TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Blog • Perfecting your Craft
Posted on Jun 21, 2017

12 Types of Travel Writing Every Writer Should Know
So, you want to be a travel writer?
There are plenty of reality doses out there already, so we’re going to focus on the positives, and what you can do to maximize your chances of travel writing professionally. One of the first steps: you should absolutely know your markets, and what types of travel writing are popular in them. In today’s competitive market, this knowledge can both help you structure your article and target the right audience.
In this post, we break down modern travel writing into three distinct categories: freelance journalism , blogging, and book writing. Then we identify the prevalent types of travel writing each category is known for, to give you an initial sort of compass in the industry.
Freelance Travel Journalism

The truth is this: the travel sections in major publications (New York Times, Washington Post, Wall Street Journal) are slimmer now, so competition will be tall. But there are other outlets. Local newspapers are sometimes open to travel pitches from freelancers. Certain websites pay for travel articles, while magazines can be great for targeting niche audiences.
So what are the common types of freelance travel journalism?
Destination articles
Here, the game’s in the name: destination articles tell readers about a place they might want to travel one day. One of the most standard type of travel stories, these pieces act as the armchair reader’s bird-eye view of a place. Useful or interesting facts pepper the writing. History, points of interest, natural scenery, trendy spots: a destination article can touch upon them all within the framework of a broad narrative.
Where the average article gives readers a sense of the destination, the best of the best convinces readers that this is a destination they want, nay, need to visit. As such, though some destination articles are written in first person, the focus is rarely on the writer. Instead, the destination is the star of the show.
For examples of destination articles, check out:
- Besalú, the most interesting Spanish village you probably don’t know (LA Times)
- In Indonesia (Washington Post)
- 36 Hours In The Finger Lakes Region of New York (New York Times)

Special-interest articles
Special-interest articles are offshoots of destination articles. Instead of taking the reader on a tour of an entire country or city, these pieces cover one particular aspect of the destination. This kind of writing can cover anything from art in Colombia, ghost towns in the U.S., trekking in Patagonia, alpaca farms in Australia, motorbiking in Brazil, railroads in France, volunteering in Tanzania — you get the gist.
Since special-interest articles are narrower in topic, many writers tailor them for niche magazines or websites. Before you start pitching, we recommend flipping through the Writer’s Handbook , one of the most useful guides to the freelance publishing market, to see which publications fit your target audience.
For a taste of some special-interest articles, see:
- Exploring Portugal — From Pork To Port (epicurious.com)
- This Unsung Corner of Spain is Home to Fabulous Food (Washington Post)
- Karsts of China's Getu River region attract rock climbers, other travelers (CNN Travel)
Holiday and special events
Holiday and special events travel articles ask writers to write about a destination before the event takes place. The biggest global events are magnets for this type of travel writing, such as the World Cup, the Olympics, the World Expo, fashion weeks, and film festivals. Depending on the publication, regional events work just as well.
Want to see what special events pieces look like? Have a read through these:
- This summer’s solar eclipse is southern Illinois’ chance to shine (Chicago Tribune)
- How To Plan A Trip To The 2016 Rio Olympics (Travel & Leisure)
You’ll recognize a round-up article when you see one, as it’ll go, “40 best beaches in West Europe,” or, perhaps, “20 of the greatest walks in the world!” It’s a classic tool in any magazine or newspaper writer’s toolbox, taking a bunch of destinations and grouping them all under one common thread.
Ultimately, a clear motif makes this type of article a breeze to read, as they’re a play on the ubiquitous List Format. But, OK, before you jump at this excuse to sacrifice your belly at 99 food trucks in New York City, remember that your premise should be original, not to mention practical. What’s tough is coming up with X ways to do Y in the first place, as that demands you put in the travel and research to produce a thorough write-up.

Want even more examples of round-up articles? Here you go:
- 12 new art exhibits to see this summer (Smithsonian)
- 21 ways to see America for cheap (Huffington Post)
- 41 places to go in 2011 (New York Times)
Personal essays
Publishers are experiencing something of a personal essay fatigue , so the market for more might be scarce these days. However, quality trumps all, and a good personal travel essay is just plain good writing in disguise: something that possesses a strong voice while showing insight, growth, and backstory.
Just don’t make it a diary entry. In an interview with The Atlantic , travel writer Paul Theroux said: “The main shortcut is to leave out boring things. People write about getting sick, they write about tummy trouble. They write about waiting. They write three pages about how long it took them to get a visa. I’m not interested in the boring parts. Everyone has tummy trouble. Everyone waits in line. I don’t want to hear about it.”
Here’s a jumping-off point for personal travel essays:
- Taking the Great American Roadtrip (Smithsonian)
Have a burning opinion to share? Sometimes publications end up giving op-eds to staff, but there are always open calls for opinion pieces.
Travel op-eds are much rarer than political opinion pieces, but there’s a pattern to the ones that make the cut: good persuasive writing. If you can come at a topic from a unique angle (and argue your case clearly) then you may be able to publish your opinion.
If you’re in the mood for travel op-ed articles, see:
- The West Coast Is The Best Coast For Food In America (Food & Wine)
- Why Climate Change Is Actually Relevant To Travel (Conde Nast)
Travel Blogging

When typing “travel blog” into Google returns 295 million results, we can guess it’s a fairly competitive market.
Here’s the plus side: bloggers get to write what they want and go where they please. When it comes to blog posts, there are no editors, no gatekeepers. Only you and the “PUBLISH” button.
We won’t go revisit the types of travel writing we covered earlier (such as the roundup format). Instead, we’ll explore some of the other formats bloggers use to tell their travel stories. Since the rules of travel blogging are next to non-existent, our tally below is by no means definitive. And, again, our best advice is to note what your favorite bloggers do on their blogs.
Already running a successful travel blog? You might consider turning it into a full-length book !
How-to articles are already fairly popular in magazines, but they’re positively omnipresent in the travel blogging world. Blogs provide a direct communication platform, allowing trust to build up quicker with the readers. As a result, for the search query, “How to travel Europe on a budget,” six out of the top ten results are posts from trusted independent blogs.
A How-To article is the most standard form of advice column a travel blogger can produce. It’s intrinsically useful, promising that it’ll teach something by article’s end. A blogger’s challenge is delivering fully on that promise.
How to read more How-To articles? We got you covered:
- How To Start A Travel Blog (Nomadic Matt)
- How To Travel Solo To A Party Destination (Adventurous Kate)
- How to Visit Penang’s Kek Lok Si Temple (Migrationology)
Itineraries
Itineraries reveal the schedule that the writer took at a given destination, city-by-city or sight-by-sight. They’re meant for the traveler who’s embarking on a similar trip and needs a template. Typically, you’ll find that an itinerary post is an easy place for you to slip in recommendations, anything from the accommodation you used or the restaurants you tried.
You can use itinerary posts to reinforce your blog’s brand. For instance, an itinerary posted on a blog focused around budget travel will probably maximize cost-saving chances.
For more itineraries, see:
- My Trip To Japan (A Complete Japan Itinerary)
- Backpacking Vietnam on a budget: 2-3 Weeks Itinerary + Tips
Longform posts
Longform travel blogging tells a travel story through extended narrative content, as it takes a week’s worth of adventure and shapes it into a story. Longform blog posts about travel often end up being creative nonfiction : a way to present nonfiction — factually accurate prose about real people and events — in a compelling, vivid, dramatic manner.
Photography can add another dimension to the form, as Emmanuel Nataf (our co-founder!) shows on his travel blog . And Reedsy's very own Arielle provides a glimpse into why she prefers longform travel writing on her blog, Steps, a Travel Journal :
My favourite kinds of stories are the ones that give you a real sense of place. That’s why I enjoy longform travel blogging: I get to describe the character of a place through the experiences I encountered there.
If you want to dip your toe into the sea of longform posts, you can also read:
- The Cow Head Taco Philosopher King of Oaxaca (Legal Nomads)
- The Best Worst Museum In The World

When it comes to writing a book, you can take all the challenges about travel writing from above and magnify it times 2,000. If you’re asking readers to commit to you for more than 100 pages, you’d best make sure that your book is worth their while.
As far as examples go, travel writing’s boomed in the mainstream book market recently. But there’s much more to it than Eat, Pray, Love and its descendants.
Travelogues
In travelogues, authors record their adventures in a way that illustrates or sheds insight upon the place itself. Travelogues possess a storied past, from Lady Mary Wortley Montagu’s Turkish Embassy Letters in 1763 to Mark Twain’s 1867 The Innocents Abroad , which paved the way for the sort of comic travelogues that Bill Bryson’s perfected today.
Up for some travelogues? Check out:
- Notes From A Small Island , by Bill Bryson
- In Patagonia , by Bruce Chatwin
- Travels with Charley In Search of America , by John Steinbeck
Travel memoirs
Nowadays, travel memoirs are practically synonymous with Elizabeth Gilbert’s wildly popular Eat, Pray, Love and Cheryl Strayed’s bestselling Wild , both of which were recently adapted into Hollywood blockbusters.
That said, be aware that you’ll need a pretty exceptional personal story for your memoir to compete in today’s market . If you’re still set on writing or self-publishing a travel memoir, it’s tricky to balance personal backstory and travel for 400 pages, so think about taking on a professional for a second pair of eyes.
Did you know? You can find Nicki Richesin , a top Bloomsbury editor who’s edited for Cheryl Strayed, on our marketplace.
In addition to Eat, Pray, Love and Wild , you can read:
- Under the Tuscan Sun , by Frances Mayes
- Coasting , by Jonathan Raban
- Wind, Sand, and Stars , by Antoine de Saint-Exupéry
As Oscar Wilde said, “I never travel without my diary. One should always keep something sensational to read in the train.” But these days, people are replacing diaries with travel guides — the ubiquitous Lonely Planet becoming one of the more common sights on transit.
Travel writing in guidebooks is straightforward, informative, and fact-filled. In addition, a certain amount of responsibility comes with the job. Lonely Planet alone is read by millions of travelers worldwide.
General Tips and Guidelines

As we mentioned before, the trick to producing great travel writing is ultimately simply writing well . To that extent, you should make sure to follow all the guidelines of good writing — not least, spell-checking your article before submitting or publishing it anywhere. You don’t want an editor or reader to see it while it stilll reads lik edis.
Also, keep in mind the tone, style, and vibe of the publication and platform (and by extension, your audience). A story about a moon-rock could go into a kid's magazine or it could go into Scientific America .
Finally, some category-specific tips:
- If you’re freelance writing, always check submission guidelines. Publications may accept only pitches or they may welcome articles “on spec” (pre-written articles). Some sources only take travel articles that were written within 6 months of the trip.
- If you’re blogging, brand your website (same advice if you’re an author who’s building a homepage ).
- If you’re writing a book, get a professional editor! An unedited book is an unwieldy thing, and professional eyes provide direction, continuity, and assonance. ( Layout designers can be important if you’re publishing a travel photography book, in the meanwhile.)
Travel writing isn't a cinch. In fact, it's a long and often hard grind. But by figuring out what type of travel writing you want to try your hand at, you're taking the crucial first step.
7 responses
Amanda Turner says:
20/03/2018 – 16:20
Thank you, this was very helpful. Here's one of mine: http://vagabondingwithkids.com/every-mothers-guide-to-piranha-fishing-in-the-amazon/
Travalerie says:
24/05/2018 – 18:42
I landed on this page Googling for one thing and coming up with another. Haha! But what I found instead was helpful as I'm devouring as much as I can on travel writing. A few months ago, I started a new travel business, revamped my website including a new blog, and am in the process of writing, writing, writing. I took 2 trips this year so far and wrote what seemed like a mini-novella. Burning out in the process. I know I can do better. But I had no idea what I was writing could be re-worked to fit a certain category of travel writing -- which is what I found helpful in this post above. Thanks https://www.travalerie.com/blog
Surya Thakur says:
04/03/2019 – 12:39
Very good information. Lucky me I discovered your blog by chance (stumbleupon). I’ve saved as a favorite for later! KuLLuHuLLs
David Bishop says:
08/05/2019 – 12:28
Thanks for this good article. I'm in my third year on the road and recently started my senior solo adventure travel website. I think my site has some pretty good stuff, of course. Take a look and tell me what you think. www.davidhunterbishop.com
Iris C. Permuy says:
23/05/2019 – 18:03
Thank you very much for all of these useful pieces of advice. I will make sure to implement them all on my travel blog, which is a combination of travel and gastronomy and uses the memoir and itinerary types, apart from recipes. Come check it out if you feel like it! I am more than open, eager for some professional feedback :)
Serissa says:
26/10/2019 – 14:53
This post is the perfect diving board for aspiring travel writers. I plan to link to this page from my travel blog if that is alright! ?? The link on my website will appear as "[title of this post] by Reedsy Blog". I assume this is alright, but if not, please email me directly to let me know! Thanks so much!
↪️ Martin Cavannagh replied:
29/10/2019 – 10:11
We'd be absolutely delighted if you shared this article on your blog :)
Comments are currently closed.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

450+ Powerful Adjectives to Describe a Person (With Examples)
Want a handy list to help you bring your characters to life? Discover words that describe physical attributes, dispositions, and emotions.

How to Plot a Novel Like a NYT Bestselling Author
Need to plot your novel? Follow these 7 steps from New York Times bestselling author Caroline Leavitt.

How to Write an Autobiography: The Story of Your Life
Want to write your autobiography but aren’t sure where to start? This step-by-step guide will take you from opening lines to publishing it for everyone to read.

What is the Climax of a Story? Examples & Tips
The climax is perhaps a story's most crucial moment, but many writers struggle to stick the landing. Let's see what makes for a great story climax.

What is Tone in Literature? Definition & Examples
We show you, with supporting examples, how tone in literature influences readers' emotions and perceptions of a text.

Writing Cozy Mysteries: 7 Essential Tips & Tropes
We show you how to write a compelling cozy mystery with advice from published authors and supporting examples from literature.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

We made a writing app for you
Yes, you! Write. Format. Export for ebook and print. 100% free, always.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
Trending Post : 52 Best Things to do in Ireland

Great Travel Writing Examples from World Renowned Travel Writers
Are you ready to be a better travel writer? One of the best ways to do this is to read great travel writing examples from great travel writers.
Writing about travel in a way that keeps your reader reading is not always easy. Knowing how to write an irresistible first paragraph to entice the reader to keep reading is key. Writing a lede paragraph that convinces the reader to finish the article, story or book is great travel writing. This article features travel writing examples from award-winning travel writers, top-selling books, New York Times travel writers, and award-winning travel blogs.
Ads are how we pay our bills and keep our blog free for you to enjoy. We also use affiliate links; if you make a purchase through them, we may receive a small commission at no cost to you.

The writers featured in this article are some of my personal favorite travel writers. I am lucky to have met most of them in person and even luckier to consider many friends. Many I have interviewed on my podcast and have learned writing tips from their years of travel writing, editing and wisdom.
11 Great Travel Writing Examples
Writing with feeling, tone, and point of view creates a compelling story. Below are examples of travel writing that include; first paragraphs, middle paragraphs, and final paragraphs for both travel articles as well as travel books.
I hope the below examples of travel writing inspire you to write more, study great travel writing and take your writing to a higher level.
Writing Example of a Travel Book Closing Paragraphs

Don George is the author of the award-winning anthology The Way of Wanderlust: The Best Travel Writing of Don George , and the best-selling travel writing guide in the world: How to Be a Travel Writer .
He is currently Editor at Large for National Geographic Travel, and has been Travel Editor at the San Francisco Examiner-Chronicle, Salon, and Lonely Planet.
I had the wonderful opportunity to see Don speak at Tbex and read from one of his books as well as interview him on the Break Into Travel Writing podcast. You can listen to the full podcast here .
Below is the closing of Don’s ebook: Wanderlust in the Time of Coronavirus: Dispatches from a Year of Traveling Close to Home
I continued hiking up to Lost Trail and then along Canopy View Trail. Around noon I serendipitously came upon a bench by the side of the trail, parked my backpack, and unpacked my lunch. Along with my sandwiches and carrot sticks, I feasted on the tranquility and serenity, the sequoia-swabbed purity of the air, the bird and brook sounds and sun-baked earth and pine needle smells, the sunlight slanting through the branches, the bright patch of blue sky beyond.
At one point I thought of shinrin-yoku, forest bathing, the Japanese practice that has become widely popular in the U.S. This was a perfect example of shinrin-yoku, I thought: Here I am, alone in this forest, immersed in the sense and spirit of these old-growth redwoods, taking in their tranquility and timelessness, losing myself to their sheer size and age and their wild wisdom that fills the air.
I sat there for an hour, and let all the trials, tremors, and tribulations of the world I had left in the parking lot drift away. I felt grounded, calm, quiet—earth-bound, forest-embraced.
In another hour, or two, I would walk back to the main paved trail, where other pilgrims would be exclaiming in awe at the sacred sequoias, just as I had earlier that day.
But for now, I was content to root right here, on this blessed bench in the middle of nowhere, or rather, in the middle of everywhere, the wind whooshing through me, bird-chirps strung from my boughs, toes spreading under scratchy pine needles into hard-packed earth, sun-warmed canopy reaching for the sky, aging trunk textured by time, deep-pulsing, in the heart of Muir Woods.
- You can read the whole story here: Old Growth: Hiking into the Heart of Muir Woods
- Please also download Don’s free ebook here: Wanderlust in the Time of Coronavirus
- In addition to writing and editing, Don speaks at conferences, lectures on tours around the world, and teaches travel writing workshops through www.bookpassage.com .

Writing Example of a Travel Book Intro Paragraphs
Francis tapon.

Francis Tapon , author of Hike Your Own Hike and The Hidden Europe , also created a TV series and book called The Unseen Africa, which is based on his five-year journey across all 54 African countries.
He is a three-time TEDx speaker. His social media username is always FTapon. I interviewed Francis on the Break Into Travel Writing podcast about “How to Find An Original Point of View as a Travel Writer “. You can listen to the full podcast here .
Below is the opening of Francis’ book, The Hidden Europe:
“This would be a pretty lousy way to die,” I thought.
I was locked in an outhouse with no way out. Outhouses sometimes have two latches—one on the outside and one on the inside. The outside latch keeps the door shut to prevent rodents and other creatures who like hanging out in crap from coming in. Somehow, that outer latch accidentally closed, thereby locking me in this smelly toilet. I was wearing a thin rain jacket. The temperature was rapidly dropping.
“This stinks,” I mumbled. It was midnight, I was above the Arctic Circle, and the temperatures at night would be just above freezing. There was no one around for kilometers. If I didn’t get out, I could freeze to death in this tiny, smelly, fly-infested shithole.
My mom would kill me if I died so disgracefully. She would observe that when Elvis died next to a toilet, he was in Graceland. I, on the other hand, was in Finland, not far from Santa Claus. This Nordic country was a jump board for visiting all 25 nations in Eastern Europe.
You can find his book on Amazon: The Hidden Europe: What Eastern Europeans Can Teach Us
For $2 a month, you can get Francis’ book as he writes it: Patreon.com/ftapon
Intro (Lede) Paragraph Examples of Great Travel Writing Articles
Michele peterson.

Former banking executive Michele Peterson is a multi-award-winning travel and food writer who divides her time between Canada, Guatemala, and Mexico (or the nearest tropical beach).
Former banking executive Michele Peterson is a multi-award-winning travel and food writer who divides her time between Canada, Guatemala, and Mexico (or the nearest tropical beach). Her writing has appeared in Lonely Planet’s Mexico from the Source cookbook, National Geographic Traveler, Conde Nast’s Gold List, the Globe and Mail, Fifty-five Plus and more than 100 other online and print publications.
She blogs about world cuisine and sun destinations at A Taste for Travel website. I met Michele on my first media trip that took place in Nova Scotia, Canada. I also had the pleasure of interviewing about “ Why the Odds are in Your Favor if you Want to Become a Travel Writer” . You can listen to the full podcast here .
Michele’s Lede Paragraph Travel Writing Example
I’m hiking through a forest of oak trees following a farmer who is bleating like a pied piper. Emerging from a gully is a herd of black Iberian pigs, snuffling in response. If they weren’t so focused on following the swineherd, I would run for the hills. These pigs look nothing like the pink-cheeked Babe of Hollywood fame.
These are the world’s original swine, with lineage dating back to the Paleolithic Stone Age period where the earliest humans decorated Spain’s caves with images of wild boars. Their powerful hoofs stab the earth as they devour their prized food, the Spanish bellota acorn, as fast as the farmer can shake them from the tree with his long wooden staff. My experience is part of a culinary journey exploring the secrets of producingjamón ibérico de Bellota, one of the world’s finest hams.
You can read the full article here: Hunting for Jamón in Spain
Perry Garfinkel

Perry Garfinkel has been a journalist and author for an unbelievable 40 years, except for some years of defection into media/PR communications and consulting.
He is a contributor to The New York Times since the late ’80s, writing for many sections and departments. He has been an editor for, among others, the Boston Globe, the Middlesex News, and the Martha’s Vineyard Times.
He’s the author of the national bestseller “ Buddha or Bust: In Search of the Truth, Meaning, Happiness and the Man Who Found Them All ” and “ Travel Writing for Profit and Pleasure “.
Perry has been a guest on my podcast twice. He gave a “ Master Class in Travel Writing ” you can listen to the full podcast here . He also shared “ How to Find Your Point Of View as a Travel Writer ” you can listen to the full episode here .
Perry’s Lede Travel Article Example from the New York Times
SAN FRANCISCO — A block off Grant Avenue in San Francisco’s Chinatown – beyond the well-worn path tourists take past souvenir shops, restaurants and a dive saloon called the Buddha Bar – begins a historical tour of a more spiritual nature. Duck into a nondescript doorway at 125 Waverly Place, ascend five narrow flights and step into the first and oldest Buddhist temple in the United States.
At the Tien Hau Temple, before an intricately carved gilded wooden shrine and ornate Buddha statues, under dozens of paper lanterns, Buddhists in the Chinese tradition still burn pungent incense and leave offerings to the goddess Tien Hau in return for the promise of happiness and a long life.
You can read the full article here: Taking a Buddhist pilgrimage in San Francisco
Elaine Masters

Elaine Masters apologizes for pissing off fellow travelers while tracking story ideas, cultural clues, and inspiring images but can’t resist ducking in doorways or talking with strangers.
She’s recently been spotted driving her hybrid around the North American West Coast and diving cenotes in the Yucatan. Founder of Tripwellgal.com, Elaine covers mindful travel, local food, overlooked destinations and experiences. Elaine was a guest on my podcast where we spoke about “ How to Master the CVB Relationship “. You can listen to the full podcast here .
Elaine’s Lede Example
I jiggered my luggage onto the escalator crawling up to the street. As it rose into the afternoon light, an immense shadow rose over my shoulder. Stepping onto the sidewalk, I burst into giggles, looking like a madwoman, laughing alone on the busy Barcelona boulevard. The shadow looming overhead was the Sagrada Familia Cathedral. It had mesmerized me forty years earlier and it was the reason I’d finally returned to Spain.
You can read the full article here: Don’t Miss Going Inside Sagrada Familia, Barcelona’s Beloved Cathedral

Along with his wife, photographer Mary Gabbett, Bret Love is the Co-Founder/Editor In Chief of Green Global Travel and the Blue Ridge Mountains Travel Guide.
He’s also an award-winning writer whose work has been featured by more than 100 publications around the world, including National Geographic, Rolling Stone, American Way, the Washington Post, and the New York Times.
Bret’s Lede Example
Congo Square is quiet now. Traffic forms a dull drone in the distance. A lone percussionist taps out ancient tribal rhythms on a two-headed drum. An air compressor from Rampart Street road construction provides perfectly syncopated whooshes of accompaniment.
Shaded park benches are surrounded by blooming azaleas, magnolias, and massive live oaks that stretch to provide relief from the blazing midday sun. It’s an oasis of solitude directly across the street from the French Quarter.
Congo Square is quiet now. But it’s here that the seeds of American culture as we know it were sown more than 200 years ago. And the scents, sounds, and sights that originated here have never been more vital to New Orleans than they are now, more than a decade after Hurricane Katrina devastated the city.
You can read the full article here: Treme, New Orleans (How Congo Square Was The Birthplace Of American Culture)
Middle Paragraph Examples of Great Travel Writing Articles
Mariellen ward.

Canadian travel writer and blogger Mariellen Ward runs the award-winning travel site Breathedreamgo.com , inspired by her extensive travels in India.
She has been published in leading media outlets worldwide and offers custom tours to India through her company India for Beginners. Though Canadian by birth, Mariellen considers India to be her “soul culture” and she is passionate about encouraging mindful travel.
Mariellen’s Middle Paragraph Example
While the festival atmosphere swirled around me, I imbued my diya with hope for personal transformation. I had come to India because a river of loss had run through my life, and I had struggled with grief, despair and depression for eight years. I felt I was clinging to the bank, but the effort was wearing me out. Deciding to leave my life and go to India was like letting go of the bank and going with the flow of the river. I had no idea where it would lead me, what I would learn or how I would change. I only knew that it was going to be big.
You can read the full article here: The River: A tale of grief and healing in India

Joe Baur is an author and filmmaker from Cleveland currently based in Berlin. His work has appeared in a variety of international publications, including BBC Travel, National Geographic, and Deutsche Welle.
He regularly reports for the Jewish Telegraphic Agency and is the author of Talking Tico detailing his year of living in Costa Rica and traveling around Central America. I interviewed Joe about “ How to Find Unique Travel Stories “. You can listen to the full podcast here .
Joe Baur’s Middle Paragraph Example
I first became aware of the Harz mountains and the Brocken when reading the works of some of Germany’s great writers, like Goethe and Heinrich Heine. Legends of witches congregating with the devil being the main theme of the mountain’s mythology. I, however, was more interested in a refreshing time spent in nature rather than reveling with the devil.
The first stage from Osterode to Buntenbock was a warm-up to the more rigorous stages ahead. It began on sidewalks before sliding into the forest sporting a healthy shade of green — a gentle jaunt that made my hiking boots feel a bit like overkill given the dry, pleasant weather.
You can read the full article here: Follow the witch through the forest: 5 days hiking Germany’s Harz
Samantha Shea

Samantha is a freelance travel writer with bylines in Matador Network, GoNomad and more. She also runs the travel blog Intentional Detours which provides thorough guides and tales related to offbeat adventure travel in South Asia and beyond.
When she’s not writing she enjoys cycling, hiking, the beach, as well as language learning.
Samantha Shea’s Middle Paragraph Example
Suddenly, the spark of a match pulsed through the early-fall afternoon and my head snapped towards the men. Amir touched the flame to an unidentifiable object that seconds later made itself known by the deep earthy scent of Pakistani hashish.
Amir’s ice blue eyes focused intently on his creation: a combination of tobacco and nuggets of greenish-brown charas. He forced the mixture back into the cigarette, before bringing it to his pursed lips, flicking the match, and setting flame to his high.
I reached out from the cot to take my turn and took a deep inhale, acutely pleased. I savored the familiar burn of the drag, the rows and rows of corn and apple plants in front of me, the stuttered cacophony of animal exclamations behind me, and the generosity of the men to my left, some of whom we had just met an hour before.
You can read the full article here: Thall Tales: A Hazy Afternoon in Thall, Pakistan
Final Paragraph Example of Great Travel Writing Articles
Cassie bailey.
Cassie is a travel writer who has solo backpacked around Asia and the Balkans, and is currently based in Auckland. Alongside in-depth destination guides, her blog has a particular focus on storytelling, mental health, and neurodiversity.
Cassie’s Final Paragraphs Example
So my goal is to feel, I guess. And I don’t mean that in a dirty way (although obvz I do mean that in a dirty way too). This is why we travel, right? To taste crazy new foods and to feel the sea breeze against our skin or the burn on the back of our legs on the way down a mountain. We want to feel like shite getting off night buses at 4am and the sting of mosquito bites. We know we’re going to feel lost or frustrated or overwhelmed but we do it anyway. Because we know it’s worth it for the ecstasy of seeing a perfect view or making a new connection or finding shitty wine after a bad day.
My goal is never to become numb to all of this. To never kid myself into settling for less than everything our bodies allow us to perceive. I’m after the full human experience; every bit, every feeling.
You can read the full article here: Goals inspired by life as a solo backpacker
Lydia Carey

Lydia Carey is a freelance writer and translator based out of Mexico City who spends her time mangling the Spanish language, scouring the country for true stories and “researching” every taco stand in her neighborhood.
She is the author of “ Mexico City Streets: La Roma ,” a guide to one of Mexico City’s most eclectic neighborhoods and she chronicles her life in the city on her blog MexicoCityStreets.com .
Lydia’s Final Paragraphs Example
Guys from the barrio huddle around their motorcycles smoking weed and drinking forties. Entire families, each dressed as St. Jude, eat tacos al pastor and grilled corn on a stick. Police stand at a distance, keeping an eye on the crowd but trying not to get too involved.
After this celebration, many of the pilgrims will travel on to Puebla where they will visit some of the religious relics on display in the San Judas church there. But many more will simply go back to their trades—legal and illegal—hoping that their attendance will mean that San Judas protects them for another year, and that he has their back in this monster of a city.
You can read the full article here: San Judas de Tadeo: Mexico’s Defender of Lost Causes

I hope you enjoyed these examples of travel writing and they have inspired you to want to write more and write better! The next article that will be published is a follow-up to this and will include travel writing examples from my first travel writing teacher, Amanda Castleman. This article will include travel writing tips from Amanda and travel writing examples from her students as well as one from her own writing.

Follow 52 Perfect Days on Facebook | Twitter | Pinterest | Instagram
If you liked it, please share it. Thank you!
- Pinterest 1
Alexa Meisler is the editorial director of 52 Perfect Days. Born in Paris, France she has since lived in Chicago, San Francisco, Los Angeles and Portland, Oregon. She currently resides in San Diego with her husband and son where they enjoy exploring California and Mexico.
Travel has always been a part of her life; traveling to such places as Morocco, Tangiers and Spain as a young child as well as taking many road trips to Mexico with her grandparents as a young girl. Since then, she has traveled abroad to locations such as Russia, Taiwan and throughout Europe.
Prior to working at 52 Perfect Days she was a freelance travel writer; focusing on family and women’s adventure experiences.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
What You Should Know About Travel Writing
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Travel writing is a form of creative nonfiction in which the narrator's encounters with foreign places serve as the dominant subject. Also called travel literature .
"All travel writing—because it is writing—is made in the sense of being constructed, says Peter Hulme, "but travel writing cannot be made up without losing its designation" (quoted by Tim Youngs in The Cambridge Introduction to Travel Writing , 2013).
Notable contemporary travel writers in English include Paul Theroux, Susan Orlean, Bill Bryson , Pico Iyer, Rory MacLean, Mary Morris, Dennison Berwick, Jan Morris, Tony Horwitz, Jeffrey Tayler, and Tom Miller, among countless others.
Examples of Travel Writing
- "By the Railway Side" by Alice Meynell
- Lists and Anaphora in Bill Bryson's "Neither Here Nor There"
- Lists in William Least Heat-Moon's Place Description
- "London From a Distance" by Ford Madox Ford
- "Niagara Falls" by Rupert Brooke
- "Nights in London" by Thomas Burke
- "Of Trave," by Francis Bacon
- "Of Travel" by Owen Felltham
- "Rochester" by Nathaniel Hawthorne
Observations About Travel Writing
Authors, journalists, and others have attempted to describe travel writing, which is more difficult to do than you might think. However, these excerpts explain that travel writing—at a minimum—requires a sense of curiosity, awareness, and fun.
Thomas Swick
- "The best writers in the field [of travel writing] bring to it an indefatigable curiosity, a fierce intelligence that enables them to interpret, and a generous heart that allows them to connect. Without resorting to invention , they make ample use of their imaginations. . . . "The travel book itself has a similar grab bag quality. It incorporates the characters and plot line of a novel, the descriptive power of poetry, the substance of a history lesson, the discursiveness of an essay , and the—often inadvertent—self-revelation of a memoir . It revels in the particular while occasionally illuminating the universal. It colors and shapes and fills in gaps. Because it results from displacement, it is frequently funny. It takes readers for a spin (and shows them, usually, how lucky they are). It humanizes the alien. More often than not it celebrates the unsung. It uncovers truths that are stranger than fiction. It gives eyewitness proof of life’s infinite possibilities." ("Not a Tourist." The Wilson Quarterly , Winter 2010)
Casey Blanton
- "There exists at the center of travel books like [Graham] Greene's Journey Without Maps or [V.S.] Naipaul's An Area of Darkness a mediating consciousness that monitors the journey, judges, thinks, confesses, changes, and even grows. This narrator , so central to what we have come to expect in modern travel writing , is a relatively new ingredient in travel literature, but it is one that irrevocably changed the genre . . . . "Freed from strictly chronological , fact-driven narratives , nearly all contemporary travel writers include their own dreams and memories of childhood as well as chunks of historical data and synopses of other travel books. Self reflexivity and instability, both as theme and style , offer the writer a way to show the effects of his or her own presence in a foreign country and to expose the arbitrariness of truth and the absence of norms." ( Travel Writing: The Self and the World . Routledge, 2002)
Frances Mayes
- "Some travel writers can become serious to the point of lapsing into good ol' American puritanism. . . . What nonsense! I have traveled much in Concord. Good travel writing can be as much about having a good time as about eating grubs and chasing drug lords. . . . [T]ravel is for learning, for fun, for escape, for personal quests, for challenge, for exploration, for opening the imagination to other lives and languages." (Introduction to The Best American Travel Writing 2002 . Houghton, 2002)
Travel Writers on Travel Writing
In the past, travel writing was considered to be nothing more than the detailing of specific routes to various destinations. Today, however, travel writing has become much more. Read on to find out what famous travel writers such as V.S. Naipaul and Paul Theroux say about the profession.
V.S. Naipaul
- "My books have to be called ' travel writing ,' but that can be misleading because in the old days travel writing was essentially done by men describing the routes they were taking. . . . What I do is quite different. I travel on a theme . I travel to make an inquiry. I am not a journalist. I am taking with me the gifts of sympathy, observation, and curiosity that I developed as an imaginative writer. The books I write now, these inquiries, are really constructed narratives." (Interview with Ahmed Rashid, "Death of the Novel." The Observer , Feb. 25, 1996)
Paul Theroux
- - "Most travel narratives—perhaps all of them, the classics anyway—describe the miseries and splendors of going from one remote place to another. The quest, the getting there, the difficulty of the road is the story; the journey, not the arrival, matters, and most of the time the traveler—the traveler’s mood, especially—is the subject of the whole business. I have made a career out of this sort of slogging and self-portraiture, travel writing as diffused autobiography ; and so have many others in the old, laborious look-at-me way that informs travel writing ." (Paul Theroux, "The Soul of the South." Smithsonian Magazine , July-August 2014) - "Most visitors to coastal Maine know it in the summer. In the nature of visitation, people show up in the season. The snow and ice are a bleak memory now on the long warm days of early summer, but it seems to me that to understand a place best, the visitor needs to see figures in a landscape in all seasons. Maine is a joy in the summer. But the soul of Maine is more apparent in the winter. You see that the population is actually quite small, the roads are empty, some of the restaurants are closed, the houses of the summer people are dark, their driveways unplowed. But Maine out of season is unmistakably a great destination: hospitable, good-humored, plenty of elbow room, short days, dark nights of crackling ice crystals. "Winter is a season of recovery and preparation. Boats are repaired, traps fixed, nets mended. “I need the winter to rest my body,” my friend the lobsterman told me, speaking of how he suspended his lobstering in December and did not resume until April. . . ." ("The Wicked Coast." The Atlantic , June 2011)
Susan Orlean
- - "To be honest, I view all stories as journeys. Journeys are the essential text of the human experience—the journey from birth to death, from innocence to wisdom, from ignorance to knowledge, from where we start to where we end. There is almost no piece of important writing—the Bible, the Odyssey , Chaucer, Ulysses —that isn't explicitly or implicitly the story of a journey. Even when I don't actually go anywhere for a particular story, the way I report is to immerse myself in something I usually know very little about, and what I experience is the journey toward a grasp of what I've seen." (Susan Orlean, Introduction to My Kind of Place: Travel Stories from a Woman Who's Been Everywhere . Random House, 2004) - "When I went to Scotland for a friend's wedding last summer, I didn't plan on firing a gun. Getting into a fistfight, maybe; hurling insults about badly dressed bridesmaids, of course; but I didn't expect to shoot or get shot at. The wedding was taking place in a medieval castle in a speck of a village called Biggar. There was not a lot to do in Biggar, but the caretaker of the castle had skeet-shooting gear, and the male guests announced that before the rehearsal dinner they were going to give it a go. The women were advised to knit or shop or something. I don't know if any of us women actually wanted to join them, but we didn't want to be left out, so we insisted on coming along. . . ." (Opening paragraph of "Shooting Party." The New Yorker , September 29, 1999)
Jonathan Raban
- - "As a literary form, travel writing is a notoriously raffish open house where different genres are likely to end up in the bed. It accommodates the private diary , the essay , the short story, the prose poem, the rough note and polished table talk with indiscriminate hospitality. It freely mixes narrative and discursive writing." ( For Love & Money: Writing - Reading - Travelling 1968-1987 . Picador, 1988)
- - "Travel in its purest form requires no certain destination, no fixed itinerary, no advance reservation and no return ticket, for you are trying to launch yourself onto the haphazard drift of things, and put yourself in the way of whatever changes the journey may throw up. It's when you miss the one flight of the week, when the expected friend fails to show, when the pre-booked hotel reveals itself as a collection of steel joists stuck into a ravaged hillside, when a stranger asks you to share the cost of a hired car to a town whose name you've never heard, that you begin to travel in earnest." ("Why Travel?" Driving Home: An American Journey . Pantheon, 2011)
- Quotes About Being Alone—but Not Lonely
- A List of Every Nobel Prize Winner in English Literature
- 100 Major Works of Modern Creative Nonfiction
- What is Nature Writing?
- Defining Nonfiction Writing
- Creative Nonfiction
- First-Person Point of View
- Sports Writing as a Form of Creative Nonfiction
- Tips on Great Writing: Setting the Scene
- Point of View in Grammar and Composition
- An Introduction to Literary Nonfiction
- John McPhee: His Life and Work
- 11 Things You Should Know About Trees
- Definition and Examples of Humorous Essays
IB Language and Literature 2.0
Group 1 english higher and standard level, faraway places: travel writing.
“Is it lack of imagination that makes us come to imagined places, not just stay at home?” Elizabeth Bishop, poet (1911–1979)
In this section you’ll come to understand the conventions of travel writing , learn a bit about the history of the genre, question why people are compelled to travel – and to write about it – and investigate the overlap between language and literature that exists in the wide and varied genre of travel writing. You’ll read non-fiction texts that feel like stories and see imaginary scenes presented as fact. You’ll learn to decode elements of travel writing and question texts more closely, finding analysis points and learning to evaluate various pieces of writing. These kinds of skills underpin your success in Paper 1 at the end of your course. Begin your study by reading The Travel Narrative from the list of articles below, and then choose one or two more pieces of wider reading to enrich your study:
- The Travel Narrative (IB Textbook)
- A Short History of Travel Writing (Traveltester article)
Reading Challenge
This is a longer and more challenging piece of reading, but spending time on this piece, and discussing it with your teacher, will help you master this topic:
- The Elasticity of Place (an interview with a travel writer)
Class Activit y 1: why do we travel?

As you will have learned by now, people travel – and write about the places they visit – for a variety of reasons. the most common are:
- to find the self
- curiosity about the ‘other’
- religious or spiritual reasons;
- to search for one’s roots;
- to be informed
- to experience ‘awe’
In this activity, you’ll practice identifying these purposes in travel writing. Visit Travel Tales, a collection of stories and articles curated and edited by Lavinia Spalding. Slowly scroll down the home page of her site, reading the titles and blurbs of the various stories you find there. Can you infer the purpose of travel from these snippets of information? Refer to The Travel Narrative (above) for more information of the purposes of travel writing.
Class Activity 2: seven travel stories
The travel genre is wide and varied – and this small collection of travel stories will give you a little taste of some famous (and not-so-famous) writers’ work. You may recognise one or two of these names, such as Bram Stoker and Bill Bryson.
Inside the booklet you’ll find seven short travel tales: either read them yourself, or divide them amongst the people in your class. Use this powerpoint to record your observations about the genre of travel writing. However many extracts you attempt, feed back what you’ve done to the rest of the class.
Areas of Exploration Guiding Conceptual Question
‘Cultural practices’ refers to traditional or customary practices of a particular ethnic, national or cultural group. They can be considered in the same way as symbolism in literary texts; physical manifestations of abstract beliefs and values . One reason we travel is to discover the beliefs and values of different people, as practiced in rites and traditions which have often been passed down from generation to generation. Before you work through the resource below, can you think of any practices that are special in your culture? These may include religious, medical, artistic, culinary, political, family or any other behaviour that reveals underlying beliefs and values:
- H ow do texts reflect, represent or form a part of cultural practices?
Discussion Points
After you’ve got your head around the material in this section, pair up, pick a question, spend five minutes thinking and noting down your thoughts – then discuss your ideas with a friend and report back to the class:
- Why is travel writing important? How is it different from other kinds of journalism?
- In the twenty-first century, is travel writing still necessary? Given that technology can connect us with people and places all around the world, and we can watch videos, read blogs, and browse the social media of people who live in other places, what is the point of reading first person accounts of travel by outsiders to those places?
- Is there a difference between a traveller and a tourist? What makes a person one rather than the other? Is it preferable to be one over the other?
Learner Portfolio
Watch Livinia Spalding’s Tedtalk (above) and, if you have not done so already, visit Travel Tales to browse some of the stories from her collection. Near the end of this talk Lavinia issues a challenge: to write your own literary travel story, inspired by a place you’ve been or a person you’ve met on a journey you have taken. Take her up on this challenge by writing a piece of literary non-fiction about a place you have been ora journey you have taken in your life. Make the purpose of your writing clear: is it to find the self; discover the ‘other’; become informed; search for your roots; take a religious or spiritual journey, experience ‘awe’ – or some combination of purposes?
Paper 1 Text Type Focus: travel writing
At the end of your course you will be asked to analyze unseen texts (1 at Standard Level and 2 at Higher Level) in an examination. You will be given a guiding question that will focus your attention on formal or stylistic elements of the text(s), and help you decode the text(s)’ purpose(s). Travel writing is an extremely fluid genre and you could be presented with a text that contains a variety of tropes (such as maps, photographs, itineraries, reported or direct speech, humour, metaphors… the list goes on) and may even share similarities with literary texts. Use these practice texts to familiarise yourself with the different features of Travel Writing and add them to your Learner Portfolio; you will want to revise text types thoroughly before your Paper 1 exam. You can find more information – including text type features and sample Paper 1 analysis – by visiting 20/20 . Read through one or two of the exemplars, then choose a new paper and have a go at writing your own Paper 1 analysis response:
- A Fish with Hair
- The Mangyan of Mindanao
- Enter Tasmania’s Labyrinth ( Past Paper)
- Cycling Tips (Past Paper)
- Taj Mahal (Past Paper)
- Long Enough in Jo’burg (Past Paper)
- Travel Tales (Past Paper)
- Hunting Moose (Past Paper)
Key features of travel writing
- Viewpoint: travel writing often documents the personal experiences of someone exploring a new place or country so is often first person.
- Perspective: an outsider’s perspective is common when reading travel writing, particularly if the destination is new, exotic or remote. Alternatively, the piece might be written from an insider’s perspective and is inviting you to visit or share an experience in a different part of the world.
- Structure: look out for chronological timelines, past – present structures or a linear journey of discovery. Guidebooks will have clear headings and subheadings and will probably include box-outs and the like.
- Information: travel writing often seeks to be informative and can present you with facts and figures, names and dates, historical or architectural or geographical information and more.
- Description: if the writer is trying to make the destination tantalising, or to help transport the reader, you might find examples of visual imagery, vivid description , even figurative comparisons , helping you visualise a far-off place.
- Visuals: photographs, maps , or floor plans of famous locations are all visual features that you might encounter in travel writing, particularly guidebooks.
Body of Work: Alison Wright Photography
Alison Wright is an author, photographer and speaker who has published several collections of photo-essays including Faces of Hope: Children of a Changing World and The Spirit of Tibet: Portrait of a Culture. Her most recent collection from 2018 is titled Human Tribe . Her mission is to document endangered cultures and traditions from around the world, including raising awareness of human rights and other issues. Alison has won numerous awards and accolades including the Dorothea Lange Award in Documentary Photography for her photographs of child labor in Asia and a two-time winner of the Lowell Thomas Travel Journalism Award. She was named a National Geographic Traveler of the Year in 2013. Here is a small selection of her photography to use in class, or you can explore Alison’s complete body of work here .
The presentation of beliefs and values through images is a powerful tool that can help preserve minority cultures in the face of globalisation and help to balance historical injustice by educating those who have lost touch with the past or with alternative ways of living. Texts of all kinds – written, spoken, visual – can help protect cultural heritage that might otherwise be lost. Alison Wright’s work can be seen in the wider context of cultural preservation , an important global issue in our increasingly homogenised and globalised world.
Towards Assessment: Individual Oral
“Supported by an extract from one non-literary text and one from a literary work, students will offer a prepared response of 10 minutes, followed by 5 minutes of questions by the teacher, to the following prompt: Examine the ways in which the global issue of your choice is presented through the content and form of two of the texts that you have studied. (40 marks) “
Alison Wright’s photography would make a good text to consider using in your Individual Oral. Here are two suggestions as to how you might use this Body of Work to create a Global Issue. You can use one of these ideas, or develop your own. You should always be mindful of your own ideas and class discussions and follow the direction of your own thoughts, discussions and programme of study when devising your assessment tasks:
- Field of Inquiry: Culture, Identity and Community
- Global Issue: Cultural Preservation
Though the colonial era has passed, its legacy lives on in the education systems, laws, political systems and other cultural practices that have displaced indigenous traditions and beliefs. In this context, the reassertion of minority cultures through texts is a powerful tool that can help balance out historical injustices and educate those who have lost touch with alternative ways of life. You could easily pair her work with any literary text that reveals aspects of culture, describes cultural practices, or reflects cultural beliefs and concerns.
- Field of Inquiry: Beliefs, Values and Education
- Global Issue: Encountering the ‘Other’
An important purpose of travel writing is for us to encounter ‘other’ people and make connections with people who may be very different to ourselves. In a world of suspicion and insularity, it is through building bridges between cultures and learning to understand different ways of life that we can settle our differences peaceably. In this context, Alison Wright’s photography invites us to ‘meet’ individuals from cultures that are very different to the urbanised or westernised cultures a lot of us may be more familiar with.
Sample Individual Oral Here is a recording of the first ten minutes of an individual oral for you to listen to. You can discuss the strengths and weaknesses of this talk as a way of improving your own oral presentations. Be mindful of academic honesty when constructing your own oral talk. To avoid plagiarism you can: talk about a different global issue; pair Alison Wright’s photography with a different literary work; select different passages to bring into your talk; develop an original thesis.
Possible Literary pAirings
- Broken April by Ismail Kadare – you might like to consider the idea that some cultural traditions are worth preserving, while others should rightly be consigned to the dustbin of history and Kadare subtly implies the Kanun is a dying tradition.
- John Keats’ poetry – In Ode on a Grecian Urn , the speaker tries to imagine what life might have been like for the people engraved on the surface of an urn.
- Pygmalion by George Bernard Shaw – the play is awash with peculiar Victorian mores revealing all kinds of beliefs and attitudes about class, poverty, prudery, morality and more. Doolittle’s speeches, Mrs Higgins’ at-home or conversations between Higgins, Pickering and Mrs Pearce could all be passages that you might like to select for this activity.
- Border Town by Shen Congwen – written just as China was beginning to modernise, and recently rediscovered by a new generation of Chinese readers, Congwen’s novella paints a picture of the lives and traditions of local Miao people in West Hunan, and can be valued as a record of a way of life that has largely disappeared in one of the world’s fastest-changing countries.
- The Elephant Vanishes by Haruki Murakami – these stories are set in a world traumatised by history, and most of the characters are victims of a peculiar kind of ‘collective amnesia’. They seem stuck in the present and can’t move on in their lives. Some critics have interpreted Murakami’s writing as a response to the tumultuous events of Japan’s history – a past that many would like to simply forget. Approaching this activity from this unusual angle would be a challenging, but possibly very interesting, way to pair a literary and non-literary body of work.
- Charlotte Mew’s poetry – writing at the start of the twentieth century, what does Charlotte Mew reveal about the lives, attitudes and values of the people in her poems? What kind of society did she live in? What was life like for ordinary people – and for women, disabled people and those who were mentally impaired?
- Waiting for the Barbarians by J.M. Coetzee – the ‘civilised’ world’s encounter with the fearsome ‘other’ is a major theme of Coetzee’s novel and could make an ideal piece with which to compare Alison Wright’s photography.
Towards Assessment: HL Essay
Students submit an essay on one non-literary text or a collection of non-literary texts by one same author, or a literary text or work studied during the course. The essay must be 1,200-1,500 words in length. (20 marks) .
If you are an HL student who enjoyed this section of work, and find the topic of travel writing interesting, you might consider this Body of Work to write your Higher Level Essay. You could extend your research beyond Human Tribe to include some of her other published collections. Angles of investigation might include: to what extent you think she is successful in her aim of bridging the gap between different cultures; whether her photography constitutes a modern form of travel writing; to what extent her photography reveals and represents cultural practices; whether you feel the photographs form or impose an identity onto people from an outsider’s perspective. Here are some suggestions for you – but always follow your own lines of inquiry should your thoughts lead you in a different direction:
- How is colour and composition used to present ideas about identity in Alison Wright’s photography?
- How does Alison Wright imply a close connection between people and the natural world in her photography collections?
- How does Alison Wright use metonymy in her photographic work?
- Explore the symbolism of eyes in Alison Wright’s photographic collections.
- In what ways does Alison Wright’s photography meaningfully negotiate our encounter with unfamiliar people and places?
Wider Reading and Research
- Outpost Magazine – a Canadian adventure-travel publication published six times a year, Outpost is known for its long-form adventure narratives from across the world.
- My Favourite Travel Book – six famous travel writers nominate their favourite travel books.
- The Most Inspiring Talks on Travel – a selection of the best Tedtalks about travel, including Lavinia Spalding’s talk.
- The Truth About Tribal Tourism – visit this Rough Guide blog to discover how your sustainable tour may not be as friendly to people or places as you might have thought…
Share this:
Categories: Time and Space
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- Travel writing tips
- Travel Blogging
- Travel Books
- Travel Writers
Types of travel writing. What path do you choose?
- 11/07/2022 11/25/2022
In any discipline, there are specific standards and rules. When we talk about a text coming out of a writer’s mind – and here we include travel writers – we think about the fact that it has ‘erupted’ freely, imaginatively, and very personally. However, every writer needs to know that any good text follows the rules of certain structural conventions. Travel writing can be divided into several categories, and it is quite important for a person who wants to become a travel writer to know and use the types of travel writing as such, as this is one of how he will prove his professionalism.
Knowing the types of travel writing will make discussions with the editors to whom you will send your texts more accessible. If an editor tells you they want an article about beach destinations or a humorous essay about how a train journey through India went, you’ll know what they expect. When you ask yourself what the length of the text you have to write should be, you’ll have an idea if you know exactly what category it falls into. Once you’ve established what type of travel article you’re working on, you’ll be able to develop the topic and add details or situations, depending on the nature of the article.
A person aspiring to become a travel writer has a highway with many lanes in front of them. It is up to the individual which path he wants and can walk in, just as there is the possibility of walking in several simultaneously because the genre allows for the development of such paths.

Narrowing things down somewhat, from a certain point of view, we could define five major types of paths for travel writers to follow : travel journalism, travel blogging, travel guides, travel memories, and the travelogue. Let’s take them one by one:
1 Travel journalism
Travel journalists go to various global destinations intending to discover and report facts. The result is objective travel articles, which usually tell the stories of other people and places rather than aiming for a personal narrative. Travel journalists can be freelance writers or work full-time for a newspaper, magazine, website, or news agency.
The Internet is full of travel sites eager to publish quality travel journalism and ready to pay for quality stories. If you have had unique encounters on your travels that may result in a remarkable story, submit your proposal to such a publication, and you may have the chance to bring it to life.
2 Travel blogging
Travel bloggers share first-person accounts of their travels. In recent years, many people have become travel bloggers simply because setting up a travel blog is simple and can be done with little investment. You can even create a blog for free.
Blogging is the fastest way to publish a travel story and showcase your writing style. If it’s valuable and has an audience, you can build an audience large enough to monetize your blog, and it will end up producing enough to self-fund your travels. You can also use your blog as a portfolio for collaboration with serious travel publications or other travel entities.
3 Travel guides
Travel guides are indispensable to the travel industry, as tourists worldwide rely on them when visiting a new place. You can start a travel writing career with travel guide writing, and you don’t even have to travel far to do it. You need to explore the city you’re staying in to the fullest, then take turns exploring neighboring towns or nearby tourist areas. So, you have to speculate as much as you can about the presentation of each potentially exciting tourist spot.
4 Travel memoirs
Writing travel memoirs involves reflecting on past travel experiences and how these experiences have shaped your worldview. Depending on your goals, you can self-publish your travel memoir as an “on-demand” book or propose to a publisher to see if they find the project interesting enough to publish it widely.
5 The Travelogue
A travelogue is a diary of one person’s journey to another place. It is both a narrative account describing personal experiences and a collection of factual details that other travelers might find helpful. It incorporates practical advice, vivid descriptions, actionable information, and genuine emotions.
Travelogue takes readers through your journey with words, pictures, and even videos.
An exemplary travelogue is as engaging as a story, practical as a guidebook, and visually and emotionally appealing as a magazine article.
Conclusion about the types of travel writing
If you’re at the start of a travel writing career, think about which of these roads you’d most like to take. Each has its paths, streets, and boulevards that you can flood throughout your career with quality writing. The important thing is to begin to know every meter of them, to understand how to dodge potholes, to be aware of crossing intersections, and, in general, to step on them – figuratively, of course – like a king acclaimed by the crowds on the sidelines.
Regarding the types of travel writing, any of them can be successful, as long as – after all, as in any profession – you treat it professionally and add the ingredients along the way that can bring you fame and money.
You may also like: 7 tips on how to make a travel story attractive to your readers

Join the conversation Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Examples of Great Travelogue Writing to Inspire Your Next Adventure

“Traveling – it leaves you speechless, then turns you into a storyteller.” – Ibn Battuta.
Ah, the joy and thrill of travel! Discovering new places, meeting strangers, and immersing yourself in unfamiliar cultures. But what’s the point of all this if you can’t capture the essence of your expedition in words? That’s where travelogue writing comes in.
Have you ever read a post that made you feel like you are experiencing the adventure alongside the writer? Well, that’s the power of a well-written travelogue.
It can transport your readers to far-off lands and make them feel right there with you. Add vivid descriptions, engaging anecdotes, and personal reflections, and voila! - You’ve got yourself some entertaining travel tales to share.
So, are you ready to unlock your inner travelogue writer?
Craft captivating tales that will leave your readers wishing for more. Let’s get started and master the art of travel writing!
Discover the Art of Travelogue Writing
From ancient Greece to modern-day blogs, travelogue writing has existed for centuries. It is a form of creative non-fiction that combines memories and factual data. But it’s not just about facts and statistics - a journey of self-expression, storytelling, and adventure.
Remember - it is your travel tale, not a guidebook!
Travelogue writing captures a location’s essence in conveying its beauty and complexity. The key is to immerse yourself in the culture and environment of the places you visit.
Tips for Crafting Engaging Travel Narratives
Once you’ve gathered your thoughts and experiences, it’s time to craft them into compelling narratives. Here are a few tips with examples to help you get started:
Start With a Strong Hook
A vivid description, intriguing anecdote, or thought-provoking question can do the trick. For instance, the following example firmly sets the scene for the travelogue.
“Ever wondered what it’s like to explore Tokyo’s bustling streets? To taste fresh sushi, see neon lights, and immerse yourself in tradition and innovation? That’s what I did on my recent trip to Japan.”
Create a Sense of Place
Use descriptive language to create a vivid image for your readers. The following passage skillfully portrays the same.
“The narrow streets of Marrakech were alive with color and sound. The scent of spices and grilled meats filled the air, and vibrant textiles hung from every stall. As I made my way through the bustling souk, I couldn’t help but feel swept up in the city’s energy.”
Show, Don’t Tell
Suppose you visited a beach and want to write a travelogue about it. Don’t write, “The beach was beautiful.” Instead, convey as shown in the given example.
“During sunset, the sun casts a warm glow over the white sand. The sound of waves filled the air as I dug my toes into the sand and breathed in the sea breeze.”
Now you know the difference. Use dialogue and sensory details to immerse your readers in your destination.
Include Personal Reflections
Share your thoughts and feelings. Connect your experiences to broader themes and ideas. For example,
“Standing atop the fort’s ancient ruins, I was amazed by the stunning views and intricate stonework. But as I gazed over, I reflected on the fragility of human achievement”.
Be Vulnerable
“Doubt crept in as I stood at the peak’s base. Could I make it to the top? But I pushed on and conquered my fear. The sight from the top was nothing short of spectacular”.
In the passage, the writer shares their fears and triumphs in a concise and relatable way.
Use Dialogue
Check out the following example. Here the writer uses dialogue to bring the woman to life and let her speak for herself. It adds depth and personality to your travelogue.
“An old lady chuckled as I haggled with a vendor over a silk scarf in Istanbul. She said, ‘You drive a hard bargain, but everything’s negotiable.’ We chatted about her travel stories as a young trader. ‘Those were the days,’ she sighed. ‘Now, I leave the traveling to the young ones like you.’”
Inspiring Travel Journal Entries to Ignite Your Wanderlust
Reading inspiring travel journals and memoirs is perfect for igniting your wanderlust. Here are a few examples to inspire your travelogue writing.
“Eat, Pray, Love” by Elizabeth Gilbert: A memoir of the author’s journey through Italy, India, and Indonesia in search of balance and purpose. Vivid descriptions and inspiring encounters.
“A Year in Provence” by Peter Mayle: A memoir of the author’s first year in a French village. Witty observations and charming anecdotes transport you to the countryside.
“On The Road” by Jack Kerouac: A classic novel of freedom and self-discovery, chronicling the adventures of two friends on a cross-country road trip.
“In A Sunburned Country” by Bill Bryson: A witty and informative travelogue about the author’s adventures in the land down under.
In ‘The Great Railway Bazaar,’ Paul Theroux invites us on a captivating train journey from London to Tokyo. Along the way, he explores the rich cultures and stunning landscapes.
Final Thoughts
Travelogue writing is a beautiful way to connect with your destinations on a deeper level and encourage others.
- Take inspiration and learn from given epic travelogue writing examples.
- Use your own words – dont copy from examples or websites.
- Inject your feelings and make your stories conversational.
Unleash the beauty of your travel experiences through vivid descriptions and captivating storytelling. Make Text Mercato your partner in this expedition and become a master of the travelogues.
1. What travelogue writers can I look to for inspiration?
There are several great writers you can look for motivation. Here are some personal favourites:
- Bill Bryson is a prolific travel writer with excellent humour and wit. His book, “A Walk in the Woods,” is a perfect engaging travelogue.
- Paul Theroux is known for his deep cultural and historical insights.
- Pico Iyer is known for introspective cultural pieces. For instance, his contemplative travelogue - “The Art of Stillness.”
- Jan Morris writes beautifully descriptive travelogues with her lyrical and evocative style.
2. What are some common themes in engaging travelogue writing?
- Cultural exploration: Write engaging travelogues by exploring the unique cultures of a place.
- Adventure: Discover and write about exotic locations or thrilling activities.
- Food and drink: Review local cuisine, which can be a cornerstone of local culture.
- Personal growth: Focus on self-discovery as you travel to new destinations.
3. How can I apply the techniques of great travelogue writing to my work?
- Have a keen eye for detail and a strong sense of narrative.
- Take the time to observe the people, architecture, and landscapes around you.
- Tell a compelling story and evoke emotions in your readers.
- Use persuasive language to paint pictures and challenge conventional thinking.
- Use humor - add some fun to your writing to engage the reader.
Give your readers a sense of closure .
Tags : Marketing , SEO , Digital Marketing ,
Recent Blog
Newsletters, let’s hear from you on how we can positively contribute to your goals.

Quality content is the key to add value to the success of your business, connect with your audience, and keep them coming back for more. TextMercato is designed to power your digital content needs to the next level.
Content Type
- Website Blogs
- Website Content
- SEO Articles
- Copywriting
- Whitepapers
- Social Media
- Thought Leadership
- Product Descriptions
- Buying & Selling Guide
- Market Reports
- Text Content
- Transcriptions
- Translations
- Real Estate
- Hospitality
© 2023 Text Mercato Solutions Pvt Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Cookie policy | Privacy policy | Terms of use | Contact us
- For Customers
- For Clickworkers
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- clickworker News
- Crowdsourcing
- Digital Marketing
- Tips and Tricks
Table of Contents
What are Travel Texts and Destination Texts?
What makes travel texts good traveling texts.
- Travel Text Example - "San Francisco – the colorful city on the Pacific"
- Where Do I Get Travel Texts From?
Evolution and Future Directions of Travel Texts
Travel texts, destination texts, travel descriptions: the ultimate guide.
Ines Maione
Ines Maione brings a wealth of experience from over 25 years as a Marketing Manager Communications in various industries. The best thing about the job is that it is both business management and creative. And it never gets boring, because with the rapid evolution of the media used and the development of marketing tools, you always have to stay up to date.

When you look out the window and see gray skies, and temperatures have been near zero for weeks on end then you know that the time has come to plan your next vacation. Many people use travel portals before booking their trip, or inform themselves about possible travel destinations in travel blogs. An important part of the pages are descriptions of destinations and travel texts. They provide the reader with background information, practical tips and get him in the mood for a holiday as well as offering good decision guidance.
However, destination texts are just as varied as the destinations. In addition to descriptions of individual countries, their regions or popular cities, local restaurants and trendy bars, shopping facilities and leisure activities as well as tourist attractions, insider tips and descriptions of excursions can be of interest to the reader. Emotional travel reports published in magazines also belong in this category.
Table of Contents What are Travel Texts and Destination Texts? Best Traveling Text types Benefits Use Cases Goal What makes Travel Texts good Traveling Texts? What a Travel Text should include Design an effective Traveling Text Turn a Traveling Text into an Adventure Travel Text Example – “San Francisco – the colorful city on the Pacific” Where Do I Get Travel Texts From? Things to consider ordering a Travel Text Travel Text Services by clickworker Evolution and Future Directions of Travel Texts Virtual Reality Travel Conclusion FAQs
When you’re planning a vacation, you may come across a lot of different terms that are used to describe the various aspects of travel. Two of the most common terms are “travel texts” and “destination texts.”
Travel texts are simply descriptions of destinations that appear in travel-related media such as magazines, websites, or brochures. They provide information about a particular destination, including its features and highlights. In contrast, destination texts are written by tourist organizations for their own website or publication. These texts typically include more detailed information about a destination than what’s found in travel texts.
So what’s the difference between travel and destination texts? Travel texts focus on providing an overview of a destination, while destination texts go into greater detail about each individual attraction or activity available there. As a result, they can be much more helpful when deciding where to go on your next vacation!
Best Traveling Text Types
There are many different types of traveling texts. Some of the most popular ones include:
- Blogs: Blogs are a great way to get personal insights into a destination from someone who has actually been there. They can be about anything – from restaurants to hotels to attractions.
- Brochures: Brochures are a classic way to get information about a destination. They often have detailed descriptions of attractions, as well as maps and other important information.
- Guides: Guides provide an overview of a destination, including its history, culture, and sights. They can be useful for getting an idea of what you want to see and do in a place before you go there.
- Descriptions: Descriptions give more detail about specific places or things in a destination. They might include historical information, tips on what to look for when sightseeing, or lists of the best restaurants and hotels in town.
- Journals: Journals offer first-hand accounts of people’s experiences traveling somewhere new. This can be really interesting (and sometimes helpful) if you’re looking for ideas on where to go or what to do when you get there.
- Literature: There is some great travel writing out there! Reading books by well-known authors or travel bloggers can give you a lot of insights into different destinations.
- Sightseeing Tips: Sightseeing tips offer practical advice on how to make the most of your time in a destination. They might include lists of the best places to go, things to do, and where to eat.
- Best Of: The best of anything is usually pretty great! When it comes to traveling, there are lots of resources that list the top places or things to see and do in a particular destination. Checking these out before you go can help you make sure you don’t miss anything important.
Benefits of Travel Texts and Descriptions of Destinations
Travel operators and airlines are the first to think of travel texts. They need to ensure that their customers are well-informed about their upcoming trips, so they can make the best choices possible. Hotel chains, agencies, or portals rely on authentic descriptions of destinations. They want to be able to offer their customers as much information as possible about a destination before they book a trip. That’s why destination texts are often long and include thorough information about accommodation, excursions and entertainment tips.
Publishers want destinations to be described in detail for their magazines. This is because readers of such magazines often want more than just a brief overview of a city or region before they decide to visit it. Consequently, these publishers are always on the lookout for talented writers who can provide them with engaging and informative destination texts
Use Cases for Travel Texts and Destination Texts
- Travel operators and airlines rely on destination descriptions for their business. They need to be able to offer a wide range of accommodations, so they need detailed, authentic descriptions of destinations.
- Leading hotel chains across Europe and the world need detailed, authentic descriptions of destinations because they offer a wide range of accommodations. This is where destination texts come in handy – they provide all the necessary information for hotels to make a decision about where to stay.
- Publishers of travel magazines have a demand for texts about countries and regions. Customers want interesting information that will help them plan their trips. You can order the texts with proofreading for an additional charge and get texts that your visitors and search engines like.
- Destination texts are information specific to the location, such as restaurant recommendations or historical facts. They’re helpful for people who are already familiar with a destination and want more details about what’s available there.
- Travel texts are general information about destinations, with a focus on helpful tips and advice. They can help first-time travelers figure out what they need to know before they go anywhere.
Goal of a Travel Text and Description of Destinations
The main objective of a travel text or destination text is to encourage the reader’s desire to go on vacation. The use of persuasive language and keywords are used in the text, increasing search engine ranking and Google searches for the site. Before brainstorming content ideas, it’s important to ask why the goal is being done, as this will help define goals for both writer and reader.
A “SMART” goal is one that is Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic and Time-bound. To ensure that your goal is measurable and specific, make sure you can answer how many people you want to reach with your content piece. Additionally, make sure the goal is realistic in terms of time and reachable.

There are many things that make a good travel text. But, most importantly, the author must remember to entertain the reader, not recruit them. After all, no one wants to read a dry list of facts about a destination. Instead, they want to be entertained and informed about what is available at their chosen destination.
At clickworker, we know this better than anyone. That’s why we offer information about destinations and travel tips in an engaging way that will have you itching to pack your bags and go! Our tone is casual and our style light-hearted, so you can feel like you’re chatting with a friend who just happens to know everything about the best places to go on vacation.
We don’t reuse facts from tourist brochures–instead, we provide authentic information and insider tips that will make the trips – promoted on your site – unforgettable. Text Creation Services
What Should the Travel Text include?
When it comes to creating a travel text, there are many things that you can include. Some of the most important things are information on what to pack, how to get there, and which countries are popular among tourists.
You should also think about including images and descriptions of different destinations, as well as a map that points out where they are located. Additionally, it can be helpful to list the capitals of European countries and some of the most popular attractions in Europe.
There are many things one would like to know before starting a journey. We have collected a few aspects that might be of interest for vacation texts:
- Getting there: Where is the nearest airport, and what transportation options are available to reach the travel destination (car or public transportation)? What kind of transfer is available from the airport to the hotel?
- Cultural offers: Does the destination have any interesting museums, theaters and movie theaters?
- Hotels: Information about the types/price ranges of the local hotels, for example first-class hotels, family hotels or hostels.
- Activities: Sports facilities, interesting hikes, trips near the city?
- Food: What kind of gastronomical selection does the travel destination offer? Can you offer some good tips?
- Transportation: What (public) transportation options can be used to reach the hot spots of the city?
- History/Culture of the country: Events, sights such as castles or monuments
- Travel advice: What do you have to keep in mind in the destination country? Are there any special precautions or behavior that are important?
It is of course very useful if you have already travelled to the destination and can share personal experiences. Otherwise, you will have to do thorough research.
How to design an effective Traveling Text
You should focus on certain aspects of a destination, such as its culinary features or sports activities, depending on what is specified in the order description. Remember that your text should match the other articles on the page in terms of tone and content.
Each paragraph needs to contain a subheading for paragraphs that fall under a particular subheading in order for it to flow smoothly with other texts on the page. Use first person narration in your text to make it more personal. Address your reader directly, with a form of “you” throughout the text.
Remember to keep your tone and content matched to the target audience so that they will find your text attractive!
Once you know what type of traveler your target audience is, it’ll be easier to choose the right photos and design. What is the vacation they’re looking to have? If you’re targeting people who want to relax on their vacation, go for light blues and greens. On the other hand, if your target customer is adventurous, then use bright colors and daring fonts. Whatever route you decide to take, make sure the photos complement each other so that there’s a unified feeling across the entire brochure. And don’t forget – color scheme should always match the feel of your destination!

The Best Travel Texts: How to turn a Traveling Text into an Adventure
One of the joys of reading travel texts is that it can take you away from your everyday life and into an adventure. Good travel writers are able to transport their readers so that they forget time and place, and after reading the viewer wants to go on vacation. However, a good travel text does more than just describe a location; it also tells a story. This makes the reader feel as if they are right there experiencing everything with the writer.
Additionally, a good travel text subtly sells the idea of traveling. It entices the reader with images and descriptions of different places in such a way that they cannot help but want to visit them for themselves. All of these elements work together to create an enjoyable experience for the reader.
Sounds complicated and time-consuming? It is! You are in luck, because there is the possibility to have travel texts created.
Travel Text Example San Francisco – the colorful city on the Pacific San Francisco is in the state of California on the West Coast of the United States. Its “manageable” size makes it easy to orientate oneself. Its steep streets, Victorian houses and the historic cable cars give the “City by the Bay” an European flair. San Francisco offers a number of tourist attractions. These include the lively Fisherman’s Wharf, the former penitentiary island, Alcatraz, and the charming fisherman’s village, Sausalito, north of the city. It is worth walking or cycling across the Golden Gate Bridge to Sausalito; with a bit of luck you can spot dolphins and sealions from the bridge. The Mission District offers numerous restaurants, bars and clubs as well as a busy nightlife. And for those of you who enjoy shopping, you will find plenty of stores on Haight Street and Union Square. San Francisco’s gastronomical range is impressive. Owing to Mexican immigration, you can get good, inexpensive food in the Mexican bistros. However, you will also find excellent restaurants that serve hamburgers, steaks or seafood. For tourists who are interested in wines, tours to the world-famous winegrowing areas in Napa or Sonoma Valley are a must. Water sports enthusiasts, such as surfers or kite surfers, will thoroughly enjoy what the Bay has to offer. Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco Attractive hotels and inexpensive hostels in San Francisco If you want to stay in an elegant hotel, the “Charlotte Hotel” is a perfect choice. The historical house, built in 1921, was modernized in 2014. Its central location, its luxurious rooms and an exquisite breakfast buffet with homemade pastry are unique. In addition, it offers a wellness area that includes a swimming pool, a sauna and a whirlpool. The cuisine of the elegant hotel restaurant has won numerous awards for exceptional quality. Travelers on a smaller budget can stay at the California Hostel, located only three blocks away from Union Square. The hostel has 5 double rooms and 10 multiple-bed rooms with 4 to 8 beds. The rooms are equipped with a private bathroom, towels and WiFi. The breakfast that is free of charge consists of coffee, fruit and pancakes. How to get there A direct flight from Frankfurt (Main) to San Francisco, for example with United Airlines or Lufthansa, takes about 11 hours. Delta Airlines or British Airways fly to the destination with a stop in e.g. New York City or Atlanta. San Francisco International Airport (SFO), is approximately 20 kilometers from the center of the city. A taxi to town costs approximately $45. Shuttle busses are much cheaper: only $15. Certainly this applies here, too: The client’s requirements and demands will determine what the travel text looks like in the end!
Where do I get Travel Texts from?
There are a variety of places you can get travel texts from. However, it is important to make sure that the text is high-quality and matches the tone and style of your website.
If you are looking for a descriptive and intriguing text, then you should try to find an author who can write in an engaging way. Short, concise sentences will help keep the reader interested.
Most people research on travel portals and read reports on several travel blogs before they make their decision about where to go on vacation. This is because there are so many options available today with regards to traveling destinations. It can be challenging to decide where they want to go because there are so many great choices!
Things to consider ordering a Travel Text
When ordering a travel text, there are several things to keep in mind:
- Who is your target group?
- What type of trip is it?
- Is formal or casual language more appropriate?
- Do you want emotional or factual texts?
- Do you need expert knowledge or can unskilled writers do the job?
- Are you looking for authentic and insider advice, or general tips for tourists?
Travel Text Services by clickworker
As a hotel, airline, online travel agency or tour operator professional destination content is key. You need to provide interesting and informative material for your web visitors if you want them to stick around and potentially book a trip with you.
Fortunately, our pool of international Clickworkers can help! We have a large number of qualified writers who can create top-notch travel content in a variety of languages for your website, blog, or online magazine needs. Our team can also supply entertaining as well as informative articles for your readership. Best of all, our services are fast, reliable and affordable.
What’s more, our exclusive content is written by native speakers who really know their destinations inside out. So why not give us a try today? You won’t be disappointed! Contact our Sales Team

It’s hard to say for certain what the future of travel texts holds. After all, forecasts are many and often unreliable. However, there are a few things we can be sure of. Firstly, the travel season is only weeks or days away- so get your bags packed! Secondly, family and multigenerational travel will continue to be popular in the years to come. Finally, as our world becomes increasingly digitized, the way we consume and write about travel is bound to change as well.
There has been an increase in more creative mixed-genre literary travel writing in recent years. This is likely due to readers becoming tired of overly consumable pieces written for mass audiences.
That said, there are also some negative trends worth noting. For one thing, there has been an oversaturation of personal essays in recent years (think listicles disguised as stories). Additionally, many long-form pieces seem to be disappearing from view entirely. It’s harder than ever to find quality writing that isn’t constrained by the limitations of a listicle or quick-hit blog post.
All in all, it seems that travel writing is evolving and heading in new directions. The key for writers is to experiment with different forms and explore the world around them with curiosity. At the end of the day, that’s what readers are looking for- authentic stories from real people.
Virtual Reality Travel containing traveling texts and travel description
The coronavirus has caused the cancellation of a number of flights and hotels all around the world. The travel industry has been affected by this disease in a variety of ways such as the number of tourists visiting the countries where outbreaks have occurred. We need to think about other ways to give people some well-deserved time off. What good is a travel text if people can’t book a vacation?
The world is vast, and with Oculus Quest, you can travel anywhere from home. With just a few taps, you can be transported to the places of your choice- all while wearing your headset. During your virtual tour, you can view descriptions and travel texts for all possible points of interest. There are many virtual reality (VR) travel apps available now that let you explore real-world locations in fully volumetric 3D environments. BRINK Traveler is one such app that is available for the Oculus Quest and Rift Platforms along with Steam. The app lets you visit over a dozen gorgeous locations around the world, including:
- Horseshoe Bend
- White Pocket
- Death-Valley National Park
- Mount Morrison
- Mount Whitney
- Alabama Hills
- Arches National Park
- Antelope Canyon
- Háifoss (Iceland)
- and many more…
We hope you enjoyed this guide on optimal travel texts and destination descriptions. As you can see, using these texts to your advantage can really help you market your business and attract more customers. So don’t hesitate to put them to good use!
FAQs on Travel Texts
How do you write a trip in text.
When writing a trip in text, be sure to include the destination, the reason for going there, how you will get there, what you will do while there, and when you will return. Also, be sure to describe the trip in an interesting and engaging way so that readers will want to follow along.
How do you write a travel report?
When writing a travel report, it is important to be clear, concise, and informative. The report should include an introduction, background information on the destination, a description of the trip, and conclusions and recommendations.
What is a travel text?
A travel text is a type of literature that describes the experience of traveling to and visiting different places. Travel texts can be found in many different formats, including books, articles, blog posts, destination descriptions and even social media posts.
Related Posts
- Descriptions of Hotels and what is important in writing hotel descriptions
- The Ultimate Guide to Machine Learning in Finance: Revolutionizing the Future of Financial Institutions
- Solutions Overview
- Audio Datasets & Voice Datasets
- Image Datasets & Photo Datasets
- Video Datasets
- Image Annotation
- Product Categorization & Tagging
- Image & Video Tagging
- Sentiment Analysis
- Video Analysis
- Search Relevance
- Customer FAQ
- About Crowdsourcing
- Crowdsourcing Glossary
- Content Marketing Glossary
- AI Glossary
- Clickworker Job
- Clickworker FAQ
- Clickworker Registration
- Clickworker App
- Clickworker Data Security
clickworker USA
2 Park Avenue, 20th Floor New York, NY 10016 USA
clickworker Europe
Büropark Bredeney Theodor-Althoff-Str. 41 45133 Essen, Germany

- Cookie Declaration
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
- Additional Cookies
This website uses cookies to provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookies are small text files that are cached when you visit a website to make the user experience more efficient. We are allowed to store cookies on your device if they are absolutely necessary for the operation of the site. For all other cookies we need your consent.
You can at any time change or withdraw your consent from the Cookie Declaration on our website. Find the link to your settings in our footer.
Find out more in our privacy policy about our use of cookies and how we process personal data.
Necessary cookies help make a website usable by enabling basic functions like page navigation and access to secure areas of the website. The website cannot properly operate without these cookies.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as additional cookies.
Please enable Strictly Necessary Cookies first so that we can save your preferences!
- Accessories
- Freewrite Plus
- Find Your Freewrite Quiz
- Learn To Freewrite (NEW!)
- Written On Freewrite
- Writing Time Friday (WTF)

Your Cart is Empty
- $0.00 Subtotal
Taxes and shipping calculated at checkout

Smart Typewriter
Best for travelers. Light & Portable with an e-ink screen

Special edition

Hemingwrite

18 Irresistible Types of Travel Writing
Photo by josh nezon on unsplash, today’s guest post is by corinne lincoln-pinheiro . corinne is a journalist with experience as a freelance legal digital reporter, military journalist, city junior newspaper editor and health blogger. she is a military spouse blogger and also writes about military-family travel. corinne is also a p ublished creative nonfiction writer and poet..
Finally, you’re ready to take the plunge into the travel writing sphere. Now what? What types of travel writing are right for you? Well, whether you’re a novice or seasoned writer searching for something new, there are multiple avenues from which to turn an aspiration into a part-time gig or full-time career.
Modern travel writing appears in many forums, from travel blogs and websites, in-flight travel magazines, trade magazines, newspapers, free periodicals, books and more. But before all that comes the decision as to which one(s) suits you best.
The Travel Writer’s Guide
Of course, deciding on what’s a good fit depends on your interests and expertise. Because many travel writing categories overlap and have similar templates and requirements, you can do more than one type of writing simultaneously. You should ask yourself: how much time do I want to devote to research, how many articles can I produce a week, and how far am I willing to travel and how often? Am I drawn to travel journalism? Whether this venture is a stepping stone to something else, supplement income, or a new career altogether, travel writing is competitive and writers are typically poorly compensated.
The best travel writers are unique and bring a fresh perspective. Being able to pitch great ideas, following through, and having something interesting to say is indispensable. Whatever you do, be authentic, candid, and creative in your approach.
I once pitched a two-week travel extravaganza (from Forks, Washington State to Eugene, Oregon), and wrote more than 20 pieces about (sometimes little known) attractions along the West Coast. The travel series on gems near Highway 101, ran both online and in print.
Creativity is one thing but you must have your readers’ interest at heart. After an all-expenses-paid trip to the South, I didn’t give outstanding reviews to all of the attractions (unlike the travel bloggers in attendance). But my audience—primarily military families, often had to take vacations on a budget, if they took one at all, and they appreciated the advice about attractions that weren’t worth the price.
This guide will provide a brief overview of 18 types of travel writing options to help you narrow down which one(s) you’d like to pursue.
Types of Travel Writing:
1. weekend warrior 2. content and social media marketing 3. roundups and "best of" lists 4. holidays and special events 5. side trips 6. destination pieces 7. travel and lifestyle blogging 8. how-to travel guides 9. advice articles 10. travel itineraries 11. food and travel 12. guidebooks 13. travel humor 14. personal travel essays 15. travel memoirs 16. travel modes 17. news travel 18. travel op-eds, 1. weekend warrior.
Are you one of those people who gravitate toward articles about the perfect day trip? Local or regional attractions are great for this type of piece. This is a mashup of a few ways to travel write—it can be an outdoor expedition, recreational indoor activity, weekend getaway, or a combination. It may focus on a fishing trip, bike or hiking trails, scenic road trips, or indoor rock climbing for example. It’s a destination piece with an element of adventure that gives the reader a glimpse of what they could be doing this weekend.
Travel writers should know the market, the publication and their vocabulary. Consider if the piece will be family-oriented, what are some interesting things to do outside of the must-see attractions, how to get the most out of the day or weekend, along with descriptions of the scenery and facts about the activity. Whether it's water sports, glamping or packaged adventures, if you live it, why not write about it? This can also be a version of roundups (see below) and may include additional specifics on a destination’s happy-hours specials, shopping, food, drink, the arts, and nightlife.
Photo by Corinne Lincoln-Pinheiro
2. content and social media marketing.
Travel companies sometimes hire freelance content and social media writers to promote their product and services via blog posts, video clips, and articles. You’ll need to write quickly, vary the tone for targeted audiences and engage with followers and update posts. If you favor succinct tweets, Instagram blasts and Facebook blurbs, you’ll like this option.
Side note: As a travel writer, you should have a social media presence anyway. While you’re traveling, you can upload videos and pictures to promote the attractions and things to do at the destination. Also, during complimentary travel, businesses like the fact that you’re able to “bring along your followers to visit” their destinations and spread the word instantly.
Finally, most companies have social media pages and as more people turn to them for ideas, travel content and social media writers are in demand, especially if you employ SEO practices. There are even content marketing companies that hire travel writers specifically to research and write content for other businesses.
3. Roundups and "Best of" Lists
Very popular these days, roundups are bullet-point lists that collect information on different destinations with a common theme, like the “10 Best B&B’s in San Francisco.” It isn’t too in-depth and because it’s brief, the catch is finding ways to spice up descriptions and avoid clichés. The introductory paragraph setups the common thread/angle and bullet points justify why the destination made the list. Roundups should be accurate and well-researched to produce quality pieces (even better is visiting the destinations and providing original content).
If your roundups are in the same region (like the B&Bs in San Francisco) before you visit you can request complimentary accommodations. Better yet, contact local tourism agencies and they’ll help set up tours, press passes, create your itinerary and provide tour guides, on occasion. Roundups get a lot of online views and are easily scan for pertinent information (it helps build your portfolio, too).
4. Holidays and Special Events
A travel story involving holidays and special events such as New Year’s or Germany’s Oktoberfest should be pitched and planned well in advance. If you’re new to travel writing, you can start with local festivals and fairs. One lesson I learned early on as a journalist who also covered travel writing—these events can produce multiple pieces and can be a treasure-trove for new leads.
For example, the first piece can be a 200-word announcement of the event. Closer to the occasion, an interview with an event official about last year’s successes and what to expect this year serves as a reminder. As you cover the event, talk to everyone. If you do multiple types of travel stories your next lead or resource could be around the corner.
Photo by Corinne Lincoln-Pinheiro
5. side trips.
A side trip is a “side-step” on the way to or from (or nearby) a major destination. It focuses on another city or lesser known location or attraction. Magazines usually plan for and arrange side trips to complement the issue’s featured travel article. Pitching these ideas early on can help them plan around the issue. Side pieces detail how to get there, attractions details such as hours of operation, so readers can know what to expect when visiting.
Side trips are usually day-trips and travel writers maximize the benefits by also using these destinations (or information from them) in roundups or even weekend warrior angles.
6. Destinations Pieces
Destination pieces that are feature articles are usually very in-depth. It finds the right angle to draw the reader into the painting the travel writer creates and entices them to visit. Features can be seasonal but should always be relevant. Often, editors assign these to established writers or those they have a working history and familiarity with. Well organized pieces seamlessly integrate facts, anecdotes, historical information, encounters, storylines, and the “Five W’s” of who, what, when, where, and why (and sometimes how). The challenge remains, as with all popular attractions, finding a fresh way to retell something many others have done before.
It’s usually told in the first person and the voice is more of a delivery tool than the focus. Great travel writers avoid meaningless descriptions and write compelling articles that make the reader hungry for the next detail. Destinations can also highlight overlooked attractions and little-known gems.
7. Travel and Lifestyle Blogging
Travel blogging allows writers to set the tone and pace because there are no editors or deadlines or templates, just you and your readers. You can also be a guest contributor or invite guest bloggers to increase visibility. As for lifestyle blogging, it’s great for multiple ways of travel writing because you set the terms, here as well. However, it’s very competitive so the key is to build trust and rapport and be a credible resource for readers.
You can write longform posts, roundups, destinations, weekend warriors angles and itineraries, you name it. Itineraries can take the form of where to eat, stay, and play, whereas longform posts are more narrative in nature with characters and vivid details. Bloggers keep the reader’s attention by being witty, creative and engaging, even intimate; they are active (in life and online), giving readers repeated reasons to return.
8. How-To Guides
The how-to travel piece imparts invaluable advice and information, making travel writers a tour guide of sorts. You can help solve readers’ travel problems before they occur, and this alone will generate more shares if it's relatable and reliable.
A how-to can focus on just one aspect of travel like how to get around complex international airports for example. “How-to” travel advice is a frequently googled topic, such as, “How to travel on a budget.” Travel writers should be comfortable conducting thorough research and have knowledge of the destination, where applicable. Great how-to articles are honest and trustworthy and teach readers essential tips beyond what the attraction entails.
9. Travel Advice Articles
A how-to article can easily turn into an advice piece which discusses, for example, mishaps that can happen on a trip. Advice on overcoming language barriers, what to do if you have to deal with law enforcement, foods to avoid, what to do if you lose your luggage, scams, where to get discounts and bargains, what to do if you miss your flight or if you become lost, all of these are advice a reader may not know they need. Whatever you recommend, it must be well-researched and interviews with credible experts help reinforce the advice given. Editors often assign these pieces to staff writers and not freelancers.
How-to and advice travel articles can be in-depth standalone pieces, but often this information is incorporated in other pieces such as destination articles. Readers appreciate the one-stop “shopping,” especially if the advice is destination-specific and integral to the region. Many see this type of advice as essential to any travel piece.
10. Travel Itineraries
Itineraries are city-by-city, region, destination, or sight-by-sight recount of all the details from planning to returning home, so the traveler can use it as a stencil. There are recommendations on where to visit and how to maximize time and save money. It goes into greater detail about the challenges of visiting a specific location, drive times and routes, weather and road conditions, crowds and busy times, and what clothing and gear to pack.
Itineraries can be first-person accounts, relaying door-to-door experiences with a narrative thread that runs throughout.
11. Food and Travel
This is a prized gig for foodies—exploring diverse cuisines, cultures, and dishes, all the while visiting interesting places. This is a staple in the travel writing industry because there are evergreen opportunities to explore. If you have a genuine interest in food and basic cooking knowledge, this dream job can lead to interesting discoveries, making for well-rounded pieces.
Food and travel articles are not reviews and are more than just why a meal is great or where it falls short or the restaurant’s location. It’s the presentation, the ambiance, the way this dish makes you feel, the amazing hole-in-the-wall gems.
You get to write about: how in some places food is passed on as an inheritance; how it can be the marking of a culture and its people; how it intersects with history and traditions and is a celebration of living.

12. Travel Guidebooks
If you’re more of a straight-forward kind of writer, then this might be a better fit for you. Its factual, practical, and linear. It can be part-time or full-time employment but if constant travel isn’t appealing, you can be a local or regional writer.
Guidebooks cover a wide variety of subjects and are heavy on descriptions, and to stay current must have up-to-date listings. Many set boundaries and divide the guide into sights to see. Don’t rely on internet research alone, it’s best to see the place because knowledge of your destination is paramount, along with a good understanding of maps. Guidebooks may include quality beaches, five-diamond lodging and independent hotels, museums, history, architecture and local traditions. However, work can monotonous.
13. Travel Humor
Do you have a knack for writing humorous stories? This can be a niche in and of itself in travel writing, and humor is sought after and well received by editors. It requires a clear voice, firsthand experiences, a storyline that engages, and sticking to an angle (and in a refreshing way). It builds rapport with readers, especially if the joke is at your expense.
The downside is the risk of insulting someone, unintentionally singling out a group of people or being culturally insensitive, using offensive language, or accidentally letting your prejudices creep into your writing, or worse, using your wit as a weapon. Many travel writers stick to universal misadventures, misassumptions, misunderstandings, and tongue-in-cheek humor. But finding that delicate balance in tone, and keeping humor relevant, light-hearted enough, inclusive, and tolerant is no short order.
14. Personal Travel Essays
A well-written, insightful personal travel essay is every editor’s dream, but it’s not always in demand or easy to write. A distinct voice, great backstory, a universal theme and/or lesson, the ability to tell a travel-related story imbued with metaphors and comparisons that reaches the reader, are all part of great travel personal essays. Switching between views—from wide to medium to close-level lenses, add depth, as well.
Personal travel essays are more like a journey of discovery as the piece matures; its rich in perspective and a balanced travel narrative. The travel aspect shouldn’t hide inside your personal essay, your purpose should live amongst its storyline. Places can often invoke revelations that arise through reflection, writers learn about themselves, explore emotional issues, and make hidden connections.
15. Travel Memoirs
Travel memoirs are even harder to write and many never make it to publication, especially if it reads like a diary entry. They aren’t autobiographical as traditional creative-nonfiction memoirs but like a personal essay, it has to be well-written, possesses a strong voice and point of view, something exceptional to say, even a metaphorical journey. Time and place, scenery, culture, and a distinctive narrative create a window into your experience.
Knowing the targeted audience, developing fully-realized characters and storylines, and remaining focused (not every mishap should make it into your memoir), are the marking of a successful travel memoir.
Finally, as with any book, know your publishing options, find an editor who is willing to work with you (even secure an agent), ask for help if you need it, walk away from time to time, and don’t doubt your abilities. Most of all start writing today, you have nothing to lose. At the very least it can be one or more exceptional personal travel essay. Or you can self-publish an eBook which you can use to market your writing skills.
16. Travel Modes
The travel modes focus isn’t destinations but the form of transportation i.e. how you get there and the voyage itself. Transportation modes include vintage trains, railroads, ships, and automobiles. Not a how-to or advice piece, it can overlap in some ways but the central theme is the discoveries along the way, the way it makes the author feel, and other nostalgic and historical angles. Facts, a vivid narrative, (and photos even), elevate these expedition pieces.
17. News Travel
Writing about places that made the new cycle either because of war, civil unrest or terrorism can become popular after the chaos is over. Places like Egypt and Israel, with its rich biblical history, monuments, and locations like Mt. Sinai and the Red Sea, are of interest to many a reader and traveler, alike. This is a tricky mixture because though tourism is alive in these places, civil and economic disturbances (afterward) affect interest levels and thus publication opportunities. (Though there are readers who enjoy learning about such places, even if they have no intention of visiting.)
Another intersection with travel writing and the news is if to travel to destinations that experience natural disasters. The occurrence of tsunamis, hurricanes, and earthquakes, can open the way for a how-to about keeping safe and what to do in case it happens while on vacation.
Discounts, bargains and cheap travel packages to nearby locations (where tourism may also suffer) make for travel articles, as well.
18. Travel Op-Eds
Op-ed pieces are not as commonplace as other travel writing mediums. However, these travel writers are intimately familiar with each publication’s tone, style, and platform, and check (and adhere to) submission details and deadlines. Again, being original and persuasive, having a clear decisive voice, something valuable to share, and an angle increases publication opportunities.
There you have it, 18 ways to get started as a travel writer. Do you have experience with travel writing? We'd love to hear your story in the comments!

Corinne has freelanced as a legal digital reporter for ICS and ten of their national publications . She has served as a military journalist, travel writer, and photographer for Swarner Publications and their newspapers on Joint Base Lewis-McChord (JBLM), including The Ranger, the Northwest Veteran (NW), the Northwest Airlifter, and their two online magazines, JBLM Spouses and JBLM Singles. At Fort Hood, she was a reporter and health blogger for the Killeen Daily Herald and a junior editor for its former local paper, the Copperas Cove Herald. As a former military spouse, she’s written for Military.com and its subsidiary site, SpouseBuzz .
She has published essays and poems and has a Master’s degree in Creative Nonfiction from Vermont College of Fine Arts, and a Bachelor’s degree in English from Pacific Lutheran University . Corinne also has a background in Human Resources.

Recommended articles
More recommended articles for you.
At 33, I’ve experienced more loss than most adults. When it hits, grief hangs over me like a shroud. I can go about my day as usual, but everything is dulled. Sights and sounds are less vivid. I’m distracted during conversations.
I started writing to heal myself. However, one day, I wrote a piece that brought me so much peace I thought it could help others navigating similar traumatic loss. So, I took a chance and shared it. The following are a few things I’ve discovered along the way that I hope will help others write to recover from the loss of a loved one.
"I can't focus." We've all said these words before.
But the reality is not that we can't focus — after all, the human brain is always paying attention and, consciously or not, focusing on something — but rather that we can't control our focus.
Let's look into the psychology of attention and focus to better understand how we can control our focus — and our productivity.
In 1872, Bram Stoker, the author of Dracula , wrote a raw, gushing fan letter to his poetry idol, Walt Whitman.
But it wasn’t until four years later that Stoker would finally have the guts to mail it, along with an introduction letter — a letter within a letter — beginning with: “If you are the man I take you to be you will like to get this letter.”
In four separate instances in his missive, Stoker instructs Whitman to place both letters in the fire “without reading any further,” if “this” is a mistake.
Strange and cryptic. And with a tragic backstory.
Join us in an exploration of vampires, art, and the heart-breaking fight to be yourself when being yourself is illegal.
What is Travel Writing?
For thousands of years, travellers have written about their experiences exploring the furthest reaches of the world, both to record their journeys for personal reasons and as a guide for those who might follow.
Before the internet age, even as far back as Ancient Greece, stories of distant lands were popular because many people would never have had an opportunity to visit themselves.
But what is travel writing like today? With the internet, sharing experiences of our travels has never before been so easy, and arguably travel writing in one form or another is more popular ever.
Definition of travel writing
Travel writing is a genre that describes a writer’s experiences, observations, and feelings while travelling to different places.
It often includes descriptions of the landscape, culture, people, and events that the writer encounters, as well as their personal thoughts and reflections on these experiences.

Sonnets are one of the most popular forms of poetry, and they have been for hundreds of years. The strict format and short length make…
How Many Pages is 3,000 Words?

On average, 3,000 words is equivalent to 6 pages of A4 single-spaced or 12 pages if double-spaced. This takes into account a font size of…
How Long Does it Take to Write a 3,000 Words Essay?

Writing an essay and completing it before a deadline is an important skill for any student, but even those experienced in time management might find…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Beginners Guide to Travel Writing
So you want to be a travel writer? Good. You can! This beginners guide to travel writing intends to answer your most basic questions and get you pointed in the right direction.
Thousands of people from various backgrounds – many with no previous media or journalism experience – share stories of their trips and adventures on countless websites, blogs, magazines, newspapers, newsletters and social media platforms. No degree or certification is required and doing so doesn’t require a lot of money – no additional money, in fact, if you already own a computer with internet access and a smart phone.
At its best, travel writing offers deep personal enrichment, unforgettable experiences and a little side income to boot. Understand this, however, pursuing travel writing typically works best for those using it as a side hustle, primarily for experiences and perks, or in retirement, separate of a primary income. While there are thousands of travel writers, there are very few full-time, on-staff with a media outlet, professional, this-is-how-I-support-myself travel writers. There are more professional athletes than there are travel writers making their living exclusively this way.
As you read our guide to travel writing for beginners , no attempt will be made to sugarcoat the realities, to oversell the benefits or discount the obstacles. This guide is informed directly by the personal experiences of TRAVEL WRITERS UNIVERSITY and the TRAVEL WRITERS CAFÉ staff and the hundreds of successful and failed beginning travel writers we have worked with.
The best news is, if you’re serious about starting travel writing, there is a proven, repeatable, simple – but not easy – step-by-step process to follow which will get you there and a supportive network of likeminded people going through a similar journey. The process and teachings are cataloged in detail at TRAVEL WRITERS UNIVERSITY and the support network exists in our TRAVEL WRITER’S CAFÉ Facebook group.
TWU is a premium on-line resource where members receive access to hundreds of informational articles related to advancing in the field from tips on improving your writing and photography, to editor contact information and pitching strategy. The CAFÉ is our Facebook members community where we share member’s published stories, hot leads from editors looking for pitches, and general support along with regular instructional video webinars and chats. One monthly membership of only $49 dollars provides access to both services.
TWU and CAFÉ founder Noreen Kompanik started her travel writing career exactly where you are today . She was a registered nurse who loved traveling with no writing experience. She was intrigued about the possibilities of travel writing. Through some relatively expensive in-person and online courses, a lot of trial and error, and dogged determination, she has worked her way to the top of the travel writing profession with over 600 “bylines” – published stories – in major print and digital outlets. She takes roughly 20 “press trips” – all expenses paid, invitation only trips to write about a destination or accommodation – every year to Europe, Mexico, the Caribbean and across the United States. She earns tens of thousands of dollars annually for the privilege of doing so.
This lifestyle can be the upside of travel writing.
TWU and the CAFÉ share what she’s learned, along with the expertise of her travel writer business partners, streamlining the process from beginner to intermediate , providing a clear blueprint to follow in her footsteps.
TRAVEL WRITERS UNIVERSITY / TRAVEL WRITERS CAFÉ ADVANTAGE
“I love being a part of the community where I can learn from the best what I need to succeed as a travel writer. The monthly Roadmaps and Bonus Articles include actionable information that has upped my writer’s game. Opening the Travel Write’s Cafe Facebook group is the first thing I do each morning. The support and encouragement from fellow members helps me to stay motivated. Kristi and Noreen have given me the tools and confidence I need to continue to reach for higher goals. In the past year, I have landed press trips I never dreamed would happen.” – TRAVEL WRITERS CAFÉ member Sharon Kurtz.
Freelancing

As mentioned, full-time travel writing jobs are exceptionally scarce. Filling them, most times, are writers, reporters and journalists with degrees in those fields and years of experience which have allowed them to slowly work up the ranks in that field.
Don’t let that discourage you. The VAST majority of travel writing is not done by these people, it’s done by a global community of freelancers. Freelancers are non-staff writers, independent contractors typically writing for a variety of different publications – online and in print.
Publications would love to have large teams of exclusively staff writers producing stories, but doing so is far too expensive. Even two or three staff writers earning a livable salary with benefits and travel stipends to report their stories would require a vastly greater investment from the publication than using even hundreds of freelancers each year and paying them a couple hundred dollars per article.
Freelancing is a hustle, no doubt, but if you want to start travel writing without starting your own blog or website – and we’ll get to that later – freelancing is how you’re going to do it.
Almost all travel publications, even the big ones like National Geographic and BBC, rely heavily on freelancers for content (stories). Freelancing involves “pitching” editors story ideas you’d like to write. This means sending the editor(s) at the publication you’d like to see your article appear in an email detailing the story you’d like to write and why it would be a good fit for that outlet.

Who to pitch? Where to pitch? How to pitch?
These are the first obstacles encountered by beginning travel writers. At TWU and in the CAFÉ, we take the mystery out of this process leading writers by the hand through it. With our travel media industry contacts, we have hundreds of editor email addresses and are constantly updating our members about new writing opportunities.
Travel publications NEED content. They NEED freelancers. They’re constantly on the lookout for new writers. We go where they go to look for writers and pass their “calls for submission” – want ads for stories – on to our members.
To have stories published as a freelancer, you first pitch publications and if they’re interested, an editor will tell you exactly what story angle to take, word length, etc.
Pitching editors can be a time consuming, exhausting, frustrating effort. For beginners and experienced travel writers alike, many pitches go unanswered. Pitching also happens to be essential for beginning and advancing your travel writing journey.
At TWU and the CAFÉ, we make this process as painless as possible by continually providing members hot leads to editors looking for stories – editors with smaller publications and at the biggest media companies. Editors across the globe looking for an endless variety of stories from all seven continents and subjects ranging from dining and drinking, to resorts, museums, family travel, budget travel, sports, theme parks, art and culture, nature, history, outdoors, all-inclusive, you name it.
Our expert staff personally review member pitches when necessary, making sure every word is just right to maximize its potential for being accepted.
TWU co-founder Kristi Dosh ran her own successful public relations company, Guide My Brand , for several years. She successfully pitched her clients to media outlets across the world. She is an expert on pitching and works with TWU and CAFÉ members on crafting their pitches.
TWU also provides members with instructional ROADMAPS to improve their pitching success . ROADMAPS are detailed explainers written by seasoned travel writers providing insight into a specific travel writing related subject. ROADMAPS are one of the most important resources offered by TWU for beginning and intermediate travel writers alike
ROADMAPS focused on pitching include:
“Perfecting your pitch strategy”
“Improve your pitching success with timing”
“Pitches that work”
“Overcoming your fear of pitching”
“Successful pitches – word for word!”
TWU and CAFÉ members also have the opportunity to receive individual help with their pitching and specific pitches. Our pitch review service puts your pitches in the hands of our experts for a word-by-word analysis to ensure your pitch has the greatest opportunity at success.
TRAVEL WRITERS UNIVERSITY / TRAVEL WRITER’S CAFÉ ADVANTAGE
Not only do we aide writers with their pitch strategy and individual pitches, we connect our writers directly to editors. This may be the most valuable service offered at TWU and in the CAFÉ.
TWU has an entire section of FEATURED PUBLICATIONS profiling dozens of travel-related outlets in-depth, what kind of stories they’re looking for, and contact information for editors.
TWU also features ROUNDUPS , bite-sized entries offering hundreds of suggested travel publications to write for and how to contact them.
Check out this FREE article specifically for beginners providing a list of 13 travel websites which accept pitches and stories from FIRST-TIME, unpublished writers.
Another obstacle beginning writers face is how to achieve their first few “clips” – examples of their published writing. Most editors require would-be writers send them links to a few of their previous clips to demonstrate their writing ability. Anyone new to travel writing, naturally, won’t have any examples of their previous work so this often presents a roadblock to advancement.
We remove that roadblock for beginners and, best of all, the TWU and CAFÉ travel writing ecosystem also includes our own travel websites! We own and operate Rovology.com , a general North American focused travel website, TravelbyVacationRental.com , a global review service for travel by vacation rental properties, and BookCottages.com , a European focused general travel and vacation rental review site.
Writing for these publications is open EXCLUSIVELY to TWU and CAFÉ members, guaranteeing our members respected bylines and advancing them through the difficult beginning stages of travel writing. Countless TWU and CAFÉ members have used story assignments and/or promised coverage on one of our owned and operated websites to secure free rental stays and travel perks.
Lastly, every Friday in the CAFÉ, we post FREELANCER FRIDAY compiling the best travel-related calls for submissions we’ve discovered after scouring our contacts and industry sites for travel editors in need of fresh stories.
Here’s an example of a FREELANCER FRIDAY from December of 2022:
No travel writing instructional service does more to put its writers directly in contact with editors than TWU and the CAFÉ. Period.
TWU and the CAFÉ go beyond the empty promises and lofty aspirations where other beginning travel writing educators stop. Our program offers serious tools for beginners committed to travel writing and access to resources clearly laying out the steps to follow to advance your career. Actionable, specific, detailed advice with direct, individual support available at every stage of your development.
Starting your own travel blog or website

Many beginning travel writers chose to start their own blog or website as opposed to, or in addition to, freelancing. Doing so prevents them from having to pitch ideas to editors and allows them to write about whatever they want, whenever they want, however they want. Until said blog or website begins receiving enough traffic to start generating revenue, this will be done without monetary reward, but the freedom and flexibility are attractive.
Starting your own travel blog or website does require additional knowledge of basic coding, content management systems, graphic design – or your willingness to pay someone for helping you. While not terribly expensive, the web hosting and support does require an additional monetary investment on your end.
Understanding search engine optimization best practices and social media marketing will prove invaluable in any effort to launch your own travel blog or website.
If you have these skills, if you’ve created websites previously, this may be the right path for you. Hundreds of travel bloggers writing for sites of their own creation you’ve never heard of make great money and travel widely producing content exclusively for their own sites. A hundred times more tried unsuccessfully and quit.
TWU co-founder Kristi Dosh also specializes in the economics and realities of launching personal websites. A blogger, website creator, writer, reporter and journalist since the early 2000s, Dosh has built a brand and career around her sports website – businessofcollegesports.com – and has also developed the TWU and CAFÉ owned and operated sites.
From SEO strategies and social sharing, to advertising networks, sponsored content, direct sales, affiliate sales, WordPress, web hosting, backlinks and more, Dosh understands the nitty-gritty, back-end work required of successful websites living in that world daily. She shares what she has learned and continues to learn through her ongoing education in these always-evolving field.
Dosh works regularly with TWU and CAFÉ members, counseling them on if starting a personal blog or website is a good idea for achieving their goals, and if so, how best to pursue doing so.
TWU has published a “travel blogging toolkit” to assist your efforts.
What to write about
Paris, London, Rome, African safari, India, Mexico City, Yellowstone National Park – all of these can make for wonderful travel stories. All of them have made for countless wonderful travel stories. Compelling travel writing, however, doesn’t require a popular destination, fabulous resort or luxury experience.
Chances are you live in, adjacent to or within 50 miles of a city, town, park, attraction, beach, river, lake, hotel, hiking trail, museum or historical site that people visit which, in the right hands, could make for a fantastic travel story. Does your city, or one nearby, host an annual festival, concert, sporting event? These can make for great stories.
Your beginning travel writing journey should start local, with what you know best. As much as travel publications are looking for once-in-a-lifetime “travel porn” stories from Tierra Del Fuego, they also want the quirky festival story from a small town. Under the radar, off the beaten path, undiscovered, out of the way locations and attractions which haven’t already been written about endlessly make for great pitches and stories.
Bottom line is, you needn’t spend a lot of money traveling to become a travel writer. Start in your own back yard.
We have an entire ROADMAP detailing how to start your travel writing career by focusing on stories local to you.
When thinking about what to write, and how to distinguish yourself in the crowded field of freelance travel writers, think about niches. What aspect of travel are you most passionate about? What aspect of travel are you most knowledgeable about?
TWU and CAFÉ expert and travel writer Chadd Scott has developed his personal niche of arts writing within the travel sector to a contributor position at Forbes.com and freelance bylines for Fodors.com, SouthernLiving.com and Afar.com, along with various print publications. Doing so has landed him so many press trip invitations, he’s had to TURN DOWN invitations to Venice, Vienna, Toronto, Miami and other destinations because he’s simply too busy.
Scott helps members define their niches, like he has. He’s found that by identifying a niche, writers are better able to focus their efforts and stand out to editors. Instead of writing about an ecotourism experience in Utah one week and air travel trends the next, writers committing to a niche they’re passionate and knowledgeable about write with greater authority and attract the attention of editors and industry professionals in those areas more quickly, accelerating their rate of advancement.
Effective niches are often related to geographies – specific cities, states/provinces, regions or countries. Madison, WI, British Columbia, England’s Lake District, Kenya. Scott has further established a niche around Florida, where he lives, hosting a weekly podcast and writing regularly about the state.
Effective niches can also be related to activity. Birdwatching, camping, backpacking, sailing, music, golf, genealogy.
Effective niches can target specific travelers: luxury travel, LGBTQ+ travel, travel for women, travel with kids, Black History travel, travel targeting specific religious affiliations.
Food and wine are popular travel niches. Too popular, in fact, to be effective for most. Drill down. Instead of defining your niche as “food” writing, how about pizza, barbecue, tacos, food trucks or sushi? Instead of writing about “wine,” focus on a specific varietal or region of production. Food and wine are such popular niches, you’ll need to drill down on them.
Anywhere people travel and anything they do while traveling or travel for, could represent a travel niche for you to explore and advance your career.
Here’s another FREE article from TRAVEL WRITERS UNIVERSITY offering advice to help start your creative juices flowing!
How good of a writer do I have to be?
Are you a good enough writer to be a travel writer? Answer these questions honestly:
- Do you like reading?
- Do you write clear, effective emails at work? Do you write professional proposals or summaries or reviews at your current job?
- Did you get good grades in grammar and writing classes?
- Could you write a good book review? Did you work for your student newspaper or yearbook?
- Do you enjoy writing? Do you journal?
- Do you have something to say? Are you funny? Are you observant? Are you empathetic?
If you answered “yes” to any of these questions, chances are, you are a good enough writer to begin travel writing. And you’ll improve the more you write.
Most travel writing isn’t brilliant prose. You don’t need to have Maya Angelou or Earnest Hemmingway talent to become a travel writer. It takes no particular storytelling genius to write “7 best pubs in Chicago” and similar list-based stories popular with many travel publications.
Writing is a talent, sure. We each have an innate ability to communicate through the written word we’re born with. It is also a skill that can be improved with instruction and practice.
Like most things in life, you don’t have to be great to start, but you’ve got to start to be great… and candidly, 99% of travel writers never achieve “great.”
TWU has published many ROADMAPS related to improving your writing including:
“5 structural elements of an article”
“Writing strong ledes” (a “lede” is an opening to a story)
“Creating a sense of place”
“Creating a compelling title”
“5 ways to become a better writer”
Our staff also offers one-on-one coaching to assist anyone who feels they need extra attention to improve their writing skills.
Expectations

When will that first press trip invitation to the Four Seasons in Fiji land in your inbox? Are you a celebrity with millions of social media followers and direct access to editors at major media outlets? If so, pretty soon. If not, it could take a while.
In all seriousness, beginning travel writing takes time. It takes time before you’re receiving invitations to free stays at hotels and free meals at chic restaurants. It takes time before you’re being paid for your writing. It takes time before your bylines appear in outlets your friends and family read.
How much time depends on your willingness to put in the work, to send the pitches, to be consistent with your efforts. Countless beginning travel writers who are all fired up about the potential of this pursuit lose interest after a few weeks and a few unreturned pitches. They lose interest when the reality of the grind and the work and the writing – which, make no mistake, is hard – push the fantasies of jetting off to Tokyo on a press trip out of their head.
They lose interest when life gets in the way. When kids and jobs and spouses and families evaporate their available free time to pitch and write and network and learn. When those same things fail to support the pursuit. When available nights and weekends to pursue beginning travel writing necessitate being filled with movies and music and downtime to give your body and mind a break.
Travel is supposed to be fun, and there’s nothing wrong with simply being a traveler, not a travel writer.
How do you know if you have what it takes?
Can you commit three hours a week to your beginning travel writing? To reading Roadmaps, to reading travel writing, to pitching, to writing? If so, if you adhere to the TWU program and participate in the CAFÉ, we can almost guarantee you’ll be a published travel writer after four months. Published in “Travel + Leisure?” No. Published somewhere, yes.
Will you get paid for that work? Maybe, maybe not. If you are paid, it might only be $20 USD. Even the biggest travel publications, the one’s you’ve heard of, only pay freelancers a few hundred dollars for articles of 1,000 words or more.
We can’t state this more directly, do NOT pursue beginning travel writing if your primary motivation for doing so is monetary.
When will that first press trip invitation come? Again, how fiercely are you willing to pursue this? To pitch? To write? To pitch progressively bigger and bigger outlets? Maybe a year? Probably longer, but here’s another benefit to membership with TWU and the CAFÉ: Noreen, Kristi, Chadd and our staff receive so many press trip invitations we can’t take them all and regularly share leads and contacts for them with members.
TWU and CAFÉ membership has been kept purposefully limited. We’re not spending thousands of dollars a month on Facebook ads targeting dreamers and the easily deceived into joining our programs with little hope of success. We take our greatest satisfaction in our members succeeding. In their bylines and press trips.
We are distinguished by the individual attention we provide our members. We don’t have thousands of members, we don’t have hundreds of members, but the members we do have, we care about, we support, and we are invested in seeing succeed.
We hope you’ll become one of those few and experience the rewards of travel writing we have.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Quintus Curtius
Fortress of the mind, the three types of travel writing, and their uses.

Travel writing is a popular genre. We live in an age of travel, where it is easy to plan a sojourn to the most remote of locations. Most people today hardly give a thought to the fact that their routine international destinations of travel were, until very recently, accessible only by ship or overland travel. Even as late as the 1860s, the source of the Nile River in Africa was unknown.
The ease of travel has greatly expanded the walls of our species’ Petrie dish, but has only infrequently raised levels of wisdom commensurate with these boundaries. The obese dullard that is your neighbor, for example, has probably been to Singapore, blissfully unaware that the bones of Second World War POWs at Changi Prison lie compressed under the tarmac at the city’s international airport. Likewise, the modern globe-trotter pokes his nose curiously amid the chambers and tunnels of the Great Pyramid, clad in biker shorts, wondering how all those great stones fell into place so precisely.
Most modern travelers carry their ignorance about themselves as a protective cloak, ever ready to ward off the threat of uncomfortable knowledge.
But enough of these matters. We will discuss the three general varieties of travel writing.
1. The first type of travel writing is the direct, straight-forward “travel guide” intended as a practical aid to travelers. The journey is described in a linear fashion, with specific dates, places, environments, and experiences faithfully related. These types of books are useful as long as the reader expects no great revelations from them. Utilitarianism is the rule here, rather than insight.
2. The second type of travel book is what I would call the “historico-geographical” tour type of book. This kind of book is rare in modern literature. We find it more in classical or Renaissance writings.
The historico-geographical guide describes different cities and geographic regions, and relates historical anecdotes, regional stories, and other such interesting trivia for the reader. Flavio’s Italia Illuminata is packed with classical quotations, stories, and amusing asides about each and every region he describes, as he ranges across the entire Italic peninsula.

3. The third type of travel book is the “personal discovery” type of account. The author visits a certain place, or makes some sort of journey, and in the process makes profound observations about himself or his locale. The goal here is not so much to impart information about the placed traveled in; the goal is to explore deeper psychological or moral themes. This type of travel account is relatively new in world literature.
How fascinating it is…to see these limbs in their close knee-breeches, so definite, so manly, with the old fierceness in them still. One realizes, with horror, that the race of men in almost extinct in Europe. Only Christ-like heroes and woman-worshipping Don Juans, and rabid equality-mongrels. The old, hardy, indomitable male is gone. His fierce singleness is quenched. The last sparks are dying out in Sardinia and Spain. Nothing left but the herd-proletariat and the herd-equality mongrelism, and the wistful poisonous self-sacrificial cultured soul. How detestable.
These words were written in 1921.

So these, then, are the three general types of travel writing. Each has its use. A good product will result if the writer follows these rules: (1) Do not take yourself with yourself, when traveling. That is, leave your prejudices and preconceptions at home. (2) Be sincere and honest in your observations. (3) Make accurate observatory details by keeping a journal or calendar while traveling. (4) Have something interesting to say, especially about your misfortunes, problems, and emergencies.
To find out more about the need for travel and adventure, read Thirty-Seven and Pantheon:

Share this:

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Shel Sweeney
A worded life.

Narrative Techniques in Travel Writing

Travel writers can effectively borrow from fiction, using narrative techniques and literary devices to improve their non-fiction writing. Creative non-fiction is engaging as well as informative. In my critique of ‘The Year We Seized the Day’ by Elizabeth Best and Colin Bowles, I examine the techniques these authors use to sweep readers up in the story of their journey.
In his article ‘Roads Not Taken’ (2001), Thomas Swick concludes, “Enlightenment and love – there are no more compelling reasons to travel, or write about it.” Authors Elizabeth Best and Colin Bowles spent 36 days walking the Camino, through Spain. Though far from being religious pilgrims, both were physically, emotionally and spiritually transformed by days spent in contemplation of their own lives and witnessing the wonders of humanity along this old pilgrim route. In reading their book, ‘The Year We Seized the Day’, the reader is swept along with each step. Through the use of a day-by-day episodic narrative structure, intimate characterisation of themselves, enlightening observations of those they met along the way, and the humour that they bring to what was a life changing journey, the reader is able to access the transformation undergone by Best and Bowles. “Travelers are everywhere, but great travel writers from Marco Polo to Mark Twain and Bruce Chatwin all knew that a reader’s attention needs to be gripped with vivid anecdotes, humor, narrative – in short, good storytelling.” (Perrottet, T, 2009). In ‘The Year We Seized the Day’, both Best and Bowles engage their readers through the use of effective strategies: engaging the readers through their use of imagination, characterisation and humour.

BIBLIOGRAPHY
Bassnett, S 2002, ‘Travel writing and gender’, in P Hulme and T Youngs (eds), The Cambridge companion to travel writing , Cambridge University Press, UK, pp. 225-41.
Best, E and Bowles, C, The Year We Seized the Day , Allen and Unwin, Australia, 2007.
France, A in The Best Travel Writing , Solas House, Inc., California, pp. vii.
O’Reilly, J 2009, ‘Publisher’s Preface’, in The Best Travel Writing, Solas House, Inc., California, pp. xiii-xv.
Perrottet, T 2009, ‘Introduction’, in The Best Travel Writing, Solas House, Inc., California, pp. xvi-xiix.
Swick, T 2001, ‘Roads Not Taken’, Columbia Journalism Review , vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 65-7, retrieved 6 April 2009, Expanded Academic ASAP database.
For more about Colin Bowles (AKA Colin Falconer), see his blog: Looking for Mr Goodstory
Photo credit: adventurer
Photo credit: travel

2 thoughts on “ Narrative Techniques in Travel Writing ”
Pingback: Life Writing: Borrowing From Fiction :: Shel SweeneyShel Sweeney
Pingback: Life Writing: Borrowing From Fiction - A Worded Life
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How to Write a Travelogue: 8 Tips To Write Better Travel Stories

As I wrote in a previous article , a travelogue is a truthful account of an individual’s experiences traveling, usually told in the past tense and in the first person. In that article, I focused on how travelogues compared to modern travel books. In this article, I will offer tips on how to write a captivating travelogue. You will learn how to avoid writing a traditional (and boring) “Dear Diary” travelogue and craft a modern and compelling travel story.
What does a travelogue contain?
A travelogue contains vivid descriptions of the place you’re traveling in, descriptions of the subjective experiences of visiting a place (your thoughts, blunders, fears), informed commentary about a place (its history and culture), and accounts of your interactions with local people. Above all, a travelogue must tell a story.
A travelogue is not academic writing, so you need not make a formal argument and present evidence—keep formal language at bay. A travelogue is not a write-up for a tourism board or a marketing agency, so don’t try to “sell” the destination to your readers. A travelogue is not a guidebook or a blog post, so you need not be helpful, list “the top 10 best restaurants,” or offer practical travel tips or suggestions.
Rather, a travelogue is a creative narrative of your experiences traveling.
Tell one specific story
Traditionally, travelogues were mundane accounts of what a person saw, did, and ate while traveling. But try to avoid giving a “Dear Diary” account of your travels. You will bore your readers if you write a step-by-step report of what you did, ate, and saw.
Instead, a travelogue will be more effective if it focuses on one interesting story from your travels. A destination is not a story. Neither is simply traveling from point A to point B.
Now that you’ve returned from your travels and want to write an essay or an article about your trip, review your notes and reflect on your experiences. Does a particular story stand out? Is there an experience that you can’t stop telling people about? Did you have a haunting, transformative, or enlightening experience? Did something bad or unexpected happen? If so, it might be a good candidate to write about.
Be descriptive
Now that you have your travel story in mind, think about the setting.
Details and descriptions are essential in travel writing. They will make your writing and story more vivid. What sounds, scents, tastes, and textures did you experience?
Give your readers a sense of what it is like to be there. Transport your reader to that specific time and place.
Be forthcoming
A travelogue is special because it gives us a glimpse of a foreign place, but it does so through the lens of the writer. We want to know your specific take on things.
We are all human. We all think, have opinions, and get scared. What did you feel? Did your experience stir up old memories? Were you frightened? Did you embarrass yourself? Was there a misunderstanding? What did you learn?
Be honest with your own flaws, biases, and assumptions. Give your reader subjective and emotional insight.
Be engaging
We travel (and read travel stories) to engage with and learn about other cultures. And our best travel stories almost always involve interactions with local people you’ve met.
So, while it is good that your reader gets a glimpse into the subjective world of the author, we will want to hear other voices in your story too.
What conversations did you have with the locals? Did anyone tell you something interesting, alarming, or enlightening? Who did you meet? Who were they? What did they look like? Did they have a particular manner of speaking? A distinctive feature?
Be informed
The point of a travelogue is to entertain, but sometimes it is good to inform. Sprinkle relevant information into your story.
Is there historical or cultural details that will help your reader understand why something is so? Did a local person reveal something interesting about the politics or history of a place?
How do you start a travelogue?
If a travelogue is a narrative account of your travels, then consider starting the travelogue with an inciting incident. Begin your travel story with something that will draw your reader in. Highlight a problem, conflict, struggle, or tension that will propel your story along.
As Seth Kugel says, the best travels stories are when things go wrong.
For example, you can begin your travelogue by stating your quest or mission, and then complicating that with an obstacle that gets in the way. Or, you can start with an intrigue, curious statement, declaration, or observation. You can start in media res , and then fill in the story later.
The trick is to hook your reader.
How do you end a travelogue?
Like any story, a memorable travelogue will offer a resolution. Consider ending your story with a transformation or a resolution, a return to the beginning, a moral, a message, or a revelation.
You want to give your reader a sense of closure, that the specific story has ended.
Tips to write a better travelogue
- Tell a specific story
- Describe the outer world using vivid descriptions
- Reveal the inner world (your thoughts, mistakes, missteps, blunders, excitements, etc.)
- Provide informed commentary (historical, political, cultural, etc.)
- Talk to locals and describe your interactions with them
- Use a conversational tone and avoid fancy/big words, marketing jargon, and guidebook speak
- Begin with an intrigue, something going wrong, or a compelling or captivating moment
- End with a resolution, a moral, a message, or a revelation
Do you have any other tips on how to write a better travelogue?
Last Updated on 29 November 2020 by Travel Writing World
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)

Travel Writing World
With an emphasis on travel books and long-form travel literature, host Jeremy Bassetti talks with the world’s most inspiring travel writers about their work and about the business and craft of travel writing in this award-winning podcast and website. In addition to the podcast, the site also features travel writer profiles, book reviews, and articles.
You may also like
Note-taking apps for travel writers, travel journalists, and..., apple notes for writers, crossing cultural boundaries, books to help writers cultivate and create a..., 10 travel book subgenres with examples, travel writing awards competitions.
What I want to know is how to write your thoughts? In Italics so the readers knows that’s your thoughts or constantly writing “I remember thinking…” “I thought to myself”. I prefer just writing my thoughts as italics but is this the accepted way? Will an editor hate it and want me to rewrite is what I’m asking.
You’re talking about “internal dialog.” Do a google search to see what others think, but here is my take. Italics and quotes are both accepted forms. There is also a third way: don’t use italics, quotes, or thought/dialog tags at all. While this depends on the point of view of the work, I’m assuming that that you’re writing in the first-person present or past if you’re writing a travelogue. Why not use italics, quotation marks, or tags if you’re writing in the first-person? It will be implied that the narrator who says “I” or “me” is the one doing the thinking. So, instead of writing Why did the man steal my purse , I thought… You could simply write: Why did the man steal my purse? as it will be implied that the narrator is the one having the thought.
Just finished my travelogue book
Great. What is it about?
Just starting up and very much enjoyed this article.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We'll assume you're ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Accept Read More
National Geographic content straight to your inbox—sign up for our popular newsletters here

The Masterclasses 2023: 10 travel writing tips from our experts
From establishing a niche to tackling writer’s block, the autumn series of The Masterclasses saw 12 of the UK’s leading travel journalists share the tips and tricks behind their success.
The Masterclasses by National Geographic Traveller (UK) returned in September 2023 with a brand-new series of insightful, hour-long online sessions curated for aspiring travel writers and photographers.
Leaving no stone unturned, the expert panel of travel writers explored everything from penning that all-important opening line to forming good relationships with editors. Throughout the three sessions, they shared a wealth of inside knowledge — offering up advice that will prove invaluable to anyone hoping to make travel writing a full-time career.
These are their 10 top tips on getting your story published, navigating the industry and using structure to elevate your travel writing.
1. Know your reader
“I would say the number one mistake freelance writers make when pitching is they don’t understand the audience of the title. The best thing you can do if you’re really interested in writing for a publication is to go out and buy yourself the magazine and familiarise yourself with the content, the tone and the kinds of things that the readership might find of interest.” — Alicia Miller, Pitching and getting published
2. Be patient
“If you’re really interested in something, then there will be an audience out there for that story. It’s just about finding the right home for it. Don’t get discouraged — and believe in your idea! Because if you find it interesting, other people will too.” — Daniel Stables, Pitching and getting published
3. Win over commissioning editors
“When I first started freelancing, editors didn’t know who I was. One way of showcasing my knowledge was deeply researching a destination and including a taste of that in the pitch. Make it concise, but also show that you have knowledge about the destination. If I was working with a new editor for the first time, I would always include links to previous work, or somehow demonstrate my expertise in the subject.” — Qin Xie, Pitching and getting published
4. Utilise social media
“Dinosaurs like me may absolutely despise it, but the reality is that if you’re a travel writer and you have no presence on social media, you have no presence.” — Tharik Hussain, How to be a savvy travel writer in 2023
5. Know today’s travel writing landscape
“Perhaps 10 years ago, 20 years ago, travel writing came from a person’s appreciation of a destination. Now what we’re looking at is trying to capitalise on what other people in the big internet landscape are looking for… Travel writing is kind of evolving away from being that destination-led 'this was my experience, and this is how you can recreate it' and it’s turning to using travel as a sort of lifestyle trend.” — Cathy Adams, How to be a savvy travel writer in 2023
6. Find a niche
“Editors, increasingly, are looking for people either based in a destination or people who know a place really well and really understand the culture. And so, a couple of benefits of having a niche are that it helps editors find you: they can remember what your patch is. And then, on a personal level, I find it really satisfying to find those stories that take you to the deeper levels of a destination. You have to have a really genuine passion for the place because it’s a bit like writing a book: you still have to find it interesting after 50,000 words.” — Zoey Goto, How to be a savvy travel writer in 2023

7. Find the right working environment
“Usually, I’ll find some travel writing from a writer I really like, and I’ll kind of read over their pieces just to get in the right frame of mind. I’ll usually listen to some quite amped-up music — usually the same playlist I use for running — because it kind of gets you in the mood to do things. For actual writing, I’m a big fan of white noise. Having narrowed it down over several years, I think my favourite type of white noise is the tumble dryer; there’s a whole tumble dryer playlist on Spotify that I am really dedicated to.” — Georgia Stephens, How to structure your storytelling
8. Write as though talking to a friend
“You don’t have to use highfalutin prose to make an intro work. Often, it’s the simple stuff. Good journalism is a bit like talking to a friend. Just tell me what’s happening… And in the same way that your friends wouldn’t when you tell them about your travels, [the reader] won’t listen to more than two sentences of description. With the greatest of respect, no one cares.” — James Stewart, How to structure your storytelling
9. Make the most of quotes
“Quotes are a way to deliver information to your reader from a different perspective — and it’s so much more powerful coming from someone else other than you. It’s definitely important to use quotes, especially when you’re writing about communities that you may not be a part of. Allowing people to tell their stories in their own words as much as possible, is so important.” — Katherine Gallardo, How to structure your storytelling
10. Don't be afraid of writer's block
“As someone who has come to this relatively recently, I would say that even the best writers struggle to write sometimes. Everybody gets writer’s block, even published authors. Just don’t beat yourself up. If it’s not coming, it’s not coming. Just come back to it another day.” — Georgia Stephens, How to structure your storytelling
Related Topics
- ADVENTURE TRAVEL
- TRAVEL AND ADVENTURE
- STORYTELLING
You May Also Like

A Croatian coastal odyssey: why road-tripping from Split to Dubrovnik is easier than ever

Four culinary experiences to try in Hokkaido
Fourth of july special.
Get National Geographic magazine for $10 off

How new flights to Akureyri are opening up northern Iceland

The essential guide to Switzerland

10 best things to do in Switzerland

An insider's guide to Denver, Colorado's wildly creative capital

A guide to Hamburg, north Germany's fiercely independent maritime hub
- Environment
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Interactive Graphic
- Paid Content
- Adventures Everywhere
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
- Writing Courses

Travel Writing Tips for Beginners: How to Structure Your Travel Tales
Part two in this week’s three-part series: beginnings, middles, and endings.
By Dave Fox Tioman Island, Malaysia
Welcome to part two in this three-part series on how to turn your travel diaries into publishable travel tales. In part one , we looked at writing about specific events or topics rather than skimming the surface of an entire trip. Today, we explore how to structure those stories – the beginning, the middle, and the end.

Artwork: “Joshua Writing” – flickr/kafka4prez
Start with a compelling lead. Your “lead” paragraph must reel in readers right away. If you can’t hook them in the first 35 words, chances are you’re going to lose them. You’ve dreamed for years of visiting Africa? That’s not an exciting first sentence. You’re on a trip with your significant other? That’s not interesting either. You taught Kalahari Bushmen how to play Frisbee? Now we’re getting somewhere. Many beginning travel writers clog their leads with too much background information. When they do this, readers never get to the exciting part. An audience will move on to something else if the beginning of a story is mundane. So pounce into the action right away. Make your theme clear and enticing at the outset.
Develop your story thematically or chronologically, but keep it moving. Many travel tales unfold with a simple chronological sequence. Others follow a series of scenes or anecdotes. Let’s go back to that flan in Guadalajara we talked about in part one of this series. After your first toe-curling taste, you decide to embark on a weeklong mission to find the best flan in town. Over the next seven days, you scarf down twelve helpings of the caramelly custard. You might write about your five or six favorites. And maybe a couple of not-so-favorites. You don’t have to cover them in the order you ate them. Instead, write in the order that best builds excitement. Just as you want to catch readers’ attention right away with a strong lead, the body of your story must hold readers’ fascination by maintaining – and ideally increasing – the action and energy. Occasionally, you need to include a detail that’s not so enthralling to keep the story flowing. That’s okay, but get through those points concisely. Move on quickly and then zing your readers with more thrills.
End with a lesson, a discovery, or a personal transformation. Riding into the proverbial sunset can be a natural way to end a tale but you’ll conclude on a more powerful note if you demonstrate some sort of transformation. Have you learned something new about yourself or the world? Changed your way of thinking or seen somebody else change theirs? Big insights come frequently when we’re away from our everyday world and culture. Share those insights with your readers so those who wander vicariously through your writing can share in your discoveries.
Want to Learn More?
I offer two fun and super-informative online workshops to help you become a travel writer. Once you sign up, you can watch the video lessons and do the writing exercises whenever you have time. You get lifetime membership in the course and each workshop comes with a 30-day money-back guarantee. Follow the links below for discount coupons, free sample lessons, and all the details!
- Globejotting: How to Write Extraordinary Travel Journals offers creative and effective techniques to capture the most exciting details of your trips. You’ll discover how to splash lots of bold detail into your travel diary – quickly – so that journaling enhances your journeys rather than gobbling up precious vacation time. Includes 75 minutes of lessons plus fun writing exercises and access to our online classroom. Follow this link for a big discount!
- Travel Writing: Explore the World and Publish Your Stories picks up where the above course leaves off. Learn how to turn your “rough draft” journals into polished travel tales that readers (and editors) will love! Share your adventures with friends and family, post them on a blog, or publish them professionally in newspapers, magazines, and anthology books. This comprehensive travel writing course includes three-and-a-half hours of video lessons plus hands-on writing exercises and access to our online forums. Follow this link for a huge discount!
- Part 1: Travel Writing Tips for Beginners: Get Specific
- Part 2: How to Structure Your Travel Tales
- Part 3: Putting the Final Sparkle in Your Stories
If you’ve got questions about travel writing, I’m happy to answer them! You can send them to me on the Ask Dave page and I’ll try to cover them in a future online column.
You may also be interested in
- Be Your Own Travel Writing Coach
- Free Travel Writing Webinar
- Story Overload: The Tales You Don’t Have Time to Write
- Travel Writing Lesson: Storyfinding and the Art of Talking to Strangers
- Travel Writing Tip: The Question You Must Answer Before Writing Your Story
- A Lucky Strike in France
- Adventures in (Travel) Writer’s Block
- Podcast: Travel Writing - Live from the Singapore Writers Festival
- Travel Writing Class in Singapore
- Migraine Memoirs
- The Most Overused Cliché in Travel Writing
- Travel Writing Tips for Beginners: Putting the Final Sparkle in Your Stories
- Travel Writing Tips for Beginners: Get Specific
- Travel Catastrophes for Fun and Profit
- Ask Dave: Maintaining Post-Travel Writing Momentum
- Travel Journals: The Ultimate Souvenir
3 Responses to “Travel Writing Tips for Beginners: How to Structure Your Travel Tales”
It is very interesting and inspiring particularly for those writers who want to write but due to one reason or another they can’t
Leave a Reply
Name (required)
Mail (will not be published) (required)
XHTML: You can use these tags: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
Subscribe to my free newsletter
Writing and Life Coaching

If you’ve got big writing goals, dreams you want to achieve but you’re not sure how to get there, or if you’re struggling with something and you need help turning things around, Dave can help you create a path to more fulfilling and authentic life.
>> Personal Development & Expat Coaching
>> Writer Coaching
Online Workshops
Dave's online writing and travel courses get RAVE reviews! Follow the links below for special discounts!
- Travel Journaling: Capture your travel memories in words.
- Travel Writing & Publishing: Transform your journals into stories you can publish.
- Humor Writing: Professional humor tricks for writers, speakers, and other misfits.
- The Psychology of Writing 1: Overcome writer's block and write with confidence.
- The Psychology of Writing 2: Defeat distractions, stop procrastinating, and write!
- Deep Travel: Have adventures no guidebook can tell you about.
Books by Dave Fox

Details and Free Sample Chapters >>
Read Globejotting.com on Kindle! You can now download stories from Globejotting.com and read them on your Amazon Kindle device! Find Out More >>
Follow Globejotting

Almost All Categories
- Travel Tales & Tips
- Travel Journaling
- Humor Columns
- Random Outbursts
- Dave’s Books
- Writing Tips & Musings
- Online Writing Classes
- Share Your Stories
- Top Stories
- Expat Radio
- Guest Writers
- Life Coaching
- Personal Development
- Dave’s Books
- Copyright Dave Fox 2012
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Free AI Writing Generator
Unlock your creativity effortlessly with our free AI writing tool. Explore different modes to continue writing in a particular style.
Original Text
Start typing, paste or use
Generated Text
Your text will appear here, limit reached. want to continue.
Sign up to get 3 Sparks per day or check out our paid plans to get even more.
Something went wrong
We are unable to generate rephrasings for this text. Please try a different piece of text.
Why choose our AI writing generator?
Choose how to write.
Add sensory detail, counterarguments, dialogue, or examples.
Generate unique text in a single click. Simply try again if you’re not satisfied with the result.
Strengthen your writing
Craft engaging text that captivates your readers.
Trusted by industry leaders

Write more efficiently with ProWritingAid
Our AI writing generator takes your writing to new heights.
Ideate with AI
Discover new ways to extend your writing with AI Sparks Continue. Add new lines of dialogue, analogies, quotes, and even definitions—the possibilities are endless.

Rewrite text
Find the best way to express your thoughts and ideas. Try enhancing readability, summarizing text, or incorporating descriptive detail.
Fix grammar and spelling mistakes
ProWritingAid corrects grammar and spelling errors in real time, so you can be sure your work is error-free.
Evaluate your writing
ProWritingAid's reports provide comprehensive feedback on various aspects of your writing with statistics, insights, and suggestions for enhancement.
ProWritingAid is used by every type of writer
Join over 3 million users improving their writing.
I am continually impressed with the positive input this program offers me every time I sit down to write. My skills have improved immensely since I bought it, and I heartily recommend it to anyone who wants to have more confidence in their own writing.

Ginger Wakem
I’ve tried every free and paid writing/editing/grammar extension out there, and this by far is the best one my team and I have found. It’s fast, accurate, and really helps improve your writing beyond simple grammar suggestions.

Joel Widmer
ProWritingAid has been a resource in my writer toolkit for many years. The program helps me to craft and clarify my stories for a better reader experience. Your editor will thank you for making their job easier.

Siera London
Works wherever you do
Try our AI writing generator in Word, Google Docs, or in your browser.
AI Writing Generator FAQs
What is prowritingaid.
ProWritingAid is a grammar checker, text enhancer, and writing coach all in one helpful tool.
By signing up for a ProWritingAid account, you gain access to various features. These include advanced grammar and spelling checks, style suggestions, AI capabilities for rewriting text and generating ideas, as well as over 25 other reports to help you improve and polish your writing.
Is ProWritingAid free?
A free account allows you to edit and run reports on up to 500 words. It also gives you three AI Sparks per day, which is needed to generate text. If you want more, you’ll need to upgrade to a paid plan .
How do I generate text in-app?
Follow these steps:
Write a prompt or short sentence for our generator to expand on.
Highlight the text.
Click on "Sparks."
Choose how you want AI to continue writing.
Try generating emotion detail, explanations, examples, quotes, and even jokes.
What software integrations does ProWritingAid offer?
ProWritingAid seamlessly integrates with MS Word, Google Docs, Scrivener, Atticus, Vellum, and more. We also offer browser extensions (Google Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Microsoft Edge), so you can work almost anywhere online.
Does ProWritingAid have a plagiarism checker?
Yes. ProWritingAid’s plagiarism checker will check your work against over a billion web pages, published works, and academic papers, so you can be sure of its originality. Find out more about pricing for plagiarism checks here .
Try our AI writing generator today
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

Text Types and Different Styles of Writing: The Complete Guide
A guide to understanding different types of writing and text types.
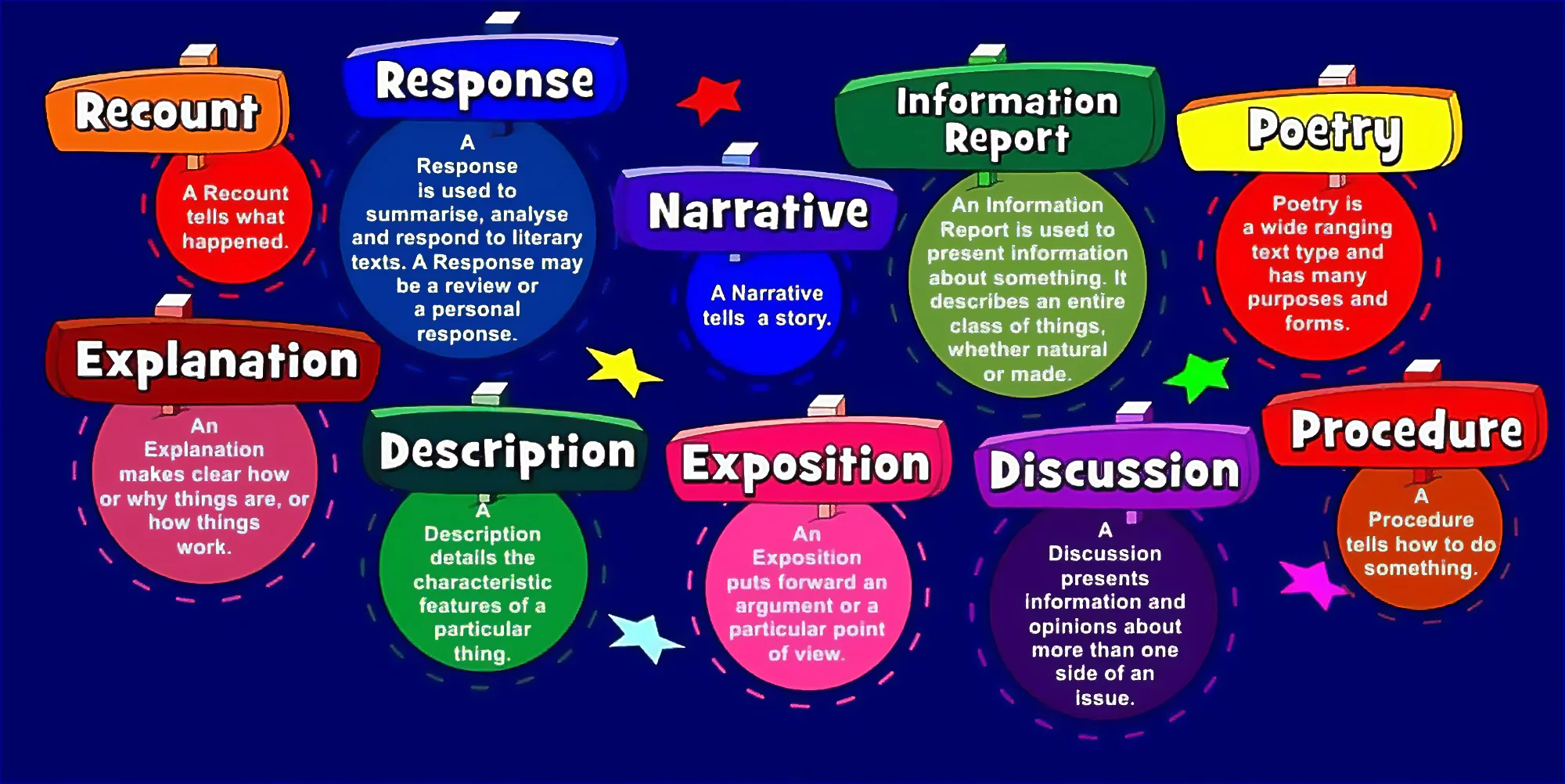
Reading and writing are complex skills that demand much from students. As they progress, we must assist them in going beyond grammar, punctuation, and spelling and understanding the conventions and structures of the various text types or genres.
By understanding the significance of each text type, educators can tailor their teaching strategies to meet the specific demands of different written contexts.
When students comprehend the purpose of an essay they have been assigned, they can approach it strategically and customize it to the intended audience.
Whether students are deciphering a Shakespearean sonnet, grappling with a scientific research paper, or crafting a persuasive argument, a nuanced understanding of text types will help them confidently navigate the intricacies of language.
In this article, we’ll explore the purpose of literary and factual text types. For greater insight, be sure to read the full guides attached to each type.
What are the main text types?
There are many ways to categorize the broad range of reading and writing materials we encounter daily. But, generally speaking, it’s helpful to think of them in terms of two overarching and broad categories: factual and literary.
We will discuss various sub-categories that fall under these two broad categories. It’s worth noting that different curricula might refer to text types in varying ways. For instance, a recount is also known as a personal narrative in certain regions, and there are several text types with multiple names.
FACTUAL TEXTS
Endeavor to inform, instruct, or persuade through the use of facts and information., literary texts, seek to entertain, enlighten, or elicit emotion through a creative use of language and structure., daily quick writes for all text types.

Our FUN DAILY QUICK WRITE TASKS will teach your students the fundamentals of CREATIVE WRITING across all text types. Packed with 52 ENGAGING ACTIVITIES
Factual Text Types
Argumentative texts.

An argumentative essay is a type of writing in which the author takes a stance on a particular issue or topic and presents arguments and evidence to support that position.
The primary goal is to persuade the reader to adopt the author’s viewpoint or consider it seriously, at the least.
Argumentative Texts are commonly assigned to students in grades three and above. They require them to critically analyze information, develop a clear thesis or main idea, and present a well-structured and reasoned argument.
Argumentative essays are used for debates, policy advocacy, public discourse, critical thinking development, research, and expressing personal views, contributing to social and intellectual dialogue.
Quick Writing Activity: An effective way to lead to writing a discussion text is to hold a discussion or debate in the classroom on a contentious issue or a topic that piques the interest of your class. For example, Should video games be considered a sport? or should homeschooling replace traditional schooling due to technology?
The style of an argumentative essay is typically formal, and the tone is persuasive. The writer should aim to engage the reader and convey the issue’s importance.
Biographies
Biographies are written accounts of people’s lives, providing a comprehensive and detailed narrative of their experiences, achievements, and societal impact. These works offer insight into the individual’s character, contributions, and the historical or cultural context in which they lived. Biographies can take various forms, including books, articles, documentaries, or online profiles, and they are valuable for preserving and sharing the stories of notable individuals.
Examples of biographies include “The Diary of Anne Frank” by Anne Frank, “Steve Jobs” by Walter Isaacson, and “The Wright Brothers” by David McCullough. Biographies play a crucial role in documenting the lives of influential individuals, preserving their stories, and inspiring readers with accounts of human achievement and resilience.
Quick Writing Activity: As a warm-up to biographical writing, St udents imagine themselves as the subject of the biography and write diary entries from that person’s perspective. This activity encourages empathy, deepens understanding of the character’s emotions, and fosters creative expression while maintaining a connection to factual information.
DISCUSSIONS

A discussion essay is a type of academic writing that presents and explores different perspectives on a given topic.
Unlike an argumentative essay, where the author takes a specific stance and argues in favour of it, a discussion essay requires the writer to consider various viewpoints, analyze the strengths and weaknesses of each, and present a well-rounded view of the issue.
The goal is not necessarily to persuade the reader to adopt a particular position but to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Discussion essays are often assigned in academic settings to assess students’ ability to analyze complex issues, consider different perspectives, and present a well-reasoned discussion. They are commonly found in subjects such as philosophy, sociology, and political science, where exploring diverse viewpoints on a topic is crucial for a comprehensive understanding.
EXPOSITORY TEXTS & Explanatory ESSAYS

Explanatory texts, expository texts, or explanatory essays are written compositions that aim to provide information, clarify concepts, or explain a particular subject to the reader. The primary purpose of explanatory texts is to convey factual information in a clear, organized, and easily understandable manner. These texts can be found in various forms, including essays, articles, manuals, textbooks, and reports.
Suggested Activity: Task students with going to the library and gathering a range of explanatory texts on various topics. In groups, students go through these texts analyzing the various features they have in common. From their findings, students draw up a detailed list of criteria they can use to write their explanatory texts later.
Information Reports

Information reports, often categorized as expository or informative writing, are compositions that present factual information on a specific topic in a clear, concise, and organized manner. These reports aim to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of the subject, and they are commonly found in educational, scientific, and professional contexts. Information reports follow a structured format and are characterized by their focus on delivering objective information without personal opinions or biases
Examples of information reports include scientific research papers, academic reports, technical manuals, and informational articles. These reports serve the purpose of presenting information objectively, helping readers gain insights into a specific topic, and serving as a valuable resource for reference and learning.
Suggested Activity: Students will enjoy creating an information report about their favourite animal. Providing facts and information about aspects such as appearance, habitat, movement, food and life cycle. Images and Diagrams will significantly enhance the finished product.
Procedural Texts & INSTRUCTIONAL ESSAYS

Procedural texts, also known as procedural documents or instructional texts, are written compositions that provide step-by-step guidance on how to perform a specific task or achieve a particular goal. Their primary purpose is to inform the reader about a process, procedure, or set of instructions clearly and concisely. These texts are often found in instructional manuals, recipe books, user guides, technical documents, and other contexts where a systematic set of instructions is necessary.
Procedural texts are essential for conveying information in a format that is easily accessible to individuals who need to perform specific tasks or follow a particular process.
Suggested Activity: Partner students up for this writing task. Ask the students to think of something they know how to do well. It could be anything from how to tie shoelaces to how to perform a cartwheel. It doesn’t matter what it is, as long as the student clearly understands how to do it. Students then write an explanatory text that explains how to do it. Partners swap their work with each other. They then try to perform the task exclusively following the explanation within the text. If they can’t perform the task as it’s meant to be done, then the writer needs to redraft their work until it can be done.

Persuasive Texts / OPINION WRITING

Persuasive texts cover a broad collection of opinions, and argumentative writing styles are designed to sway the reader’s opinion towards a specific viewpoint or prompt them to undertake a particular action. These texts employ language, style, and tone strategically to present compelling arguments, evidence, and reasoning, aiming to convince the audience. They are prevalent in diverse contexts, encompassing academic writing, advertising, public speeches, and opinion pieces.
Examples of persuasive texts include opinion articles in newspapers or magazines, political speeches, advertising campaigns promoting products or services, letters of recommendation, and persuasive essays within academic settings.
Suggested Activity: Distribute copies of a persuasive text to students in groups. For example, this could be an advertisement or newspaper editorial. Challenge students in their groups to identify various persuasive strategies employed within the text, whether in terms of structure, presentation, visuals, or language. Students can compare and contrast their findings between groups.
Non-chronological reports

Non-chronological reports are informative writing that presents information about a particular topic without following a strict chronological order. Unlike narratives or historical accounts that organize information based on a sequence of events over time, non-chronological reports present facts, descriptions, and details in a logical and thematic structure. These reports are commonly used in educational contexts, informational articles, and reference materials.
Examples of non-chronological reports include scientific reports, encyclopedia entries, informational articles in magazines, and educational materials. These reports are valuable for presenting information in a structured and thematic manner, making them accessible for readers seeking specific details about a particular topic.
Suggested Activity: An informational leaflet is one form of a non-chronological report. Challenge students to produce an information leaflet on something they know, such as a local attraction or historical site. When students have completed their leaflets, please encourage them to review each other’s work and offer feedback.

Recounts are a form of writing that involves retelling past events or experiences. The primary purpose of a recount is to inform or entertain the reader by providing a detailed account of what happened. Recounts can take various forms, including personal narratives, diary entries, news reports, or historical retellings. They often use a chronological structure to present events in the order in which they occurred.
Personal narratives, autobiographical accounts, eyewitness testimonies, travel diaries, and historical retellings are examples of recounts. They serve as a means of sharing personal experiences, preserving memories, and conveying information about past events in a compelling and engaging way.
Suggested Activity: In the library, challenge students to gather as many different types of recounts as possible. In their groups, students review the various recounts and compile a list of criteria for this text type. As a whole class, the groups share their results. Encourage students to pay particular attention to the range of topics that can be presented as recounts and how this can affect the language style. For example, recounting a science experiment will use more technical and formal language than the informal and personal style that might be employed to recount a travel adventure.
Literary Text Types

Poetry is a form of artistic expression that uses language to evoke emotions, convey images, and create a rhythmic and musical effect. It is a genre of literature characterized by a heightened use of language, often employing techniques such as meter, rhyme, and metaphor. Poems come in various forms and styles, each with its own unique structure and purpose. Poetry is a rich and diverse literary tradition that allows for creatively exploring themes, emotions, and perspectives.
Examples of famous poets include William Shakespeare, Emily Dickinson, Langston Hughes, and Maya Angelou. Poetry can take various forms, including sonnets, haikus, free verse, and epic poems. Its versatility allows poets to experiment with language, form, and structure to create unique and expressive works.
Suggested Activity: Find an anthology of poetry that groups poems together according to themes. Task your students to look at poems exploring a common theme. Have the students look at the features these poems have in common and the features that differ. Can the students identify the different types of poems?

A narrative is a form of writing that tells a story or recounts a series of events. Narratives can take various forms, including short stories, novels, autobiographies, and even some types of essays. The primary goal of a narrative is to engage the reader by presenting a compelling and coherent sequence of events that unfold over time using the story elements of character, setting, plot, theme and conflict.
Examples of Narratives include Charlotte’s Web by E.B. White and Charlie and the Chocolate Factory by Roald Dahl.
Narratives entertain, inform, or convey a message through the artful arrangement of events and characters in a story.
Suggested Activity: This task can be completed using novels, short stories, or even concerning movies the students are familiar with. Have the students draw an x and a y-axis on a piece of paper. Students label the x-axis time and the y-axis action. Students then plot and label the narrative’s introduction, complication, rising action, climax, and resolution. The more intense the action at each point of the story, the higher on the y-axis the point will be plotted. The points are then joined with a line. This will give the students a sense of the ‘shape’ of the story. Internalizing an understanding of this general storytelling pattern will help students immensely in their writing.

Written drama, often known as a play or script, is a form of literature designed for performance on stage. It involves creating characters, dialogue, and a plot structure to convey a narrative through the characters’ interactions and conflicts.
Written drama incorporates dramatic elements, such as setting, conflict, climax, and resolution, to engage an audience emotionally and intellectually.
Playwrights employ unique techniques, including dialogue, stage directions, and sometimes monologues, to bring their stories to life in a theatrical context, offering a distinct blend of literary and performative artistry.
Suggested Activity: Students can explore the different conventions, similarities, and differences between prose and drama by taking a story written in a prose genre, such as a fable, short story, etc., and converting it into a script for a drama.
A COMPLETE YEAR OF WRITING FOR STUDENTS – 1000+ PAGES

This HUGE BUNDLE offers over 1000 PAGES of COMPLETE UNITS of work that would easily fill a year of writing, all created with STRUCTURE, INSIGHT AND KNOWLEDGE to improve student writing skills. EDITABLE / DIGITAL & PRINT formats. No preparation is required.
In Conclusion
Understanding the various aspects of the different writing genres will help students navigate writing that serves a wide range of purposes.
It will also help students with their own text compositions. Understanding the various underlying text structures will provide students with an effective means of organizing their work, helping to ensure their writing is fit for purpose.
Exposing your students to as many different genres as possible and providing opportunities to explore how these text types operate will go a long way to helping them develop into adaptive and organized readers and writers in the future.

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES FROM LITERACYIDEAS.COM


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Round-ups. You'll recognize a round-up article when you see one, as it'll go, "40 best beaches in West Europe," or, perhaps, "20 of the greatest walks in the world!". It's a classic tool in any magazine or newspaper writer's toolbox, taking a bunch of destinations and grouping them all under one common thread.
Tips for travel writing. Open with a compelling and snappy anecdote or description to hook the reader's interest from the beginning. Give the reader a strong sense of where you are through vivid language. Ground the reader in time, in climate, and in the season. Introduce yourself to help the reader identify with you and explain the reason ...
11 Great Travel Writing Examples. Writing with feeling, tone, and point of view creates a compelling story. Below are examples of travel writing that include; first paragraphs, middle paragraphs, and final paragraphs for both travel articles as well as travel books. I hope the below examples of travel writing inspire you to write more, study ...
Non-fiction text types - AQA Travel writing. Non-fiction texts come in many types, and have many different purposes. They surround us in everyday life but can also come in more sophisticated forms.
The aim of literary travel writing is to entertain. Readers consume it "for pleasure, and for its aesthetic merits," Thompson notes, instead of for practical insight. Literary travel writing can take the shape of books, novels, memoirs, articles, poems, journals and diaries, journalism, personal essays, travelogues, op-eds, blog posts, and ...
Unit 3: Different types of travel writing 12 Unit 4: Different types of travel articles 14 Unit 5: Writing your first travel story 18 Unit 6: Structuring your story and finding your voice 22 Unit 7: The art of pitching 26 Unit 8: Essential editorial skills in a digital age 30 Unit 9: The importance of having your own blog 34 ...
Rule 2: Keep Track of Everything as You Travel. Being a travel writer is all about observation. As you move through the world, you do your best to capture the sights, sounds, smells, and feel of a destination so that a reader on the other side of the planet can be transported to, say, the streets of Vietnam.
Thomas Swick. "The best writers in the field [of travel writing] bring to it an indefatigable curiosity, a fierce intelligence that enables them to interpret, and a generous heart that allows them to connect. Without resorting to invention, they make ample use of their imaginations. . . . "The travel book itself has a similar grab bag quality.
Teaches the Art of the Short Story. Teaches Storytelling and Humor. Teaches Writing for Television. Teaches Screenwriting. Teaches Fiction and Storytelling. Teaches Storytelling and Writing. Teaches Creating Outside the Lines. Teaches Writing for Social Change. Teaches Fiction, Memory, and Imagination.
Use these practice texts to familiarise yourself with the different features of Travel Writing and add them to your Learner Portfolio; you will want to revise text types thoroughly before your Paper 1 exam. You can find more information - including text type features and sample Paper 1 analysis - by visiting 20/20.
However, every writer needs to know that any good text follows the rules of certain structural conventions. Travel writing can be divided into several categories, and it is quite important for a person who wants to become a travel writer to know and use the types of travel writing as such, as this is one of how he will prove his professionalism.
Craft captivating tales that will leave your readers wishing for more. Let's get started and master the art of travel writing! Discover the Art of Travelogue Writing. From ancient Greece to modern-day blogs, travelogue writing has existed for centuries. It is a form of creative non-fiction that combines memories and factual data.
Literature: There is some great travel writing out there! Reading books by well-known authors or travel bloggers can give you a lot of insights into different destinations. ... A travel text is a type of literature that describes the experience of traveling to and visiting different places. Travel texts can be found in many different formats ...
2. Content and Social Media Marketing. Travel companies sometimes hire freelance content and social media writers to promote their product and services via blog posts, video clips, and articles. You'll need to write quickly, vary the tone for targeted audiences and engage with followers and update posts.
Travel writing is a genre of writing that captures the essence of a place and its culture, through the eyes of the writer. It's a blend of journalism, storytelling, and personal reflection that provides readers with an immersive experience of the destination. Whether it's a guidebook, an essay, or a memoir, travel writing offers a unique ...
This beginners guide to travel writing intends to answer your most basic questions and get you pointed in the right direction. Thousands of people from various backgrounds - many with no previous media or journalism experience - share stories of their trips and adventures on countless websites, blogs, magazines, newspapers, newsletters and ...
The first type of travel writing is the direct, straight-forward "travel guide" intended as a practical aid to travelers. The journey is described in a linear fashion, with specific dates, places, environments, and experiences faithfully related. These types of books are useful as long as the reader expects no great revelations from them.
Narrative Techniques in Travel Writing. Travel writers can effectively borrow from fiction, using narrative techniques and literary devices to improve their non-fiction writing. Creative non-fiction is engaging as well as informative. In my critique of 'The Year We Seized the Day' by Elizabeth Best and Colin Bowles, I examine the techniques ...
Tips to write a better travelogue. Tell a specific story. Describe the outer world using vivid descriptions. Reveal the inner world (your thoughts, mistakes, missteps, blunders, excitements, etc.) Provide informed commentary (historical, political, cultural, etc.) Talk to locals and describe your interactions with them.
4. Utilise social media. "Dinosaurs like me may absolutely despise it, but the reality is that if you're a travel writer and you have no presence on social media, you have no presence ...
This comprehensive travel writing course includes three-and-a-half hours of video lessons plus hands-on writing exercises and access to our online forums. Follow this link for a huge discount! Part 1: Travel Writing Tips for Beginners: Get Specific. Part 2: How to Structure Your Travel Tales. Part 3: Putting the Final Sparkle in Your Stories.
ProWritingAid is a grammar checker, text enhancer, and writing coach all in one helpful tool. By signing up for a ProWritingAid account, you gain access to various features. These include advanced grammar and spelling checks, style suggestions, AI capabilities for rewriting text and generating ideas, as well as over 25 other reports to help you ...
Structure: This type of text begins with a defined objective or goal, often forming the title. Usually, a list of resources, equipment, etc., will be included, followed by a step-by-step description of the process to achieve the desired outcome. Often, the written process is supported by diagrams and/or illustrations.
Erica Lamberg is a personal finance and travel writer based in suburban Philadelphia. She is a regular contributor to USA Today and her writing credits include NBC News, U.S. News & World Report ...
Students should approach using AI with caution, and refrain from using these tools to write long pieces of text to avoid false statements and content lacking detail. It's key to strike a balance between creating a high-quality piece of work, and using the tools effectively, to avoid the territory of plagiarism.
Every business plan is different, and the steps you take to complete yours will depend on what type and format you choose. That said, if you need a place to start and appreciate a roadmap, here's what Cobello recommends: 1. Conduct your research. Before writing your business plan, you'll want to do a thorough investigation of what's out ...