźniki elektryczne
- Przekładnia
- Przekładnia główna
- Przekładnia hydrokinetyczna
- Przekładnia kierownicza
- Przekładnia planetarna
- Przekładnia ślimakowa
- Przekładnia zębatkowa
- Przełożenie
- Przepływomierz
- Przepustnica
- Przewód hamulcowy
- Przewód paliwowy
- Przewód zapłonowy
- QOHC - Quadruple Over Head Camshaft
- Rama podwoziowa
- RDS - Radio Data System
- RDW - Tire Pressure Warning System
- Rear assist
- Recyrkulacja powietrza
- Reflektory bi-ksenonowe
- Reflektory ksenonowe
- Reflektory laserowe
- Regulacja podparcia odcinka lędźwiowego
- Regulator faz rozrządu
- Rekuperacja
- Resor piórowy
- Ropa naftowa
- Rozstaw osi
- Rozstaw otworów mocujących
- RTI - Road and Traffic Information
- RWD - Rear Wheel Drive
- SAHR - Saab Active Head Restraint
- Samochód kempingowy (campingowy)
- SBC - Sensonic Brake Control
- SDI - Saug Diesel Direct Injection
- SDIS - Saab Direct Ignition System
- Selespeed (przekładnia)
- Servotronic
- Short shifter
- Side assist
- Silentblok (tuleja metalowo-gumowa)
- Silnik chłodzony cieczą
- Silnik chłodzony powietrzem
- Silnik czterosuwowy
- Silnik dwusuwowy
- Silnik krokowy
- Silnik spalania zamkniętego
- Silnik spalinowy
- SIPS - Side Impact Protection System
- SKD - Semi Knocked Down
- Skok jałowy
- Skrzynia biegów
- Skrzynia korbowa
- Skrzynia redukcyjna
- Skrzynia rozdzielczo-redukcyjna (reduktor)
- Skrzynia sekwencyjna
- SLS - Self Levelling Suspension
- SOHC - Single Over Head Camshaft
- Solar sunroof
- Sonda lambda
- Spalanie stukowe
- Spawy laserowe
- SPI - Single Point Injection
- Spinning wheels
- Sprężyny zawieszenia
- Spryskiwacze reflektorów
- Sprzegło samonastawne
- Sprzęgło Haldex
- Sprzęgło hydrokinetyczne (hydrauliczne)
- Sprzęgło wiskotyczne
- SRS - Supplemental Restraint System
- Stabilizator
- Statyczne doświetlanie zakrętów
- STC - Stability and Traction Control
- Sterownik silnika
- Stopień sprężania
- Strefy kontrolowanego zgniotu
- Submarining
- SUV - Sport Utility Vehicle
- SVC - Saab Variable Compression
- Synchronizator
- System pokolizyjny
- świeca platynowa
- Światła do jazdy dziennej
- Światła drogowe
- Światła mijania
- Światła pozycyjne
- świeca zapłonowa
- Świeca żarowa
- Tarcza hamulcowa
- TCS - Traction Control System
- TDCI - Turbo Diesel Common rail direct Injection
- TDI - Turbodiesel Direct Injection
- TDS - Intercooled Turbodiesel
- Tempomat (Cruise Control)
- Test zderzeniowy
- TMC - Traffic Message Channel
- TPMS (Tyre Pressure Monitoring System)
- Trzypunktowe pasy bezpieczeństwa
- TS - Twin Spark
- TSI - Turbo Stratified Injection
- TSR - Traffic Sign Recognition
- Turbodoładowanie
- Turbodziura
- Turbosprężarka
- Turbosprężarka o zmiennej geometrii
- TUV - Technischer Überwachungsverein
- Twincharger
- Układ chłodzenia
- Układ hamulcowy
- Układ jezdny
- Układ kierowniczy
- Układ napędowy
- Układ smarowania
- Układ wtryskowy
- Układ wydechowy
- Układ zapłonowy
- Uszczelka podgłowicowa
- Uwarstwione spalanie
- Valvetronic
- Vario xenon
- Variocam plus
- VCU - Viscous Coupling Unit
- VDC - Vehicle Dynamics Control
- Videorejestrator
- VSC - Vehicle Stability Control
- VTEC - Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control
- VTG - Variable Turbinen Geometrie
- VVC - Variable Valve Control
- VVT-i - Variable Valve Timing with inteligence
- Wał Kardana
- Wał korbowy
- Wał napędowy
- Wałek królewski
- Wałek rozrządu
- Wałki wyrównoważające
- WHIPS - Whiplash Protection System
- Wielowahaczowe zawieszenie
- WIL - Whiplash Injury Lessening
- Włókno węglowe
- WRC - World Rally Championship
- Wspomaganie układu kierowniczego
- Współczynnik Cx
- Wstępne napinacze pasów
- Wtrysk paliwa
- Wtrysk pilotażowy
- Wtryskiwacz
- Wtryskiwacz benzynowy (wielopunktowy)
- Wyciągarka samochodowa
- Wycieraczki samochodowe
- Wyłącznik wstrząsowy
- Wymiary opon
- Wymiennik ciepła
- Wypadanie zapłonów
- Wypadek drogowy
- Wzmocnienia boczne
- Zagłówki aktywne
- Zaprawka lakiernicza
- Zawieszenie
- Zawieszenie hydropneumatyczne
- Zawieszenie niezależne
- Zawieszenie pneumatyczne
- Zawieszenie wielowahaczowe
- Zawieszenie zależne
- Zawory przełączające
- Zbieżność kół
- Zbiornik toroidalny
- Zbiornik walcowy
- Zderzaki absorbujące energię zderzenia
- Zderzenie boczne
- Zderzenie czołowe
- Zderzenie ze słupem
- Zespół napędowy
- Zestaw naprawczy do opon
- ZF Servolectric
- ZLEV - Zero Emission Vehicle
- Zmienne fazy rozrządu
- Zwrotnica koła
- Żarówka halogenowa
- Katalog nowych aut
- Dane techniczne
- Raporty zużycia paliwa
- Nasze pomiary
- Ceny aut używanych
- Dziennik kosztów
- Opinie o instalacjach LPG
- Testy zderzeniowe
- Mapa portalu
- Rankingi aut
- Wirtualny alkomat
- Benzyna czy diesel?
- Kalkulator LPG
- Kredyt czy leasing?
- Mapa stacji paliw
- Sprawdź VIN
- Oceń instalację LPG
- Oceń motocykl
- Pierwsza pomoc
- Dokumenty dla kierowcy
- Prawo jazdy
Popular Searches
SUBARU STARLINK In-Vehicle Technology
Eyesight Driver Assist Technology
Parts and Accessories
Helpful Links
Customer Service
Vehicle Recalls
All Vehicles
Special Offers
Local Inventory
Our Company
Meet the Subaru Family
What is adaptive cruise control (acc).
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) is an intelligent driver assistance feature that works as an enhancement to traditional cruise control. Using a system of advanced sensors such as radar and cameras, ACC determines the speed and conditions of surrounding traffic and automatically adjusts cruising speed to maintain a safe distance within the flow of traffic. Many ACC systems can also recognize sudden changes in traffic conditions and alert the driver to take action to prevent a crash.
Depending on vehicle manufacturer and the system itself, any number of other terms might be used interchangeably with Adaptive Cruise Control, including:
- Active Cruise Control
- Dynamic Cruise Control
- Automatic Cruise Control
- Intelligent Cruise Control
- Smart Cruise Control
- Radar Cruise Control
How does Adaptive Cruise Control Work?
ACC uses a set of intelligent sensors including radar, lidar, lasers, GPS, and cameras. These sensors are placed around a vehicle’s exterior to monitor the road and nearby vehicles. Gathering real-time data on the distance away and speed of the vehicle in front, these sensors allow the ACC system to adjust the car’s speed as-needed. Typically, the driver sets their desired cruising speed when they engage ACC on the highway. The system then automatically accelerates and decelerates to stay at a safe distance from other cars within the flow of traffic.
Much like using traditional cruise control, activating ACC is intentionally simple so that a driver can easily use it while keeping their eyes safely on the road. Generally, the dedicated ACC button or switch is located on the steering wheel or control panel. Pressing or toggling this mechanism allows the driver to set their initial cruising speed. In some systems, drivers can also set their desired following distance.
While operating, certain ACC systems can take extra measures for safety and convenience purposes:
- Maintaining a particular distance from vehicles ahead
- Making complete stops in traffic and restarting from a complete stop when traffic resumes
- Remaining engaged at low speeds in city traffic
- Anticipating and automatically slowing around upcoming curves
- Adjusting to posted speed limits as they change
Once in operation, the ACC system remains working until the driver disengages by either pressing the brake pedal or manually deactivating the system using the dedicated switch or button. Sometimes, ACC will use visual and audio cues to alert the driver to brake if it detects a possible collision ahead. In these instances, the driver must then re-engage the system once traffic resumes.
Benefits of Adaptive Cruise Control
Some of the benefits of adaptive cruise control include creating a more relaxed driving experience, particularly during long road trips and on highways, thanks to the system’s ability to adjust automatically to traffic speed variations and road conditions. Additionally, ACC encourages safe driving practices and helps reduce crash risk by monitoring following distance and alerting the driver or intervening if a vehicle is quickly approaching. Drivers using ACC may also see improved fuel efficiency, especially on the highway, since the system helps maintain an even speed and reduces unnecessary acceleration and braking.
Advanced Adaptive Cruise Control in Subaru Vehicles
The Subaru application of ACC is known as Advanced Adaptive Cruise Control. This feature functions seamlessly as part of our EyeSight ® Driver Assist technology —a comprehensive suite of safety features designed to enhance the driving experience. Nearly all Subaru models and trims come standard with EyeSight and Advanced Adaptive Cruise Control, including some of our most popular models like the Outback , Forester , Crosstrek , and Impreza . EyeSight is an available feature on our performance sports models with automatic transmissions, including the WRX and the BRZ , as well as those with manual transmissions.
Complementing its active cruise control functionality, EyeSight includes additional advanced features including Pre-Collision Braking and Throttle Management, Automatic Emergency Steering, Lane Centering, and Lane Departure Assist designed to help keep drivers safer. In particular, Lane Departure Assist and Lane Centering monitor lane markings and can help assist drivers with steering to avoid accidental drifting into another lane. The advanced ACC sensors can also recognize another driver approaching and adjust your vehicle’s placement within the lane to create a safer distance on all sides.
Read more about our EyeSight technology.
Discover the Safety and Convenience of Subaru EyeSight Driver Assist Technology. Visit Us to Experience it in Action and Find your Perfect Subaru Today!
Advanced adaptive cruise control is a useful feature that can help make driving easier, smoother, and safer. Explore Subaru Vehicles equipped with the full suite of EyeSight features today!
Explore Subaru
Our vehicles will inspire drivers like you to become a Subaru owner for life. Find out what makes us more than a car company.
Connect with Us
About Subaru
Other Subaru Sites
© Subaru of America, Inc. Use of this site signifies your acceptance of the Terms & Conditions .
- Privacy Policies
- California Privacy
- Cookie and Ad Preferences
* MSRP does not include destination and delivery charges, tax, title, and registration fees. Destination and delivery includes handling and inland freight fees and may vary in some states. Prices, specifications, options, features, and models subject to change without notice. Select colors may be subject to an additional charge. See your retailer for more information.
** EPA-estimated fuel economy. Actual mileage may vary. For Crosstrek Hybrid and Solterra, EPA-estimated MPG equivalent on a full battery charge. Actual mileage will vary.
*** Limited warranties are contingent on age and mileage. Whatever comes first concludes the warranty.
† Connected Services depend on factors outside Toyota's control, including an operative telematics device, a cellular connection, GPS signal and the availability of a compatible wireless network, without which system functionality and availability may be limited or precluded, including access to response center and emergency support. Service may vary by vehicle and region. Apps and services subject to change at any time without notice. Requires app download/registration and subscription after trial (if applicable). Terms of Use apply. Data usage and charges may apply. To learn about Toyota’s connected services data collection, use, sharing and retention practices, please visit toyota.com/privacyvts
Safety Connect: Stolen vehicle police report required to use Stolen Vehicle Locator. Automatic Collision Notification activates only in limited circumstances.
Remote Connect: Use only if aware of circumstances surrounding vehicle and it is legal and safe to do so (e.g., do not remotely start engine if vehicle is in an enclosed space or vehicle is occupied by a child). Remote start/stop not available on manual transmission-equipped vehicles.
Drive Connect: Services not available in every city or roadway.
Service Connect: Information provided is based on the last time data was collected from the vehicle and is not real time data. Service Connect is not renewable as a stand-alone service and requires a subscription to any of Safety Connect, Remote Connect or Drive Connect upon trial expiration.
Wi-Fi Connect: Eligible vehicle and wireless service required. Wi-Fi Connect coverage and service not available everywhere. Valid in the contiguous U.S. and Alaska. Do not drive distracted. Go to att.com/solterra for terms and conditions. Up to 5 devices can be supported using in-vehicle connectivity. The Wi-Fi Connect trial begins at the time of enrollment activation and expires when 30 days or the earlier of 3GB of data is used or the 1-month period ends. Subscription required after trial. Integrated Streaming requires subscription for third-party provider services.
Subaru has the utmost respect for the environment and is a proud partner of Leave No Trace. Care was taken not to harm the environment when taking this photo.
The materials displayed on this website, including but not limited to all text, audio, video, images, photographs, illustrations, artwork, animation files and other graphics, names, logos, trademarks, and service marks, are property of Subaru or its parent or affiliated companies or its licensors and are protected by copyright, trademark, and other intellectual property laws. This site may be displayed, downloaded, and/or printed solely for your personal, non-commercial home use, provided that you do not delete or modify any copyright, trademark, or other proprietary notices. Any other use of the material on this site without the prior written consent of Subaru is strictly prohibited.
iPod and iPad are registered trademarks of Apple Inc.; Brembo is a registered trademark of Freni Brembo S.p.A.; Alcantara is a registered trademark of Alcantara S.p.A and Alcantara is produced by Toray Group.; Ultrasuede® is a registered trademark of Toray Industries, Inc.; TORSEN LSD® is a registered trademark of JTEKT TORSEN North America, Inc BBS is a registered trademark of BBS Kraftfahrzeugtechnik AG.; Bluetooth is a registered trademark of Bluetooth SIG, Inc.; HomeLink® and the HomeLink® house icon are registered trademarks of Gentex Corporation.; Tom Tom is a registered trademark of TomTom International BV; Aha and Harman Kardon are a registered trademarks of Harman International Industries, Inc.; Android is a trademark of Google Inc.; HD Radio is a registered trademark of iBiquity Digital Corporation.; SiriusXM and SiriusXM NavTraffic are registered trademarks of SiriusXM Satellite Radio, Inc.; iHeart is a registered trademark of Clear Channel.
PLEASE REVIEW THESE IMPORTANT DISCLOSURES.
Subaru of America, Inc. reserves the right to make changes at any time without notice or obligation to the information contained on this Internet site, prices, incentive programs, specifications, equipment, colors, materials, product illustrations and to change or discontinue models. All prices are based upon Manufacturer's Suggested Retail Prices ('MSRP') in U.S. dollars (unless otherwise indicated) and exclude taxes, title fees, licensing, options and destination charges unless specifically included. Retailers are independent businesses and are free to set their own retail prices. All information contained at this Internet site is intended for the USA market only.
** EPA-estimated fuel economy. Actual mileage may vary. For Crosstrek Hybrid and Solterra, EPA-estimated MPG equivalent on a full battery charge. Actual mileage will vary.
Ad-free. Influence-free. Powered by consumers.
The payment for your account couldn't be processed or you've canceled your account with us.
We don’t recognize that sign in. Your username maybe be your email address. Passwords are 6-20 characters with at least one number and letter.
We still don’t recognize that sign in. Retrieve your username. Reset your password.
Forgot your username or password ?
Don’t have an account?
- Account Settings
- My Benefits
- My Products
- Donate Donate
Save products you love, products you own and much more!
Other Membership Benefits:
Suggested Searches
- Become a Member
Car Ratings & Reviews
2024 Top Picks
Car Buying & Pricing
Which Car Brands Make the Best Vehicles?
Tires, Maintenance & Repair
Car Reliability Guide
Key Topics & News
Listen to the Talking Cars Podcast
Home & Garden
Bed & Bath
Top Picks From CR
Best Mattresses
Lawn & Garden
TOP PICKS FROM CR
Best Lawn Mowers and Tractors
Home Improvement
Home Improvement Essential
Best Wood Stains
Home Safety & Security
HOME SAFETY
Best DIY Home Security Systems
REPAIR OR REPLACE?
What to Do With a Broken Appliance
Small Appliances
Best Small Kitchen Appliances
Laundry & Cleaning
Best Washing Machines
Heating, Cooling & Air
Most Reliable Central Air-Conditioning Systems
Electronics
Home Entertainment
FIND YOUR NEW TV
Home Office
Cheapest Printers for Ink Costs
Smartphones & Wearables
BEST SMARTPHONES
Find the Right Phone for You
Digital Security & Privacy
MEMBER BENEFIT
CR Security Planner
Take Action
Guide to Adaptive Cruise Control
How this convenience feature works to reduce your stress on long drives

Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is like traditional cruise control, but smarter. ACC systems allow you to set a desired speed until your vehicle encounters slower-moving traffic. Then it will brake to maintain a set distance from the car ahead. Once the traffic starts moving again or if there is no longer a car in the lane ahead, ACC will accelerate to resume the previous set speed. Although ACC systems may take some getting used to, our survey respondents told us they appreciated the stress relief the feature brings.
“I use the feature mostly on the freeway and in stop-and-go traffic. I find it reduces tension and fatigue,” wrote a 2020 Subaru Outback owner. A 2018 Audi Q5 driver agreed. “It is so nice to just set it and let the car worry about the traffic,” they told CR.
The systems use lasers, radar, cameras, or a combination of those. If traffic slows to a stop, most ACC systems will bring the car to a complete stop, then bring it back up to speed when traffic gets going again. Others work only within certain speeds and/or might not start to accelerate automatically.
Adaptive cruise control (ACC): Cruise control that also assists with acceleration and/or braking to maintain a driver-selected gap to the vehicle in front. Some systems can come to a stop and continue while others cannot. If the car comes to a full stop, you may have to press the accelerator or a button on the steering wheel to start moving again.
Not all systems work at low speeds, so drivers who plan to use ACC in slow traffic should check the limitations of any system they plan to buy. These particular systems will often have the words “traffic jam” or “stop and go” in their name.
These features are usually activated using a button on the steering wheel with the image of a car next to a speedometer with an arrow pointing at it. A conventional cruise control system does not automatically keep a set distance away from the car in front, and it is indicated by a similar logo without the car next to the speedometer. A tip to know if your car has adaptive cruise control or regular cruise control is to look for the “gap distance” button, which usually shows a symbol of a car with horizontal distance bars in front. This button will determine how much space your car leaves between its front bumper and the rear of the car it is following.
In our most recent survey, we asked CR members to rate their experiences with the advanced safety and driver assistance systems on their model-year 2017 to 2022 cars. Respondents answered questions about their satisfaction with the systems. The survey covered about 47,000 vehicles. Most respondents told us they were “very satisfied” with ACC. Satisfaction was higher for older drivers.
OVERALL SATISFACTION
What to Look For in an Adaptive Cruise Control System
Every ACC system works slightly differently, says Kelly Funkhouser, manager for vehicle technology at CR. Some do a better job than others at recognizing merging traffic and automatically apply the brakes, while others wait too long to slow your car, requiring the driver to take control—especially when a vehicle in front of you cuts you off with a close merge.
“Most ACC systems can only be set to speeds above 20 mph but will slow the vehicle to speeds below that in stop-and-go traffic,” she says. “There are a few systems out there that don’t bring the car all the way to a stop but instead just shut off at low speeds. That can be dangerous when you’re traveling behind another slowing vehicle.” She recommends reading the automaker’s website closely and learning about the speed ranges before using ACC while on your test drive.
ACC is meant for convenience, not as a replacement for an alert driver, Funkhouser says. So don’t use adaptive cruise control as an excuse to get distracted. “Just because the car is controlling your speed doesn’t mean that you can check out,” she says. “These systems do not do well at detecting or slowing for vehicles ahead if you approach them at a high rate of speed. The driver should always be monitoring the surrounding traffic and looking ahead for potential hazards.”
Keith Barry
Keith Barry has been an auto reporter at Consumer Reports since 2018. He focuses on safety, technology, and the environmental impact of cars. Previously, he led home and appliance coverage at Reviewed; reported on cars for USA Today, Wired, and Car & Driver; and wrote for other publications as well. Keith earned a master’s degree in public health from Tufts University. Follow him on Twitter @itskeithbarry .
Sharing is Nice
We respect your privacy . All email addresses you provide will be used just for sending this story.
Trending in Car Safety
Popular Cars to Avoid and What to Buy Instead
Best Cars of the Year: 10 Top Picks of 2024
Safest New Cars of 2024, According to the IIHS
Best Used Cars for You
Cars for sale
Sell my car, car research, sign in, what is adaptive cruise control, this advanced driver-assistance tech can modulate a car’s speed for you..

Article QuickTakes:
- How does adaptive cruise control differ from regular cruise control?
- Are all adaptive cruise control systems the same?
- Which vehicles have adaptive cruise control?
Using forward-facing sensors such as radar and/or cameras, adaptive cruise control (ACC) detects a vehicle in front of you and, working in concert with the brakes and powertrain, automatically adjusts your vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance. This high-tech feature is available on many new cars and can make highway driving or congested-road commuting safer and more relaxing.
How Does Adaptive Cruise Control Differ from Regular Cruise Control?
On an open road, ACC works just like regular cruise control, keeping your car at a set speed. You can increase or decrease your car’s velocity with buttons on the steering wheel, and should you wish to take over, simply press the accelerator to temporarily override the system (say, to pass someone) or tap the brakes or steering-wheel button to cancel it. Once ACC detects a slower-moving vehicle in your path, though, it will lower your car’s speed for you, by reducing the vehicle’s power or even applying the brakes to keep your car a reasonable distance away from the vehicle ahead of you. If the slowpoke you’re following begins to move faster, ACC will tell your car to accelerate to match it up to your set speed. Just how big of a gap does ACC leave between you and the car ahead? That depends on how quickly you’re traveling, as faster-moving vehicles need more room to stop than slower ones, and your comfort level, as many systems allow drivers to adjust the gap length via a button on the steering wheel.
Are All Adaptive Cruise Control Systems the Same?
Not all ACC systems work at every speed, but the most advanced have what’s known as stop-and-go operation. This means ACC can bring the car to a complete halt, perhaps behind a vehicle at a red light, and then get it going again as the car ahead of it moves forward. Depending on how long the stop is, you may have to push the accelerator to resume ACC. It’s a particularly useful feature in heavy traffic, as letting the car deal with road congestion allows you to relax a little. A couple of systems—such as the one offered by Mercedes-Benz—can work with traffic-sign recognition and automatically adjust the vehicle’s speed to the posted limit as it changes. Before you let your car take over braking and acceleration, though, know that ACC typically won’t respond to pedestrians or stationary objects, and many systems struggle to make sense of motorcycles.
Which Vehicles Have Adaptive Cruise Control?
Since debuting in the U.S. in the 2000s, ACC has become widely available. Subaru now installs it in every model with an automatic transmission, for instance. But it’s not standard across the industry. Some automakers bundle ACC with other features in option packages, as Ford does in the F-150 with Ford BlueCruise , or restrict the tech to more costly trim levels, as Chevrolet does with the Equinox compact SUV. Like Wi-Fi at a high-end hotel, ACC is often an extra-cost item on luxury vehicles, too. For instance, in the lowliest GLC and GLE SUVs, Mercedes-Benz makes buyers spec a pricey package for ACC. And it’s not even available on the base Audi Q3 and Q5.

Related Articles
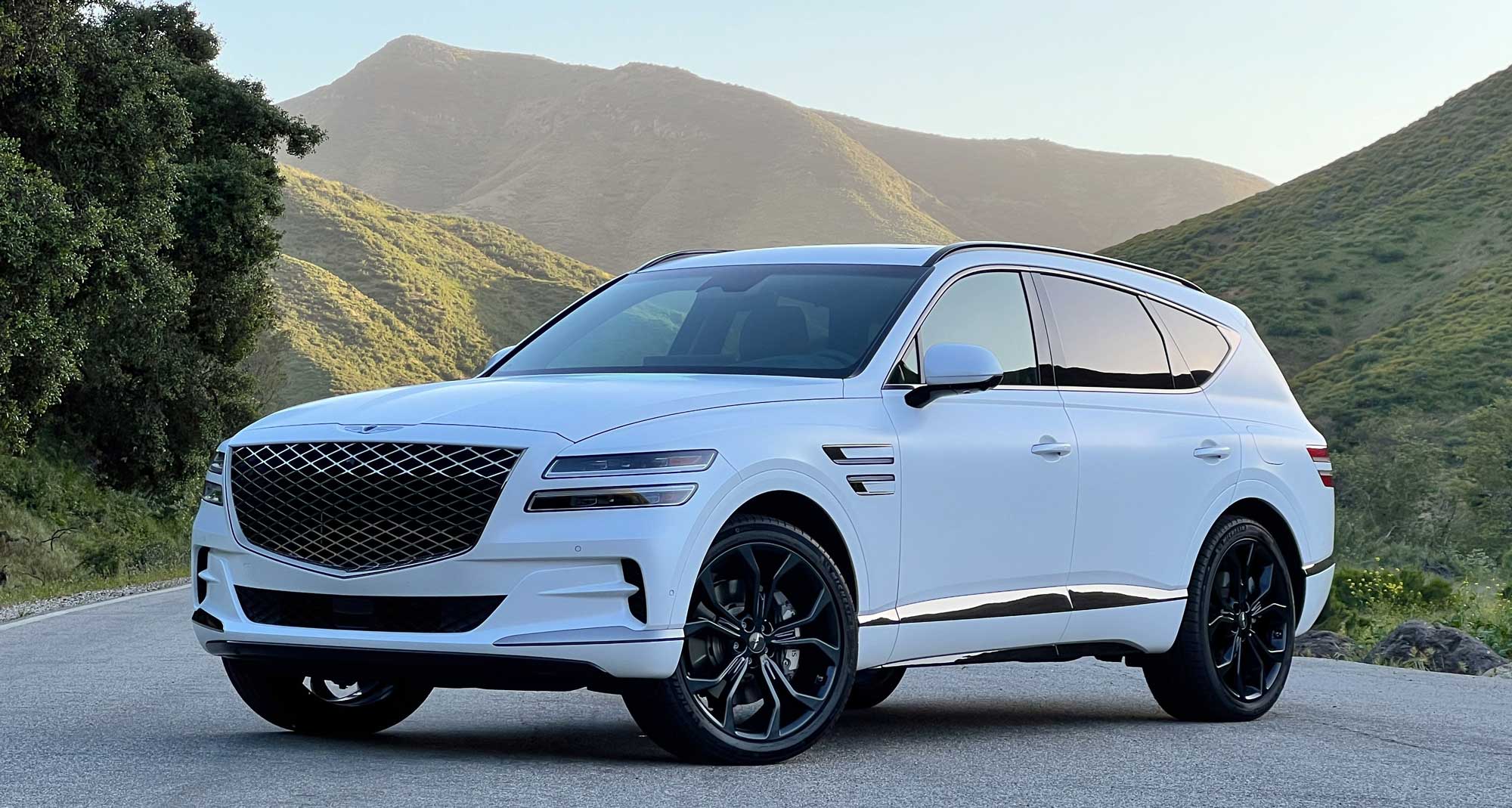

Emphasizing style, luxury, and refinement, the midsize SUV is also a more pleasant drive than expected.
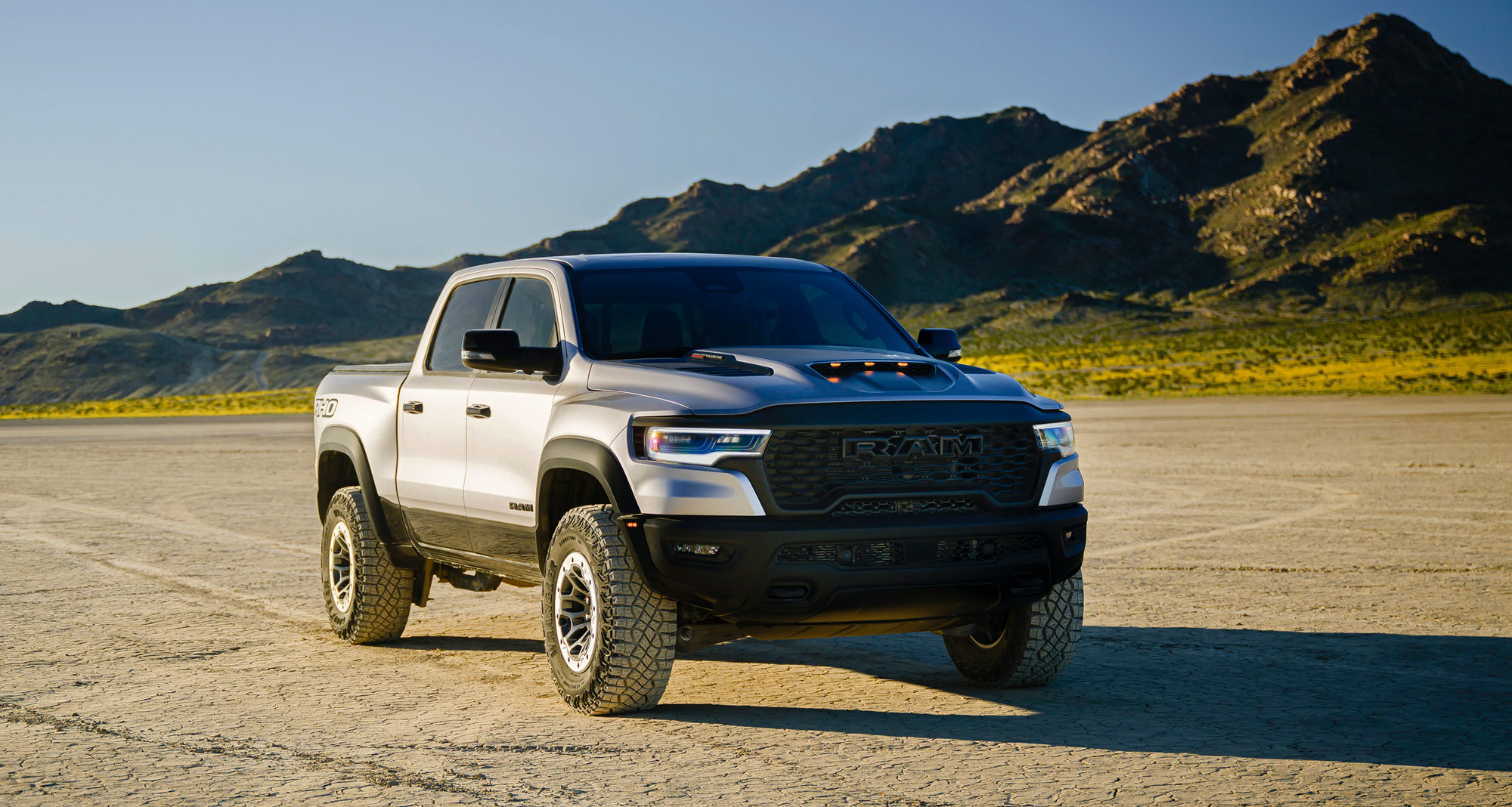

The RHO takes the Ram performance mantle with a downsized turbo six and a lower price than the TRX.
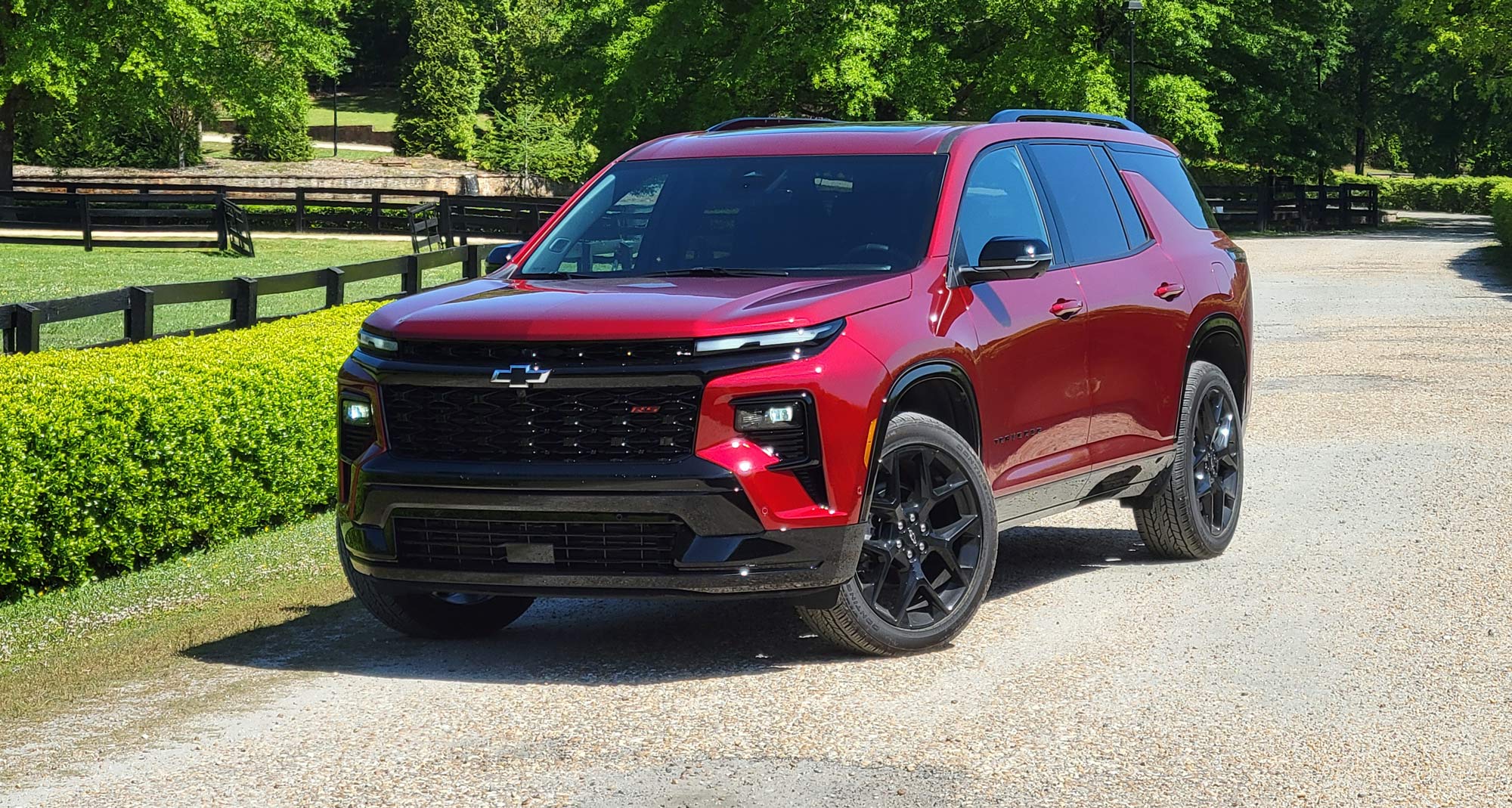

The bow-tie brand's roomy three-row midsize SUV gets a timely overhaul.

- Schedule Calibration Appointment
- Location Announcements
- ADAS Technician Training
- Press Releases
- Own A Calibration Center
- ADAS Glossary
Adaptive Cruise Control: What is ACC in ADAS?
- June 3, 2021

Table of Contents
What is ACC in ADAS?
When it comes to cars, ACC stands for Adaptive Cruise Control. In a Consumer Reports survey , 85 percent of drivers with Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) on their vehicles said they were very satisfied with it. What’s more, 19 percent said their ACC system helped to avoid a crash.
Standard cruise control has been around since the 1950s . Adaptive cruise control has been in development since the 1990s . Mercedes was the first automaker to bring ACC to the U.S. market in 1999 . Twenty years later, automakers are still working to improve their cruise control offerings. In the meantime, ACC technology has become one of the building blocks of autonomous driving.
In this article, we will explain adaptive cruise control and how it works, provide examples of ACC features in ADAS packages, and explain the importance of adaptive cruise control calibration.
What is Adaptive Cruise Control?
Adaptive cruise control or Active Cruise Control (ACC) is an advanced driver assistance system (ADAS) that automatically adjusts a vehicle’s speed when there are slow-moving vehicles ahead, with the aim of maintaining a safe following distance. When the road ahead is clear, ACC automatically accelerates to your pre-set speed. Adaptive cruise control is ideal for highway speeds.
ACC is a major component and precursor of fully autonomous vehicles. According to SAE , Driving Automation Level 1 driver support features provide steering OR brake/acceleration to the driver while the jump to Level 2 requires features that provide both steering AND brake/acceleration to the driver. On its own, ACC is a Level 1, but when combined with another driver assist feature that steers, your vehicle reaches Level 2 on the Driving Automation scale – a step closer to fully autonomous driving .
As a foundation of autonomous driving, ACC has the capability of reducing driver stress and radically improving driver safety. A study from the Highway Loss Data Institute studied insurance claims data from 2013-2017 BMW vehicles to see how ADAS affected collision, damage, and injury rates. The BMW Driving Assistance package added ACC to the following ADAS: Forward Collision Warning , Lane Departure Warning , Front Automatic Emergency Braking . With the addition of ACC, this package reduced the rates of property damage by 27 percent and bodily injury claim rates by 37 percent.
How does Adaptive Cruise Control work?
Just as with traditional cruise control, the adaptive cruise control system requires drivers to choose their preferred speed. Next, ACC requires drivers to set their preferred following distance from the vehicle’s pre-set options. Many have close, medium, and far selections to toggle between.
Sensors Used in Adaptive Cruise Control
Vehicles with adaptive cruise control use ACC sensor data to tell your car’s speed, distance from other vehicles, and the speed of vehicles ahead of you. There are many types of adaptive cruise control technology. The following types of sensors have all been used for ACC:
- Laser (Lidar)
Most (but not all) current forms of this ADAS use radar as their main source of information. A radar sensor mounted in the front of the vehicle is used to analyze the road ahead. It does this by emitting radio waves and measuring how long they take to return to the ACC sensor. A few internal calculations and your vehicle can tell the car’s distance and speed. Data from the radar distance sensors and the vehicle speed sensors are used to adjust your speed and keep your car a set distance from the one ahead of you.
ACC System Versions and Commonly Bundled ADAS
Most automakers have their own version of adaptive cruise control. Not everyone uses the same names for their ACC system. Here are a few industry terms that are all different names for ACC:
- Dynamic cruise control
- Intelligent cruise control
- Radar cruise control
- Radar adaptive cruise control
- Dynamic laser cruise control
- Autonomous cruise control
- Smart cruise control
- Dynamic radar cruise control
ACC with Stop & Go, Traffic Jam
Beyond the similar naming, there are several different features that adaptive cruise control is often bundled with to provide sensor fusion. One example of this is a feature called ACC with Stop and Go or ACC with Traffic Jam Assist. This adds the ability to come to a complete stop via automatic braking and then re-accelerate to the car’s set speed as traffic moves. All the while, data from sensors is used to keep a set, safe distance from cars ahead when you encounter heavy traffic.
Because it’s not an autonomous car, those with stop and go capabilities will only “go” again within three seconds if traffic flow allows. If it’s longer than three seconds, driver action is needed to re-engage the system.
ACC + Forward Collision Warning & Automatic Braking
Forward Collision Warning and Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) advanced driver assistance systems are often combined with ACC to provide audible alerts, instrument panel alerts, and tactile warnings of a forward collision risk, then automatic braking to prevent or mitigate damage from a collision.
ACC + Lane Centering
Adaptive Cruise Control works well with others. As previously mentioned, when adaptive cruise control is combined with an ADAS with steering capabilities like lane centering and proactive lane keeping assist systems, your car is considered a Level 2 on the SAE autonomous driving scale — meaning that the vehicle can accelerate, decelerate, and steer on its own — under very specific conditions, including initiation speed and weather. While it’s a step up in terms of driving automation, for safety, a human driver is still required to supervise constantly, including steering, braking, or accelerating.
ACC + GPS or Traffic Sign Recognition
Some ACC systems offer advanced traffic sign recognition , while others utilize GPS speed limit data. These optional ACC features help to combat the use of ACC technology to speed.
4 Examples of Adaptive Cruise Control
There are many different flavors of ACC. Names, tech, and bundled features make the automotive landscape — dotted with endless features, diverse names, and function variations — a bit tricky to navigate. To help you recognize ACC features, here are four automaker examples.
Ford Adaptive Cruise Control
Ford is one example of an automaker with adaptive cruise control. Here’s how Ford’s describes its system and capabilities:
“Available on select Ford vehicles is a series of Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) features employing advanced radar and camera technology. ACC lets you set a cruising speed and distance from the vehicle ahead of you. When it slows down, you automatically do too; when traffic picks back up, you resume your preset speed and distance. Then comes ACC with Stop-and-Go, which enables you to come to a complete stop when the vehicle ahead stops. Now add Lane Centering, which scans the lane markings to help you stay in your lane if the system detects you’re drifting out of it. And that’s not all. Now there’s Intelligent Adaptive Cruise Control, which includes all of these features plus new Speed Sign Recognition that can automatically adjust the set speed of your vehicle to the posted speed limit.”
Honda Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) with Low-Speed Follow
In the Honda Sensing ADAS package, the automaker offers ACC on many 2021 models with what it calls Low Speed Follow. Here’s how Honda describes it :
“Cruising on the open highway has never been easier! Honda’s Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) with Low-Speed Follow lets you set your cruise speed and interval behind a vehicle detected ahead, and then maintains that interval by braking your vehicle or applying the throttle. And the Low-Speed Follow function can bring your vehicle to a complete stop when a vehicle detected ahead slows to a stop, and it lets you resume operation by pressing a button or the accelerator.”
Hyundai Smart Cruise control (SCC) with Stop & Go
Hyundai offers adaptive cruise control, including on the Santa Fe. Here’s how the automaker describes it :
“While traveling at a speed set by you, it uses radar to maintain a safe distance from the car ahead. When the system slows the vehicle to a stop, it will reactivate if the vehicle in front moves within 3 seconds.”
Hyundai also offers Highway Driving Assist that works together with Smart Cruise Control. Here’s how Hyundai describes this feature :
“Your “co-pilot” for highway driving, when actively engaged with Smart Cruise Control or Lane Following Assist, this smart convenience automatically helps keep you centered in your lane and traveling at a safe distance behind the car ahead. Not only that, it also can keep you driving at the right speeds, automatically setting your pace based on GPS and highway data.”
Subaru EyeSight Adaptive Cruise Control
As part of Subaru’s Eyesight Driver Assist Technology Package, ACC is standard on many of the brand’s 2021 models and optional on the rest. It uses dual forward-facing color cameras mounted near the rearview mirror. Here’s how Subaru describes its ACC system in a promotional video :
“With adaptive cruise control, eyesight can help you stay with the flow of traffic. When you set cruise control, you can select from up to four present following distances. EyeSight watches ahead and if it detects traffic is slowing, adaptive cruise control adjusts your speed accordingly to keep your selected distance. Once traffic starts moving faster, it can automatically accelerate back up to your set speed. It can even work in stop-and-go traffic.
For some, it’s less worry about adjusting cruise control. For others, it’s like having an extra set of eyes on the road.”
Adaptive Cruise Control Limitations
Drivers should know that they are responsible for what happens when they are behind the wheel. Every company makes sure to include an asterisk and notice that drivers are still needing to be actively engaged in driving. Some drivers are using ACC to speed . A study of 40 drivers by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) found that they were more likely to speed when equipped with ACC.
ACC works well in clear day and night driving, and in light weather. However, if there is fog, heavy rain, or snow, it won’t work. Additionally, if dirt, snow, or ice are on the sensors, they won’t work. ACC also has trouble on winding roads.
With or without ACC, it’s important to always leave more space during poor driving conditions, including inclement weather.
Adaptive Cruise Control Calibration
ACC is one of the most common ADAS features in vehicles today. Like other ADAS systems, ACC needs to have sensors recalibrated after a collision and many vehicle services like windshield replacement . ADAS calibration keeps ACC systems working properly.
What is adaptive cruise control calibration?
Adaptive Cruise Control calibration takes place when the camera, lidar, and radar sensors that inform your vehicle’s actions are re-aligned to improve or re-establish sensor accuracy.
Getting a car calibrated takes drivers knowing about it and recognizing the warning signs.
ACC Calibration Warnings for Drivers
For drivers, the biggest sign that you need a car calibration is a recent collision. Other circumstances that necessitate Adaptive Cruise Control calibration include any time you repair or replace something nearby the location of a sensor. Another sign would be an overly sensitive ACC system, even when you have changed the settings (where possible). Here are some related warning messages that may signal it’s time to get an ADAS calibration:
- Adaptive cruise control sensor blocked
- Adaptive cruise control failure
- Adaptive cruise control temporarily unavailable
ADAS Calibration for Auto Shops
When a car comes into the shop, techs need to know when to order or perform ADAS calibrations . They also need to understand their importance. If calibrated incorrectly, ACC systems may have following distance settings that drivers aren’t used to. They can also make the systems overly sensitive, or not sensitive enough.
Every new model year brings more and more ADAS-equipped vehicles to the streets. Cars need to be calibrated after collisions, and any repairs that may affect sensor alignment. If you want to capitalize on this impending influx of needed calibrations, Car ADAS Solutions can help. We are at the forefront of the ADAS calibration services industry. We provide turnkey ADAS calibration solutions with framework, specialty software, training, and support, built-in. Contact Car ADAS Solutions today !
Additional ACC Resources:
- Cars with Adaptive Cruise Control – Car and Driver
- 10 Best Cars with Adaptive Cruise Control – TrueCar
- Adaptive Cruise Control – MyCarDoesWhat.org
Adaptive Cruise Control FAQs
What is Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) and how does it differ from regular cruise control?
Adaptive Cruise Control is an advanced driver assistance feature that automatically adjusts your vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle in front. Unlike traditional cruise control that maintains a constant speed, ACC can speed up or slow down based on the flow of traffic.
ACC uses a combination of radar, cameras, and various other sensors to monitor the distance to the vehicle ahead and its relative speed. This data is processed by the car’s computer systems to adjust the throttle and apply brakes if necessary, ensuring a safe following distance.
Can Adaptive Cruise Control bring my car to a complete stop?
Yes, many modern Adaptive Cruise Control systems come with stop-and-go technology that can bring your vehicle to a complete stop and then resume driving when traffic starts moving again.
Is Adaptive Cruise Control safe to use in all driving conditions?
While ACC is designed to increase safety and convenience, it is most effective in steady traffic conditions on highways or well-marked roads. It is not recommended for use in city driving, in adverse weather conditions, or on roads with poor lane markings as these factors can reduce the system’s effectiveness.
Will Adaptive Cruise Control work with any vehicle ahead of me?
Adaptive Cruise Control is generally designed to recognize and respond to most passenger vehicles and trucks. However, it may not detect objects small vehicles like motorcycles and bikes, or pedestrians. This is why it’s best to avoid using in dense cities.
Share this post
Related Articles

What is ADAS? Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) Guide

Understanding ADAS: Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB)

Rear AEB: The ADAS That’s Putting the Brakes on Backing Crashes

New Automotive Night Vision ADAS Technology Illuminates Driving at Night

Basic Guide: ADAS Calibration Equipment

Implementing ADAS Calibration: 6 ADAS Challenges Most Shops Face (and What to Do About Them)
Subscribe To Blog Updates
Get notified when a new blog post is released!
Own Your Own ADAS Calibration Center
Enjoy high profits in an industry that is growing exponentially!
- Privacy Policy
Salt Lake City Calibration
- SLC Calibration Center
- ADAS Calibration Services
- Schedule Calibration
Calibration Centers
- Calibration Center Locations
- (801) 810-1150
- (855) 500-1533 Toll Free
- [email protected]
© 2020 Car ADAS | All rights reserved | Utah SEO & Utah Website Design by Ranksey

A Deep Dive into the Adaptive Cruise Control System. What Is It?

A Quick Overview
What is adaptive cruise control.
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) is a technology in modern vehicles that helps drivers maintain a safe distance from the vehicle in front of them while cruising on the highway. It uses sensors, cameras, and radar to detect the distance between the driver’s car and the one in front. ACC automatically adjusts the speed of the vehicle, brakes, or accelerates as needed to maintain a safe distance from the car in front.
How Does Adaptive Cruise Control Work?
The following are the key components of an Adaptive Cruise Control system:
Most cars equipped with ACC use radar-based sensors to detect the distance and speed of the vehicle ahead. These sensors work by sending out radio waves that bounce off the car in front and return to the sensor. The time it takes for the radio waves to return determines the distance between the two vehicles.
Some of the latest vehicles with ACC also come with a camera-based system that can detect the distance and speed of the car in front of them. Cameras can detect vehicles at longer ranges than radar sensors.
Control Module
The control module is responsible for processing the data collected by the sensors and cameras and making adjustments to the speed of the vehicle. The module is programmed to maintain a certain distance from the vehicle ahead, and it will slow down or speed up as needed to keep that distance.
Braking System
ACC uses the car’s braking system to slow down or stop when needed. The system works by applying the brakes gradually if the distance between the vehicles is closing too quickly or if the vehicle ahead is coming to a stop.
Benefits of Adaptive Cruise Control
ACC provides several benefits to drivers, including:
Increased safety: ACC helps reduce the risk of rear-end collisions by maintaining a safe distance from the car in front.
Comfortable driving experience: With ACC, drivers can relax and enjoy a more comfortable ride, without having to constantly adjust their speed on the highway.
Reduced fuel consumption: By maintaining a consistent speed, ACC helps drivers save on fuel consumption.
👉 You may also like - Can Your Cruise Control Get Stuck? Here’s What to Do If it Happens
What is Adaptive Cruise Control System?
Adaptive cruise control system (ACC) is an advanced driver assistance system (ADAS) technology that helps vehicles regulate speed and maintain a safe distance from other cars on the road. This system utilizes sensors, cameras, and radar to detect other cars on the road and adjust speed accordingly.
How does Adaptive Cruise Control System work?
The ACC system uses sensors to detect other cars on the road and radar to determine their distance, speed, and direction of travel. Based on this information, the system calculates the appropriate speed and distance to maintain and adjusts the car’s speed and braking accordingly.
What are the benefits of using Adaptive Cruise Control System?
The benefits of using an ACC system include increased safety, reduced driver fatigue, improved traffic flow, and enhanced fuel efficiency.
Is there any limitation to the Adaptive Cruise Control System?
Yes, there are limitations to the ACC system. It may not function properly in adverse weather conditions, such as heavy rain or snow, and can be impacted by glare or reflections from sunlight or other vehicles.
Can the Adaptive Cruise Control System be turned off?
Yes, most modern cars with an ACC system allow the driver to turn off the system if desired.
How fast can the Adaptive Cruise Control System adjust the vehicle’s speed?
The ACC system can adjust the vehicle’s speed quickly, usually within a second. This high-speed responsiveness is one of the main benefits of this system.
Is Adaptive Cruise Control System suitable for all driving conditions?
No, the ACC system is not suitable for all driving conditions. It works best on highways or open roads with minimal traffic and consistent speeds. It should not be used in heavy traffic or on winding roads where sudden changes in speed and direction may occur.

Understanding Camshaft Position Sensor Wiring.
The throttle position sensor & its different types.

Mastering ASE Testing - The Ultimate Guide for Success

Keeping Current - Charging System Diagnosis and Repair

The complete ASE practice test with answers and explanations

Enhancing the Ride - Accessories Diagnosis and Repair
What Is Adaptive Cruise Control? [Full Explanation!]
By: Author Zach Reed
![co to znaczy adaptive cruise control What Is Adaptive Cruise Control? [Full Explanation!]](https://vehicleanswers.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/What-Is-Adaptive-Cruise-Control-Full-Explanation-720x405.jpg)
We’ve all heard of semi or fully autonomous vehicles on our roads that are meant to improve our driver experiences. And one aspect of a fully autonomous car is adaptive cruise control (ACC) .
If you’re wondering what it is or what it does, here’s the answer.
Adaptive cruise control is an active vehicle safety system that maintains a cruising speed and automatically varies the speed of your car to match the speed of the car in front of you. If the vehicle ahead accelerates or changes lanes your car will accelerate up to a set speed.
For example, if you come up to a car moving slower than your preset cruising speed, your car’s adaptive cruise control system will detect a decelerating or slower car ahead.
It will automatically adjust your cruising speed to match the lead car’s speed without getting dangerously close.
And that’s not all, read on to find out more on adaptive cruise control and why you should or shouldn’t have one in your car.
What Does Adaptive Cruise Control Do?
Adaptive cruise control systems are evolving with the advancement in motor vehicle technologies. Modern-day cruise control systems enable safe and comfortable driving by working in unison with other safety features present in our cars.
It not only sets your preferred cruising speed but also gives you an additional option to set your driving mode.
Comfort, Sport, and Economical are typical car driving modes that you can pair with your adaptive cruise control system.
Additionally, it sets a speed using data and information from the car’s sensors and cameras.
Information on the road curvature, speed limits, roadblocks, or construction sites influence the automatic speed that the car will cruise at that given point.
Advantages of Adaptive Cruise Control
Early cruise control systems were designed to enhance driver comfort rather than safety initially.
The driver was required to be highly vigilant since the car couldn’t respond as quickly to a change in road conditions on its own. Hence, better, more intelligent, and safer adaptive cruise control systems are needed.
Here are some of its advantages
It Reduces the Level of Stress Placed on the Driver
While driving for long distances, the ACC eliminates the need for the driver to always be on the steering wheel and throttle.
Keeping the foot on the gas pedal for extended periods is unhealthy and very uncomfortable, especially to drivers who aren’t accustomed to long-distance driving. With ACC, you’ll be able to cruise while you relax and then deactivate it if you wish to take control of the wheel.
A driver can concentrate more on the traffic and act if they feel that they’re in a situation whereby it’s best if they take over the driving from the ACC.
It Supports Driving at a Safe Distance Between Cars
Driving too close to some drivers might intimidate them, causing them to misbehave.
If a driver feels that you’re driving too close to them, they might be tempted to accelerate or drive even slower.
Reduces Chances of Rear-End Collisions
Rear-end collisions will become a thing of the past if more vehicles on the road will adopt the adaptive cruise control system . When you’ve set the cruising distance between you and the car ahead, it’s the car’s task to brake or alert you that you’re closing in on the lead car.
You’ll then act accordingly to avoid hitting the lead car’s rear.
It Improves Traffic Flow in Cities
The presence of adaptive cruise control in as much as half of the vehicles on the road will improve traffic in cities.
In addition to other traffic flow systems on our roads, maintaining a safe and constant distance between cars eases traffic flow.

Improves Driving Experience
Most drivers, especially when tired, find it difficult cruising at highway speeds. They end up creeping up too close to other cars or drifting too far back that they force other drivers to change lanes to avoid collisions.
The car will cruise at your set speed and adjust according to the road conditions and speed limits with adaptive cruise control.
Disadvantages of Adaptive Cruise Control
Like all evolving technologies, we haven’t had perfect adaptive cruise control yet. There’s room for improvement as the world slowly adapts to safer semi and fully autonomous vehicles.
Additionally, adaptive cruise control improves driver safety and driving experience, but it has some significant drawbacks.
Some of these drawbacks result from human error and some from road conditions. Nevertheless, you need to be aware of the following drawbacks of adaptive cruise control systems.
- It’s easier to zone off or get distracted while on the road
- It’s very inappropriate to drive with adaptive cruise control in bad weather
- Increased chances of overspeeding as you need to adjust your speed to drive within the speed limits
What Is the Difference Between Cruise Control and Adaptive Cruise Control?

Cruise Control
It’s a vehicle system that enables a car to maintain a reasonably constant speed with little or no human interference. The system can take over the car’s throttle, acceleration, and speed once the driver activates it and sets the speed to the desired level.
It’s a technology that has lasted over 70 years, and with the ever-growing road traffic, there was a need for better navigation technology.
Engineers and drivers noted that the cruise control failed massively in detecting road conditions ahead or stopping a vehicle in an emergency.
There was a need for a system that works well in both a highway and city traffic setting, a system that could correctly appreciate the vehicle’s speed ahead.
Adaptive Cruise Control
It’s a more advanced and safer version of cruise control technology.
Adaptive cruise control is not only more hands-free compared to cruise control, but it’s safer on the road. It will match the car’s speed ahead of you as long as it’s within the speed limit that you’ve set.
Also, it maintains a safe distance behind the car ahead. You can set the following distance in meters or seconds as the system allows you to set the distance between the lead car and your car.
Is Adaptive Cruise Control Bad for Your Car?
No. Adaptive cruise control is a meaningful and resourceful update to any vehicle. Allowing the car to take over most of the braking and acceleration while on the road is crucial in prolonging its lifespan.
Unlike cruise control, adaptive cruise control allows a car to study the road conditions and “adapt” accordingly.
However, some adaptive cruise control systems don’t offer the best driving experience. If your ACC is designed in a way that allows for irregular or aggressive braking and acceleration, it may wear down the brake disks quicker.
Also, your car doesn’t have the vision and judgment of a human being and will fail to notice sharp turns or water puddles in time.
How Do I Know if My Vehicle Has Adaptive Cruise Control?
Consult your dealership or car manufacturer to determine if the car has adaptive cruise control features.
Most major car brands such as Chevrolet, Mercedes-Benz, Hyundai, Kia, Toyota, Porsche, Audi, BMW, Ford, Lincoln, Nissan, Infiniti, Dodge, Jeep, Volkswagen, etc. have the ACC feature.
Furthermore, since adaptive cruise control systems are partnered with other driver-assist modes, I’d recommend that you take time to find the car that suits you best.
When Should You Use Adaptive Cruise Control?
Adaptive cruise control is an excellent safety and comfort feature in most vehicles, especially with the need for more autonomous vehicles. But does it mean that it should replace human effort when driving?
No. We can’t use adaptive cruise control in certain conditions that make the road unpredictable or hinder the car sensors from normal functioning.
Listed below are the best times when you should use adaptive cruise control
- When the road traffic is minimal
- You’re alert and fully aware of what’s transpiring on the road
- When traveling in good weather whereby you won’t struggle to control the car on your own
- The road conditions are favorable and on a relatively flat surface
When to Avoid Using Adaptive Cruise Control
Adaptive cruise control isn’t as fool-proof as some car companies and dealerships may lead you to believe. Here are some situations whereby it’s safer to avoid using adaptive cruise control
When the Weather Conditions Are Unfavorable
Unfavorable weather conditions include stormy, exceedingly dusty, or foggy conditions that hinder the working of the sensors.
If the sensors are partially blocked, or the signals are damped due to external interference, your car might misjudge the road and the traffic.
In Unpredictable Road Conditions
Your adaptive cruise control enabled car may not stop in time if the car ahead stops suddenly.
You need to be fully alert to hit the brakes and take over control of the vehicle. Avoid using ACC when you notice that there’s a lot of traffic or hazards on the road.
When Tired or Having Highway Hypnosis
Some long-distance drivers may suffer from highway hypnosis at one given point in their driving.
If you find that you often fail to recall some sections of your travel while in control of the wheel, avoid using adaptive cruise control.
Highway hypnosis results from mental fatigue whereby a driver is on an “auto-pilot” or in a trance-like driving state.
On Wet/ Icy Roads
Wet/ icy roads have very minimal traction, and your car will lose grip and start spinning.
Unfortunately, adaptive cruise control can’t control a spinning or out-of-control vehicle, worsening the situation.
Does Adaptive Cruise Control Use Brakes?
Absolutely. Adaptive cruise control has a brake feature that slows or stops a car when required. The system will use engine braking and disk brakes to safely and smoothly bring a car to a stop.
It will also light up the brake lights on hard deceleration, similar to when you’re manually braking.
However, while having adaptive cruise control systems, cars will need a driver to pair them with collision avoidance and lane centering assist systems.
If not, the car will only use warning systems such as lights and sounds to notify the driver to step on the brakes. Remember that some cars have emergency brake systems but lack adaptive cruise control. Don’t assume that a car has both because it has the other.
As much as adaptive cruise control improves your driving experience, you must be cautious and fully aware of what’s going on around you.
The system isn’t here to substitute human effort but rather to complement it.
Furthermore, if your car doesn’t have to stop and go frequently, it’s better to turn off the feature when you don’t need it. You’ll drive faster, safer, and avoid zoning out while driving.
Hi, I'm the founder of VehicleAnswers.com! Having owned a wide variety of vehicles in my life, I was astounded at how hard it can be to find answers to common automotive questions. Rather than sit idly, I decided to create this website to help others!
Price reductions on selected cars , from £250 - £1000 off
- Ask the experts
- What is adaptive cruise control and is it worth it
What is adaptive cruise control – and is it worth it?
Lots of cars feature adaptive cruise control technology these days, but not everybody knows how to make best use of it. Here are some useful tips to get the most out of this impressive kit.
)
What is adaptive cruise control?
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is a driving assistance feature that can control a car's accelerator and brakes to reduce your workload behind the wheel.
It's essentially an evolution of traditional cruise control that's able to not only hold your speed, but also follow the traffic ahead and maintain a safe distance.
In some cars, the adaptive cruise control system only works at motorway speeds.
In others, it can safely bring the car to a stop of the traffic ahead slows down, and then get the car moving again when the road clears.
How does adaptive cruise control work, and how is it different to standard cruise control?
Standard cruise control has been a feature on cars for quite some time now, and the way that the most basic version works is simple.
You’ll reach your desired speed, turn on cruise control, and your car will progress at this speed until you turn off the control or start to brake.
Adaptive cruise control is a more intelligent system:
You’ll first need to reach the desired speed by accelerating as normal.
Once you’re happy with your speed, you can press the ‘set’ button.
You’ll now be able to set the distance you’d like to keep between your vehicle and the one in front. If the car ahead starts to slow, your vehicle will either notify you to start braking, or slow down itself to maintain the distance you set.
If you do start to brake, this will deactivate the ACC system.
The principle behind ACC is similar to standard cruise control. Thanks to the adoption of a camera (or cameras) to the front of a car, it can essentially 'see' the road ahead.
This makes the car aware of the distance to the car in front, meaning not only can the adaptive cruise control hold your speed, it can also hold the space – even if the car ahead slows.
If the car ahead speeds up, the ACC will only accelerate you back to the speed you have set – it won't go beyond that.
The latest ACC systems can also work in low-speed traffic, creeping the car forwards, and stopping and starting with the congestion ahead.
If you do press the brakes (or, in the case of manual cars, press the clutch pedal), then the adaptive cruise control switches off, putting you back in full control.
)
Adaptive cruise control is a feature found on newer vehicles. It uses sensors to monitor the distance between your car and the one in front of you and then automatically adjusts your speed to maintain a safe following distance. This can help relieve some of the stress of driving in stop-and-go traffic or on long road trips.
If you’re considering purchasing a vehicle with adaptive cruise control, it’s important to understand how it works and its limitations. Some adaptive cruise control systems can also bring your car to a complete stop if necessary and then resume driving when the way is clear.

Lilit is a seasoned content editor with a keen eye for detail and a passion for crafting compelling narratives in the automotive realm. With a career spanning several years, she has dedicated herself to refining and perfecting the written word.
- Editorial Guidelines
Car Insights
- Years to avoid
- Collections

Cruise control and adaptive cruise control in a car: How it works?
T he array of new car launches equipped with ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems) has brought in adaptive cruise control (ACC) in many cars. While cruise control isn't a new feature, adaptive cruise control is relatively new for the Indian market. Here's all you need to know about this technology.
What is cruise control?
Cruise control is a feature that lets you set a particular speed for your car and as the name suggests — 'cruise'. One doesn't need to use the throttle or accelerator to keep the car going at the set speed. This system controls and brings in some amount of automation in driving a car at a particular speed.
What is adaptive cruise control?
Further to the aforementioned automation, adaptive cruise control is a step up to add more modernisation to this tech. All cars equipped with ADAS most certainly get adaptive cruise control. In this case, once a speed is set, the car will continue to be controlled by this system but will move according to the surrounding traffic speed. That is, if the car in front of you is moving at a speed of 40kmph, adaptive cruise control will maintain a safe distance from that car and keep the speed of your car in accordance with it. The added advantage is that automatic braking will slow down/stop the car without the driver having to intervene till asked to do so by the system.
How do cruise control and adaptive cruise control work?
The cruise control system uses an actuator to control the throttle input and maintain a pre-set speed. This same servomechanism is used in adaptive cruise control too but with the application of brakes through ADAS. In a way, it mimics the way human drivers accelerate and brake in traffic and coast on a highway.
How to use cruise control?
Usually, there are buttons either on the steering wheel or on the stalks behind the steering wheel to set, reset, increase, and decrease the speed of the car. Some cars may have the activation button on the dashboard. Nonetheless, the function is the same, that is, to activate/deactivate it. You can adjust the required speed using buttons '+/-', fix it using 'SET', and cancel with 'CANCEL'. In cars with cruise control, the system's control is anyway cancelled with the application of brakes. Additionally, with 'RESET', the last memory of the set speed can be recalled. Once the process is set, the driver can leave the throttle and just focus on the steering and braking inputs as the car accelerates on its own and cruises at the set speed.
When to use cruise control?
Dual-carriage highways are the most recommended places to use this feature citing safety concerns. But with adaptive cruise control, its applications are even in traffic, making a car a semi-autonomous vehicle with ADAS. But the ideal place remains to be a highway where the driver has to otherwise constantly press the accelerator pedal to cruise at a constant speed. Cruise control will eliminate the need to pin the throttle for this period. Do note, the driver's reaction time to respond to unexpected changes in driving conditions and traffic also tends to reduce with cruise control doing its thing.
Cruise control cars in India
Earlier, only the higher-end cars used to have this feature but now we have cars priced below Rs. 10 lakh with cruise control. The prime examples are the Hyundai Nios and the Tata Punch. And this feature is not limited to the top-spec variants but has trickled down to lower mid-spec trims as well.
Disclaimer: Here's a word of caution regarding the use of this tech as it can't be totally dependable. Engage it only when it feels safe and there are no unusual weather and driving conditions including poor lighting, rain, snow, etc.
For more news , reviews , videos and information about cars, visit CarWale.com .

Research on Adaptive Cruise Control Strategy Considering Driving Style
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.

Cruise FAQs
How to calibrate adaptive cruise control.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Professional technician consultation is important for complex calibration troubleshooting and specialized knowledge required for common calibration issues.
- Regular maintenance and inspection are crucial for the longevity and performance of adaptive cruise control, including troubleshooting techniques and cleaning sensors to remove debris or dirt.
- Ensuring secure and corrosion-free electrical connections is vital for optimal performance, with regular testing of connections to ensure accurate detection and response to vehicles.
- Calibrated adaptive cruise control offers benefits such as improved accuracy in maintaining distance, better responsiveness to changing traffic conditions, enhanced collision avoidance capabilities, and a serene and secure driving experience.
Understand the Basics of Adaptive Cruise Control

Locate the Calibration Procedure in Your Vehicle’s Owner’s Manual
Prepare your vehicle for calibration, find a safe and open road to perform the calibration, follow the step-by-step instructions for calibration, test the adaptive cruise control system after calibration, make adjustments if necessary, consult a professional if calibration issues persist, regularly maintain and inspect your adaptive cruise control system.
- Check for any debris or dirt that may be blocking the sensors and clean them if necessary.
- Verify that all the electrical connections are secure and free from corrosion.
- Test the system periodically to ensure that it is accurately detecting and responding to vehicles in front of you.
Enjoy a Safe and Smooth Driving Experience with Calibrated Adaptive Cruise Control
Frequently asked questions, what is the purpose of calibrating adaptive cruise control, how often should adaptive cruise control be calibrated, can i calibrate adaptive cruise control myself, or do i need professional assistance, are there any specific safety precautions to take during the calibration process, what potential issues can arise if adaptive cruise control is not calibrated correctly.

Meet Asra, a talented and adventurous writer who infuses her passion for exploration into every word she writes. Asra’s love for storytelling and her insatiable curiosity about the world make her an invaluable asset to the Voyager Info team.
From a young age, Asra was drawn to the power of words and their ability to transport readers to far-off lands and magical realms. Her fascination with travel and cultures from around the globe fueled her desire to become a travel writer, and she set out on a journey to turn her dreams into reality.
How To Cancel Msc Cruise
How To Book A Cruise For A Family Of 6

Meet Asra, a talented and adventurous writer who infuses her passion for exploration into every word she writes. Asra’s love for storytelling and her insatiable curiosity about the world make her an invaluable asset to the Voyager Info team. From a young age, Asra was drawn to the power of words and their ability to transport readers to far-off lands and magical realms. Her fascination with travel and cultures from around the globe fueled her desire to become a travel writer, and she set out on a journey to turn her dreams into reality.

You may like
Cruising from baltimore: a convenient and relaxing getaway guide.
Bask in the allure of cruising from Baltimore, but beware of hidden surprises that may lurk beneath the surface.
- Enjoy stress-free vacations with all-inclusive packages from the Port of Baltimore.
- Explore diverse destinations like Bahamas, Bermuda, and Canada/New England from Baltimore.
- Maximize relaxation with spa treatments, poolside activities, and planned shore excursions.
- Immerse in Baltimore's charm pre-cruise with historic sites, nightlife, and iconic Inner Harbor.
Benefits of Cruising From Baltimore
Popular Destinations From Baltimore

Tips for a Relaxing Cruise Experience
Exploring Baltimore Before Departure

Making the Most of Your Cruise
Where Do Cruises Out of Baltimore Go To?
Where can i get laid on a cruise ship?, is there a cruise to nowhere out of baltimore?, what is the funnest cruise line for adults?.

Claire, a creative soul with an unquenchable thirst for storytelling, is an integral part of the Voyager Info team. As a dedicated writer, she weaves captivating narratives that transport readers to enchanting cruise destinations and beyond.
Claire’s love affair with writing began at an early age when she discovered the magic of words and their ability to craft worlds and emotions. Her innate curiosity led her to explore various literary genres, but it was travel writing that truly captured her heart. Drawing inspiration from her own globetrotting adventures and encounters with diverse cultures, Claire embarked on a journey to become a travel writer par excellence.
The Ultimate Kid-Friendly Cruise Lines for Your Family Adventure
Sail through the top kid-friendly cruise lines for an unforgettable family adventure, where endless fun awaits – are you ready to discover the ultimate choice?

- Royal Caribbean International offers age-specific activities and family-friendly staterooms for kids of all ages.
- Disney Cruise Line provides themed kids clubs, interactive dining, and entertainment to create a magical family experience.
- P&O Cruises offer complimentary kids clubs, family-friendly dining, and a Night Nursery for supervised activities.
- Norwegian Cruise Line features Splash Academy, Entourage teen lounge, and exciting amenities like go-kart tracks and Aqua Parks.
Royal Caribbean International for Kids
Disney Cruise Line Family Fun

Family Adventures With P&O Cruises
Norwegian Cruise Line for Families

MSC Cruises Kids Club
Is Royal Caribbean or Carnival More Kid Friendly?
Which cruise line is best for small kids?, what is the best length of cruise for kids?, are royal caribbean cruises kid friendly?, what makes icon of the seas the ultimate family cruise experience?.
Astonishingly innovative entertainment and relaxation blend on Icon of the Seas, setting it apart as the ultimate family cruise experience.

- Family-friendly activities like Splashaway Bay and Carousel for all ages
- Exciting entertainment options such as high-diving stunts and comedy clubs
- Over 40 restaurants including specialty venues for diverse dining experiences
- Relaxing amenities for parents like spa treatments and peaceful retreats
Family-Friendly Activities for All Ages
Exciting Entertainment Options Onboard

- Ice-skating at Absolute Zero℠
- High-diving stunts at AquaDome℠
- Comedy clubs, music halls, and engaging performances
Dining Experiences Catered to Families
Relaxing Amenities for Parents

- Spa Treatments : Escape the hustle and bustle of daily life with rejuvenating spa treatments designed to soothe the mind and body.
- Specialty Dining : Experience exquisite cuisine at specialty dining venues, where parents can savor gourmet meals in a sophisticated ambiance.
- Entertainment Venues : Enjoy adult-oriented entertainment options, from live shows to music performances, ensuring a vibrant and enjoyable atmosphere.
Safety and Security Measures for Families
What Is Special About Icon of the Seas?
Is icon of the seas kid friendly?, what is our all new stay all day family neighbourhood called icon of the seas?, how much does the ultimate family townhouse icon of the seas cost?.

Affiliate disclaimer
As an affiliate, we may earn a commission from qualifying purchases. We get commissions for purchases made through links on this website from Amazon and other third parties.

Unveiling the All-New MSC Seaside: a Grand Voyage From Europe to Miami

Unveiling Jo Diggs' Artistry: Fabric and Stitching in the Natural World

What Is The Weather Like On A Transatlantic Cruise In April

How to Contact Someone on a Carnival Cruise Ship
Decoding Norwegian Cruise Line’s Gratuities and Service Charges

Carnival’s Cruise Industry Recovery: Challenges, Progress, and Optimistic Outlook

What Is The Average Age Of Passengers By Cruise Line

Azamara Onward: Origins, Renovation, and Future Plans
Anthony Bourdain: Unconventional Culinary Icon and Global Influencer

Authentic Tacos and Local Delights: A Culinary Adventure in Cabo San Lucas

Arctic Adventure: Uncharted Destinations With Le Commandant Charcot

Authentic Art, Exciting Auctions: The Ultimate Cruise Ship Experience!

Which Celebrity Cruise Ships Have Been Refurbished

What Drinks Can You Bring On Princess Cruise

How To Turn On Cruise Control Tesla Model 3

How To Set Cruise Control Tesla Model Y

How To Check Weather For A Cruise

How To Get From Venice To Chioggia Cruise Terminal


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ACC (z ang. Adaptive Cruise Control), jest to rozbudowana wersja tempomatu pierwszej generacji CCS (z ang. Cruising Control System), określana mianem adaptacyjnego lub aktywnego tempomatu. Obecnie w pojazdach możemy spotkać dwie kolejne generacje adaptacyjnych tempomatów.
Adaptive Cruise Control. Schemat działania urządzenia. Adaptive Cruise Control ( ACC ), Intelligent Cruise Control ( ICC ), pol. tempomat adaptacyjny - urządzenie utrzymujące odpowiedni (bezpieczny) odstęp między poruszającymi się pojazdami samochodowymi, jeśli ruch odbywa się po tym samym pasie [1] .
Most adaptive cruise control systems allow the driver to adjust the following distance at intervals ranging from close to far. Advanced systems integrate with the vehicle's navigation system and ...
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is a system designed to help road vehicles maintain a safe following distance and stay within the speed limit. This system adjusts a car's speed automatically so ...
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) is an intelligent driver assistance feature that works as an enhancement to traditional cruise control. Using a system of advanced sensors such as radar and cameras, ACC determines the speed and conditions of surrounding traffic and automatically adjusts cruising speed to maintain a safe distance within the flow of traffic.
Adaptive cruise control by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (example video) Adaptive cruise control ( ACC) is a type of advanced driver-assistance system for road vehicles that automatically adjusts the vehicle speed to maintain a safe distance from vehicles ahead. As of 2019, it is also called by 20 unique names that describe that ...
Adaptive Cruise Control, Defined. Like traditional cruise control, adaptive cruise control will keep your vehicle at a desired speed so you can remove your foot from the accelerator. Unlike traditional cruise control, ACC will monitor the vehicle ahead of you and, should said car slow down, automatically reduce your vehicle's speed to ...
Updated May 9, 2022. Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is like traditional cruise control, but smarter. ACC systems allow you to set a desired speed until your vehicle encounters slower-moving traffic ...
Adaptive cruise control as of 2013 ranges from $2,500 at the high end to as little as $500. Less costly "partial ACC" only works at speeds of 20 or 25 mph and up, but it's markedly cheaper.
Simple to use, all you need to do is turn on the system in your vehicle, reach your desired cruising speed, and set it. The system then assumes control of the accelerator, maintaining the set ...
Using forward-facing sensors such as radar and/or cameras, adaptive cruise control (ACC) detects a vehicle in front of you and, working in concert with the brakes and powertrain, automatically adjusts your vehicle's speed to maintain a safe following distance. This high-tech feature is available on many new cars and can make highway driving ...
1. To turn the feature on, press the cruise control On/Off button on the steering wheel. Your vehicle will default to the type of cruise control you last used when you turned your vehicle off. When the system is turned on, you'll see a white Adaptive Cruise Control icon in your cluster display or on your Head-Up Display, if your vehicle has ...
By Scott Hinderer 04/19/2023 12:04pm. Adaptive cruise control is an advanced form of cruise control that can increase or slow vehicle speeds to maintain a programmed distance from the car ahead ...
Adaptive Cruise Control is an advanced driver assistance feature that automatically adjusts your vehicle's speed to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle in front. Unlike traditional cruise control that maintains a constant speed, ACC can speed up or slow down based on the flow of traffic.
How ACC works. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) uses a smart team of sensors. Most systems rely on a combination of a radar and a camera, depending on the carmaker. The radar acts like a super ...
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) is an advanced driver assistance system that automatically adjusts the vehicle's speed to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead. 2. Working Principle. ACC uses sensors, such as radar or cameras, to detect the distance and speed of the preceding vehicle, adjusting the vehicle's speed accordingly. 3.
Adaptive cruise control uses radar, lasers, cameras, or a combination of any of those items to calculate your surroundings. Its sensors and processors judge what the car in front of you is doing and regulate your car in relation to the one in front of you to maintain a safe distance, braking when they slow down and accelerating when they do, up ...
Adaptive Cruise Control has limited braking capability, so if the vehicle you're following stops too suddenly, you'll get an alert to take action by quickly applying the brakes yourself. If your vehicle has the Driver Attention System (DAS) on the steering column, Adaptive Cruise Control may automatically resume and follow the vehicle ahead ...
With an adaptive cruise control system the car tries to maintain your chosen speed, but will also keep a safe distance to the car in front. If the vehicle ahead slows down or someone cuts into your lane, the car eases off the accelerator or uses the brakes to slow down and keep an appropriate distance. Often you can tell the system whether you ...
Adaptive cruise control is an active vehicle safety system that maintains a cruising speed and automatically varies the speed of your car to match the speed of the car in front of you. If the vehicle ahead accelerates or changes lanes your car will accelerate up to a set speed. For example, if you come up to a car moving slower than your preset ...
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is a driving assistance feature that can control a car's accelerator and brakes to reduce your workload behind the wheel. It's essentially an evolution of traditional cruise control that's able to not only hold your speed, but also follow the traffic ahead and maintain a safe distance.
Adaptive cruise control is a feature found on newer vehicles. It uses sensors to monitor the distance between your car and the one in front of you and then automatically adjusts your speed to maintain a safe following distance.
The cruise control system uses an actuator to control the throttle input and maintain a pre-set speed. This same servomechanism is used in adaptive cruise control too but with the application of ...
Abstract: To build a more accurate and realistic adaptive cruise strategy, demand for ACC in different driving styles should be considered. Therefore, in this paper, an adaptive cruise control strategy considering driving style is proposed. The NGSIM dataset is divided and screened, and an evaluation method based on objectivity score coefficients is proposed to classify driving styles into ...
Activate the cruise control and set your desired speed. Observe how the system responds to the surrounding vehicles. Pay close attention to the distance between your vehicle and the one in front of you. Advertisement. If the system maintains a safe distance and adjusts the speed smoothly, then the calibration was successful.